A Phenomenological Model for Estimating the Wear of Horizontally Straight Slurry Discharge Pipes: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
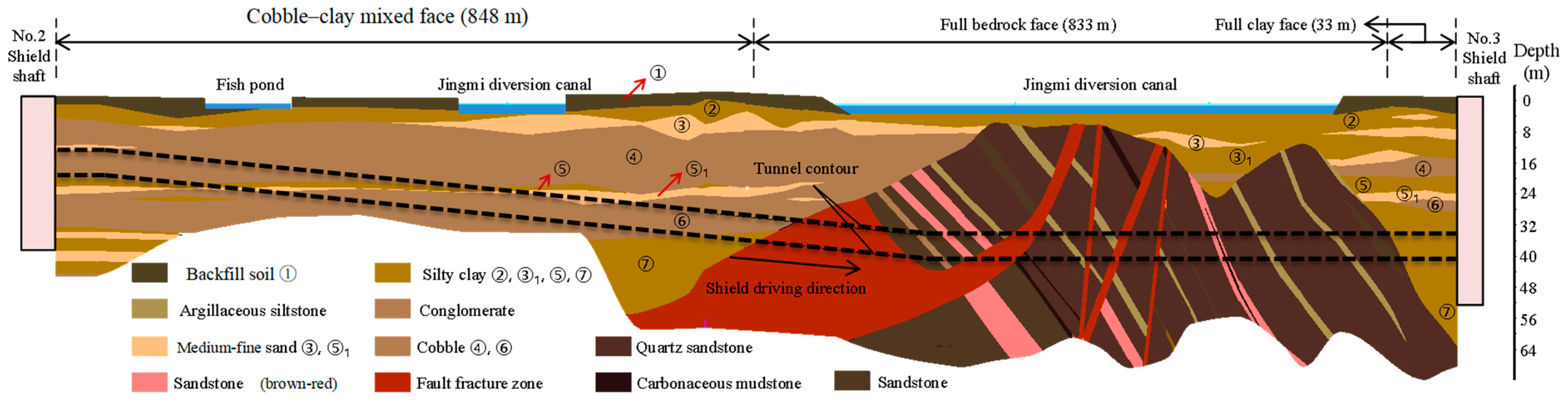
2. Project Overview
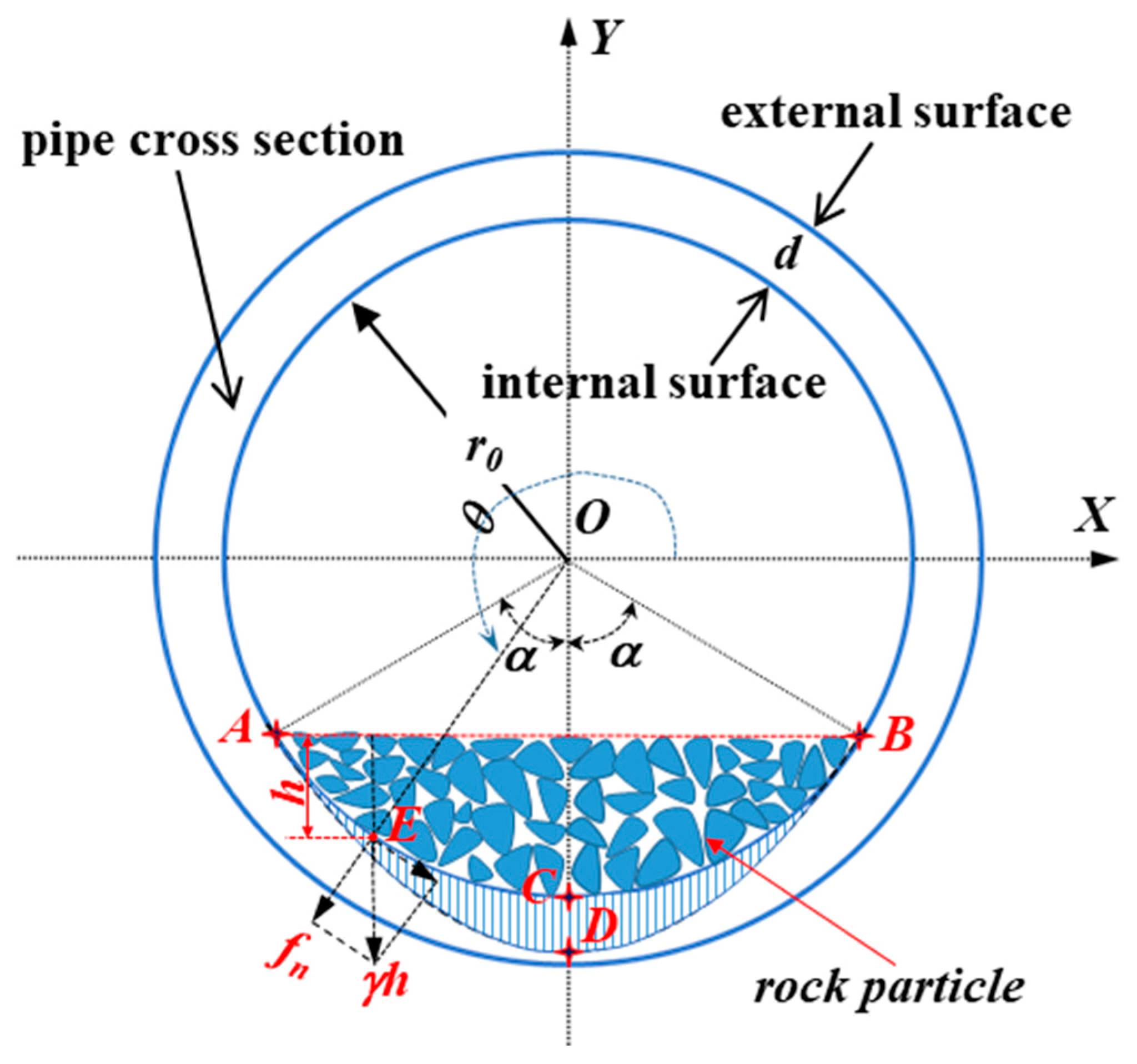
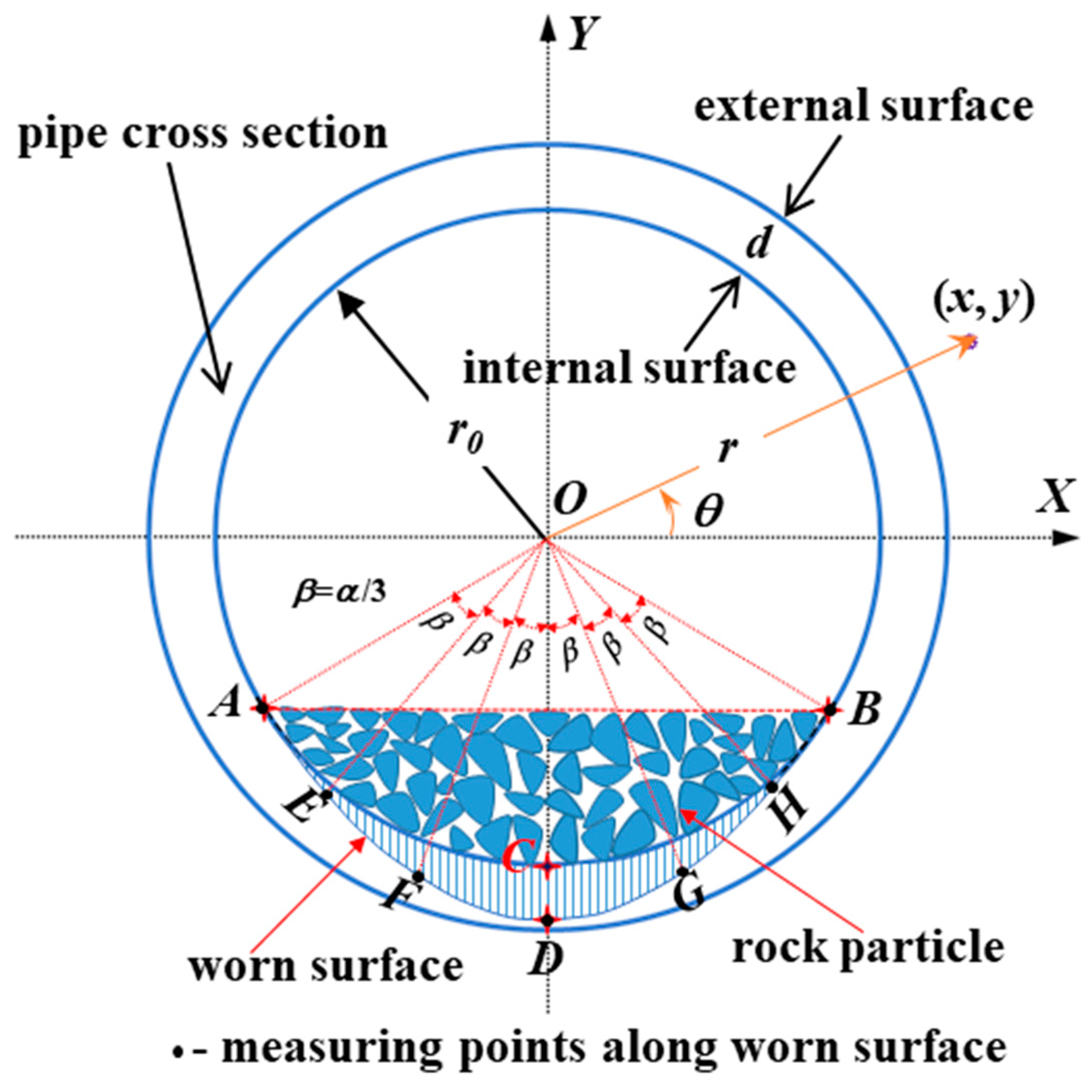
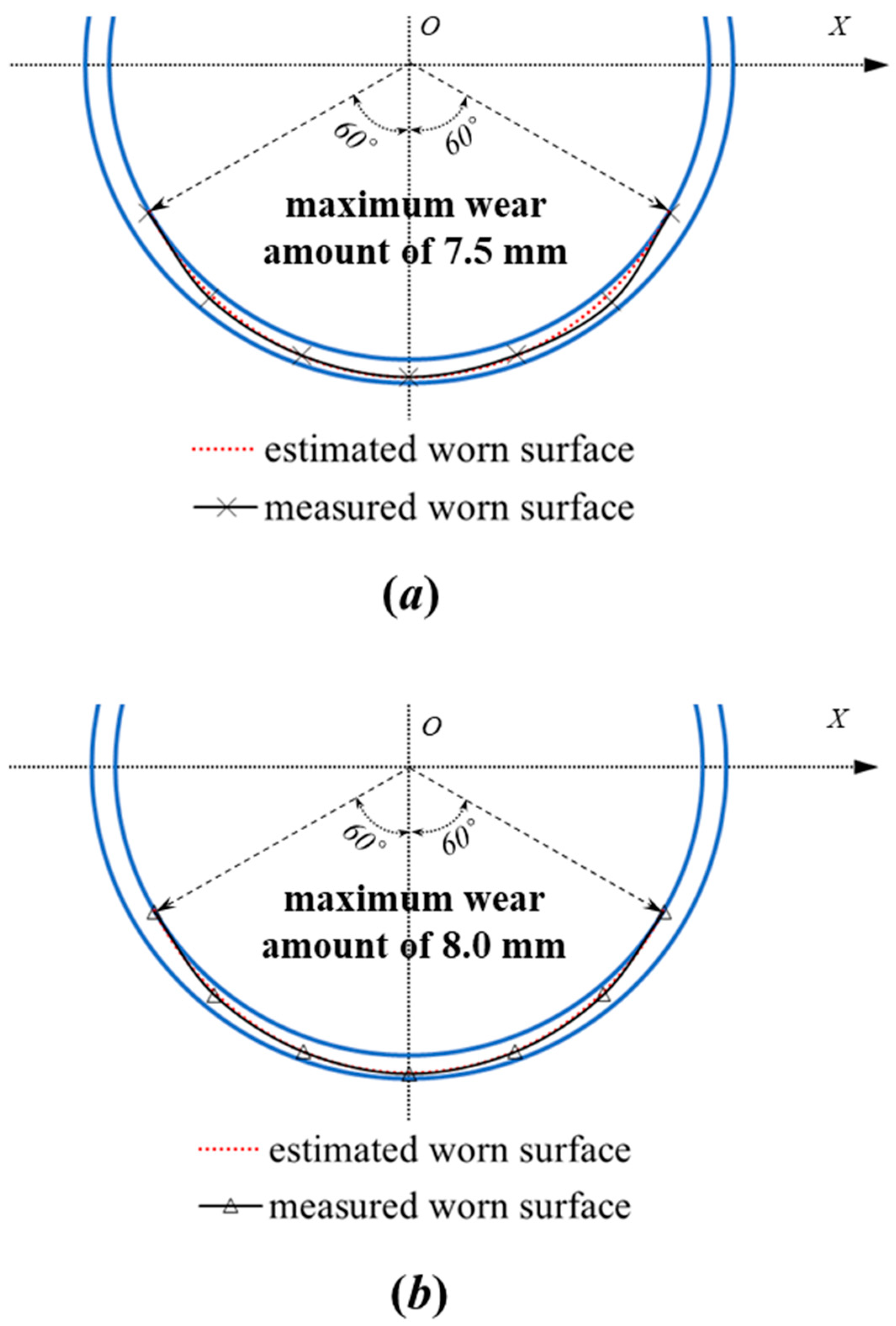
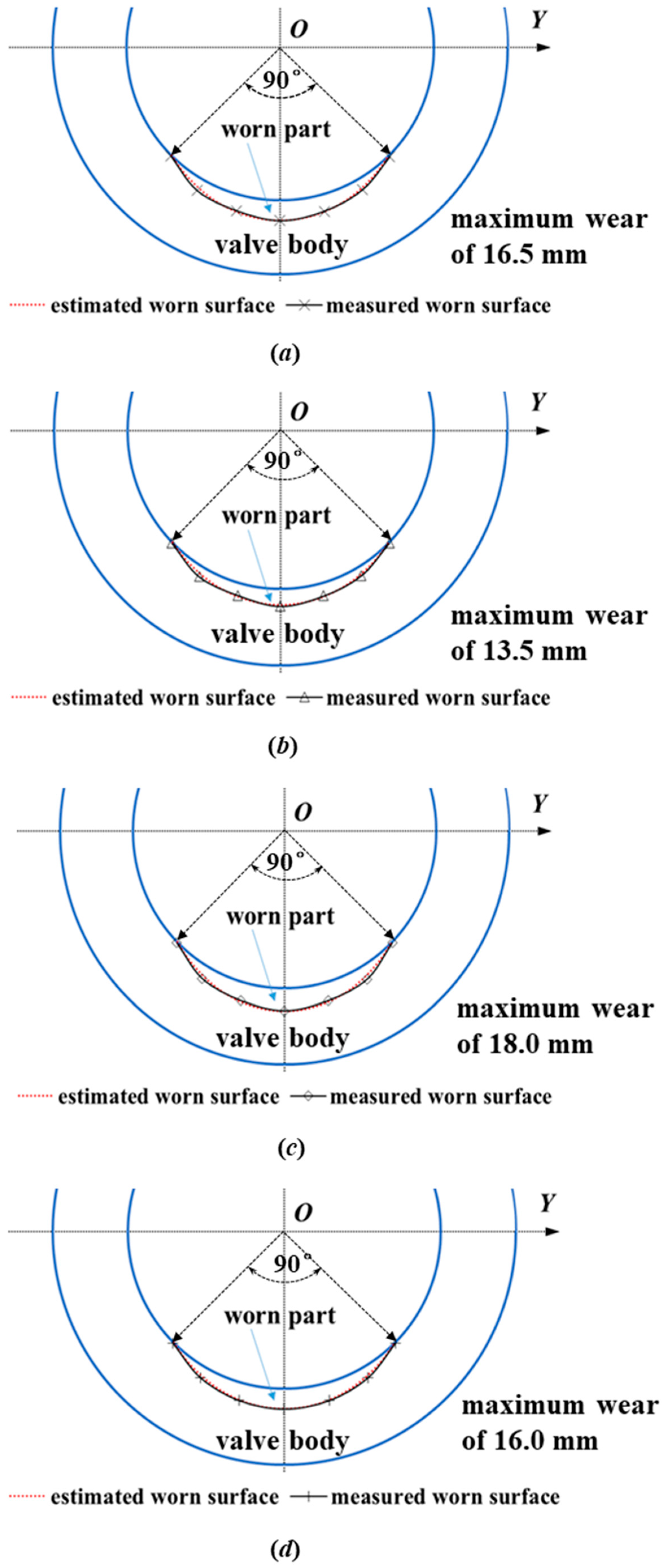
3. Pipeline Wear Estimation Model
4. Discussions
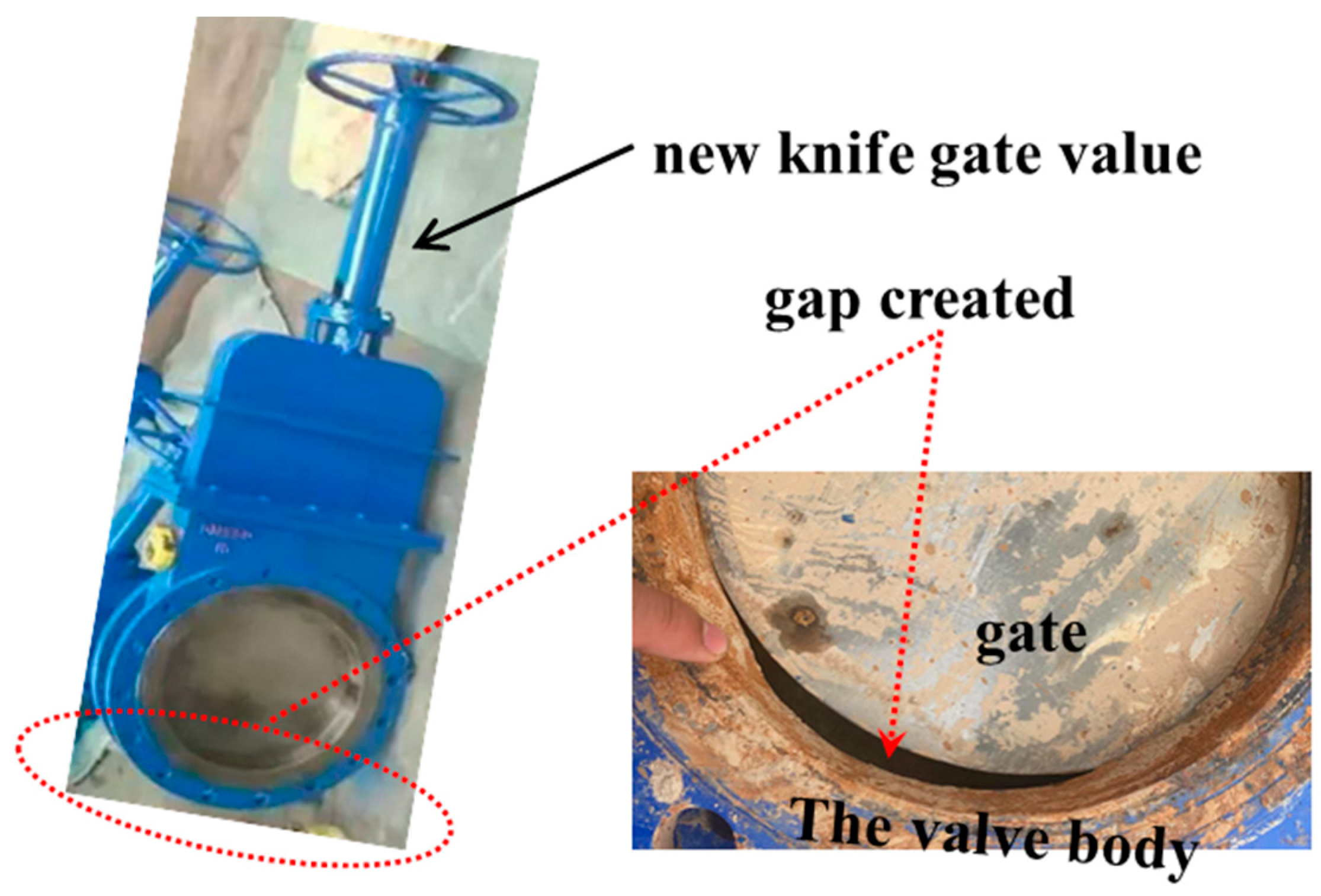
4.1. Flow Characteristics of Slurry and Rock Particles in Horizontally Straight Pipes
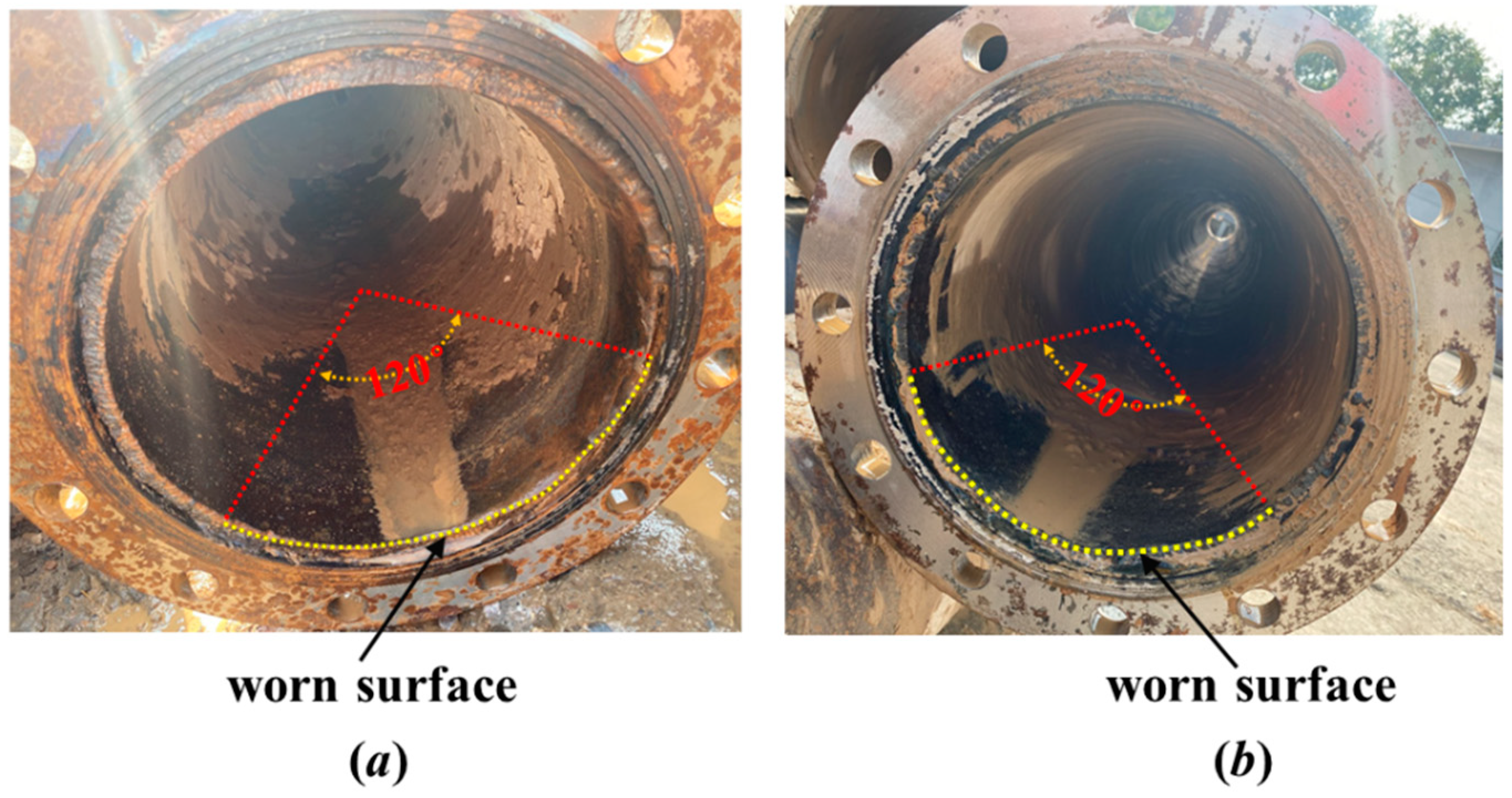
4.2. The Central Angle 2α Used to Define the Worn Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| r0 | Internal radius of pipe |
| d | Wall thickness of pipe |
| 2α | Central angle |
| δmax | Maximum wear amount |
| δ | Wear amount |
| fn | Normal force |
| γ | Equivalent specific gravity |
| h | Equivalent specific height |
| θ | Polar angle |
| k | Wear coefficient |
| λ | Wear rate |
| L | Excavated tunnel length |
References
- Cui, W.; Liu, D.; Song, H.F.; Pu, G.J. Development and experimental study on environmental slurry for slurry shield tunneling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 216, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, H. Investigation into the flow characteristics of slurry shield pipeline system under sandy pebble stratum: Model test and CFD-DEM simulation. Powder Technol. 