Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Friction and Wear Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Materials and Tribological Tests
3. Analytical Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Analytical Transmission Electron Microscopy
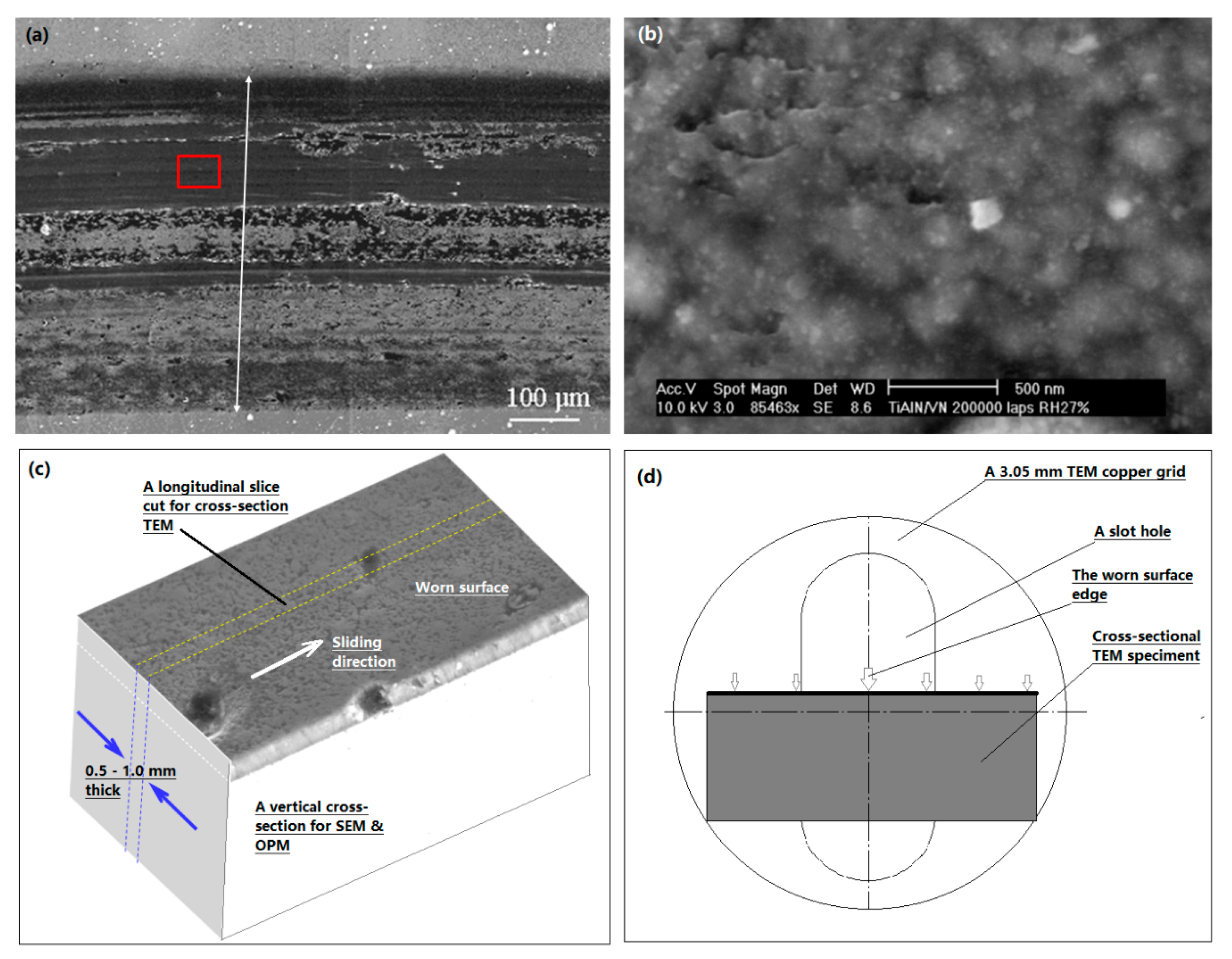
5. Sample Preparation for Wear Mechanism Study
6. A Few Examples
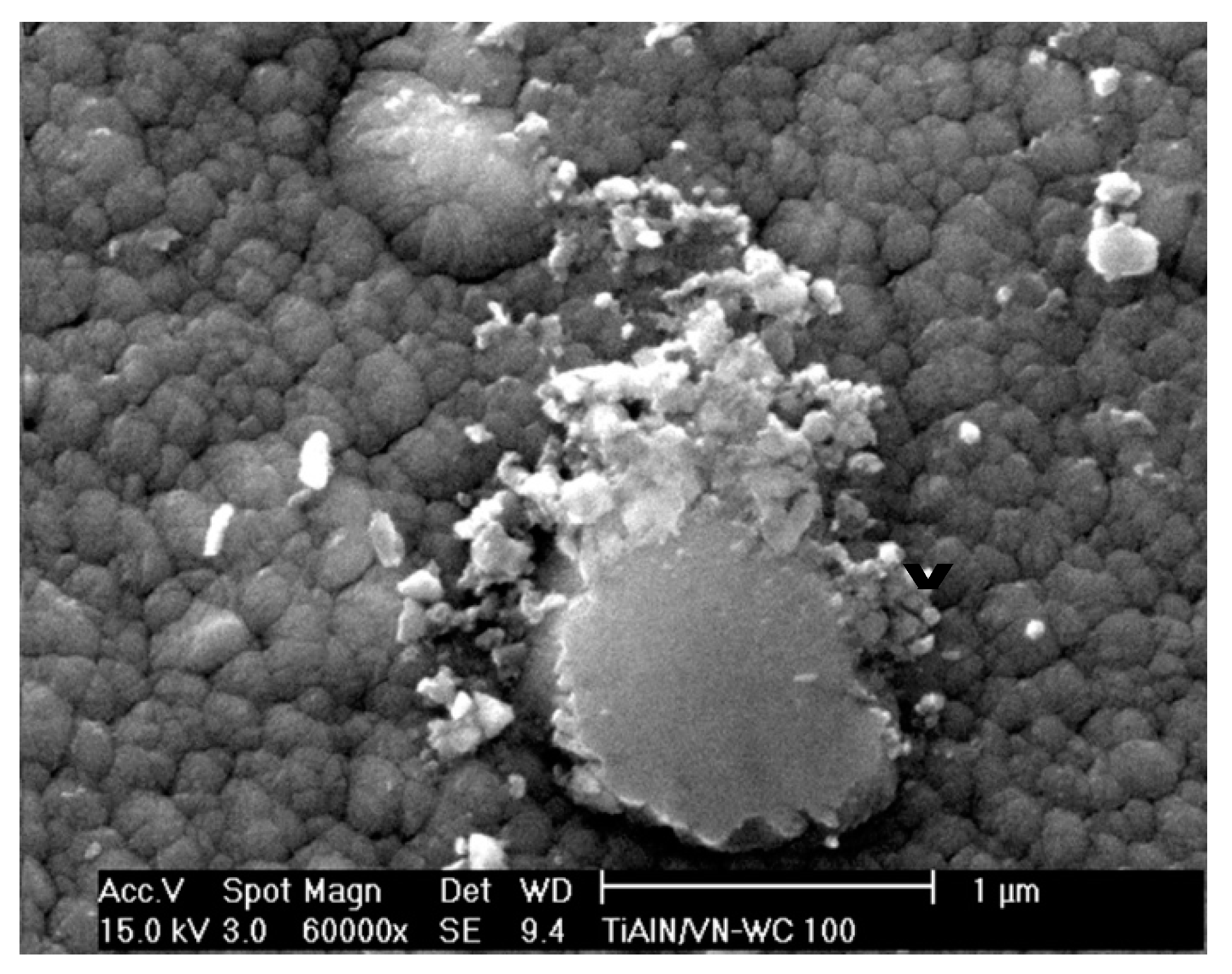
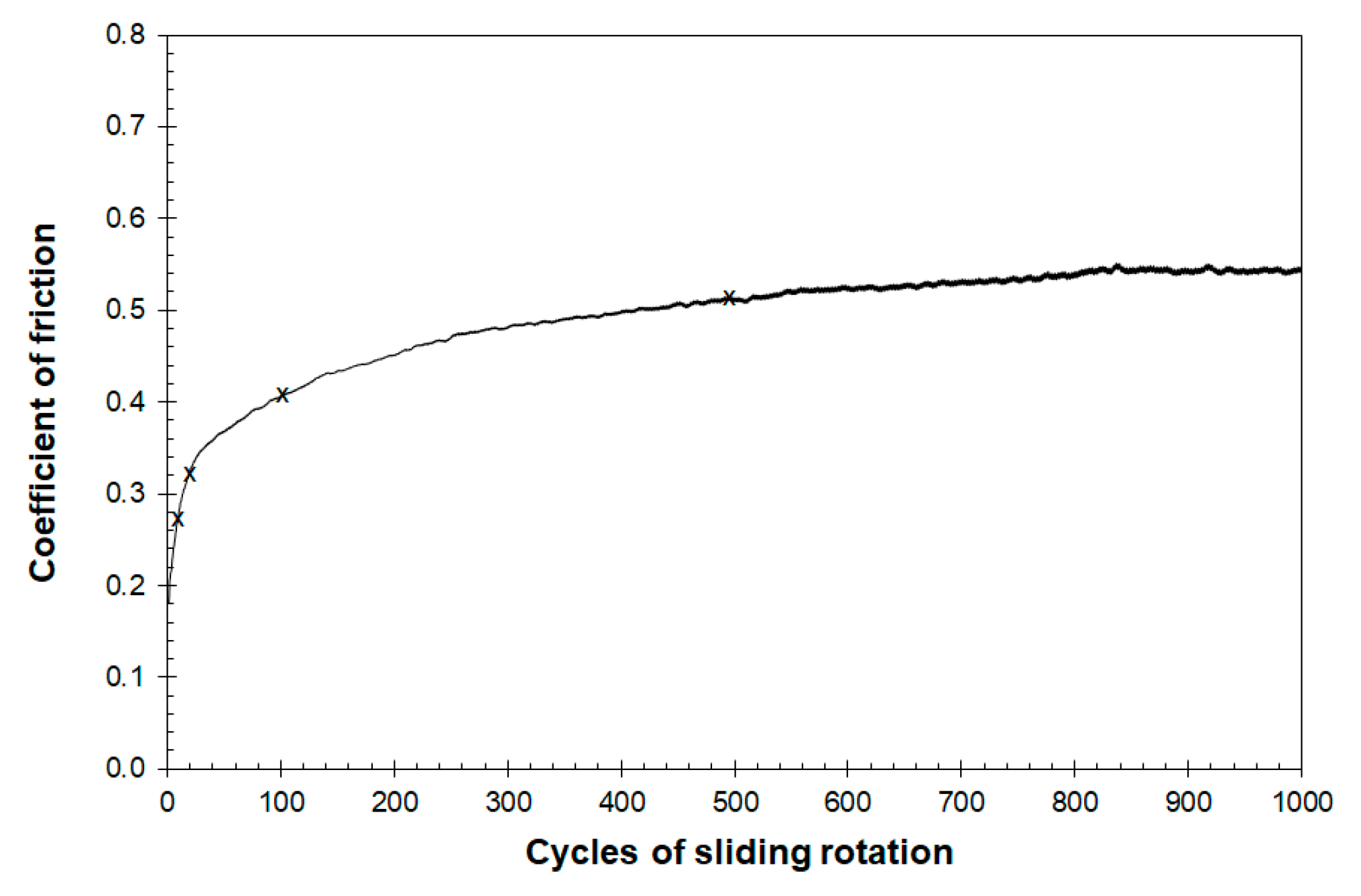
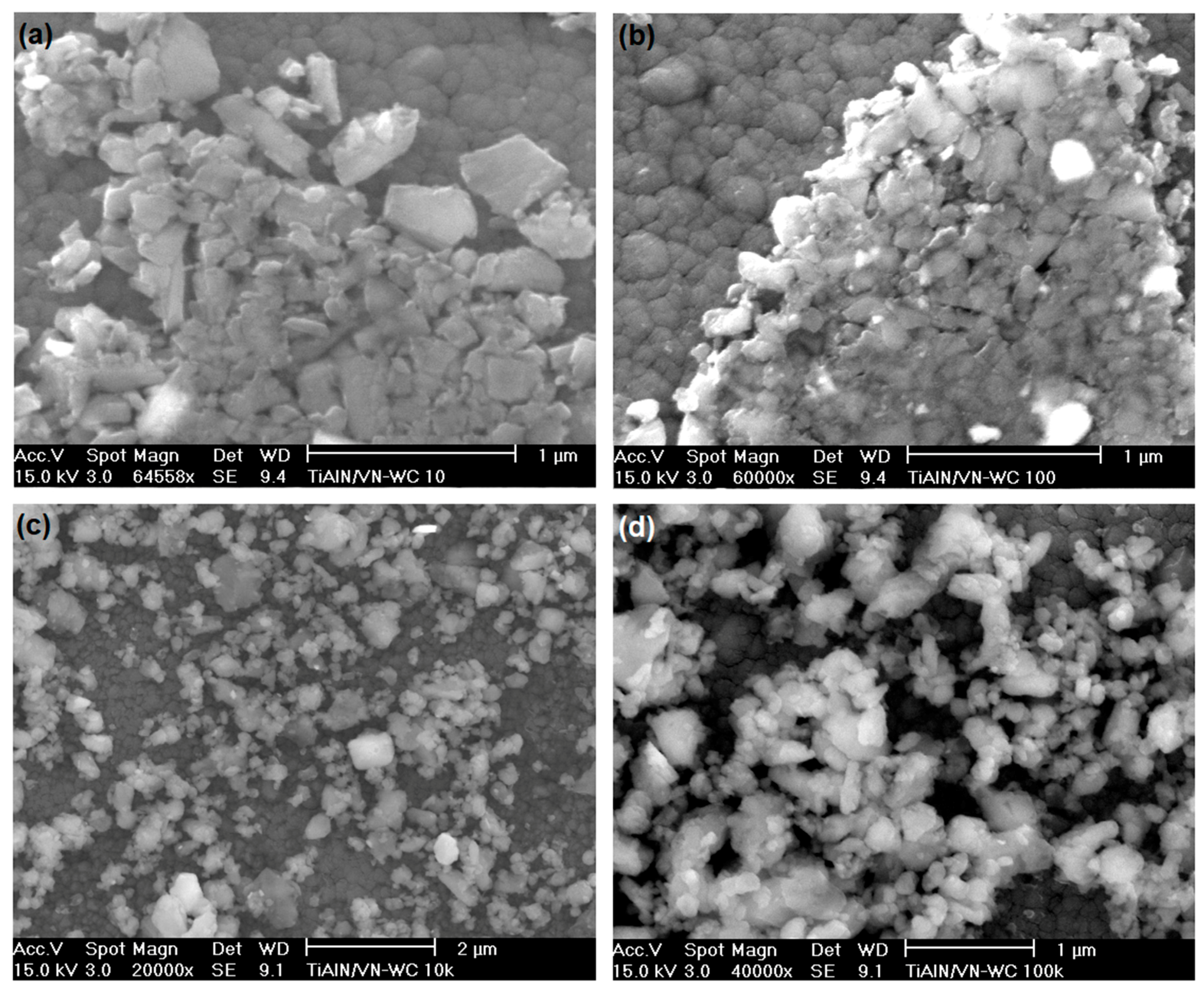
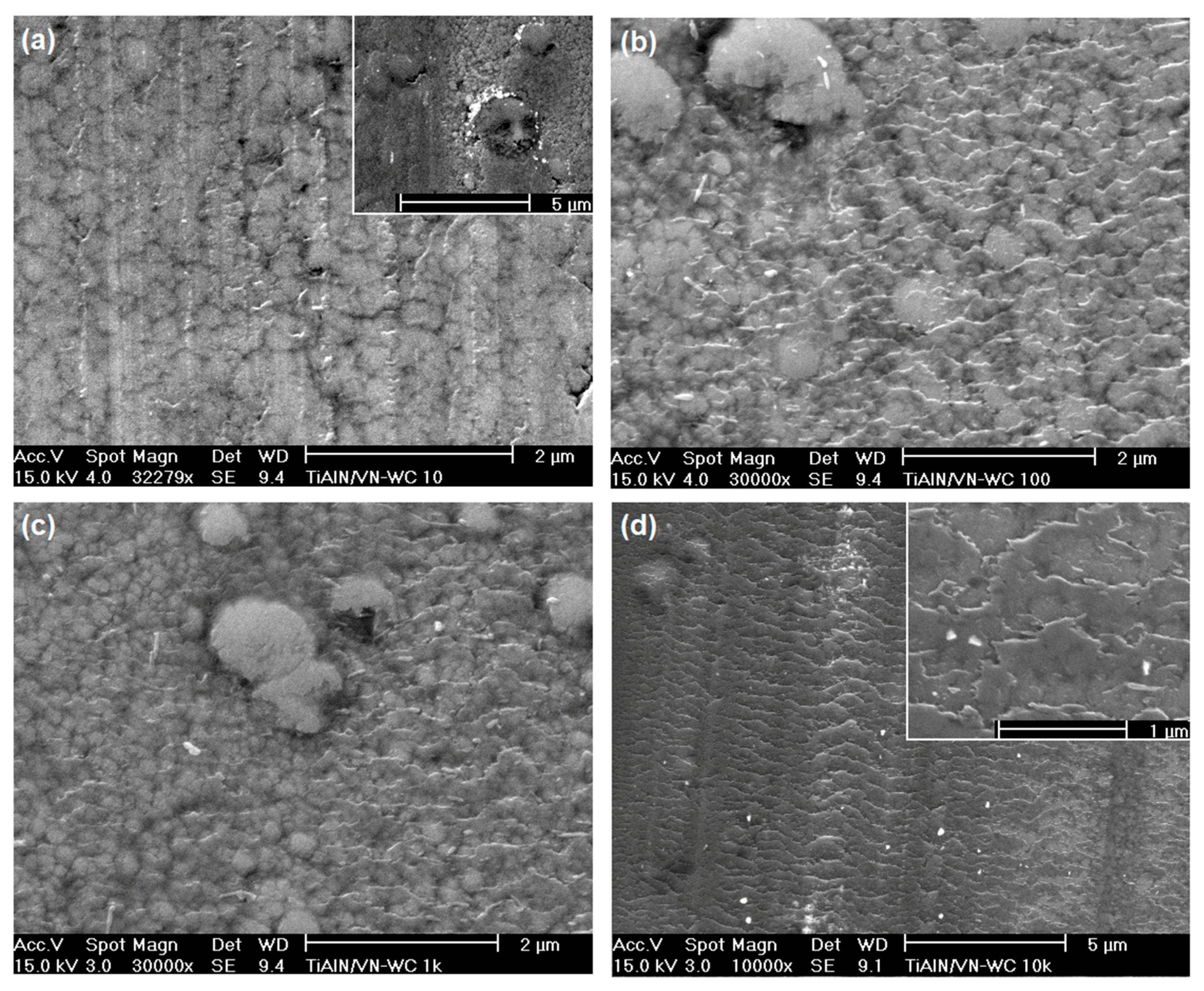
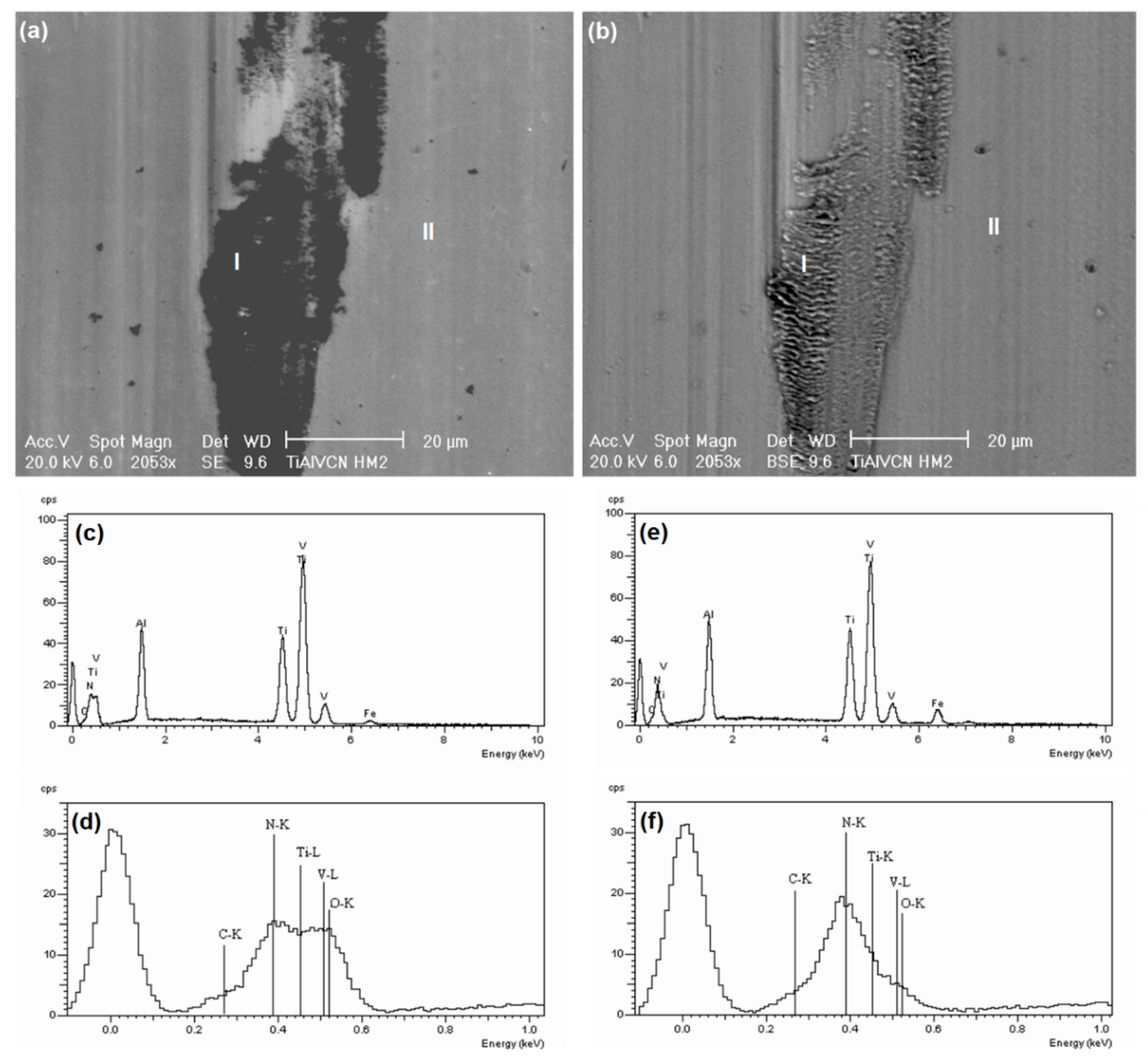
6.1. FEG-SEM Observation on the Running-In Friction
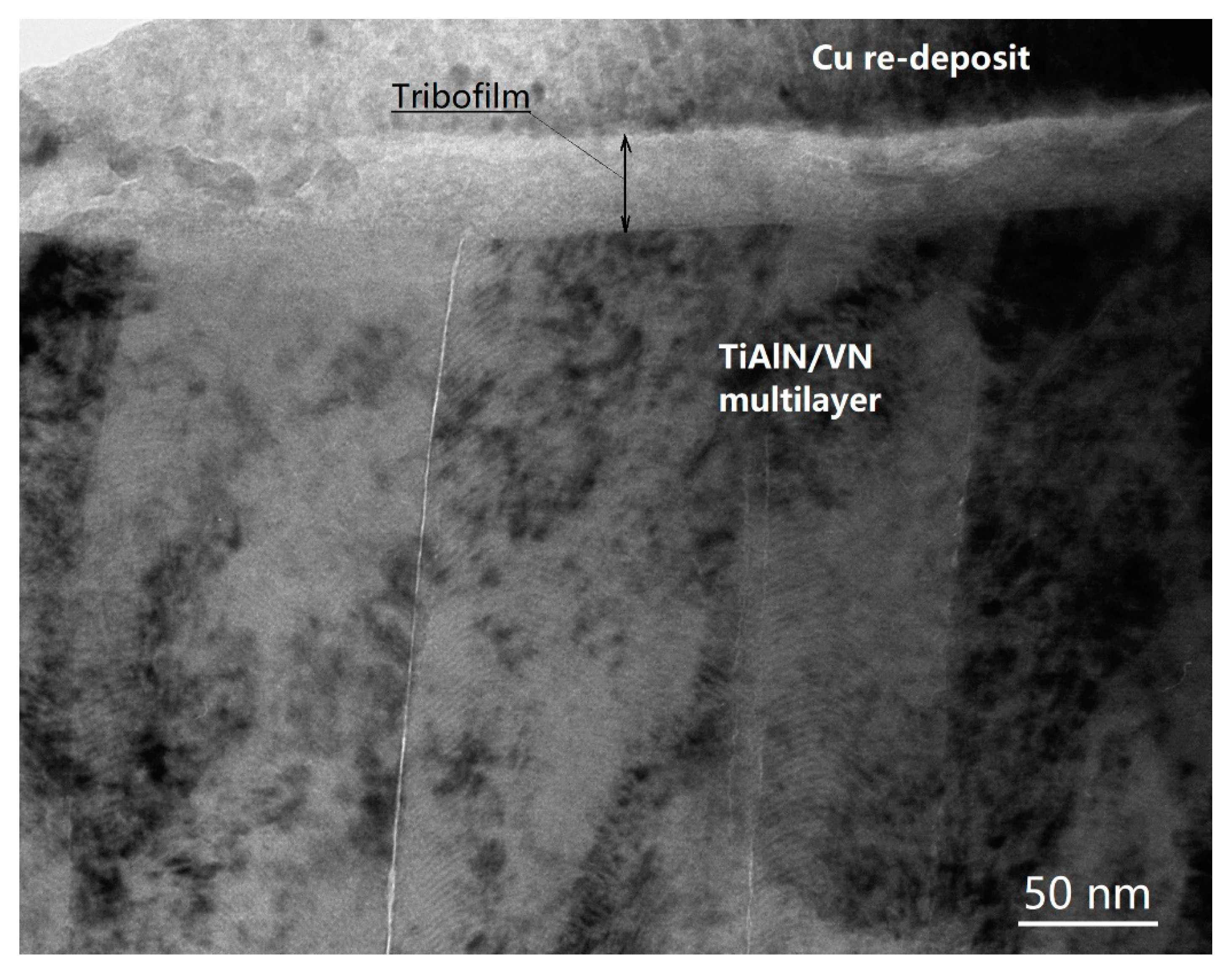
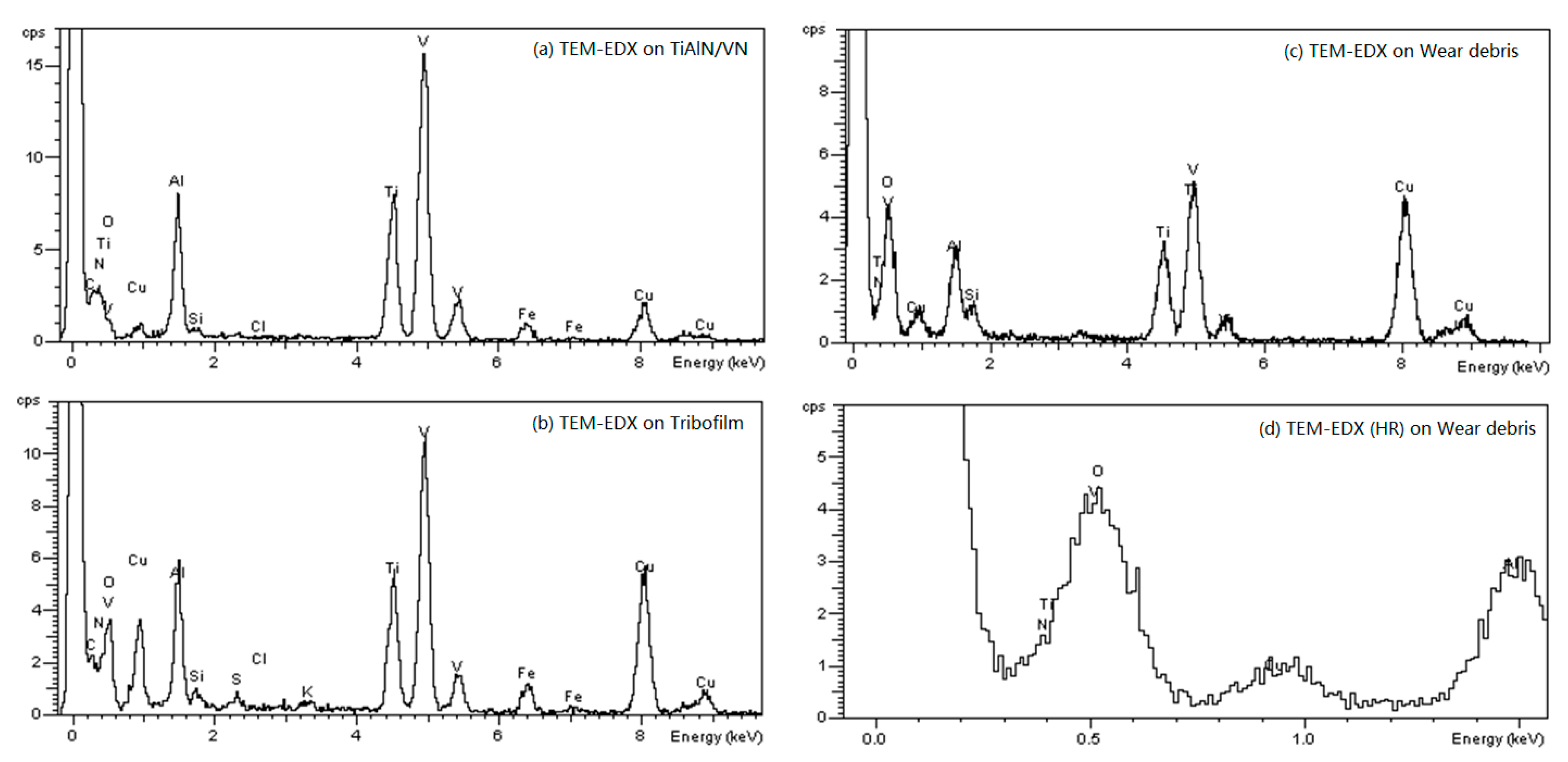
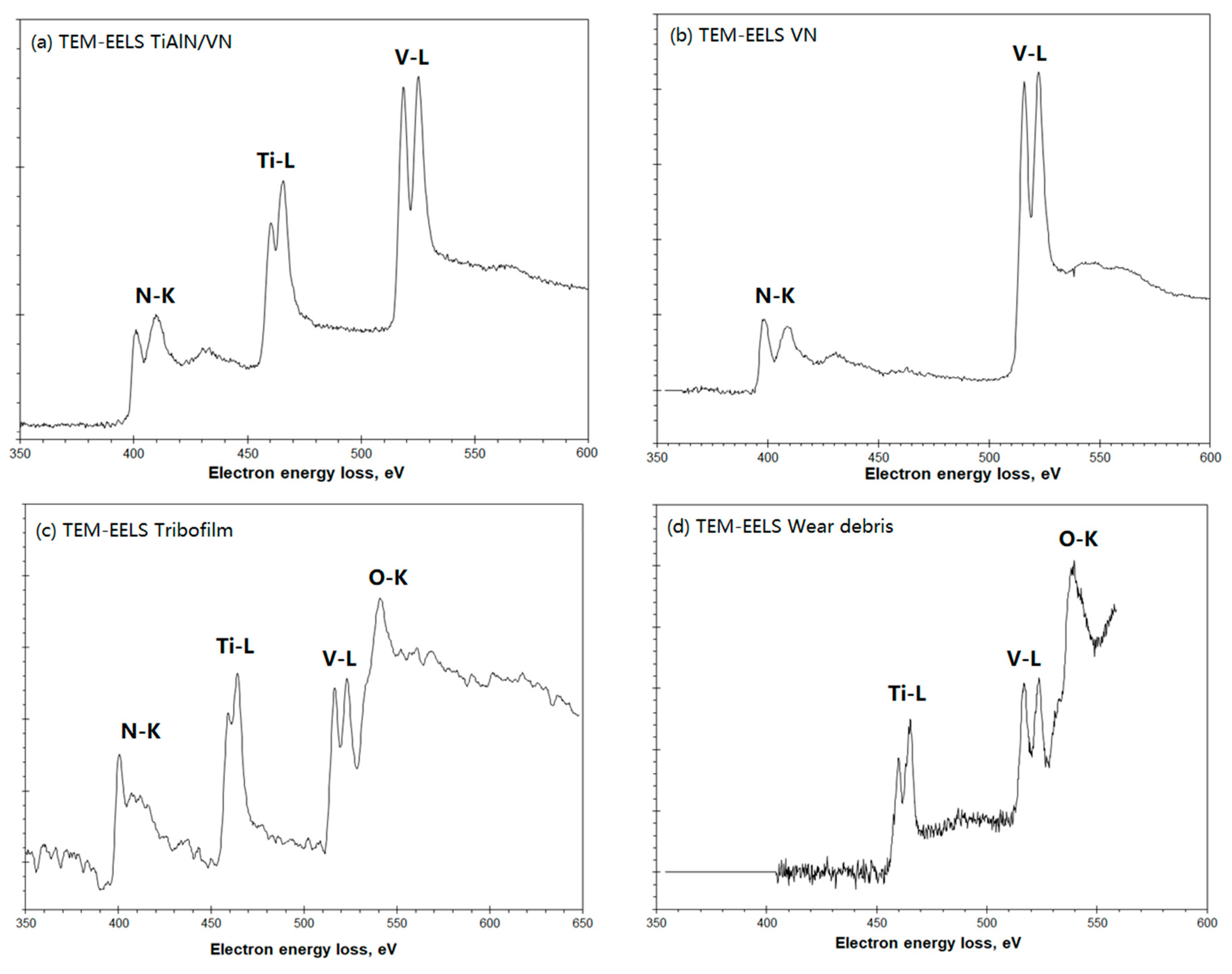
6.2. TEM, EDX, and EELS Analysis of Tribofilms
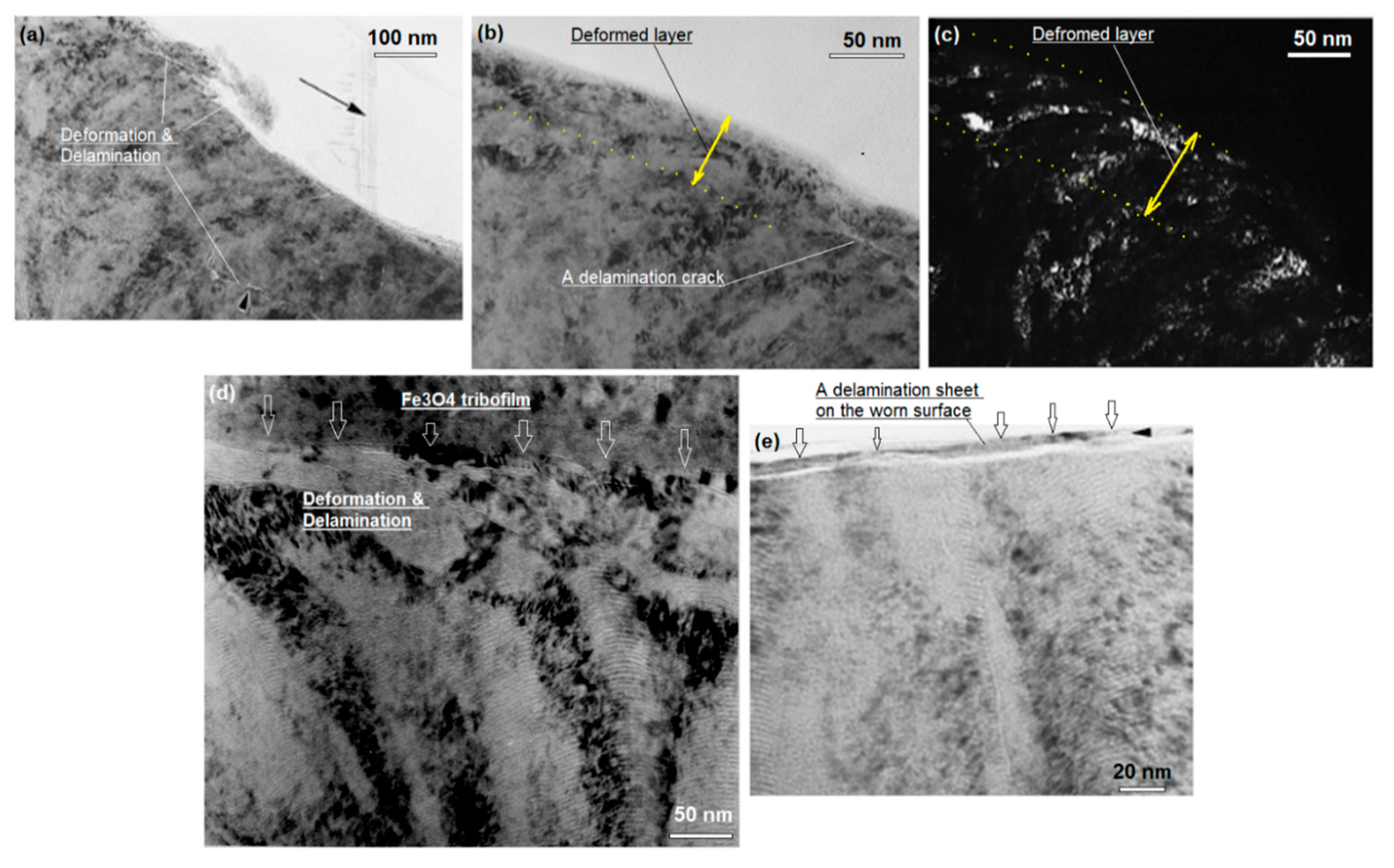
6.3. XTEM of Wear Induced Subsurface Microstructure Changes
7. Summary
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Münz, W.D. Titanium aluminium nitride films—A new alternative to TiN coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1986, 4, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldeys, S.; Deevi, S.C. Single layer and multilayer wear resistant coatings of (Ti,Al)N: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, A342, 58–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, U.; Todorova, S.; Barnett, S.A.; Sandgren, J.E.; Markert, J.C.; Greene, J.E. Growth of single-crystal TiN/VN strained-layer superlattices with extremely high mechanical hardness. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, W.D.; Donohue, L.A.; Hovsepian, P.E. Properties of various large-scale fabricated TiAlN- and CrN-based superlattice coatings grown by combined cathodic arc-unbalanced magnetron sputter deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 125, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veprek, S.; Reiprich, S.; Li, S. Superhard nanocrystalline composite materials: The TiN/Si3N4 system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 2640–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Mai, Y.M.; Shen, Y.G. Recent advances on understanding the origin of superhardness in nanocomposite coatings: A critical review. