Exact Model Order Reduction for the Full-System Finite Element Solution of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations
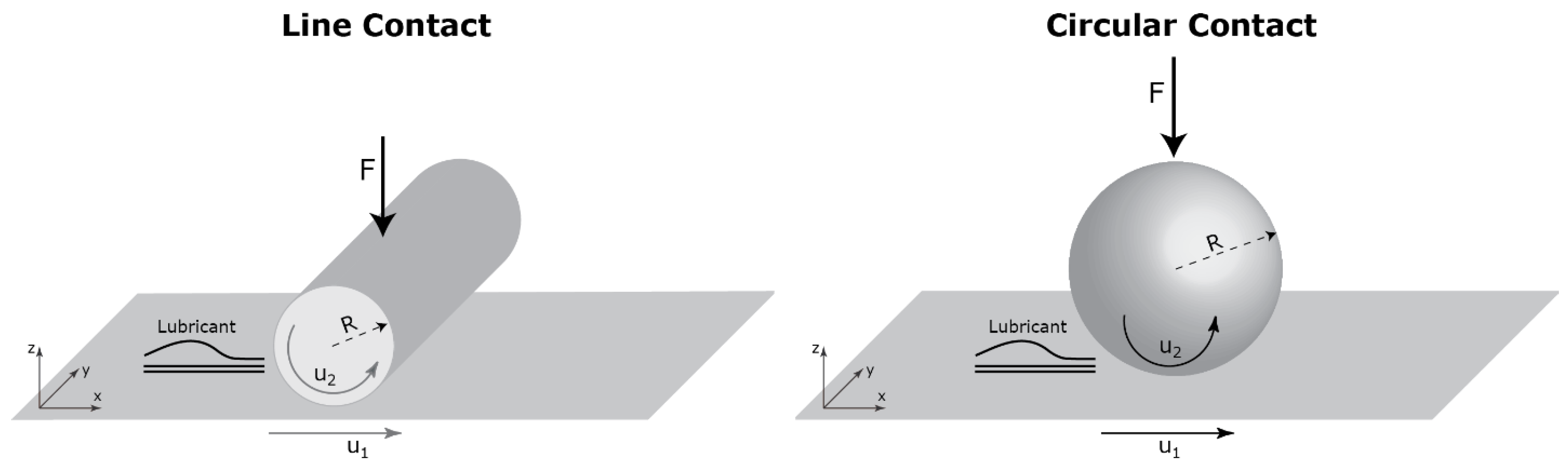
2.1. Line Contact
2.2. Circular Contact
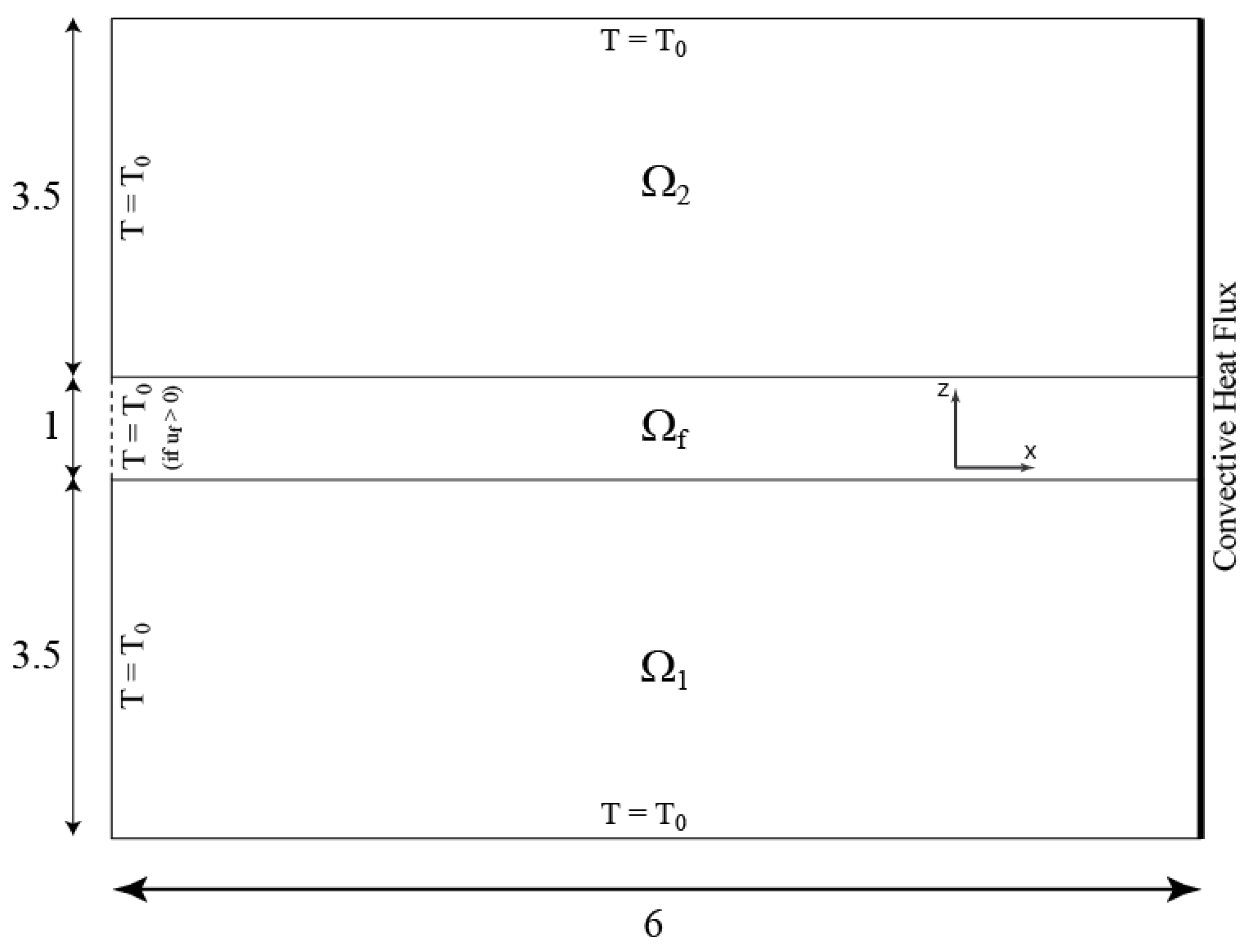
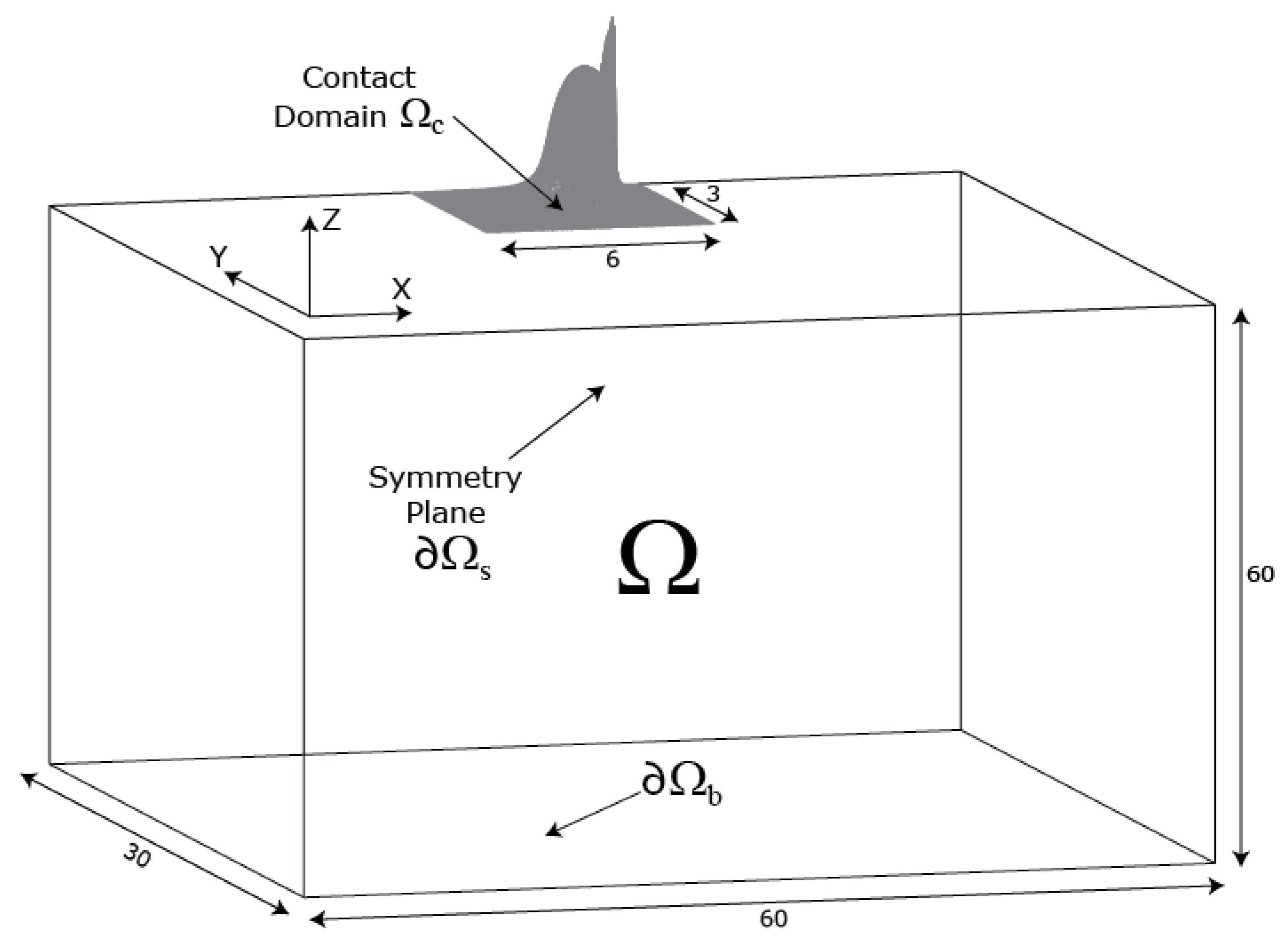
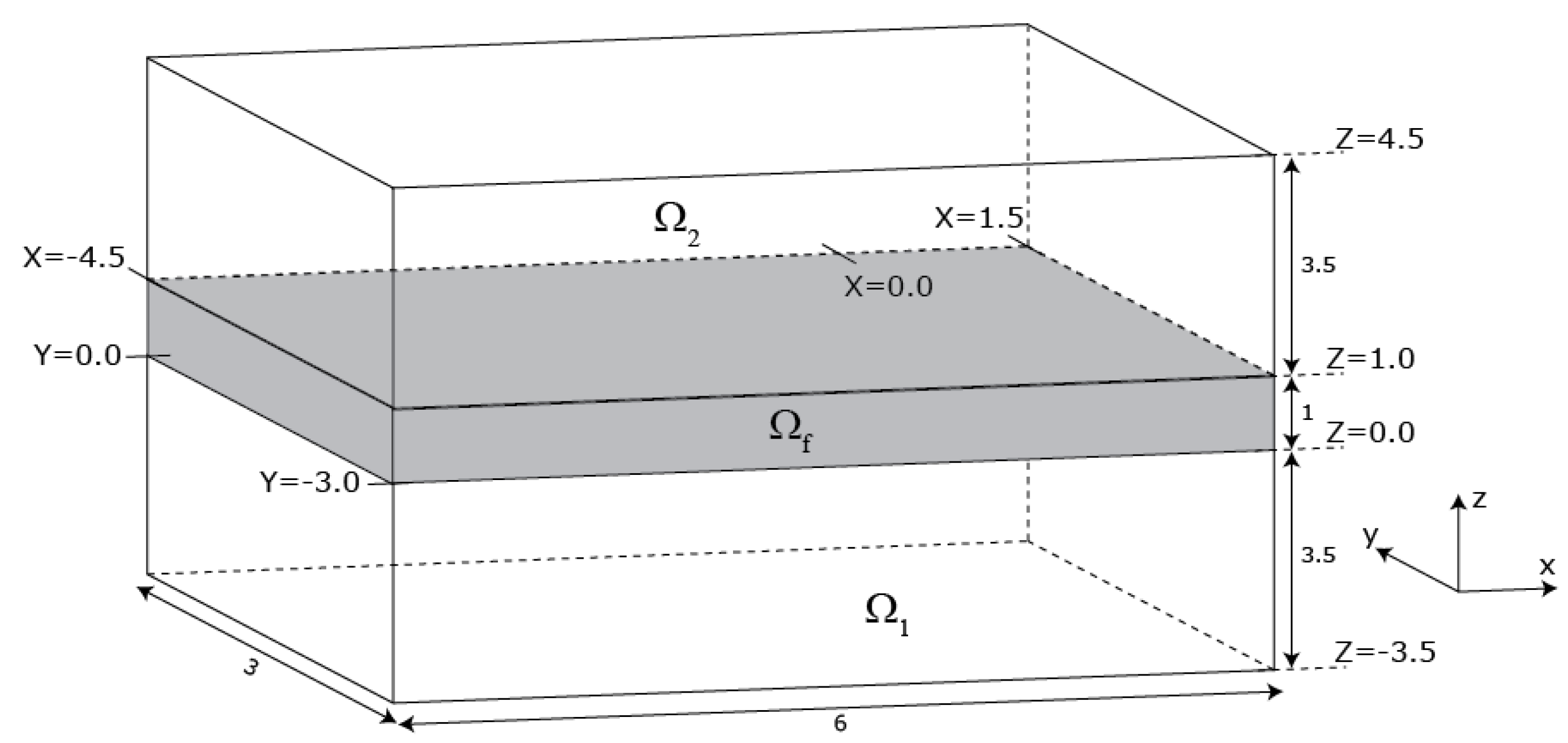
3. FEM Full Model
4. Model Order Reduction
4.1. Static Condensation
4.2. Splitting Procedure
4.3. Overall Numerical Procedure
5. Results and Discussion
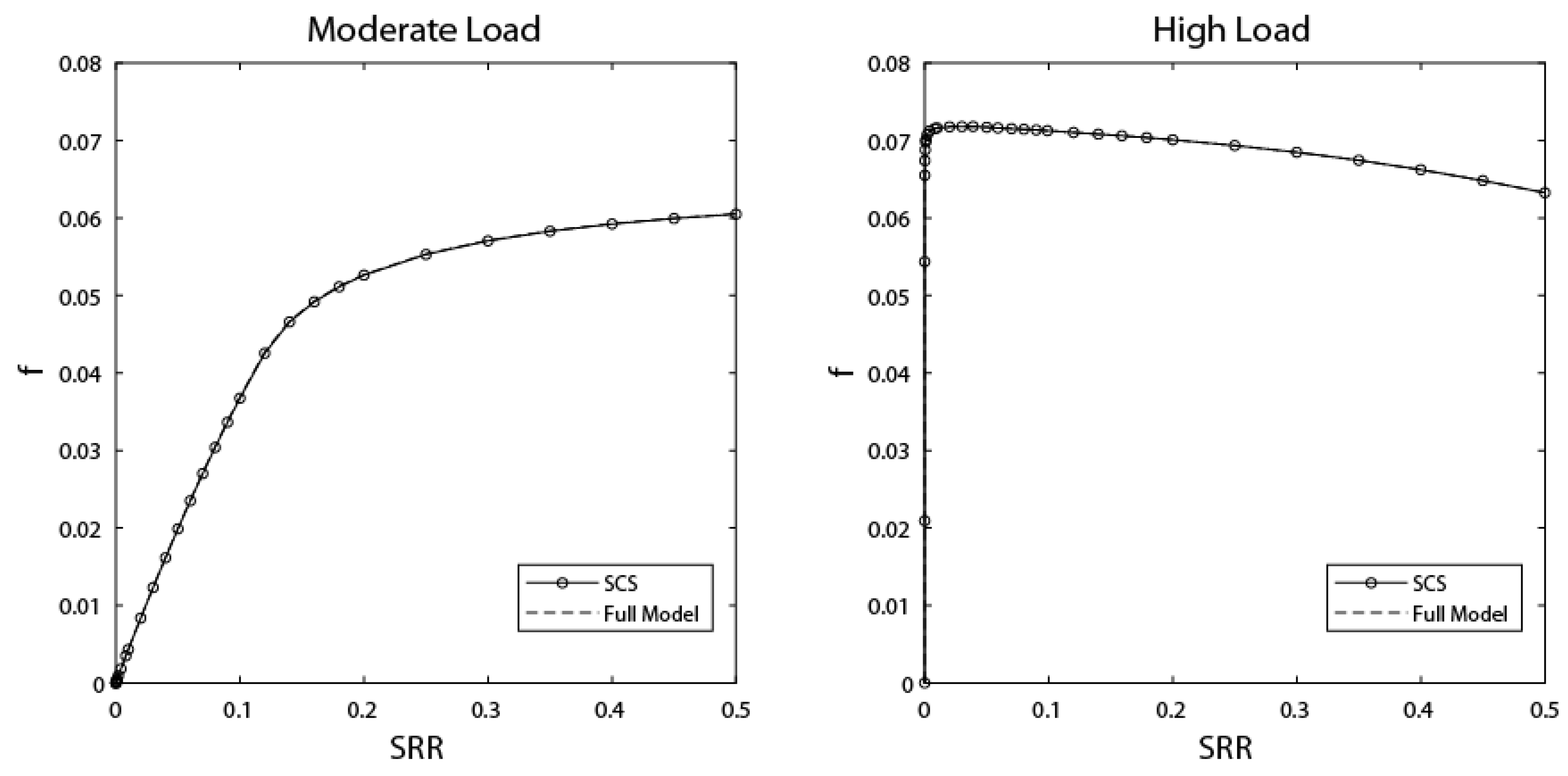
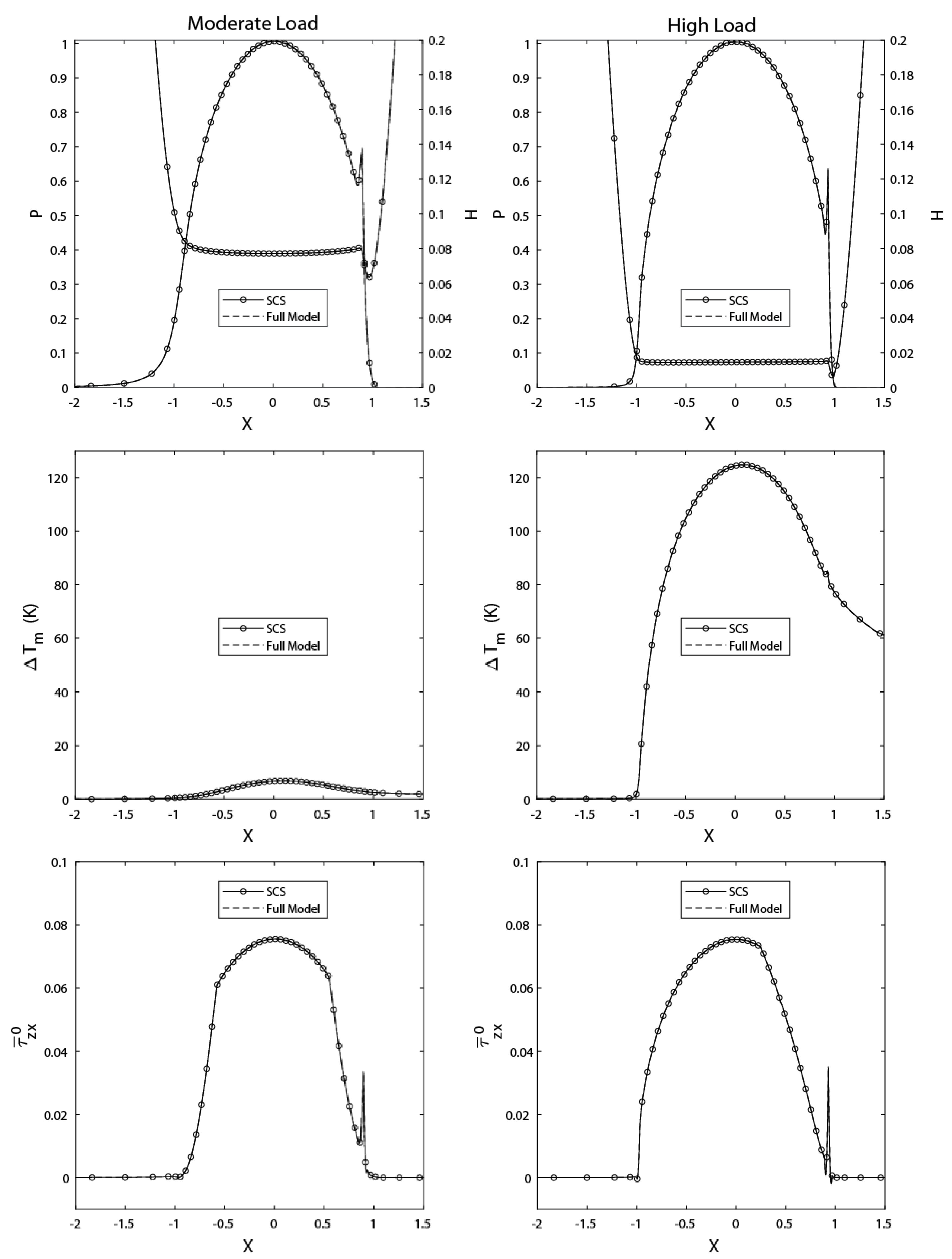
5.1. Line Contacts
5.2. Point Contacts
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Lubricant viscosity-pressure coefficient (Pa−1) | |
| Lubricant viscosity-temperature coefficient (K−1) | |
| Lubricant generalized-Newtonian viscosity (Pa·s) | |
| Lubricant dimensionless generalized-Newtonian viscosity | |
| Dimensionless first-order cross-film lubricant viscosity integral | |
| Dimensionless second-order cross-film lubricant viscosity integral | |
| Lubricant viscosity at reference state (Pa·s) | |
| Dowson and Higginson EoS density-temperature coefficient (K−1) | |
| Lubricant shear rate in the j-direction within a plane having i as normal (s−1) | |
| Lubricant low-shear/Newtonian viscosity at reference state (Pa·s) | |
| , | Dimensionless lubricant first and second Newtonian viscosities |
| , | Lubricant first and second Newtonian viscosities at reference state (Pa·s) |
| Equivalent solid Poisson coefficient | |
| , | Poisson coefficient of solids 1 and 2 |
| Equivalent solid computational domain | |
| Contact computational domain | |
| Lubricant film computational domain within thermal part | |
| , | Computational domain of solids 1 and 2 within thermal part |
| Symmetry boundary of | |
| Fixed boundary of | |
| Symmetry boundary of | |
| Lubricant limiting shear stress-pressure coefficient | |
| Lubricant density (kg/m3) | |
| , | Density of solids 1 and 2 (kg/m3) |
| Lubricant dimensionless density | |
| Dimensionless first-order cross-film lubricant density integral | |
| Dimensionless first-order cross-film density-to-viscosity double-integral | |
