Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens
2.2. Micromachining and Surface Characterization
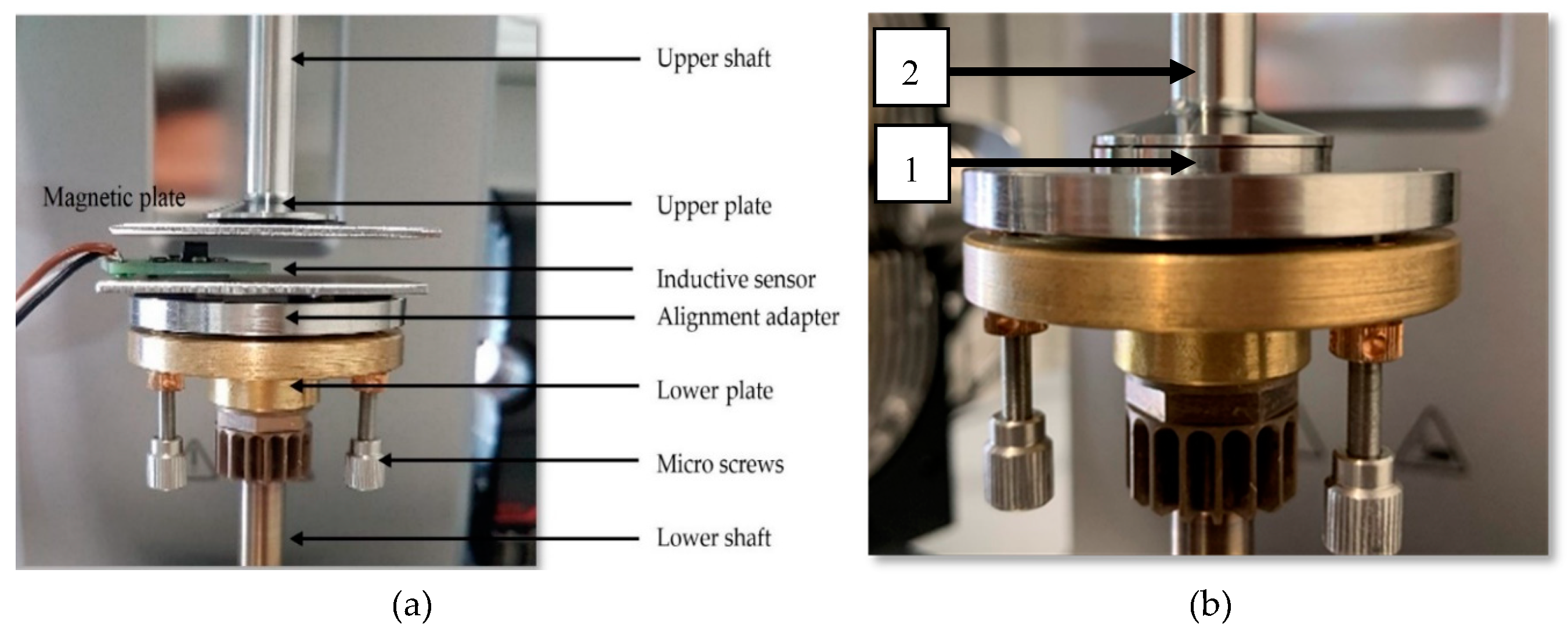
2.3. Rheological Setup and Determination of Viscosity in Thin Gaps
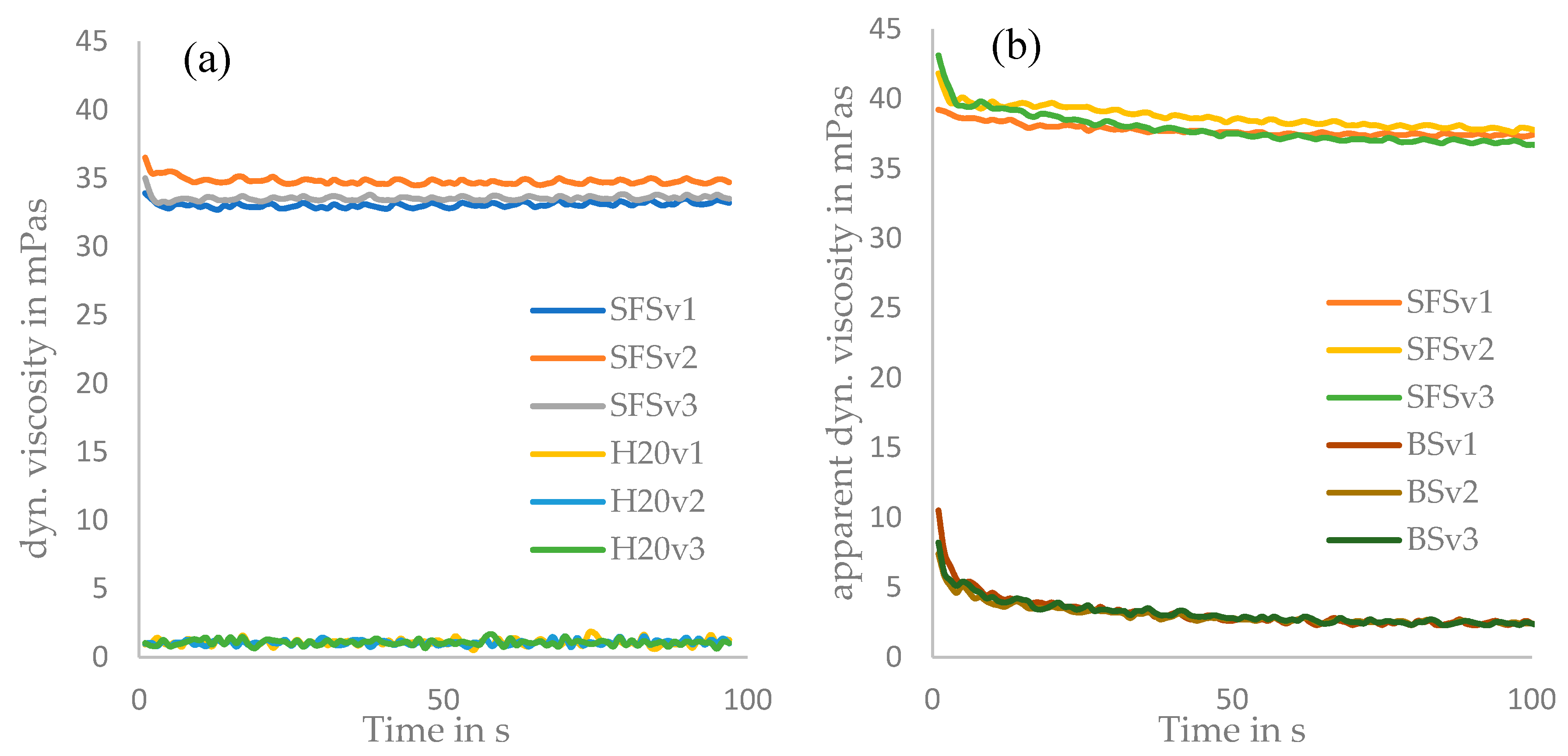
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kung, M.S.; Markantonis, J.; Nelson, S.D.; Campbell, P. The Synovial Lining and Synovial Fluid Properties after Joint Arthroplasty. Lubricants 2015, 3, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D. Surgery and joint replacement for joint disease. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1998, 69, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M.; Kriegsmann, J.; Gehrke, T.; Bertz, S. Abriebpartikel: Schlüssel der aseptischen Prothesenlockerung? Der Pathologe 2006, 27, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Hsu, S.; Costa, H. A critical assessment of surface texturing for friction and wear improvement. Wear 2017, 372, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wong, P.; Gachot, C. Facilitating the Study of the Texturing Effect on Hydrodynamic Lubrication. Lubricants 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Liu, Y.W. Design and optimization of a new geometric texture shape for the enhancement of hydrodynamic lubrication performance of parallel slider surfaces. Biosurface Biotribol. 2016, 2, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropper, D.; Wang, L.; Harvey, T.J. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured surfaces: A review of modeling techniques and key findings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Mao, J.; Hu, Y.; Luo, J. Optimization of groove texture profile to improve hydrodynamic lubrication performance: Theory and experiments. Friction 2018, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Grützmacher, P.G.; Rosenkranz, A. Laser Surface Texturing of TiAl Multilayer Films—Effects of Microstructure