Tribological Performance of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Additives in Lithium Lubricating Grease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
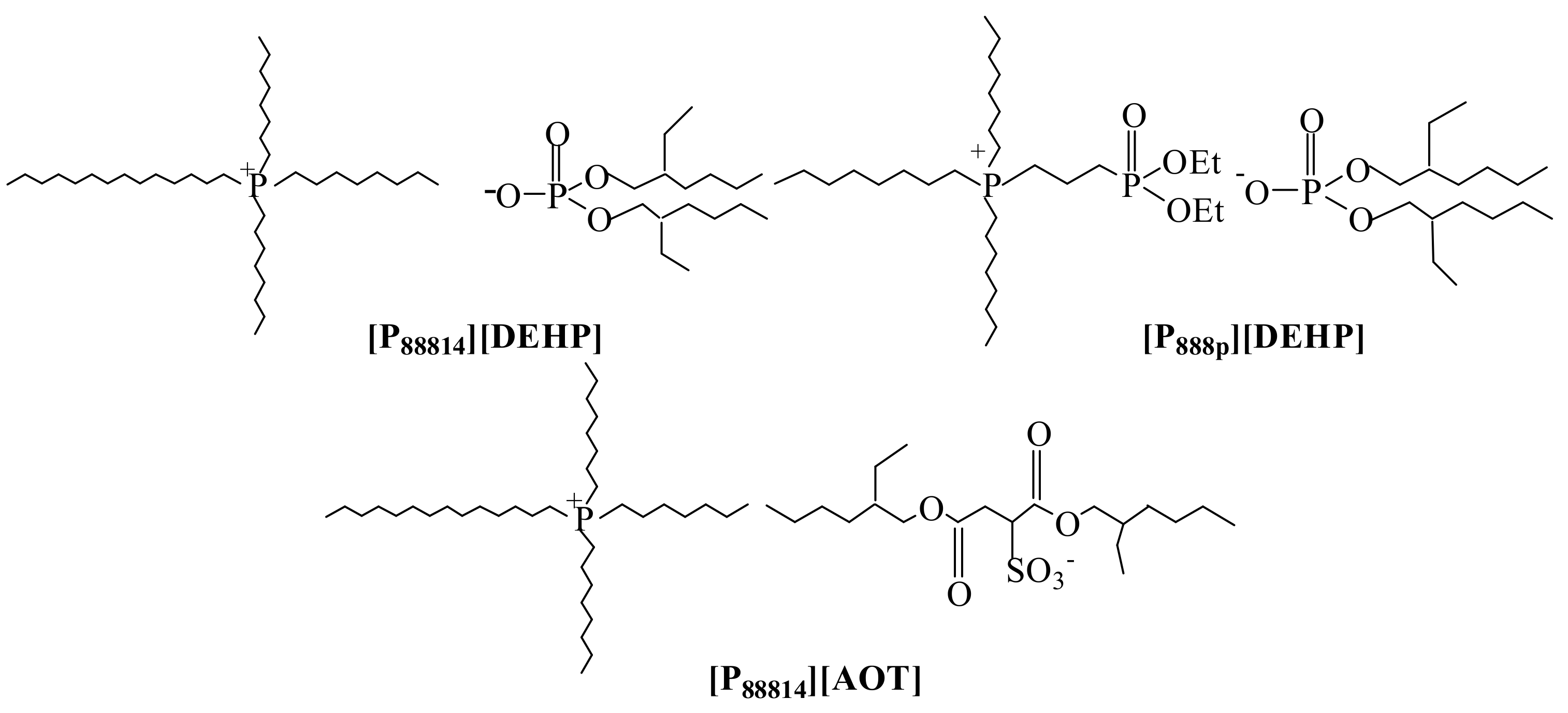