| Dimensionless second-order cross-film density-to-viscosity double-integral | |
| Lubricant density at reference state (kg/m3) | |
| Normal component of 2D or 3D stress tensor (Pa) | |
| Tangential component of 2D stress tensor (Pa) | |
| Vector of tangential components of 3D stress tensor (Pa) | |
| Lubricant resultant shear stress (Pa) | |
| Lubricant dimensionless resultant shear stress over plane surface | |
| Lubricant limiting shear stress (Pa) | |
| Reference shear stress (Pa) | |
| Shear stress in the j-direction within a plane having i as normal (Pa) | |
| Dimensionless shear stress in the j-direction within a plane having i as normal | |
| Dimensionless lubricant shear stress over plane surface | |
| θ | Heaviside function |
| Penalty term parameter | |
| Hertzian contact half-width (line contact) or radius (circular contact) (m) | |
| , | Double-Newtonian modified Carreau model parameters |
| , | Specific heat of solids 1 and 2 (J/kg·K) |
| Equivalent solid Young’s modulus of elasticity (Pa) | |
| , | Young’s moduli of elasticity of solids 1 and 2 (Pa) |
| Friction coefficient | |
| Contact external applied load (N/m: line contacts or N: point contacts) | |
| Lubricant critical shear stress (Pa) | |
| Lubricant film thickness (m) | |
| Dimensionless rigid-body separation | |
| Dimensionless lubricant film thickness | |
| Lubricant thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | |
| , | Thermal conductivities of solids 1 and 2 (W/m·K) |
| Total number of degrees of freedom of FEM model | |
| Total number of degrees of freedom of reduced FEM model | |
| , | Numbers of master and slave dofs in reduced FEM model |
| Pressure (Pa) | |
| Hertzian contact pressure (Pa) | |
| Reference pressure (Pa) | |
| Dimensionless pressure | |
| Compressive heat generation per unit volume (W/m3) | |
| Shear heat generation per unit volume (W/m3) | |
| Equivalent roller radius (m) | |
| Slide-to-roll ratio | |
| Temperature (K) | |
| Dimensionless temperature | |
| Reference temperature (K) | |
| Ambient temperature (K) | |
| , | Surface x-velocity components of solids 1 and 2 (m/s) |
| , | Lubricant velocity field components in the x, y-directions (m/s) |
