Abstract
Copper matrix self-lubricating composites are critical for high-temperature industrial applications. In this study, Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites with 3–7 wt.% graphite were fabricated via spark plasma sintering (SPS). The influence of graphite content on microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological behavior from room temperature (RT) to 500 °C were systematically investigated. The results demonstrate that increasing graphite content progressively reduces density, hardness, and yield strength, whereas it significantly enhances high-temperature tribological performance. The composites with 7 wt.% graphite addition achieve outstanding self-lubricity and wear resistance across the RT-500 °C, achieving an average friction coefficient of 0.09 to 0.21 and a wear rate of 1.32 × 10−6 to 7.52 × 10−5 mm3/N·m. Crucially, temperature-dependent lubrication mechanisms govern performance: graphite-dominated films enable friction reduction at RT, while synergistic hybrid films of graphite and in situ-formed metal oxides (Cu2O, CuO, NiO) sustain effective lubrication at 300–500 °C.
1. Introduction
Metal-based self-lubricating composites are critical advanced materials for sliding components in aerospace, rail transportation, and marine engineering due to their unique combination of high strength, thermal stability, and superior tribological performance [1,2,3,4]. These composites integrate an alloy matrix with solid lubricants, thereby exhibiting high mechanical strength alongside excellent lubricity. During friction, the solid lubricants facilitate the formation of a continuous lubricating film on the contact surface, which effectively reduces friction and wear by preventing direct contact between the sliding pairs [5,6].
Among these, copper-based composites are particularly valued in applications such as bearing systems and electrical contacts because of their outstanding load-bearing capacity, thermal conductivity, and inherent lubricity [7,8,9]. The introduction of graphite as a cost-effective solid lubricant further enhances their tribological performance, leading to the broad utilization of copper-graphite composites in components including bushings and brushes [10,11,12]. However, the evolving demands of modern industry—such as higher loads, speeds, and operating temperatures—pose serious challenges to conventional copper-graphite composites [13]. A primary limitation is the inherent compromise between lubricity and mechanical integrity: higher graphite content improves lubrication but degrades mechanical integrity. Moreover, matrix softening at elevated temperatures accelerates wear, thereby constraining their application in more severe environments [14].
To overcome these issues, one promising approach is to utilize a high-strength copper alloy as the matrix [15]. Cu-Ni-Sn alloys, which are typical age-hardening materials and have been developed since the 1970s, are recognized as promising alternatives to toxic Cu-Be alloys. They possess high strength, superior wear resistance, stable electrical conductivity, and excellent resistance to thermal stress relaxation [16,17,18]. Furthermore, numerous studies have demonstrated that micro-alloying (adding a fourth or even fifth element to the alloy, such as V, Ni, Zr, B, etc.) can further improve the microstructure and enhance the properties of Cu-Ni-Sn alloys [19,20,21,22]. Previous research [23,24] have confirmed that additions of Mo can significantly improve the microstructure and enhance its mechanical properties of Cu-12.5Ni-5Sn alloy. Despite its potential, the combination of this Mo-enhanced Cu-Ni-Sn matrix with graphite lubricant has received limited attention.
Spark plasma sintering (SPS), a technique employed for rapid material consolidation at lower temperatures and with short holding times, produces sintered components with fine microstructures and superior performance [25,26]. Therefore, this study aims to fabricate novel self-lubricating composites by integrating graphite (3–7 wt.%) into a high-performance Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo alloy matrix via SPS. The influence of graphite content on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological behavior across a range of temperatures (RT, 300 °C, and 500 °C) were systematically investigated, and the underlying wear mechanisms were elucidated. These results are anticipated to offer critical guidance for advancing the design of high-performance copper-based self-lubricating composites.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
The Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo alloy matrix, with a nominal composition of Cu-12.5Ni-5.0Sn-1.0Mo (wt.%), was fabricated via SPS using commercially available powders of Cu (99.96% purity, 250 mesh), Ni (99.96% purity, 250 mesh), Sn (99.99% purity, 300 mesh), and Mo (99.99% purity, 300 mesh). To produce the self-lubricating composites, flake graphite (99.00% purity, 125 μm) was incorporated as a solid lubricant into the prepared alloy matrix. The composites with different graphite additions are denoted as CG0, CG3, CG5, and CG7, corresponding to graphite contents of 0 wt.%, 3 wt.%, 5 wt.%, and 7 wt.%, respectively. The nominally chemical compositions of the Cu-12.5Ni-5Sn-1.0Mo-Graphite composites are listed in Table 1. The constituent powders were mechanically blended for 4–5 h using a three-dimensional vibrational mixer to ensure homogeneity. Subsequently, the powder mixtures were loaded into a graphite die and consolidated via SPS fast hot pressure sintering equipment (SPS-20T-10). The sintering process was carried out at 870 ± 5 °C under a pressure of 25 MPa for 25–30 min, with a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The resulting sintered samples measured 25 mm in diameter and 10 mm in height. Following sintering, the composites were aging treated at 400 °C for about 4 h in an energy-saving box electric furnace (SX-G36123) and were then furnace cooled.

Table 1.
Nominal compositions and densities of the Cu-12.5Ni-5Sn-1.0Mo-Gr composites.
2.2. Material Characterization
The actual density of the aged Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites was measured using the Archimedes method, with the relative density derived from the ratio of the measured density to the theoretical value. Phase analysis was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, PANalytical). Microstructural characterization was conducted using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, JSM-5600LV) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS) The Brinell hardness was measured on an HBS-3000 tester with a load of 187.5 kgf applied for 30 s, the reported value for each sample represents the average of five measurements. Compression properties were evaluated on an electronic universal testing machine (UTM 5205) with a compression speed of 0.1 mm/min, and a minimum of three tests were performed per specimen for repeatability.
2.3. Friction and Wear Tests
The tribological behavior was evaluated on a high-temperature ball-on-disk friction tester (HT-1000). Commercial Si3N4 balls, with a diameter of 6 mm, were employed as the counterparts. All friction specimens were ground sequentially with 180#, 400#, 600#, and 800# grit SiC abrasive paper. The dry sliding tests were performed at RT, 300 °C, and 500 °C for 30 min per test, under a constant applied load of 5 N, a sliding speed of 0.224 m/s, and a wear track radius of 4 mm. Each condition was replicated three times to ensure reliability. The coefficient of friction (COF) was monitored and recorded in real-time by a dedicated data acquisition system. After testing, the cross-sectional area of the wear track was determined using a non-contact 3D surface profilometer (MicroXAM-800). The wear volume, V (mm3), was calculated from the product of the average cross-sectional area (A) and the track circumference (l). Subsequently, the specific wear rate, W (mm3/N·m), was derived using the equation W = V/(F·L), where F is the applied load (N) and L is the total sliding distance (m). To investigate the wear mechanisms, the morphology and chemical composition of the worn surfaces were characterized in detail using SEM, EDS, micro-beam X-ray diffraction (Bruker D8 Discover), and confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy (LabRAM HR Evolution, 532 nm laser wavelength).
