Boric Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive in Glycerol Ethoxylate Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introductions
2. Experiments
2.1. Lubricant and Additive
2.2. Equipment and Methods
- (1)
- Friction properties
- (2)
- Lubricant characterizations
- (3)
- Film-forming performance
- (4)
- Extreme pressure performance
3. Results and Discussion
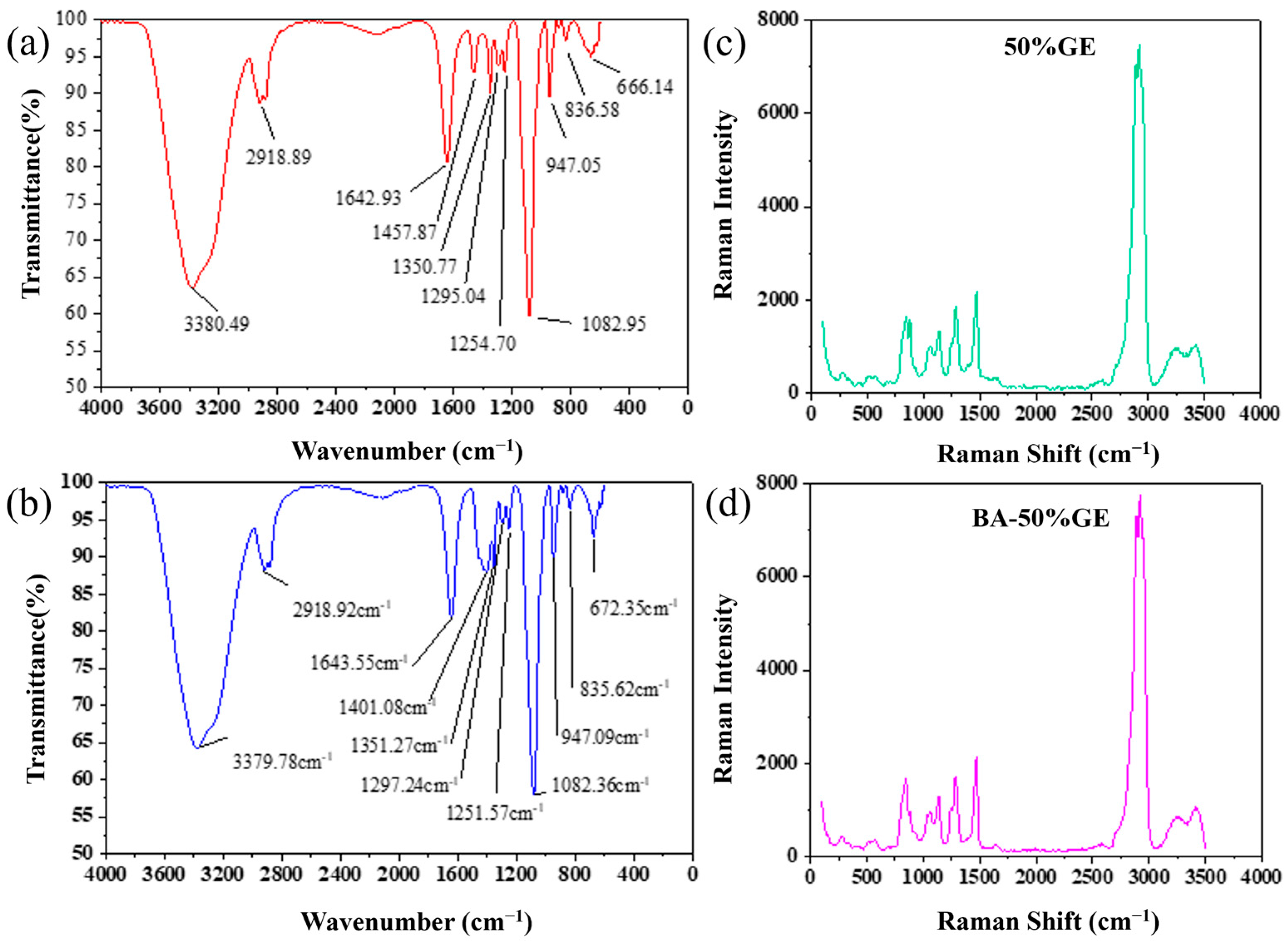
3.1. FT-IR and Raman
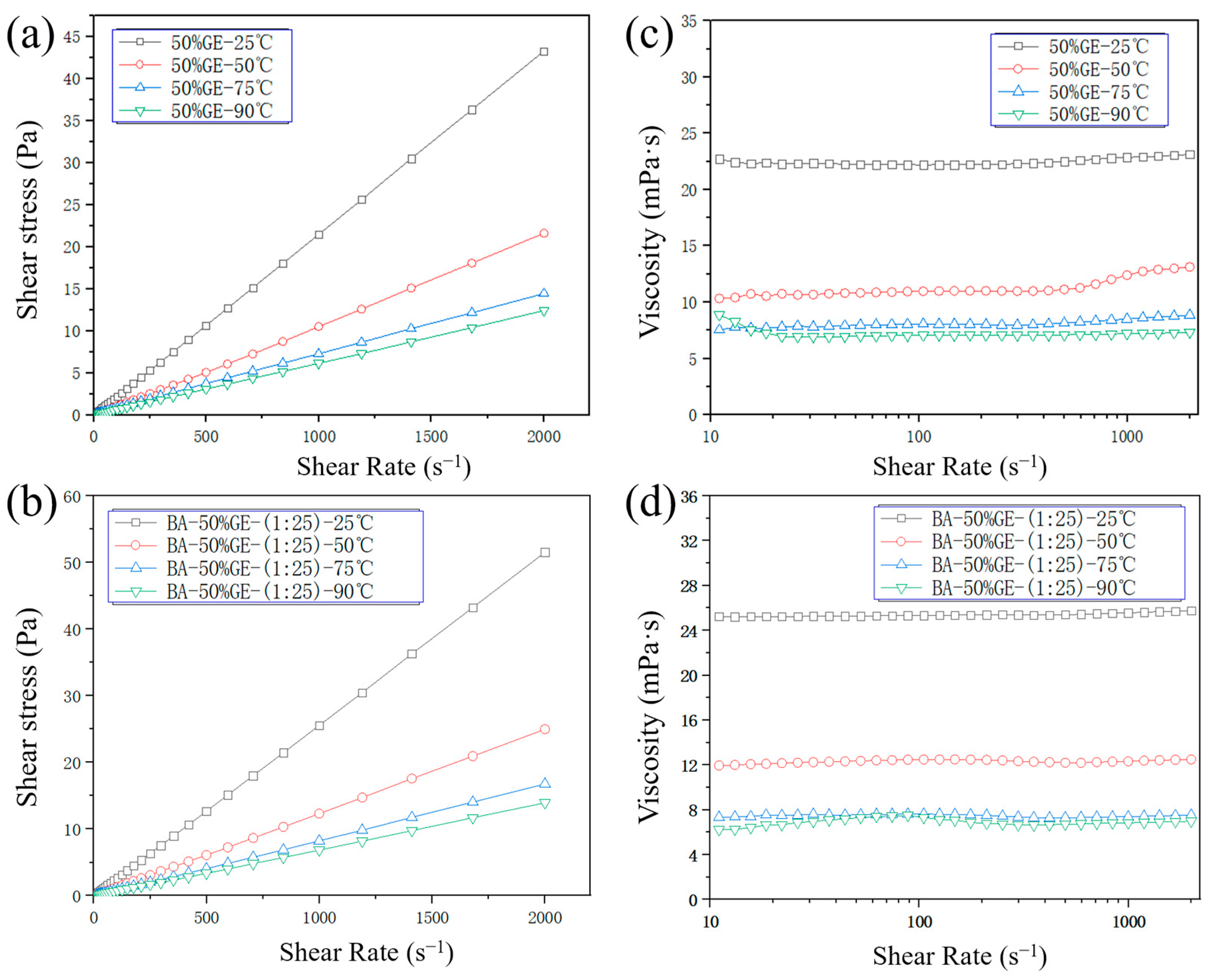
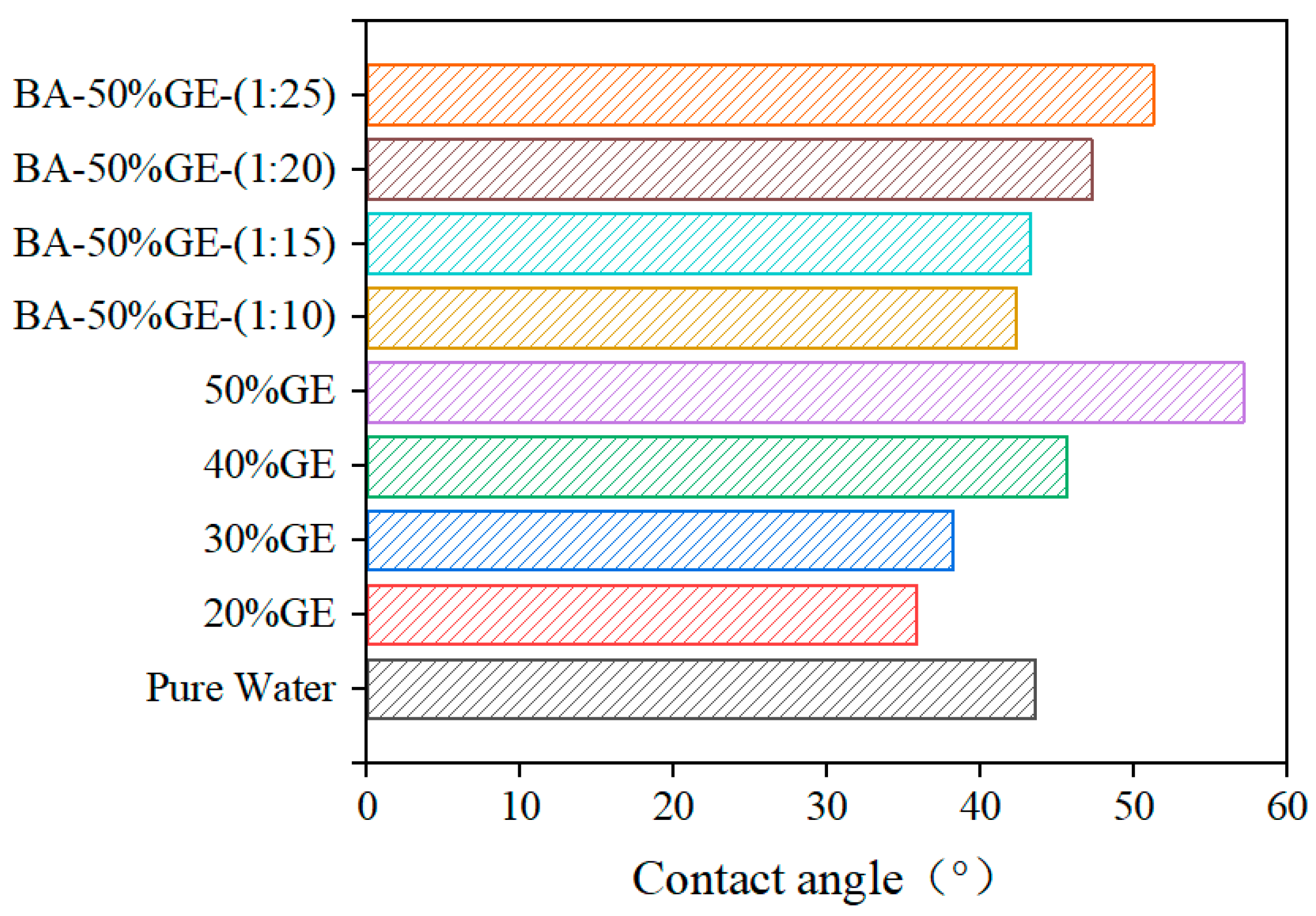
3.2. Rheological and Wettability Properties
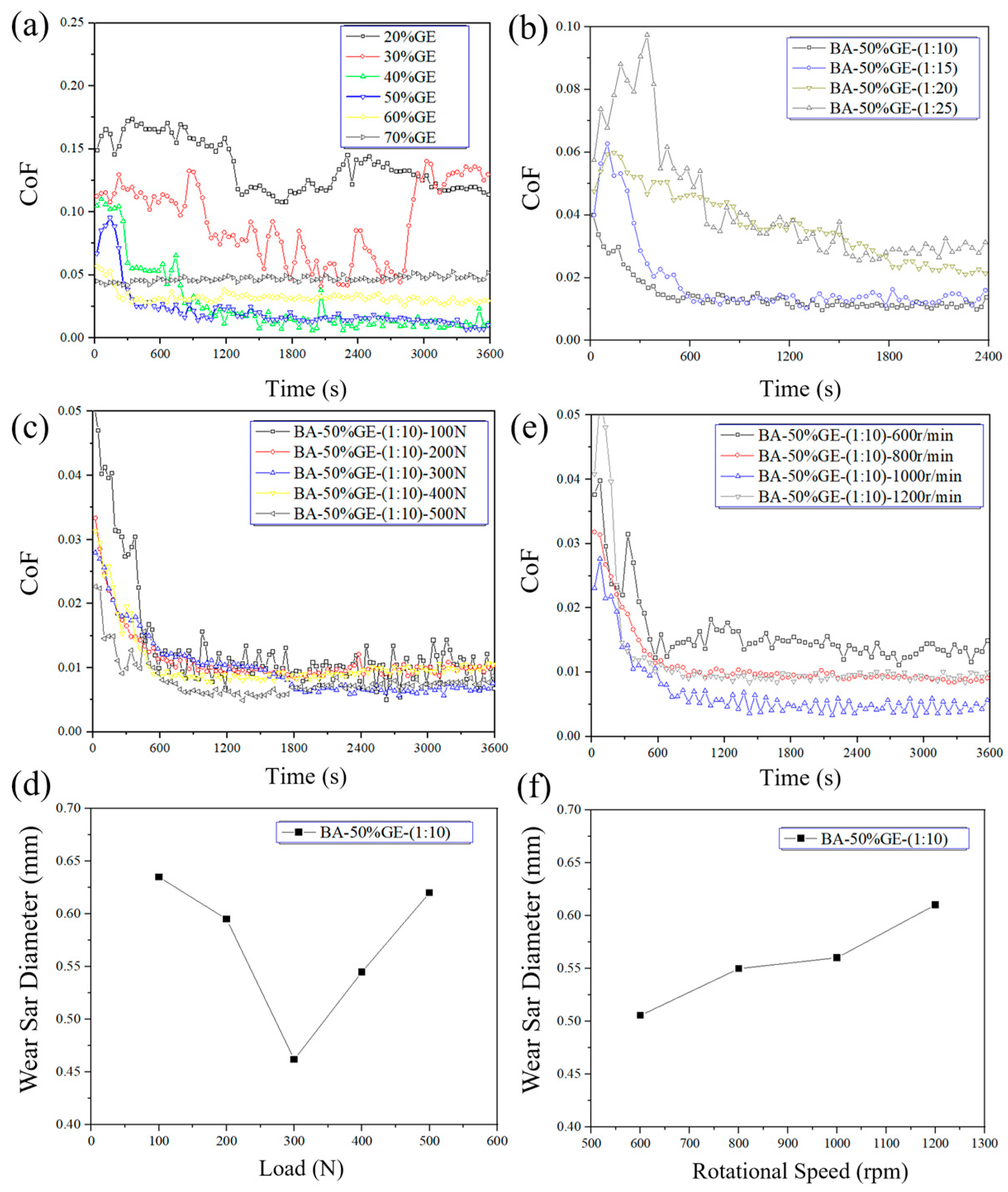
3.3. Friction and Wear Properties
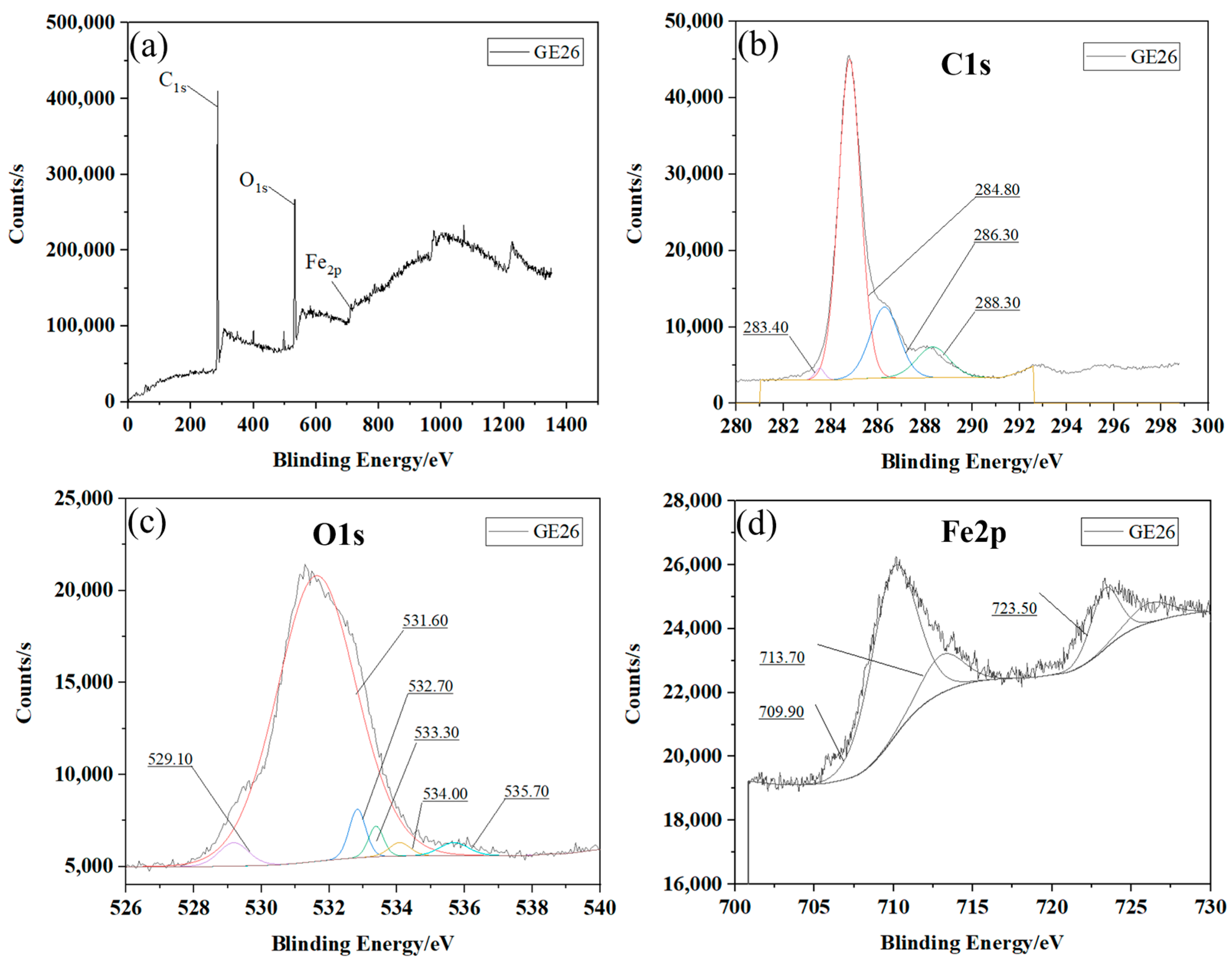
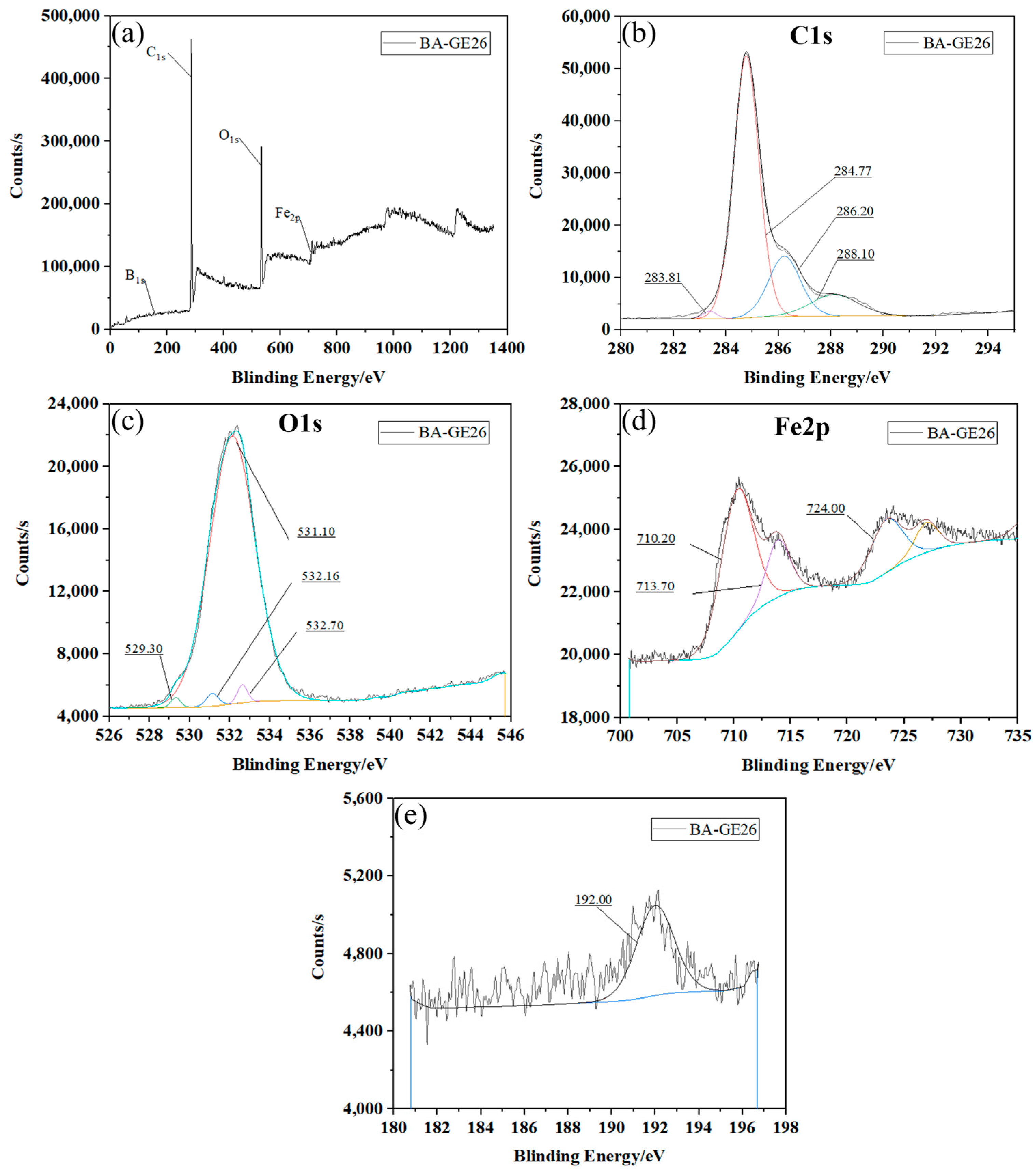
3.4. XPS Energy Spectrum
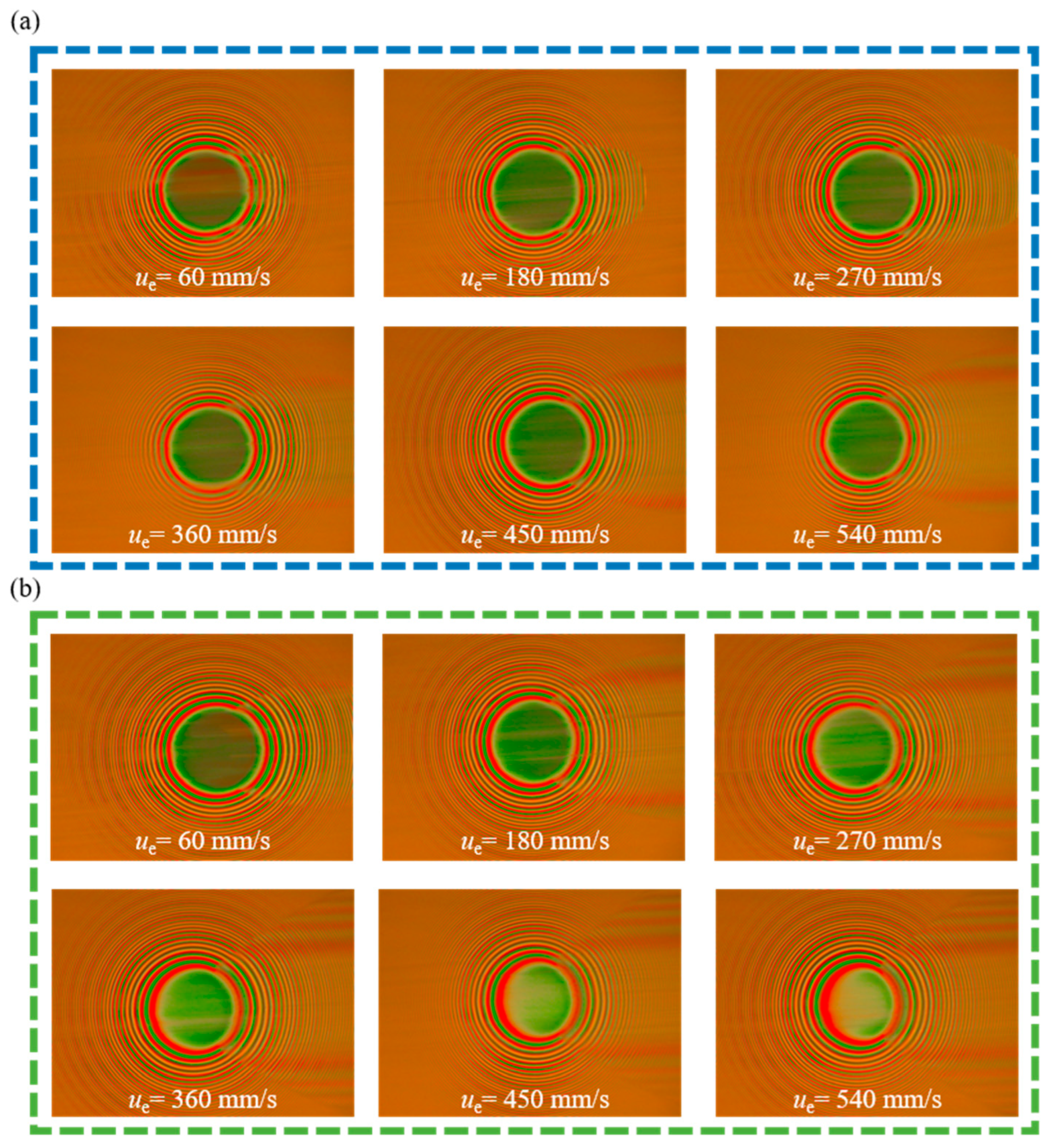
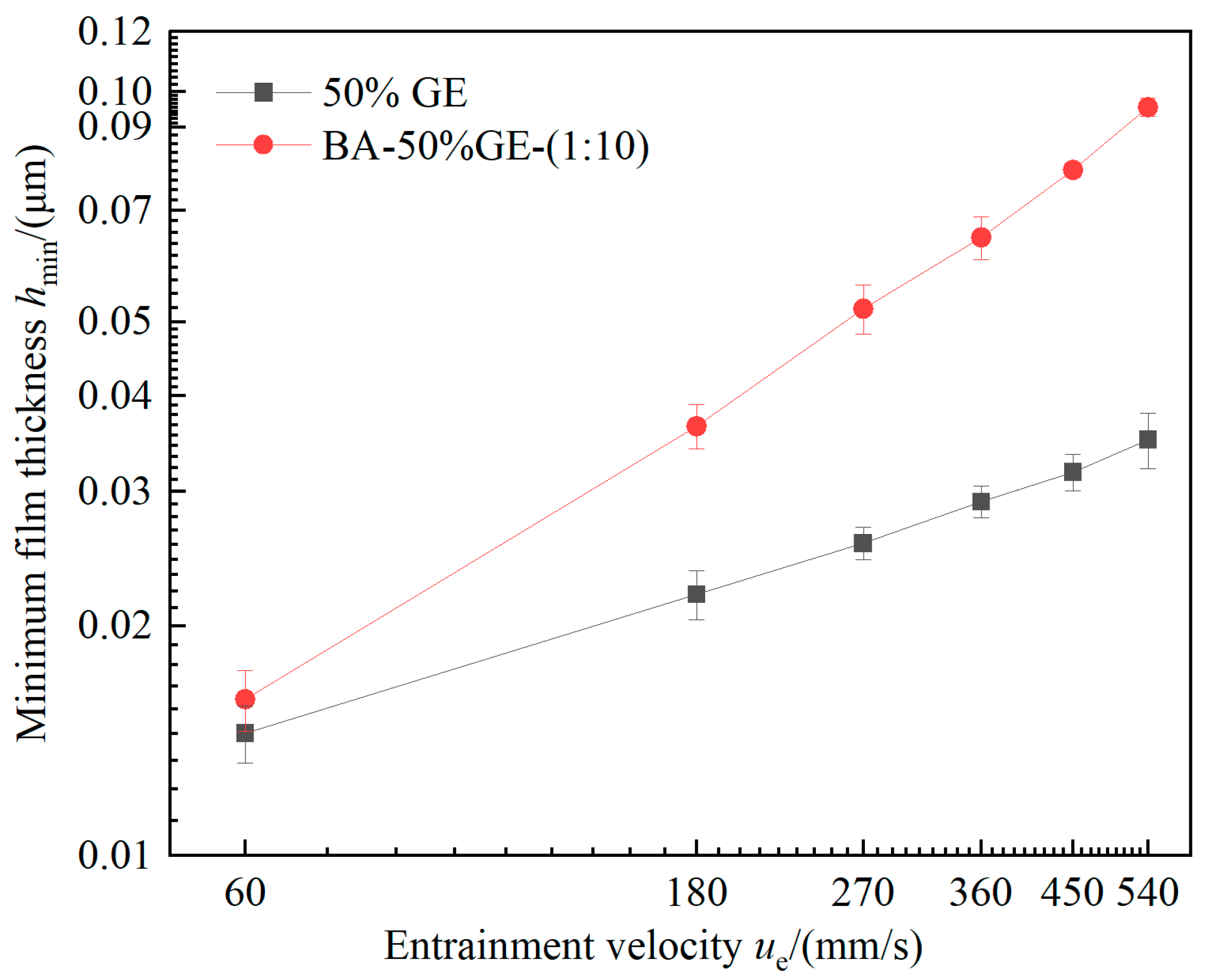
3.5. Film-Forming Performance
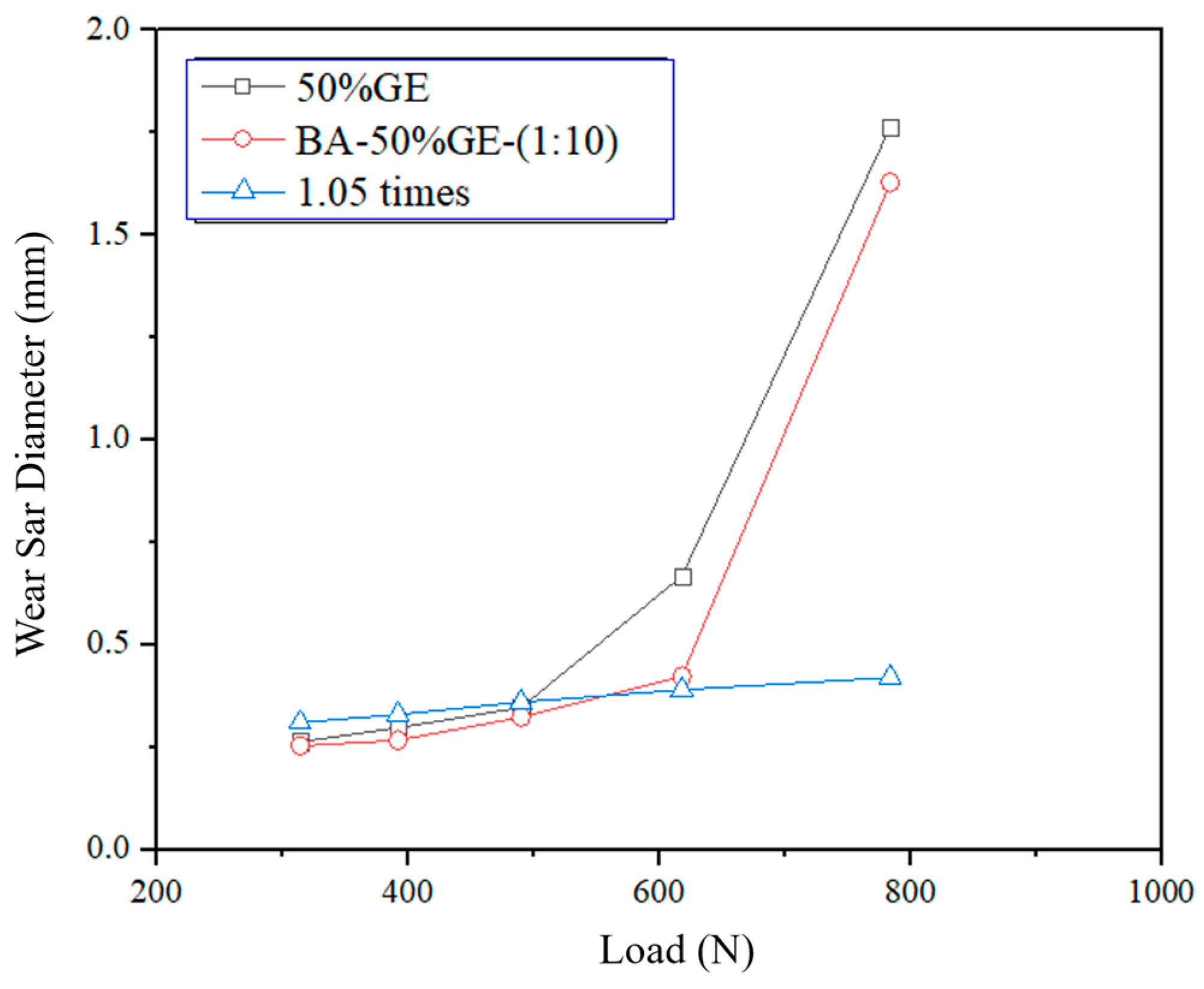
3.6. Extreme Pressure Performance and Anti-Rust Ability
- (1)
- Extreme pressure performance
- (2)
- Anti-rust ability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, M.H.; Warneke, H.; Webbert, H.; Rodriguez, J.; Austin, E.; Tokunaga, K.; Rajak, D.K.; Menezes, P.L. Water-Based Lubricants: Development, Properties, and Performances. Lubricants 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Water-Based Nanolubricants. Lubricants 2021, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, L.; Tong, Y.; Yan, M.; Yang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Shangguan, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. Research progresses of nanomaterials as lubricant additives. Friction 2024, 12, 