| , , | Equivalent solid deformation components in the x, y, z-directions (m) |
| Contact mean entrainment speed in the x-direction (m/s) | |
| , , | Equivalent solid dimensionless deformation components in x, y, z-directions |
| Equivalent solid dimensionless deformation vector | |
| , , | Space coordinates (m) |
| , , | Dimensionless space coordinates |
| Subscripts | |
| Flat plane | |
| Cylinder (line contacts)/ball (point contacts) | |
| Fluid domain | |
| Elastic domain | |
| Hydrodynamic domain | |
| Load balance domain | |
| Master dofs | |
| Shear stress domain/Slave dofs | |
| Thermal domain | |
| Superscripts | |
| Plane surface | |
| Far dofs | |
| Near dofs |
References
- Cheng, H.S.; Sternlicht, B. A numerical solution for the pressure, temperature and film thickness between two infinitely long, lubricated rolling and sliding cylinders, under heavy loads. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1965, 87, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S. A refined solution to the thermal-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of rolling and sliding cylinders. ASLE Trans. 1965, 8, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wen, S. A full numerical solution for the thermo-elastohydrodynamic problem in elliptical contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 1984, 106, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yang, P.; Qu, S. On the theory of thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication at high slide-roll ratios—Circular glass-steel contact solution at opposite sliding. ASME J. Tribol. 2001, 123, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Yang, P.; Kaneta, M. Non-Newtonian thermal analyses of point EHL contacts using the Eyring model. ASME J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Sadeghi, F. Three-Dimensional Temperature Distribution in EHD Lubrication: Part I—Circular Contact. ASME J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Saka, N. Thermal Non-Newtonian Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Rolling Line Contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, R.; Kubo, A. The Application