Abstract
Compared with traditional lubricants, polyol ester lubricants exhibit superior oxidative stability and have been widely applied in extreme operating conditions such as aviation engines. However, under high-temperature conditions, polyol esters are still susceptible to oxidation and therefore require the addition of antioxidants. N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine is an excellent high-temperature antioxidant used in polyol ester. However, a notable issue is that oil sludge may form when this antioxidant is used at high temperatures. Excessive sludge can lead to a series of problems such as oil circuit blockage, more severe mechanical wear, and poor heat dissipation performance. In this work, oil sludge formation from N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine was simulated via high-temperature oxidation experiments in a polyol ester base oil. The formed sludge was then characterized by various advanced techniques, such as FT-IR, GPC, TGA, MALDI-TOF MS, and XPS. The results showed that the oil sludge was mainly composed of derivatives of polyol esters and N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine, along with some metal components. Further analysis showed that polymerization reactions between antioxidant molecules are the key factors leading to sludge generation, and polycyclic aromatic compounds formed by polymerization are responsible for inducing sludge generation in polyol esters.
1. Introduction
It is estimated that approximately one-third of global primary energy is consumed in overcoming friction each year, and up to 80% of mechanical component failures are associated with wear [1]. Lubricants mitigate friction and wear by forming a protective film on contacting surfaces, thereby preventing direct metal-to-metal contact. With the continuous advancement of modern industry, mechanical systems increasingly operate under extreme conditions, including high temperatures (>200 °C), high pressures, and heavy loads, which pose significant challenges to the reliability and efficiency of lubrication systems. Traditional hydrocarbon lubricants, such as mineral oils and poly-α-olefin (PAO) synthetic oils, are increasingly unable to meet the demands of extreme operating conditions due to their limited thermal stability and susceptibility to oxidation. In contrast, polyol esters have become the key base oils in aviation turbine engine lubricants [2], hydraulic fluids [3], refrigerants [4], and other specialty oils, due to their excellent thermal and oxidative stability, outstanding viscosity–temperature characteristics and superior lubrication performance. However, polyol ester can be significantly oxidized at the temperature above 200 °C, leading to higher oil viscosity, increased total acid number, and harmful sludges [5,6].
Adding high-temperature antioxidants has proven to be an effective strategy for delaying the oxidation of polyol esters under elevated temperatures [7,8]. Among them, alkylated diphenylamines and N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine (PANA) are two widely used aromatic amine antioxidants. Studies have shown that lubricants containing PANA exhibit a higher initial oxidation temperature, a longer oxidation induction period, and a stronger ability to suppress acid value growth compared with alkylated diphenylamines [9,10]. Owing to its excellent high-temperature oxidation resistance, PANA has been an indispensable component of aviation turbine engine lubricants since the last century [11,12,13]. However, despite these advantages, PANA suffers from a significant drawback: its strong tendency to generate oil sludge during high-temperature service [14]. This sludge deposition within the oil circuit can block passages, hinder lubricant flow, and compromise the integrity of the oil film, ultimately leading to lubrication failure between metal components. Furthermore, sludge adhering to component surfaces obstructs lubricant circulation and significantly reduces the system’s heat dissipation capacity. In practice, dispersants or detergents are often incorporated to mitigate sludge formation, but this inevitably increases the overall formulation cost.
In view of the significant hazards of oil sludge, researchers have devoted considerable attention to its composition and formation mechanism in the past few decades. Early studies mainly focused on analyzing the chemical composition of oil sludge. For instance, Kunina et al. [15] reported that the sludge in aviation turbine engine lubricant (B-3V) mainly consisted of severe oxidation products of additives, along with metal oxides from the engine components. Liu et al. [16] also analyzed the composition of sludge in turbine oil. The results showed that metals, antioxidants, defoamers, rust inhibitors, and emulsion breakers were potential contributors to sludge formation. Regarding the formation mechanism of the sludge in oil, Kauffman et al. [17] proposed the mechanism in which excessive polymerization of lubricant oil resulted in the formation of deposits. They also found that antioxidants inhibited the polymerization process but were simultaneously incorporated into the formed deposits, thereby increasing the total amount of sludge. Lillywhite et al. [18] demonstrated that oxidation and nitration of lubricating oil are critical to sludge formation through laboratory simulations replicating gasoline engine blowby gas conditions. These reactions exhibit a distinct induction period due to the presence of antioxidant/anti-nitration additives, which terminates with the depletion of Zinc Dithiophosphate (ZDTP), as evidenced by infrared spectroscopy. Zeman et al. [19] demonstrated that during thermo-oxidative aging of ester oil, the oxidation product of phenothiazine triggered the formation of sludge due to its low solubility in the oil. The above studies illustrate the strong correlation between sludge formation and the use of antioxidants. However, previous studies were primarily focused on analyzing the sludge composition and the influencing factors of sludge formation. In addition, there is a lack of thorough investigation on the complete chemical transformation pathway and detailed molecular-level mechanism of PANA from the initial radical reaction to the final sludge generation in polyol ester system.
Therefore, in this study, the sludge generated from PANA in polyol ester system was obtained by simulated high-temperature oxidation experiments. The composition of sludge was analyzed in depth by advanced characterization techniques such as Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Based on comprehensive characterization results, the intrinsic mechanism of PANA triggering sludge formation in polyol ester system was proposed. The transformation pathway of PANA and its role in sludge formation under thermo-oxidative conditions were clearly elucidated, which provides not only guidance for the development of new antioxidants with low deposition, but also a basis for optimizing the formulation of antioxidants in this system.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
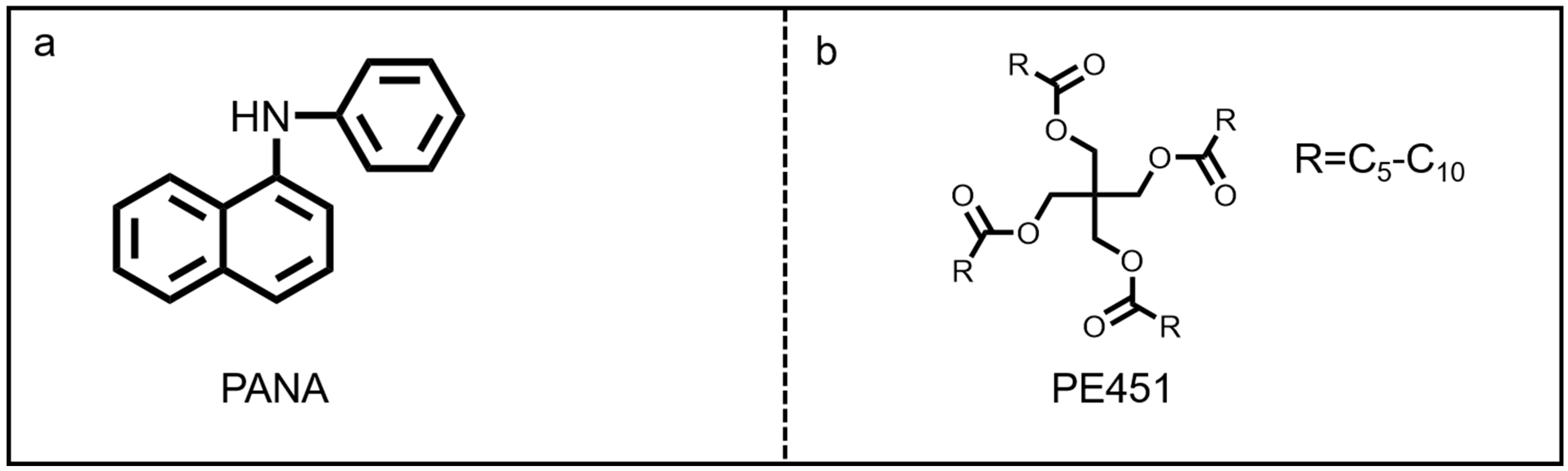
The antioxidant named as N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine (PANA, industrial grade, purity ≥99%) was purchased from Jinzhou Chenghua New Materials Co. Ltd. (Jinzhou, China), and its chemical structure is shown in Figure 1a. The pentaerythritol mixed ester-based oil (PE451, C5-C10 carboxylic acid ester) was supplied by Yingkou Xinghuo Chemical Co., Ltd. (Yingkou, China). The molecular structure of PE451 is shown in Figure 1b, and the detailed physical and chemical properties are shown in Table 1.
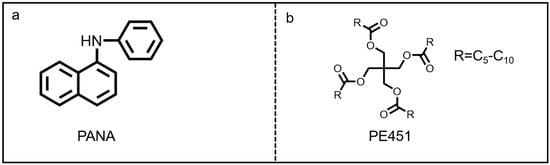
Figure 1.
The structure of (a) PANA and (b) PE451.

Table 1.
Physical and chemical properties of PE451.
Petroleum ether (boiling range 60–90 °C, analytically pure) was purchased from Shanghai Titan Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The copper wire (99.9%) and iron wire (99.5%) with a diameter of 1.6 ± 0.05 mm were used for catalytic oxidation reactions, which were ultrasonically cleaned with petroleum ether before using.
