Luminous Blue Variables
Abstract
1. Historic Background and Naming
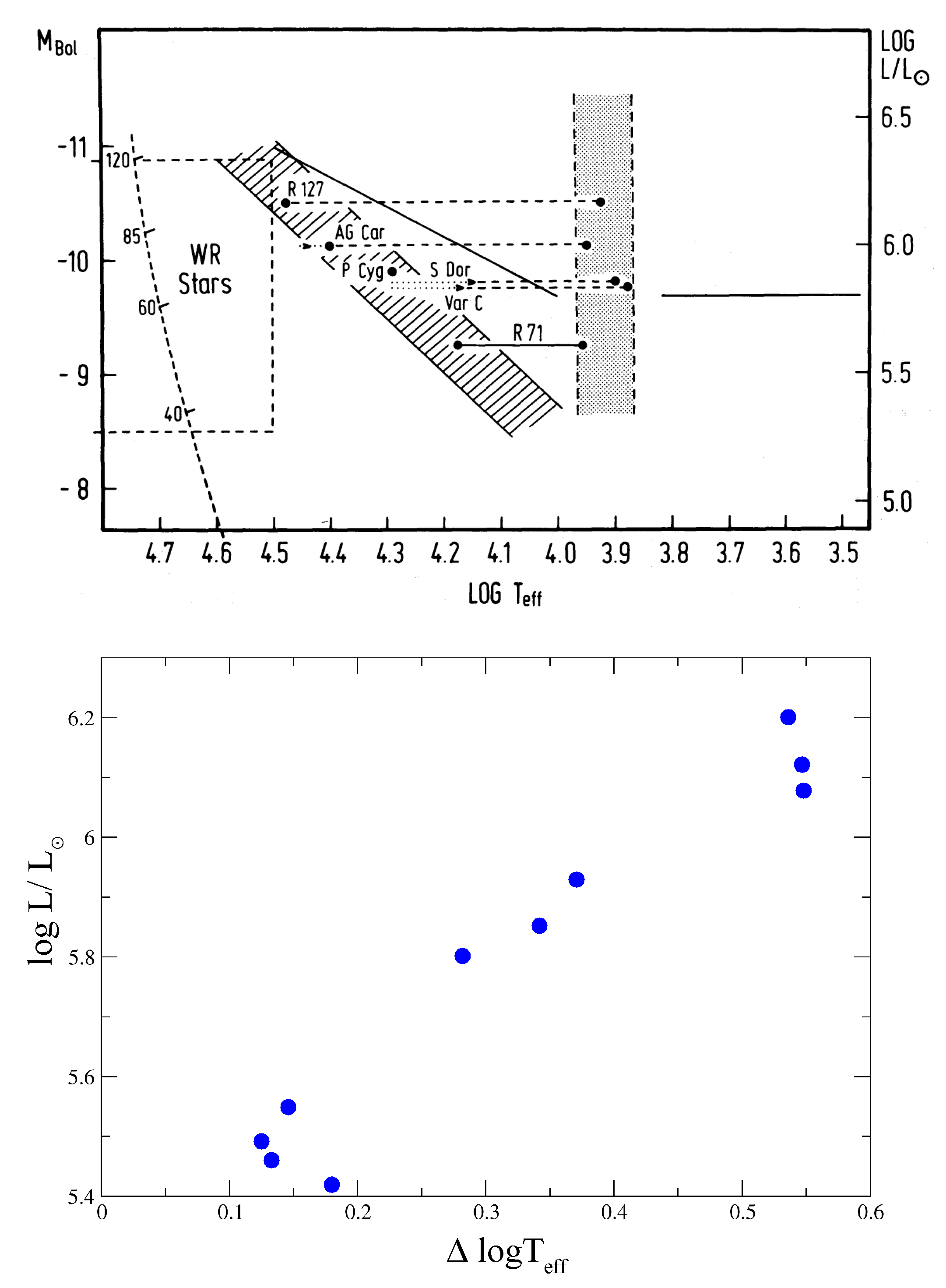
2. Characteristic of Luminous Blue Variables
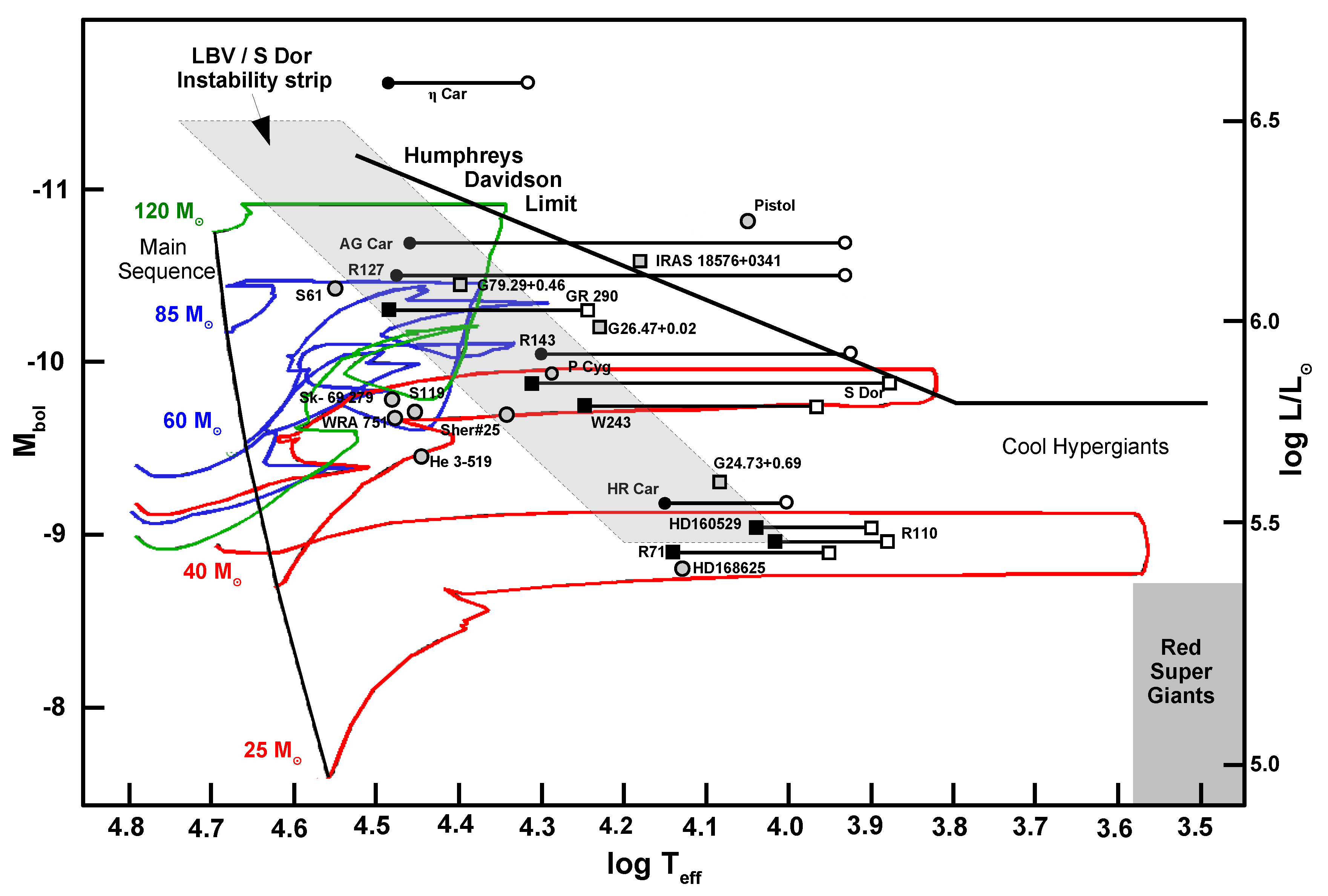
3. The Evolutionary Status of LBVs
4. Nebulae around LBVs
4.1. Emission Line Nebulae
4.2. Dust Nebulae
4.3. P Cygni
4.4. Carinae — the Most Peculiar LBV?
- A giant eruption that took place in 1843
- A binary system with two massive components one with 60 M the second with 30 M [89]
- A nebula that has at least three section: The little Homunculus, The Homunculus, The outer ejecta.
