Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. PCA
2.4. Ultrastructural Analysis
2.5. Preparation of Genomic DNA
2.6. PCR Amplification of CO1
2.7. Nucleotide Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphology and Ultrastructure of Three Legs from Four Cicada Exuviae
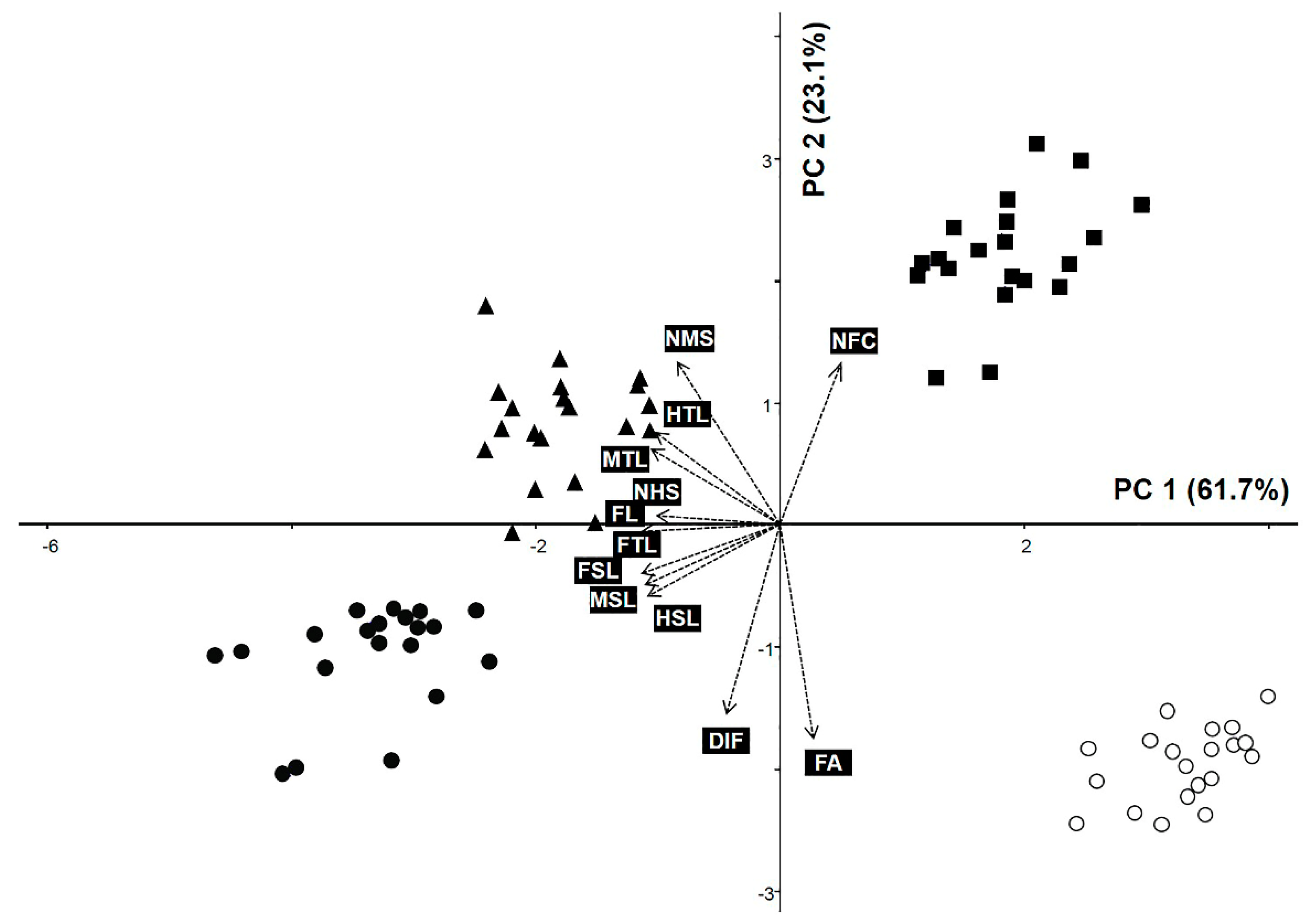
3.2. Principal Component Analysis
3.3. Taxonomic Key Based on Leg Morphology
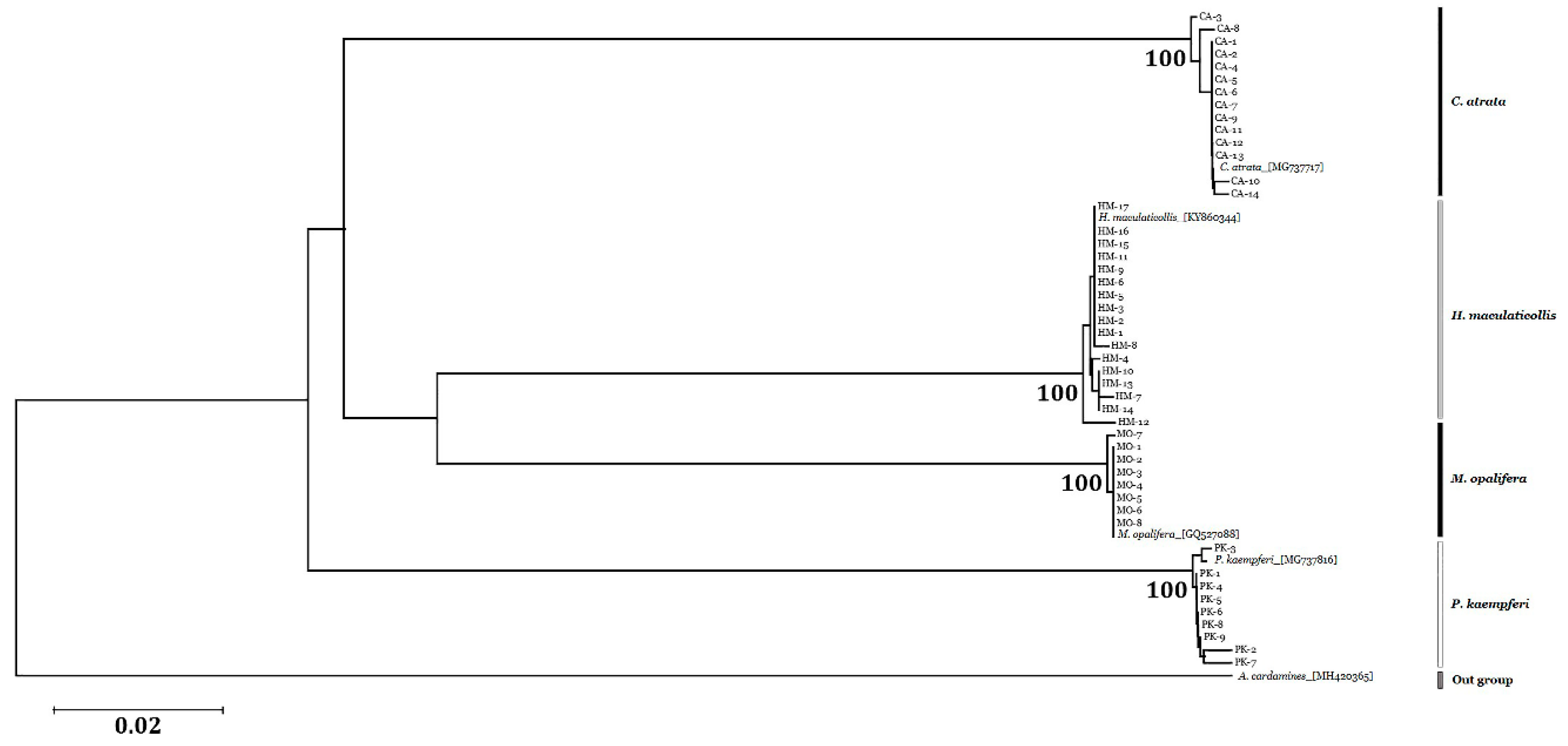
3.4. Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Relationships
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, D.; Bennet-Clark, H.C. The role of the tymbal in cicada sound production. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boulard, M. Notes sur la biologie larvaire de las cigales (Hom. Cicadidae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1965, 1, 503–521. [Google Scholar]
- Pachas, P.O. La chicharra de la yerba mate (Fidicina mannifera, Fab., 1803) su biología e observaciones sobre los métodos de control en Misiones (República Argentina). Idia 1966, 217, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, K.S.; Simon, C. The ecology, behavior, and evolution of periodical cicadas. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 40, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J. Cicada of Korea; Geobook: Seoul, Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, D. Nymphal development and lifecycle length of Kikihia ochrina (Walker) (Homoptera: Cicadidae). Weta 2006, 31, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dybas, H.S.; Lloyd, M. The habitat of 17-year periodical cicadas (Homoptera: Cicadidae: Magicicada Spp.). Ecol. Monogr. 1974, 44, 279–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Kim, Y.I.; Borzée, A.; Jang, Y. Efficient isolation method for high-quality genomic DNA from cicada exuviae. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 8161–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. The Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia, 4th ed.; 1st Supplement; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety: Osong, Korea, 2013; pp. 243–244.