of Newton-Raphson Method to Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 1994, 116, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazama, T.; Ehret, P.; Taylor, C.M. On the Effects of the Temperature Profile Approximation in the Thermal Newtonian Solutions of Elastohydrodynamic Line Contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2001, 215, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ehret, P.; Dowson, D.; Taylor, C.M. Thermal elastohydrodynamic analysis of circular contacts, Part 1: Newtonian model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2001, 215, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ehret, P.; Dowson, D.; Taylor, C.M. Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Analysis of Circular Contacts, Part 2: Non-Newtonian Model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2001, 215, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wong, P.L.; Zhang, Z. Thermal Non-Newtonian EHL Analysis of Rib-Roller End Contact in Tapered Roller Bearings. ASME J. Tribol. 1995, 117, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.T.; Hsu, C.H.; Kuo, W.F. Multilevel Solution for Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Rolling-Sliding Circular Contacts. Tribol. Int. 1995, 28, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R. A Numerical Solution of the Elastohydrodynamic Problem. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1959, 1, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Dowson, D. Isothermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Point Contacts. Part I—Theoretical Formulation. ASME J. Lubr. Technol. 1976, 98, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.P.; Rohde, S.M. Numerical Solution of the Point Contact Problem Using the Finite Element Method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1977, 11, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, S.M.; Oh, K.P. A Unified Treatment of Thick and Thin Film Elastohydrodynamic Problems by Using Higher Order Element Methods. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1975, 343, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.A.; Evans, H.P.; Hughes, T.G.; Snidle, R.W. Transient Elastohydrodynamic Point Contact Analysis using a New Coupled Differential Deflection Method. Part I: Theory and Validation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2003, 217, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyere, V.; Fillot, N.; Morales-Espejel, G.E.; Vergne, P. Computational Fluid Dynamics and Full Elasticity Model for Sliding Line Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2012, 46, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W. Finite Element Modeling of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2018; ISBN 9781119225126. [Google Scholar]
- Habchi, W.; Eyheramendy, D.; Vergne, P.; Morales-Espejel, G. A Full-System Approach of the Elastohydrodynamic Line/Point Contact Problem. ASME J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Eyheramendy, D.; Vergne, P.; Morales-Espejel, G. Stabilized Fully-Coupled Finite Elements for Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 46, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.R. A Penalty Formulation and Numerical Approximation of the Reynolds-Hertz Problem of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1986, 24, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Issa, J. Fast and Reduced Full-System Finite Element Solution of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems: Line Contacts. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2013, 56, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, D.; Hager, C.; Hetzler, H.; Fillot, N.; Vergne, P.; Dureisseix, D.; Seemann, W. A Nonlinear Model Order Reduction Approach to the Elastohydrodynamic Problem. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, D.; Hager, C.; Hetzler, H.; Fillot, N.; Vergne, P.; Dureisseix, D.; Seemann, W. Fast Solution of Transient Elastohydrodynamic Line Contact Problems using the Trajectory Piecewise Linear Approach. ASME J. Tribol. 