Hybrid Additives of 1,3-Diketone Fluid and Nanocopper Particles Applied in Marine Engine Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
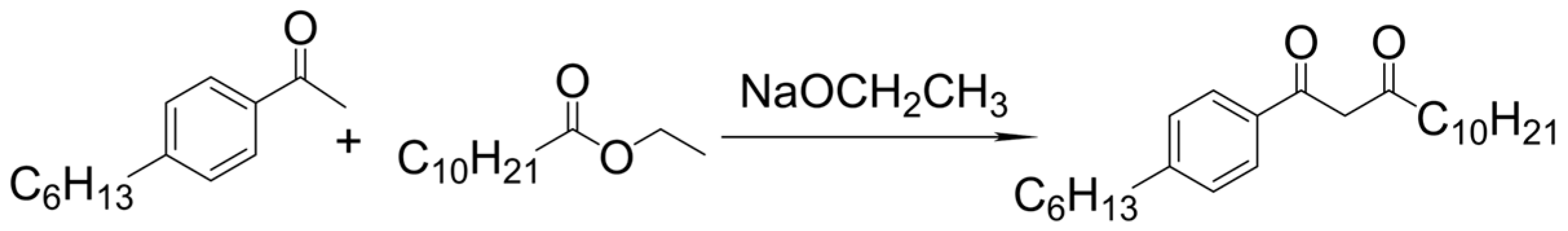
2.1. 1,3-Diketone Fluid
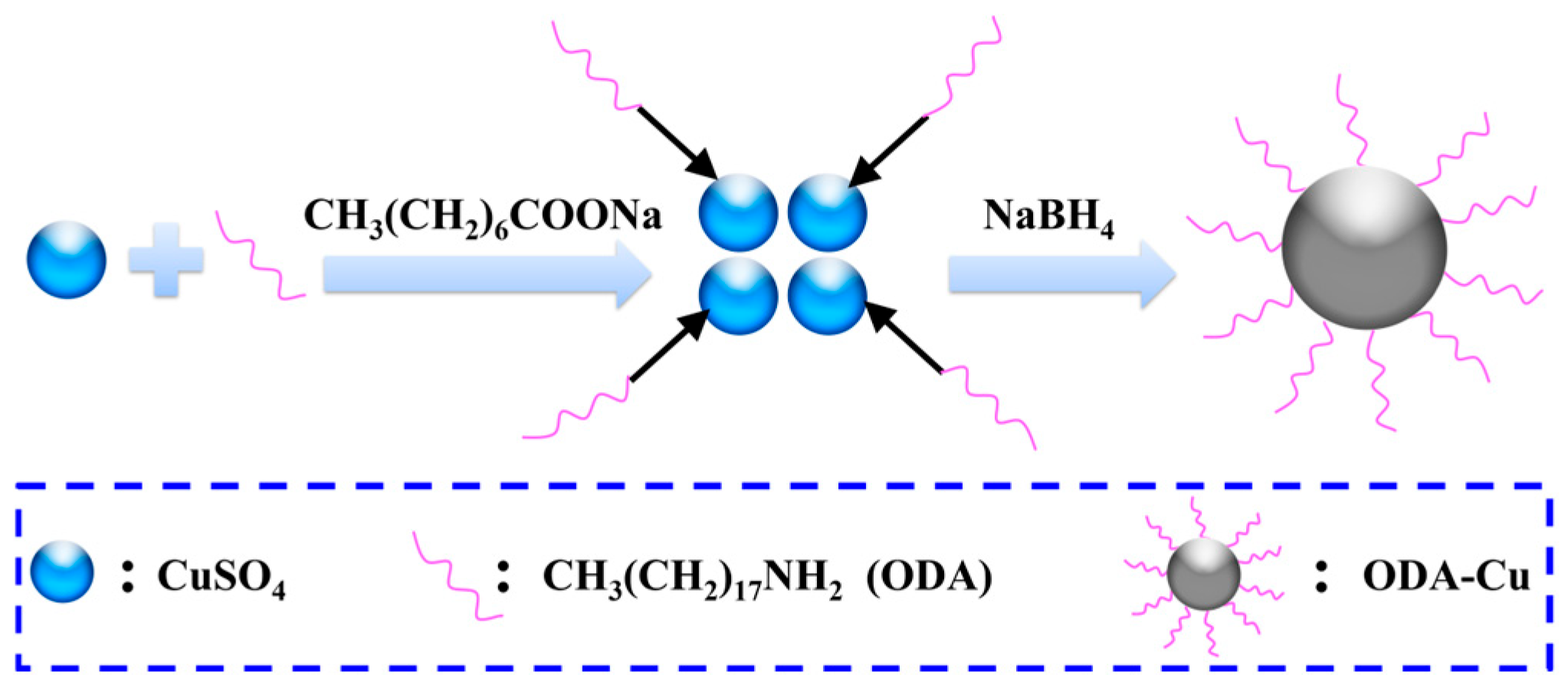
