Combined Effect of Fluid Cavitation and Inertia on the Pressure Buildup of Parallel Textured Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Models
2.1. Geometrical Model
2.2. Mathematical Model
- The roughness of parallel surfaces is neglected, and the slip flow between the surfaces and the fluid film are not considered.
- The flow regime of the fluid film is laminar, as calculated from Re.
2.2.1. Mixture Mass and Momentum Equations
2.2.2. Mass Transfer Equations
2.2.3. Cavitation Source Term: RPE Model
2.2.4. Boundary Conditions
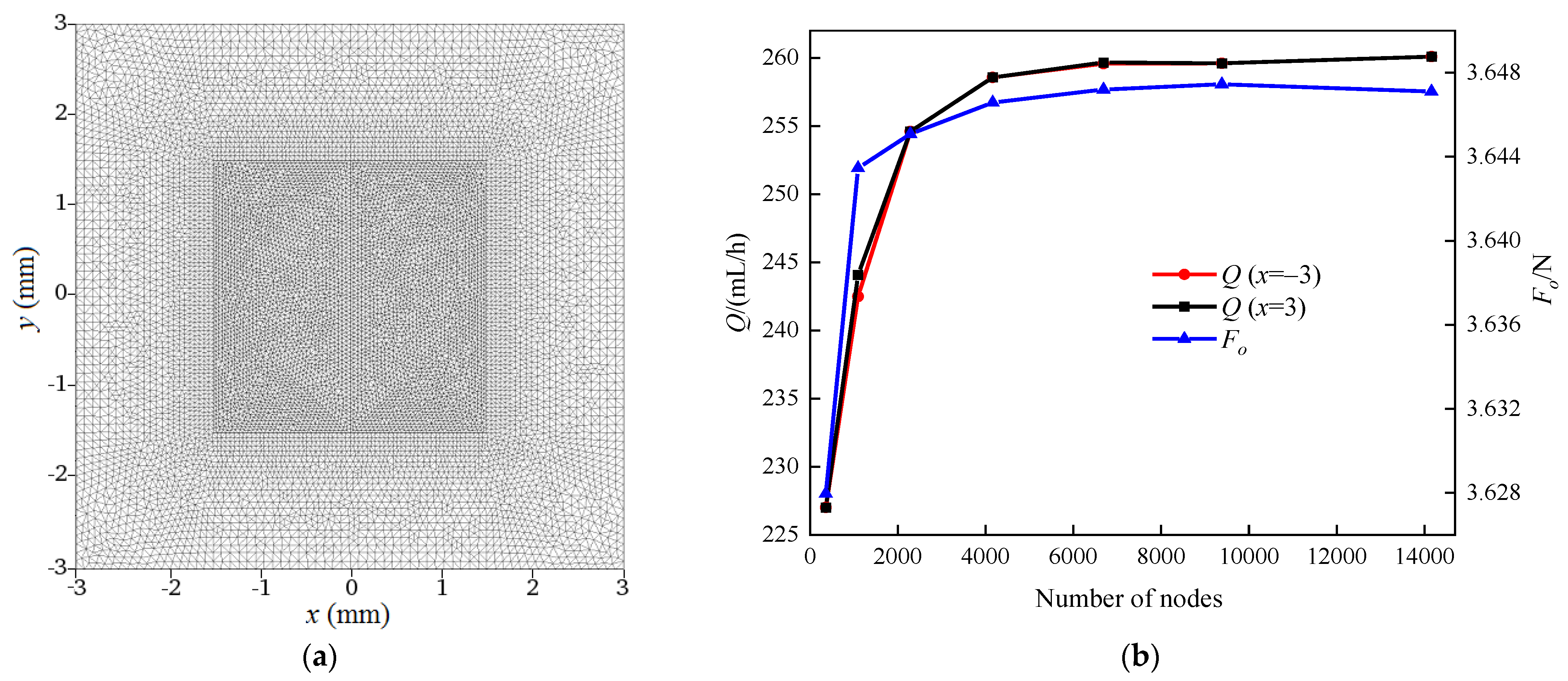
3. Numerical Procedure
- (1).
- Input geometric and operating parameters.
- (2).
- Give initial values X(0) (p(0), qx(0), qy(0), FL(0)) to unknown variables X (p, qx, qy, FL), and impose pre-boundary conditions.
- (3).
- Calculate the physical property parameters ρ, μ and flow characteristic parameters Ixx, Ixy, and Iyy.
- (4).
- Solve Equation (38) and obtain the pressure and flow rate distributions.
- (5).
- Solve Equation (39) based on step (4) and obtain the liquid volume fraction distribution.
- (6).
- Check the convergence criterion. If the unknowns meet the tolerance, end the iteration; otherwise, go to step (3) and repeat the procedure.
- (7).
- Output results and post-processing.