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J. Physical and mechanical properties of hard nanocomposite films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. In Nanostructured Hard Coatings; De Hosson, J.T.M., Cavaleiro, A., Eds.; Springer Science: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 407–463. [Google Scholar]
- Martınez-Martınez, D.; Lopez-Cartes, C.; Justo, A.; Fernandez, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.C. Self-lubricating Ti–C–N nanocomposite coatings prepared by double magnetron sputtering. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Shen, Y.G. Nanostructure transition: From solid solution Ti(N,C) to nanocomposite nc-Ti(N,C)/a-(C,CNx). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 221913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A.; Donnet, C. Tribology of diamond-like carbon films: Recent progress and future prospects. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, R311–R327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, J.C.; Erdemir, A.; Donnet, C.; Rojas, T.C. Friction-induced structural transformations of diamondlike carbon coatings under various atmospheres. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, A.P.; Erdemir, A.; Eryilmaz, O.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Marks, L.D. In situ TEM studies of tribo-induced bonding modifications in near-frictionless carbon films. Carbon 2010, 48, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, M.; Wilhelmsson, O.; Jansson, U.; Wiklund, U. Tribofilm formation and tribological properties of TiC and nanocomposite TiAlC coatings. Wear 2009, 266, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Rainforth, W.M.; Hovsepian, P.E. TEM-EELS study of low-friction superlattice TiAlN/VN coating: The wear mechaisms. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 24, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Xie, J.P.; Song, Y.P. Effects of microstructure on the abrasive wear behaviour of spheroidal cast iron. Wear 1995, 184, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Xie, J.P.; Lu, W. Investigation of the wear failure mechanism of a flour milling roller. Wear 1993, 161, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Rainforth, W.M.; Münz, W.D. TEM observation of wear mechanisms of TiAlCrN and TiAlN/CrN coatings grown by combined steered-arc/unbalanced magnetron deposition. Wear 1999, 225–229, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Rainforth, W.M.; Münz, W.D. TEM study of the wear of TiAlN/CrN superlattice coatings. Scrip. Mater. 2001, 45, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Rainforth, W.M.; Münz, W.D. Wear mechanisms of monolithic and multicomponent nitride coatings grown by combined arc etching and unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 146–147, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, I.A.; Datta, S.; Du, H.L.; Burnell-Gray, J.S.; Luo, Q. Microscopy of glazed layers formed during high temperature sliding wear. Wear 2003, 254, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Mckay, S.; Luo, Q.; Rainforth, M.; Chen, L.; Hovsepian, P. Investigating Worn Surface of NanoscaleTiAlN/VN Coating Using FIB and TEM. EMAG-Nano Imaging Anal. Fabr. Nanoscale J. Phys. Ser. 2006, 26, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Hovsepian, P.E. Transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy on the worn surface of nano-structured TiAlN/VN multilayer coating. Thin Solid Films 2006, 497, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Rainforth, W.M.; Bolton, M. Effect of tribofilm formation on the dry sliding friction and wear properties of magnetron sputtered TiAlCrYN coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 34, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Schimpf, C.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Chen, L.; Hovsepian, P.E. Structure and wear mechanisms of nano-structured TiAlCN/VCN multilayer coatings. Plasma Processes Polym. 2007, 4, S916–S920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Tribofilms in solid lubricants. In Encyclopedia of Tribology; Wang, Q.J., Chung, Y.