2.2. Oil Sludge Acquisition
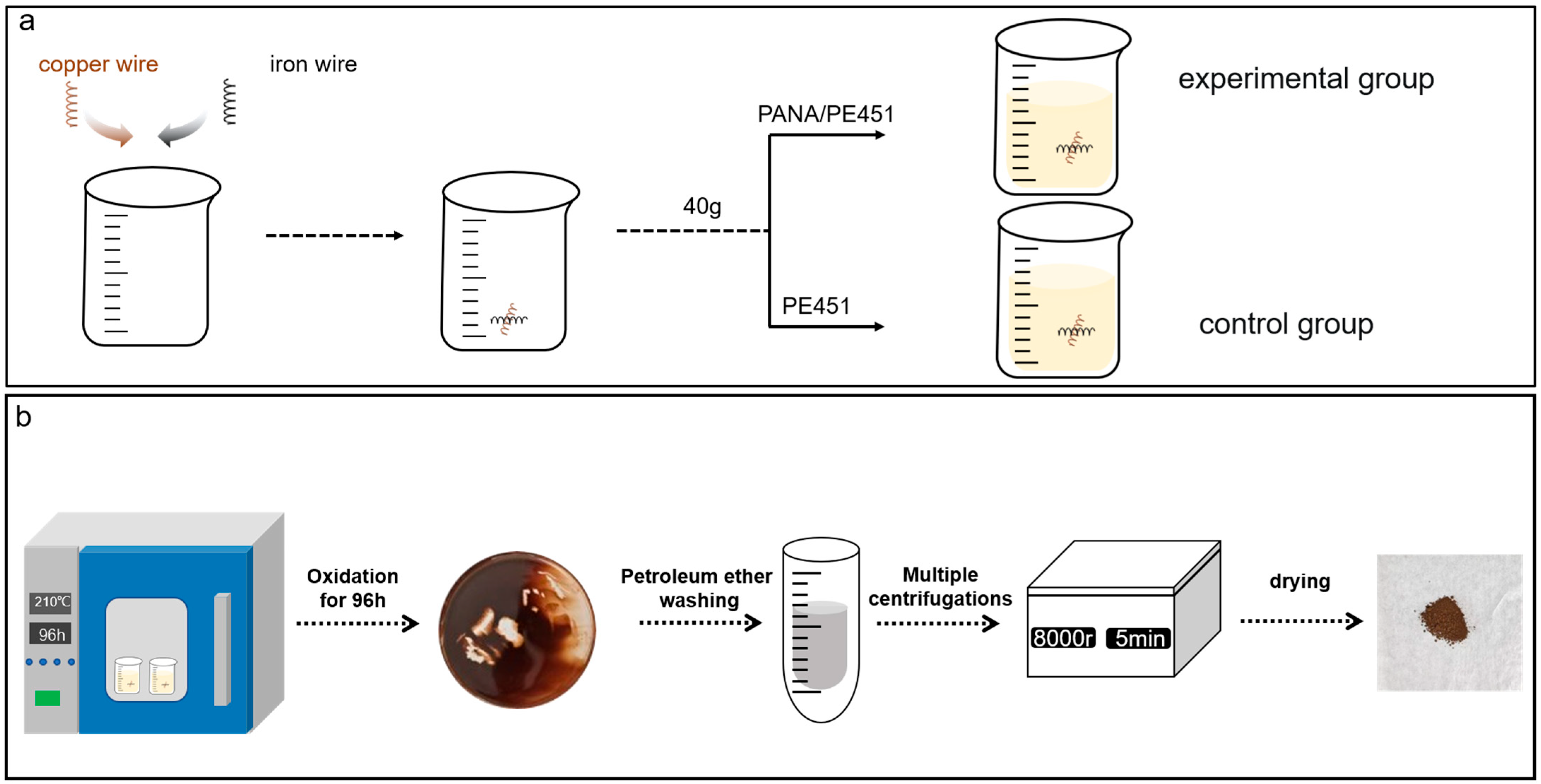
PANA (0.5 g) was placed in a 150 mL beaker with PE451 (99.5 g), as followed by stirring at 60 °C for 30 min. The sample was labeled as PANA/PE451. Subsequently, PANA/PE451 (40.0 g) sample was added into a 150 mL beaker with copper (5.0 g) and iron (5.0 g) wires, labeled as experimental group (Except for special instructions, all experiments were conducted using 5g of copper and iron metals as catalysts.). The control group was established by replacing PANA/PE451 into equal amount of PE451 base oil (Figure 2a).
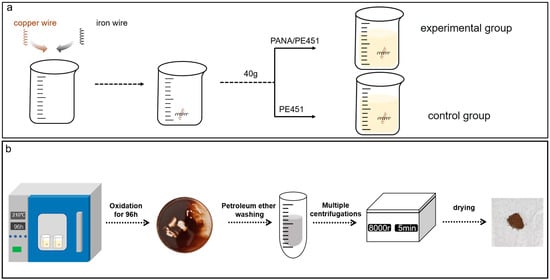
Figure 2.
(a) Experimental group arrangement; (b) schematic diagram of the oil sludge acquisition process.
The simulated oxidation experiments of the above two groups were conducted in a forced convection oven at 180 °C, 190 °C, 200 °C, and 210 °C for 96 h, respectively. Then, the deposit at the bottom of the beaker after oxidation at 210 °C was collected. The deposit was subjected to washing by petroleum ether and centrifugation (8000 rpm, 5 min) to remove the excess waste oil. This process was repeated until the supernatant in the centrifuge tube became transparent. The final sediment was naturally dried in a fume hood for 24 h to obtain a brown powder, named as oil sludge. The oil sludge acquisition process was shown in Figure 2b.
2.3. Measurements and Characterizations
After 96 h of lubricant oxidation, the kinematic viscosity was tested based on NB/SHT 0956-2017 [25] (Standard test method for kinematic viscosity of transparent and opaque liquids by automated houillon viscometer) by using SL-SF04 Automatic Folding Tube Kinematic Viscometer (Hunan Deterrence Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Changsha, China). The total acid number was determined by potentiometric titration using a fully automatic potentiometric titrator (905 Titrando, Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland), in accordance with GB/T 7304-2014 [26] for the determination of acid number of petroleum products.
The functional groups of the samples were characterized by a Fourier transform-infrared spectrometer (FT-IR, PerkinElmer Spectrum Two, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a PIKE Gladi ATR attenuated total reflection accessory (resolution 4 cm−1, 32 scans) in the range of 4000–500 cm−1. The thermal weight loss behavior was characterized by a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA, TA Instruments Q50, New Castle, DE, USA) under a nitrogen or air atmosphere (flow rate: 60 mL/min), with a heating rate of 10 °C/min from room temperature to 800 °C. The molecular weight distribution was determined by gel permeation chromatography (Malvern GPC305, Malvern, UK). Tetrahydrofuran was used as the mobile phase, and the polystyrene standard was used to construct a calibration curve, with detection by a differential refractive index detector. The low molecular weight components (<2000 Da) were analyzed by a MALDI-TOF MS (Bruker ultrafle Xtreme, Karlsruhe, Germany) in positive ion mode. Surface elemental composition and chemical state analysis were conducted using an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS, Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, Waltham, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. High-Temperature Antioxidation Behavior
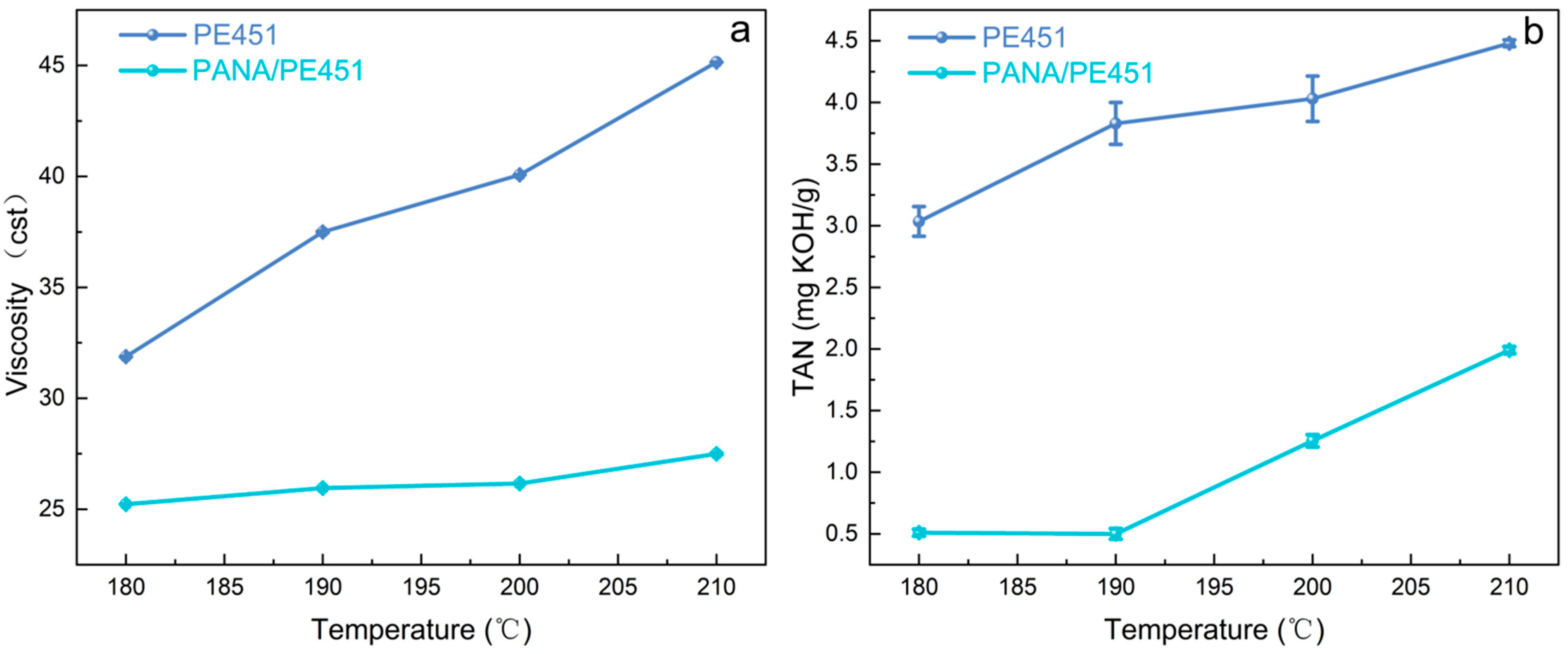
Under high-temperature conditions, lubricating oil underwent accelerated oxidation reactions, generating a series of oxidation products, which led to a significant increase in the viscosity and total acid number (TAN) [27,28,29]. As shown in Figure 3a,b, both the total acid number (TAN) and viscosity of PE451 increased with rising temperature after 96 h of oxidation. However, the addition of PANA significantly suppressed the oxidative of PE451 across different temperatures. As a high-temperature antioxidant, PANA effectively inhibited the increase in viscosity and TAN of the lubricating oil during oxidation, demonstrating excellent high-temperature antioxidant performance.