4. Results and Discussion
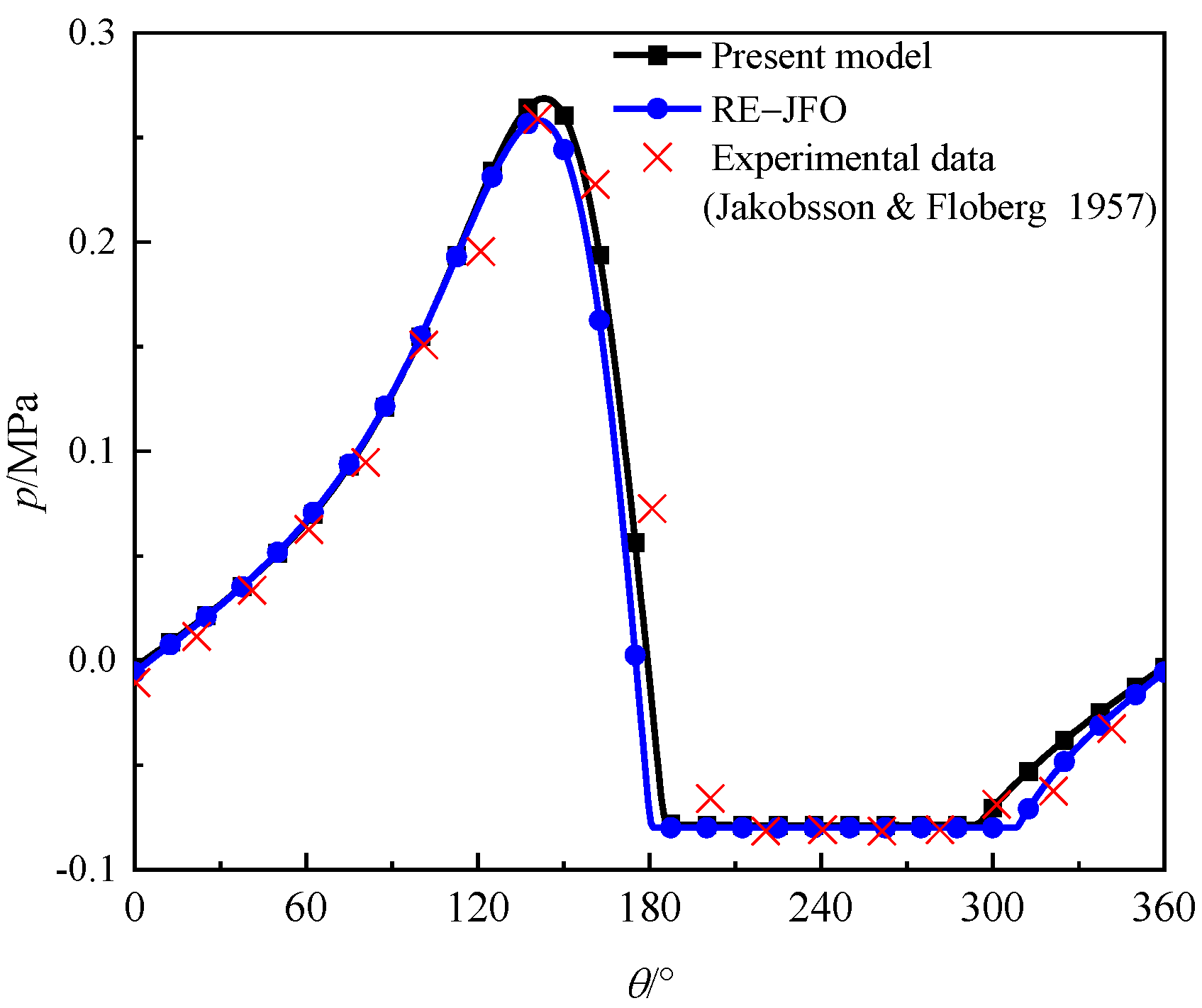
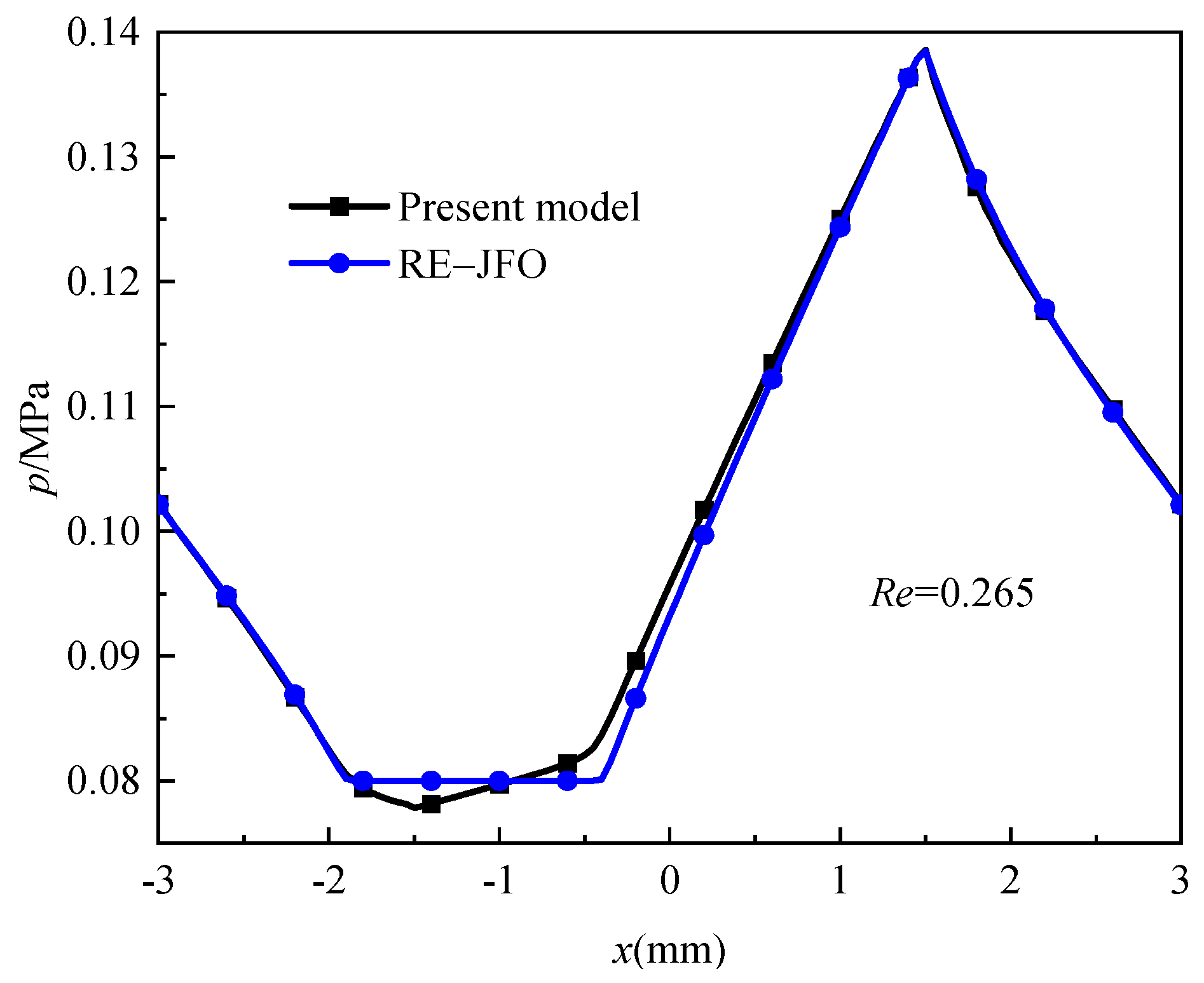
4.1. Validation
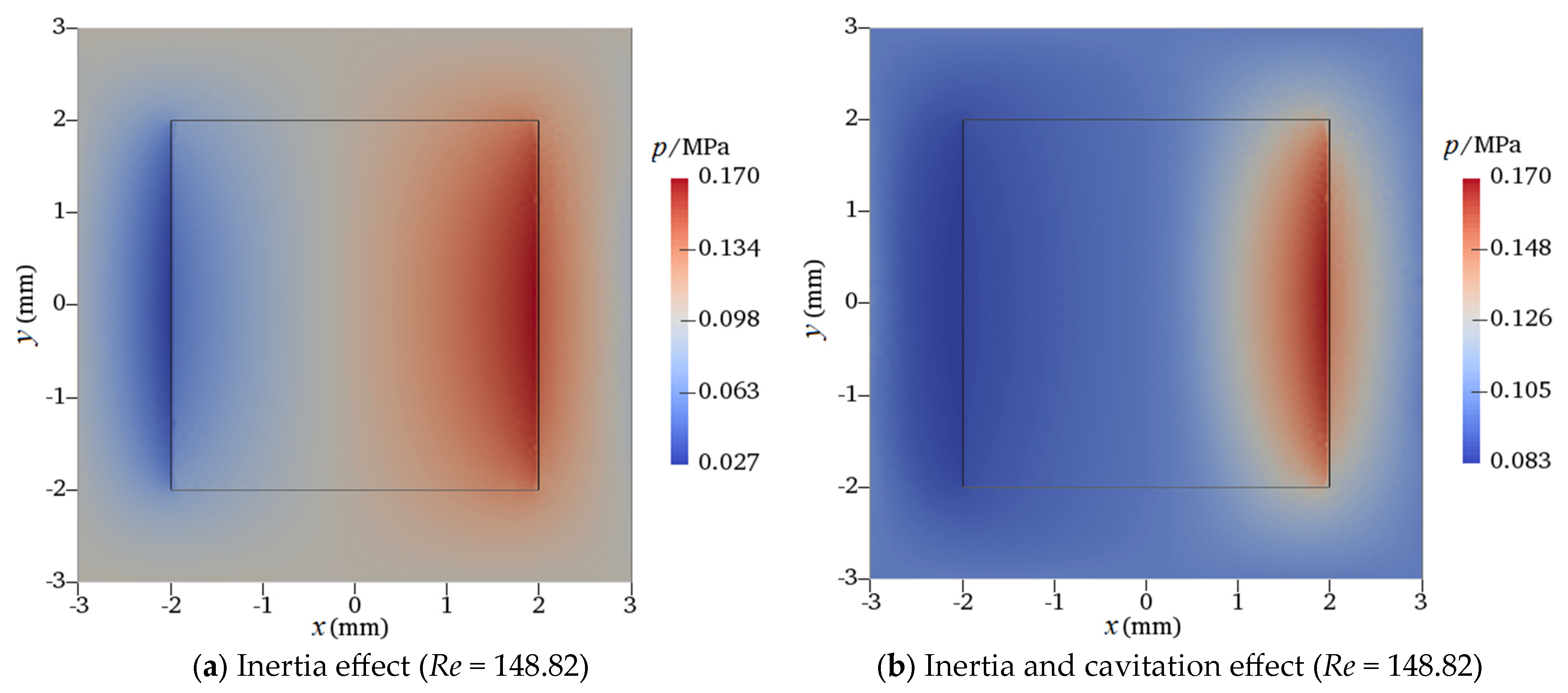
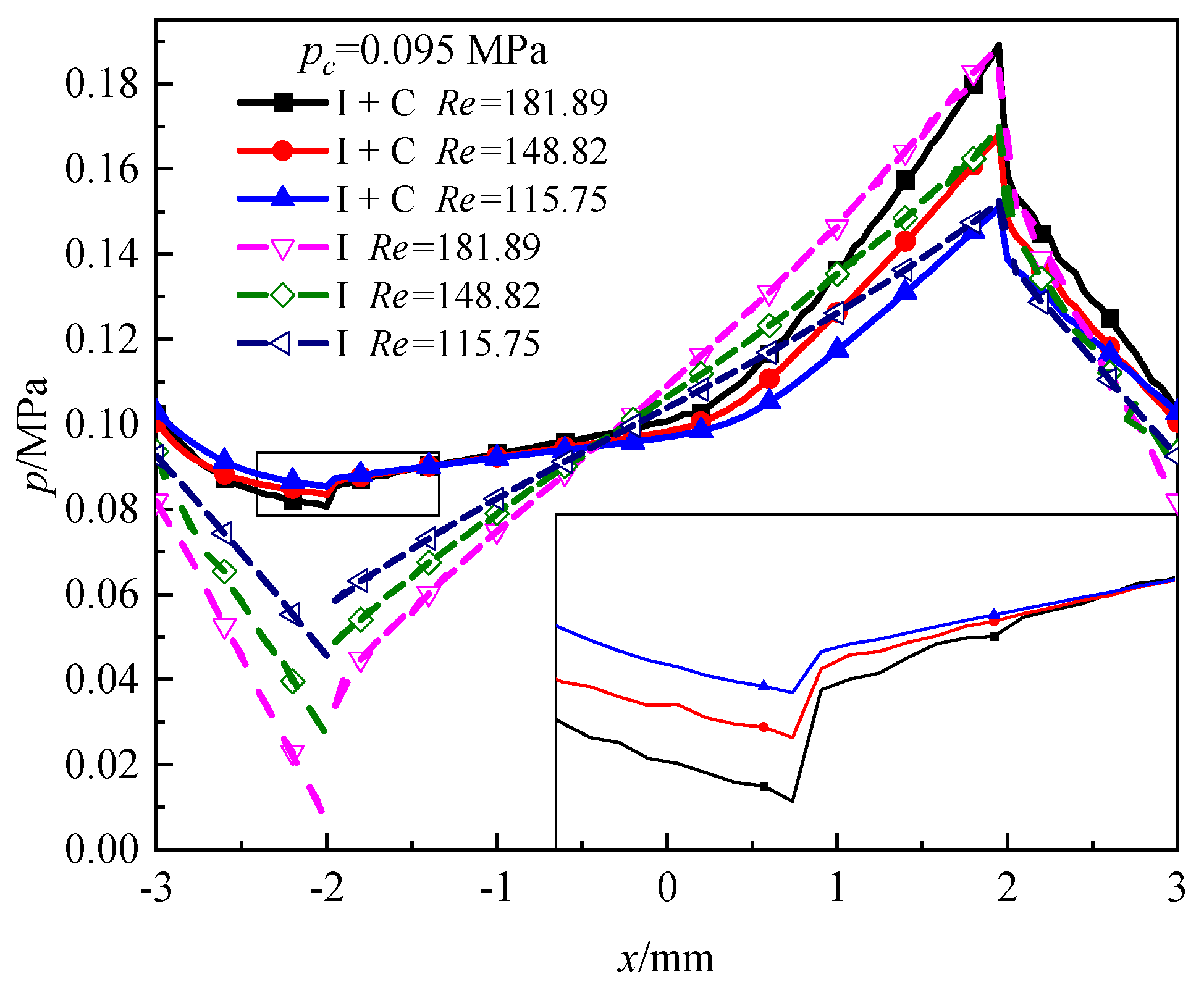
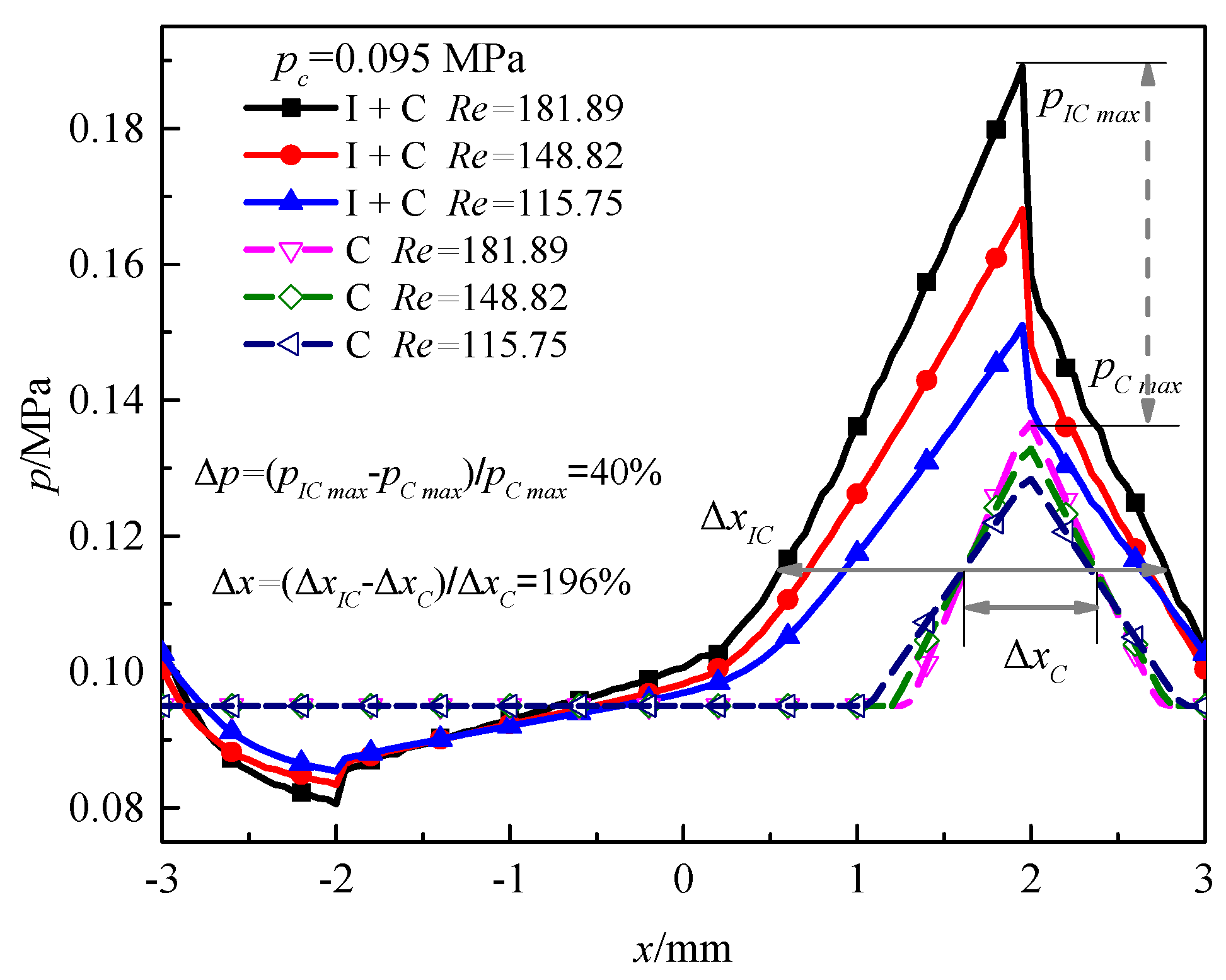
4.2. Effect of Re
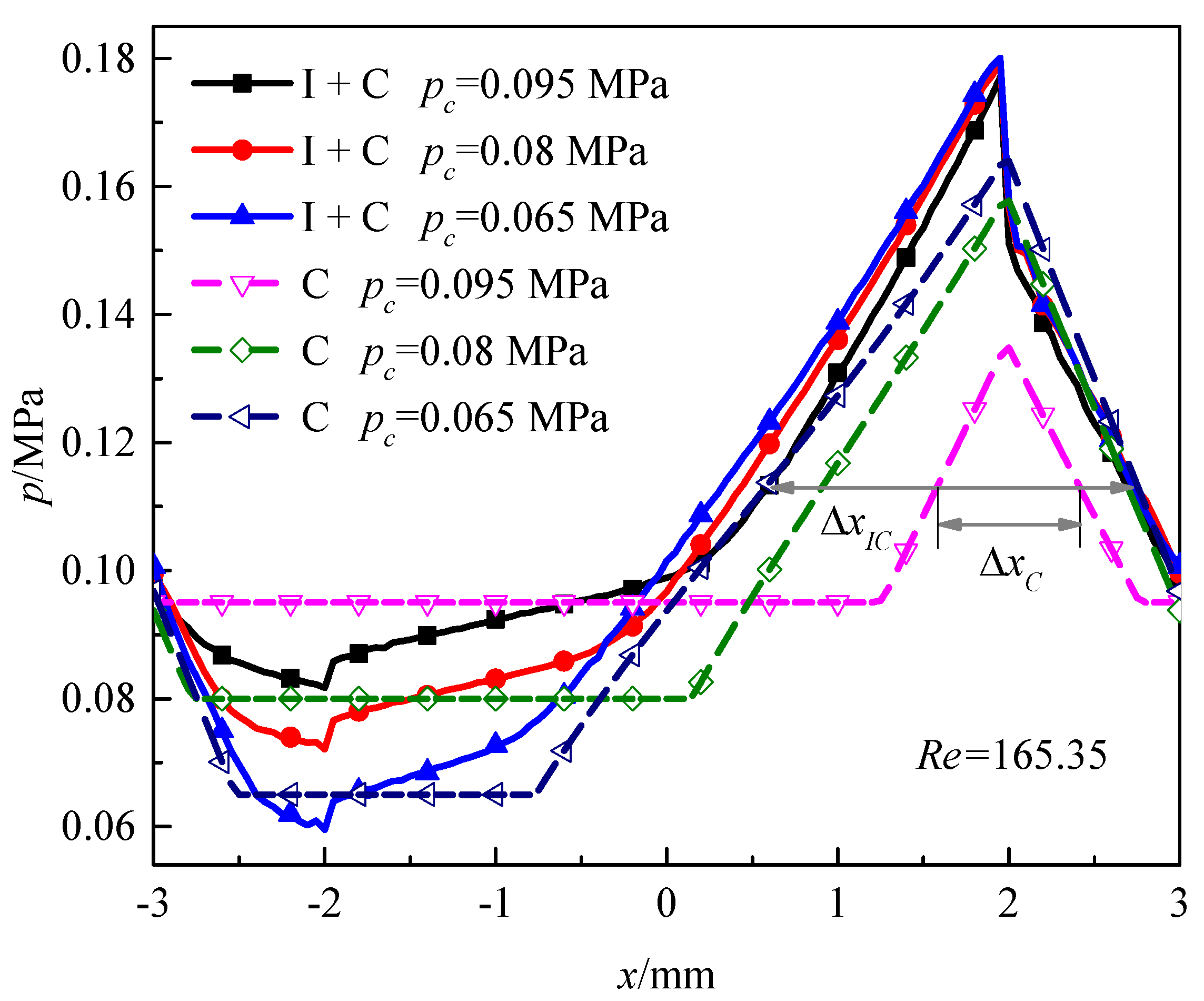
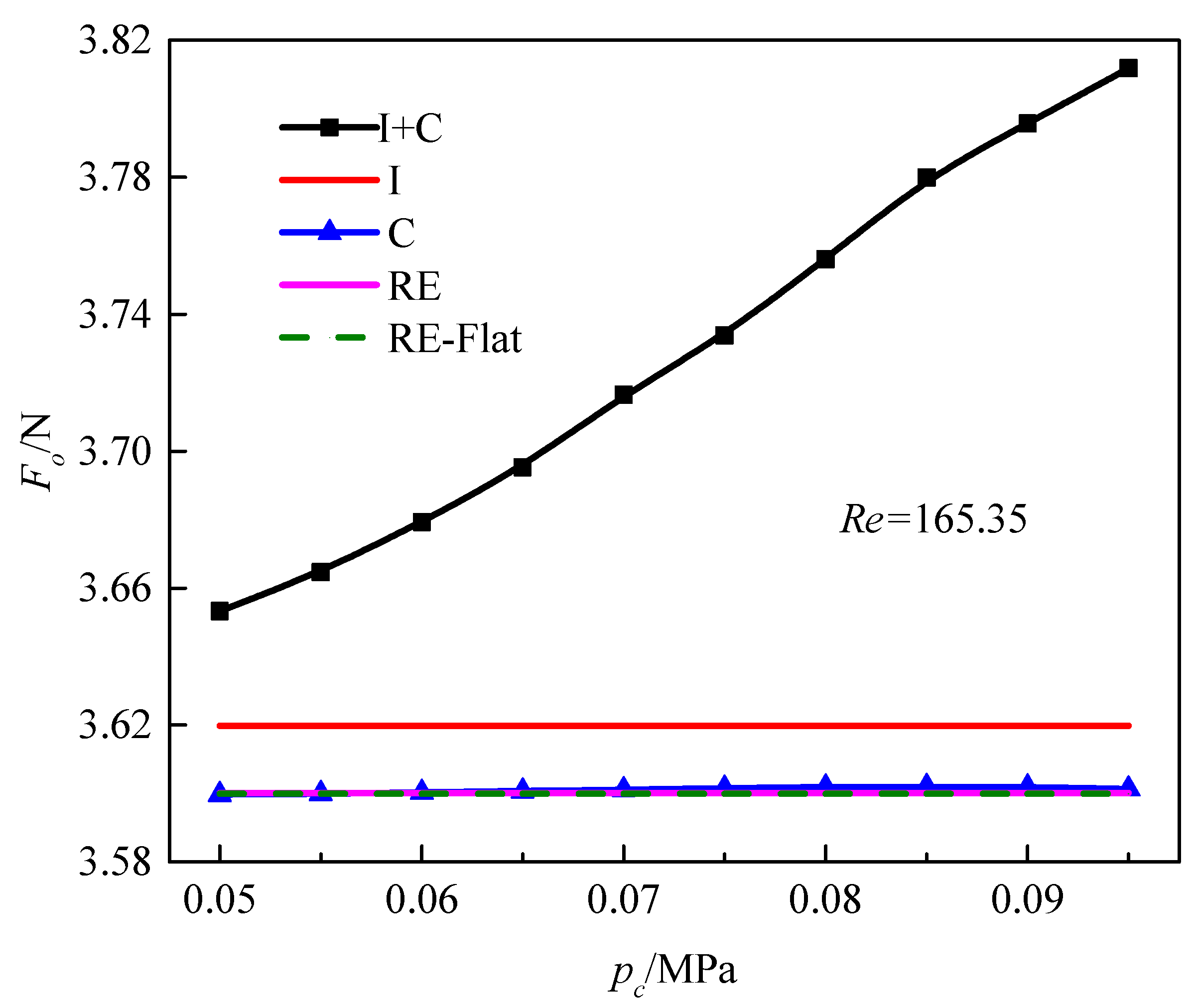
4.3. Effect of pc
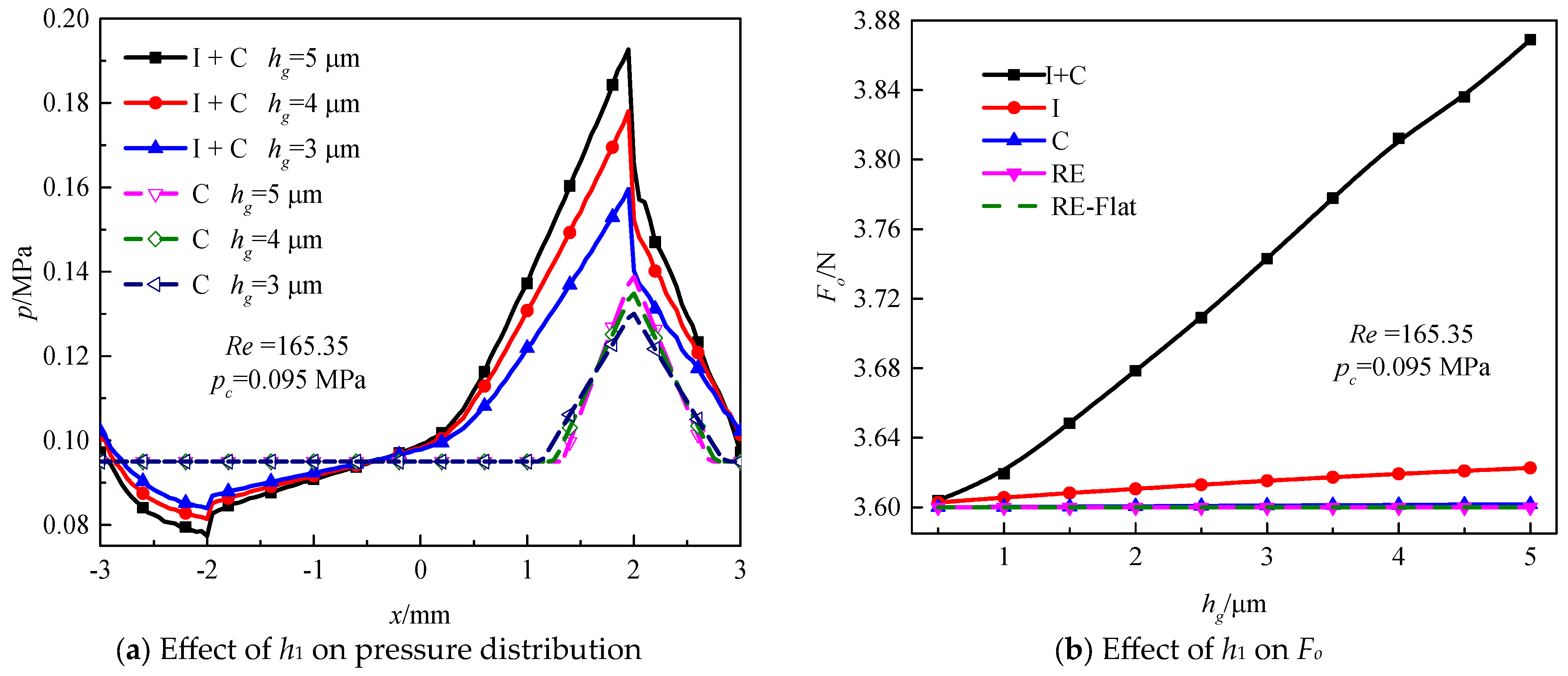
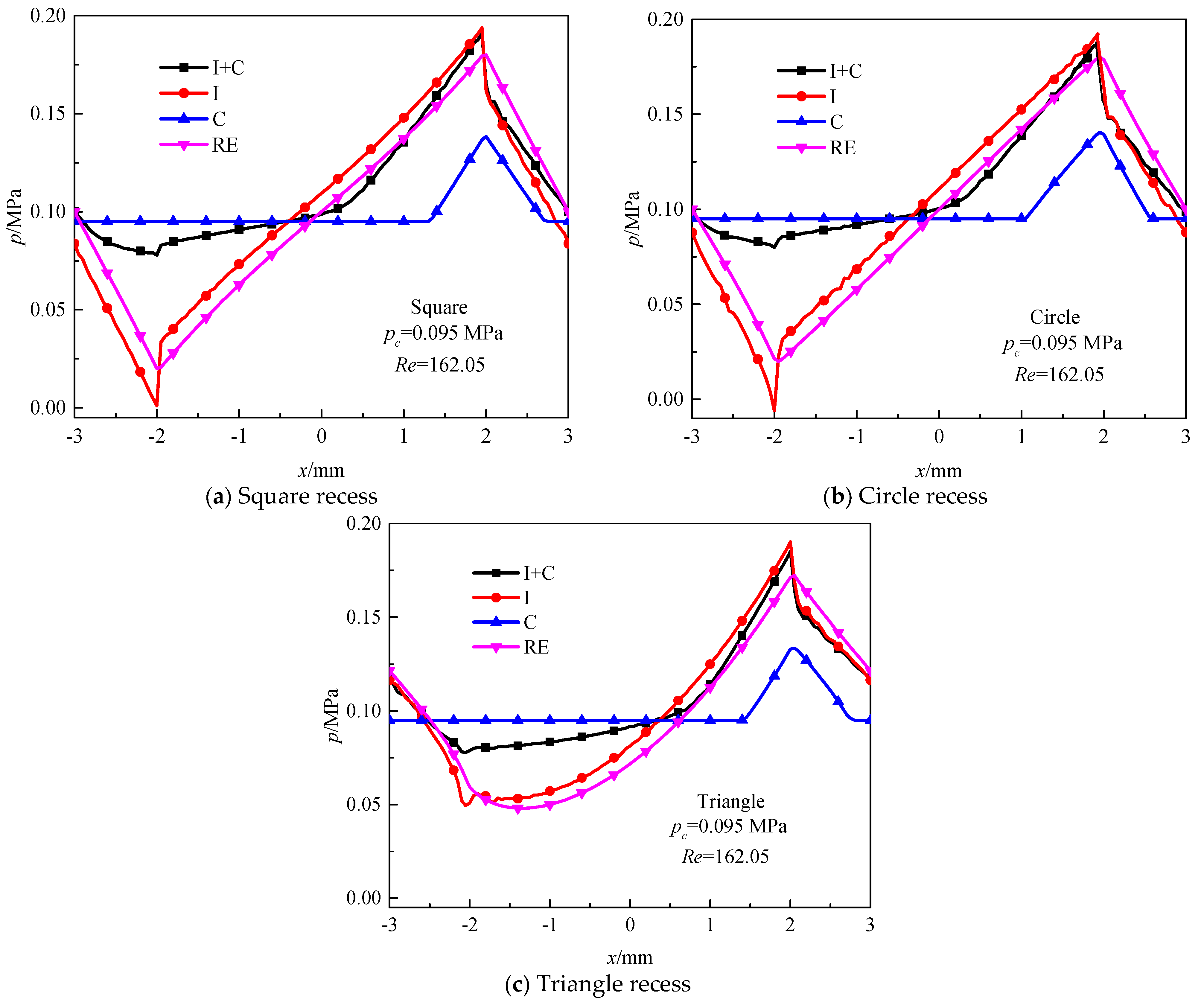
4.4. Effect of Sr, h1 and Shapes
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ŕb | Dynamic radius of cavitation bubbles, m | Re | Reynolds number, Re = ρLu0h0/μL |
| C1, C2 | Empirical coefficient of vapor liquid transition | S | Cavitation source term, kg/(m3∙s) |
| FG, FL | Vapor and liquid volume fraction per unit volume | T | Comprehensive coefficient |
| Fo | Load-carrying capacity, N | u | Velocity in x direction, m/s |
| h | Fluid film thickness, m | u0 | Sliding velocity in x direction, m/s |
| h0, h1 | Gap thickness and square recess depth, m | v | Velocity in y direction, m/s |
| Ixx, Ixy, Iyy | Flow characteristic parameters, m3/s2 | v0 | Sliding velocity in y direction, m/s |
| lx, ly | Unit vectors in x and y directions | VG, VL | Vapor and liquid volume |
| N | Number of initial bubbles per unit volume | w | Velocity in z direction, m/s |
| p | Fluid film pressure, Pa | W0, W1 | Slider and square recess length, m |
| pa, pc | Ambient pressure and cavitation pressure, Pa | x, y, z | Cartesian coordinate, m |
| Q | Flow rate, m3/s | λF, λqp | Downhill factors |