3. Results
3.1. Material Features
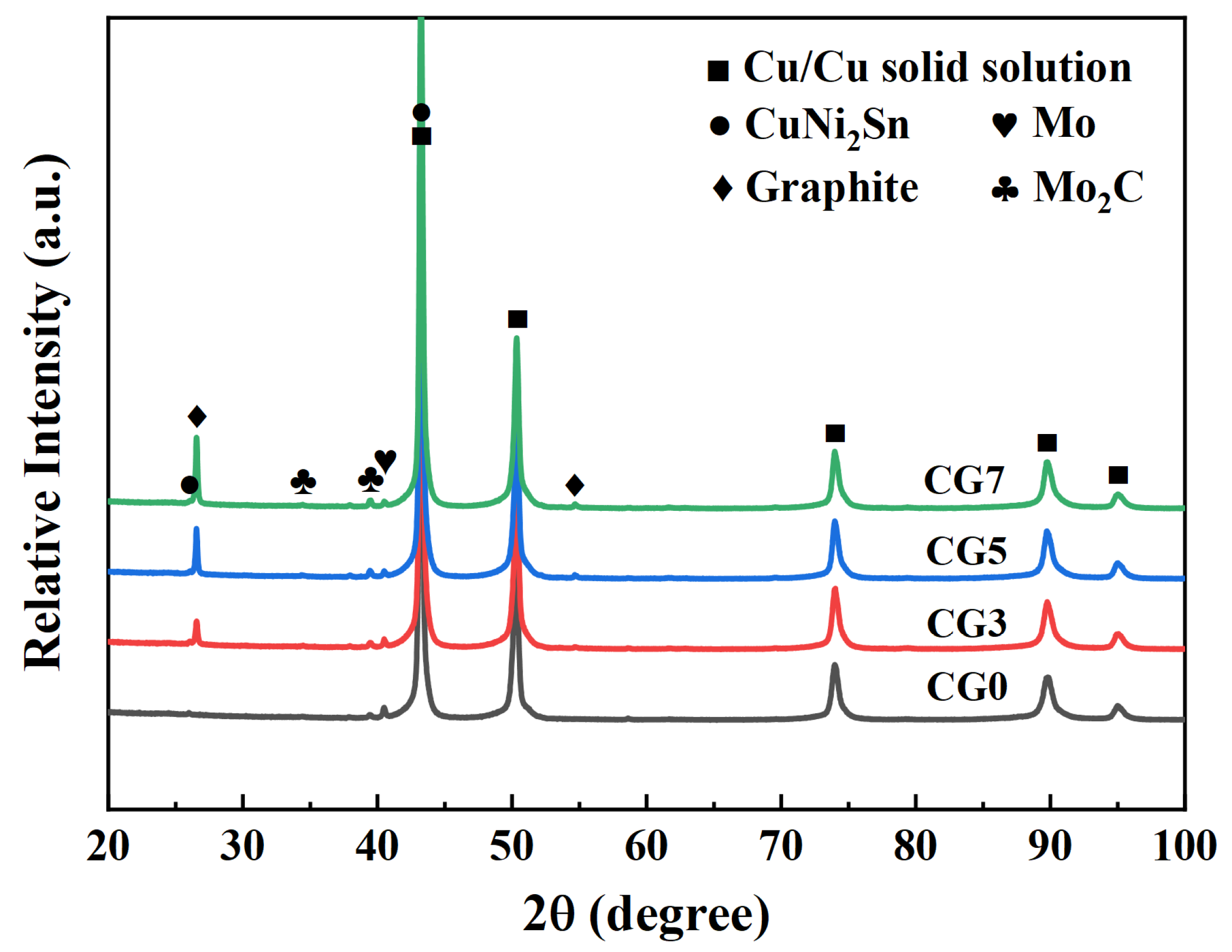
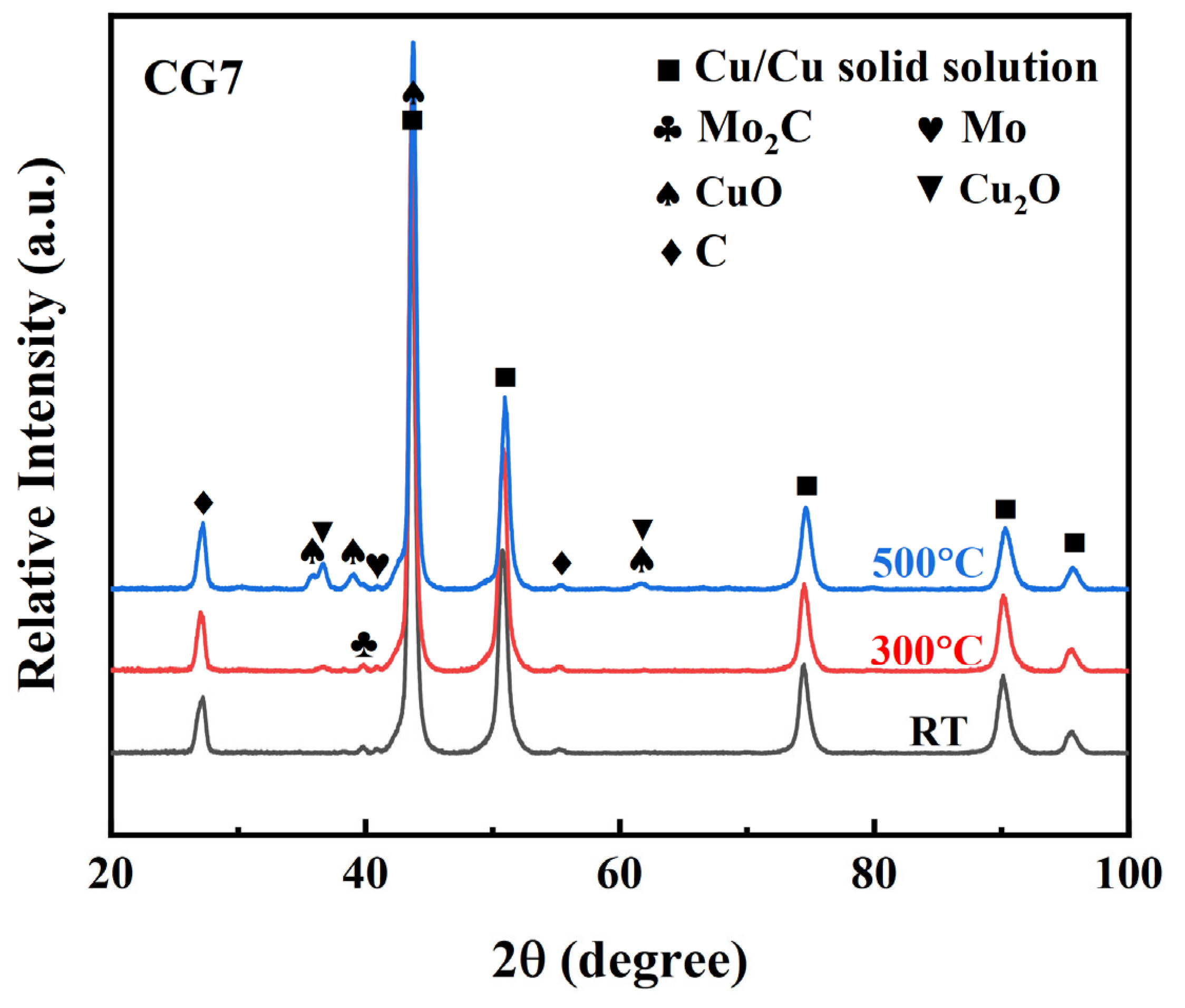
Figure 1 displays the XRD patterns of the sintered Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites. The sintered composites consist of Cu solid solution, γ-CuNi2Sn, Mo, graphite, and Mo2C. As the graphite content increases, the relative intensity of the characteristic graphite diffraction peaks progressively strengthens, while the intensity of the peaks corresponding to Mo2C also rises. This trend indicates that graphite reacts with Mo during sintering to form the stable carbide Mo2C. The presence of Mo2C may enhance the wettability of graphite within the Cu matrix, promoting the formation of an effective interface bond between graphite and the Cu matrix [27,28]. Additionally, Mo carbides possess high hardness and strength, which can strengthen the matrix [29], thereby improving the wear resistance of the composites.
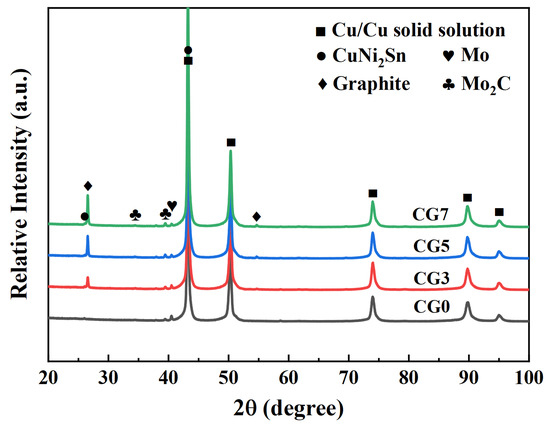
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of the Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites.
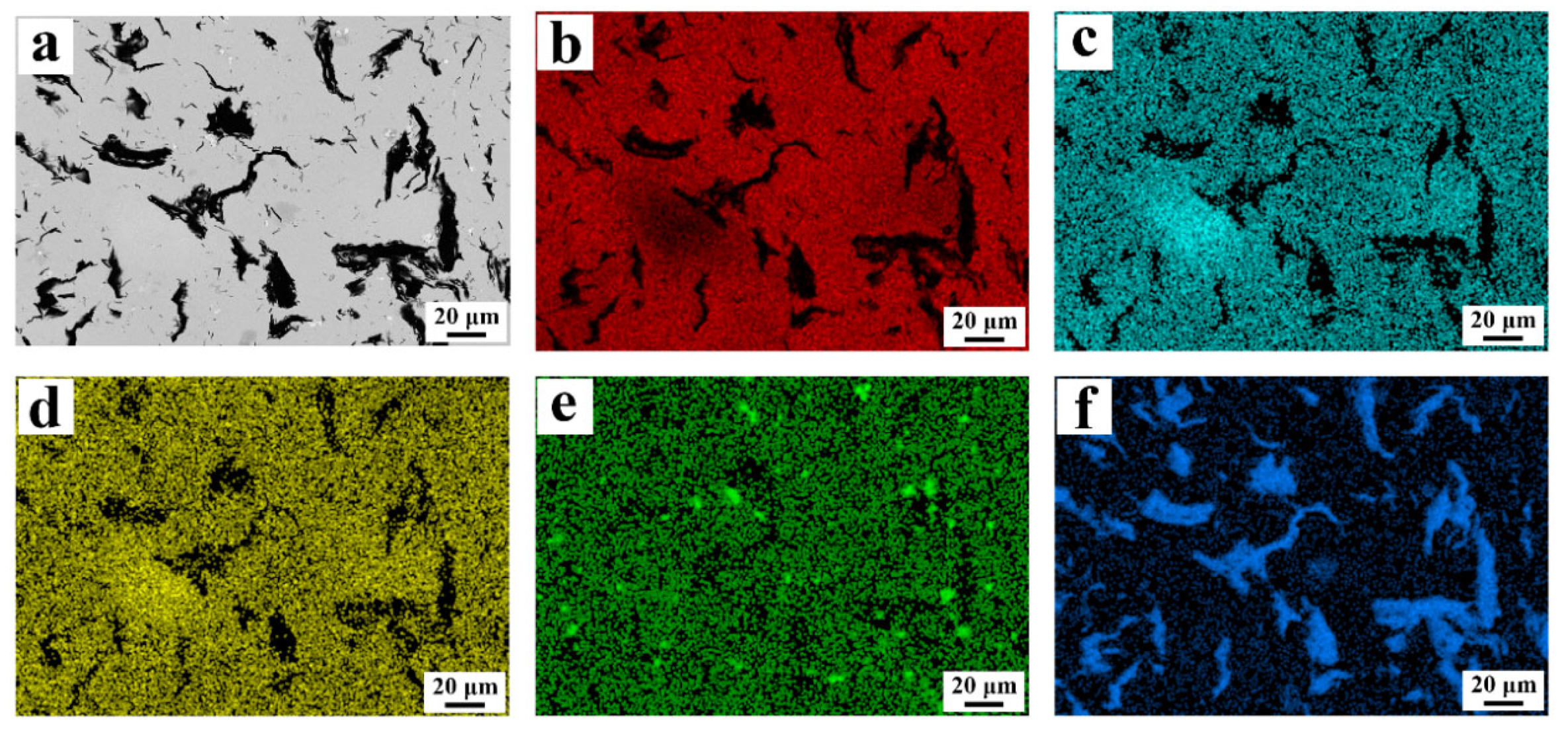
The typical SEM micrograph of the CG5 composites along with corresponding element mapping is presented in Figure 2. The microstructure reveals three primary phases: a gray matrix phase, discrete black regions, and distinct white particles. Combined with the XRD results (Figure 1) and elemental distribution, the gray phase is confirmed as the copper solid solution matrix, the black phase represents graphite, and the white phase, showing significant Mo enrichment, corresponds to Mo and Mo2C phases. Notably, scaly graphite shows uniform dispersion throughout the copper matrix, whereas the Mo2C appears as homogeneously distributed particles.