-W., Eds.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3760–3767. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q. Origin of friction in running-in sliding wear of nitride coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 37, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rainforth, W.M.; Luo, Q.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Ojeda, J.J.; Romero-Gonzalez, M.E. Wear and friction of TiAlN/VN coatings against Al2O3 in air at room and elevated temperatures. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2912–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, S.C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, L. Structure characterization and tribological study of magnetron sputtered nanocompositenc-TiAlV(N,C)/a-C coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9746–9756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Temperature dependent friction and wear of magnetron sputtered coating TiAlN/VN. Wear 2011, 271, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, E.; Luo, Q.; Owens, D. Cast study: Wear mechanisms of NiCrVMo-steel and CrB-steel scrap shear blades. Wear 2018, 398–399, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.Z.; Sarhan, A.A.D.; Yusuf, F.; Hamdi, M. Biomedical materials and techniques to improve the tribological, mechanical and biomedical properties of orthopaedic implants—A review article. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 714, 636–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hove, R.P.; Sierevelt, I.N.; van Royen, B.J.; Nolte, P.A. Titanium nitride coating of orthopaedic implants: A review of the literature. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapaj, L.; Wendland, J.; Markuszewski, J.; Mroz, A.; Wisniewski, T. Retrieval analysis of titanium nitrtide (TiN) coated prosthetic demoral heads articulating with polyethylene. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 55, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affatato, S.; Roggiero, A.; De Mattia, J.S.; Taddei, P. Does metal transfer affect the tribological behaviour of demoral heads? Roughness and phase transformation analyses on retrieved zirconia and Biolox Delta composites. Compos. Part B 2016, 92, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namus, R.; Zheng, P.; Rainforth, W.M. Correlation of the wear transition in CoCrMo alloys with the formation of a nanocrystalline surface layer and a proteinaceous surface film. Wear 2017, 376–377, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Rana, A.; Thompson, R.; Rainforth, W.M. Subsurface characterisation of wear on mechanically polished and electro-polished bilmedical grade CoCrMo. Wear 2015, 332–333, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, L.; Neville, A.; Qiao, L. (iv) Tribofilm on hip implants. Orthop. Trauma 2013, 27, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonaker, M.; Goswami, T. Review of wear mechnaisms in hip implants: Paper II—Ceramics IG004712. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Rainforth, W.M.; Inkson, B.J.; Stewart, T.D. Transmission electron microscopy analysis of worn alumina hip replacement prostheses. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Rainforth, W.M.; Stewart, T.D. Characterisation of the wear mechanisms in retrieved aluminium-on-alumina total hip replacements. Wear 2017, 376–377, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Lewis, D.B.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Münz, W.D. Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffrac-tion investigation of the microstructure of nano-scale multilayers TiAlN/VN grown by unbalanced magne-tron deposition. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.B.; Creasey, S.; Zhou, Z.; Forsyth, J.J.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Luo, Q.; Rainforth, W.M.; Münz, W.M. The effect of (Ti + Al): V ratio on the structure and oxidation behavior of TiAlN/VN nano-scale multilayer coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177–178, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovsepian, P.E.; Lewis, D.B.; Luo, Q.; Münz, W.D.