and Topography on Friction and Wear. Lubricants 2018, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Chyr, A.; Sanders, A.P.; Raeymaekers, B. Designing prosthetic knee joints with bio-inspired bearing surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2014, 77, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyr, A.; Qiu, M.; Speltz, J.W.; Jacobsen, R.L.; Sanders, A.P.; Raeymaekers, B. A patterned microtexture to reduce friction and increase longevity of prosthetic hip joints. Wear 2014, 315, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjali, A.; Langhorn, J.; Monson, K.; Raeymaekers, B. Using a patterned microtexture to reduce polyethylene wear in metal-on-polyethylene prosthetic bearing couples. Wear 2017, 392, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Yang, P.; Dymond, I.; Fisher, J.; Jin, Z. Effect of surface texturing on the elastohydrodynamic lubrication analysis of metal-on-metal hip implants. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Rebenda, D.; Sasaki, S.; Hekrle, P.; Vrbka, M.; Zou, M. Enhanced lubricant film formation through micro-dimpled hard-on-hard artificial hip joint: An in-situ observation of dimple shape effects. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 81, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhling, U.; Scholz, J.; Grundei, H.; Thomas, W. Bionische Oberflächengestaltung der Metall/Metall-Gleitpaarung in der Hüftendoprothetik Optimierung tribologischer Eigenschaften / Bionic surface design in metal on metal bearings for total hip arthroplasty–Optimization of tribological characteristics. Biomed. Tech. Eng. 2005, 50, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Choi, H.-J. Optimization of Surface Texturing for Contact between Steel and Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Under Boundary Lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorn, J.; Borjali, A.; Hippensteel, E.; Nelson, W.; Raeymaekers, B. Microtextured CoCrMo alloy for use in metal-on-polyethylene prosthetic joint bearings: Multi-directional wear and corrosion measurements. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawano, H.; Warisawa, S.; Ishihara, S. Study on long life of artificial joints by investigating optimal sliding surface geometry for improvement in wear resistance. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabolsi, M.; Klassen, T.; Mantwill, F.; Gaertner, F.; Siegel, F.; Schulz, A.-P. Patterned CoCrMo and Al2O3surfaces for reduced free wear debris in artificial joint arthroplasty. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Kaneda, K.; Yuhta, T.; Nishimura, I.; Yasuda, K.; Matsuno, T. Reduction of polyethylene wear by concave dimples on the frictional surface in artificial hip joints. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Fleming, L.; Wudebwe, U.; Bowen, J.; Grover, L.M. Development of a synovial fluid analogue with bio-relevant rheology for wear testing of orthopaedic implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 32, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortel, E.L.; Charbonnier, B.; Heuberger, R. Development of a Synthetic Synovial Fluid for Tribological Testing. Lubricants 2015, 3, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, M.; Manjoo, A.; Shaw, P.; Niazi, F.; Rosen, J. A Comparison between Rheological Properties of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Preparations and Reported Human Synovial Fluid. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.P. The viscosity of normal and pathological human synovial fluids. Biochem. J. 1955, 59, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucco, D.; McKinley, G.H.; Scott, R.D.; Spector, M. Rheology of joint fluid in total knee arthroplasty patients. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagatia, M.; Jin, Z.M. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication analysis of metal-on-metal hip prostheses under steady state entraining motion. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2001, 215, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myant, C.; Cann, P. On the matter of synovial fluid lubrication: Implications for Metal-on-Metal hip tribology. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myant, C.; Cann, P. The effect of transient conditions on synovial fluid protein aggregation lubrication. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myant, C.; Underwood, R.; Fan, J.; Cann, P. Lubrication of metal-on-metal hip joints: The effect of protein content and load on film formation and wear. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. State of the Art in Laser Surface Texturing. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichkov, B.; Momma, C.; Nolte, S.; Alvensleben, F.; Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raillard, B.; Mücklich, F. Ablation effects of femtosecond laser functionalization on surfaces. In Laser Surface Engineering; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 565–581. [Google Scholar]
- Drescher, P.; Oldorf, P.; Dreier, T.; Peters, R.; Seitz, H. Modification of joint prosthesis surfaces by ultrashort pulse laser treatment for improved joint lubrication. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 5, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wierschem, A.; Dakhil, H. Measuring low viscosities and high shear rates with a rotational rheometer in a thin-gap parallel-disk configuration. Appl. Rheol. 2014, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14242-1:2014. Implants for Surgery-Wear of Total Hip-Joint Prostheses-Part 1: Loading and Displacement Parameters for Wear-Testing Machines and Corresponding Environmental Conditions for Test. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63073.html (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Balazs, E.A.; Watson, D.; Duff, I.F.; Roseman, S. Hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid. I. Molecular parameters of hyaluronic acid in normal and arthritic human fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1967, 10, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Choudhury, D.; Ghosh, S.; Bin Mamat, A.; Pingguan-Murphy, B. Improved friction and wear performance of micro dimpled ceramic-on-ceramic interface for hip joint arthroplasty. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.B.; Greiling, H. Viscoelastic properties of pathological synovial fluids for a wide range of oscillatory shear rates and frequencies. Rheol. Acta 1978, 17, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, R.I. An Alternative Mechanism for the Lubrication of Synovial Joints. Phys. Med. Boil. 1966, 11, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintenfass, L. Lubrication in Synovial Joints. J. Bone Jt. Surgery-American Vol. 1963, 45, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.; Greiner, C.; Schneider, J.; Gumbsch, P. Efficiency of laser surface texturing in the reduction of friction under mixed lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2014, 77, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFountain, A.; Johnston, G.J.; Spikes, H.A. Elastohydrodynamic Friction Behavior of Polyalphaolefin Blends. In Tribology Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 34, pp. 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, D.B.; Walowit, J.A.; Allen, C.M. A Theory of Lubrication by Microirregularities. J. Basic Eng. 1966, 88, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H. The effect of surface texturing on reducing the friction and wear of steel under lubricated sliding contact. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Geometric Shape Effects of Surface Texture on the Generation of Hydrodynamic Pressure between Conformal Contacting Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesanghary, M.; Khonsari, M.M. On the optimum groove shapes for load-carrying capacity enhancement in parallel flat surface bearings: Theory and experiment. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiong, D. The effect of laser surface texturing on frictional performance of face seal. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
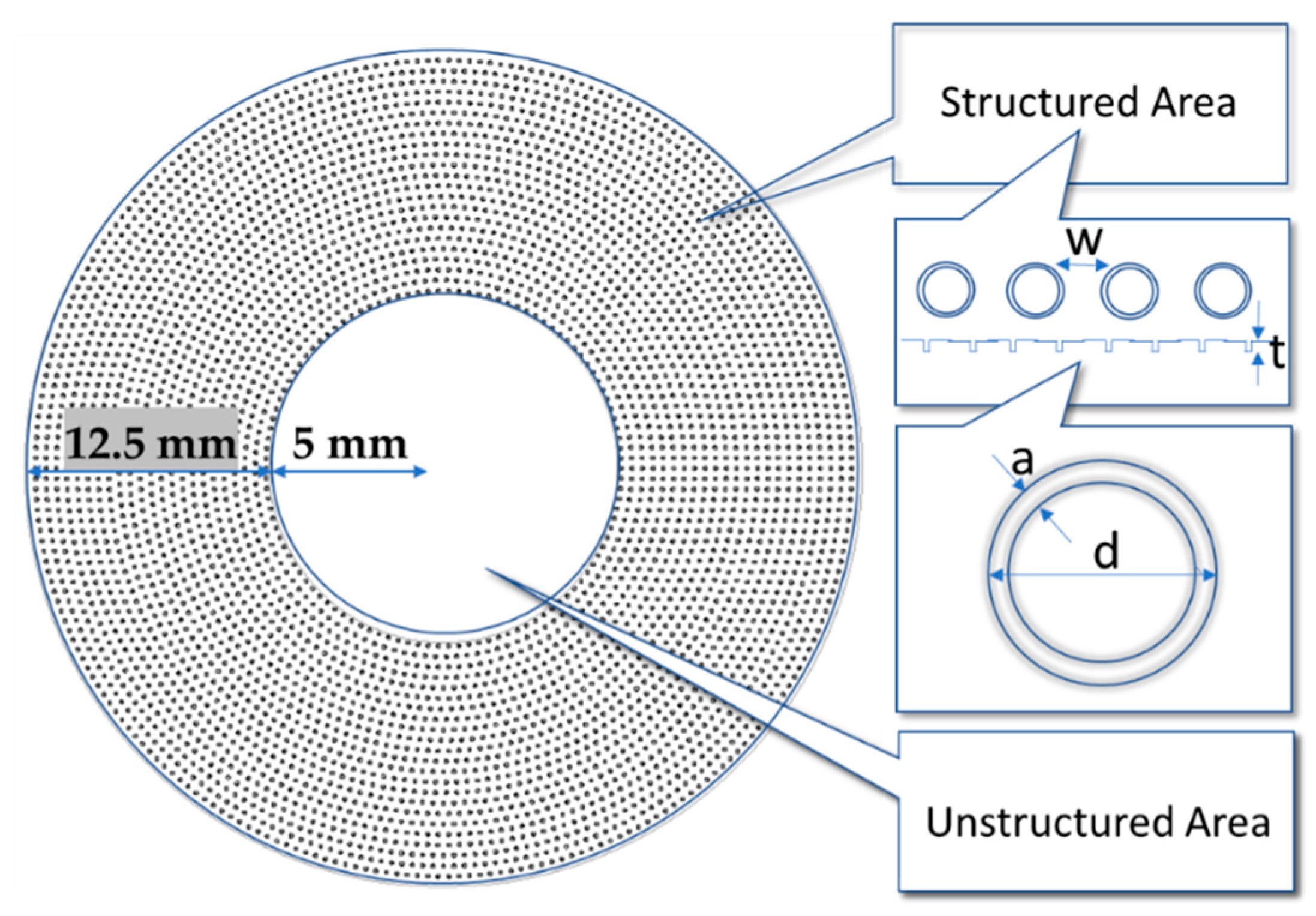

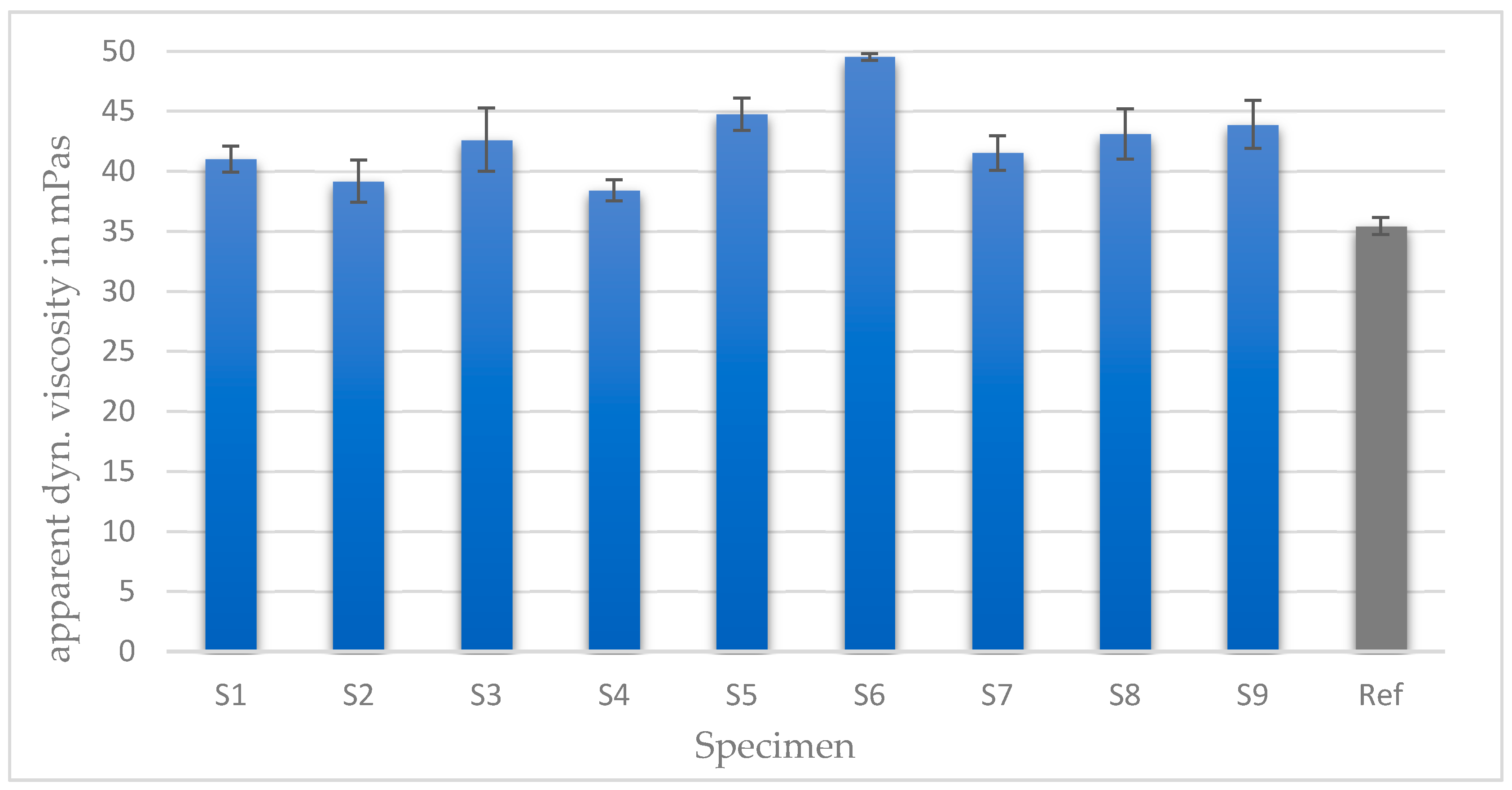

| ID | Lateral Distance w (µm) | Gap Width a (µm) | Gap Depth t (µm) | Aspect Ratio (-) | Texture Area Density (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 300 | 15 | 20 | 1.33 | 2.6 |
| S2 | 200 | 15 | 20 | 1.33 | 5.9 |
| S3 | 150 | 15 | 20 | 1.33 | 10.5 |
| S4 | 300 | 15 | 10 | 0.66 | 2.6 |
| S5 | 200 | 15 | 10 | 0.66 | 5.9 |
| S6 | 150 | 15 | 10 | 0.66 | 10.5 |
| S7 | 300 | 15 | 5 | 0.33 | 2.6 |
| S8 | 200 | 15 | 5 | 0.33 | 5.9 |
| S9 | 150 | 15 | 5 | 0.33 | 10.5 |
| Ref | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drescher, P.; Oldorf, P.; Dreier, T.; Schnell, G.; Peters, R.; Seitz, H. Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses. Lubricants 2020, 8, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8040045
Drescher P, Oldorf P, Dreier T, Schnell G, Peters R, Seitz H. Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses. Lubricants. 2020; 8(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrescher, Philipp, Paul Oldorf, Tim Dreier, Georg Schnell, Rigo Peters, and Hermann Seitz. 2020. "Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses" Lubricants 8, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8040045
APA StyleDrescher, P., Oldorf, P., Dreier, T., Schnell, G., Peters, R., & Seitz, H. (2020). Ring-Shaped Surface Microstructures for Improved Lubrication Performance of Joint Prostheses. Lubricants, 8(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8040045