1347–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krim, J.; Smirnov, A.I. Fundamental Mechanisms Underlying the Effectiveness of Nanoparticle Additives to Lubricants: 25 Examples Linking Nano- to Macroscale Friction. Lubricants 2024, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wu, J.; Yu, L.; Bi, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. Two-dimensional nanomaterials as lubricant additives: The state-of-the-art and future prospects. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 4327–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Lu, H.; Zhong, Q.; He, Z.; Lei, J.; Zhu, X. Tribology Properties of Water-soluble Triazine Derivative Containing Sulfur and Phosphorus on Cemented Carbide. Lubr. Eng. 2016, 41, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, H.; Soltani, R.; Alaei, M.; Soleymani, M. Tribological properties of water-based drilling fluids with borate nanoparticles as lubricant additives. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, C.; Nie, C. Tribological properties of carbon nanotube/SiO2 combinations as water-based lubricant additives for magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y. Black phosphorus quantum dots: A new-type of water-based high-efficiency lubricant additive. Friction 2021, 9, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Du, X.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Ma, L.; Fan, M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Facile Preparation and Tribological Properties of Water-Based Naphthalene Dicarboxylate Ionic Liquid Lubricating Additives. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, F.; de Freitas, F.; Nunes, D.; Iglauer, S.; Gramatges, A.; Nascimento, R.; Lachter, E. Alkyl glyceryl ethers as water-based lubricant additives in mixtures with xanthan gum. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 634, 127881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Simic, R.; Liu, Y.; Spencer, N. Effect of contact geometry on the friction of acrylamide hydrogels with different surface structures. Friction 2022, 10, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Superlubricity Achieved by a Transparent Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) Composite Hydrogel with Glycerol Ethoxylate in Ocular Conditions. Langmuir 2024, 40, 6816–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Geng, X. Tribological Investigation of a Mixed Solution with Superlubricity Achieved. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 58, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. Liquid Superlubricity of Polyethylene Glycol Aqueous Solution Achieved with Boric Acid Additive. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3578–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, H.; Mofidi, A.; Al-Fadhli, A.; Aramesh, M. Solid Lubricants Used in Extreme Conditions Experienced in Machining: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Developments and Applications. Lubricants 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Ma, J.; An, Y. Advanced developments in environmentally friendly lubricants for water-based drilling fluid: A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22853–22868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakani, B.; Salem, H.; Entezami, S.; Sedaghat, A.; Grecov, D. Effect