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Ionic Liquids
2.2. Preparation of the Lithium Greases
2.3. Characterization of the Lithium Greases
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Properties of the Lithium Greases
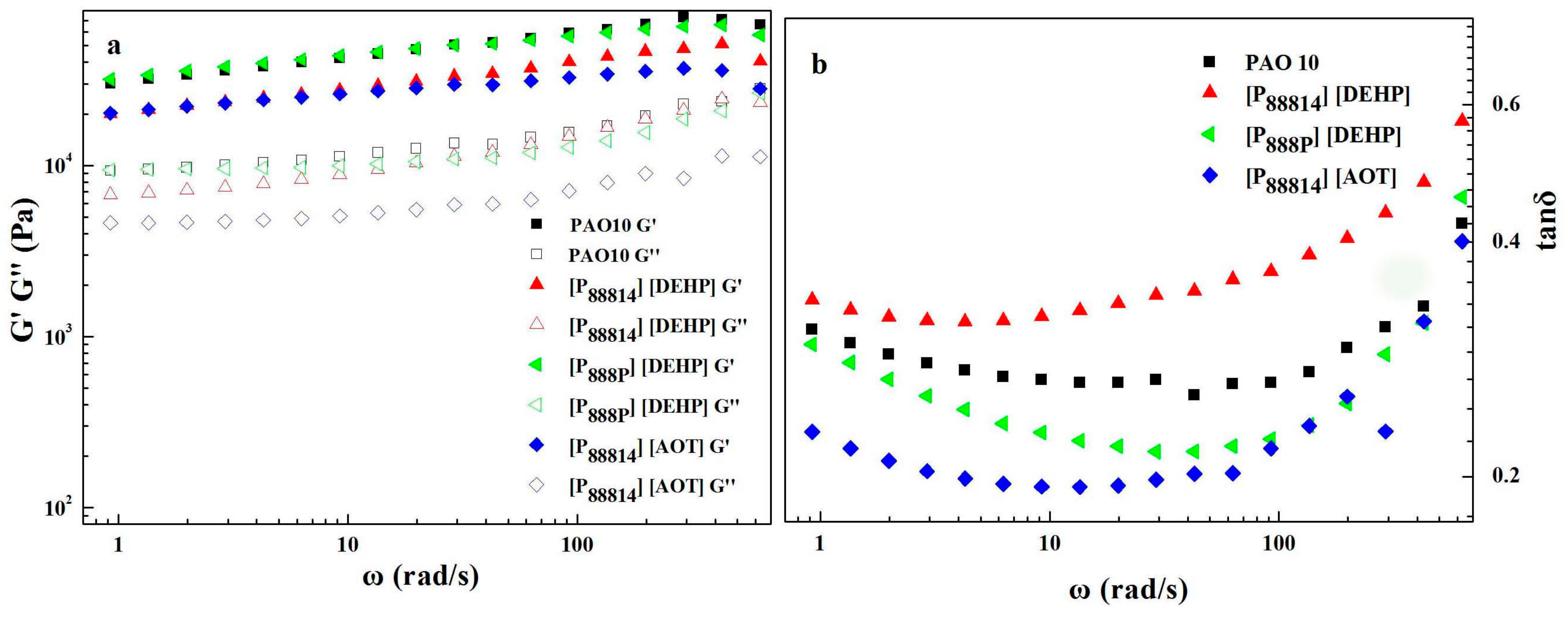
3.2. Rheological Properties
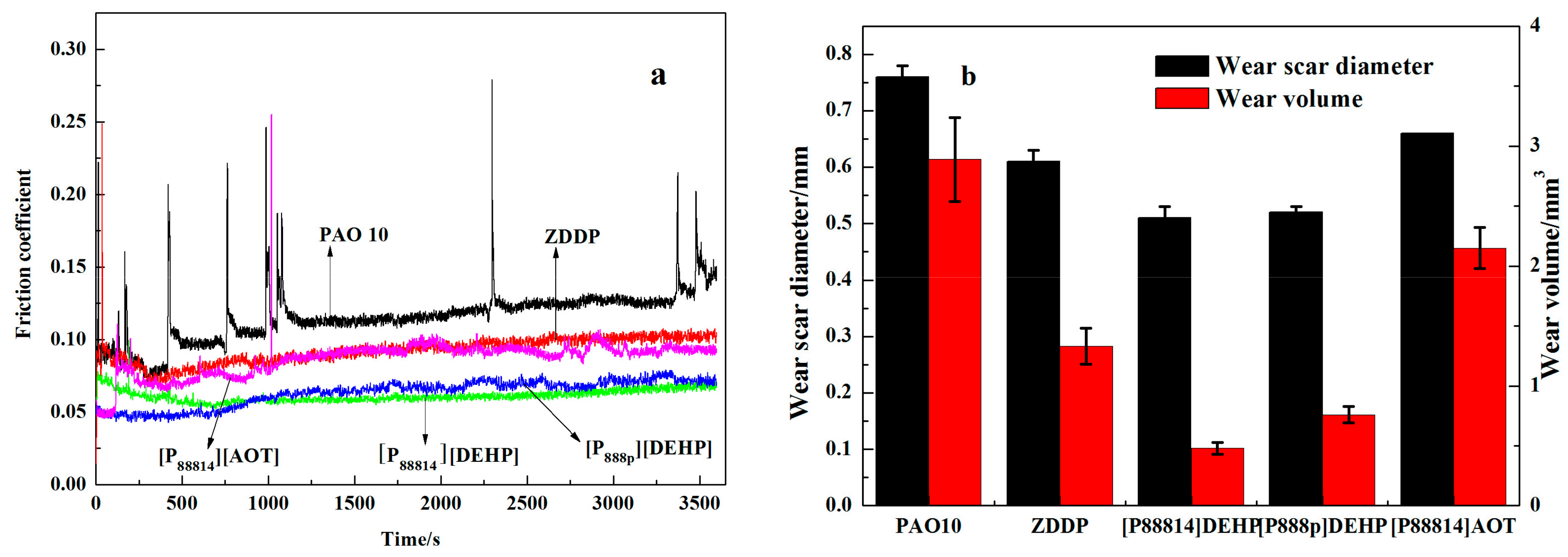
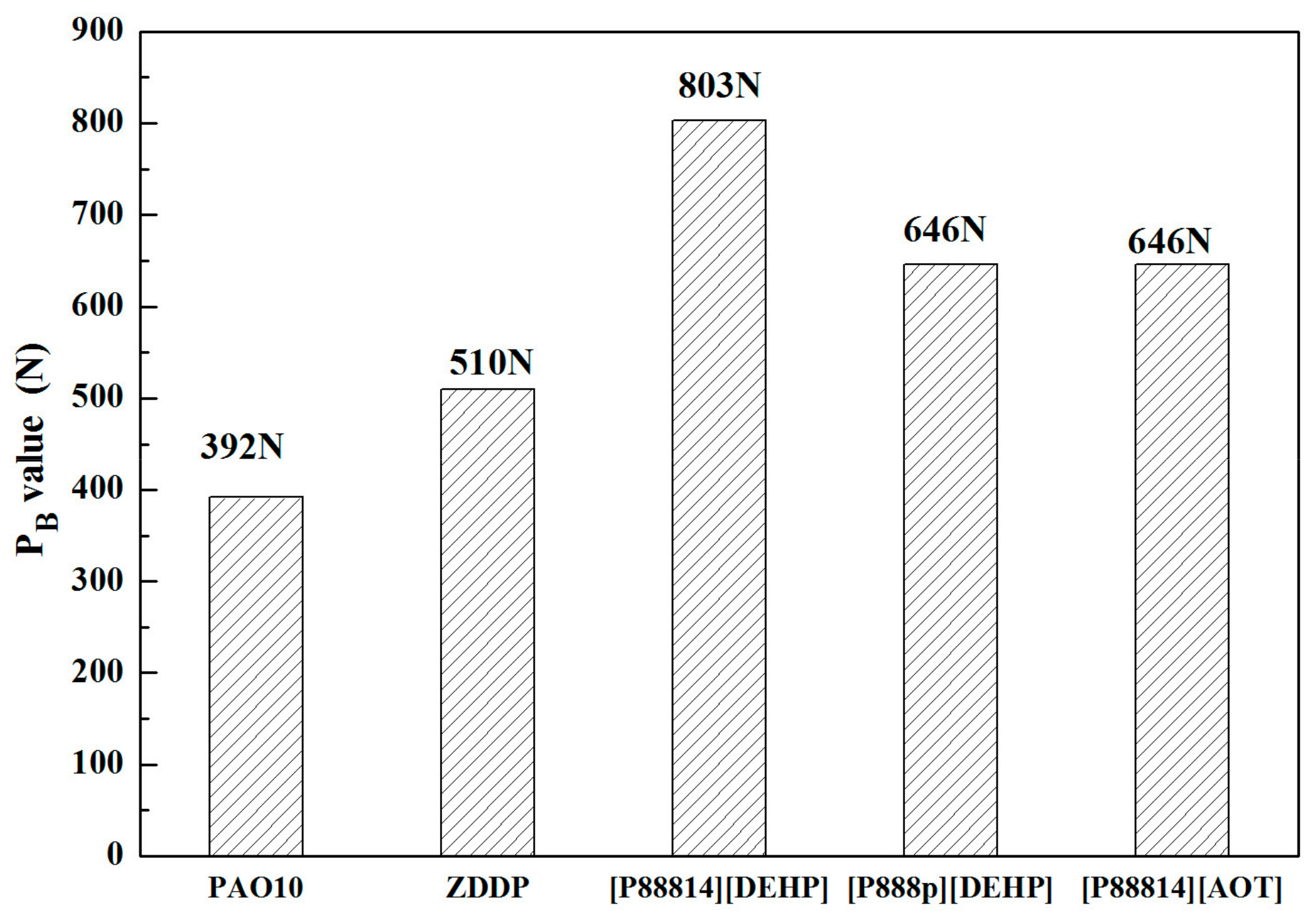
3.3. Tribological Properties