5. Instabilities and the Origin of Variability
6. The LBV Wolf-Rayet Star Connection
7. Links of SN Impostors and LBVs
8. Multiplicity of LBVs
9. LBV and Their Neighborhood
10. The Population of LBVs
11. LBVs in Low Metallicity Systems
12. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSG | Blue Supergiant |
| ESO | European Southern Observatory |
| HRD | Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram |
| HST | Hubble Space Telescope |
| JWST | James Webb Space Telescope |
| LBV | Luminous Blue Variable |
| LMC | Large Magellanic Cloud |
| LSST | Large Synoptic Survey Telescope |
| MMT | (converted) Multi Mirror Telescope |
| NOAO | National Optical Astronomy Observatory |
| RSG | Red Supergiant |
| SMC | Small Magellanic Cloud |
| SN | supernova |
| WFIRST | Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope |
| WHT | William Herschel Telescope |
| WR | Wolf-Rayet star |
References
- Hubble, E.; Sandage, A. The Brightest Variable Stars in Extragalactic Nebulae. I. M31 and M33. Astrophys. J. 1953, 118, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.C. Three Variable Stars and Suspected Nova in the Spiral Nebula M 33 Trianguli. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1922, 34, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M. Zwei neue Veränderliche. Astronomische Nachrichten 1923, 217, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandage, A.; Tammann, G.A. Steps toward the Hubble constant. IV. Distances to 39 galaxies in the general field leading to a calibration of the galaxy luminosity classes and a first hint of the value of H0. Astrophys. J. 1974, 194, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M. The spectra of AE Andromedae and the Hubble-Sandage variables in M31 and M33. Astrophys. J. 1975, 200, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. III. Comments on the evolution of the most massive stars in the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys. J. 1979, 232, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, C. The stability limit of hypergiant photospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 138, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The Relationship between the Eddington Limit, the Observed Upper Luminosity Limit for Massive Stars, and the Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 1988, 324, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.C. Large Magellanic Clouds. Popular Astronomy 1897, 5, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feast, M.W.; Thackeray, A.D.; Wesselink, A.J. The brightest stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1960, 121, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.S. Basic Observational Constraints on the Evolution of Massive Stars. In Observational Tests of the Stellar Evolution Theory; Maeder, A., Renzini, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984; Volume 105, p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Bohannan, B.; Walborn, N.R. The Ofpe/WN9 Class in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1989, 101, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The OB Zoo: A Digital Atlas of Peculiar Spectra. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2000, 112, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genderen, A.M.; de Groot, M.; Sterken, C. New perceptions on the S Doradus phenomenon and the micro variations of five Luminous Blue Variables (LBVs). Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1997, 124, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genderen, A.M.; Sterken, C.; de Groot, M. New discoveries on the S DOR phenomenon based on an investigation of the photometric history of the variables AG Car, S Dor and η Car. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 318, 81–98. [Google Scholar]
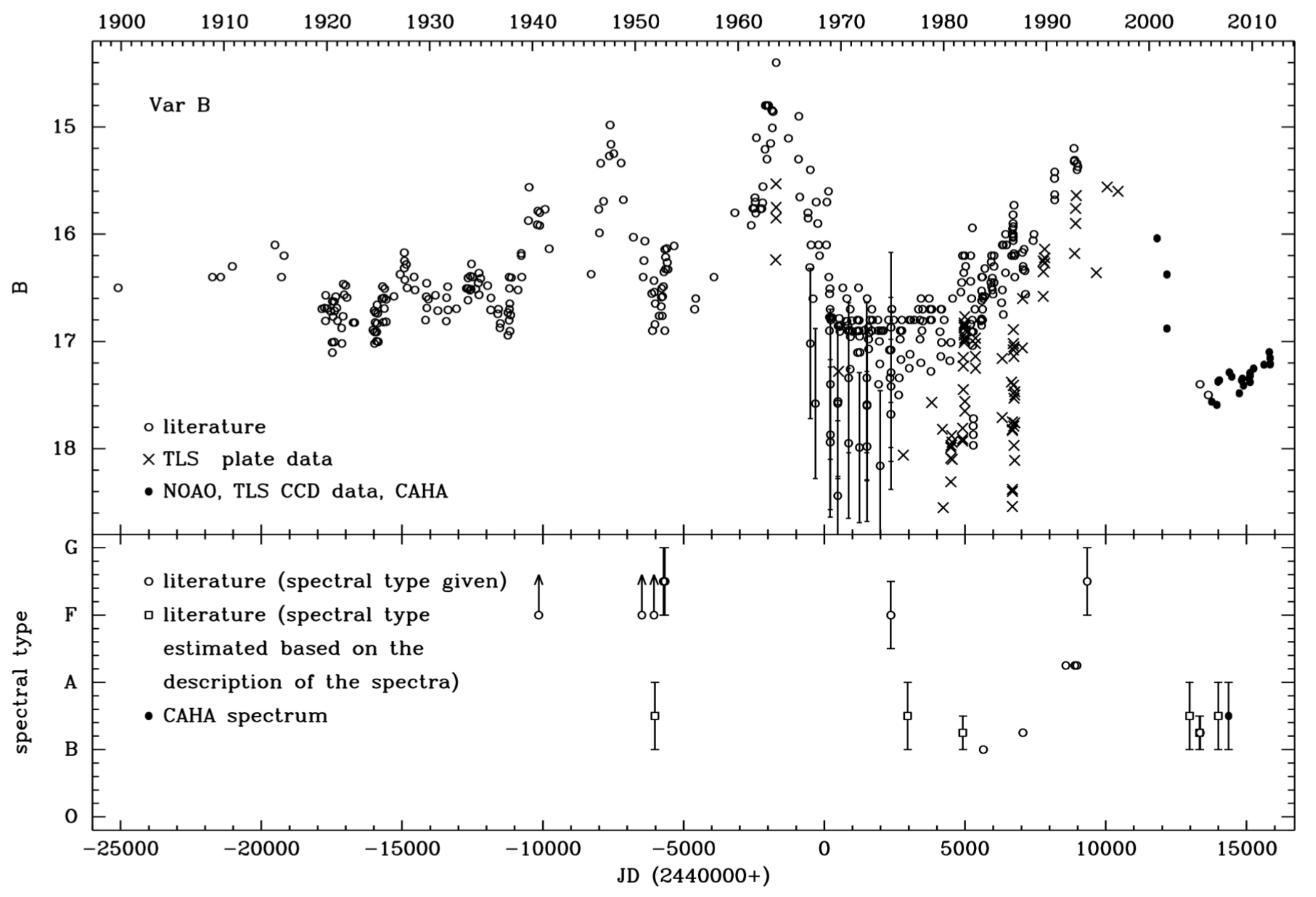
- Burggraf, B.; Weis, K.; Bomans, D.J.; Henze, M.; Meusinger, H.; Sholukhova, O.; Zharova, A.; Pellerin, A.; Becker, A. Var C: Long-term photometric and spectral variability of a luminous blue variable in M 33. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 581, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, B. Empirical amplitude-luminosity relation of S Doradus variables and extragalactic distances. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 217, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Burggraf, B. LBVs in M33: Variability and Evolutionary State. Ph.D. Thesis, Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genderen, A.M. S Doradus variables in the Galaxy and the Magellanic Clouds. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 366, 508–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn-Wallenstein, T.Z.; Levesque, E.M.; Davenport, J.R.A. Short-term Variability of Evolved Massive Stars with TESS. Astrophys. J. 2019, 878, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Smith, N. η Carinae’s Second Eruption and the Light Curves of the η Carinae Variables. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1999, 111, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Humphreys, R.M. Eta Carinae and Its Environment. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 35, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, M. The most luminous stars in the universe. Irish Astron. J. 1988, 18, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tammann, G.A.; Sandage, A. The Stellar Content and Distance of the Galaxy NGC 2403 IN the M81 Group. Astrophys. J. 1968, 151, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicky, F. NGC 1058 and its Supernova 1961. Astrophys. J. 1964, 139, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, R.W.; Stringfellow, G.S.; Penrod, G.D.; Filippenko, A.V. SN 1961V: an Extragalactic Eta Carinae Analog? Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitherer, C. Mass Loss from LBVs: Observational Constraints. In Luminous Blue Variables: Massive Stars in Transition; Nota, A., Lamers, H., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 120, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, O.; Jankovics, I.; Kovács, J.; Wolf, B.; Schmutz, W.; Kaufer, A.; Rivinius, T.; Szeifert, T. Long-term spectroscopic monitoring of the Luminous Blue Variable AG Carinae. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 375, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.H.; Damineli, A.; Hillier, D.J. LBVs and the nature of the S Dor cycles: the case of AG Carinae. In Revista Mexicana de Astronomia y Astrofisica Conference Series; Instituto de Astronomía: Ciudad de México, México, 2008; Volume 33, pp. 