Abstract
Radio relics are arc-like synchrotron sources at the periphery of galaxy clusters, produced by cosmic-ray electrons in a G magnetic field, which are believed to have been (re-)accelerated by merger shock fronts. However, not all relics appear at the same location as shocks as seen in the X-ray. In a previous work, we suggested that the shape of some relics may result from the pre-existing spatial distribution of cosmic-ray electrons, and tested this hypothesis using simulations by launching AGN jets into a cluster atmosphere with sloshing gas motions generated by a previous merger event. We showed that these motions could transport the cosmic ray-enriched material of the AGN bubbles to large radii and stretch it in a tangential direction, producing a filamentary shape resembling a radio relic. In this work, we improve our physical description for the cosmic rays by modeling them as a separate fluid which undergoes diffusion and Alfvén losses. We find that, including this additional cosmic ray physics significantly diminishes the appearance of these filamentary features, showing that our original hypothesis is sensitive to the modeling of cosmic ray physics in the intracluster medium.
1. Introduction
In galaxy cluster mergers, the kinetic energy of the clusters’ hot plasma (the intracluster medium, ICM) is dissipated via shock waves and turbulence into heat, the amplification of magnetic fields, and acceleration of cosmic rays (CRs). CR electrons (CRe) with ∼– are observed in clusters via synchrotron radio emission in the ∼G magnetic field of clusters. The brightest sources are the radio lobes associated with active galactic nuclei (AGN), produced by jets from black holes (BHs).
However, many clusters have other radio sources which are more diffuse and are not directly associated with an AGN. These sources generally fall into two categories: radio halos and radio relics [1]. Radio halos are volume-filling, unpolarized, and diffuse, and can either be “giant” or “mini” radio halos, the former occurring in clusters with major mergers and the latter seen in the cool cores of relaxed clusters. Radio halos are thought to arise from the reacceleration of CRe with by merger-driven turbulence [2,3,4], but radio mini-halos may originate via turbulence [5] or hadronic interactions between cosmic ray protons (CRp) and the thermal population, producing secondary CRe which emit in the radio [6,7,8]. Radio relics (or “radio gischts” [9], “radio shocks” [1]) are typically found in the outskirts of clusters, are elongated, and strongly polarized. These narrow radio arcs are usually concentric with the cluster X-ray emission and sometimes have counterparts on the opposite side of the cluster.
Originally, it was assumed that these latter features mark the location of shock fronts propagating in the ICM which accelerate ICM electrons to ultrarelativistic energies via a first-order Fermi process, which would then cool rapidly and produce narrow (∼100 kpc) radio features. It has been shown that this scenario implies an implausibly high acceleration efficiency for the low-Mach () cluster merger shocks (e.g., [10]). It is more likely that shocks re-accelerate long-lived CRe with lower from past acceleration events [11,12,13,14]. Aside from this, not all radio relics exhibit ICM shocks in the X-ray at their front edges, as expected in a simple re-acceleration picture, the best example of this being the most prominent and well-studied CIZA J2242.8+5301 Sausage relic [15,16,17].
In a previous work ([18], hereafter Z21), we explored the alternative possibility that radio relics, such as the Sausage, trace the nonuniform distribution of the seed CRe rather than the ICM shocks. Assuming the distribution of CRe originates from injections by AGN from the cluster center and other galaxies, which are subsequently transported throughout the cluster by gas motions, we may expect that those regions have sharp boundaries and shapes as long arched filaments or sheets concentric with the cluster, and that the magnetic fields within those regions are stretched along the filaments. A shock passage across such a region would create a radio relic with all the observed relic properties. We may catch the shock front while it crosses such a region, creating a radio relic at the shock position. When the shock moves out (but not too far, in order to satisfy the electron cooling timescale constraint), the relic “front edge” would delineate the sharp boundary of the polluted region.