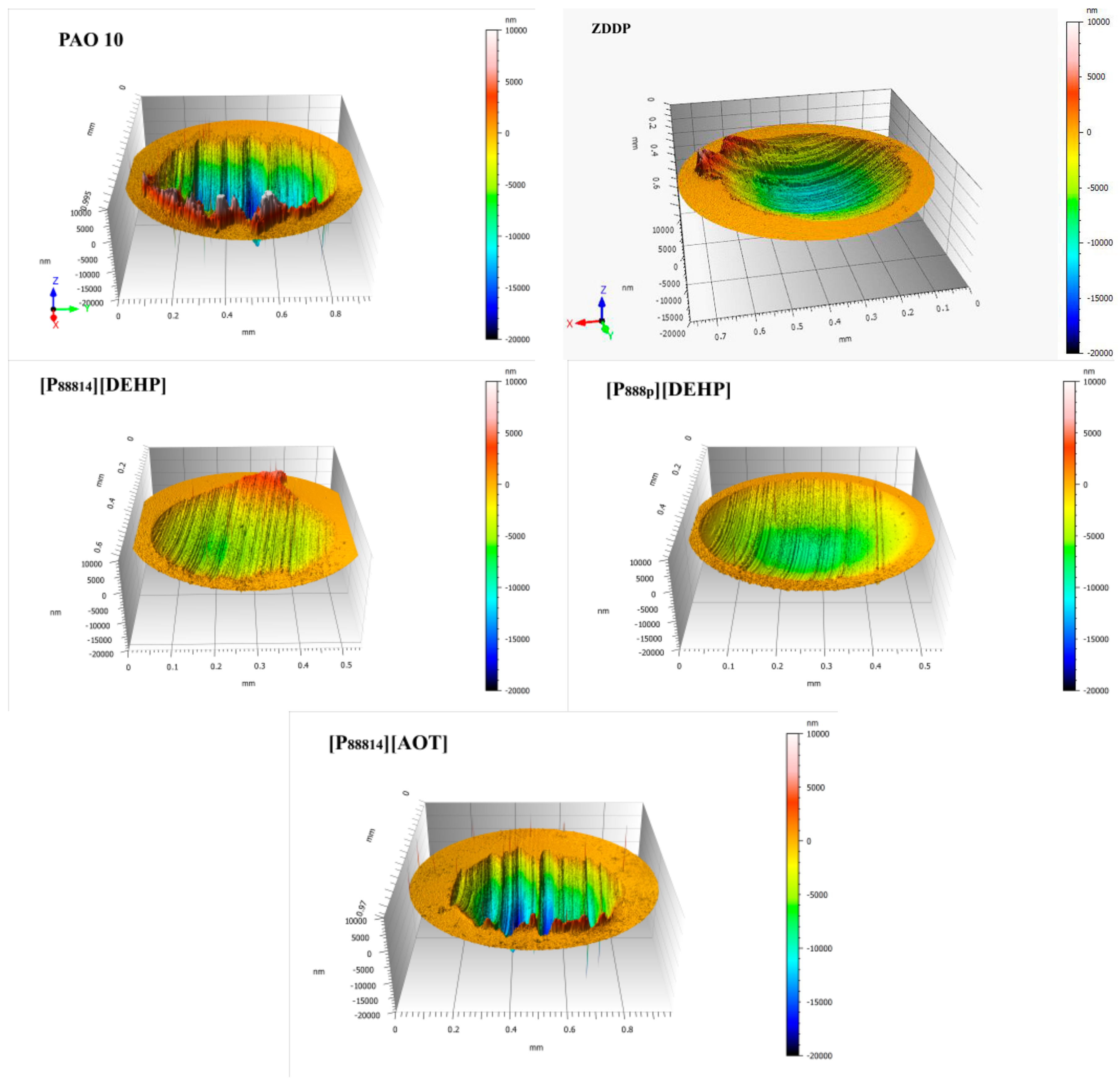
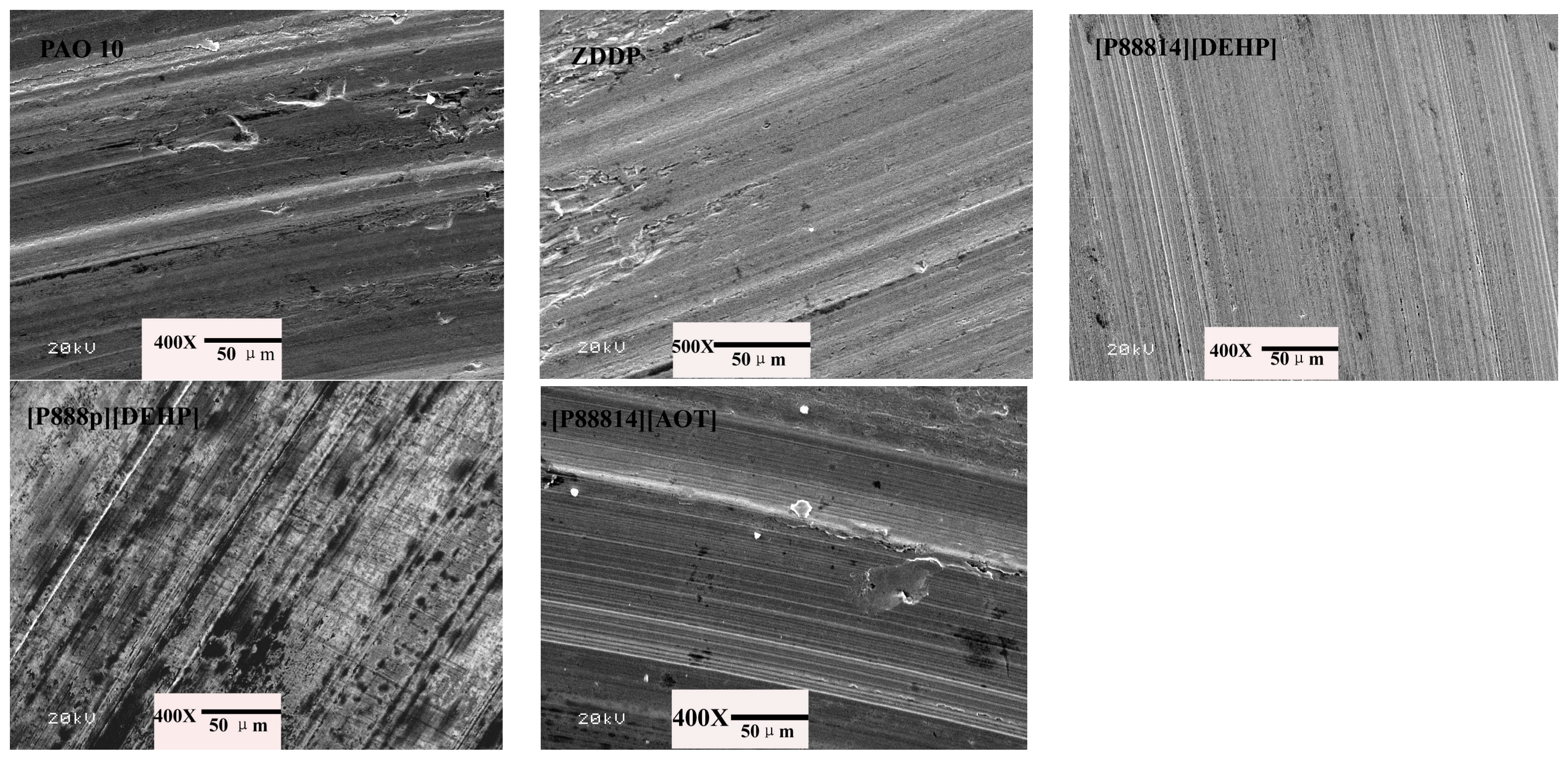
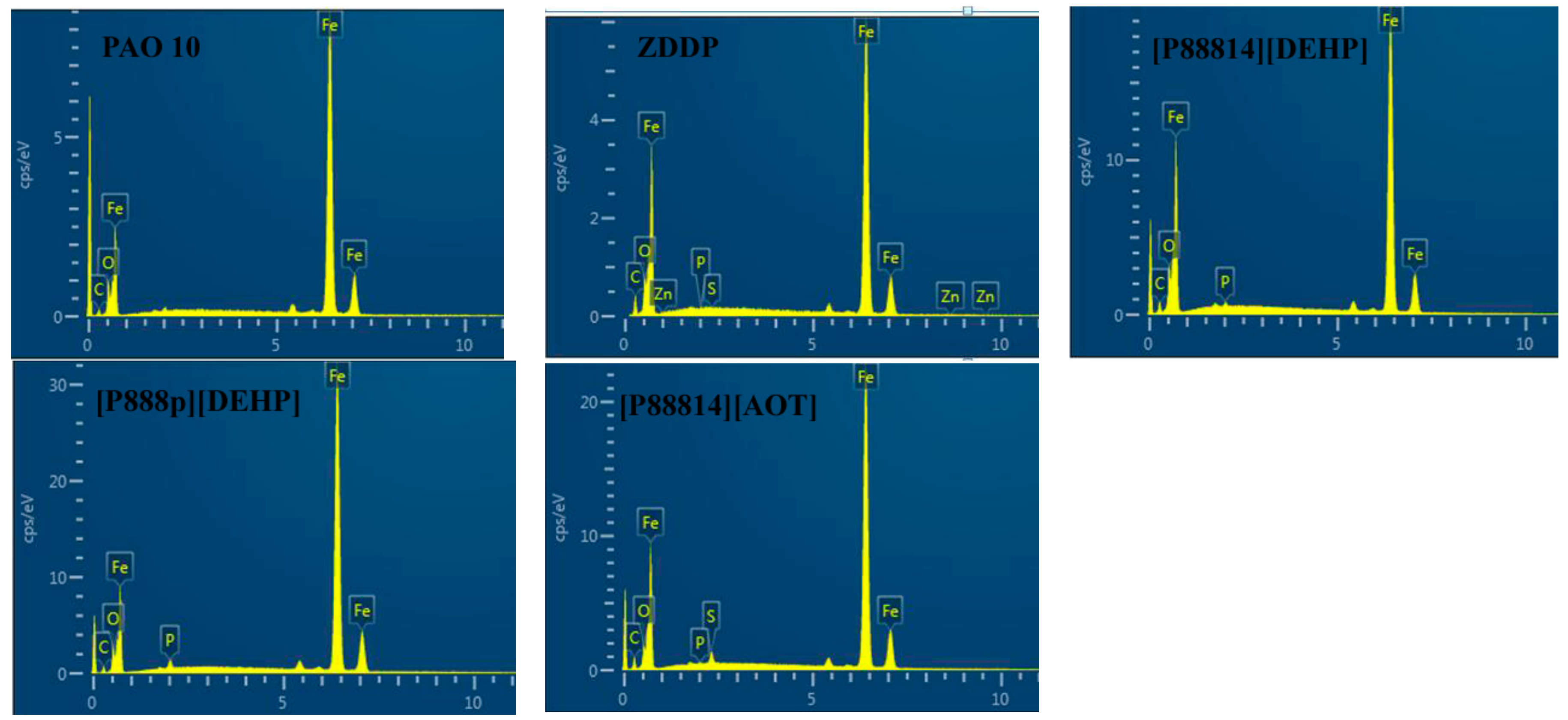
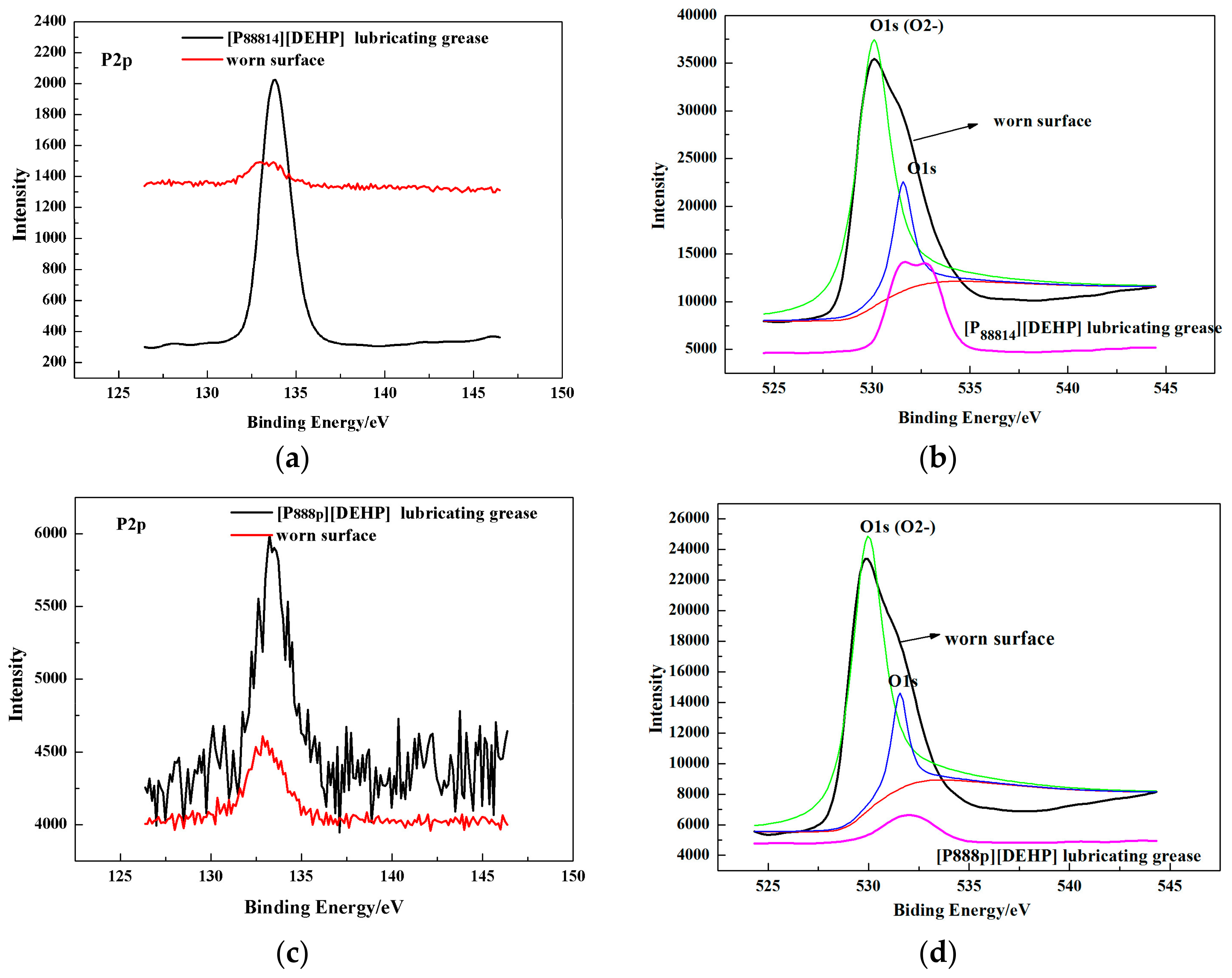
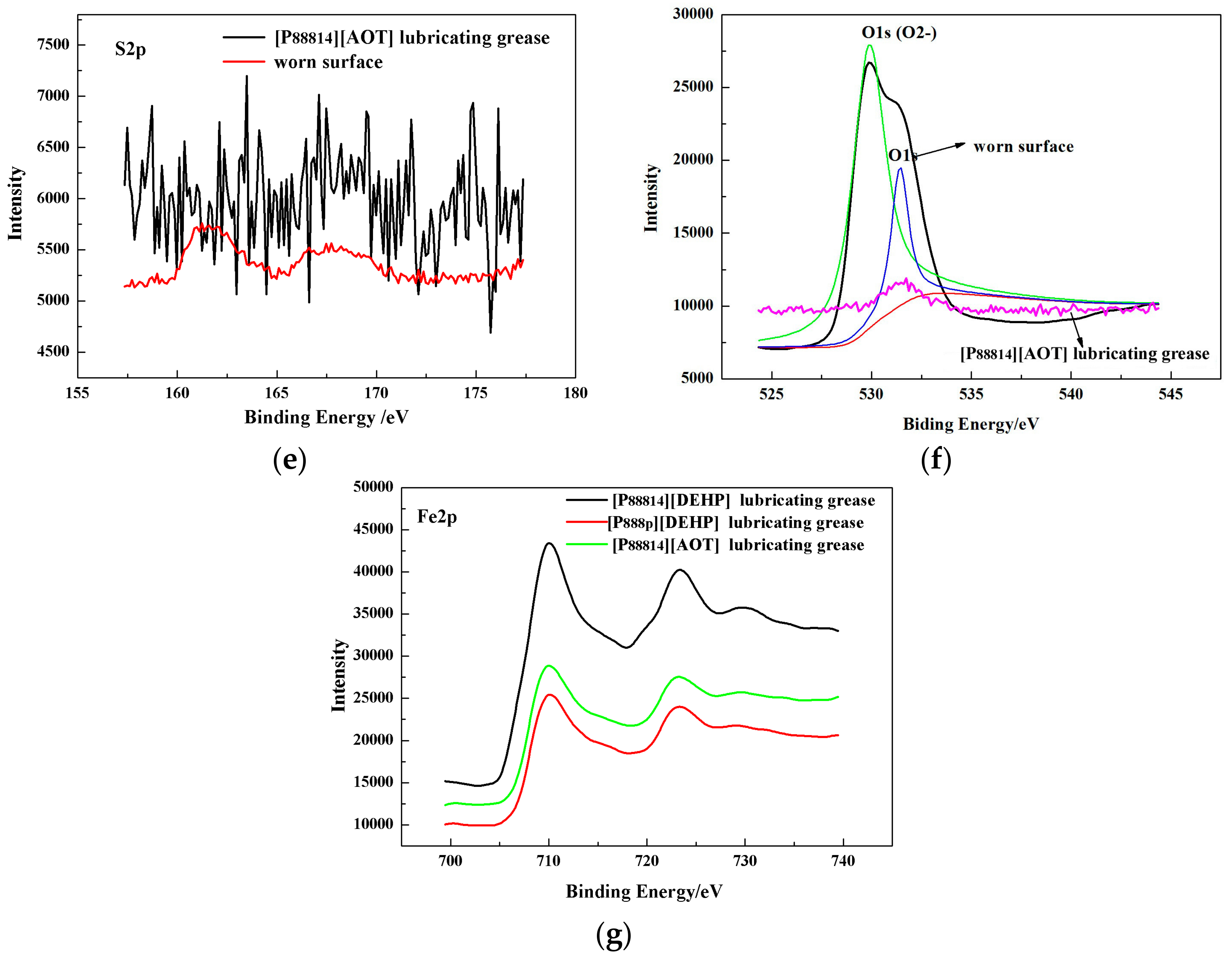