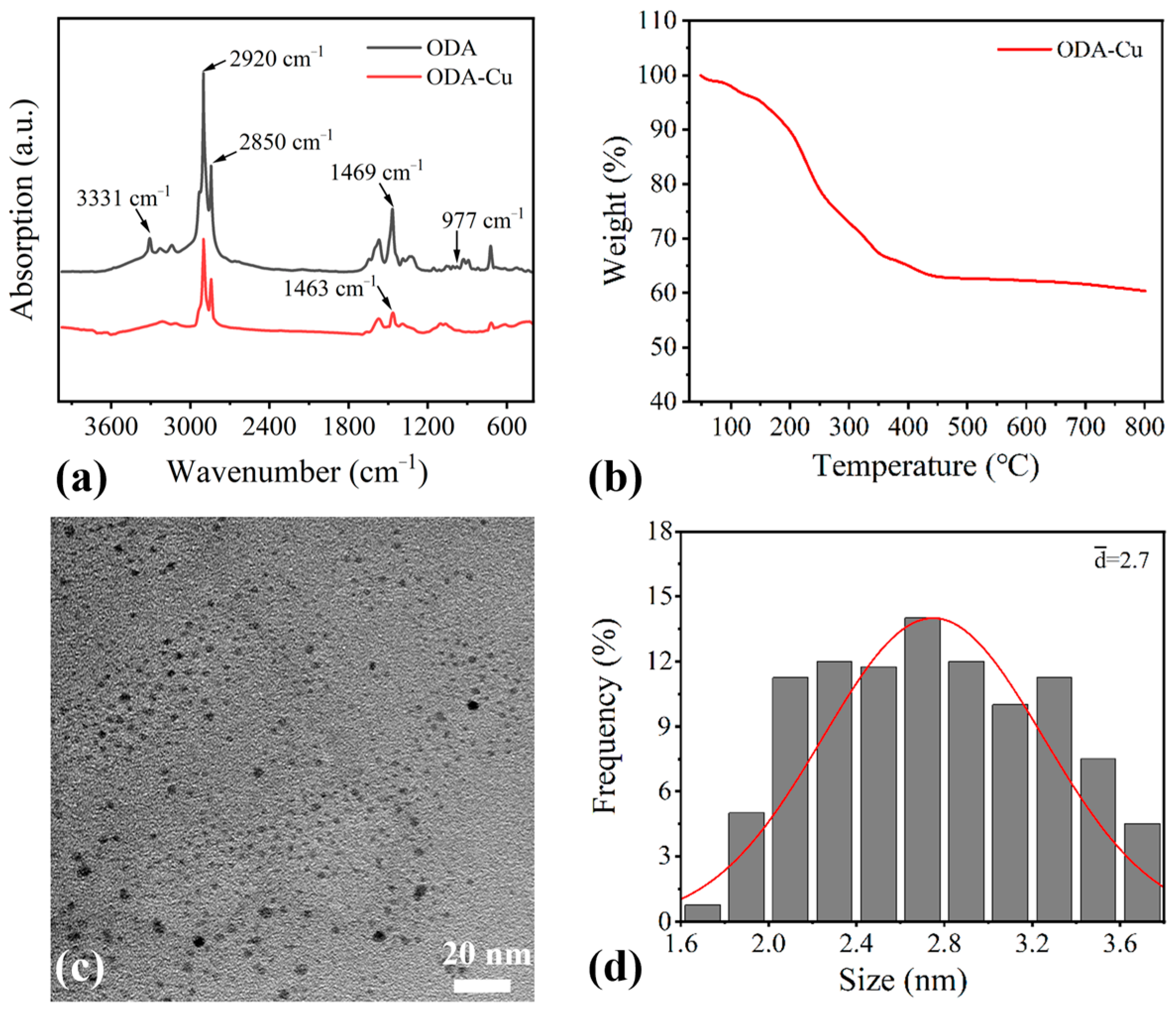
2.2. Functionalized Nanocopper Particles
2.3. Lubricating Oils
2.4. Tribological Tests
2.5. Wear Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
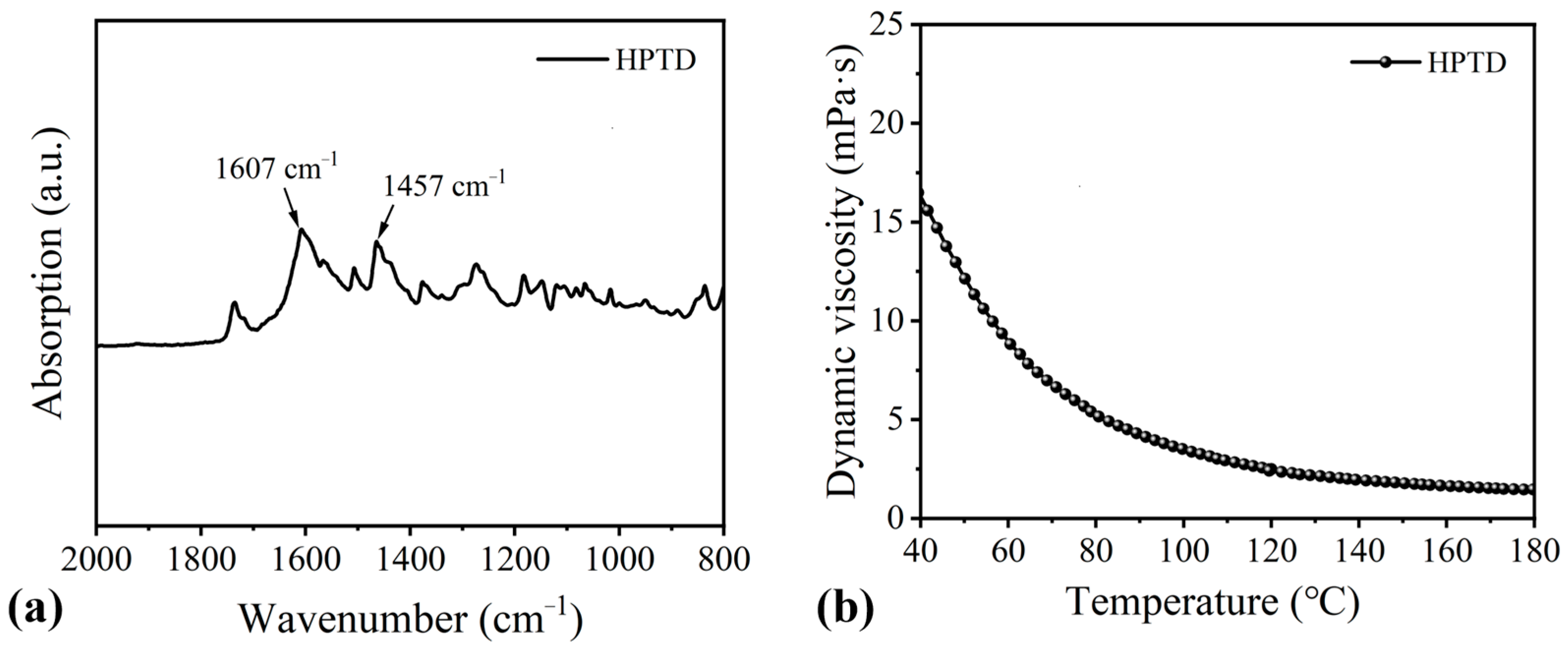