In Z21, we tested this hypothesis using magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulations of AGN feedback in clusters which have had their ICM stirred by recent merging activity. In these simulations, the central BH fires jets into the cluster core, producing highly magnetized buoyant bubbles, which then rise. As they rise, the material from the bubbles is advected by the merger-driven gas motions, and eventually this material is mixed with the ICM. We were able to track the evolution of the material from the bubbles by following a passive tracer injected with the jet and advected with the gas. We showed that in some cases, the gas motions can be fast and widespread enough to advect the bubble material from the cluster core to very large radii, and produce large, elongated (∼1 Mpc), cluster-centric CR-enriched regions that resemble radio relics. We also showed that in these regions, magnetic fields are naturally stretched tangentially along the filaments, helping to explain the large degree of polarization in relics.
In Z21, the physics of the injected jet material was very simplified–the same kind of magnetized, thermal plasma as the ICM itself. The “cosmic rays” in the simulations were marked by a passive scalar injected by the jet, which is subsequently advected by gas motions. However, the physics of the CRs which are injected into ICM by jets is more complicated than this in reality. These CRs are unstable to the streaming instability [19] and resonantly excite Alfvén waves, on which they subsequently scatter and transfer their energy into heat. Depending on the prevailing damping process of these Alfvén waves, CRs can either stream (if damping is weak), diffuse (if damping is strong), or are transported by a combination of both processes along the direction of the local magnetic field [20].
In this work, we implement this additional CR physics in one of the simulations from Z21, to determine if our previous results regarding the formation of relic-like CRe features are affected.
2. Methods
The simulations we perform consist of (1) an idealized binary merger between two clusters with a high mass ratio, in which a small subcluster perturbs the center of a large, cool-core cluster, initiating sloshing motions and turbulence, followed by (2) the injection of AGN jets from a central BH. Since most of the details of the simulations have been discussed in Z21, we will only briefly outline them here, and devote more discussion to the additional physics added in this work.
We perform our simulations using the AREPO code [21], which employs a finite-volume Godunov method on an unstructured moving Voronoi mesh to evolve the equations of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), and a Tree-PM solver to compute the self-gravity from gas and dark matter. The magnetic fields are evolved on the moving mesh using the Powell 8-wave scheme with divergence cleaning employed in [22] and in the IllustrisTNG simulations [23]. These simulations also include dark matter particles, which make up the bulk of the cluster’s mass and only interact with each other and the gas via gravity.
2.1. Merger Simulations
The idealized binary merger simulation consists of a large, “main” cluster with a total mass of , and a smaller infalling subcluster five times less massive. The main cluster includes DM and hot plasma, where the fraction of gas mass to dark matter mass is 0.12. The subcluster is DM-only (perhaps stripped of its gas on a previous cluster passage). The initial conditions in the simulation explored here are the same as in previous works ([24,25,26,27,28] and Z21), and produce spiral-shaped cold fronts in an otherwise relatively relaxed cluster very similar to those observed in X-ray observations. In Z21, this simulation also produced thin strips of bubble material which closely resembled radio relics more than the “Merger2” simulation from that work.
The plasma is modeled as a magnetized, fully ionized ideal fluid with and mean molecular weight . For the magnetic field in the simulation, we follow the procedure from [29] and references therein. Briefly, we set up a divergence-free turbulent magnetic field on a uniform grid with a Kolmogorov spectrum which is isotropic in the three spatial directions. The average magnetic field strength is scaled to be proportional to the square root of the thermal pressure such that is constant, with an initial value of everywhere. The magnetic field components are then interpolated from this grid onto the cells in the simulation.
2.2. Simulation of Jets and Cosmic Rays
For simulating the effects of AGN in the simulations we use the method of [30]. This method injects a bi-directional jet from a BH particle located at the cluster potential minimum, which is kinetically dominated, low density, and collimated. Kinetic, thermal, and magnetic energy is injected into two small spherical regions a few kpc from the location of a black hole particle. The material injected by the jet is marked by a passive tracer field and is advected along with the fluid for the rest of the simulation.