| qx, qy | Flow rates of unit length in x and y directions, m2/s | μ, μG, μ L | Mixture, vapor and liquid dynamic viscosity, Pa∙s |
| Rb | Bubbles initial average radius, m | ρ, ρG, ρ L | Mixture, vapor and liquid density, kg/m3 |
References
- Braun, M.J.; Hannon, W.M. Cavitation formation and modelling for fluid film bearings: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2010, 224, 839–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salant, R.F.; Homiller, S.J. Stiffness and leakage in spiral groove upstream pumping mechanical seals. Tribol. Trans. 1993, 36, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Burstein, L. A model for mechanical seals with regular microsurface structure. Tribol. Trans. 1996, 39, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Y.; Khonsari, M.M. Performance analysis of full-film textured surfaces with consideration of roughness effects. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 021704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X. Suction effect of cavitation in the reverse-spiral-grooved mechanical face seals. Tribol. Int. 2019, 132, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Bao, Q.; Li, K.; Khonsari, M.M.; Zhao, H. An investigation into the transient behavior of journal bearing with surface texture based on fluid-structure interaction approach. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, J.P.; Ge, S.R. Hydrodynamic lubrication of microdimple textured surface using three-dimensional CFD. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, J.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ge, S.R.; Zhu, H. Hydrodynamic lubrication of surfaces with asymmetric microdimple. Tribol. Trans. 2011, 54, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Peng, X. Fluid inertia effect on spiral-grooved mechanical face seals considering cavitation effects. Tribol. Trans. 2021, 64, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausas, R.; Ragot, P.; Leiva, J.; Jai, M.; Bayada, G.; Buscaglia, G.C. The impact of the cavitation model in the analysis of microtextured lubricated journal bearings. J. Tribol. 2007, 129, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Y.; Khonsari, M.M. On the prediction of cavitation in dimples using a mass-conservative algorithm. J. Tribol. 2009, 131, 041702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Meng, Y.G. Direct observation of cavitation phenomenon and hydrodynamic lubrication analysis of textured surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 46, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.K.; Athavale, M.M.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y. Mathematical basis and validation of the full cavitation model. J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, F.; Rey, R.; Gerber, A.G.; Belamri, T.; Hutchinson, B. Numerical and experimental investigations of the cavitating behavior of an inducer. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2004, 10, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesset, M.S. The dynamics of cavitation bubbles. J. Appl. Mech. 1949, 16, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.J.; Shahmohamadi, H.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Garner, C.P. Combined experimental and multiphase computational fluid dynamics analysis of surface textured journal bearings in mixed regime of lubrication. Lubr. Sci. 2018, 30, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohamadi, H.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Garner, C.P.; Dowson, D. Big end bearing losses with thermal cavitation flow under cylinder deactivation. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 57, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhande, D.Y.; Pande, D.W. Multiphase flow analysis of hydrodynamic journal bearing using CFD coupled fluid structure interaction considering cavitation. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2018, 30, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupillard, S.; Glavatskih, S.; Cervantes, M.J. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of a journal bearing with surface texturing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2008, 222, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Choudhury, A.; Sahu, S. CFD investigation of influences of reverse textures on bearing surface of a journal bearing. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2014, 7, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Gu, C.W. Development and validation of a three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics analysis for journal bearings considering cavitation and conjugate heat transfer. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2015, 137, 122502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, W.F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Y.M. A homogeneous phase change model for two-phase mechanical seals with three-dimensional face structures. J. Tribol. 2014, 136, 041708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, V.N.; Galetuse, S. Operating characteristics of journal bearings in turbulent inertial flow. J. Lubr. Technol. 1982, 104, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetière, N.; Tournerie, B. Finite element solution of inertia influenced flow in thin fluid films. J. Tribol. 2007, 129, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, W.F.; Liu, X.F.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y.M. Experimental study of two-phase mechanical face seals with laser surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Stephens, L.S.; Wenk, J.F. Experimental benchmarking of the numerical model of a radial lip seal with a surface textured shaft. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.V.V.L.N.; Rani, A.M.A.; Nagarajan, T.; Hashim, F.M. Analysis of slider and journal bearing using partially textured slip surface. Tribol. Int. 2012, 56, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.T.; Sadeghi, F.; Rateick, G.R.; Rowan, S.; Laboda, D. Temperature distribution in pocketed thrust washers. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanik, E. Modelling the hydrodynamic support of cylinder bore and piston rings with laser textured surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgut, M.; Nobile, E.; Bilus, I. Comparison of mass transfer models for the numerical prediction of sheet cavitation around a hydrofoil. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2011, 37, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, B.; Floberg, L. The Finite Journal Bearing, Considering Vaporization; Chalmers Tekniska Högskolas Handlingar: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.K.; Bai, S.X.; Peng, X.D. Lubrication film flow control by oriented dimples for liquid lubricated mechanical seals. Tribol. Int. 2014, 77, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Ludwig, L.P. Observation of pressure variation in the cavitation region of submerged journal bearings. ASME J. Lubr. Tech. 1982, 104, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.C.; Brewe, D.E. A high-speed photography study of cavitation in a dynamically loaded journal bearing. ASME J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.C.; Brewe, D.E.; Abel, P.B. Simultaneous pressure measurement and high-speed photography study of cavitation in a dynamically loaded journal bearing. ASME J. Tribol. 1993, 115, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
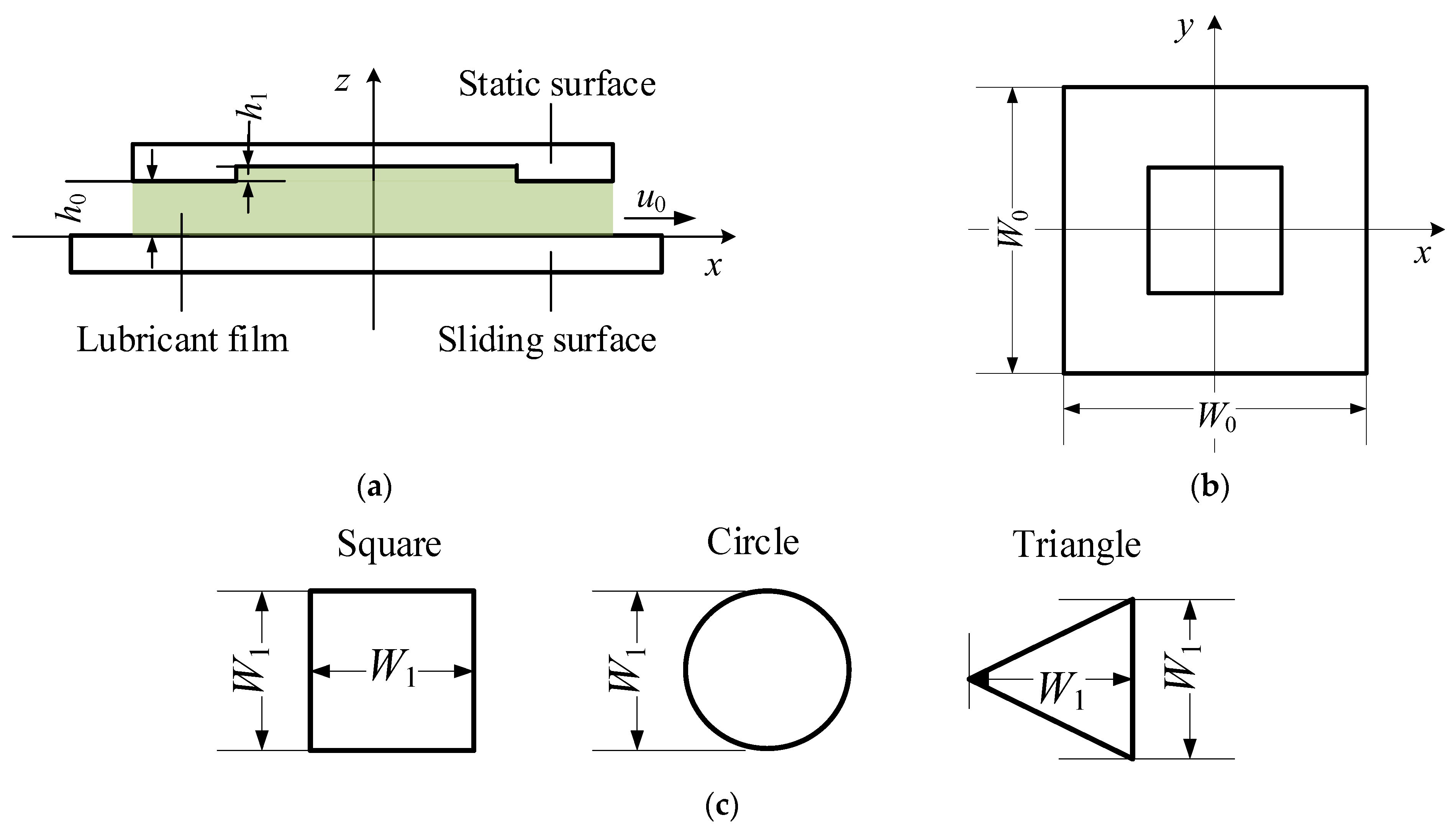



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Textured surface cell side length, W0/(mm) | 6 |