3.1. Determination of HPTD Content
3.2. Determination of ODA-Cu Content
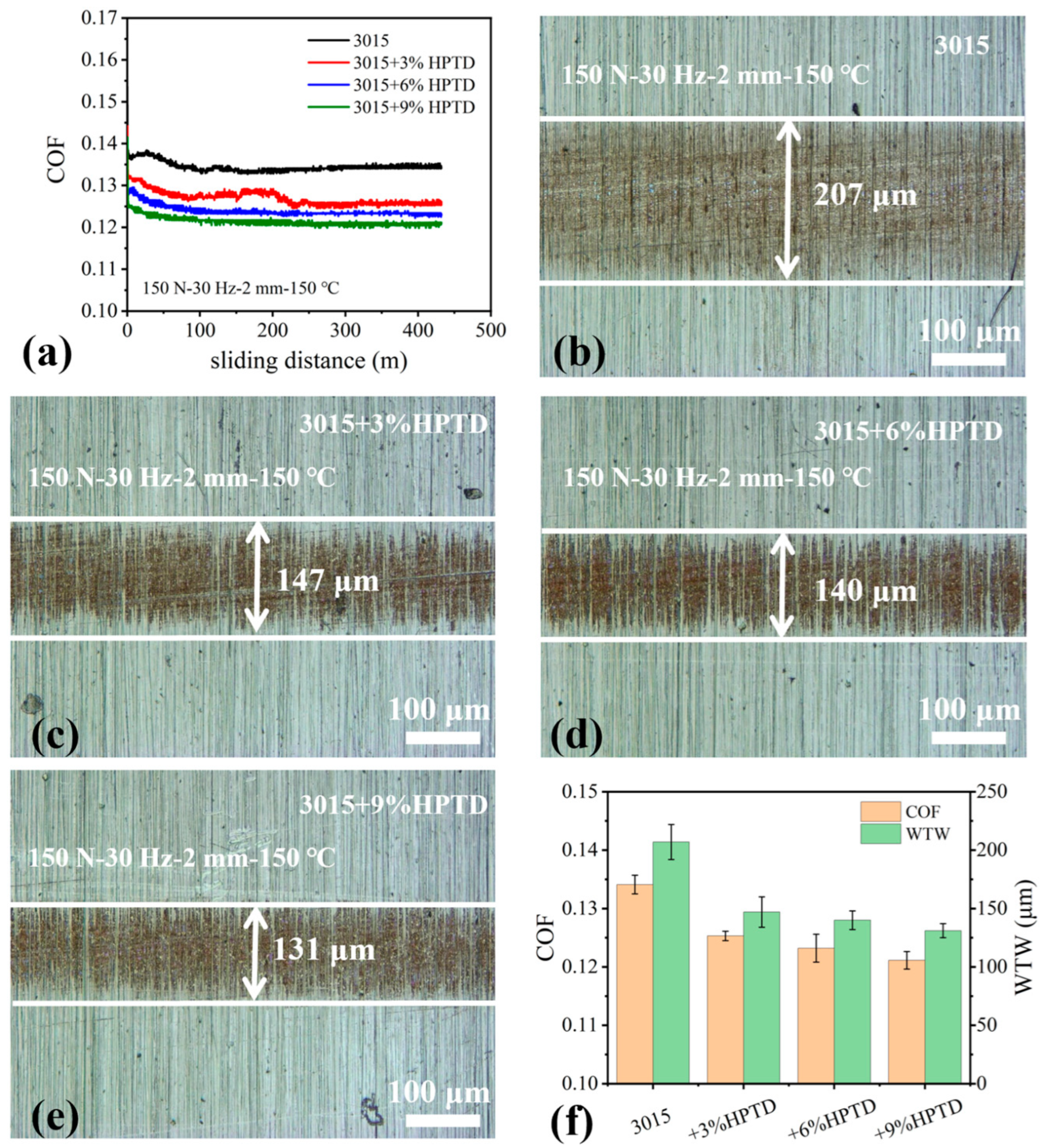
3.3. Friction Tests of m3015 Under Various Operating Conditions
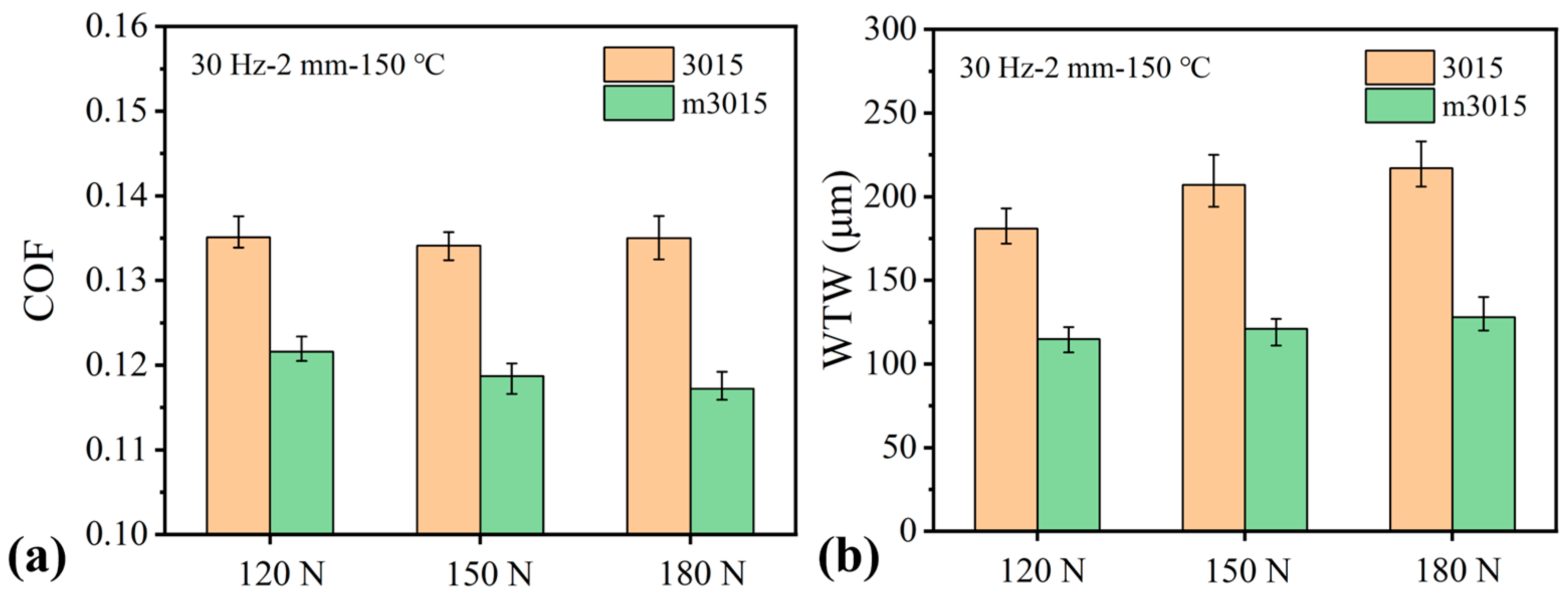
3.3.1. Effect of Normal Load