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Snow, T.P.; Lindholm, D.M. Terminal Velocities and the Bistability of Stellar Winds. Astrophys. J. 1995, 455, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. On the nature of the bi-stability jump in the winds of early-type supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 350, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Eddington, A.S. On the radiative equilibrium of the stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1916, 77, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, A.; Meynet, G. Stellar evolution with rotation. VI. The Eddington and Omega -limits, the rotational mass loss for OB and LBV stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 361, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Groh, J.H.; Hillier, D.J.; Damineli, A. AG Carinae: A Luminous Blue Variable with a High Rotational Velocity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 638, L33–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.H.; Damineli, A.; Hillier, D.J.; Barbá, R.; Fernández-Lajús, E.; Gamen, R.C.; Moisés, A.P.; Solivella, G.; Teodoro, M. Bona Fide, Strong-Variable Galactic Luminous Blue Variable Stars are Fast Rotators: Detection of a High Rotational Velocity in HR Carinae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 705, L25–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M. The Wolf-Rayet Connection - Luminous Blue Variables and Evolved Supergiants (review). In Wolf-Rayet Stars and Interrelations with Other Massive Stars in Galaxies; van der Hucht, K.A., Hidayat, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; Volume 143, p. 485. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, P.S. On the relationship between Of and WR stars. Memoires of the Societe Royale des Sciences de Liege 1975, 9, 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Maeder, A.; Conti, P.S. Massive Star Populations in Nearby Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 32, 227–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynet, G.; Maeder, A. Stellar evolution with rotation. XI. Wolf-Rayet star populations at different metallicities. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 429, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K. The Relation between Apparent Temperature and Mass-Loss Rate in Hypergiant Eruptions. Astrophys. J. 1987, 317, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K. The Luminous Blue Variables: Astrophysical Geysers. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1994, 106, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitherer, C.; Schmutz, W.; Abbott, D.C.; Hamann, W.R.; Wessolowski, U. Atmospheric Models for Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 1989, 346, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Schmutz, W. Variability of luminous blue variables. II. Parameter study of the typical LBV variations. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 306, 501. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N.; Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A. The Missing Luminous Blue Variables and the Bistability Jump. Astrophys. J. 2004, 615, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S. Mass-Loss Rates of Very Massive Stars. In Very Massive Stars in the Local Universe; Vink, J.S., Ed.; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 412, p. 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolmasov, P. Stochastic variability of luminous blue variables. New A 2011, 16, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfener, G.; Owocki, S.P.; Vink, J.S. Stellar envelope inflation near the Eddington limit. Implications for the radii of Wolf-Rayet stars and luminous blue variables. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.H.; Hillier, D.J.; Damineli, A. On the Nature of the Prototype Luminous Blue Variable AG Carinae. II. Witnessing a Massive Star Evolving Close to the Eddington and Bistability Limits. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, O. Circumstellar ejecta around LBV’s. In IAU Colloq. 113: Physics of Luminous Blue Variables; Davidson, K., Moffat, A.F.J., Lamers, H.J.G.L.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 157, pp. 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. Nebulae around Luminous Blue Variables—large bipolar variety. In Active OB Stars: Structure, Evolution, Mass Loss, and Critical Limits; Neiner, C., Wade, G., Meynet, G., Peters, G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 272, pp. 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weis, K. Gone with the wind: Nebulae around LBVs. Bull. Soc. R. Sci. Liege 2011, 80, 440–444. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. On the structure and kinematics of nebulae around LBVs and LBV candidates in the LMC. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 408, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Duschl, W.J.; Bomans, D.J. An outflow from the nebula around the LBV candidate S 119. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 398, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K. 28 years of Luminous Blue Variables. In 370 Years of Astronomy in Utrecht; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Seriesl; Pugliese, G., de Koter, A., Wijburg, M., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 470, p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. Family ties of WR to LBV nebulae yielding clues for stellar evolution. In Proceedings of the Wolf-Rayet Stars: Proceedings of an International Workshop, Potsdam, Germany, 1–5 June 2015; pp. 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K.; Duschl, W.J. Outflow from and asymmetries in the nebula around the LBV candidate Sk-69o279. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 393, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nota, A.; Pasquali, A.; Clampin, M.; Pollacco, D.; Scuderi, S.; Livio, M. The Nebula around HD 168625: Morphology, Dynamics, and Physical Properties. Astrophys. J. 1996, 473, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K. The outer ejecta of η Carinae. In The Fate of the Most Massive Stars; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Humphreys, R., Stanek, K., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 332, p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. The Outer Ejecta. In Eta Carinae and the Supernova Impostors; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Davidson, K., Humphreys, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 384, p. 