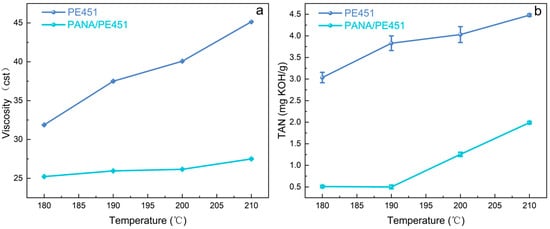
Figure 3.
(a) Viscosity of the control group (PE451) and the experimental group (PANA/PE451) after oxidation at different temperatures (b) TAN after oxidation at different temperatures in the control group (PE451) and the experimental group (PANA/PE451).
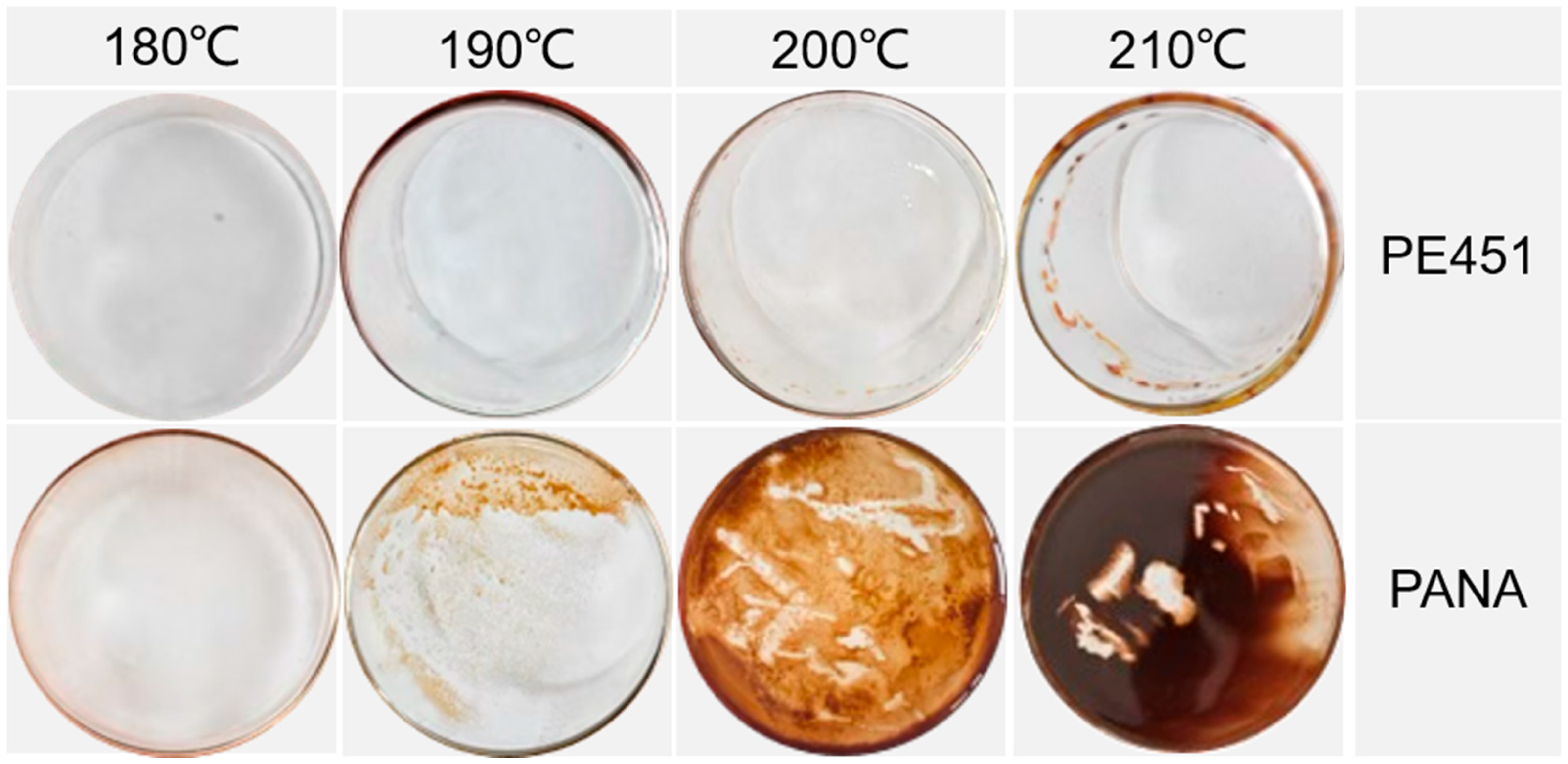
The sludge formation at the bottom of the beaker after oxidation is shown in Figure 4. A clear contrast in sludge formation tendency between PE451 and PANA/PE451 under different temperatures can be observed. The PE451 sample without antioxidant did not exhibit significant sludge formation at any of the tested temperatures—180 °C, 190 °C, 200 °C, or 210 °C. In contrast, the sample containing 0.5% PANA produced sludge at all temperatures except 180 °C. Moreover, it is evident that the amount of sludge formed is strongly correlated with temperature: as temperature increased, so did the sludge formation. Although PANA acts as an antioxidant, it clearly promoted sludge formation in the polyol ester system under high temperatures.

Figure 4.
The formation of oil sludge at the bottom of the beaker after oxidation of PE451 and PANA/PE451 at different temperatures.
3.2. FT-IR Analysis
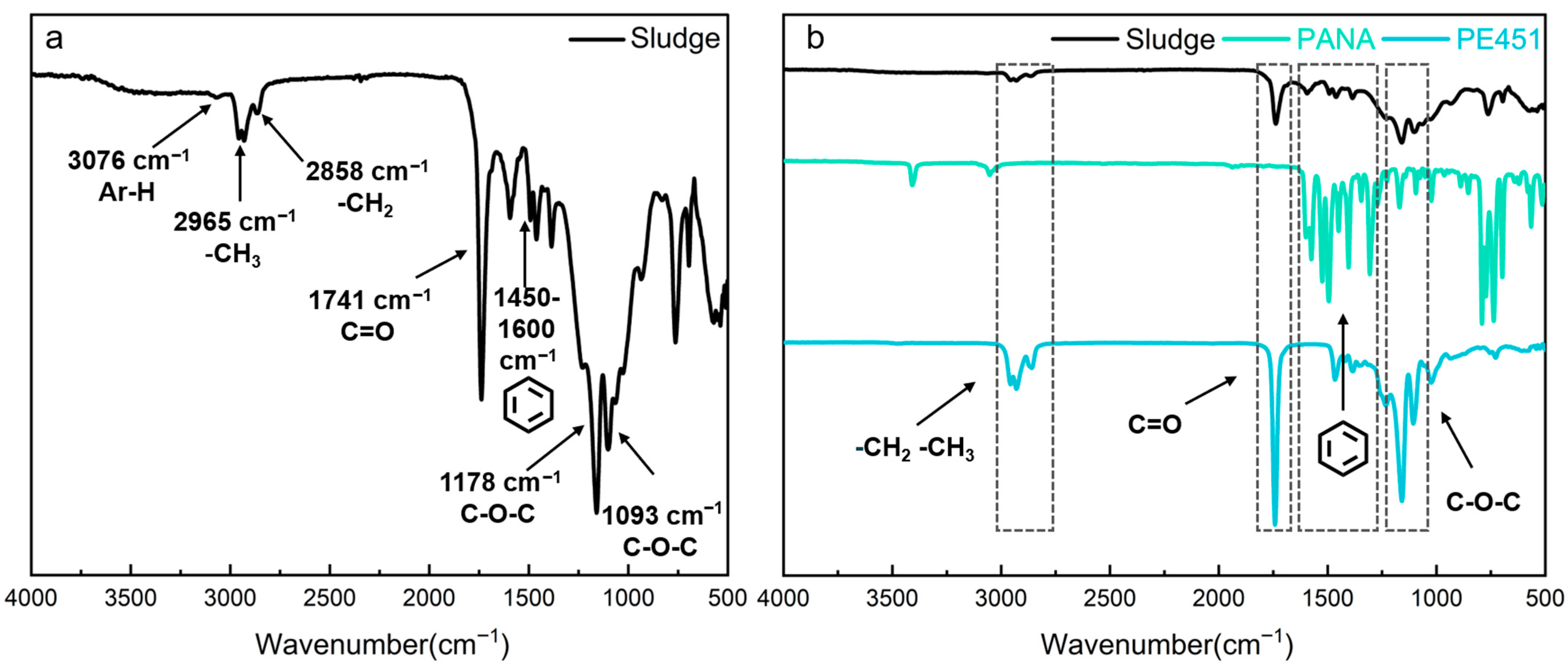
FT-IR was used to characterize the functional groups of PE451 and PANA, as well as the oil sludge, which was obtained at 210 °C. The detailed FT-IR result of sludge was shown in Figure 5a. The characteristic peaks of sludge at 3076 cm−1 was attributed to the stretching vibration of C-H bond in aromatic ring, which indicated that there was benzene ring structure in sludge [30]. The strong absorption peaks at 2965 cm−1 and 2858 cm−1 corresponded to the antisymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of -CH3 and -CH2- groups in alkyl chains, respectively, revealing the presence of long-chain alkane structures [31]. The characteristic peak at 1741 cm−1 was the C=O stretching vibration [32] in carbonyl groups. The multiple absorption bands observed in the range of 1450–1600 cm−1 corresponded to the vibrations of aromatic rings skeleton, confirming their presence in the sludge [33]. In addition, the double peaks at 1178 cm−1 and 1093 cm−1 were typical asymmetric stretching vibrations of ether bonds (C-O-C) [34]. In combination with the presence of carbonyl groups, this result suggested the existence of ester compounds in the oil sludge.