3.4. Surface Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
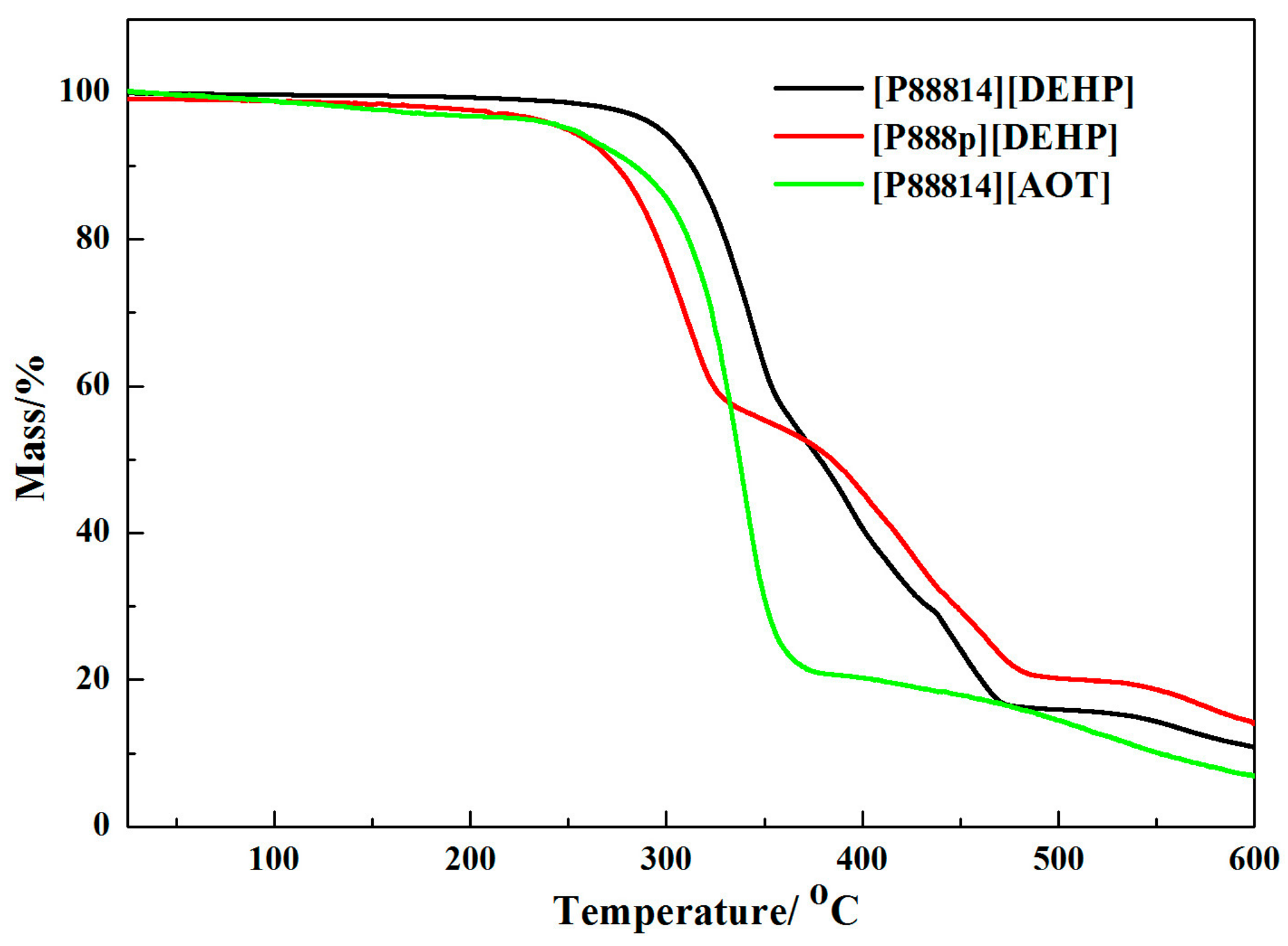
- The [P88814][DEHP] grease showed a higher dropping point than the PAO 10 grease, and the dropping point of the [P888p][DEHP] grease and the [P88814][AOT] grease is lower than that of the PAO 10 grease. All of the lubricating greases are noncorrosive to copper.
- (2)
- Compared with the PAO 10 grease, the values of the linear viscoelasticity modulus of the [P88814][DEHP] and [P88814][AOT] greases decreased. However, the same values of the linear viscoelastic functions were found for the [P888p][DEHP] grease.