2023, 415, 118149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, P.; Zeng, G.; Zhao, X. Numerical investigation of pipeline transport characteristics of slurry shield under gravel stratum. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 71, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, C.; Ji, J.; Liu, J. A study on the excavation face failure of pressurized slurry shield. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Min, F.; Lyu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Recycling waste sand from slurry shield tunneling: A sustainable filter aid for waste slurry dehydration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Zhu, W.; Lin, C.; Guo, X. Opening the excavation chamber of the large-diameter size slurry shield: A case study in Nanjing Yangtze River Tunnel in China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 46, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbl, A. Swinoujscie Tunnel—Using a slurry shield under the Baltic Sea. Geomech. Tunn. 2021, 14, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendl, K.; Scholz, M.; Thuro, K. Charakterisierung der ingenieurgeologischen Vortriebsdokumentation von Hydroschildvortrieben am Beispiel der Baulose H3-4 und H8 im Unterinntal. Geotechnik 2012, 35, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, P. Additives for slurry shields in highly permeable ground. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2007, 40, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.K.L.; Kwong, A.K.L. Geotechnical risks, mitigation measures and performance of tunnel boring machine (TBM) tunnels for the Tuen Mun—Chek Lap Kok Link Project. HKIE Trans. 2019, 26, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.R.; Ingole, S.P.; Bhatt, D.V.; Menghani, J.V. The study of slurry erosion wear behaviour of coal bottom ash slurry handling pipeline. In TMS 2019, 148th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, Proceedings of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–14 March 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 697–710. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, H.S.; Singh, H.; Agrawal, A. A phenomenological model for slurry erosion prediction of thermal spray coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, R.M. A review of pipeline slurry erosion measurements and research recommendations. In Slurry Erosion: Uses, Applications, and Test Methods; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1987; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, S.K. Modeling of erosion wear of sand water slurry flow through pipe bend using CFD. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2019, 12, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.I.; Okamura, K.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact, Part 1: Effects of impact parameters on a predictive equation. Wear 2005, 259, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.I.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact, Part 2: Mechanical properties of materials directly associated with erosion damage. Wear 2005, 259, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.C.; Souza, F.; Martins, D. Numerical prediction of the erosion due to particles in elbows. Powder Technol. 2014, 261, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabnejad, H.; Mansouri, A.; Shirazi, S.A.; McLaury, B.S. Development of mechanistic erosion equation for solid particles. Wear 2015, 332–333, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Singh, S.N.; Seshadri, V. Erosion wear studies on high concentration fly ash slurries. Wear 2017, 378, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, E.H.; Peursem, D.V. The erosion of horizontal sand slurry pipelines resulting from inter-particle collision. Wear 2018, 400, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheria, V.; Portera, D.; Kuokkalab, V. Slurry erosion of steel—Review of tests, mechanisms and materials. Wear 2018, 408, 248–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.R.; Bhatt, D.V.; Menghani, J.V. Failure analysis of coal bottom ash slurry pipeline in thermal power plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 90, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, M.; Adane, K.F. Validation of a dense slurry pipeline erosion-corrosion model. In Proceedings of the Corrosion 2020, Online, 14–18 June 2020; pp. 1545–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J. A Review on mechanisms and testing of wear in slurry pumps, pipeline circuits, and hydraulic turbines. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 090801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Wu, A.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Qiu, Z. Wear characteristics of the pipeline transporting cemented paste backfill containing coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 410, 134170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, P. CFD-DEM analysis of hydraulic conveying of non-spherical particles through a vertical-bend-horizontal pipeline. Powder Technol. 2024, 434, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, Z. Effect of cement-to-tailings ratio and flow rate on the wear performance of filling pipeline. Powder Technol. 