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K. The outer ejecta of Eta Carinae. In Eta Carinae and Other Mysterious Stars: The Hidden Opportunities of Emission Spectroscopy; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Gull, T.R., Johannson, S., Davidson, K., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 242, p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. The AG Carinae Nebula—Bigger than ever? In Mass Loss from Stars and the Evolution of Stellar Clusters; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; de Koter, A., Smith, L.J., Waters, L.B.F.M., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 388, p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K.; Duschl, W.J.; Bomans, D.J.; Chu, Y.H.; Joner, M.D. The bipolar structure of the LBV nebula around HR Carinae. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 320, 568–574. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, K. A kinematic and morphological investigation of the asymmetric nebula around the LBV candidate WRA 751. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 357, 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- Figer, D.F.; Morris, M.; Geballe, T.R.; Rich, R.M.; Serabyn, E.; McLean, I.S.; Puetter, R.C.; Yahil, A. High-Resolution Infrared Imaging and Spectroscopy of the Pistol Nebula: Evidence for Ejection. Astrophys. J. 1999, 525, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, W.; Grebel, E.K.; Chu, Y.H.; Weis, K. Ring Nebula and Bipolar Outflows Associated with the B1.5 Supergiant Sher 25 in NGC 3603. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 475, L45–L48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mizuno, D.R.; Kraemer, K.E.; Flagey, N.; Billot, N.; Shenoy, S.; Paladini, R.; Ryan, E.; Noriega-Crespo, A.; Carey, S.J. A Catalog of MIPSGAL Disk and Ring Sources. Astron. J. 2010, 139, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Povich, M.S.; Kendrew, S.; Lintott, C.J.; Bressert, E.; Arvidsson, K.; Cyganowski, C.; Maddison, S.; Schawinski, K.; Sherman, R.; et al. The Milky Way Project First Data Release: a bubblier Galactic disc. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 2442–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, C.N.; Goodman, A.A.; Kendrew, S.; Williams, J.P.; Simpson, R. The Milky Way Project: Leveraging Citizen Science and Machine Learning to Detect Interstellar Bubbles. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2014, 214, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Fabrika, S.; Sholukhova, O.; Berdnikov, L.N.; Cherepashchuk, A.M.; Zharova, A.V. MN112: a new Galactic candidate luminous blue variable. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 405, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, S.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Hoard, D.W.; Kafka, S.; Morris, P.W. A Hidden Population of Massive Stars with Circumstellar Shells Discovered with the Spitzer Space Telescope. Astron. J. 2010, 139, 2330–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagey, N.; Noriega-Crespo, A.; Billot, N.; Carey, S.J. Spitzer/InfraRed Spectrograph Investigation of MIPSGAL 24 μm Compact Bubbles. Astrophys. J. 2011, 741, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Flagey, N.; Noriega-Crespo, A.; Billot, N.; Carey, S.J.; Paladini, R.; Van Dyk, S.D. Spitzer/Infrared Spectrograph Investigation of MIPSGAL 24 μm Compact Bubbles: Low-resolution Observations. Astrophys. J. 2014, 796, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagey, N.; Noriega-Crespo, A.; Petric, A.; Geballe, T.R. Palomar/TripleSpec Observations of Spitzer/MIPSGAL 24 μm Circumstellar Shells: Unveiling the Natures of Their Central Sources. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Fabrika, S. Revealing evolved massive stars with Spitzer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 405, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Wachter, S.; Morris, P.W.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Hoard, D.W. Discovery of Twin Wolf-Rayet Stars Powering Double Ring Nebulae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 724, L78–L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Berdnikov, L.N.; Langer, N.; Stringfellow, G.S.; Todt, H.; Hamann, W.R.; Grebel, E.K.; Buckley, D.; et al. Discovery of two new Galactic candidate luminous blue variables with Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Berdnikov, L.N.; Langer, N.; Grebel, E.K.; Bestenlehner, J.M. Discovery of a new Galactic bona fide luminous blue variable with Spitzer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, L84–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvaramadze, V.V.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Berdnikov, L.N. Discovery of a new bona fide luminous blue variable in Norma. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, 3710–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniazev, A.Y.; Gvaramadze, V.V.; Berdnikov, L.N. WS1: one more new Galactic bona fide luminous blue variable. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, L60–L64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniazev, A.Y.; Gvaramadze, V.V.; Berdnikov, L.N. MN48: a new Galactic bona fide luminous blue variable revealed by Spitzer and SALT. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrigone, L.; Umana, G.; Buemi, C.S.; Hora, J.L.; Trigilio, C.; Leto, P.; Hart, A. Spitzer observations of a circumstellar nebula around the candidate luminous blue variable MWC 930. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 562, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umana, G.; Buemi, C.S.; Trigilio, C.; Hora, J.L.; Fazio, G.G.; Leto, P. The Dusty Nebula Surrounding HR Car: A Spitzer View. Astrophys. J. 2009, 694, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gail, H.P.; Duschl, W.J.; Ferrarotti, A.S.; Weis, K. Dust formation in LBV envelopes. In The Fate of the Most Massive Stars; Humphreys, R., Stanek, K., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 332, p. 323. [Google Scholar]
- Van Marle, A.J.; Meliani, Z.; Keppens, R.; Decin, L. Computing the Dust Distribution in the Bow Shock of a Fast-moving, Evolved Star. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 734, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, M.J.; Drew, J.E.; Meaburn, J.; Massey, R.M. The Shock-Excited P-Cygni Nebula. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 268, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaburn, J.; López, J.A.; O’Connor, J. The Kinematical Association of a Giant Lobe with the Luminous Blue Variable Star P Cygni. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 516, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiacono, C.; Ragazzoni, R.; Morossi, C.; Franchini, M.; di Marcantonio, P.; Kulesa, C.; McCarthy, D.; Briguglio, R.; Xompero, M.; Busoni, L.; et al. A high-resolution image of the inner shell of the P Cygni nebula in the infrared [Fe II] line. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Humphreys, R.M. Eta Carinae and the Supernova Impostors; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madura, T.I.; Gull, T.R.; Owocki, S.P.; Groh, J.H.; Okazaki, A.T.; Russell, C.M.P. Constraining the absolute orientation of η Carinae’s binary orbit: a 3D dynamical model for the broad [Fe III] emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 2064–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviola, E. Eta Carinae. I. The Nebulosity. Astrophys. J. 1950, 111, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Gull, T.R.; Davidson, K.; Smith, N.; Lanz, T.; Lindler, D.; Feggans, K.; Verner, E.; Woodgate, B.E.; Kimble, R.A.; et al. Discovery of a Little Homunculus within the Homunculus Nebula of η Carinae. Astron. J. 2003, 125, 3222–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R. The complex outer shell of Eta Carinae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1976, 204, L17–L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Duschl, W.J.; Bomans, D.J. High velocity structures in, and the X-ray emission from the LBV nebula around η Carinae. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 367, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Corcoran, M.F.; Bomans, D.J.; Davidson, K. A spectral and spatial analysis of η Carinae’s diffuse X-ray emission using CHANDRA. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Corcoran, M.F.; Davidson, K. On the X-ray Emission of η Carinae’s Outer Ejecta. In The High Energy Universe at Sharp Focus: Chandra Science; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Schlegel, E.M., Vrtilek, S.D., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 262, p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Glatzel, W. Instabilities in the Most Massive Evolved Stars. In The Fate of the Most Massive Stars; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Humphreys, R., Stanek, K., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 332, p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Vink, J.S. Eta Carinae and the Luminous Blue Variables. In Eta Carinae and the Supernova Impostors; Astrophysics and Space Science Series Library; Davidson, K., Humphreys, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 384, p. 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owocki, S.P. Instabilities in the Envelopes and Winds of Very Massive Stars. In Very Massive Stars in the Local Universe; Vink, J.S., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 412, p. 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, J.A. Instability Considerations for Massive Star Eruptions. In The Fate of the Most Massive Stars; Humphreys, R., Stanek, K., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2005; Volume 332, p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Lovekin, C.C.; Guzik, J.A. Pulsations as a driver for LBV variability. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalari, V.M.; Vink, J.S.; Dufton, P.L.; Fraser, M. How common is LBV S Doradus variability at low metallicity? Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 618, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Cantiello, M.; Bildsten, L.; Quataert, E.; Blaes, O.; Stone, J. Outbursts of luminous blue variable stars from variations in the helium opacity. Nature 2018, 561, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, W.R.; Feldmeier, A.; Oskinova, L.M. Clumping in hot-star winds. In Proceedings of the an International Workshop, Potsdam, Germany, 18–22 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist, J.O.; Puls, J.; Feldmeier, A.; Owocki, S.P. Mass loss from inhomogeneous hot star winds. II. Constraints from a combined optical/UV study. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 528, A64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J.; Vink, J.S.; Najarro, F. Mass loss from hot massive stars. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 16, 209–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Botticella, M.T.; Trundle, C.; Taubenberger, S.; Mattila, S.; Kankare, E.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Benetti, S.; Duszanowicz, G.; Hermansson, L.; et al. Multiple major outbursts from a restless luminous blue variable in NGC 3432. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D.; Bahcall, J.N.; Kirshner, R.r.P.; Woosley, S.E. Supernova 1987A. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 27, 629–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Della Valle, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Zampieri, L.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Mazzali, P.A.; Patat, F.; Spiro, S.; Turatto, M.; et al. A very faint core-collapse supernova in M85. Nature 2007, 449, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, K.; Bomans, D.J. SN 2002kg - the brightening of LBV V37 in NGC 2403. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 429, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomans, D.J.; Weis, K. SN Impostors, a complex mix-bag of transients. Astron. Astrophys. 2019. in prep. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M. Supernova impostors and other gap transients. Nature Astronomy 2019, 3, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Li, W.; Silverman, J.M.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Filippenko, A.V. Luminous blue variable eruptions and related transients: diver sity of progenitors and outburst properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 773–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomans, D.J.; Mueller, A.; Becker, A.; Weis, K.; Granzer, T. Gaia16ada: the most recent outburst of the supernova impostor in NGC 4559. The Astronomer’s Telegram 2016, 8755, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sana, H.; de Mink, S.E.; de Koter, A.; Langer, N.; Evans, C.J.; Gieles, M.; Gosset, E.; Izzard, R.G.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; Schneider, F.R.N. Binary Interaction Dominates the Evolution of Massive Stars. Science 2012, 337, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.S. Close Binary Models for Luminous Blue Variables Stars. In IAU Colloq. 113: Physics of Luminous Blue Variables; Davidson, K., Moffat, A.F.J., Lamers, H.J.G.L.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; Volume 157, p. 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justham, S.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Vink, J.S. Luminous Blue Variables and Superluminous Supernovae from Binary Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2014, 796, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, R.; Niemela, V. HD 5980; IAU Circular: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger, G.; Morrell, N.; Hillier, D.J.; Gamen, R.; Schneider, F.R.N.; González-Jiménez, N.; Langer, N.; Barbá, R. The HD 5980 Multiple System: Masses and Evolutionary Status. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figer, D.F.; Najarro, F.; Kudritzki, R.P. The Double-lined Spectrum of LBV 1806-20. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2004, 610, L109–L112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lobel, A.; Groh, J.H.; Martayan, C.; Frémat, Y.; Torres Dozinel, K.; Raskin, G.; Van Winckel, H.; Prins, S.; Pessemier, W.; Waelkens, C.; et al. Modelling the asymmetric wind of the luminous blue variable binary MWC 314. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 559, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martayan, C.; Lobel, A.; Baade, D.; Mehner, A.; Rivinius, T.; Boffin, H.M.J.; Girard, J.; Mawet, D.; Montagnier, G.; Blomme, R.; et al. Luminous blue variables: An imaging perspective on their binarity and near environment. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 587, A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffin, H.M.J.; Rivinius, T.; Mérand, A.; Mehner, A.; LeBouquin, J.B.; Pourbaix, D.; de Wit, W.J.; Martayan, C.; Guieu, S. The luminous blue variable HR Carinae has a partner. Discovery of a co mpanion with the VLTI. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 593, A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazé, Y.; Rauw, G.; Hutsemékers, D. The first X-ray survey of Galactic luminous blue variables. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Tombleson, R. Luminous blue variables are antisocial: their isolation implies that they are kicked mass gainers in binary evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 598–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Weis, K.; Davidson, K.; Gordon, M.S. On the Social Traits of Luminous Blue Variables. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. The isolation of luminous blue variables: on subdividing the sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Humphreys, R.M.; Weis, K. LBVs and Statistical Inference. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.02007. [Google Scholar]
- Aadland, E.; Massey, P.; Neugent, K.F.; Drout, M.R. Shedding Light on the Isolation of Luminous Blue Variables. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. The isolation of luminous blue variables resembles aging B-type supergiants, not the most massive unevolved stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 4378–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Kruijssen, J.M.D.; Rix, H.W. Not all stars form in clusters – Gaia-DR2 uncovers the origin of OB associations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.06974. [Google Scholar]
- Lortet, M.C. A provisory catalogue of S-Dor candidate stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Bull. Soc. R. Sci. Liege 1988, 35, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, O.; Wolf, B. The Spectral Evolution of the LMC S DOR Variable R127 during Outburst. In The Impact of Very High S/N Spectroscopy on Stellar Physics; Cayrel de Strobel, G., Spite, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; Volume 132, p. 557. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, O.; Wolf, B.; Klare, G.; Jüttner, A.; Cassatella, A. Observation of the new luminous blue variable R 110 of the Large Magellanic cloud during an F star-phase. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 228, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, B.; Stahl, O. Inverse P Cygni-type profiles in the spectrum of the luminous blue variable S Doradus. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 235, 340. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, O.; Wolf, B.; de Groot, M.; Leitherer, C. Atlas of hig-dispersion spectra of peculiar emission-line stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1985, 61, 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Szeifert, T.; Stahl, O.; Wolf, B.; Zickgraf, F.J.; Bouchet, P.; Klare, G. R 40: the first luminous blue variable in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 280, 508–518. [Google Scholar]
- Lindegren, L. The Tycho-Gaia Astrometric Solution. In Astrometry and Astrophysics in the Gaia Sky; Recio-Blanco, A., de Laverny, P., Brown, A.G.A., Prusti, T., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 330, pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegren, L.; Hernández, J.; Bombrun, A.; Klioner, S.; Bastian, U.; Ramos-Lerate, M.; de Torres, A.; Steidelmüller, H.; Stephenson, C.; Hobbs, D.; et al. Gaia Data Release 2. The astrometric solution. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanas, S.R.; Wright, N.J.; Herrero, A.; Drew, J.E.; Lennon, D.J. Disentangling the spatial substructure of Cygnus OB2 from Gaia DR2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Stangl, S.; Gordon, M.S.; Davidson, K.; Grammer, S.H. Luminous and Variable Stars in NGC 2403 and M81. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, P.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Hodge, P.W.; Jacoby, G.H.; McNeill, R.T.; Smith, R.C.; Strong, S.B. A Survey of Local Group Galaxies Currently Forming Stars. II. UBVRI Photometry of Stars in Seven Dwarfs and a Comparison of the Entire Sample. Astron. J. 2007, 133, 2393–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, P.; McNeill, R.T.; Olsen, K.A.G.; Hodge, P.W.; Blaha, C.; Jacoby, G.H.; Smith, R.C.; Strong, S.B. A Survey of Local Group Galaxies Currently Forming Stars. III. A Search for Luminous Blue Variables and Other Hα Emission-Line Stars. Astron. J. 2007, 134, 2474–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraf, B.; Weis, K.; Bomans, D.J. LBVs in Local Group Galaxies. Astron. Nachr. 2007, 328, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Bomans, D.J.; Weis, K.; Wittkowski, M. Massive Variable Stars at Low Metallicity: The Case of NGC 3109. In Proceedings of a Scientific Meeting in Honor of Anthony F. J. Moffat; Drissen, L., Robert, C., St-Louis, N., Moffat, A.F.J., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 465, p. 508. [Google Scholar]