2016, 138, 011502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurria, L.; Fauconnier, D.; Jiranek, P.; Tamarozzi, T. A Galerkin/hyper-reduction technique to reduce steady-state elastohydrodynamic line contact problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 386, 114132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Issa, J.S. An exact and general model order reduction technique for finite element solution of elastohydrodynamic lubrication problems. ASME J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 051501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyan, R.J. Reduction of Stiffness and Mass Matrices. AIAA J. 1965, 3, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W. A Schur-complement model-order-reduction technique for the finite element solution of transient elastohydrodynamic lubrication problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 127, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W. Coupling Strategies for Finite Element Modeling of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems. ASME J. Tribol. 2016, 139, 041501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, O. On the Theory of the Lubrication and its Application to Mr. Beauchamp Tower’s Experiments, Including an Experimental Determination of the Viscosity of Olive Oil. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1886, 177, 157–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wen, S. A Generalized Reynolds Equation for Non-Newtonian Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. ASME J. Tribol. 1990, 112, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, M.; Shigeta, T.; Yang, P. Film Pressure Distributions in Point Contacts Predicted by Thermal EHL Analysis. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Tong, J.; Yang, P. Transient Thermoelastohydrodynamic Lubrication Analysis of an Involute Spur Gear. Tribol. Int. 2004, 37, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuflhard, P. Newton Methods for Nonlinear Problems, Affine Invariance and Adaptive Algorithms; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, B.M. Structural Eigenvalue Problems, Elimination of Unwanted Variables. AIAA J. 1965, 3, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Duff, I.S. An Unsymmetric-Pattern Multifrontal Method for Sparse LU Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 1997, 18, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Wang, D. An