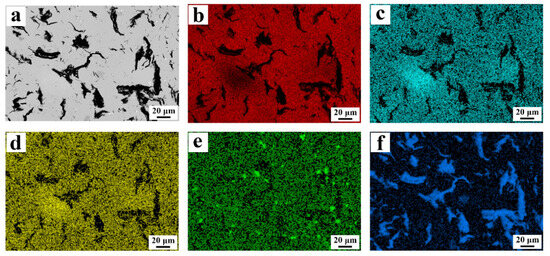
Figure 2.
(a) Typical SEM micrograph of the CG5 composites and corresponding element mapping of (b) Cu, (c) Ni, (d) Sn, (e) Mo, and (f) C.
The density of the Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites, as summarized in Table 1, decreases progressively with higher graphite content, owing to the low density of the graphite additive. Notably, the measured densities follow the same trend as the theoretical densities. However, all composites exhibit relative densities exceeding 100.0%, demonstrating the high densification achieved by the SPS process. Nevertheless, the relative density exhibits a decreasing trend with higher graphite content. This phenomenon likely stems from graphite agglomeration at elevated concentrations, which inhibits uniform densification during consolidation.
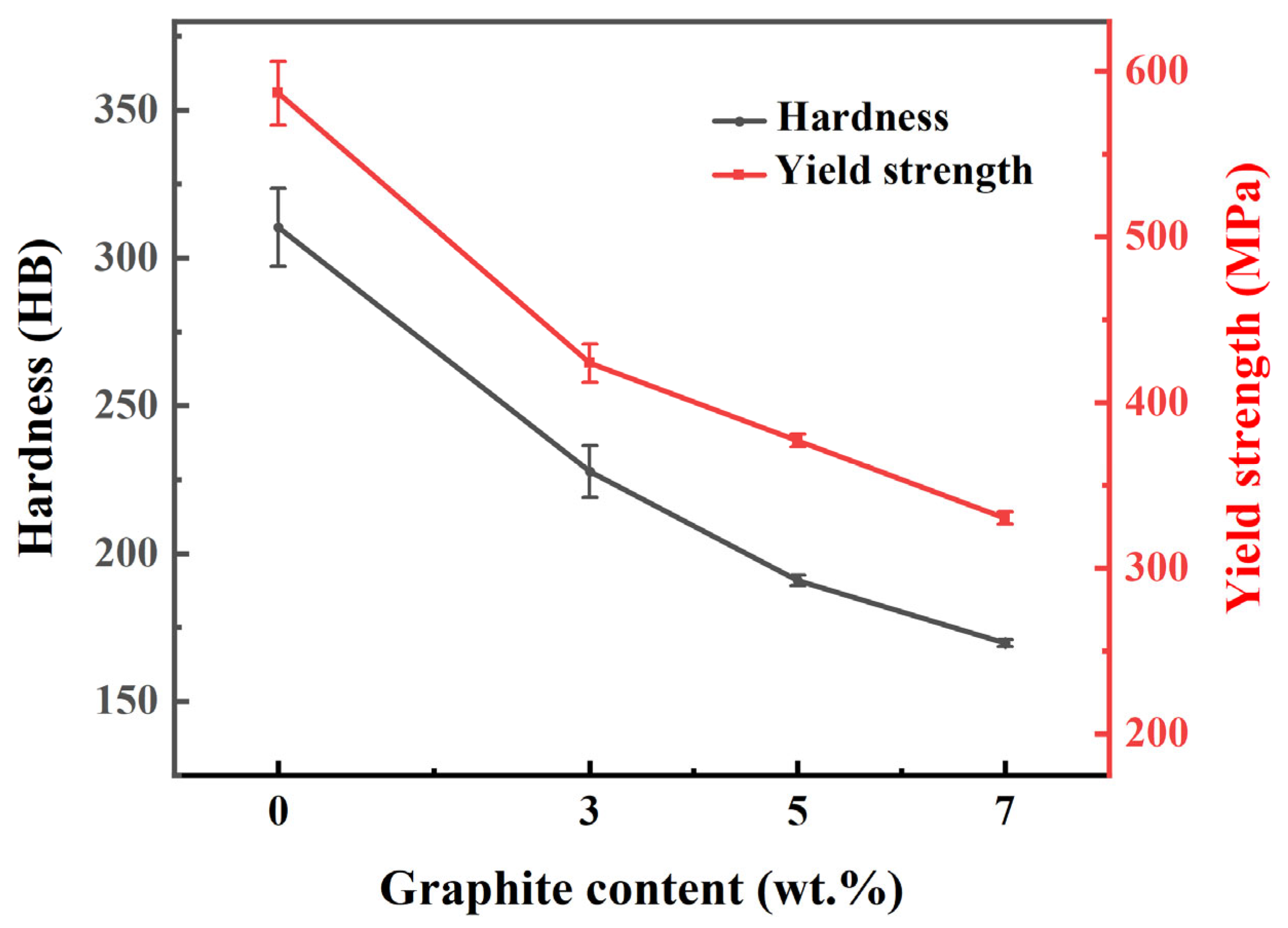
The hardness and yield strength of the composites, presented in Figure 3, exhibit a clear decreasing trend with higher graphite content. Graphite acts as a soft phase and can be regarded as pores in the copper matrix, and it has the effect of splitting the copper matrix. Consequently, a higher graphite content results in a greater degree of matrix splitting, leading to the observed decline in mechanical performance.
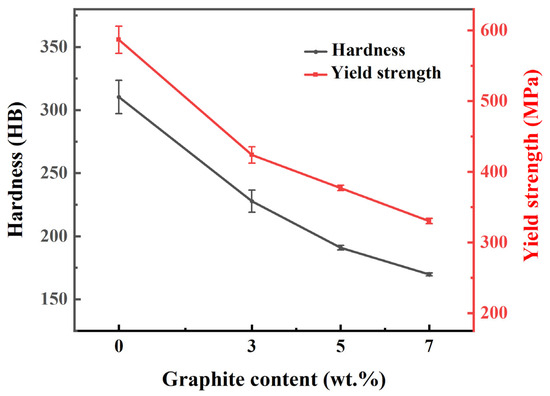
Figure 3.
The hardness and yield strength of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites.