In each simulation, the jets are fired with a luminosity erg s for a duration of Myr, so the resulting total energy injected is erg in each direction, which is a sum of kinetic, thermal, and magnetic energy. In the jet region, the magnetic and thermal pressures are equal (), and the injected magnetic field is purely toroidal. As in Z21, we fire the jet once and follow the subsequent evolution of the material it injects into the ICM.
In Z21, the jet was comprised purely of thermal gas and magnetic energy, and the only marker for the material injected by the jet was the passive tracer field . In this work, we improve upon the physical description of the jet material by following [31,32] in treating the CRs as a secondary fluid with . We set the CR and thermal pressures in the jet to be equal (), so that the total pressure in the jet is equal parts from thermal plasma, CRs, and magnetic fields. We emulate a simple model of CR acceleration by internal shocks within the jet [33] by maintaining for within cells which have .
CR diffusion and streaming is emulated via a combination of diffusion and Alfvén losses [34]. The CR energy density is advected with the gas and anisotropically diffuses along the magnetic field lines, with a constant diffusion coefficient along the local magnetic field direction and perpendicular to it [35]. For more details of the CR algorithms used here, see [32] and references therein. We compare three models: (1) the original model of Z21 without CRs, (2) the same cluster and AGN setup but with purely advective CRs (without diffusion), and (3) a model with a realistic CR diffusion coefficient in the ICM of cm s. The cross-field diffusion is significantly smaller in comparison to diffusion along the magnetic field (e.g., [36]) and thus our numerical cross-field diffusion of cosmic rays likely dominates over the physical transport in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field [35]. We demonstrate that the resulting cosmic ray distribution is mainly shaped by advective cosmic ray transport as a result of the sloshing ICM over diffusive transport along the magnetic field or our assumed diffusion coefficient of cm s, which is motivated by the cosmic ray streaming picture [32].
In model 3, The effective diffusion velocity across a CR gradient length of kpc is km s. Thus, CRs are expected to fill a significant volume of the cluster core. However, the sloshing front is expected to stretch the magnetic field lines and approximately align them with the equipotential surfaces. The CR gradient length along the magnetic field lines increases substantially so that the diffusion velocity decreases and thereby confines CRs within the sloshing front.
3. Results
Here we present the results of the “Merger1”/jet simulations from Z21 with jets oriented along the x-axis of the simulation box with additional CR physics included. These are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The simulation epoch of the quantity plotted in each row increases from left to right, with corresponding to the moment of jet injection. Figure 1 shows slices through the gas density from one of the simulations, showing the initial injection of the bubbles and their subsequent mixing into the ICM, followed by the continuation of the sloshing motions. The top row in Figure 2 shows the gradient magnitude of the projected X-ray surface brightness (SB) along the z-axis of the simulation box (from the simulation without CR physics, though the differences in the simulations are negligible in terms of the effect on the sloshing gas), to serve as a visual aid to locate the position of the cold fronts and the sloshing motions which are advecting the CRs.
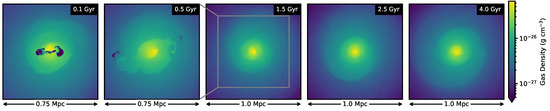
Figure 1.
Slices through the cluster center of the gas density of the “Merger1”/jet simulation from Z21 with the jets oriented along the x-axis. Several epochs are shown with time measured from the moment of jet injection.