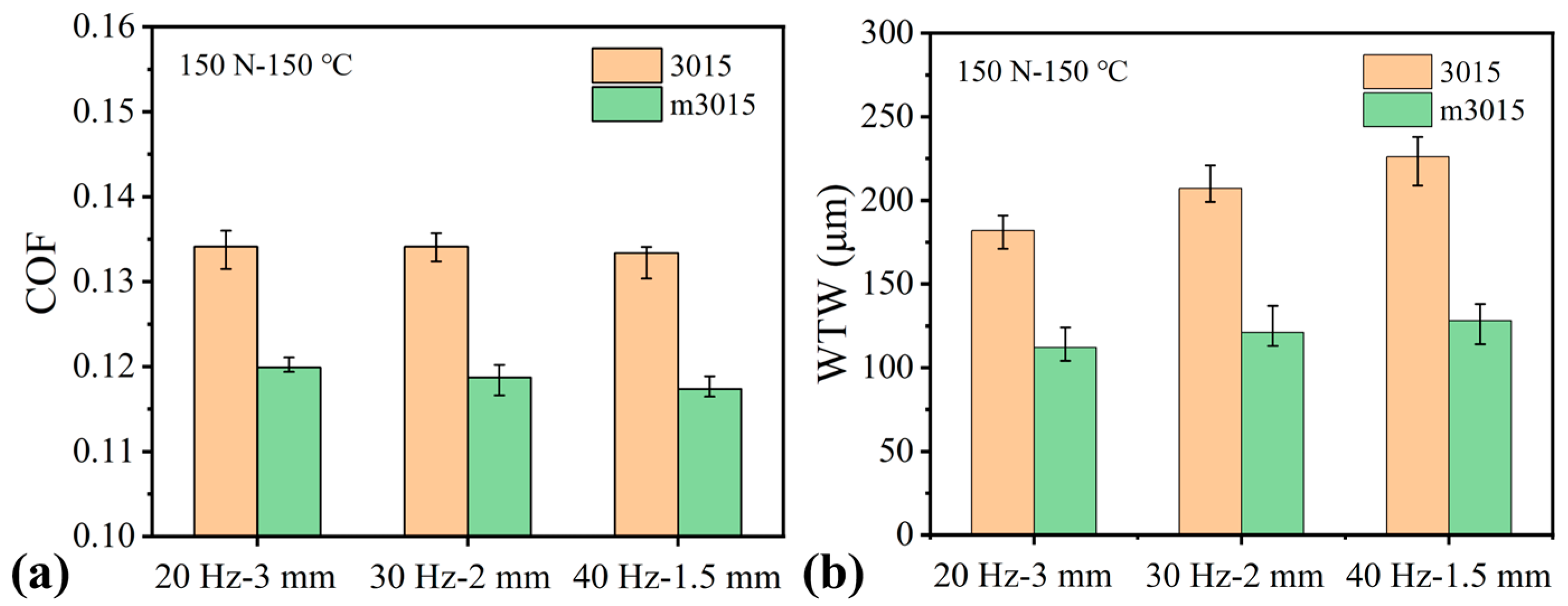
3.3.2. Effect of Reciprocating Frequency
3.3.3. Effect of Testing Temperature
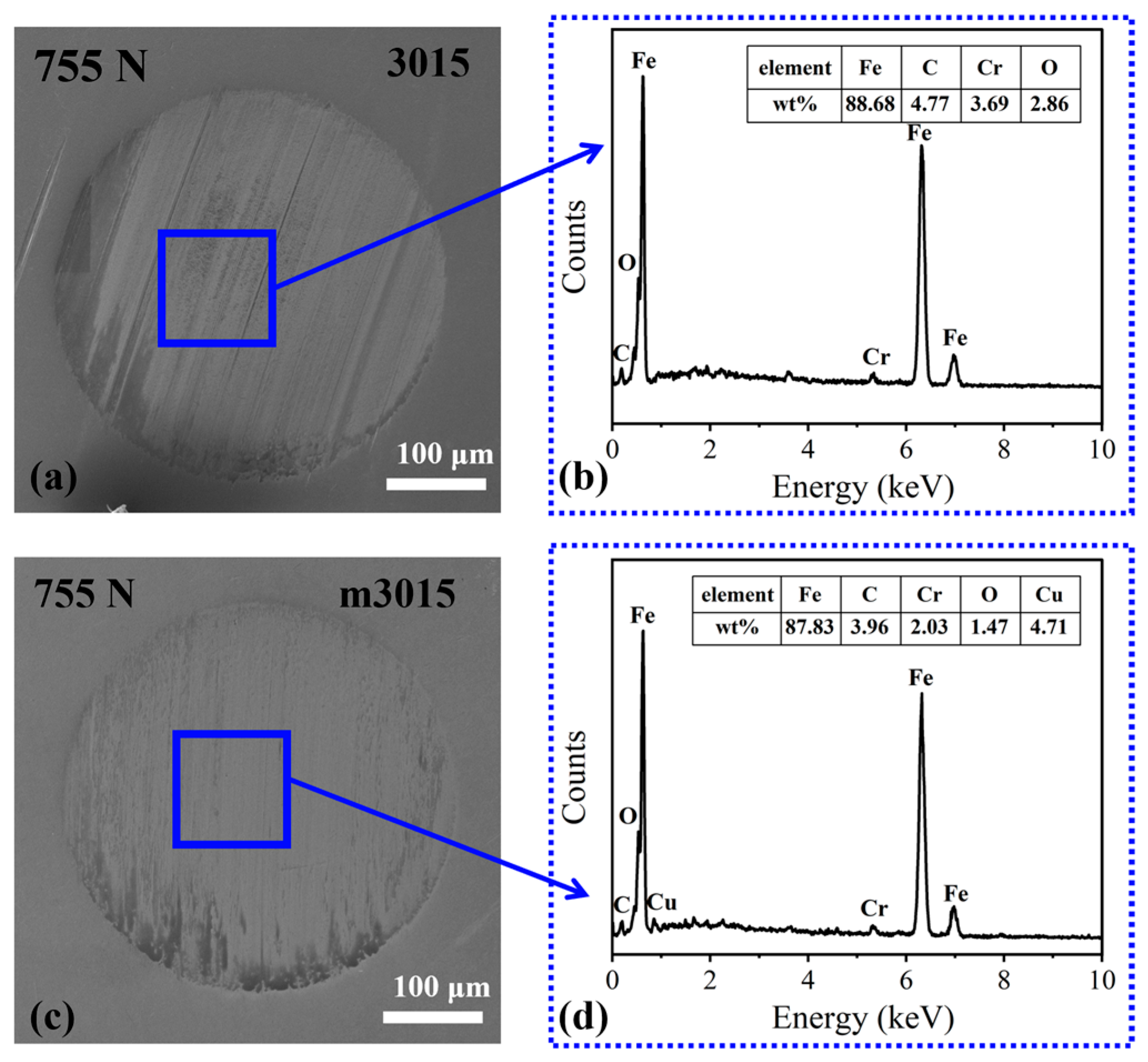
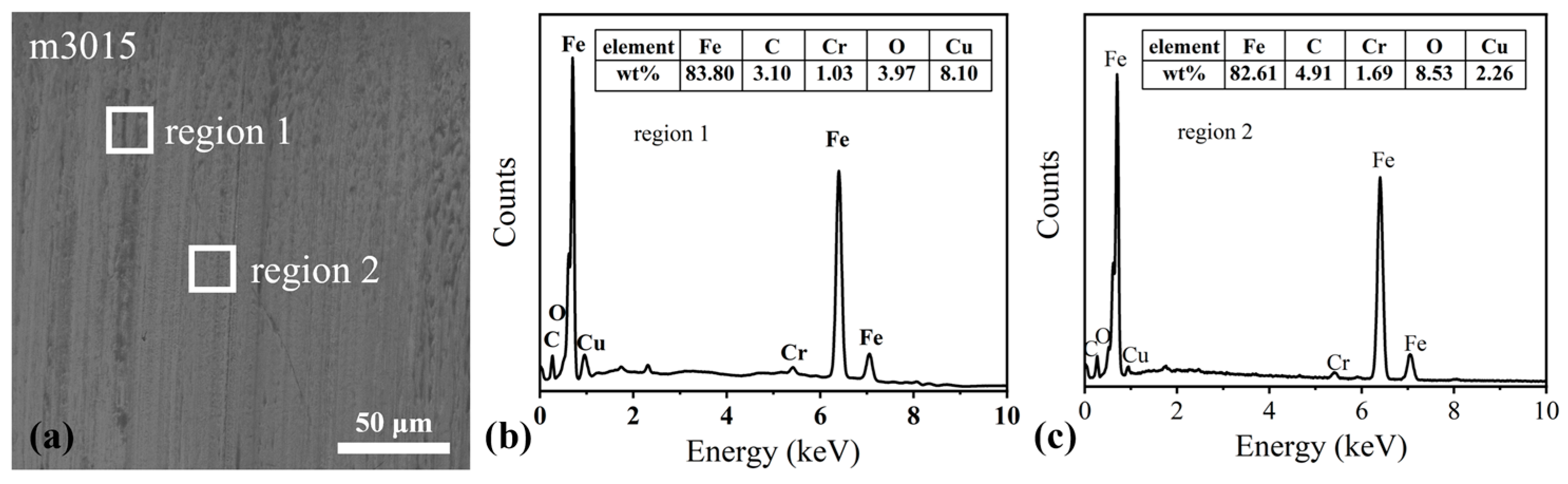
3.3.4. XPS Analysis on the Wear Track