- Spiller, F. Suche nach Leuchtkräftigen Blauen Veränderlichen und verwandten Objekten in M33, NGC 2403, M81 und M101. Ph.D. Thesis, University Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Weis, K.; Davidson, K.; Bomans, D.J.; Burggraf, B. Luminous and Variable Stars in M31 and M33. II. Luminous Blue Variables, Candidate LBVs, Fe II Emission Line Stars, and Other Supergiants. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Gordon, M.S.; Martin, J.C.; Weis, K.; Hahn, D. Luminous and Variable Stars in M31 and M33. IV. Luminous Blue Variables, Candidate LBVs, B[e] Supergiants, and the Warm Hypergiants: How to Tell Them Apart. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeifert, T.; Stahl, O.; Wolf, B.; Zickgraf, F.J. R40: First Luminous Blue Variable in the Small Magellanic Cloud. In New Aspects of Magellanic Cloud Research; Baschek, B., Klare, G., Lequeux, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 416, p. 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Martin, J.C.; Gordon, M.S. A New Luminous Blue Variable in M31. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2015, 127, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Guo, J.C.; Yuan, H.B.; Xiang, M.S.; Tian, Z.J.; Li, G.X.; et al. A New Luminous Blue Variable in the Outskirts of the Andromeda Galaxy. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 884, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M.; Davidson, K.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Gordon, M.S. A Tale of Two Impostors: SN2002kg and SN1954J in NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissen, L.; Crowther, P.A.; Smith, L.J.; Robert, C.; Roy, J.R.; Hillier, D.J. Physical Parameters of Erupting Luminous Blue Variables: NGC 2363-V1 Caught in the Act. Astrophys. J. 2001, 546, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandage, A. The brightest stars in nearby galaxies. II. The color-magnitude diagram for the brightest red and blue stars in M101. Astron. J. 1983, 88, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammer, S.H.; Humphreys, R.M.; Gerke, J. The Massive Star Population in M101. III. Spectra and Photometry of the Luminous and Variable Stars. Astron. J. 2015, 149, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandage, A. The brightest stars in nearby galaxies. III. The color-magnitude diagram for the brightest red and blue stars in M 81 and Holmberg IX. Astron. J. 1984, 89, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, L.J.; Herrero, A. Candidate LBVs in Local Group galaxies. In A Massive Star Odyssey: From Main Sequence to Supernova; van der Hucht, K., Herrero, A., Esteban, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; Volume 212, p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Bresolin, F.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Najarro, F.; Gieren, W.; Pietrzyński, G. Discovery and Quantitative Spectral Analysis of an Ofpe/WN9 (WN11) Star in the Sculptor Spiral Galaxy NGC 300. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 577, L107–L110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.M. Studies of luminous stars in nearby galaxies. V. The local group irregulars NGC 6822 and IC 1613. Astrophys. J. 1980, 238, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Ferrarese, L.; Saha, A.; Bresolin, F.; Kennicutt, Robert C., J.; Stetson, P.B.; Mould, J.R.; Freedman, W.L.; Gibson, B.K.; Graham, J.A.; et al. The Hubble Space Telescope Key Project on the Extragalactic Distance Scale. XI. The Cepheids in NGC 4414. Astrophys. J. 1998, 505, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, E.; Fugazza, D.; Mantegazza, L.; Bossi, M.; Covino, S. Variable stars in nearby galaxies. III. White light observations of Field B of IC 1613. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 363, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, A.; Garcia, M.; Uytterhoeven, K.; Najarro, F.; Lennon, D.J.; Vink, J.S.; Castro, N. The nature of V39: an LBV candidate or LBV impostor in the very low metallicity galaxy IC 1613? Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 513, A70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustilnik, S.A.; Tepliakova, A.L.; Kniazev, A.Y.; Burenkov, A.N. Discovery of a massive variable star with Z = Zsolar/36 in the galaxy DDO 68. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 388, L24–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomans, D.J.; Weis, K. The nature of the massive stellar transient in DDO 68. Bull. Soc. R. Sci. Liege 2011, 80, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Pustilnik, S.A.; Makarova, L.N.; Perepelitsyna, Y.A.; Moiseev, A.V.; Makarov, D.I. The extremely metal-poor galaxy DDO 68: the luminous blue variable, Hα shells and the most luminous stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 4985–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Adams, S.M.; Stanek, K.Z.; Kochanek, C.S.; Sonneborn, G. Discovery of Five Candidate Analogs for η Carinae in Nearby Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 815, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kochanek, C.S.; Stanek, K.Z.; Gerke, J. Finding η Car Analogs in Nearby Galaxies Using Spitzer. II. Identification of An Emerging Class of Extragalactic Self-Obscured Stars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissen, L.; Roy, J.R.; Robert, C. A New Luminous Blue Variable in the Giant Extragalactic H II Region NGC 2363. Astron. J. 1997, 474, L35–L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, V.; Drissen, L.; Crowther, P.A. Spectral Evolution of the Luminous Blue Variable NGC 2363-V1. I. Observations and Qualitative Analysis of the Ongoing Giant Eruption. Astron. J. 2006, 132, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, E.; Annibali, F.; Cignoni, M.; Aloisi, A.; Sohn, T.; Tosi, M.; van der Marel, R.P.; Grocholski, A.J.; James, B. Stellar Populations and Star Formation History of the Metal-poor Dwarf Galaxy DDO 68. Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izotov, Y.I.; Thuan, T.X. Luminous Blue Variable Stars in the two Extremely Metal-Deficient Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies DDO 68 and PHL 293B. Astrophys. J. 2009, 690, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izotov, Y.I.; Guseva, N.G.; Fricke, K.J.; Henkel, C. VLT/X-shooter observations of the low-metallicity blue compact dwarf galaxy PHL 293B including a luminous blue variable star. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 533, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.E.; Sánchez Almeida, J. An unusual transient in the extremely metal-poor Galaxy SDSS J094332.35+332657.6 (Leoncino Dwarf). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 2541–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolowsky, E.; Simon, J.D. The M33 Metallicity Project: Resolving the Abundance Gradient Discrepancies in M33. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio San Cipriano, L.; Domínguez-Guzmán, G.; Esteban, C.; García-Rojas, J.; Mesa-Delgado, A.; Bresolin, F.; Rodríguez, M.; Simón-Díaz, S. Carbon and oxygen in H II regions of the Magellanic Clouds: abundance discrepancy and chemical evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3759–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.F.; Rosales-Ortega, F.F.; Iglesias-Páramo, J.; Mollá, M.; Barrera-Ballesteros, J.; Marino, R.A.; Pérez, E.; Sánchez-Blazquez, P.; González Delgado, R.; Cid Fernandes, R.; et al. A characteristic oxygen abundance gradient in galaxy disks unveiled with CALIFA. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 563, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresolin, F. Metallicity gradients in small and nearby spiral galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 3826–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, A.V.; Lozinskaya, T.A. Ionized gas velocity dispersion in nearby dwarf galaxies: looking at supersonic turbulent motions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, B. Integral Field Spectroscopy of Late-Type Galaxies: Kinematics and Ionization Structure of Starbursts. Ph.D. Thesis, Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tully, R.B.; Rizzi, L.; Shaya, E.J.; Courtois, H.M.; Makarov, D.I.; Jacobs, B.A. The Extragalactic Distance Database. Astron. J. 2009, 138, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramper, F.; Sana, H.; de Koter, A.; Kaper, L. On the Mass-loss Rate of Massive Stars in the Low-metallicity Galaxies IC 1613, WLM, and NGC 3109. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 741, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramper, F.; Sana, H.; de Koter, A.; Kaper, L.; Ramírez-Agudelo, O.H. The properties of ten O-type stars in the low-metallicity galaxies IC 1613, WLM, and NGC 3109. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 572, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Evans, C.J.; Bestenlehner, J.M.; Bouret, J.C.; Castro, N.; Cerviño, M.; Fullerton, A.W.; Gieles, M.; Herrero, A.; de Koter, A.; et al. Massive stars in extremely metal-poor galaxies: A window into the past. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.04687. [Google Scholar]
- Bomans, D.J.; Weis, K. Massive variable stars at very low metallicity. In Active OB Stars: Structure, Evolution, Mass Loss, and Critical Limits; Neiner, C., Wade, G., Meynet, G., Peters, G., Eds.; IAU symposium; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 272, pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roth, M.M.; Sandin, C.; Kamann, S.; Husser, T.O.; Weilbacher, P.M.; Monreal-Ibero, A.; Bacon, R.; den Brok, M.; Dreizler, S.; Kelz, A.; et al. MUSE crowded field 3D spectroscopy in NGC 300. I. First results from central fields. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 618, A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wofford, A.; Ramirez, V.; Lee, J.C.; Thilker, D.A.; Della Bruna, L.; Adamo, A.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Herrero, A.; Kim, H.; Aloisi, A.; et al. Candidate LBV stars in galaxy NGC 7793 found via HST photometry + MUSE spectroscopy. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomans, D.J.; Weis, K. Long-slit échelle spectroscopy of galactic outflows: The case of NGC 4449. Astron. Nachr. 2014, 335, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
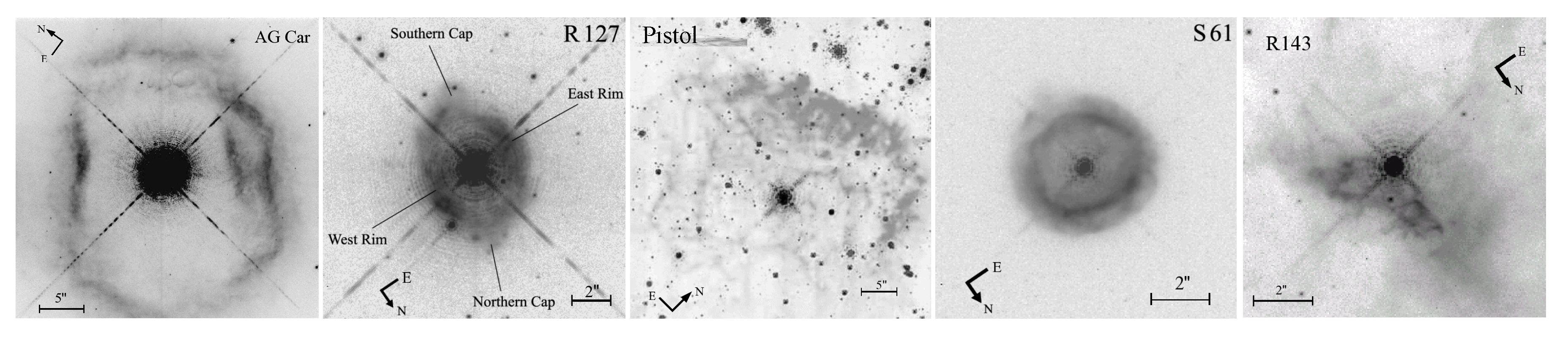
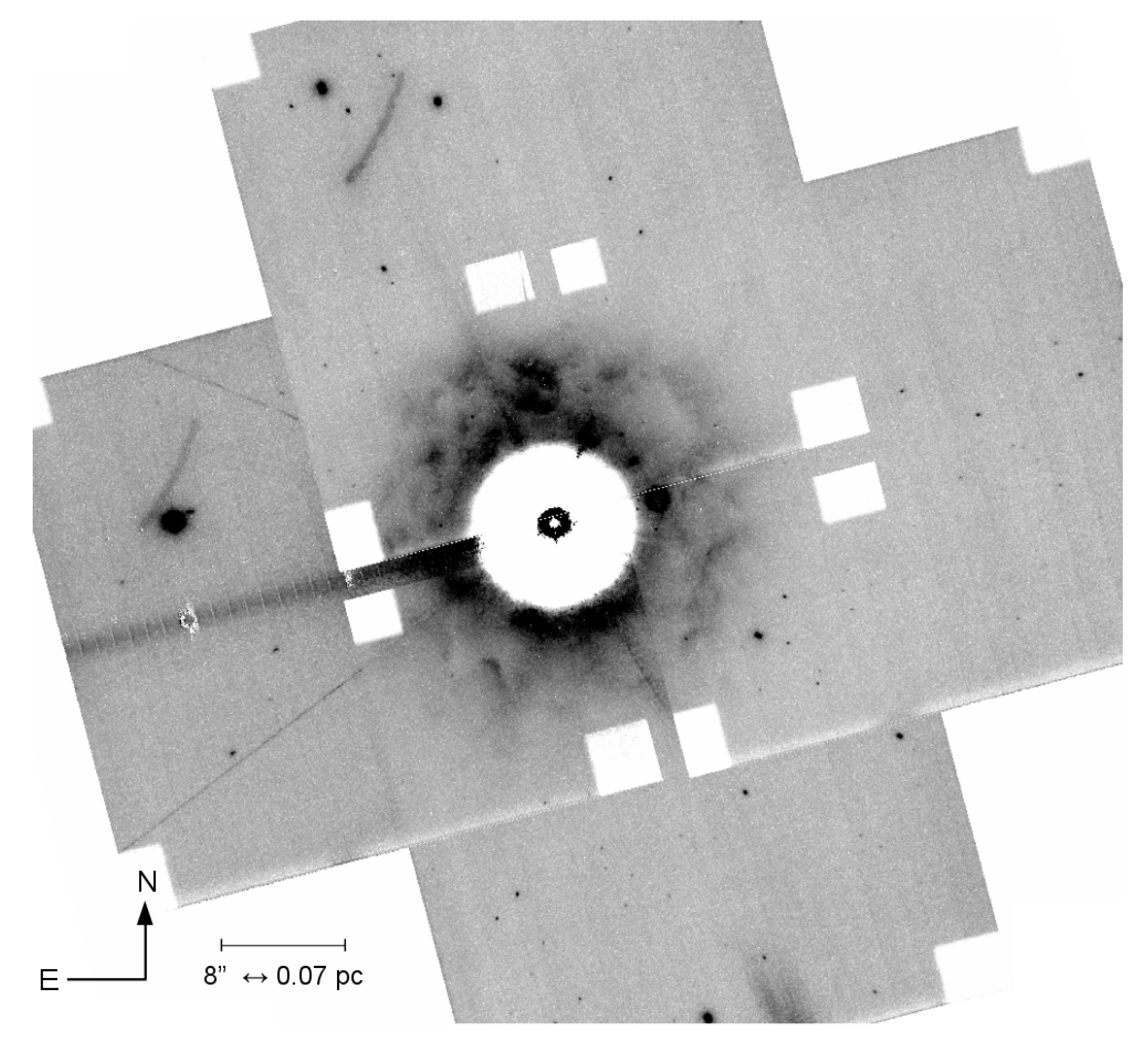
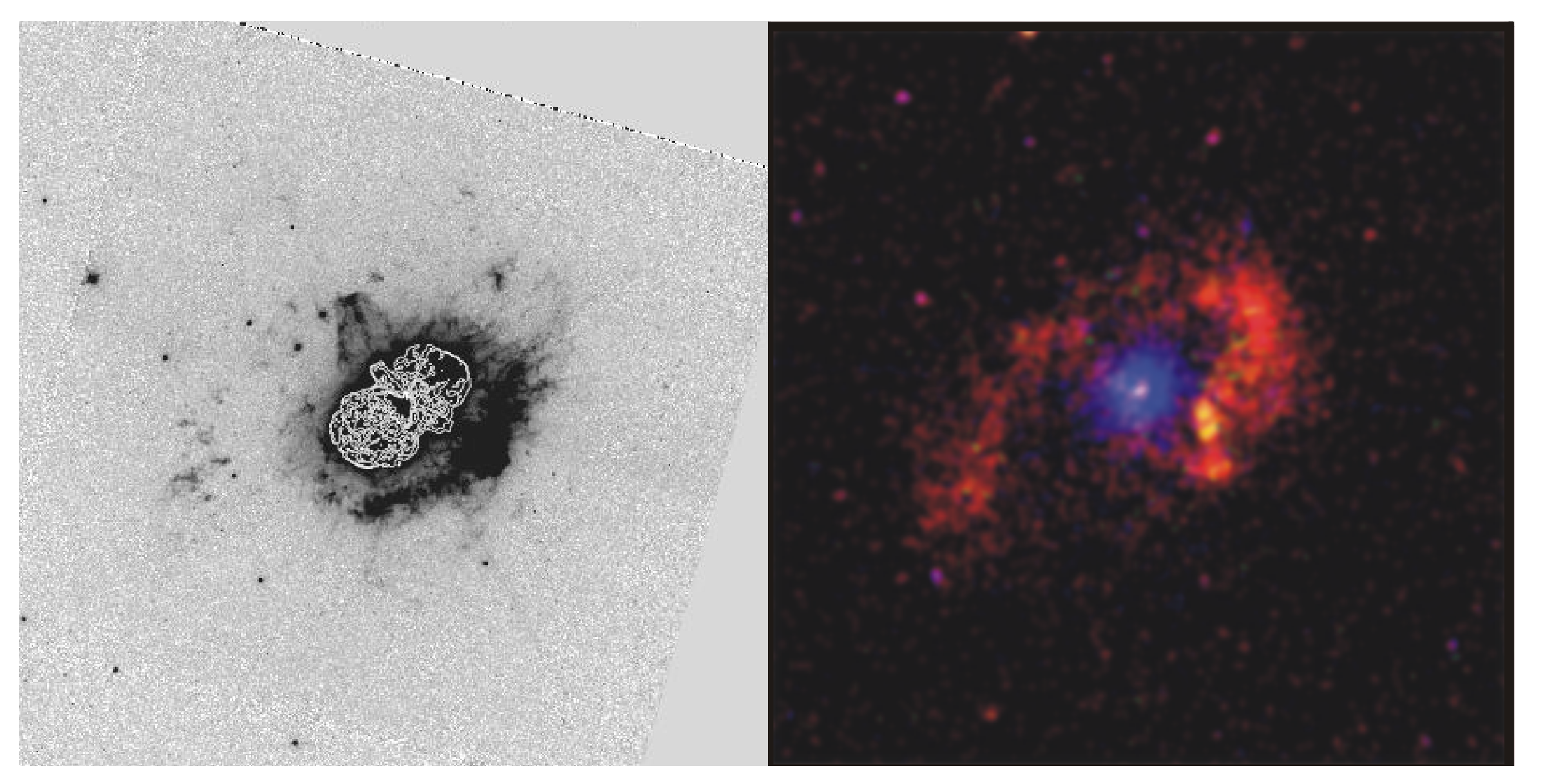
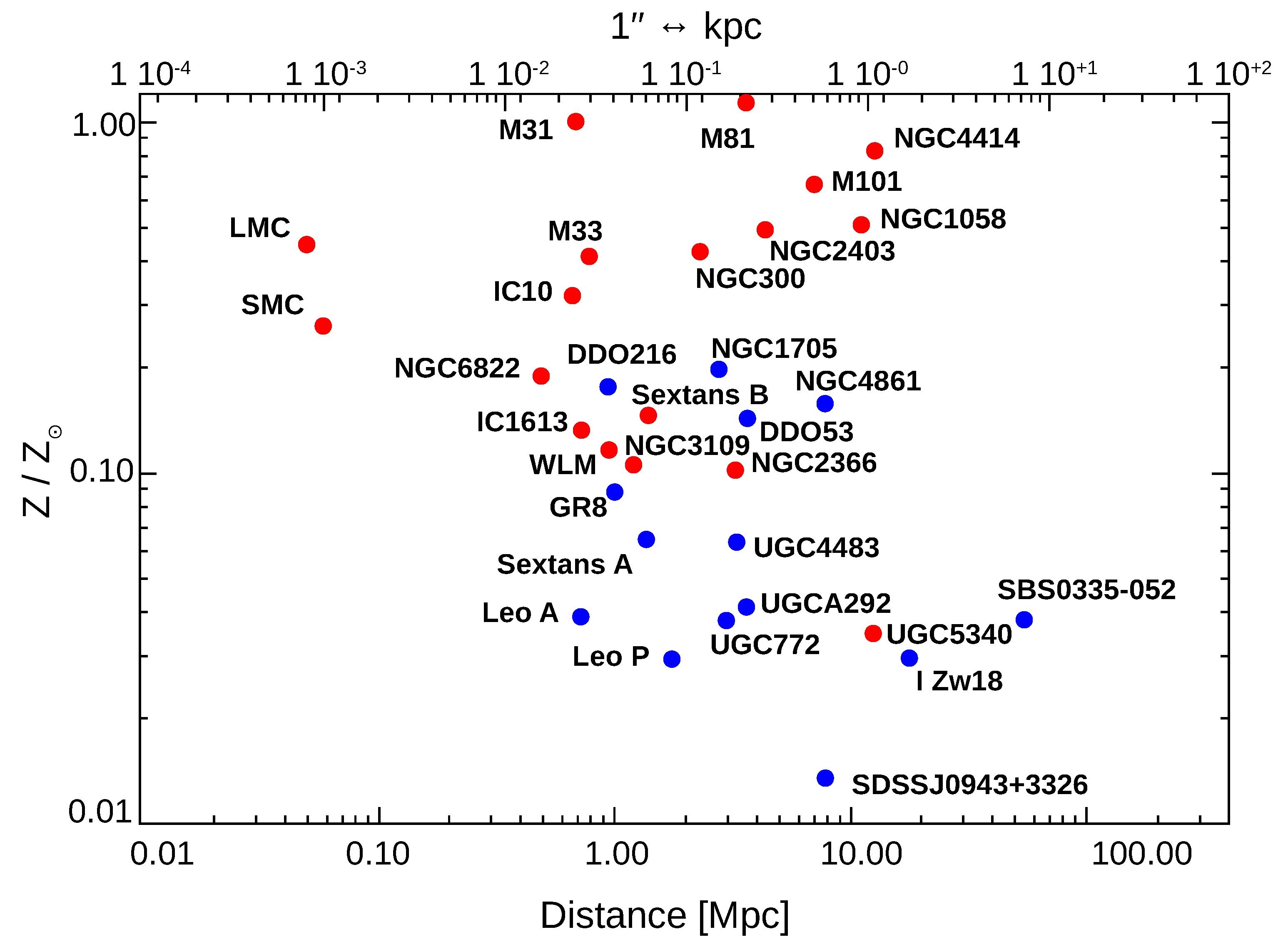
| LBV | Host Galaxy | Maximum Size | Morphology | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [pc] | [km/s] | ||||
| Carinae | Milky Way | 0.2/0.67 | 300/ | bipolar | [58,60] |
| AG Carinae | Milky Way | 1.4 × 2 | bipolar | [61] | |
| HD 168625 | Milky Way | 0.13 × 0.17 | 40 | bipolar | [57] |
| He 3-519 | Milky Way | 2.1 | 61 | spherical | [55] |
| HR Carinae | Milky Way | 1.3 × 0.65 | 75 | bipolar | [62] |
| P Cygni | Milky Way | 0.2/0.8 | /185 | spherical | see text |
| WRA 751 | Milky Way | 0.5 | 26 | bipolar | [63] |
| Pistol star | Milky Way | 0.8 × 1.2 | 60 | spherical | [64] |
| Sher 25 | Milky Way | 0.4×1 | bipolar | [65] | |
| R 127 | LMC | 1.3 | 32 | bipolar | [52] |
| R 143 | LMC | 1.2 | 24 (line split) | irregular | [52] |
| S 61 | LMC | 0.82 | 27 | spherical | [52] |
| S 119 | LMC | 1.8 | 26 | spherical plus outflow | [53] |
| Sk-69 279 | LMC | 4.5×6.2 | 14 | spherical plus outflow | [56] |
| Galaxy | LBVs | LBV Candidates | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milky Way | AG Car, Car, FMM 362, | BD+143887, BD-13 5061, B[B61] 2, | |
| [GKF2010] MN44, | G025.520+0.216, G79.29+0.46, GCIRS 16C, | ||
| [GKM2012] WS1, | GCIRS 16NE, GCIRS 16NW, GCIRS 33SE, | ||
| HD 168607, HD 160529, | GCIRS 16SW, [GKF2010] MN58, | ||
| HD 193237, HR Car, | [GKF2010] MN61, [GKF2010] MN76, | ||
| LBV G0.120-0.048, MWC 930, | [GKF2010] MN 80, [GKF2010] MN83, | ||
| P Cygni, V481 Sct, | [GKF2010] MN96, [GKF2010] MN112, | ||
| W243, WRA 751 | [GKF2010] WS2, HD 168625, HD 316285, | ||
| HD 326823, He 3-519, IRAS16278-4808, | |||
| IRAS19040+0817, J17082913-3925076, | |||
| [KMN95] Star A, | |||
| MSX6C G026.4700+00.0207, Pistol star, | |||
| Sher 25, WR 102ka, | |||
| WRAY 16-137, WRAY 16-232 | |||
| LMC | HD 269216,R 71, R 85, | HDE 269582, S 61, S 119, Sk-69 279 | |
| R 127, R 143, R 110, S Dor, | |||
| SMC | R 40 | (R 4), (R 50) | [148] |
| M 31 | AE And, AF And, | J003910.85+403622.4, J00441132+4132568, | [147,149] |
| LAMOSTJ0037+4016, | M 31-004425.18, M31-004051.59 | [150] | |
| UCAC4 660-00311, | |||
| Var A-1, Var 15 | |||
| M 33 | Var B, Var C, Var 2, Var 83, | GR 290, [HS80] B48, [HS80] B416, | [147] |
| [HS80] B517, J013228.99+302819.3, | [18] | ||
| J013235.21+303017.4,J013317.01 + 305329.87, | |||
| J013317.22+303201.6, J013334.11+304744.6, | |||
| J013337.31336+303328.8, J013351.46+304057.0, | |||
| J013354.85+303222.8, J01342475+3033061, | |||
| J01342718+3045599, J013432.76+304717.2, | |||
| J013459.36+304201.0, J01350971+3041565, | |||
| M33C-5916, M33C-10788, M33C-15235, | |||
| M33C-16364, M33C-21386, UIT 008 | |||
| NGC 2403 | SN 1954J=V12, | V 22, V 35, V 38 | [24] |
| SN 2002kg=V37 | [140,151] | ||
| NGC 1058 | SN 1961V | [25,26] | |
| NGC 2366 | NGC 2363 V1 | [152] | |
| M 101 | J140220.98+542004.38, V 1, V 2, V 4, V 9, V 10 | [153,154] | |
| M 81 | I 1, I 2 | [140,155] | |
| IC 10 | unnamed | [156] | |
| NGC 300 | B 16 | [157] | |
| NGC 6822 | unnamed | [158] | |
| NGC 4414 | unnamed | [159] | |
| IC 1613 | V 39, V1835, V2384, V3072, | [158] | |
| V3120, V0416, V0530, | [160,161] | ||
| UGC 5340 | unnamed | [162,163,164] | |
| NGC 3109 | unnamed | [144] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weis, K.; Bomans, D.J. Luminous Blue Variables. Galaxies 2020, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8010020
Weis K, Bomans DJ. Luminous Blue Variables. Galaxies. 2020; 8(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeis, Kerstin, and Dominik J. Bomans. 2020. "Luminous Blue Variables" Galaxies 8, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8010020
APA StyleWeis, K., & Bomans, D. J. (2020). Luminous Blue Variables. Galaxies, 8(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8010020