- Defining Dictionary for Medicinal Herbs. Available online: http://boncho.kiom.re.kr/codex (accessed on 4 April 2019).
- Park, J.; Choi, G. Review on herbal medicinal materials in the Korean Pharmacopoeia and the Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia. Korean Herb. Med. Inf. 2016, 4, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Yang, S.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, B.C. Studies on morphological characteristics of the original species, Cryptotympana atrata as a Cicadidae Periostracum. Korean Herb. Med. Inf. 2019, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopeia, 2nd ed.; English Version; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2013.
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, M.-T.; Peng, W.-H.; Yeh, F.-T.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S. Studies on the anticonvulsive, sedative and hypothermic effects of Periostracum Cicadae extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 35, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.S.; Wu, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.S. Evaluation of anticoagulant and fibrinolytic activities from crude extracts of insects. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 1999, 30, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Q.; Tao, G.; Gao, Q.; Lv, T.; Wang, D. Analyses on ingredients and antibacterial activity of periostracum cicadae. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2010, 47, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-W.; Cho, H.-B.; Kim, S.-B.; Choe, C.-M.; Seo, Y.-J. The anti-inflammatory effects of Cicadidae Periostracum. Korean J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 24, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.R.; Chae, J.W. Effects of Cicadae Periostracum (CP) in allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) induced by DNCB in Mice. J. Korean Orient. Pediatr. 