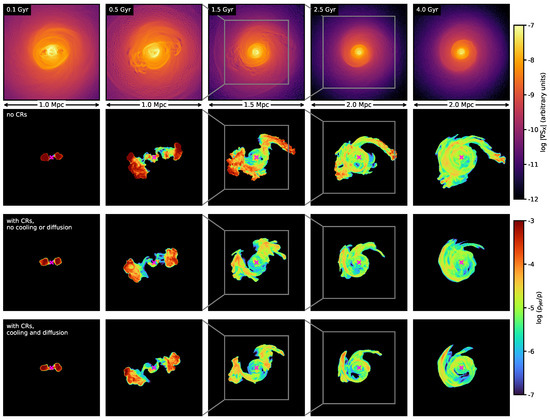
Figure 2.
Projections along the z-axis of the “Merger1”/jet simulation from Z21 with the jets oriented along the x-axis for varying CR physics. Several epochs are shown with time measured from the moment of jet injection. The top row shows the X-ray SB gradient magnitude. The second row shows the mass-weighted passive tracer from the original Z21 simulation, without additional CR physics. The third row shows the same simulation, now with the CRs included, but these are only advected with the fluid. The fourth row shows the same simulation as in the third, but in this case diffusion and Alfvén losses are included.
The following rows of panels in Figure 2 shows the mass-weighted projected passive tracer field along the z-axis, which is common to all simulations. The second row shows projected jet material in the original simulation from Z21, without CRs included in the jets. The jet-injected bubbles rise, and as their material is mixed with the surrounding ICM, it follows the sloshing gas motions. The inner region bounded by the cold fronts is filled with material originally injected by the jet, and a ∼Mpc-long strip of jet material appears at large radius by Gyr (rightmost panels of Figure 2), to the NW of the cluster core.
The third row shows projected jet material in the simulation where only the CR component has been added to the original simulation of Z21, without any additional physics. Here, the distribution of projected jet material looks qualitatively similar to the original simulation for the first Gyr, but after this it is obvious that the bubble to the W has not risen to the same height, and is unable to get caught up in the bulk motions to the N/NW to get stretched into a large filament.
The fourth row of Figure 2 shows the simulation where diffusion and Alfvén losses for the CRs have been turned on. These look qualitatively very similar to the simulation with purely advective CRs (model 2), but the smoothing out of CR gradients by diffusion has had a noticeable effect on the distribution of jet material which closely tracks the CRs in this simulation.
Figure 3 shows the projected CR energy density in the same simulations. Overall, the projected CR distribution matches the jet tracer field distribution. However, these maps more clearly show the effect of diffusion and Alfvén losses; when diffusion and cooling are present, the CR distribution is smoother, with a less irregular appearance than in the case with no cooling or diffusion, which merely support advective CR transport. Alfvén losses have reduced the CR energy density by roughly an order of magnitude. Diffusion weakens the gradients along a magnetic field line while Alfvén losses dissipate CR energy at a rate (where denotes the Alfvén velocity) and thus sharpens the CR gradients. As a result, CR gradients are maintained along filamentary magnetic field lines at the edges of our CR distribution towards the outer cluster regions. This effectively precludes the formation of such long filamentary features in the CR energy density. On the opposite side, within the core spiral structure, CR diffusion homogenizes the CR energy density, softens CR gradients, and thus minimizes Alfvén losses.
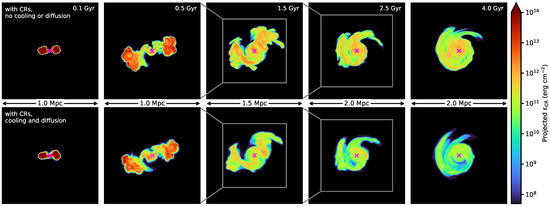
Figure 3.
Projected CR energy density along the z-axis in the same simulations with jets fired in the x-direction, for the two simulations with CRs included, with and without the effects of diffusion and Alfvén losses. Several epochs are shown with time measured from the moment of jet injection.
