Abstract
In this review a summary is given on recent theoretical work, on understanding accreting supermassive black hole binaries in the gravitational wave (GW)-driven regime. A particular focus is given to theoretical predictions of properties of disks and jets in these systems during the gravitational wave driven phase. Since a previous review by Schnittman 2013, which focussed on Newtonian aspects of the problem, various relativistic aspects have been studied. In this review we provide an update on these relativistic aspects. Further, a perspective is given on recent observational developments that have seen a surge in the number of proposed supermassive black hole binary candidates. The prospect of bringing theoretical and observational efforts closer together makes this an exciting field of research for years to come.
1. Introduction
The study of supermassive black hole binary evolution is an old research field dating back at least as far as 1980 [1,2] where key physical processes operating on a diverse range of length scales were identified. In this pioneering work it was readily realized that following a galaxy merger event, the two black holes assumed at the centers of each progenitor galaxy would slowly sink towards the center of the common gravitational potential via a combination of dynamical friction and more generally through N-body interactions with the stellar population. While the arguments draw a rather clear picture free from major ambiguities at large separations, the behavior nearing scale separations and lower would later prove to be much more involved.
1.1. : Galaxy Mergers and Relaxation, Key Physics: Newtonian Self-Gravity
The Hubble space telescope famously delivered direct images of mergers of galaxies on scales [3] thereby proving that galaxies do collide and establishing the first necessary step towards supermassive black hole binary coalescence. Finding similar evidence between and scales requires more resolution and necessarily leads to a smaller population to be observed. Despite these technical hurdles more recent observational efforts take on this challenge in a variety of different ways [4].
In many black hole (BH) systems, the mass accretion rate is at intermediate levels causing the accretion flow to be of a geometrically thin, optically thick type. In principle, by modeling the thermal radiation one can probe the location of the innermost stable circular orbit (ISCO) and hence the BH spin via the so-called continuum fitting method. However, this technique is far more powerful for stellar-mass systems and challenging to apply to active galactic nuclei (AGN) [5]. In addition, AGNs in the thin-disk regime can exhibit strong X-ray emission in the polar regions above and below the black hole that irradiates the colder disk material. This process can excite atomic transitions and gives rise to fluorescence in the process. In particular, the astrophysically-abundant iron coupled with its high fluorescent yield leads to a strong Fe K line.
Spectroscopic efforts sport an impressive spectral resolution and sensitivity [6], which allows detailed measurements of Fe K emission line profiles, which is affected by several relativistic effects. Many inferences on BH spin [5] via relativistic effects have been achieved with this method in what we believe to be single black hole systems. It is expected that Athena [7] (launch date 2031) will greatly boost the prospects of this research field. The same method can also be applied to binary black hole sources. The spectral profile of such a line is then very sensitive to the relativistic motion of the emitting gas producing asymmetric double-horned line profiles. Modeling such line profiles and comparing to observations offers a probe of the spacetime structure of the BHs in the strong-field regime. Secular trends may even be used to uncover orbital motion via an offset between the broad and narrow-line regions on the orbital time scale [8] or spectral imprints due to a radially migrating secondary [9].
Complementary efforts that also do not rely on spatially resolving the source seek to reveal periodicities in light curves and attempt to model the line profile through relativistic orbital motion [4]. Spectroscopic surveys are likely to identify numerous, additional candidate sources in the gravitational wave (GW)-driven regime [10].
An interesting candidate for a supermassive black hole (SMBH) binary is the well-known blazar source OJ-287 [11,12,13,14], whose optical lightcurve extends back 150 years showing several periodic features. However, alternative interpretations are being put forward, see e.g., the recent work in [15], that identifies the variability not with binary motion but with a precessing jet. Ultimately a combination of improvements in theoretical modeling and more observational data can be expected to inform us on the true nature of this fascinating source.
Other candidate SMBH binaries based on X-ray data (with XMM-Newton) [16] or optical data [17,18,19,20] have been proposed. Typical orbital time scales inferred in these studies are on the order of years, which is comparable to the duration of monitoring. This creates what is sometimes referred to as red noise. The main obstacle in these studies is therefore the limited observing period.