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C.; Zhou, Z.; Rainforth, W.M. TiAlN based nanoscale multilayer PVD coatings designed to adapt their tribological properties at elevated temperatures. Thin Solid Films 2005, 485, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Robinson, G.; Pittman, M.; Howarth, M.; Sim, W.M.; Stalley, M.R.; Leitner, H.; Ebner, R.; Caliskanoglu, D.; Hovsepian, P.E. Performance of nano-structured multilayer PVD coating TiAlN/VN in dry high speed milling of aerospace aluminium 7010-T7651. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Lewis, D.B.; Münz, W.D.; Kok, Y.N.; Cockrem, J.; Bolton, M.; Farinotti, A. Tribological perperties of unbalanced magnetron sputtered nanoscale multilayer coatings TiAlN/VN and TiAlCrYN deposited on plasma nitrided steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 193, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Krug, T.; Tietema, R.; Sim, W.; Luo, Q.; Hovsepian, P.E. New Tool Coatings for Light Metal Cutting. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2004, 25, 832–836. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.B.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Münz, W.D. Interrelationship between atomic species, bias voltage, texture and microstructure of nano-scale multilayers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 184, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, C.; Peters, M.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Lewis, D.B.; Luo, Q.; Münz, W.D. Novel Coating Systems Produced by the Combined Cathodic Arc/Unbalanced Magnetron Sputtering for Environmental Protection of Titanium Alloys and Titanium Aluminides. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 155, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Oluwafemi, O.; Kitchen, M.; Yang, S. Tribological properties and wear mechanisms of DC pulse plasma nitrided austenitic stainless steel in dry reciprocating sliding tests. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigle, W. Analytical transmission electron microscopy. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2005, 35, 239–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsonnet, L.; Donnet, C.; Varlot, K.; Martin, J.M.; Grill, A.; Tatel, V. EELS analysis of hydrogenated diamond-like carbon films. Thins Solid Films 1998, 319, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitternauer, C.; Hebert, C.; Kothleitner, G.; Hofer, F.; Schattschnerder, P.; Zandbergen, H.W. Electron energy loss near edge structure as a fingerprint for identifying chromium nitrides. Solid State Commun. 2004, 130, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothleitner, G.; Rogers, M.; Berendes, A.; Bock, W.; Kolbesen, B.O. A combined SNMS and EFTEM/EELS study on focused ion beam prepared vanadium nitride thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Benthem, K.; Kohl, H. Methods for ELNES-quantification: Characterization of the degree of inversion of Mg-Al-spinels. Micron 2000, 31, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, F.; Warbichler, P.; Scott, A.; Brydson, P.; Galesic, I.; Kolbesen, B. Electron energy loss near edge structure on the nitrogen K-edge in vanadium nitrides. J. Microsc. 2001, 204, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, D.; Colliex, C. Experimental study of ELNES at grain boundaries in alumina: Intergranular radiation damage effects on A1-L23 and O-K edges. Ultramicroscopy 2003, 96, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Gao, S.P.; Yuan, J. ELNES for boron, carbon, and nitrogen K-edges with different chemical environments in layered materials studied by density functional theory. Ultramicroscopy 2012, 112, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Rao, Q.; Zhou, Q. Abrasive wear resistance of Cr-family white cast irons. Acta Metall. Sin. 1987, 23, 575–580. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J. Influence of carbon content on the oxidation and wear resistance of 20% Cr alloy at elevated temperature. J. Mech. Eng. 1992, 28, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J. Correlation between the characteristics of the thermo-mechanical mized layer and wear behaviour of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 22, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, M.S.; Buiocchi, C.J. Cross-sectional specimens for transmission electron microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1974, 45, 3315–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, U.; Sundgren, J.E. Cross-sectional preparation for TEM of film-substrate combinations with a large difference in sputtering yields. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 1986, 4, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, L.A.; Stevie, F.A. A review of focused ion beam milling techniques for TEM specimen preparation. Micron 1999, 30, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyntjens, S.; Puers, R. A review of focused ion beam applications in microsystem technology. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2001, 11, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, L.; Butz, B.; Muller, E. Optimized Ar ion milling procedure for TEM cross-sectional sample preparation. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suess, M.J.; Mueller, E.; Wepf, R. Minimization of amorphous layer in Ar+ ion milling for UHR-EM. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Rainforth, W.M.; Donohue, L.A.; Wadsworth, I.; Münz, W.D. Tribological investigation of TiAlCrN and TiAlN/CrN coatings grown by combined steered-arc/unbalanced magnetron dep-osition. Vacuum 1999, 53, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q. Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Friction and Wear Mechanisms. Lubricants 2018, 6, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030058
Luo Q. Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Friction and Wear Mechanisms. Lubricants. 2018; 6(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Quanshun. 2018. "Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Friction and Wear Mechanisms" Lubricants 6, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030058
APA StyleLuo, Q. (2018). Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Friction and Wear Mechanisms. Lubricants, 6(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6030058