3.2. Tribological Properties
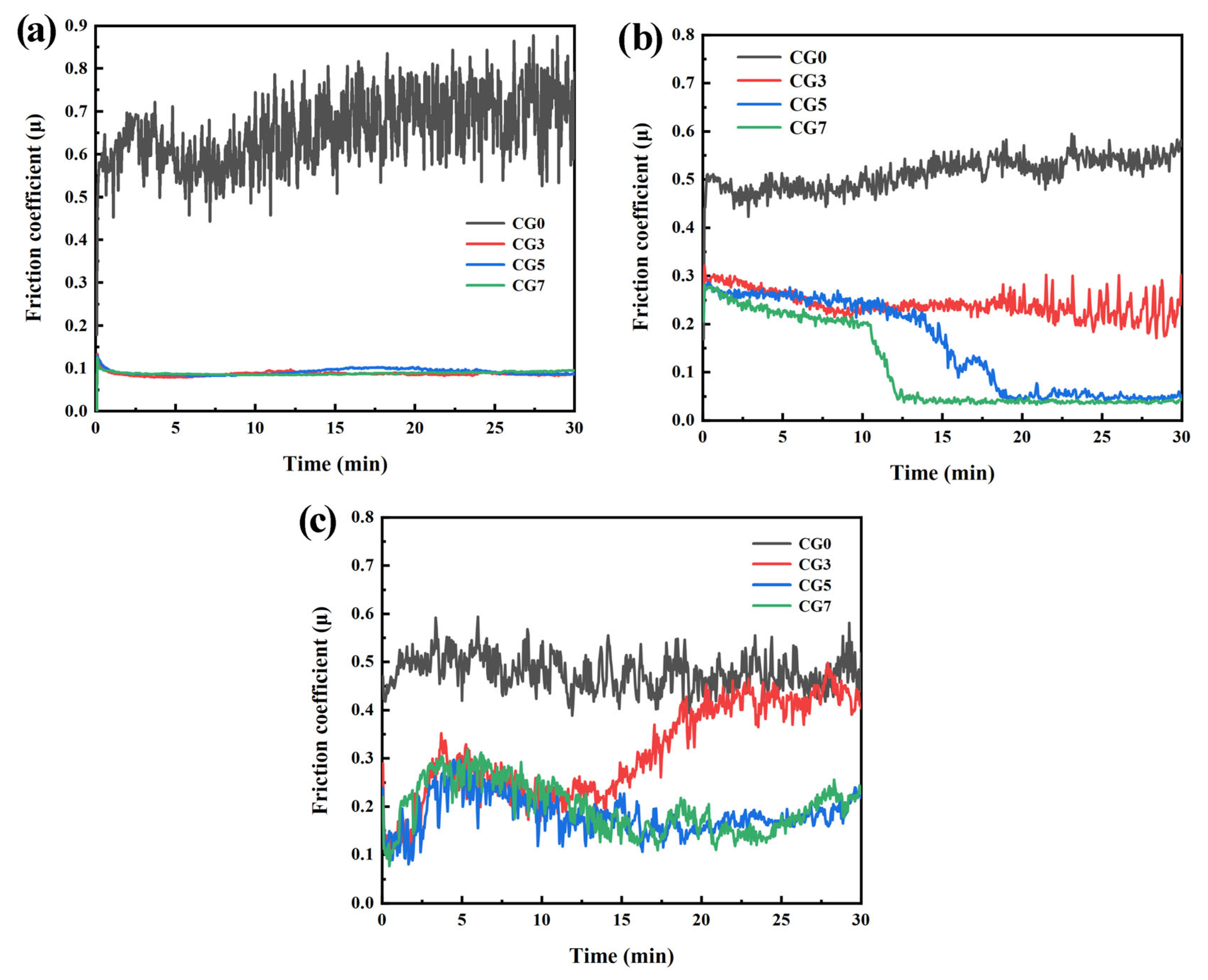
Figure 4 shows the typical instantaneous friction coefficient of the Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites with sliding time at different temperatures. Notably, the composites exhibit significantly lower and more stable friction coefficients than the graphite-free CG0 alloy. At RT, CG0 shows high friction coefficients with substantial fluctuations, while graphite-containing composites demonstrate markedly reduced friction with minimal fluctuations. As the temperature increases to 300 °C, the friction coefficient generally decreases with higher graphite content. Specifically, CG5 and CG7 composites display rapid initial friction reduction followed by stable values, with CG7 achieving the lowest and most stable friction. At 500 °C, all composites exhibit pronounced friction fluctuations. Remarkably, after the initial sliding stage, the friction coefficient of the CG3 composite gradually increases, eventually approaching that of the CG0 alloy. In contrast, the CG5 and CG7 composites show a tendency for their friction coefficients to decrease after the run-in period.
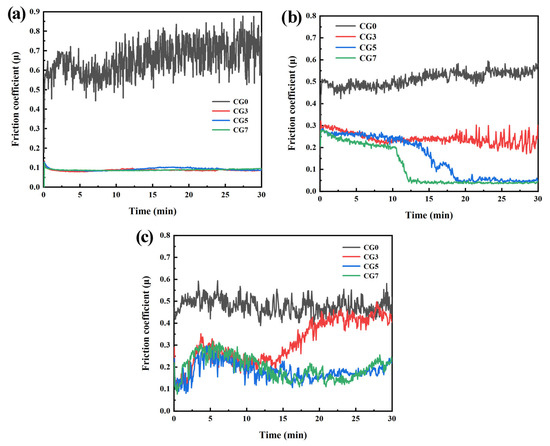
Figure 4.
Instantaneous friction coefficient of the Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites with sliding time at different temperatures: (a) RT, (b) 300 °C, and (c) 500 °C.
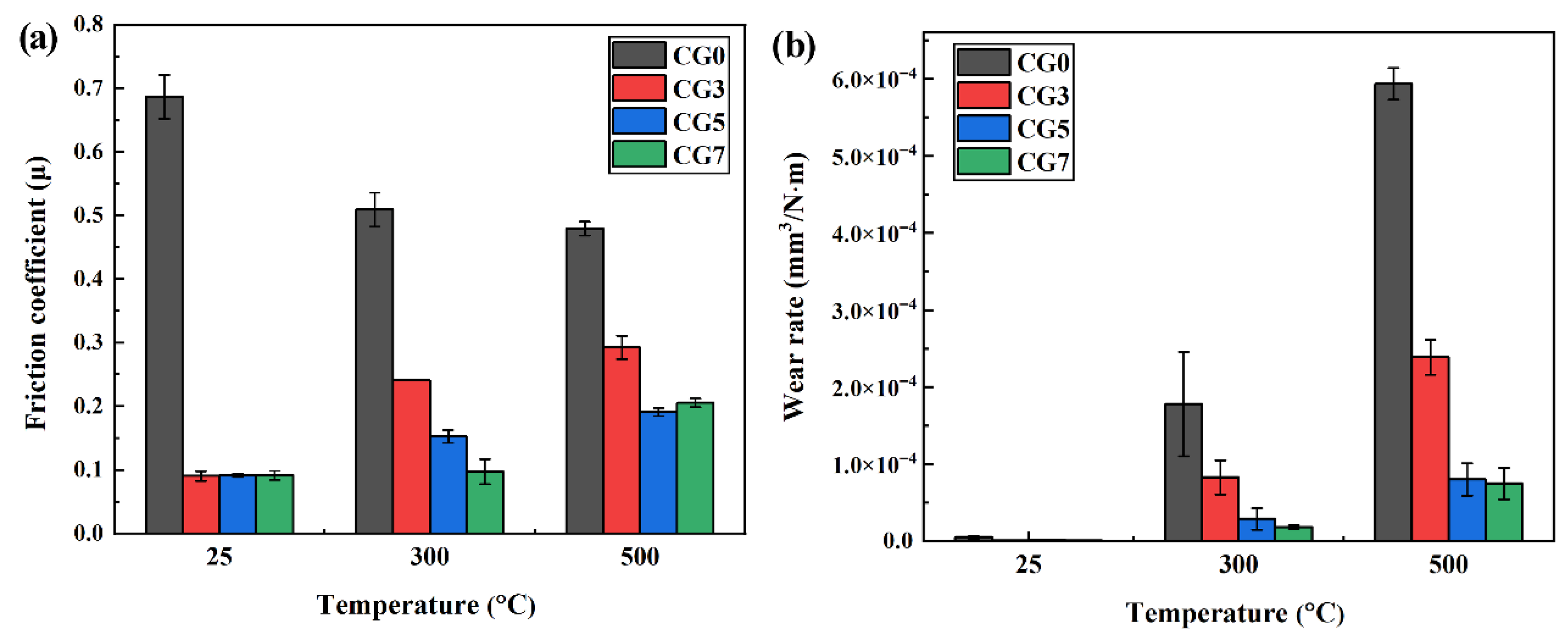
As shown in Figure 5, the average friction coefficients and average wear rates of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr self-lubricating composites at different temperatures. In Figure 5a, the friction coefficient of the graphite-free CG0 alloy decreases from 0.69 at RT to 0.48 at 500 °C, while those of graphite-containing composites increase from 0.09 to 0.29. At RT, CG0 exhibits a coefficient of 0.69, whereas composites with graphite additions show markedly reduced to 0.09. At 300 °C, CG3, CG5, and CG7 exhibit coefficients of approximately 0.24, 0.15, and 0.10 respectively—significantly lower than CG0 (0.51). Notably, CG7 maintains comparable friction coefficients at RT (0.10) and 300 °C (0.09), suggesting effective formation of a continuous lubricating film during sliding. At 500 °C, the coefficient of friction of the CG3 composite is about 0.29, while the coefficients of friction of the CG5 and CG7 composites are similar, at about 0.19 and 0.21, respectively, both lower than that of the CG0 alloy at 0.48. Collectively, these composites demonstrate effective self-lubrication from RT to 500 °C, with CG7 (7 wt.% graphite) exhibiting optimal performance.
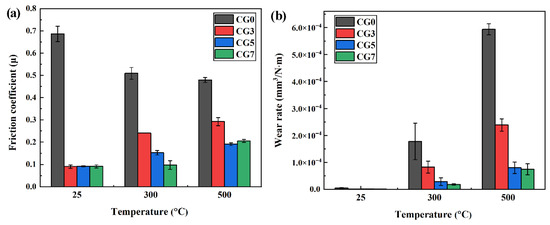
Figure 5.
Average friction coefficients and average wear rates of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites at different temperatures: (a) average friction coefficients and (b) average wear rates.
As shown in Figure 5b, the wear rates increase with temperature for all materials. Critically, the wear rate of the CG0 alloy (5.40 × 10−3–2.14 × 10−3 mm3/N·m) is significantly higher than that of the composites (1.09 × 10−6–8.04 × 10−5 mm3/N·m), indicating that the introduction of graphite effectively improves the wear resistance of the materials. At RT, the CG3 composite showed the lowest wear rate of 1.09 × 10−6 mm3/N·m, while the wear rates of the CG5 and CG7 composites slightly increased. At elevated temperatures of 300 °C and 500 °C, the CG7 composite demonstrated optimal wear resistance, with wear rates of 1.83 × 10−5 mm3/N·m and 7.52 × 10−5 mm3/N·m, respectively. Increasing graphite to 5 wt.% significantly enhances wear resistance, whereas further increase to 7 wt.% yields only marginal improvement despite continued reduction in wear rates. This demonstrates that optimal graphite addition (5–7 wt.%) effectively enhances high-temperature wear resistance through graphite’s sustained lubricity, with higher content further reducing wear rates.