It remains key to extend our observational data sets both to inform theoretical work and to better our understanding of the physical processes at work throughout this long process. The most relevant physics strongly varies with binary separation: For galaxy merger events occurring on scales and also for stellar distances on scales Newtonian gravity and perhaps hydrodynamics (without magnetic fields) is an adequate description. On scales comparable to the gravitational radius of the black holes of order gravity and spacetime itself becomes the dominant force in determining the fate of the system. Therefore, the most realistic models in the regime where GW emission with an electromagnetic counterpart can be expected, solve the equations of General Relativity (GR) and magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). We now discuss each epoch of the binary’s evolution in turn.
1.2. : The Final-Parsec Problem, Key Physics: Newtonian Self-Gravity + Hydrodynamics
At separations of relativistic aspects of gravity are still unimportant, but the local disk mass (self-gravity) cannot be ignored. A brief discussion of this Newtonian physics is in order, because all studies of relativistic aspects rest on the assumption that binaries in the GW-driven regime can form in the first place. The current understanding of SMBH binary evolution on scale orbital separation and below is necessarily largely based on theory thus far.
The theoretical description up until scale separations seems rather unambigious and uninterrupted by any major theoretical roadblocks. This situation changes when the binary reaches separations of order , because the known drivers of inward binary migration at larger scales, i.e., interaction of the binary with the surrounding stellar dynamics, may grind to a halt under some circumstances. At the heart of the problem is the fact, that only stars with the right orbital properties may come in close enough to interact with the binary and take energy out of the system. Within the assumptions of these pioneering studies, see e.g., [21,22], in particular spherically symmetric distribution of stars, purely gravitational N-body interactions, the supply of such stars with the suitable orbital properties become unavailable at scale separations. At these orbital separations gravitational radiation is not yet efficient enough to cause sufficient energy loss. Lacking a similarly obvious contender or other possible remedies at the time to drain orbital energy from the binary the term “final-parsec problem” was coined [21,22]. One unfortunate side-effect of this development was, that it generated a strong paradigm. It was suspected or assumed that SMBH binaries simply stalled at orbital separations, despite a quickly growing literature that started systematically questioning or relaxing the assumptions made [23,24,25,26,27,28,29] involving self-gravity of the hydrodynamic component, non-spherical distributions of stars, and others all showing great potential to drive binary inward migration. A full discussion of the evolution through the parsec scale is far beyond the scope of this review, but it seems increasingly more difficult to ignore the wealth of possible ways for nature to overcome the (theoretical, but not actual) parsec scale barrier. It will be of greatest interest in the context of the Laser Interferometric Space Antenna (LISA) [30,31] mission to understand in detail when and at what rate supermassive black hole binaries merge as a function of cosmic time. Here only a rough sketch is given of various phases in the binary evolution on different length scales and the dominant physics that must be modeled. See [32] for a more detailed and comprehensive discussion.
1.3. sub--: Gravitational Wave-Driven Regime, Key Physics: GR + Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
At orbital separations a somewhat below the scale or more quantitatively
where e is the orbital eccentricity, q the mass ratio, and the total mass of the binary, the binary will coalesce in less than a Hubble time merely by energy and angular momentum losses due to GW emission losses which depend sensitively on the orbital eccentricity [33,34].
Gravitational radiation therefore becomes a critical element in determining the subsequent evolution of the system as a whole. It is this regime and everything that follows where the focus of this review lies.