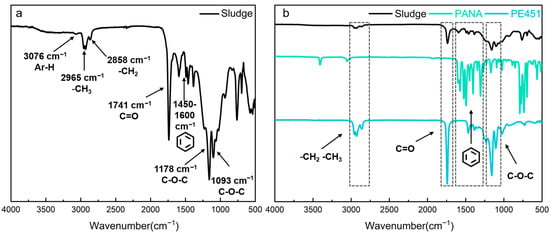
Figure 5.
(a) FT-IR of oil sludge; (b) FT-IR results comparison of oil sludge, PANA, and PE451.
Figure 5b reveals the source components of sludge by comparative analysis. The characteristic peaks of -CH3 (2965 cm−1), -CH2- (2858 cm−1), C=O (1741 cm−1), and C-O-C (1178 and 1093 cm−1) in oil sludge were highly consistent with the spectrum of PE451. This indicates that the ester compounds in the sludge mainly originated from the degradation products of PE451 base oil. In addition, the peaks of sludge at 3076 cm−1 (aromatic C-H) and in the range of 1450–1600 cm−1 (vibration of aromatic ring skeletons) showed a strong correlation with the spectrum of PANA, confirming the participation of PANA antioxidant in sludge formation. FT-IR analysis showed that the sludge contained both ester compounds derived from base oil and aromatic compounds associated with antioxidant.
3.3. TGA
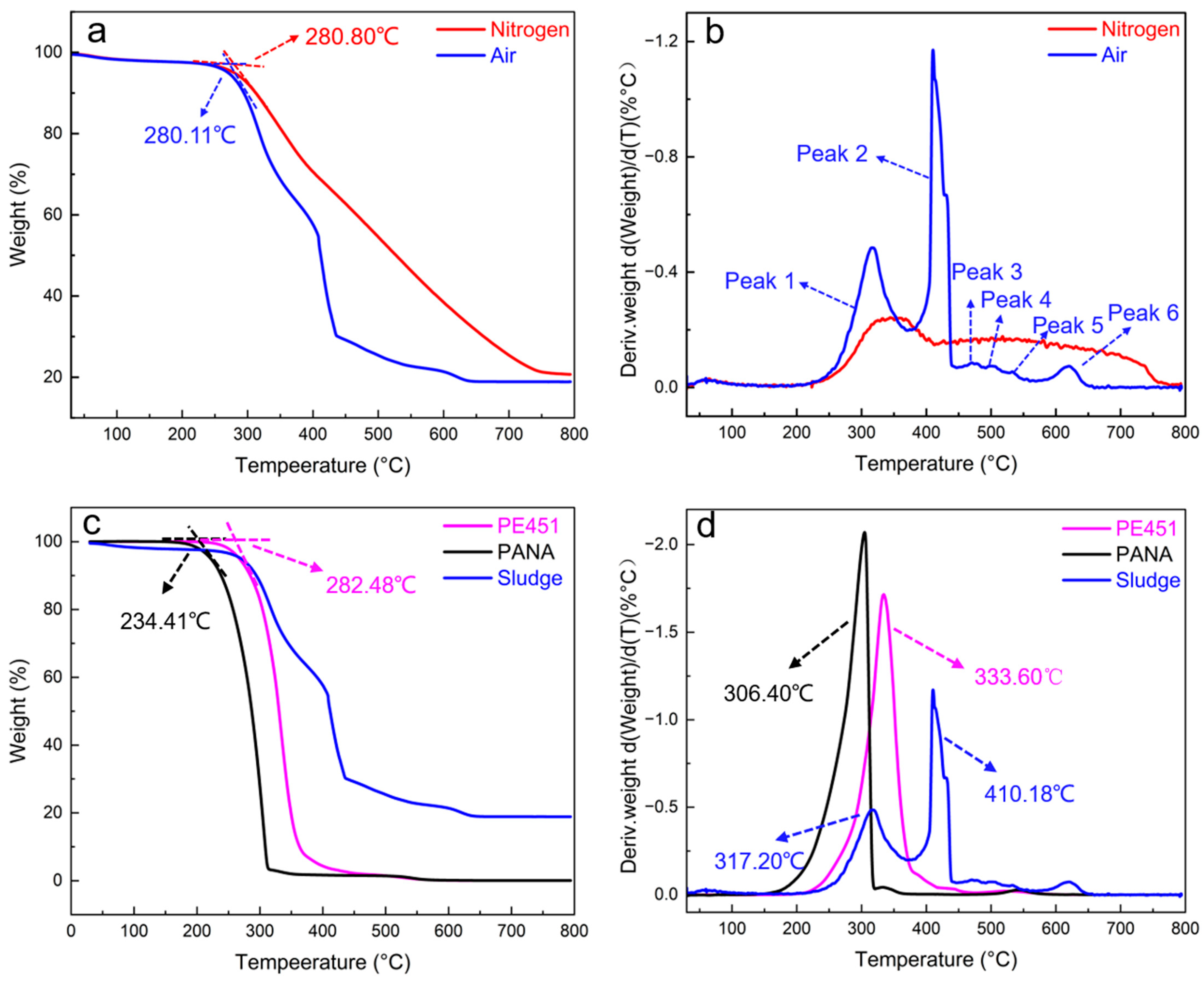
TGA experiments were carried out to systematically study the thermal decomposition characteristics of sludge under nitrogen and air atmosphere, respectively. As shown in Figure 6a, the initial pyrolysis temperature of sludge in nitrogen was 280.80 °C, while in air it was slightly lower at 280.11 °C, with a minimal difference of only 0.69 °C. This indicated that the atmosphere had a limited effect on the initial decomposition temperature. Thermal decomposition curve of sludge under nitrogen atmosphere exhibited a smooth decreasing trend. The thermal decomposition temperature was further investigated by differential thermogravimetric (DTG) analysis. As shown in Figure 6b, the DTG curve under air exhibited six peaks at 317.20, 410.18, 472.88, 503.98, 532.53, and 616.99 °C, indicating that the sludge was composed of at least six major components with different thermal stability. The DTG curve under nitrogen showed a wide and broad peak, consistent with the characteristics of inert pyrolysis.
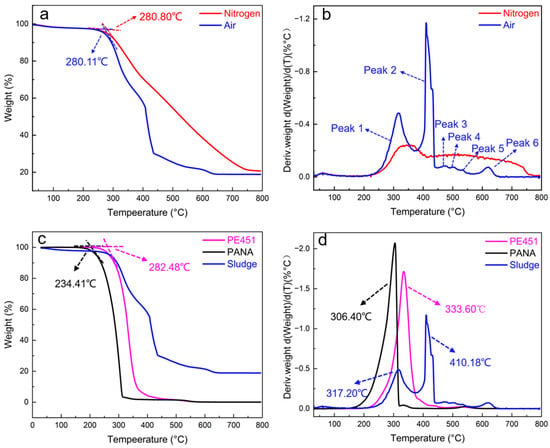
Figure 6.
(a) TGA curves of sludge under nitrogen and air; (b) DTG curves of sludge under nitrogen and air; (c) comparison of results for PE451, PANA, and sludge TGA in the air; (d) comparison of results for PE451, PANA, and Sludge DTG in the air.
It is notable that the final weights of residue were approximately 20% (20.842% in nitrogen and 18.906% in air) when the temperature was raised to 800 °C. This suggested that the sludge may contain inorganic components such as metal compounds. The high thermal stability of inorganic components can be a key factor hindering the complete decomposition of sludge.