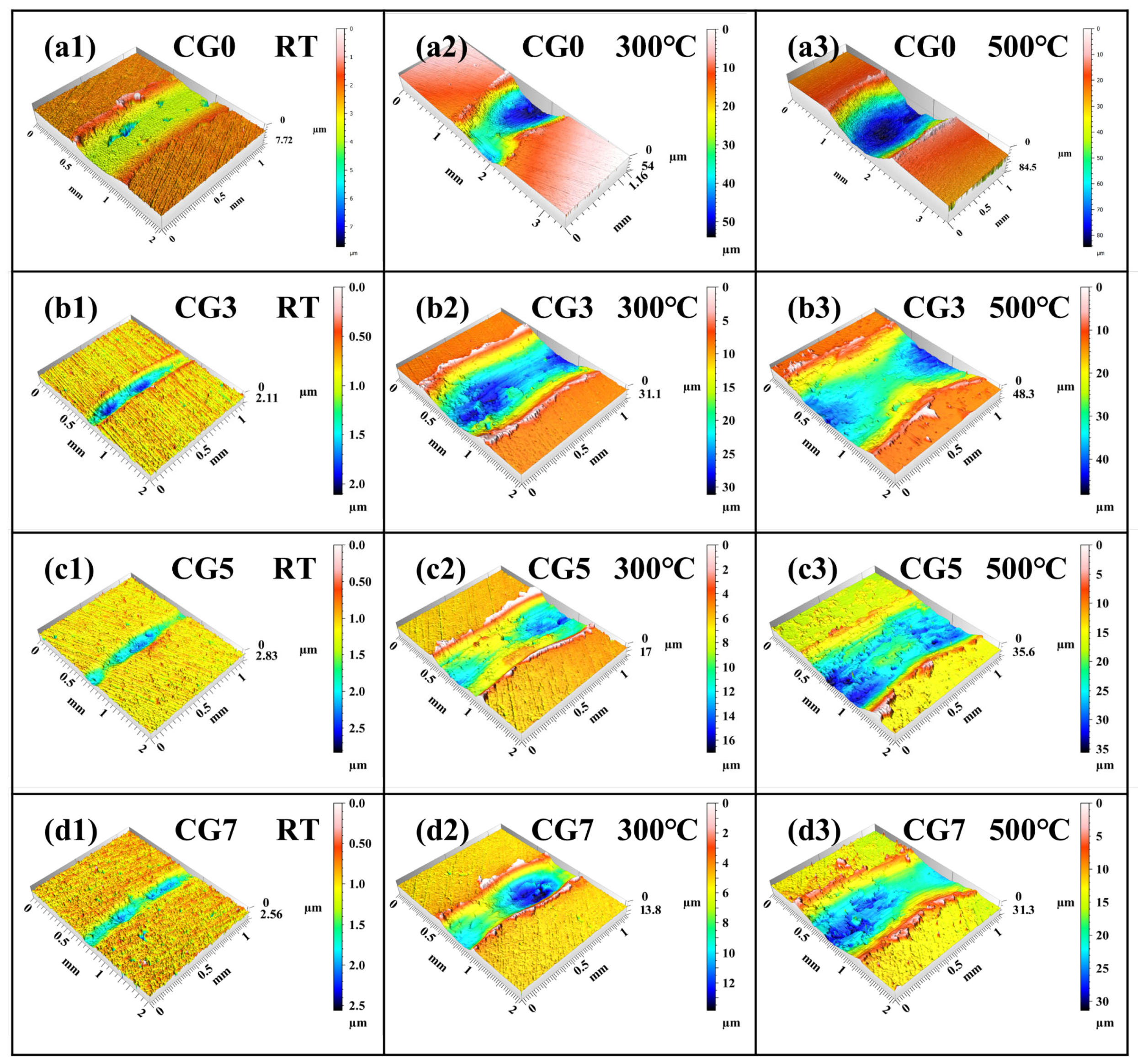
Figure 6 displays the characteristic three-dimensional wear morphologies of the Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites tested at different temperatures. Overall, the wear scars exhibit a trend of increasing width and depth with rising temperature. Nevertheless, at some temperatures, the maximum depth of the wear scar is effectively reduced with higher graphite content. At RT, the CG0 alloy exhibits a maximum wear depth of approximately 7.7 μm. The addition of graphite significantly reduces wear depth, with CG3, CG5, and CG7 composites showing comparable depths of about 2.6 μm. At 300 °C, the maximum wear depth of the CG0 alloy reaches approximately 54 μm, while the incorporation of 7 wt.% graphite substantially reduces this value to about 13.8 μm. Similarly, at 500 °C, the maximum wear depth decreases from 84.5 μm to 31.3 μm with graphite addition. These morphological observations conclusively demonstrate that the addition of graphite markedly improves the tribological performance of the composites across the temperature range studied. To gain further insight into the underlying wear mechanisms, detailed analysis of the worn surfaces was conducted.
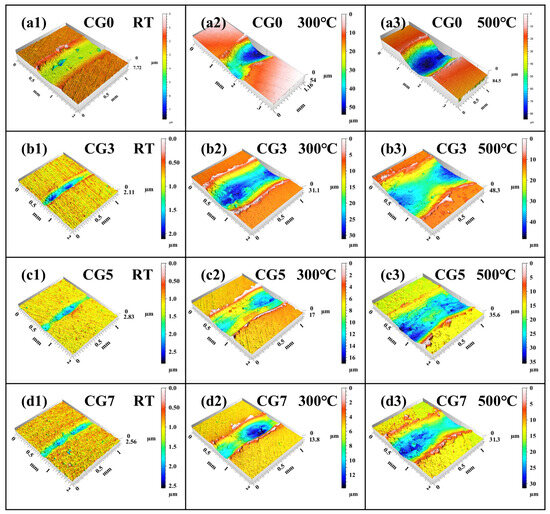
Figure 6.
Typical three-dimensional wear morphologies of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites under different temperatures: (a) CG0, (b) CG3, (c) CG5, and (d) CG7; (1) RT, (2) 300 °C, and (3) 500 °C.
3.3. Worn Surfaces and Wear Mechanism
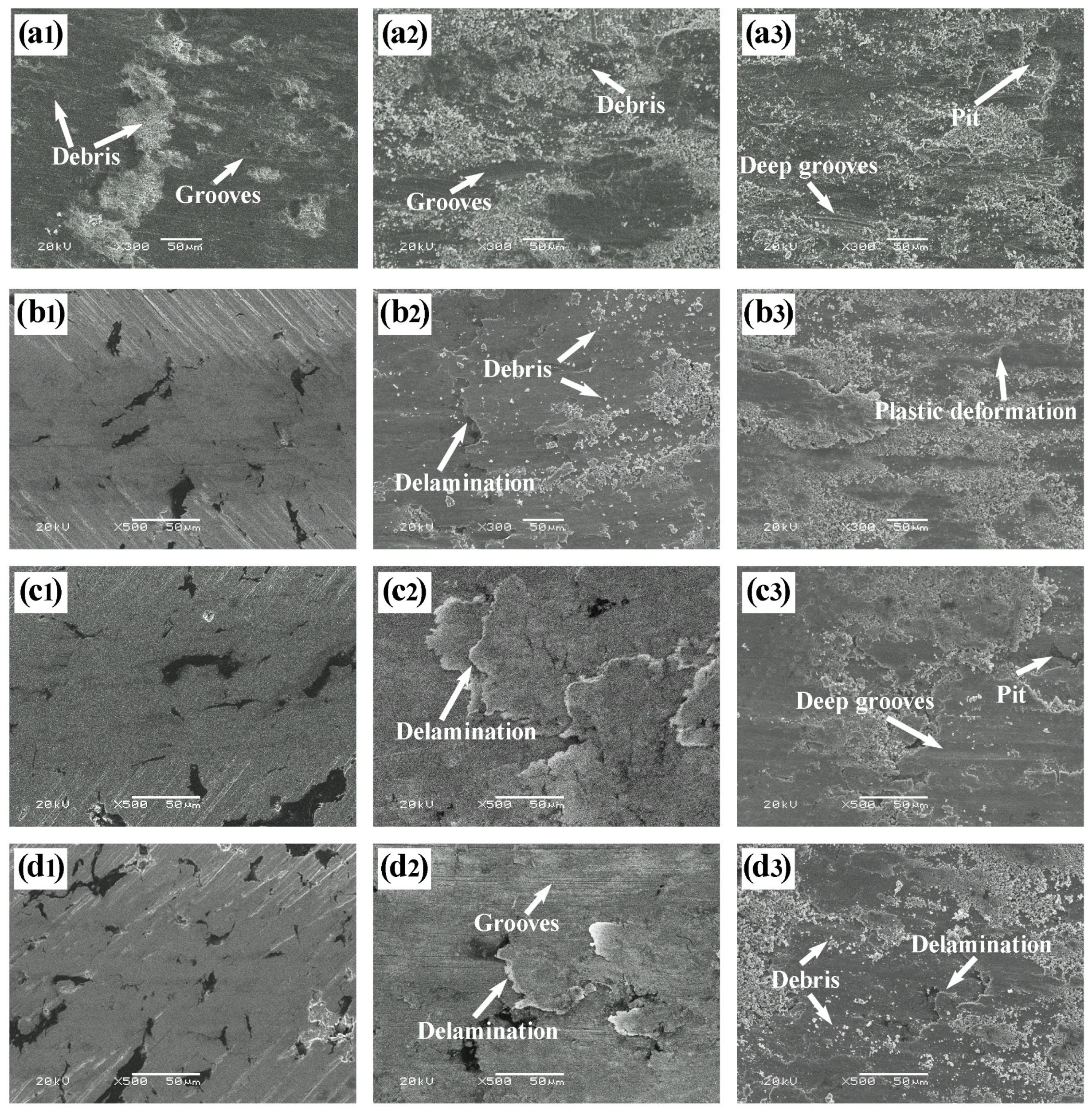
Figure 7 presents typical SEM micrographs of the wear surfaces of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites at different temperatures. For the graphite-free CG0 alloy at RT (Figure 7(a1)), distinct micro-ploughing grooves and limited abrasive debris are observed. The white contrast regions correspond to fine abrasive particles and tribo-oxides formed during unlubricated sliding, indicating that abrasive wear is the predominant mechanism. At 300 °C (Figure 6(a2) and Figure 7(a2)), the worn surface exhibits pronounced plastic deformation, deep ploughing grooves, and large wear debris particles, suggesting that abrasive wear and plastic deformation are the primary wear mechanisms. These processes account for the increased wear rate compared to that at RT. When the temperature was elevated to 500 °C (Figure 6(a3) and Figure 7(a3)), more severe damage was observed, including spalling pits, extensive plastic deformation, deep ploughing grooves, and abundant abrasive debris. The fine particles are likely products of severe oxidation induced by high-temperature and frictional heating, indicating significant oxidative wear. At this temperature, the main wear mechanisms comprise severe oxidative wear, plastic deformation, micro-ploughing, and micro-cutting, which collectively lead to a further increase in the wear rate.