At sub- length scales the impact of gravitational-wave-driven losses is still subdominant but in principle strong enough for a detection by Pulsar Timing Arrays (PTAs) [35], which are most sensitive at low () frequencies. However, only separations shorter than about milli separations ensure orbital periods of a few years or less and therefore avoid excessively long observational campaigns. This provides key information on population synthesis and the assembly of supermassive black holes through cosmic time [36,37,38,39,40]. Especially in light of recent surges in the number of proposed binary candidates, even current constraints from the unresolved GW background from PTAs are starting to become informative, favoring the hypothesis that false positives may be quite abundant in the current catalogues of proposed binary sources [41]. PTAs attempt to measure gravitational waves through detecting minute, but correlated changes in the time of arrival of pulses from a network of extremely well-timed pulsars. This galactic scale interferometer becomes more and more sensitive over time as more pulsars are discovered and the timing model of existing ones is improved further and further as more data is collected. On scales of several to hundreds of gravitational radii, the gravitational waves emitted will constitute a large signal for the LISA mission planned in the early 2030s, which e.g., would allow a pre-merger localization of the source [42].
1.4. Binary–Disk Decoupling
The rate of orbital decay of the binary due to the emission of gravitational waves [33,34] is
where is the binary mass ratio, and M the total mass1. Note, in particular, that scales differently with binary separation a than the response of the disk governed by the viscous time scale
Here is the location of the inner disk edge, the Maxwell stress (describing the effective viscosity due to magneto-rotational instability (MRI) turbulence), and the vertical scale height of the disk. As a result, there will be a separation, called the decoupling separation , where the two time scales match:
. For separations the disk can adjust to the shrinking orbit and follow the binary to smaller separations. For separations the binary orbital decay is becoming too rapid, thereby leaving the disk material behind. During these fast late inspiral phases the binary tidal torques also diminish quicker than the disk can respond. The disk material from this moment on drifts slowly radially inward.
When the black holes reach separations comparable to their size they coalesce forming one black hole. This regime marks the most significant departure from the Newtonian regime and only numerical relativity techniques can describe this regime. The merged black hole is larger than each progenitor, but the overall gravitational mass is lower than the combined mass of both progenitors due to significant energy that is radiated away in the form of gravitational waves. This reduction in total mass poses a sudden perturbation to the disk material and can cause transient effects [43,44]. If the binary configuration is not too symmetric the gravitational wave linear momentum will be radiated away in a non-spherically symmetric way imparting a GW recoil or “kick” onto the merger remnant that can either cause long term oscillatory motion between the black hole and the disk material or eject the central black hole altogether from the system. In most cases one expects the former [45,46,47] and the system will settle on several viscous time scales down to the classical accreting single black hole configuration.
1.5. Lessons Learned from Single Black Hole Accretion
In many respects, the study of the evolution of black hole binaries orbiting in a gaseous environment, can benefit greatly from insights gained from the study of single black hole accretion. The latter is a far more mature field of research with many independent groups world-wide actively contributing to solidify our knowledge of these systems. However, it is still fair to say that rather major theoretical uncertainties still prevail in some regimes, e.g., hot, puffy radiatively inefficient accretion flows [48] and the Eddington–Super Eddington regime [49], especially when it comes to their observational appearance.
It has long become the norm in single black hole accretion simulations to treat General Relativistic effects, e.g., to include the horizon and correct gravitational field properly. Studies of magnetized accretion flows onto black hole binaries by extension also must be modeled with the effects of general relativity included or risk an uncontrolled assumption in the models. In particular, a proper description of the magnetically dominated outflows, the orbital decay (and eventually decoupling) of the binary, or to incorporate a region where no stable circular orbits are possible demands general relativistic effects to be included.
2. Results
A previous review article [50] focussed on Newtonian aspects of accreting black hole binaries. Since then several studies were conducted that have taken into account relativistic aspects of gravity. These findings have advanced our understanding of the role of accreting black hole binaries as electromagnetic counterparts to gravitational wave sources. Therefore an update to [50] is in order.