2015, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryasheva, I.V. Larvae of the Cicada (Homoptera, Cicadidae) Fauna of the USSR; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Villet, M.H. Systematic status of Platypleura stridula L. and Platypleura capensis L. (Homoptera, Cicadidae). S. Afr. J. Zool. 1989, 24, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulard, M.; Mondon, B. Vies et Mémoires de Cigales: Provence, Languedoc, Méditerranée; Editions de l’Equinoxe: Barbentane, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, P.C. Cicadas (Hemiptera, Auchenorrhyncha, Cicadidae) from Brasília (Brazil): Exuviae of the last instar with key of the species. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2003, 20, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulard, M. The Cicadas of Thailand: General and Particular Characteristics; White Lotus Co.: Bangkok, Thailand, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Maccagnan, D.H.B.; Martinelli, N.M. Description and key to the fifth-instars of some cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) associated with coffee plants in Brazil. Neotrop. Entomol. 2011, 40, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midgley, J.M.; Bouwer, N.; Villet, M.H. The final instar exuvium of Pycna semiclara Germar, 1834 (Hemiptera: Cicadidae). Afr. Invertebr. 2013, 54, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Oh, S.Y.; Jang, Y. Morphometrics of the final instar exuviae of five cicada species occurring in urban areas of central Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, C. Morphology and identification of the final instar nymphs of three cicadas (Hemiptera, Cicadidae) in Guanzhong Plain, China based on comparative morphometrics. ZooKeys 2014, 425, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M. Description of the nymphs of Mogannia minuta Matsumura (Homoptera: Cicadidae), a pest of sugarcane in the Ryukyus. Kontyû 1976, 44, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson, A.R.; Andersen, D.C.; Kondratieff, B.C. Observations