Analysis of the Normal Bouncing of a Solid Elastic Ball on an Oily Plate. Wear 1994, 179, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.P.; Hughes, T.G. Evaluation of Deflection in Semi-Infinite Bodies by a Differential Method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2000, 214, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W. Reduced Order Finite Element Model for Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication: Circular Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2014, 71, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S. High Pressure Rheology for Quantitative Elastohydrodynamics, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelands, C.J.A. Correlational Aspects of the Viscosity-Temperature-Pressure Relationship of Lubricating Oils. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hogeschool, Delft, The Netherlands, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. In The Fundamental of Roller and Gear Lubrication; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1966; ISBN 9780080114729. [Google Scholar]
- Vergne, P.; Bair, S. Classical EHL Versus Quantitative EHL: A Perspective Part I—Real Viscosity-Pressure Dependence and the Viscosity-Pressure Coefficient for Predicting Film Thickness. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.; Martinie, L.; Vergne, P. Classical EHL Versus Quantitative EHL: A Perspective Part II—Super-Arrhenius Piezoviscosity, an Essential Component of Elastohydrodynamic Friction Missing from Classical EHL. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.; Winer, W.O. A New High Pressure, High Shear Stress Viscometer and Results for Lubricants. Tribol. Trans. 1990, 112, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Eyheramendy, D.; Bair, S.; Vergne, P.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Point Contacts Using a Newtonian/Generalized Newtonian Lubricant. Tribol. Lett. 2008, 30, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, W.; Vergne, P.; Bair, S.; Andersson, O.; Eyheramendy, D.