Initially, relativistic studies of black hole binaries in gaseous environments did not include magnetic fields due to numerical/technical issues arising from highly magnetized regions near the black hole event horizons, which is inherently more difficult to handle in the dynamic spacetime case compared to a time-independent spacetime like a Kerr black hole. The potential for electromagnetic (EM) counterparts to a strong GW source based on purely hydrodynamic studies [51,52,53,54] were underestimated due to the neglect of magnetic fields [55,56,57,58]. In the end, the role of binary tidal torques on driving accretion was overestimated. Instead, effective viscosity due to turbulent motion driven by the magneto-rotational instability [59,60] by far dominates angular momentum transport. This can most clearly be seen in the side-by-side comparison of a pure hydrodynamic and a magnetized model with the same code and grid setup, see Figure 6 in [57]. In fact, there were already strong indications for this in an earlier Newtonian study [61]. Now with magnetic field dynamics and relativistic gravity included, it is becoming ever more clear that accretion rates onto black hole binaries can be of the same magnitude as is known in single black hole systems, albeit with a different, certainly non-axisymmetric structure composed of two dense accretion streams. The parameter space describing an accreting binary black hole system is naturally higher dimensional and hence more computationally expensive to explore than the single black hole case.
First explorations in mass ratio [57,58], different separations [62] and disk height dependence [63] have led to an enhanced understanding of these systems.
2.1. New Structural Features in the Binary Case
The dominance of magnetically-induced, effective shear viscosity in driving accretion does not mean, however, that binary torques are unimportant. Quite to the contrary: Binary tidal torques play a dominant role in the structure of the inner disk and shape of the accretion flow, giving rise to a number of structures that are not seen in accreting systems composed of only a single black hole.
2.1.1. Cavity and Pile-Up