Figure 6c,d show the TGA/DTG curves of PE451, PANA, and the sludge in an air atmosphere. In Figure 6c, the initial decomposition temperature of PE451 (282.48 °C) is close to that of the sludge (280.11 °C). However, as shown in Figure 6d, the DTG curve of PE451 exhibits only a single peak at 333.60 °C, while the sludge presents two major peaks at 317.20 °C and 410.48 °C, indicating that PE451 is absent in the sludge. Similarly, the TGA/DTG curves of PANA display two peaks at 234.41 °C and 306.40 °C, which do not coincide with any peaks in the sludge curve, suggesting that PANA is also not present in the sludge.
Combining the FT-IR and TGA analyses, it can be concluded that the sludge is a mixture of multiple components. It contains organic compounds derived from both PANA and PE451, as well as thermally stable metallic constituents, but does not contain intact PE451 or PANA.
3.4. XPS Analysis
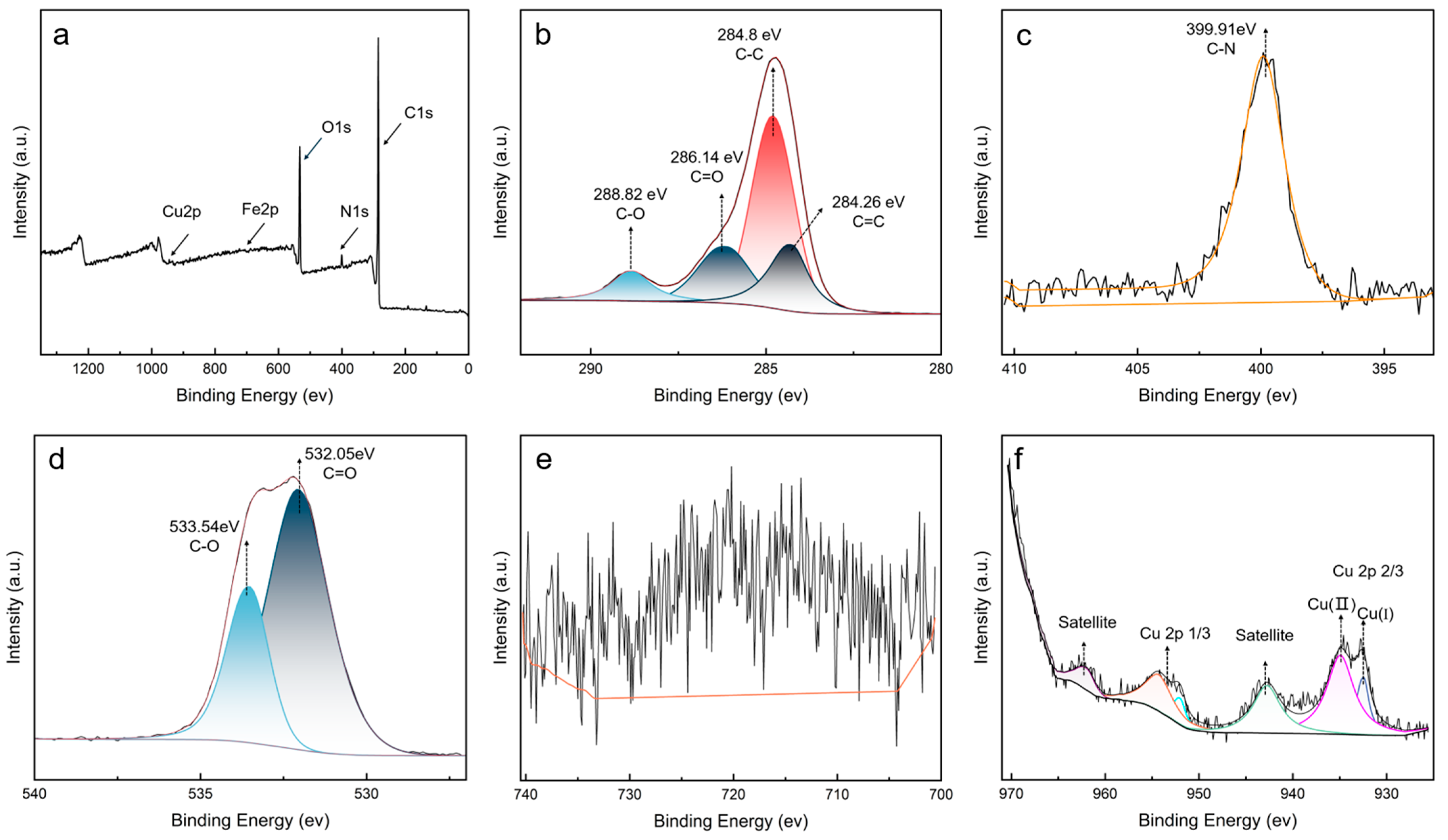
To deeply analyze the chemical composition of sludge, XPS measurements were performed for analyzing detailed elemental composition and chemical states. The XPS survey result showed that sludge contained C, O, N, Cu, and Fe elements (Figure 7a). Based on the atomic contents analysis (Table 2), the oil sludge was composed of C (78.48%), O (17.57%), N (3.26%), Cu (0.38%), and Fe (0.31%). The detection of metallic elements confirmed the inference from TGA that there were residual metallic components in sludge. The notable content of N further supported the conclusion that PANA participated in the formation of sludge.
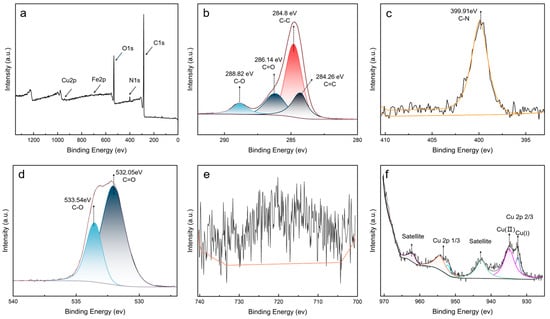
Figure 7.
XPS spectral comparison of sludge: (a) survey, (b) C 1s, (c) N 1s, (d) O 1s, (e) Fe 2p, (f) Cu 2p.

Table 2.
Relative atomic contents of elements in sludge.
High-resolution XPS spectrum was used for detailed elemental states. C 1s fine spectrum (Figure 7b) showed characteristic peaks at 284.26, 284.80, 286.14, and 288.82 eV, corresponding to C=C, C-C/C-H, C-O, and C=O bonds, respectively [35]. The presence of C-O and C=O suggested that the sludge contained a large number of ester compounds. In N 1s spectrum (Figure 7c), the significant peak at 399.91 eV can be attributed to C-N bonds, indicating the presence of antioxidant derivatives [36]. The O1s peaks at 533.54 eV and 532.05 eV are attributed to C-O bonds and C=O bonds, respectively [37] (Figure 7d). Two characteristic peaks at 932.45 eV and 934.94 eV were observed in Cu 2p spectrum, which corresponded to Cu (II) and Cu (I), respectively (Figure 7f) [38,39,40,41]. The distinct satellite peaks indicated the presence of metal oxide. The XPS results further demonstrated that the sludge was composed of antioxidant and base oil derivatives, as well as some amount of metal compounds.
3.5. The Influence of Metal Content on the Formation of Sludge and GPC Analysis
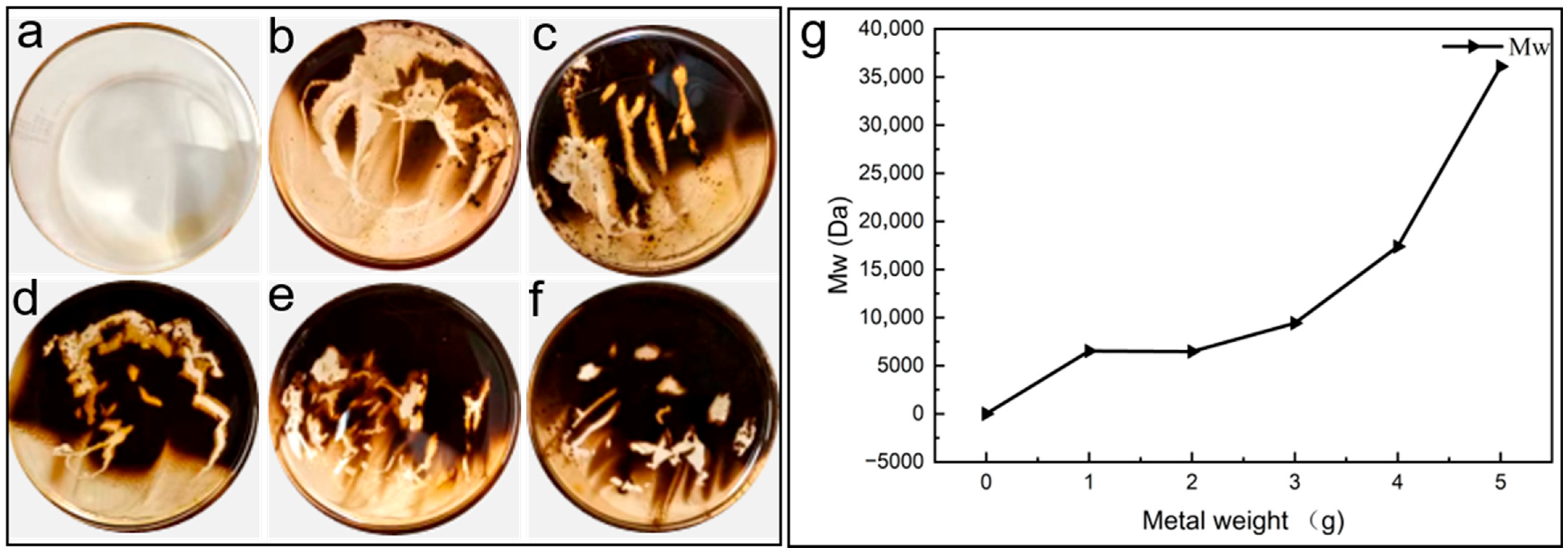
To further examine the role of metals in sludge formation, a mass-gradient experiment was conducted by introducing 0–5 g of copper and iron wires into PANA/PE451 samples. As shown in Figure 8, no sludge was detected in the absence of metal catalysts (Figure 8a), whereas the introduction of either copper or iron immediately triggered sludge formation (Figure 8b–f). With increasing metal mass, the coverage area of sludge at the bottom of the beaker expanded significantly, demonstrating that metals strongly accelerate sludge generation.