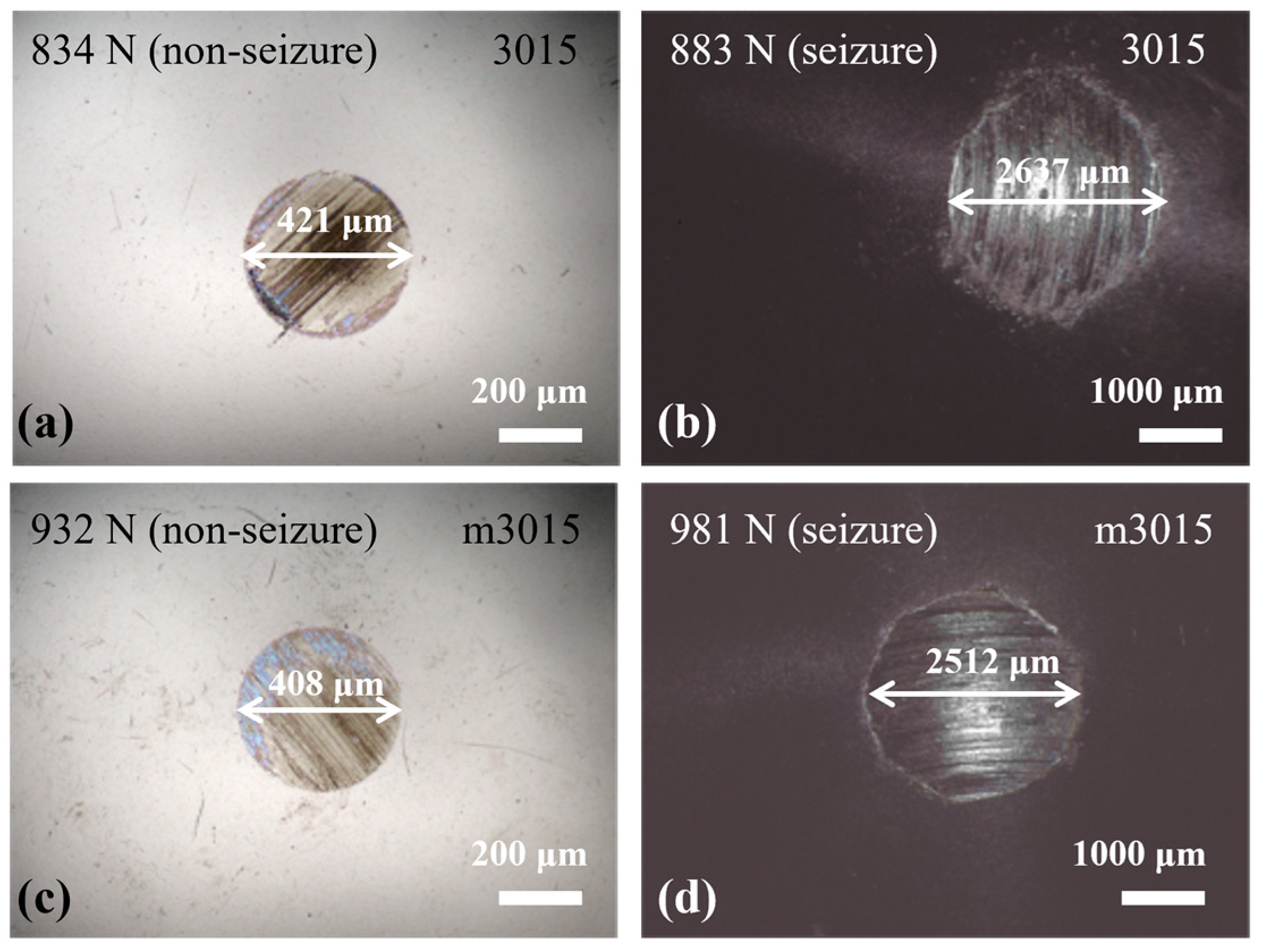
3.4. Extreme Pressure Test of m3015
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Following a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of hybrid additives on the viscosity, sulfated ash content, and friction/wear properties of 3015, the optimal composition of hybrid additives for 3015 was determined to be 9% HPTD and 0.2% ODA-Cu. This results in a modified 3015 (m3015) oil with a sulfated ash content decreased by 12%.