of particle concentration on lubrication performance of cellulose nanocrystalline (CNC) water-based lubricants: Mixed lubrication regime. Cellulose 2022, 29, 3963–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N.; Said, Z.; et al. Biological Stability of Water-Based Cutting Fluids: Progress and Application. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Adhesion behaviors on four special wettable surfaces: Natural sources, mechanisms, fabrications and applications. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 4895–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Bai, P.; Jia, W.; Xu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Ma, L.; Tian, Y. Surface wettability effect on aqueous lubrication: Van der Waals and hydration force competition induced adhesive friction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Gong, Z.; Dong, G. Effect of functional groups on tribological properties of lubricants and mechanism investigation. Friction 2023, 11, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ma, J.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, J.; Song, B.; Pei, X. A New Series of Double-Chain Single-Head Sulfobetaine Surfactants Derived from 1, 3-Dialkyl Glyceryl Ether for Reducing Crude Oil/Water Interfacial Tension. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 22, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; et al. Towards superior lubricity and anticorrosion performances of proton-type ionic liquids additives for water-based lubricating fluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Tan, X.; An, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, K.; Guo, M. Application of Hybrid Silicate as a Film-Forming Agent in High-Temperature Water-Based Drilling Fluids. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20577–20589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, Q.; Meng, Y.; Yang, H.; Hao, L. In situ visualization study of tribofilm growth process from magnesium silicate hydroxide nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isernia, L. FTIR Study of the Relation, between Extra-framework Aluminum Species and the Adsorbed Molecular Water, and its Effect on the Acidity in ZSM-5 Steamed Zeolite. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.L. A Temperature Perturbation Infrared Spectroscopy Comparison of HY and NaY Zeolite Dehydration/Rehydration. Minerals 2024, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Al-Mamary, M.; Moussa, Z. Antioxidant Activity: The Presence and Impact of Hydroxyl Groups in Small Molecules of Natural and Synthetic Origin. In Antioxidants-Benefits, Sources, Mechanisms of Action; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.; El-Dabea, T.; El-Khatib, R.; Abdou, A.; Barnawi, I.; Alshehri, H.; Al-Ghamdi, K.; El-Remaily, M. Fabrication, physicochemical characterization and theoretical studies of some new mixed ligands complexes based on N-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-guanidine and 1, 10-phenanthroline: DNA interaction, biological applications and molecular docking approach. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1310, 138328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailincai, D.; Marin, L. Eco-friendly PDLC composites based on chitosan and cholesteryl acetate. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; DellaCorte, C. Rheological Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of Water-Based Lubricants in AISI 52100 Bearing Steel. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Wang, W.; Wan, Y.; Pu, J. Tribology Properties of the Aqueous Solution of Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Mater. Sci. 2014, 4, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, C.; Ye, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, H. Research and Application of Anti-Collapse Lubricant Compound Polyalcohol for Water-Based Drilling Fluid. Open J. Yangtze Oil Gas 2021, 7, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. Lubricants 2020, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, M. Experimental and Numerical Study on Mixed Lubrication Performance of Journal Bearing Considering Misalignment and Thermal Effect. Lubricants 2022, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, N.; Nattah, A.; Al-Khafaji, Z. Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique. Open Eng. 2024, 14, 20220519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Xia, J. Analysis and comparison of tribological performance of fatty acid-based lubricant additives with phosphorus and sulfur. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Han, S. Tribological properties generated by a S-P-Cl-containing additive in water-based lubricant. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D. PEI-RGO nanosheets as a nanoadditive for enhancing the tribological properties of water-based lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Guo, P.; Bai, Y.; Zou, K.; Yi, M.; Yang, S.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F.; et al. Amino acid-based ionic liquids as water-ethylene glycol additives towards superior lubricity and corrosion resistance. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Kupčinskas, A.; Gumbytė, M.; Treinytė, J. Tribological properties of bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium oleate in glycerol and polyethylene glycol aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Additive | Performance | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfur/phosphorus-based | phosphorus-containing ricinoleic acid (PRA) sulfur-containing ricinoleic acid (SRA) S-P-Cl-containing DEPTP additive | extreme pressure (PB) [38]: water (95 N) with PRA (725 N) with SRA (842 N) CoF and wear scar diameter (WSD) (196 N, 1450 r/min) [39]: DEPTP (0.11, 0.8 mm) S-P-Cl-containing (0.084, 0.62 mm) | Harmful to the environment |
| Boron-based | water-based drilling fluids with borate nanoparticles | CoF and film strength [7]: drilling fluids (0.4592, 3881 psi) borate nanoparticles (0.0595, 39,056 psi) | Insufficient high-temperature stability and Poor hydrolysis stability |
| Nanomaterial-based | polyethylenimine-reduced graphene oxide (PEI-RGO) nanosheets in water | CoF and WSD (4 N, 3 Hz) [40]: water (0.491, 182.5 μm) 0.05 wt% PEI-RGO (0.23, 164.2 μm) | Poor dispersion stability and complex preparation process |