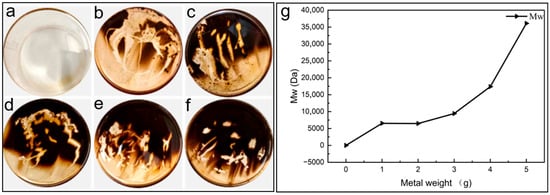
Figure 8.
(a) The bottom of the non-metallic catalytic beaker. (b) 1 g of copper wire and 1 g of iron wire catalyze the bottom of the beaker; (c) 2g of copper wire and 2 g of iron wire catalyze the bottom of the beaker; (d) 3 g of copper wire and 3 g of iron wire catalyze the bottom of the beaker; (e) 4 g of copper wire and 4 g of iron wire catalyze the bottom of the beaker; (f) 5 g of copper wire and 5 g of iron wire catalyze the bottom of the beaker; (g) weight-average molecular weight of the sludge.
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) was further employed to analyze the molecular weight distribution of organic products within the sludge. The weight-average molecular weight (Mw) distribution of sludge obtained under different metal catalytic loads is presented in Figure 8g. The results show that the Mw of organic molecules increased progressively with the mass of metal added. Thus, metal catalysis not only enhanced the quantity of sludge but also promoted the polymerization of organic molecules.
The complete GPC results for sludge catalyzed by 5 g of copper and iron wires are summarized in Table 3, while additional GPC datasets are provided in the Supporting Materials (Tables S1–S4).

Table 3.
GPC analysis results of sludge.
As shown in Table 3, the mass average molecular weight (Mw), number average molecular weight (Mn) and Z average molecular weight (Mz) of the oil sludge were 36,095 Da, 2044 Da and 189,597 Da, respectively, which were significantly higher than the molecular weights of PE451 (472~753) and PANA (219), indicating that the organic components in sludge were dominated by macromolecules.
The molecular weight distribution characteristics can be quantified by the polydispersity index (PDI), defined as the ratio of Mw/Mn. The Mn is sensitive to low molecular weight components and reflects the numerical dominance of small molecules in the system. In contrast, the Mw represents the mass share of high molecular weight components. When the PDI is 1, the system exhibits a monodisperse distribution. The molecular weight distribution becomes broader as the PDI increases. Mw_10%_low defines the molecular weight below which the lowest 10% (by mass) of the polymer chains are found. Mw_10%_high defines the molecular weight above which the highest 10% (by mass) of the polymer chains are found. The PDI of sludge was 17.658, indicating a broad molecular weight distribution. In addition, the substantial difference between the Mw_10%_low quartile (397 Da) and Mw_10%_high quartile (210,632 Da) indicates the coexistence of components ranging from low to ultra-high molecular weights. The GPC results demonstrate that the sludge consists of complex polymers with molecular weights spanning approximately three orders of magnitude, from 102 (397 Da) to 105 (210,632 Da).
3.6. MALDI-TOF MS Analysis
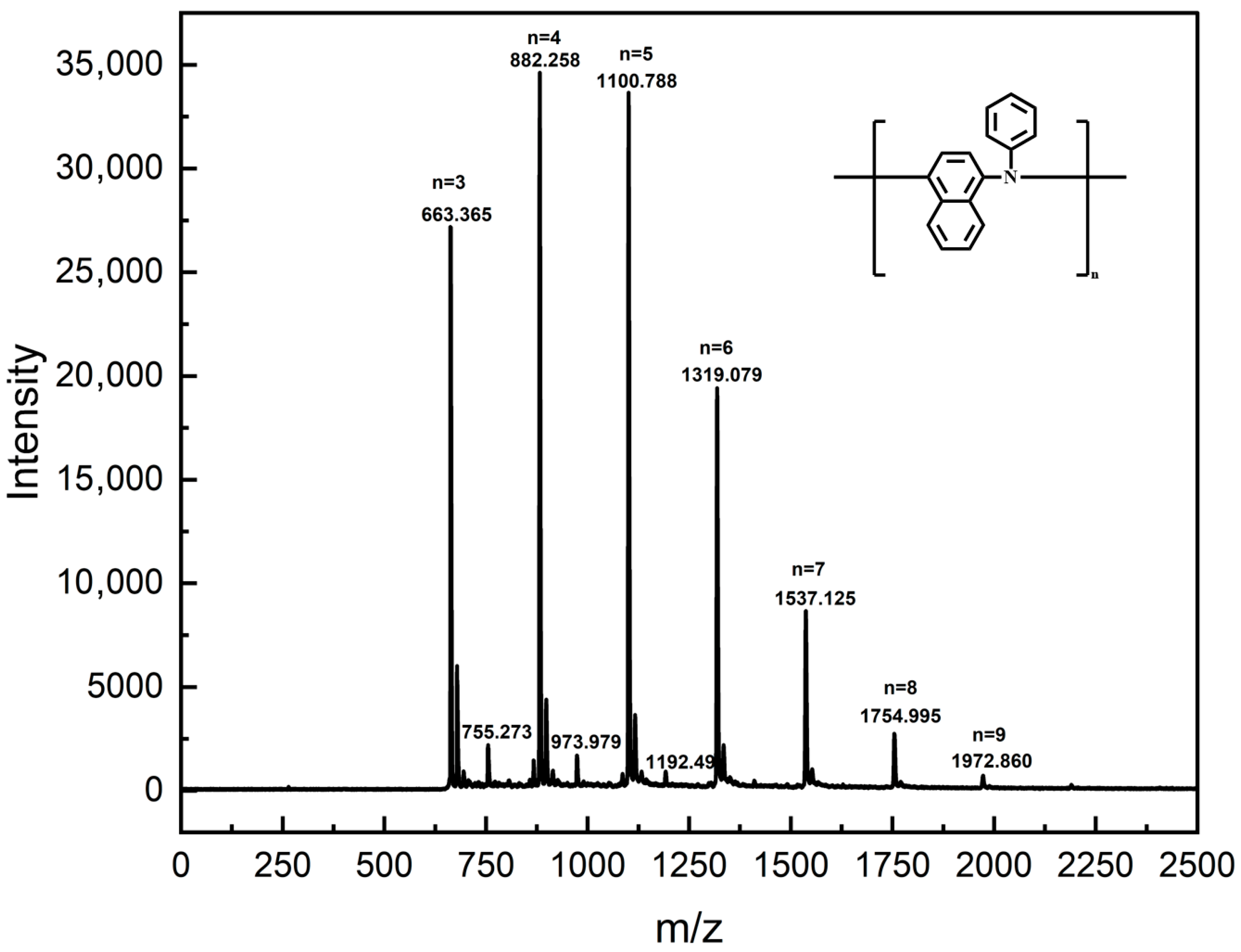
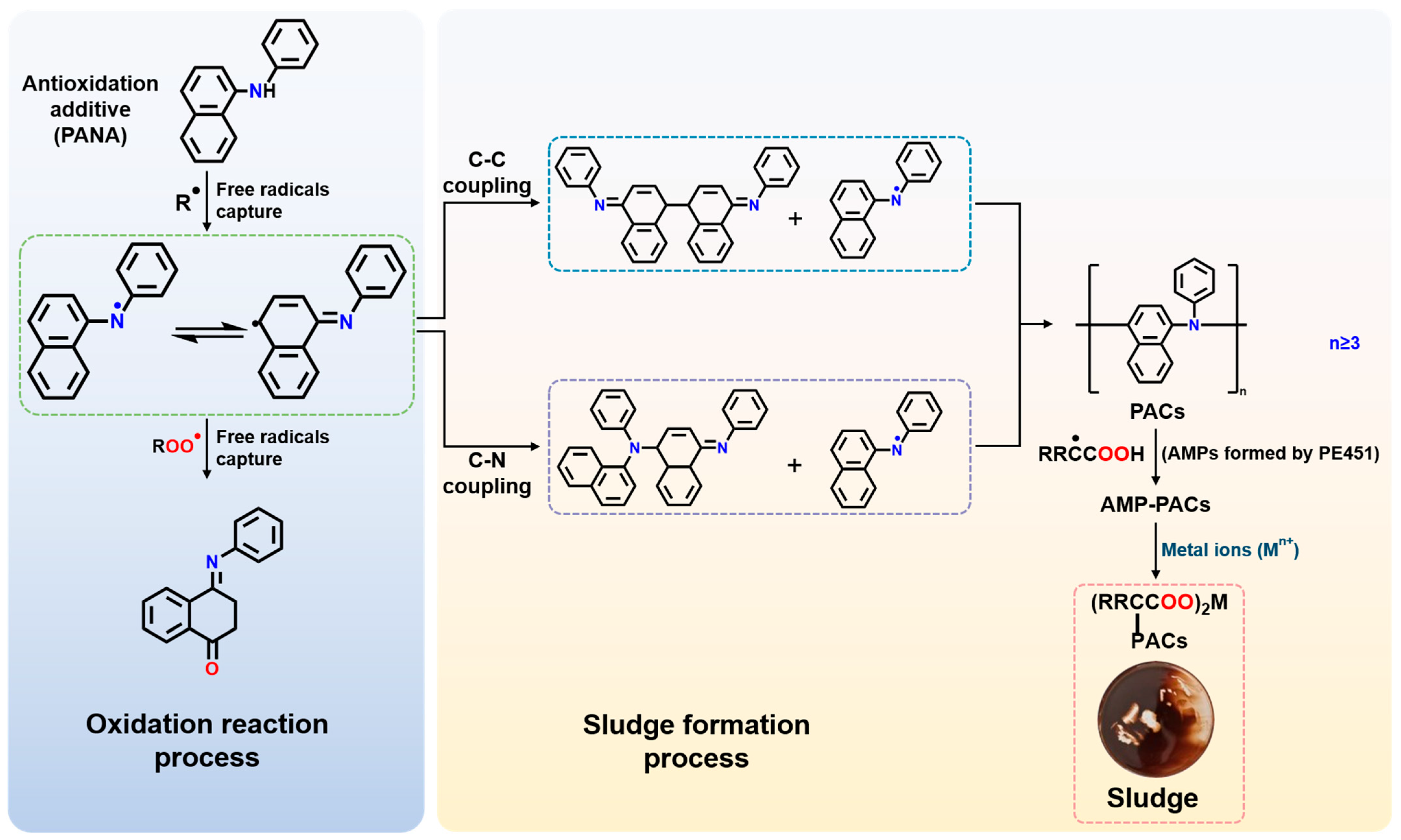
MALDI-TOF MS has been proved to be a valuable technique for characterizing the changes in polyol ester after use [42,43]. Its soft ionization properties ensure the accurate detection of molecular structure changes in oil and additives during oxidation while maintaining sample integrity. The fraction of oil sludge with molecular weight <2000 Da was characterized by MALDI-TOF MS, as shown in Figure 9. The MALDI-TOF MS spectrum of the low molecular weight fraction exhibited sharp peaks at m/z = 663.365, 882.258, 1100.788, 1319.079, 1537.125, 1754.995, and 1972.860. Due to the soft ionization nature of MALDI-TOF MS, these m/z signals corresponded directly to the relative molecular masses of specific molecules present in the sludge. Furthermore, the relative molecular mass of the antioxidant PANA was 219. Consequently, the molecular masses corresponding to the observed peaks matched the theoretical molecular masses calculated for polymerized PANA. Polymerization degrees (n) of 3 to 9 for PANA corresponded to the observed peaks at m/z = 663.365, 882.258, 1100.788, 1319.079, 1537.125, 1754.995, and 1972.860, respectively. Therefore, components in the sludge below 2000 Da originated primarily from polymerization products of the PANA formed under high-temperature operating conditions. PANA molecules were highly prone to polymerization at elevated temperatures. When the n reached 3 or higher, PANA formed oligomers insoluble in polyol esters, subsequently leading to sludge formation.
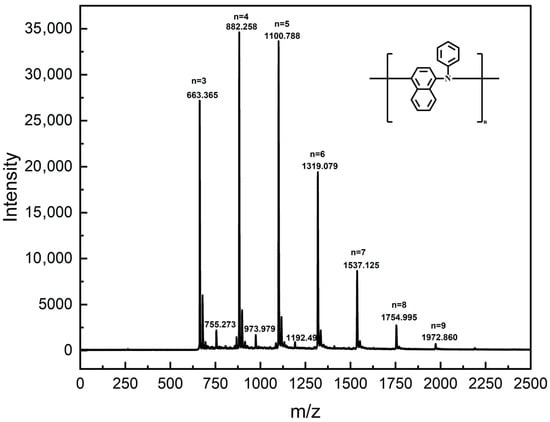
Figure 9.
MALDI-TOF MS results of sludge.
3.7. Sludge Formation Mechanism