- (2)
- When operating conditions were concerned, higher loads and temperatures promoted the tribochemical reactions of HPTD, leading to lower friction for m3015. On the contrary, the influence of reciprocating frequencies was very little. Across all tested conditions, m3015 demonstrated superior lubrication performance than that of 3015, in which the maximum COF and WTW reduction were 15% and 43%, respectively.
- (3)
- In extreme pressure tests, the hybrid additives of HPTD and ODA-Cu increased the PB of 3015 from 834 N to 932 N. Under such high loads, the load-bearing capacity of the oil was primarily provided by the mending effect of ODA-Cu.
- (4)
- As a commercial engine oil, 3015 itself contains regular anti-friction and anti-wear additives. On one hand, the results of this work suggest that the existing additives in 3015 showed no obvious antagonism with the incorporated HPTD and ODA-Cu; on the other hand, their exact coupling effect with the conventional additives, such as MoDTC or ZDDP, should be investigated in the future to further optimize the oil formulation.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLPR | cylinder liner–piston ring |
| HPTD | 1-(4-hexylphenyl) tridecane-1,3-dione |
| ODA | Octadecylamine |
| ODA-Cu | octadecylamine-functionalized nanocopper particles |
| MoDTC | molybdenum dialkyl dithiocarbamate |
| ZDDP | zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate |
| 3015 | a commercial marine engine oil from PetroChina Lubricating Oil Company |
| m3015 | modified 3015 (i.e., 3015 doped with 9% HPTD and 0.2% ODA-Cu) |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| TGA | thermal gravimetric analyzer |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| COF | friction coefficient |
| EP | extreme pressure |
| PB | maximum non-seizure load |
| LSCM | laser scanning microscope |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | energy-dispersive spectrometer |
| WTW | wear track width |
References
- Sagin, S.; Kuropyatnyk, O.; Matieiko, O.; Razinkin, R.; Stoliaryk, T.; Volkov, O. Ensuring Operational Performance and Environmental Sustainability of Marine Diesel Engines through the Use of Biodiesel Fuel. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagin, S.; Haichenia, O.; Karianskyi, S.; Kuropyatnyk, O.; Razinkin, R.; Sagin, A.; Volkov, O. Improving Green Shipping by Using Alternative Fuels in Ship Diesel Engines. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, S.; Onorati, A.; Payri, R.; Agarwal, A.; Arcoumanis, C.; Bae, C.; Boulouchos, K.; Chuahy, F.; Gavaises, M.; Hampson, G.; et al. The future of ship engines: Renewable fuels and enabling technologies for decarbonization. Int. J. Engine Res. 2023, 25, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, B.; Jin, Z.; Lv, H. Rapid Separation and API Grades Identification of Base Oil in Low Viscosity Gasoline Engine Oil SN 0W-16. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 21270–21275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Feng, Y.; Diao, Z.; Liu, Z. The Effects of Ultra-Low Viscosity Engine Oil on Mechanical Efficiency and Fuel Economy. Energies 2021, 14, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Li, T.; Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z. Lubrication analysis of the piston ring of a two-stroke marine diesel engine considering thermal effects. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 129, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tang, H.; Dai, L.; Li, X.; Lan, G.; Ai, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Sheng, C.; Wan, H. Potassium borate/graphene nanocomposite lubricant additive with anti-friction/wear and anti-corrosion functions for marine diesel engine burning low sulfur fuel. Wear 2024, 550–551, 205395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Dearn, K.D.; You, T.; Geng, J.; Hu, X. Fabrication and tribological characterization of laser textured boron cast iron surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, L. Origin of friction and the new frictionless technology—Superlubricity: Advancements and future outlook. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W.; Luo, J. Low friction of superslippery and superlubricity: A review. Friction 2023, 11, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Amann, T.; List, M.; Walter, M.; Moseler, M.; Kailer, A.; Rühe, J. Ultralow Friction of Steel Surfaces Using a 1,3-Diketone Lubricant in the Thin Film Lubrication Regime. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11033–11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Amann, T.; Zhang, C.; Yan, X. Anti-spreading behavior of 1,3-diketone lubricating oil on steel surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, J.; Amann, T.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, C.; Neville, A. Evaluation of 1,3-diketone as a novel friction modifier for lubricating oils. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Hu, X.; Song, X.; Qiu, Z.; Gong, H.; Cao, B. Morphology Evolution of ZnO Submicroparticles Induced by Laser Irradiation and Their Enhanced Tribology Properties by Compositing with Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, F.; Giner-Rajala, Ó.; López, E.R.; Amigo, A.; Fernández, J. Silanized magnetite nanoparticles as an additive for an electric vehicle transmission base fluid (polyalphaolefin 6). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 706, 163528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Cao, D.; Zhuang, W.; Yu, Q.; Cai, M.; Shi, Y. Stable Dispersed Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites in Ionic Liquids Resulting in High Lubricating Performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1902194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P. Study on the mechanism of rapid formation of ultra-thick tribofilm by CeO2 nano additive and ZDDP. Friction 2023, 11, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.N.M.; Azmi, W.H.; Ghazali, M.F. Tribological performance of Al2O3–SiO2/PAG composite nanolubricants for application in air-conditioning compressor. Wear 2022, 492–493, 204238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Xu, Y.; Rao, X.; Yuan, C. Synergetic effects of surface textures with modified copper nanoparticles lubricant additives on the tribological properties of cylinder liner-piston ring. Tribol. Int. 2023, 178, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L. Research on the effect of Cu addition on the corrosion resistance of low carbon low alloy steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Yin, Y.L.; Zhang, G.N.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhao, K.K. Study on Antiwear and Repairing Performances about Mass of Nano-copper Lubricating Additives to 45 Steel. Phys. Procedia 2013, 50, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can Yilmaz, A. Comprehensive analyses of characterization and conjoint influence of nanofuels and nanolubricants on acoustic, tribological behavior, performance and emission characteristics of a compression ignition engine. Fuel 2025, 381, 133665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, D.; Yang, G.; Gao, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P. Wide adaptability of Cu nano-additives to the hardness and composition of DLC coatings in DLC /PAO solid-liquid composite lubricating system. Tribol. Int. 2019, 138, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zaluzhna, O.; Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Modest, J.M.; Tong, Y.J. Mechanistic Insights into the Brust−Schiffrin Two-Phase Synthesis of Organo-chalcogenate-Protected Metal Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2092–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D445; Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM D874; Standard Test Method for Sulfated Ash from Lubricating Oils and Additives. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- GB/T 12583-1998; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method). Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1998.