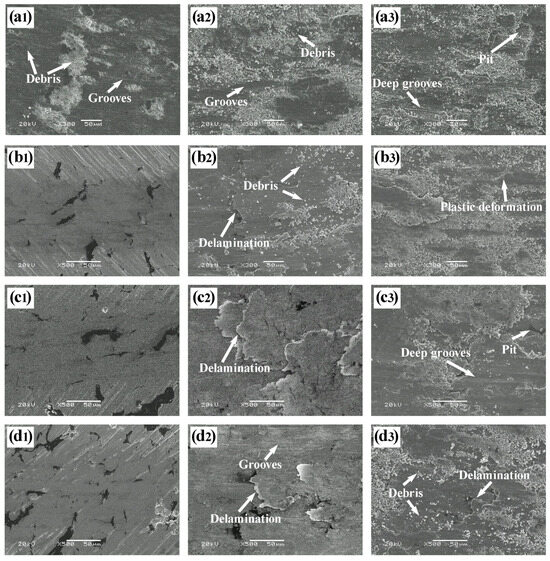
Figure 7.
Typical SEM micrographs of the wear surfaces of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites at different temperatures: (a) CG0, (b) CG3, (c) CG5, and (d) CG7; (1) RT, (2) 300 °C, and (3) 500 °C.
In contrast, graphite-containing composites demonstrate significantly smoother RT surfaces (Figure 7(b1–d1)) with only shallow scuffing and minor grooves, suggesting slight abrasive wear as the prevailing mechanism. Combining the average coefficient of friction and wear rate of the composites (Figure 5), this evidences continuous lubricating film formation during sliding, effectively isolating contacting surfaces and minimizing material loss.
At 300 °C (Figure 7(b2–d2)), the worn surfaces of the composites exhibited micro-ploughing grooves, delamination, and plastic deformation, suggesting a transition to abrasive and delamination wear mechanisms. The CG3 sample showed more severe damage, including fine abrasive debris and pronounced delamination. In contrast, the CG5 and CG7 samples maintained relatively smooth surfaces with minimal visible wear debris. These morphological features correspond well with the friction behavior presented in Figure 4b, where CG5 and CG7 exhibited a noticeable drop in friction coefficient after the run-in period, followed by stable sliding. This confirms that above 5 wt.% graphite content, a smooth and continuous lubricating film forms on the worn surface during initial sliding, significantly enhancing tribological performance at 300 °C.
At 500 °C (Figure 7(b3–d3)), all composites exhibit accelerated deterioration with abrasive debris, deep ploughing grooves, delamination, spalling pits, and plastic deformation, establishing abrasive wear, oxidative wear, and plastic deformation as the dominant mechanism. This indicates that within 500 °C, the composites also experienced significant wear, and increasing graphite content can mitigate the severity of surface damage to a certain extent. The lubricating properties confirm that the addition of graphite is effective in lowering both the friction coefficient and the wear rate [30].
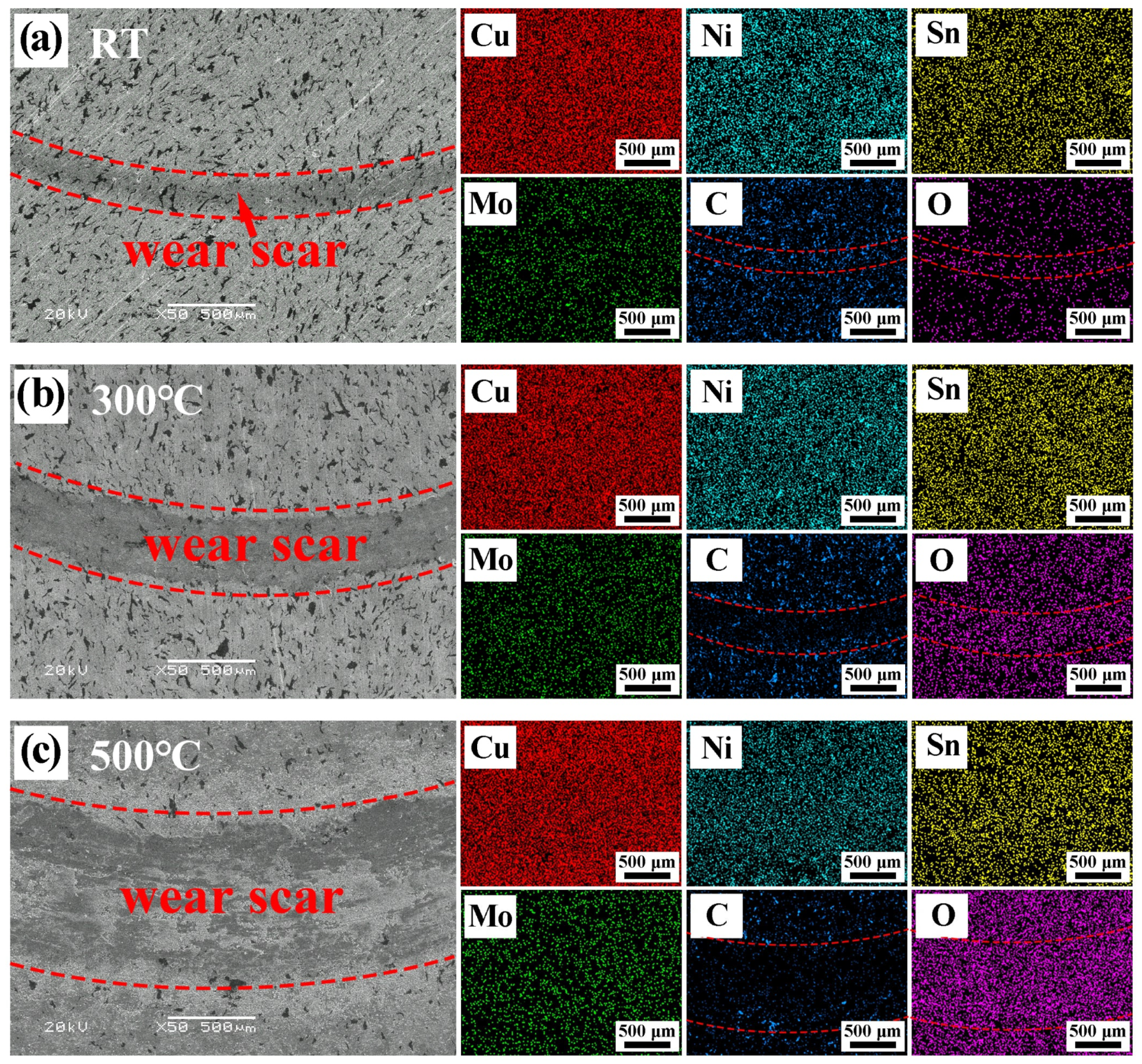
Typical SEM images, elemental maps, and corresponding EDS results of the worn surfaces for the CG7 composite at different temperatures are presented in Figure 8 and Table 2. The SEM images reveal a progressive widening of the wear track on the CG7 composite with increasing temperature, indicating an expansion of the worn area. This phenomenon is mainly due to the thermal softening of the matrix at elevated temperatures, which diminishes the material’s strength and load-bearing capacity, thereby accelerating wear. The EDS data listed in Table 2 show that at 300 °C, the contents of Ni and Sn inside and outside the wear mark surface remain mostly unchanged, while the contents of C, Cu, and Mo are slightly reduced. At 500 °C, oxygen content increases significantly with concurrent decrease in all metallic elements, confirming intensified oxidation. Elemental mappings further reveal significant carbon depletion and oxygen enrichment within the wear tracks compared to unworn regions. These results indicate that frictional-heating induced chemical oxidation reactions occur on CG7 surfaces at RT, while high-temperature oxidation processes accompany these reactions at 300 °C and 500 °C. This reflects that in situ formed oxides combine with graphite to create mixed lubrication films, partially covering graphite with oxides during sliding. The in situ formed oxides combine with graphite to form mixed lubricating films during sliding, in which graphite is partially covered by oxides, thereby contributing to the composite’s tribological performance.