In Figure 4 we show the projected CR energy density along the z-axis of the simulations with CRs at Gyr, with plane-of-sky projected magnetic field vectors overlaid. The projected magnetic field has been weighted by a factor , which will be approximately proportional to radio emission from secondary CR electrons that are produced in hadronic CR interactions with the ambient ICM emissivity with . In Z21, elongated regions of enhanced CR distribution were associated with magnetic field lines which are largely aligned lengthwise along these features, which naturally arise due to the fact that the same motions which spread the CRs out over long distances stretch and amplify the magnetic field along the same direction. While this is also generally true in the simulations presented here with CRs, we note that in the case with cooling and diffusion (right panel of Figure 4), the degree of alignment between the field line direction and the long axis of the filamentary features appears somewhat degraded in those features which are left, especially for the one ∼300 kpc north of the cluster center, indicating that these processes have altered the distribution of CRs such that the ones that remain are no longer in regions where the magnetic field is tangentially aligned as seen in the projection.
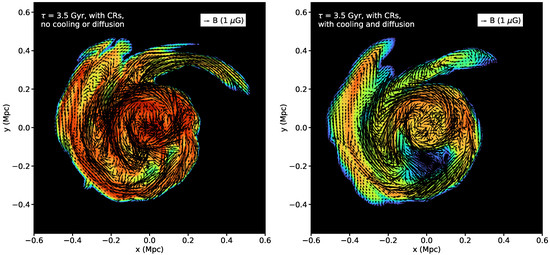
Figure 4.
Projected CR energy density and plane-of-sky magnetic field vectors for the same simulations. The magnetic field vectors are weighted proportional to .
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Z21 showed that merger-driven motions in the ICM could advect material injected by AGN jets to large radii and produce Mpc-scale thin filaments of jet material, which were posited to explain the appearance of radio relics that are not explained by the simple model of a merger shock overunning a region uniformly filled with CRe in the cluster outskirts. Under this hypothesis, the appearance of these relics emerges due to the spatial distribution of the CRe themselves as determined by the ICM motions which transported and stretched them across large distances. We have shown in this work that for a more realistic model of CRs in the simulation, whether or not we include the effects of CR diffusion and Alfvén losses, filamentary features become less prominent, and are unable to reach the same large radii that they were in the absence of the additional CR physics.
What accounts for this difference? One obvious source of this behavior is the difference in adiabatic index between a bubble which is filled with thermal gas and a bubble with an energy density which is half CRs. The reduced pressure can destabilize the rising bubble. The CR acceleration process itself may also effect the stability of the jet. CRs have a slower cooling time in comparison to the thermal gas in the center of cool cores so that they can prevent runaway thermal cooling and locally provide thermal stability [37], although gas in collisional ionization equilibrium can become unstable for certain conditions [38]. All of these issues will be examined in more detail in future simulations of jets combined with merger-driven gas motions.
For the simulation with CR streaming, Alfvén wave losses will also preclude the formation of extended filaments by dissipating the CR energy density. The formation of filaments also necessarily depends on the precise details of the cluster “weather” that a given bubble is encountering. A wider parameter space of jet axes, jet energies, and cluster gas motion characteristics is necessary to determine if the hypothesis suggested by Z21 regard a possible origin for radio relics holds up under the assumption of more realistic models for CR dynamics.