of the larval stages of Diceroprocta apache Davis (Homoptera: Tibicinidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2002, 75, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, D.; Brodbeck, S.; Holderegger, R. Characterization of microsatellite loci in Leucorrhinia caudalis, a rare dragonfly endangered throughout Europe. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2009, 1, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjeyan, K.J.; Paramasivan, R.; Tewari, S.C.; Rajendran, R.; Thenmozhi, V.; Victor Jerald Leo, S.; Venkatesh, A.; Tyagi, B.K. Molecular identification of mosquito vectors using genomic DNA isolated from eggshells, larval and pupal exuvium. Trop. Biomed. 2010, 27, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monroe, E.M.; Lynch, C.; Soluk, D.A.; Britten, H.B. Nonlethal tissue sampling techniques and microsatellite markers used for first report of genetic diversity in two populations of the endangered Somatochlora hineana (Odonata: Corduliidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, M.C.; Boyer, S.; Worner, S.; Armstrong, K. Noninvasive molecular methods to identify live scarab larvae: An example of sympatric pest and nonpest species in New Zealand. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, J.L. Insect Physiology and Biochemistry, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, N.; Midgley, J.M.; Timm, A.E.; Villet, M.H. Successful identification of the final instar nymph of Quintilia carinata (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) by DNA extraction from the exuvium. J. Nat. Hist. 2014, 48, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.C.; Moulds, M.; Hill, K.B.; Price, B.W.; Wade, E.J.; Owen, C.L.; Goemans, G.; Marathe, K.; Sarkar, V.; Cooley, J.R.