2022, 397, 117027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, Y.T.; Kim, T.K.; Ko, T.Y. A study on the discharge pipes wear of slurry shield TBM in rock strata. J. Korean Tunn. Undergr. Space Assoc. 2017, 19, 57–70. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ko, T.Y.; Pak, Y.T.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.K. Slurry pipe wear in shield TBM, YSRM 2017 & NDRMGE 2017. In Proceedings of the ISRM Specialized Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–13 May 2017; pp. 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.Y.; Pak, Y.T.; Kim, T.K.; Son, S. Effect of rock abrasiveness on slurry shield tunneling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Tunnel Boring Machines in Difficult Grounds (TBM DiGs), Wuhan, China, 20–22 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.Y.; Lee, S.S. Effect of rock abrasiveness on wear of shield tunnelling in Bukit Timah Granite. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. The difficulties and countermeasures in shield construction of Yellow River tunnel of Lanzhou Metro Line 1. Railw. Stand. Des. 2017, 61, 93–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Li, X.; Chen, C. Study of abrasion of slurry pipe of large-diameter slurry shield boring in complex strata. Tunn. Constr. 2016, 36, 490–496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B. Countermeasures for reducing wear and vibration of slurry pipe of slurry shield. Tunn. Constr. 2016, 36, 1385–1388. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Xu, Z.; Hu, X.; Guo, G. Analysis of technical difficulties and control measures for slurry shield boring in sandy cobble strata: A case study of Yellow River crossing tunnel of Lanzhou Metro. Tunn. Constr. 2018, 38, 846–850. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, X. Slurry Discharge Pipeline Damage and Wear Due to Transporting Rock Particles during Slurry Shield Tunneling: A Case Study Based on In Situ Observed Results. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.C.; Addie, G.R.; Sellgren, A.; Clift, R. Slurry Transport Using Centrifugal Pumps, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
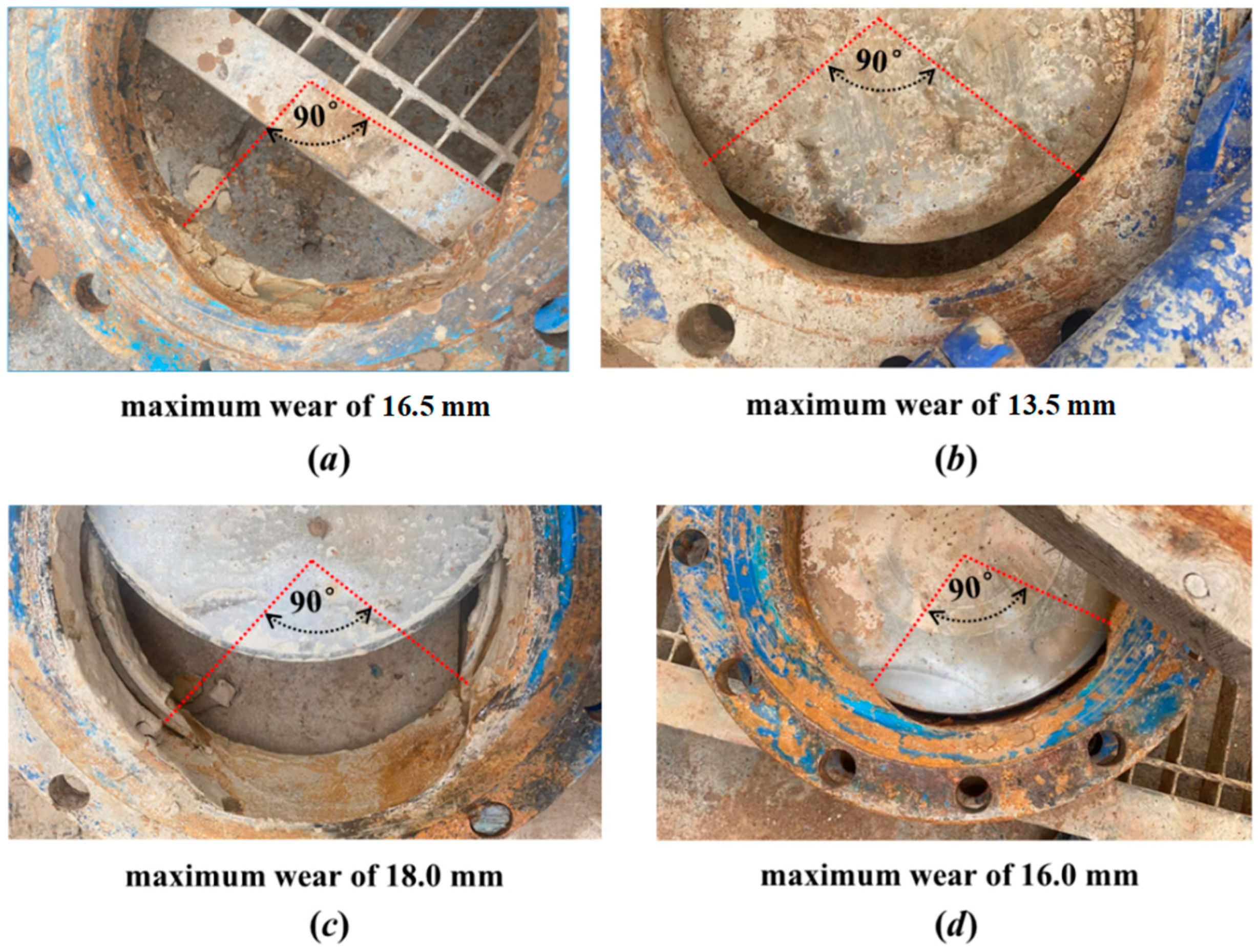






| Influencing Factor | Type of Possible Damage or Wear | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness | Abrasive Wear | Softer materials are more prone to abrasive wear from hard particles. |
| Mechanical Vibration | Fatigue Wear | Vibration induces cyclic stress, causing material fatigue damage. |
| Corrosive Environment | Corrosive Wear | Corrosive media accelerate material damage by combining with wear processes. |
| Environmental Temperature | Thermal Fatigue | High temperatures cause thermal fatigue, leading to cracks or spalling. |
| Fluid Velocity | Erosion Wear | Erosion wear results from the high-velocity impacts of fluids (especially those containing solid particles) on the inner wall. This type of wear typically occurs at pipeline bends, diameter changes, or areas with abrupt flow rate changes. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y. A Phenomenological Model for Estimating the Wear of Horizontally Straight Slurry Discharge Pipes: A Case Study. Lubricants 2024, 12, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12060228
Li X, Guo Y, Li X, Liu H, Yang Y, Fang Y. A Phenomenological Model for Estimating the Wear of Horizontally Straight Slurry Discharge Pipes: A Case Study. Lubricants. 2024; 12(6):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12060228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinggao, Yidong Guo, Xingchun Li, Hongzhi Liu, Yi Yang, and Yingran Fang. 2024. "A Phenomenological Model for Estimating the Wear of Horizontally Straight Slurry Discharge Pipes: A Case Study" Lubricants 12, no. 6: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12060228
APA StyleLi, X., Guo, Y., Li, X., Liu, H., Yang, Y., & Fang, Y. (2024). A Phenomenological Model for Estimating the Wear of Horizontally Straight Slurry Discharge Pipes: A Case Study. Lubricants, 12(6), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12060228