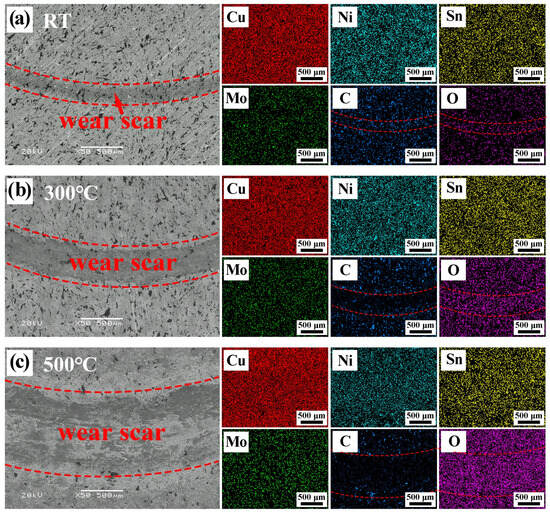
Figure 8.
Typical SEM images of the wear surface of CG7 composites at different temperatures and EDS maps of elements: (a) RT, (b) 300 °C, and (c) 500 °C.

Table 2.
EDS results of the wear surface of the CG7 composites at different temperatures.
The micro-beam XRD was further conducted to identify the constituent of worn surfaces at different temperatures. The patterns in Figure 9 confirm the formation of metal oxides on the wear surface of the CG7 composite at elevated temperatures, demonstrating that surface oxidation became more pronounced with increasing temperature. At RT, the worn surface primarily contains Cu solid solution, Mo2C, Mo, and graphite without detectable oxides. At 300 °C, Cu2O diffraction peaks emerge, indicating oxidation reactions driven by combined thermal and frictional heating during sliding. At 500 °C, CuO peaks appear alongside Cu2O, demonstrating further intensified oxidation where CuO being a newly detected phase.
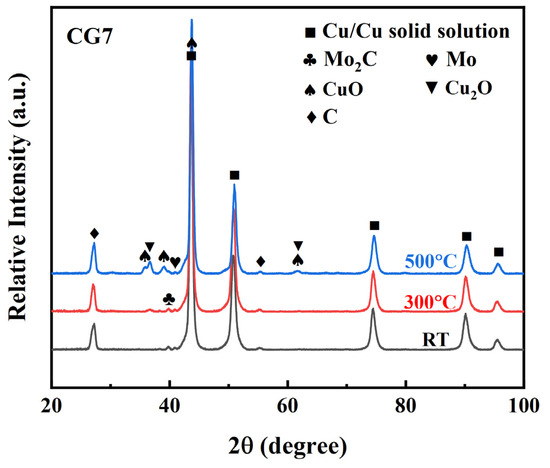
Figure 9.
Micro-beam XRD patterns of worn surfaces of CG7 composite at different temperatures.
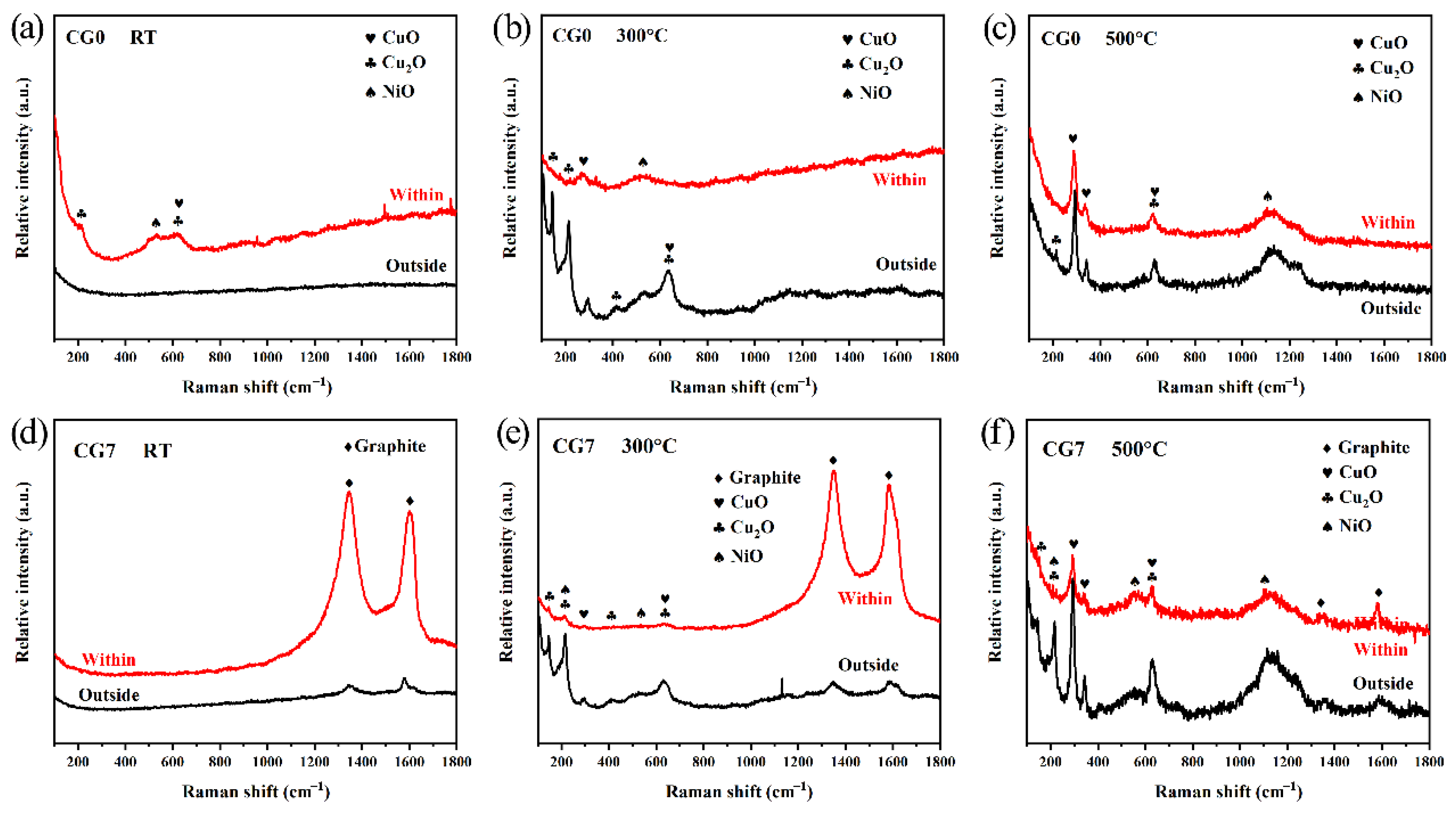
To elucidate the influence of the graphite phase and the oxidation process on the tribological properties, the worn surfaces were examined by Raman spectroscopy. Figure 10 presents the Raman spectra within and outside the worn surface of CG0 alloy and CG7 composite at different temperatures. For CG0 at RT (Figure 10a), spectra differ significantly: Regions outside the worn surface show no characteristic peaks, while spectra within the worn surface exhibit CuO, Cu2O, and NiO peaks, confirming tribo-oxidation. Conversely, CG7 (Figure 10d) displays similar spectra in both regions, dominated by intense graphite peaks with almost no metal oxides. Critically, graphite peaks within the worn surface show higher intensity than outside regions. Combined with the friction and wear results (Figure 5) and the wear morphology (Figure 7(d1)), the low friction coefficient and low wear rate of the CG7 composite are attributed to the formation of a dense and smooth lubricating film primarily composed of graphite. This film effectively prevents direct contact between the sliding surfaces, while the weak interlayer shear strength inherent to graphite’s layered structure provides solid lubrication [31], indicating its dominant role at RT.
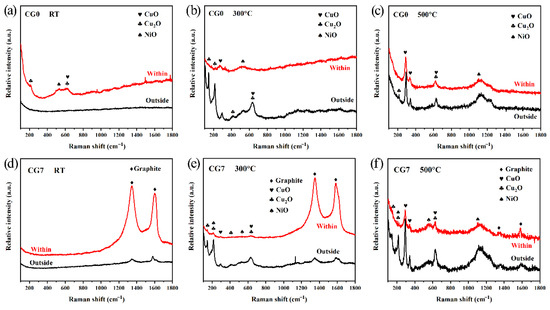
Figure 10.
Raman spectra within and outside the worn surface of CG0 alloy and CG7 composite at different temperatures.
At 300 °C/500 °C (Figure 10b,c,e,f), both materials show oxide peaks in all regions. Oxidation outside worn surfaces stems from environmental exposure, while within worn surface oxidation involves combined tribo-oxidation and thermal effects. For CG0 at 300 °C (Figure 10b), outside regions contain predominantly Cu2O and NiO, whereas within worn surface spectra feature CuO and NiO dominance, suggesting the friction chemical reaction within the wear surface may promote the conversion of some Cu2O to CuO. At 300 °C, the average friction coefficient of CG0 is lower than at RT, likely due to oxides acting as the primary lubricant. However, the wear rate increases significantly, primarily attributed to the reduction in material strength at high temperature. For CG7 at 300 °C (Figure 10e), both regions contain graphite, Cu2O, CuO, and NiO (Cu2O dominant), with within worn surface spectra showing stronger graphite peaks. This suggests the formation of a mixed lubricating film on the composite’s worn surface, predominantly composed of graphite with minor amounts of metal oxides. The formation of this mixed lubrication film is the primary reason for the composite material’s low coefficient of friction and wear rate at 300 °C [32].