- ASTM D2783; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Urdaneta, F.; Meza, L.; Márquez, R.; Franco, J.; Vera, R.E.; Urdaneta, I.; Parrish, C.; Saloni, D.; Pawlak, J.J.; Jameel, H.; et al. Comparing the impacts of wood and APMP non-wood fibers on the properties of hygiene tissue paper. Cellulose 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Z. Effect of the Molecular Structure of 1,3-Diketones on the Realization of Oil-Based Superlubricity on Steel/Steel Friction Pairs. Langmuir 2024, 40, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.I.; Panayotov, D.A.; Mihaylov, M.Y.; Ivanova, E.Z.; Chakarova, K.K.; Andonova, S.M.; Drenchev, N.L. Power of Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies to Characterize Metal-Organic Frameworks and Investigate Their Interaction with Guest Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1286–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaneri, M.J.; Teat, S.J.; Vitali, J. Cu(II) Stability and UV-Induced Electron Transfer in a Metal–Organic Hybrid: An EPR, DFT, and Crystallographic Characterization of Copper-Doped Zinc Creatininium Sulfate. J. Phys. Chem. A 2024, 128, 10380–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavov, D.; Tomaszewska, E.; Grobelny, J.; Drenchev, N.; Karashanova, D.; Peshev, Z.; Bliznakova, I. FTIR spectroscopy revealed nonplanar conformers, chain order, and packaging density in diOctadecylamine- and octadecylamine-passivated gold nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1314, 138827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frogneux, X.; Borondics, F.; Lefrançois, S.; D’Accriscio, F.; Sanchez, C.; Carenco, S. Surprisingly high sensitivity of copper nanoparticles toward coordinating ligands: Consequences for the hydride reduction of benzaldehyde. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5073–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, M.A.; Tremblay, B.; Andrieux-Ledier, A.; Maisonhaute, E.; Raouafi, N.; Courty, A. Copper nanoparticles of well-controlled size and shape: A new advance in synthesis and self-organization. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Bardhan, P.; Mandal, M.; Karak, N. Interpenetrating polymer network-based nanocomposites reinforced with octadecylamine capped Cu/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid with hydrophobic, antimicrobial and antistatic attributes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Ogi, K. Lubricated Friction and Wear Properties of P-B Bearing Flaky Graphite Cast Iron. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 457, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliotti, M.; Baptista, M.S.; Politi, M.J.; Todd, P.S.; Carl, D.S. Surface Tension Gradients Induced by Temperature: The Thermal Marangoni Effect. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Cao, Y.; Qin, S.; Ren, Y.X.; Lan, R.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Yang, H. Ultra-high N-doped open hollow carbon nano-cage with excellent Na+ and K+ storage performances. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 18, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, N.; Du, C.; Ge, Y.; Amann, T.; Feng, H.; Yuan, C.; Li, K. Tribological behavior of cellulose nanocrystal as an eco-friendly additive in lithium-based greases. Carbohyd Polym. 2022, 290, 119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Jing, X.; Yin, X.; Xia, T.; Wang, J.; Amann, T.; Li, K. Hybrid Additives of 1,3-Diketone Fluid and Nanocopper Particles Applied in Marine Engine Oil. Lubricants 2025, 13, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060252
Xu Y, Yang Y, Zhong L, Jing X, Yin X, Xia T, Wang J, Amann T, Li K. Hybrid Additives of 1,3-Diketone Fluid and Nanocopper Particles Applied in Marine Engine Oil. Lubricants. 2025; 13(6):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060252
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yuwen, Yan Yang, Li Zhong, Xingyuan Jing, Xiaoyu Yin, Tao Xia, Jingsi Wang, Tobias Amann, and Ke Li. 2025. "Hybrid Additives of 1,3-Diketone Fluid and Nanocopper Particles Applied in Marine Engine Oil" Lubricants 13, no. 6: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060252
APA StyleXu, Y., Yang, Y., Zhong, L., Jing, X., Yin, X., Xia, T., Wang, J., Amann, T., & Li, K. (2025). Hybrid Additives of 1,3-Diketone Fluid and Nanocopper Particles Applied in Marine Engine Oil. Lubricants, 13(6), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13060252