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of the cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) with a review of tribe and subfamily classification. Zootaxa 2018, 4424, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD: Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data; Version 6; Gleneden Beach, MjM Software: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.J.; Moon, B.C.; Yang, S.; Han, K.S.; Choi, G.; Lee, A.Y. Rapid authentication of the herbal medicine plant species Aralia continentalis Kitag. and Angelica biserrata C.Q. Yuan and R.H. Shan using ITS2 sequences and multiplex-SCAR markers. Molecules 2016, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Chen, H.-M.; Yang, J.-X.; Jin, J.-Q.; Jiang, K.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Murphy, R.W.; Zhang, Y.-P. Universal COI primers for DNA barcoding amphibians. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: An User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M.A. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, S.; Onogi, S. The distribution of Platypleura kaempferi (Fabricius) (Homoptera: Cicadidae) nymphs in the soil of a loquat fruit tree orchard. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1980, 24, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C. Ecology of Meimuna mongolica (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) nymphs: Instars, morphological variation, vertical distribution and population density, host-plant selection, and emergence phenology. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Łukasik, P.; Chong, R.A.; Nazario, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Bublitz, D.A.C.; Campbell, M.A.; Meyer, M.C.; Leuven, J.T.V.; Pessacq, P.; Veloso, C.; et al. One hundred mitochondrial genomes of cicadas. J. Hered. 2018, 110, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.; Ratnasingham, S.; de Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; García-Robledo, C.; Uriarte, M.; Erickson, D.L. DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Hayashi, M.; Wei, C. Morphological variation, genetic differentiation and phylogeography of the East Asia cicada Hyalessa maculaticollis (Hemiptera: Cicadidae). Syst. Entomol. 2018, 43, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