At 500 °C, the oxide composition on both inside and outside regions of the wear surface for the CG0 alloy (Figure 10c) remains similar to that observed at 300 °C, but with significantly enhanced peak intensities, indicating more severe oxidation reactions at elevated temperature. Although the average friction coefficient of the alloy further decreases—likely due to the lubricating effect of oxides—the wear rate increases as a result of thermal softening. For the CG7 composite (Figure 10f) at 500 °C, the composition inside and outside the wear surface is largely similar, consisting mainly of graphite, CuO, Cu2O, and NiO. As reported in references [33,34], the mixtures of metallic compounds and graphite can serve as effective solid lubricants from RT up to 1000 °F (538 °C), provided no chemical reactions occur between them. The wear rate of the CG7 composite at this temperature is significantly lower than that of the CG0 alloy. Combined with the worn surface morphology (Figure 7(d3)), these results confirm the formation of a mixed lubricating film composed of graphite and metallic oxides, which contributes to the improved tribological performance of the composite.
However, compared to its performance at 300 °C, both the friction coefficient and wear rate of CG7 increase at 500 °C. Raman spectroscopy reveals that at 500 °C, the relative intensity of the graphite peak decreases significantly, falling markedly below that of the oxide peak. This can be attributed to the oxidation of graphite, which begins around 400 °C, where graphite reacts with oxygen to form CO2 gas. As the temperature rises further to 500 °C, the oxidation rate increases markedly, leading to noticeable graphitic ablation [35,36]. The partial oxidation of graphite impairs its lubricity, thereby further aggravating material wear.
4. Conclusions
Novel self-lubricating Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites were successfully fabricated by SPS. The microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological behavior of these composites were systematically investigated from RT to 500 °C. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The sintered composites are primarily composed of Cu solid solution, CuNi2Sn, Mo, Mo2C and graphite. As the amount of graphite content increases, the density of the composites gradually decreases while maintaining high relative density. The hardness decreases from 227.7 HB to 169.7 HB and yield strength declines from 524 MPa to 330 MPa, attributed to graphite-induced matrix segmentation.
- (2)
- The composites demonstrate excellent tribological performance across RT-500 °C. While both friction coefficient and wear rate increase with temperature, the composite containing 7 wt.% graphite consistently exhibits the best performance, exhibiting the lowest friction coefficient (0.09 to 0.21) and wear rates (1.32 × 10−6 mm3/N·m to 7.52 × 10−5 mm3/N·m) among all composites.
- (3)
- The main lubrication mechanisms of Cu-Ni-Sn-Mo-Gr composites evolve with temperature. At RT, effective lubrication is provided mainly by a graphite-rich tribofilm formed on the worn surface. In the elevated temperature range of 300–500 °C, lubrication is governed by a synergistic lubricating film comprising both graphite and thermally formed metal oxides (Cu2O, CuO, and NiO).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.L.; validation, J.L. and S.L.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, J.W. and F.L.; resources, Z.L. and F.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and G.Y.; visualization, S.L.; supervision, Z.L. and G.Y.; project administration, Z.L. and J.W.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52165024) and the Gansu Province Science and Technology Plan (Key R&D plan) Project (Grant No. 21YF5GA098).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the teachers Dongmei Li, Guantao Kou, Yaxuan Dai, Yunxia Wang, Jie Yan, Wenjun Qu, and Bo Wang from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics for their valuable assistance with the XRD, SEM, and Raman spectroscopy measurements, respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
Songlin Lu is employed by Ningbo Intelligent Machine Tool Research Institute Co., Ltd. of China National Machinery Institute Group, Ningbo 315700, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Simões, S. Design and Development of Metal Matrix Composites. Metals 2025, 15, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chromik, R.R. Tribology of Self-Lubricating Metal Matrix Composites. In Self-Lubricating Composites; Menezes, P.L., Rohatgi, P.K., Omrani, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 33–73. ISBN 978-3-662-56528-5. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Yao, P.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, T.; Zhao, L.; Deng, M. Investigation on Speed-Load Sensitivity to Tribological Properties of Copper Metal Matrix Composites for Braking Application. Metals 2020, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalnova, S.A.; Volosevich, D.V.; Sannikov, M.I.; Magidov, I.S.; Mikhaylovskiy, K.V.; Turichin, G.A.; Klimova-Korsmik, O.G. Direct Energy Deposition of SiC Reinforced Ti–6Al–4V Metal Matrix Composites: Structure and Mechanical Properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 35076–35084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. Microstructure Evolution and Tribological Performance of Cu-WS2 Self-Lubricating Composites. Wear 2018, 412–413, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliasker, K.T.; Gopal, P.M.; Naveen, S.; Madhu, S.; Yuvaraj, K.P. Exploring the Effects of Self-Lubricating MoS2 in Magnesium Metal Matrix Composite: Investigation on Wear, Corrosion, and Mechanical Properties. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 677, 132362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of Electrical Current Density, Apparent Contact Pressure, and Sliding Velocity on the Electrical Sliding Wear Behavior of Cu–Ti3AlC2 Composites. Wear 2020, 444–445, 203156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshkian, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, I. Investigating the Role of Metal Reinforcement Particles in Producing Cu/Ni/W Metal Matrix Composites via Friction Stir Processing: Microstructure, Microhardness, and Wear at High Temperature. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.R.; Gazani, F.; Mousa Mirabad, H.; Khezri, I.; Moeini, A.; Sohrabi, N.; Kim, H.S. Recent Advances in Processing, and Mechanical, Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cu-SiC Metal Matrix Composites Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 140, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Dai, J.; Xiao, Z.; Qiu, W.; Lei, Q.; Liu, X.; Qin, L.; Ma, M. Interface Microstructure and Tribological Behaviors of Copper Matrix Composites with High Graphite Content Prepared by Short-Process Reduction and Vacuum Hot Pressing. JOM 2022, 74, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, W. Investigation on Wear and Corrosion Behavior of Cu–Graphite Composites Prepared by Electroforming. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, R.R.; Ibrahim, I.H.M.; Sedahmed, G.H. The Corrosion of Graphite/Copper Composites in Different Aqueous Environments. Mater. Lett. 1996, 28, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Antonov, M. Self-Lubricating Materials for Extreme Temperature Tribo-Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 4583–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J. High Temperature Solid-Lubricating Materials: A Review. Tribol. Int. 2019, 133, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K. The Mechanical Mixed Layer and Its Role in Cu-15Ni-8Sn/Graphite Composites. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krus, D.; Juba, D. Bearing up under 300 Tons. Mach. Des. 2005, 77, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Plewes, J.T. High-Strength Cu-Ni-Sn Alloys by Thermomechanical Processing. Metall. Trans. A 1975, 6, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-C.; Notis, M.R. Microstructure and Precipitation Kinetics in a Cu-7.5Ni-5Sn Alloy. Scr. Mater. 1998, 39, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jie, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effect of V Addition on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Cu-15Ni-8Sn Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 748, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chen, Z.; Kang, H.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Zou, C.; Wang, T. Effects of Nb Addition on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Precipitation Hardening Cu-9Ni-6Sn Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Du, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Ding, Z. Effect of Zr Addition on Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu-Ni-Sn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1015, 178887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jie, J.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Li, T. Effect of B Addition on Microstructures and Properties of Cu-15Ni-8Sn Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. Effect of Ni Content on Microstructure and Characterization of Cu-Ni-Sn Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Du, X.; Shi, W.; Yang, S. Effect of Mo Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cu-12.5Ni-5Sn Alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, F.; Seriacopi, V.; Martínez, C.; Valin, J.L.; Centeno, D.; Machado, I.F. The Effects of Pressure and Pressure Routes on the Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Copper via SPS. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 2455–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvildeev, V.N.; Panov, D.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Blagoveshchensky, Y.V.; Sakharov, N.V.; Shotin, S.V.; Kotkov, D.N. Structure and Properties of Advanced Materials Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 109, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; He, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, T.; Liu, Q.; Guo, C.; Qu, X. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Copper–Diamond Composites Using Molybdenum Carbide-Coated Diamond Particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6133–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendino, P.; Ferraris, M.; Casalegno, V.; Salvo, M.; Merola, M.; Grattarola, M. Proposal for a New Technique to Join CFC Composites to Copper. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 348, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Ni, J. Microstructure Evolution and Properties of In Situ Micro/Nanoscale Mo2C Reinforced Copper Composite Synthesized by Hot-Pressing Consolidation of Mechanical Alloying Powders. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 4604–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, G. Friction and Wear Behavior of Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with SiC and Graphite Particles. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, I.M. Solid Lubricants for Applications at Elevated Temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 3977–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, H.; Tan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Effects of Graphite Contents on the Microstructure Evolution, Mechanical Properties and High Temperature Tribological Behavior of Cu–Ni–Al/Gr Solid-Lubricating Composites. Tribol. Int. 2023, 179, 108193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, H.E. Solid Lubricant Materials for High Temperatures—A Review. Tribol. Int. 1982, 15, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.B.; Johnson, R.L. Friction Studies of Graphite and Mixtures of Graphite with Several Metallic Oxides and Salts at Temperatures to 1000 F°; NACA: Washington, DC, USA, 1956; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaowei, L.; Jean-Charles, R.; Suyuan, Y. Effect of Temperature on Graphite Oxidation Behavior. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2004, 227, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Robin, J.-C.; Yu, S. Comparison of Oxidation Behaviors of Different Grades of Nuclear Graphite. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2005, 151, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).