Based on the characterization results, a sludge formation mechanism was proposed in Figure 10. At elevated temperatures, the C-O bond between the ester group and the adjacent alpha-methylene group in pentaerythritol ester undergoes cleavage due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group, generating free radicals. Alternatively, oxidative dehydrogenation of alkyl chains within the molecule by oxygen produces alkyl radicals (R·) [44,45,46,47]. PANA can terminate the radical chain reaction by capturing the radicals. The excellent high-temperature antioxidation performance of PANA was attributed to the large intramolecular π-electron conjugation system and the ability to stabilize free radical intermediates through various resonance states. However, following hydrogen donation to scavenge free radicals, the resulting radical species derived from antioxidant PANA tended to polymerize at elevated temperatures, forming dimers through either C-C or C-N coupling [48,49,50]. When the dimer further reacted with monomeric radicals to form a trimer, its solubility in PE451 decreased significantly. MALDI-TOF MS results showed that from the trimer onwards, PANA oligomers began to trigger sludge formation. Subsequent trimer with the monomer or dimer-trimer coupling reactions resulted in the formation of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs), which further accelerated sludge precipitation. Meanwhile, the oxidation of PE451 can cause the generation of acidic macromolecular polymers (AMPs), leading to an increase in viscosity and TAN (Figure 3).
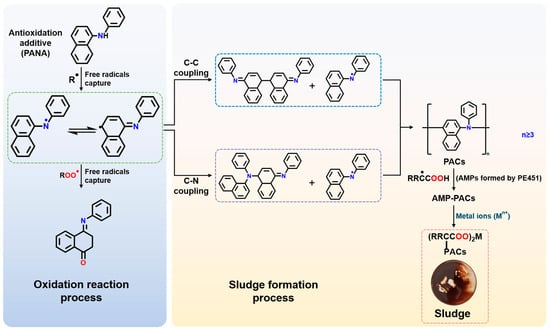
Figure 10.
Formation mechanism of oil sludge.
Although AMPs formed from base oil polymerization exhibited high molecular weight, oxidation experiments demonstrated that AMPs alone did not produce sludge (Insets in Figure 4). This absence of sludge formation can be attributed to the favorable solubility of AMPs in polyol ester, conferred by their ester groups. However, when AMPs associated with insoluble PACs to form AMP-PACs covalently bonded compound, the solubility of AMPs in P451 base oil was reduced, which promoted AMPs deposition. This explained why ultra-high molecular weight polymers were detected in the GPC analysis. Metals play a crucial role in the formation of oil sludge, as no sludge is produced in their absence (Figure 8). Furthermore, AMP–PAC species can undergo saponification reactions with metal ions (Mnn+), leading to the formation of oil-insoluble metal soaps that further aggravate sludge accumulation [51,52].
Based on the above mechanistic insights, several potential strategies can be proposed to mitigate sludge formation in polyol ester systems containing PANA. The metal catalytic gradient experiments demonstrated that both the amount and molecular weight of sludge increase with rising metal content, while TGA and XPS analyses confirmed the incorporation of metals into the sludge matrix. Therefore, the addition of suitable metal ion scavengers may effectively reduce the concentration of catalytic metals and slow down sludge generation. Furthermore, since the insolubility of polycyclic aromatic polymers produced by PANA polymerization is a critical factor leading to sludge accumulation, two additional approaches may be considered: blending PANA with other antioxidants to exploit synergistic effects and reduce the overall dosage of PANA, or chemically modifying the PANA structure by introducing appropriate substituents, such as suitably sized alkyl chains or ester groups, to improve the solubility of its polymerized products in the base oil. These strategies provide valuable guidance for developing more stable lubricant formulations with minimized sludge formation under high-temperature conditions.
4. Conclusions
Based on the above results and discussions, the following conclusions are drawn:
- The polyol ester PE451 did not generate sludge under various elevated temperatures. In contrast, the addition of PANA to PE451 led to sludge formation after oxidation at temperatures above 180 °C for 96 h, suggesting that the antioxidant itself can trigger sludge formation.
- Characterization of the sludge revealed that the sludge was derived from base oil derivatives and antioxidant derivatives, and that the sludge also contained small amounts of metal compounds.
- Metal elements were identified as an essential factor in sludge formation. In the absence of metals, PANA did not produce sludge under high-temperature oxidation conditions.
- The polymerization reaction of PANA under high temperatures is a critical factor for sludge formation. The trimerized products became insoluble in PE451 and contributed significantly to sludge deposition.