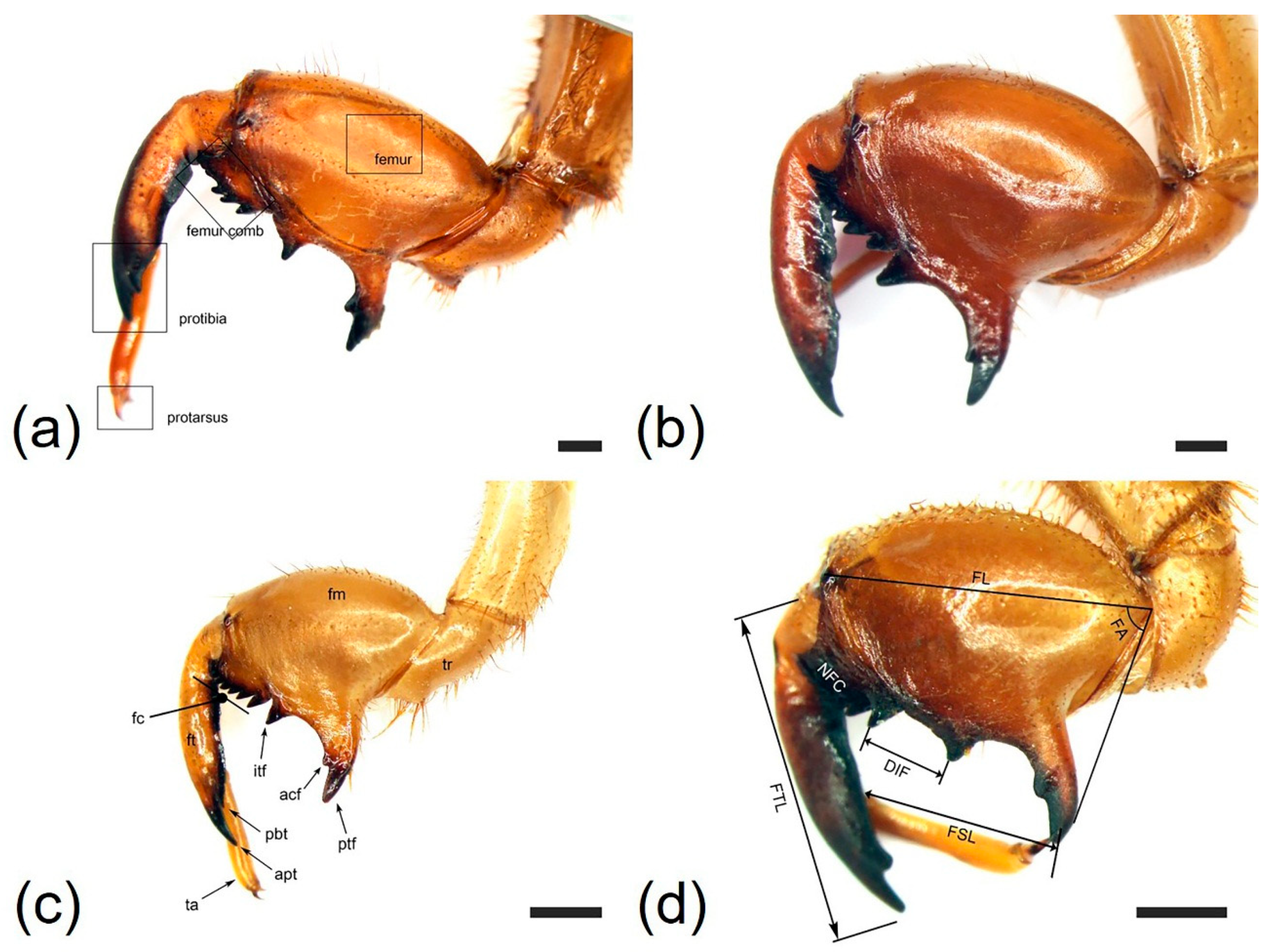
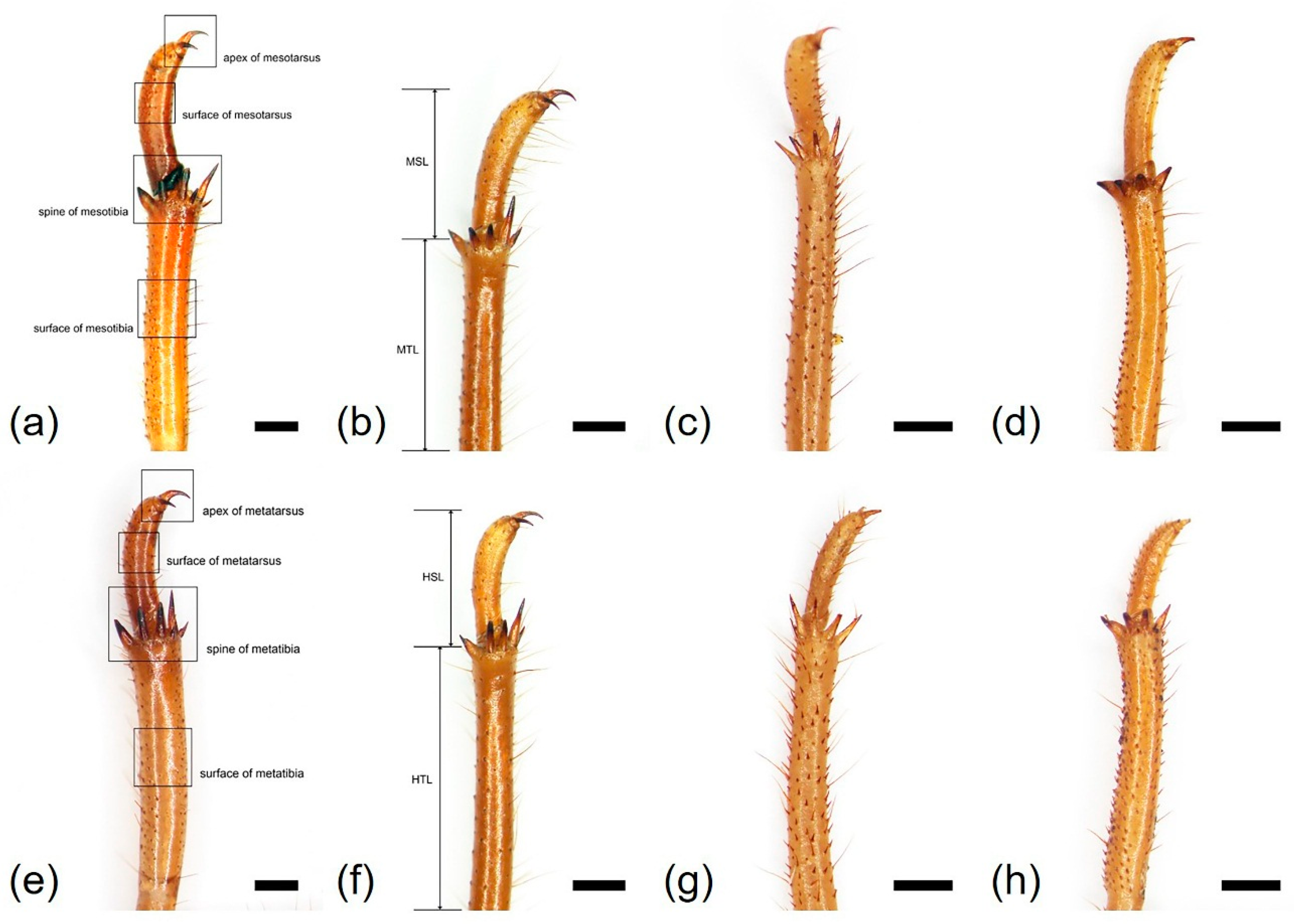
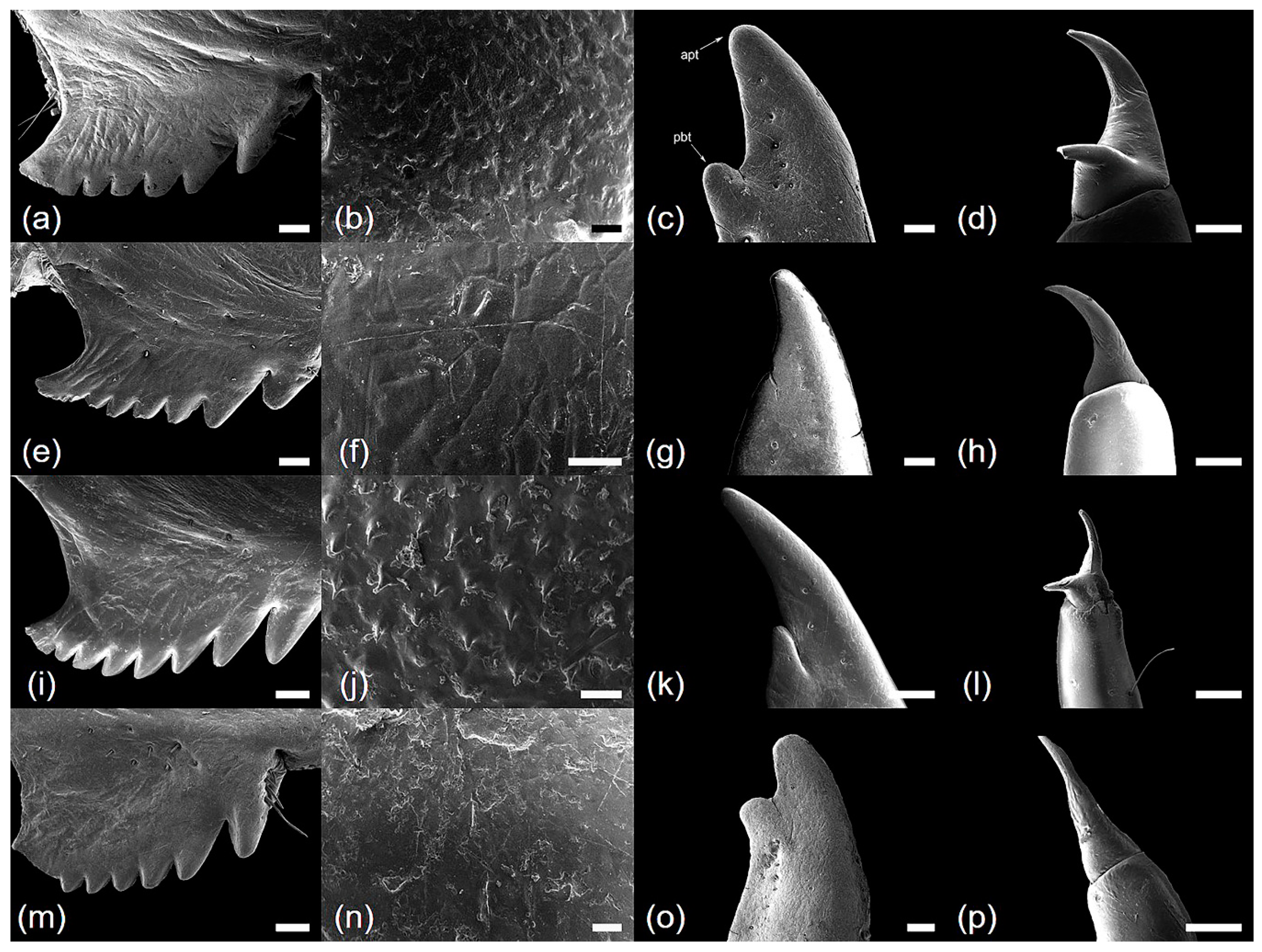

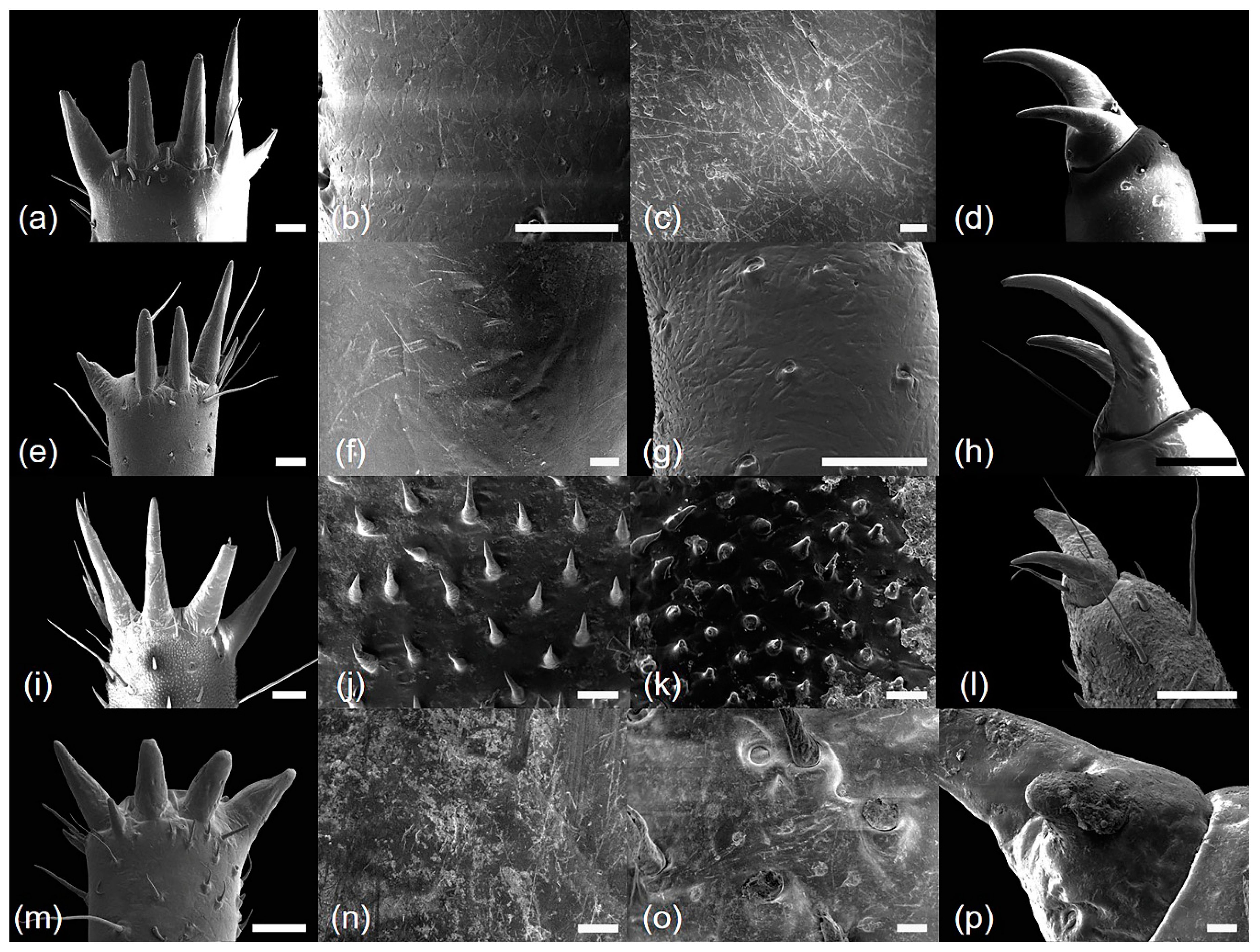
| Characteristics | Cryptotympana atrata | Hyalessa maculaticollis | Meimuna opalifera | Platypleura kaempferi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fore-leg | ||||
| Profemur surface | echinate | smooth | echinate | smooth |
| Profemur length (FL, mm) | 6.18 ± 0.28 | 5.83 ± 0.31 | 4.28 ± 0.32 | 3.85 ± 0.26 |
| Protibia length (FTL, mm) | 6.09 ± 0.34 | 6.14 ± 0.26 | 4.04 ± 0.19 | 3.93 ± 0.29 |
| Femoral comb surface | smooth | smooth | smooth | smooth |
| Femoral tooth angle (FA, °) | 70.8 ± 4.26 | 67.1 ± 4.89 | 59.4 ± 3.85 | 82.8 ± 4.32 |
| Number of femoral comb teeth (NFC) | (6)7(8) | (6)7 | (7)8 | 7 |
| Femoral formula | 2–1–7 | 2–1–7 | 2–1–8 | 2–1–7 |
| Distance between itf and ltf (DIF, mm) | 1.56 ± 0.11 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.06 | 1.15 ± 1.00 |
| Pretarsus length (FSL, mm) | 4.23 ± 0.20 | 3.73 ± 0.22 | 2.42 ± 0.26 | 2.50 ± 0.29 |
| Mid-leg | ||||
| Mesotibia surface | smooth | smooth | echinate | smooth |
| Mesotibia length (MTL, mm) | 7.48 ± 0.26 | 7.92 ± 0.40 | 6.46 ± 0.61 | 5.35 ± 0.30 |
| Number of mesotibia spine (NMS) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Mesotarsus surface | smooth | smooth | echinate | smooth |
| Mesotarsus length (MSL, mm) | 3.94 ± 0.38 | 3.22 ± 0.33 | 2.21 ± 0.29 | 2.29 ± 0.23 |
| Hind leg | ||||
| Metatibia surface | smooth | smooth | echinate | smooth |
| Metatibia length (HTL, mm) | 7.61 ± 0.28 | 8.19 ± 0.54 | 6.62 ± 0.48 | 5.20 ± 0.37 |
| Number of metatibia spine (NHS) | 6–7 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Metatarsus surface | smooth | smooth | echinate | smooth |
| Metatarsus length (HSL, mm) | 3.37 ± 0.29 | 2.58 ± 0.19 | 1.98 ± 0.14 | 2.01 ± 0.21 |
| No. | Characteristics | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (61.743%) | (23.144%) | (7.512%) | ||