- (3)
- The ILs were found to be effective lubricant additives for improving the friction-reducing and antiwear properties and the maximum non-seizure load (PB values) of PAO 10 lithium lubricating grease. A surface analysis showed that a tribochemical film was generated from the ILs to reduce friction and wear.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Valencia, C.; Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. Development of new lubricating grease formulations using recycled LDPE as rheology modifier additive. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, R.; Magnin, A. Rheology of colloidal suspensions-case of lubricating greases. J. Rheol. 1994, 38, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, S.K.; Luckham, P.F.; Tadros, T.F. Steady flow and viscoelastic properties of lubricating grease containing various thickener concentrations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M.; Valencia, C.; Gallegos, C.; Urquiola, F.; Urchegui, R. Atomic force microscopy and thermo-rheological characterisation of lubricating greases. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.J.; Yang, D.S.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, W.M.; Fu, H.Z. DOSS-based QAILs: As both neat lubricants and lubricant additives with excellent tribological properties and good detergency. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 17952–17960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.F.; Liu, W.M.; Chen, Y.X.; Yu, L.G. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, I.; Lópezm, E.R.; Reichelt, M.; Villanueva, M.; Salgado, J.; Fernández, J. Ionic liquids based on phosphonium cations as neat lubricants or lubricant additives for a steel/steel contact. ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13115–13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.W.; Yu, Q.L.; Cai, M.R.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Investigation of the lubricity and antiwear behavior of guanidinium ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Dhingra, S.; Khatr, O.P. Fatty-acid-constituted halogen-free ionic liquids as renewable, environmentally friendly, and high-performance lubricant additives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.J.; Liang, Y.M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Dramatically improved friction reduction and wear resistance by in situ formed ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 6824–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozes, R.; Cooper, P.K.; Atkin, R.; Li, H. Ionic Liquids as Grease Base Liquids. Lubricants 2017, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Hadfield, M.; Viesca, J.L.; Thomas, B.; Battez, A.H.; Austen, S. Ionic liquids as tribological performance improving additive for in-service and used fully-formulated diesel engine lubricants. Wear 2015, 334, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Bansal, D.G.; Yu, B.; Howe, J.Y.; Luo, H. Antiwear performance and mechanism of an oil-miscible ionic liquid as a lubricant additive. ACS Appl. Mat. Interface 2012, 4, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerholt, A.; Weschta, M.; Bösmann, A.; Tremmel, S.; Korth, Y.; Wolf, M.; Schlücker, E.; Wehrum, N.; Lennert, A.; Uerdingen, M.; et al. Halide-free synthesis and tribological performance of oil–miscible ammonium and phosphonium-based Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.R.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Y.M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Alkyl imidazolium ionic liquids as friction reduction and anti-wear additive in polyurea grease for steel/steel contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Xia, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.L. Comparative study of the tribological properties of ionic liquids as additives of the attapulgite and bentone greases. Lubr.Sci. 2012, 24, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.W.; Yu, Q.L.; Ma, Z.F.; Cai, M.R.; Liu, W.M. Probing the lubricating mechanism of oil-soluble ionic liquids additives. Tribol. Int. 2017, 107, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Gupta, P.; Saran, S.; Khatri, O.P. Halogen-Free Bis(imidazolium)/bis(ammonium)-di[bis(salicylato)borate] ionic liquids as energy-efficient and environmentally friendly lubricant additives. ACS Appl. Mat. Interface 2014, 6, 15318–15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, D.; Xu, B. Tribological characteristics of alkylimidazolium diethyl phosphates ionic liquids as lubricants for steel-steel. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 34, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Onset Decomposition Temperature (°C) | Density (g/mL, 25 °C) | Kinematic Viscosity (cSt) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 °C | 100 °C | |||
| PAO 10 | 225 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 70.1 ± 0.5 | 10.4 ± 0.7 |
| [P88814][DEHP] | 310 | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 803 ± 3 | 93.7 ± 1 |
| [P888p][DEHP] | 273 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 4586 ± 2 | 218 ± 3 |
| [P88814][AOT] | 273 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 664 ± 2 | 55.4 ± 0.9 |
| Lubricating Greases | Poly Alpha Olefin 10 | [P88814][DEHP] | [P888p][DEHP] | [P88814][AOT] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dropping point (°C) | 334 ± 1 | 355 ± 5 | 295 ± 1 | 213 ± 3 |
| Penetration (1/4 mm) | 73 ± 1 | 78 ± 1 | 75 ± 1 | 69 ± 1 |
| Copper corrosion (100 °C, 24 h) | 1a | 1a | 1a | 1a |
| C (At%) | O (At%) | P (At%) | S (At%) | Fe (At%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAO 10 | 8.07 | 15.83 | - | - | 58.46 |
| ZDDP | 30.96 | 11.09 | 0.09 | - | 57.81 |
| [P88814][DEHP] | 20.18 | 14.68 | 0.56 | - | 64.58 |
| [P888p][DEHP] | 13.01 | 9.37 | 1.25 | - | 76.37 |
| [P88814][AOT] | 23.37 | 7.49 | 0.17 | 1.35 | 67.61 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Cai, C. Tribological Performance of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Additives in Lithium Lubricating Grease. Lubricants 2018, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010023
Wang Z, Chang J, Cai C. Tribological Performance of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Additives in Lithium Lubricating Grease. Lubricants. 2018; 6(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zeyun, Jun Chang, and Chao Cai. 2018. "Tribological Performance of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Additives in Lithium Lubricating Grease" Lubricants 6, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010023
APA StyleWang, Z., Chang, J., & Cai, C. (2018). Tribological Performance of Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Additives in Lithium Lubricating Grease. Lubricants, 6(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010023