| Polyether-based | alkyl glyceryl ether with xanthan gum (XG) | CoF [11]: water (0.34) with XG (0.06) commercial lubricant DP400 (0.14) | Large addition amount and high cost |
| Ionic liquid-based | amino acid-based ionic liquids (Lys-DEHP, Arg-DEHP) in water-glycol protic ionic liquid (DE) in water/glycerol and water/PEGsolutions | CoF, and PB [41]: W-EG (0.2, 275 N) 1%Lys-DEHP (0.1, 1167 N) 1%Arg-DEHP (0.1, 1118 N) CoF and WSD [42]: WGL (0.099, 558 μm) WPEG (0.075, 495 μm) WGL + DE0.5 (n.d.) WPEG + DE0.5 (0.089, 475 μm) | Complex preparation process, high toxicity, and easy to cause corrosion |
| Our study | BA-50%GE in water | CoF, WSD and PB water (0.4, ≥1 mm, n.d.) 50%GE (0.024, 510 μm,496 N) BA-50%GE (0.005, 462 μm, 558 N) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Z. Boric Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive in Glycerol Ethoxylate Aqueous Solution. Lubricants 2025, 13, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090414
Huang S, Wang Z, Hao Z. Boric Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive in Glycerol Ethoxylate Aqueous Solution. Lubricants. 2025; 13(9):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090414
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shouzhi, Zhongnan Wang, and Zhongxian Hao. 2025. "Boric Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive in Glycerol Ethoxylate Aqueous Solution" Lubricants 13, no. 9: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090414
APA StyleHuang, S., Wang, Z., & Hao, Z. (2025). Boric Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive in Glycerol Ethoxylate Aqueous Solution. Lubricants, 13(9), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090414