Our simulations have also only included one jet phase of the central AGN. In reality, the CR distribution in a cool-core cluster will be the superposition of many such injections, which will have been transported around the core region by gas motions in different stages. Future work should include a self-consistent feedback model which is fed by gas which is radiative cooling to determine what the expected long-term distribution of CRs in a sloshing cool core would be. We also observe that diffusion appears to isotropize the CRs confined within the core region (right panels of Figure 3 and Figure 4), suggesting that this may provide an explanation for the existence of radio mini-halos in some clusters via emission from secondary electrons [6,7].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and C.P.; methodology, J.Z., K.E. and R.W.; software, K.E., R.W.; validation, J.Z.; formal analysis, J.Z.; investigation, J.Z.; resources, J.Z.; data curation, J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.Z., K.E., R.W. and C.P.; visualization, J.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Chandra X-ray Center, which is operated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory for and on behalf of NASA under contract NAS8-03060.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Simulation data will be made available at the Galaxy Cluster Merger Catalog1 [39], or by request to the author.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 | http://gcmc.hub.yt (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
| 2 | https://arepo-code.org (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
| 3 | https://www.astropy.org (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
| 4 | https://matplotlib.org (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
| 5 | https://www.numpy.org (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
| 6 | https://yt-project.org (accessed on 1 November 2021) |
References
- van Weeren, R.J.; de Gasperin, F.; Akamatsu, H.; Brüggen, M.; Feretti, L.; Kang, H.; Stroe, A.; Zandanel, F. Diffuse Radio Emission from Galaxy Clusters. Space Sci. Rev. 2019, 215, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, G.; Lazarian, A. Compressible turbulence in galaxy clusters: Physics and stochastic particle re-acceleration. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 378, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, G.; Jones, T.W. Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters and Their Nonthermal Emission. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2014, 23, 1430007–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinzke, A.; Oh, S.P.; Pfrommer, C. Turbulence and particle acceleration in giant radio haloes: The origin of seed electrons. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 4800–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Markevitch, M.; Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S. Turbulence and Radio Mini-halos in the Sloshing Cores of Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2013, 762, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfrommer, C.; Enßlin, T.A. Constraining the population of cosmic ray protons in cooling flow clusters with γ-ray and radio observations: Are radio mini-halos of hadronic origin? Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 413, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfrommer, C.; Enßlin, T.A. Estimating galaxy cluster magnetic fields by the classical and hadronic minimum energy criterion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 352, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Markevitch, M. Testing Secondary Models for the Origin of Radio Mini-Halos in Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2015, 801, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempner, J.C.; Blanton, E.L.; Clarke, T.E.; Enßlin, T.A.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; Rudnick, L. Conference Note: A Taxonomy of Extended Radio Sources in Clusters of Galaxies. In Proceedings of the Riddle of Cooling Flows in Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 31 May–4 June 2003; Reiprich, T., Kempner, J., Soker, N., Eds.; 2004; p. 335. Available online: http://www.astro.virginia.edu/coolflow/ (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Macario, G.; Markevitch, M.; Giacintucci, S.; Brunetti, G.; Venturi, T.; Murray, S.S. A Shock Front in the Merging Galaxy Cluster A754: X-ray and Radio Observations. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarazin, C.L. The Energy Spectrum of Primary Cosmic-Ray Electrons in Clusters of Galaxies and Inverse Compton Emission. Astrophys. J. 1999, 520, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markevitch, M.; Govoni, F.; Brunetti, G.; Jerius, D. Bow Shock and Radio Halo in the Merging Cluster A520. Astrophys. J. 2005, 627, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzke, A.; Oh, S.P.; Pfrommer, C. Giant radio relics in galaxy clusters: Reacceleration of fossil relativistic electrons? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 1061–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Ryu, D. Re-acceleration Model for Radio Relics with Spectral Curvature. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrean, G.A.; Brüggen, M.; Röttgering, H.; Simionescu, A.; Croston, J.H.; van Weeren, R.; Hoeft, M. XMM-Newton observations of the merging galaxy cluster CIZA J2242.8+5301. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 2617–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogrean, G.A.; Brüggen, M.; van Weeren, R.; Röttgering, H.; Simionescu, A.; Hoeft, M.; Croston, J.H. Multiple density discontinuities in the merging galaxy cluster CIZA J2242.8+5301. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 3416–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weeren, R.J.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Brüggen, M.; Hoeft, M. Particle Acceleration on Megaparsec Scales in a Merging Galaxy Cluster. Science 2010, 330, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Markevitch, M.; Weinberger, R.; Nulsen, P.; Ehlert, K. How Merger-driven Gas Motions in Galaxy Clusters Can Turn AGN Bubbles into Radio Relics. Astrophys. J. 2021, 914, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsrud, R.; Pearce, W.P. The Effect of Wave-Particle Interactions on the Propagation of Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. 1969, 156, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, J.; Oh, S.P.; Guo, F. Cosmic ray streaming in clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 2209–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Springel, V. E pur si muove: Galilean-invariant cosmological hydrodynamical simulations on a moving mesh. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 401, 791–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Simulations of magnetic fields in isolated disc galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinacci, F.; Vogelsberger, M.; Pakmor, R.; Torrey, P.; Springel, V.; Hernquist, L.; Nelson, D.; Weinberger, R.; Pillepich, A.; Naiman, J.; et al. First results from the IllustrisTNG simulations: Radio haloes and magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 5113–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ascasibar, Y.; Markevitch, M. The Origin of Cold Fronts in the Cores of Relaxed Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Markevitch, M.; Johnson, R.E. Stirring Up the Pot: Can Cooling Flows in Galaxy Clusters be Quenched by Gas Sloshing? Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 908–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Miller, E.D.; Simionescu, A.; Bautz, M.W. Simulating Astro-H Observations of Sloshing Gas Motions in the Cores of Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2016, 821, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Miller, E.D.; Bulbul, E.; Zhuravleva, I. What Do the Hitomi Observations Tell Us About the Turbulent Velocities in the Perseus Cluster? Probing the Velocity Field with Mock Observations. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Zavala, J.; Vogelsberger, M. Sloshing of Galaxy Cluster Core Plasma in the Presence of Self-interacting Dark Matter. Astrophys. J. 2019, 882, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzycki, B.; ZuHone, J. A Parameter Space Exploration of Galaxy Cluster Mergers. II. Effects of Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2019, 883, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, R.; Ehlert, K.; Pfrommer, C.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Simulating the interaction of jets with the intracluster medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 4530–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer, C.; Pakmor, R.; Schaal, K.; Simpson, C.M.; Springel, V. Simulating cosmic ray physics on a moving mesh. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 4500–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehlert, K.; Weinberger, R.; Pfrommer, C.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Simulations of the dynamics of magnetized jets and cosmic rays in galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2878–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucho, M.; Martí, J.M. A numerical simulation of the evolution and fate of a Fanaroff-Riley type I jet. The case of 3C 31. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 382, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, J.; Pfrommer, C.; Oh, S.P. Cosmic ray-driven galactic winds: Streaming or diffusion? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakmor, R.; Pfrommer, C.; Simpson, C.M.; Kannan, R.; Springel, V. Semi-implicit anisotropic cosmic ray transport on an unstructured moving mesh. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desiati, P.; Zweibel, E.G. The Transport of Cosmic Rays Across Magnetic Fieldlines. Astrophys. J. 2014, 791, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfrommer, C. Toward a Comprehensive Model for Feedback by Active Galactic Nuclei: New Insights from M87 Observations by LOFAR, Fermi, and H.E.S.S. Astrophys. J. 2013, 779, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempski, P.; Quataert, E. Thermal instability of halo gas heated by streaming cosmic rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZuHone, J.A.; Kowalik, K.; Öhman, E.; Lau, E.; Nagai, D. The Galaxy Cluster Merger Catalog: An Online Repository of Mock Observations from Simulated Galaxy Cluster Mergers. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 234, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astropy Collaboration; Robitaille, T.P.; Tollerud, E.J.; Greenfield, P.; Droettboom, M.; Bray, E.; Aldcroft, T.; Davis, M.; Ginsburg, A.; Price-Whelan, A.M.; et al. Astropy: A community Python package for astronomy. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, M.J.; Smith, B.D.; Oishi, J.S.; Skory, S.; Skillman, S.W.; Abel, T.; Norman, M.L. yt: A Multi-code Analysis Toolkit for Astrophysical Simulation Data. Astrophys. J. 2011, 192, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).