| Recess size length, W1/(mm) | 4 |
| Gap thickness, h0/(μm) | 50 |
| Recess depth, h1/(μm) | 4 |
| Ambient pressure, pa/(MPa) | 0.1 |
| Cavitation pressure, pc/(MPa) | 0.095 |
| Dynamic viscosity of liquid, μL/(Pa·s) | 0.0127 |
| Liquid density, ρL/(kg/m3) | 840 |
| Reynolds number, Re | 165.35 |
| Square | Circle | Triangle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆p | (pmax IC − pmax C)/ pmax C | 39.42% | 38.88% | 39.10% |
| (pmax I − pmax RE)/ pmax RE | 8.38% | 8.94% | 11.11% | |
| LCC | IC | 7.3% | 7% | 4.7% |
| I | 0.6% | 0.43% | 1.4% | |
| C | ≈0 | 0.4% | ≈0 | |
| RE | ≈0 | ≈0 | ≈0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X. Combined Effect of Fluid Cavitation and Inertia on the Pressure Buildup of Parallel Textured Surfaces. Lubricants 2023, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070270
Ma X. Combined Effect of Fluid Cavitation and Inertia on the Pressure Buildup of Parallel Textured Surfaces. Lubricants. 2023; 11(7):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070270
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xuezhong. 2023. "Combined Effect of Fluid Cavitation and Inertia on the Pressure Buildup of Parallel Textured Surfaces" Lubricants 11, no. 7: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070270
APA StyleMa, X. (2023). Combined Effect of Fluid Cavitation and Inertia on the Pressure Buildup of Parallel Textured Surfaces. Lubricants, 11(7), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11070270