| 1 | FL | −0.3579 | 0.0004 | −0.1003 |
| 2 | FTL | −0.3450 | −0.0208 | −0.2532 |
| 3 | FA | 0.0829 | −0.536 | −0.1981 |
| 4 | NFC | 0.1532 | 0.4048 | 0.4666 |
| 5 | DIF | −0.1326 | −0.4735 | 0.4615 |
| 6 | FSL | −0.3464 | −0.1239 | −0.0448 |
| 7 | MTL | −0.3216 | 0.1876 | −0.2463 |
| 8 | MSL | −0.3378 | −0.1538 | 0.0779 |
| 9 | NMS | −0.2571 | 0.4051 | 0.1295 |
| 10 | HTL | −0.3107 | 0.2297 | −0.2421 |
| 11 | HSL | −0.3309 | −0.181 | 0.2019 |
| 12 | NHS | −0.3087 | 0.0203 | 0.5205 |
| Eigenvalue | 7.409 | 2.777 | 0.901 |
| Species | Amplicon Length (bp) | 1 Intraspecific Distance (%) | 1 Interspecific Distance (%) | G + C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. atrata | 690 | 0.11 ± 0.13 | 19.67 ± 0.80 | 31.00 |
| H. maculaticollis | 690 | 0.16 ± 0.17 | 18.60 ± 1.65 | 30.87 |
| P. kaempferi | 690 | 0.21 ± 0.20 | 20.16 ± 0.07 | 30.13 |
| M. opalifera | 690 | 0.03 ± 0.07 | 17.72 ± 1.59 | 30.84 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.-H.; Kim, W.J.; Cha, J.-M.; Yang, S.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C. Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs. Insects 2019, 10, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070199
Song J-H, Kim WJ, Cha J-M, Yang S, Choi G, Moon BC. Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs. Insects. 2019; 10(7):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070199
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jun-Ho, Wook Jin Kim, Ji-Min Cha, Sungyu Yang, Goya Choi, and Byeong Cheol Moon. 2019. "Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs" Insects 10, no. 7: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070199
APA StyleSong, J.-H., Kim, W. J., Cha, J.-M., Yang, S., Choi, G., & Moon, B. C. (2019). Comparative Morphological, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Studies of Four Cicadinae Species Using Exuvial Legs. Insects, 10(7), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10070199