- Based on the mechanistic findings, sludge formation in polyol ester lubricants containing PANA can be mitigated by adding suitable metal ion scavengers, blending PANA with other antioxidants to reduce its dosage, or chemically modifying PANA with substituents such as alkyl chains or ester groups to improve the solubility of its polymerized products. These strategies provide practical guidance for developing more stable lubricants under high-temperature conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/lubricants13090403/s1, Table S1: 1g copper wire and iron wire catalyzed to form oil sludge GPC; Table S2: 2g copper wire and iron wire catalyzed to form oil sludge GPC; Table S3: 3g copper wire and iron wire catalyzed to form oil sludge GPC; Table S4: 4g copper wire and iron wire catalyzed to form oil sludge GPC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and J.L.; methodology, C.C. and J.L.; validation, C.C.; formal analysis, C.C.; investigation, C.C.; resources, J.L. and S.H.; data curation, C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and S.H.; supervision, H.L. and J.L.; project administration, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Innovation Program of Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, CAS (2024CP005).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, L. Origin of Friction and the New Frictionless Technology—Superlubricity: Advancements and Future Outlook. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Rui, W.; He, J.; Zhao, M. Synthesis, Tribological Properties and Oxidative Stability of Polyol Esters Base Oils Containing Pentaerythritol Complex Esters. Tribol. Int. 2024, 195, 109618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, N.H.; Yunus, R.; Idris, A.; Omar, R. Effects of Additives on Oxidation Characteristics of Palm Oil-Based Trimethylolpropane Ester in Hydraulics Applications. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsuzaki, S.; Homma, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Iizuka, T. Polyol Esters as Hfc-134a Compressor Lubricants. Lubr. Eng. 1994, 50, 801–807. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, P.; Wang, D.; Grant, C.S.; Oxenham, W.; Hauser, P.J. Measuring Thermal Degradation of a Polyol Ester Lubricant in Liquid Phase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, S.; Lamharess-Chlaft, N.; Sicard, M.; Raepsaet, B.; Galvez, M.E.; Da Costa, P. New Approach for Understanding the Oxidation Stability of Neopolyol Ester Lubricants Using a Small-Scale Oxidation Test Method. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 10449–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Jia, D.; Tu, J.; Zhan, S.; Yang, T.; Duan, H. Online Infrared Spectra Analysis of Multi-Phenol Antioxidants in Ester Lubricant During Friction under High-Temperature Oxidation. Tribol. Int. 2022, 176, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, J.; Lin, H.; Han, S. Research Progress of Antioxidant Additives for Lubricating Oils. Lubricants 2024, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Improvement of Oxidative Stability of Trimethylolpropane Trioleate Lubricant. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 569, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Song, H.; He, J.; Liang, Y. Study on the High-Temperature Bearing Test and Thermal-Oxidative Process of Aviation Lubricating Oils. Lubr. Sci. 2025, 37, 264–275. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolkarim, S.; Ehsan, A.; Christopher, P.; Spiridon, S.; Blakey, S. Investigation of Aviation Lubricant Aging under Engine Representative Conditions. Tribol. Trans. 2021, 64, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, J. Thermal Oxidation of Aviation Lubricating Oil: Mechanism, Influencing Factors, Evaluation Methods, and Antioxidants. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 19, e3114. [Google Scholar]
- Sniegoski, P.J. Quantitative Tlc Analysis of Amine Antioxidants in High-Temperature Jet Engine Lubricants. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1977, 15, 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Igarashi, J. Consumption of Antioxidant of Turbine Oil in Service Unit. Tribol. Trans. 1991, 34, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunina, E.A.; Kuznetsov, V.G.; Novosartov, G.T.; Boiko, L.V. Composition of Sludge Formed in B-3v Synthetic Lubricating Oil. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 1980, 16, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D.; Cheng, L.; Pang, C. Composition and Degradation of Turbine Oil Sludge. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, R.E.; Feng, A.; Karasek, K.R. Coke Formation from Aircraft Turbine Engine Oils: Part I—Deposit Analysis and Development of Laboratory Oil Coking Test. Tribol. Trans. 2000, 43, 823–829. [Google Scholar]
- Lillywhite, J.R.F.; Sant, P.; Saville, S.B. Sludge Formation: Investigation of Sludge Formation in Gasoline Engines. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 1990, 42, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zeman, A.; Von Roenne, V.; Trebert, Y. Fate of Amine Antioxidants During Thermal Oxidative Ageing of Neopentylpolyl Ester Oils. J. Synth. Lubr. 1987, 4, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D445; Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ASTM D2270; Standard Practice for Calculating Viscosity Index from Kinematic Viscosity at 40 °C and 100 °C. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM D5950; Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products (Automatic Tilt Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D92; Standard Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup Tester. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM D974; Standard Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-Indicator Titration. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- NB/SH/T 0956-2017; Standard test method for kinematic viscosity of transparent and opaque liquids by automated Houillon viscometer. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 7304-2014; Standard test method for acid number of petroleum products by potentiometric titration. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Yao, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; She, X.; Liao, X.; Shen, Y.; Gan, Z. Effect of Iron and Copper on the Thermal Oxidation Stability of Synthetic Hydrocarbon Aviation Lubricating Oil. Catal. Commun. 2021, 161, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zong, Z.-M.; Fei, Y.-W.; Ma, J.; Guo, F. Thermal Oxidation Stability of Poly-A-Olefin Lubricating Oil. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 12, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, X.; Xie, F.; Cao, J.; Hu, J. Real-Time Oxidation and Coking Behavior of Ester Aviation Lubricating Oil in Aircraft Engines. Tribol. Int. 2024, 192, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, J.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Synthesis and Application of Highly Efficient Multifunctional Vegetable Oil Additives Derived from Biophenols. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.; Spikes, H. In-Contact Ir Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbon Lubricants. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, G.; Wang, Y.; Eli, W. Synthesis and Characterisation of Antioxidant-Modified Esters of Dipentaerythritol as Lubricating Base Oil. Lubr. Sci. 2013, 25, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-Q.; Yang, S.-Z.; Zhang, J.-J.; Guo, L.; Xu, X. Synthesis and Anti-Oxidative Properties of Poly(Diphenylamine) Derivative as Lubricant Antioxidant. Pet. Chem. 2019, 59, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Faujdar, E.; Singh, R.K. Methyl Oleate Derived Multifunctional Additive for Polyol Based Lubricants. Wear 2021, 466–467, 203550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Guo, P.; Bai, Y.; Zou, K.; Yi, M.; Yang, S.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F.; et al. Amino Acid-Based Ionic Liquids as Water-Ethylene Glycol Additives Towards Superior Lubricity and Corrosion Resistance. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Hu, L. High Temperature Tribological Studies of Oil-Soluble Ionic Liquids as Extreme Pressure and Anti-Wear Additives for Ester Oils. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 419, 126761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz-Gromiuk, J.; Rusinek, I.; Kurach, Ł.; Rzączyńska, Z. Thermal and Spectroscopic (Ir, Xps) Properties of Lanthanide(Iii) Benzene-1,3,5-Triacetate Complexes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, W.; Yan, T.; Liang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X. Tribological Performances of Copper Perrhenate/Graphene Nanocomposite as Lubricating Additive under Various Temperatures. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 100, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, H.; Ji, S.; Zhao, Q.; Pollet, B.G.; Wang, R. Hollow Core-Shell Structured Cu2O@Cu1.8S Spheres as Novel Electrode for Enzyme Free Glucose Sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Guo, S.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, B. Superlubricity of Tin Coating Using Glycerol with the Addition of Cu Nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2023, 181, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Bin Wu, H. CeO2-Modified Cu Electrode for Efficient CO2 Electroreduction to Multi-Carbon Products. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 54, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartl, P.; Völkl, C. The Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Lonisation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (Maldi-Tof Ms) to the Analysis of Lubricants. Part 1. Polyol Ester Aviation Turbine Engine Oils. J. Synth. Lubr. 1998, 15, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bartl, P.; Völkl, C.; Kaiser, M. The Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionisation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (Maldi-Tof Ms) to the Analysis of Lubricants. Part 2. Used Polyol Ester Aviation Turbine Engine Oils. J. Synth. Lubr. 1999, 16, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.R.L.; Nagatomi, E.; Waddington, D.J. The Autoxidation of Simple Esters: Towards an Understanding of the Chemistry of Degradation of Polyol Esters Used as Lubricants. J. Jpn. Petr. Inst. 2003, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Zhang, N.; Hu, J.; Liao, X.; Shen, Y.; Gan, Z. Effect of Temperature on the Chemical Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Diester Aviation Lubrication Oil. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8829206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakunin, V.N.; Parenago, O.P. A Mechanism of Thermo-Oxidative Degradation of Polyol Ester Lubricants. J. Synth. Lubr. 1992, 9, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Xiang, Y.; Shang, H.; Cheng, B.; Zhan, S.; Li, J. Thermal-Oxidation Mechanism of Dioctyl Adipate Base Oil. Friction 2016, 4, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.F.; Middleton, B.S.; Ingold, K.U. Oxidation of Amines with Peroxy Radicals. I. N-Phenyl-2-Naphthylamine. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridger, R.F. Kinetics of Inhibition of Hydrocarbon Autoxidation by 1, 1’-Bis (N-Phenyl-2-Naphthylamine). J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36, 1214–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.K.; Korcek, S.; Zinbo, M.; Gerlock, J.L. Regeneration of Amine in Catalytic Inhibition of Oxidation. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 5396–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, G.; Mazzamaro, G.; Rasberger, M. Oxidative Degradation and Stabilisation of Mineral Oil-Based Lubricants. In Chemistry and Technology of Lubricants; Mortier, R., Fox, M., Orszulik, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 107–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wylde, J.J. Chapter 4—Naphthenate and Carboxylate Soap Treatment. In Flow Assurance; Wang, Q., Ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 227–285. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).