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. Influence of Pressure and Temperature Dependence of Thermal Properties of a Lubricant on the Behavior of Circular TEHD Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björling, M.; Habchi, W.; Bair, S.; Larsson, R.; Marklund, P. Towards the True Prediction of EHL Friction. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björling, M.; Habchi, W.; Bair, S.; Larsson, R.; Marklund, P. Friction Reduction in Elastohydrodynamic Contacts by Thin Layer Thermal Insulation. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material Properties | Operating Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lubricant | |||
| Line Contacts | |||
| Moderate Load | Heavy Load | ||
| Solids | |||
| Point Contacts | |||
| Moderate Load | Heavy Load | ||
| Load | Full Model | SCS Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Newt. Iter. | cpu Time (s) | # Newt. Iter. | cpu Time (s) | |
| Moderate | 90 | 126.6 | 119 | 118.4 |
| High | 421 | 487.3 | 436 | 398.8 |
| Load | Full Model | SCS Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Newt. Iter. | cpu Time (s) | # Newt. Iter. | cpu Time (s) | |
| Moderate | 85 | 107,356 | 102 | 49,937 |
| High | 451 | 572,022 | 459 | 257,302 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mounayer, J.; Habchi, W. Exact Model Order Reduction for the Full-System Finite Element Solution of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems. Lubricants 2023, 11, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020061
Mounayer J, Habchi W. Exact Model Order Reduction for the Full-System Finite Element Solution of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems. Lubricants. 2023; 11(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMounayer, Jad, and Wassim Habchi. 2023. "Exact Model Order Reduction for the Full-System Finite Element Solution of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems" Lubricants 11, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020061
APA StyleMounayer, J., & Habchi, W. (2023). Exact Model Order Reduction for the Full-System Finite Element Solution of Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Problems. Lubricants, 11(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11020061