The very first theoretical discovery of a potential signature due to a binary, that is imparted on the structure of the accretion flow, is a cavity [64,65] inside which the density of the gas is much lower than elsewhere in the accretion flow. Such a cavity is formed where binary tidal torques dominate the angular momentum budget, thereby pushing gas elements away from the binary orbit leaving behind a region of substantially lowered density. A close analogy to planet formation in protoplanetary disks [66,67,68] can be drawn here: Depending on the mass ratio of the star-giant planet system binary tidal torques may clear out a gap in the disk thereby influencing the radial motion (“migration”) of the binary. The border of the cavity/gap, i.e., the inner edge of the circumbinary disk features a pile-up, an axisymmetric overdensity caused by material being pushed from both radial directions towards this boundary. This cavity can have important observational consequences in the form of altering the main locations of emission and introducing coherent, i.e., ordered but not necessarily periodic, time variability.
2.1.2. Non-Axisymmetric Structures: Streams and Lumps
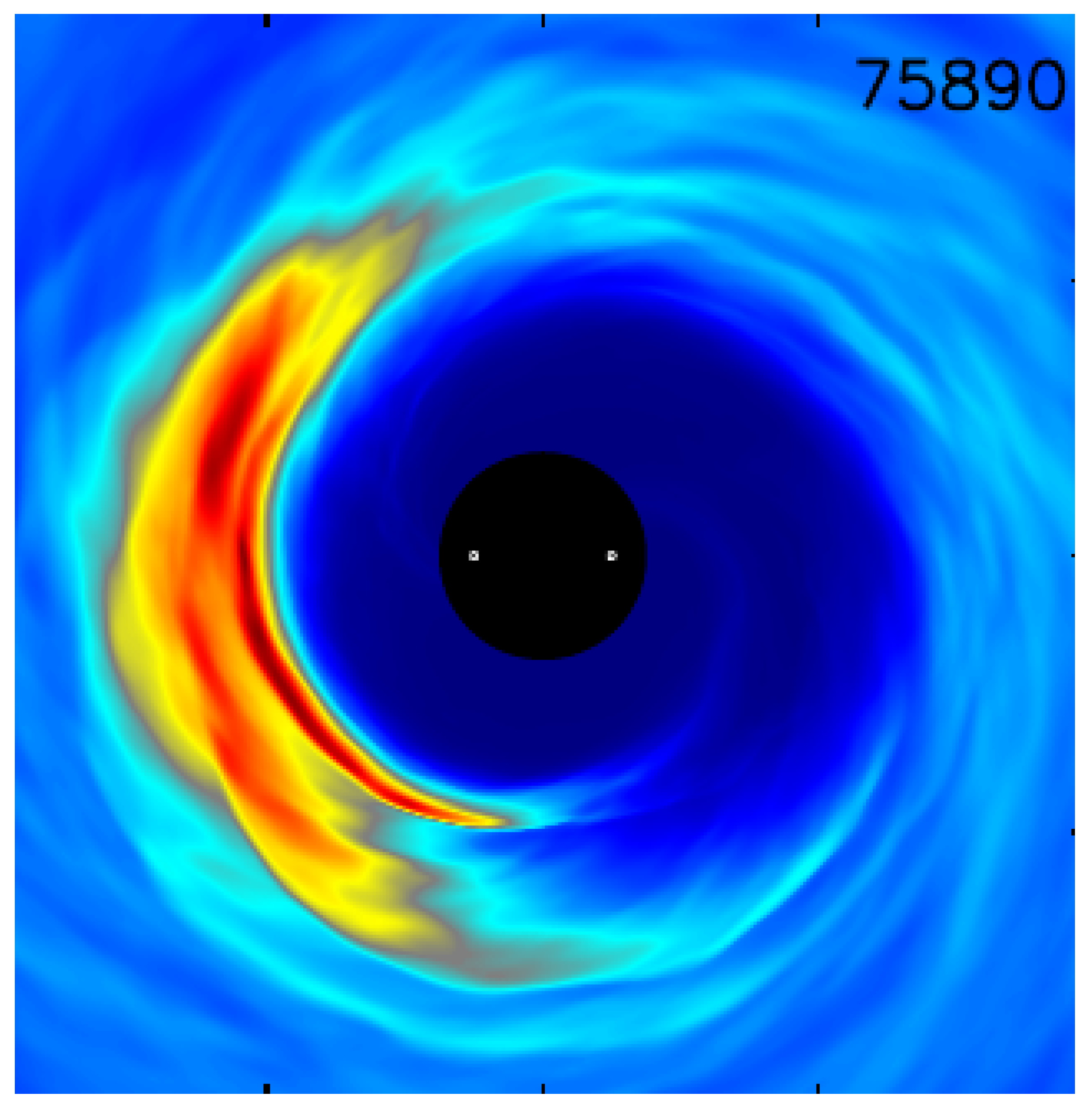
A feature also known from protoplanetary disks are overdense accretion streams across the secondary binary component. Two such dense accretion streams are readily identified in circumbinary accretion disks around SMBH binaries, too, see Figure 2. A persistent, non-axisymmetric overdensity, termed a “lump” and its implications were studied in detail in [55,61,69,70], see Figure 1. Such a feature is thought to arise due to non-accreting matter being repeatedly sloshed back towards the inner edge of the circumbinary disk. The gas that is driven back out, is ejected in a directionally preferred orientation, thereby gradually building up a somewhat local overdensity that then orbits near the inner edge of the disk. The lump exhibits overdensities of a factor of 4 over the average density in the rest of the disk and covers 1–2 radians in the azimuthal domain [69]. Crucially, in the relativistic treatment an mode appeared to dominate over modes seen in Newtonian studies [71]. Such a structure can similarly to the accretion streams produce coherent time variable signatures.
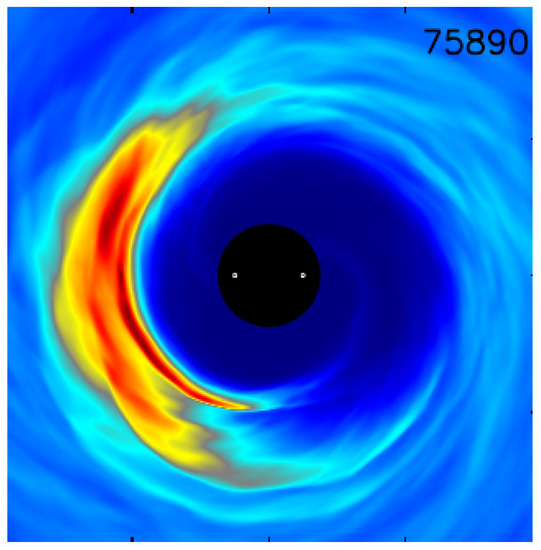
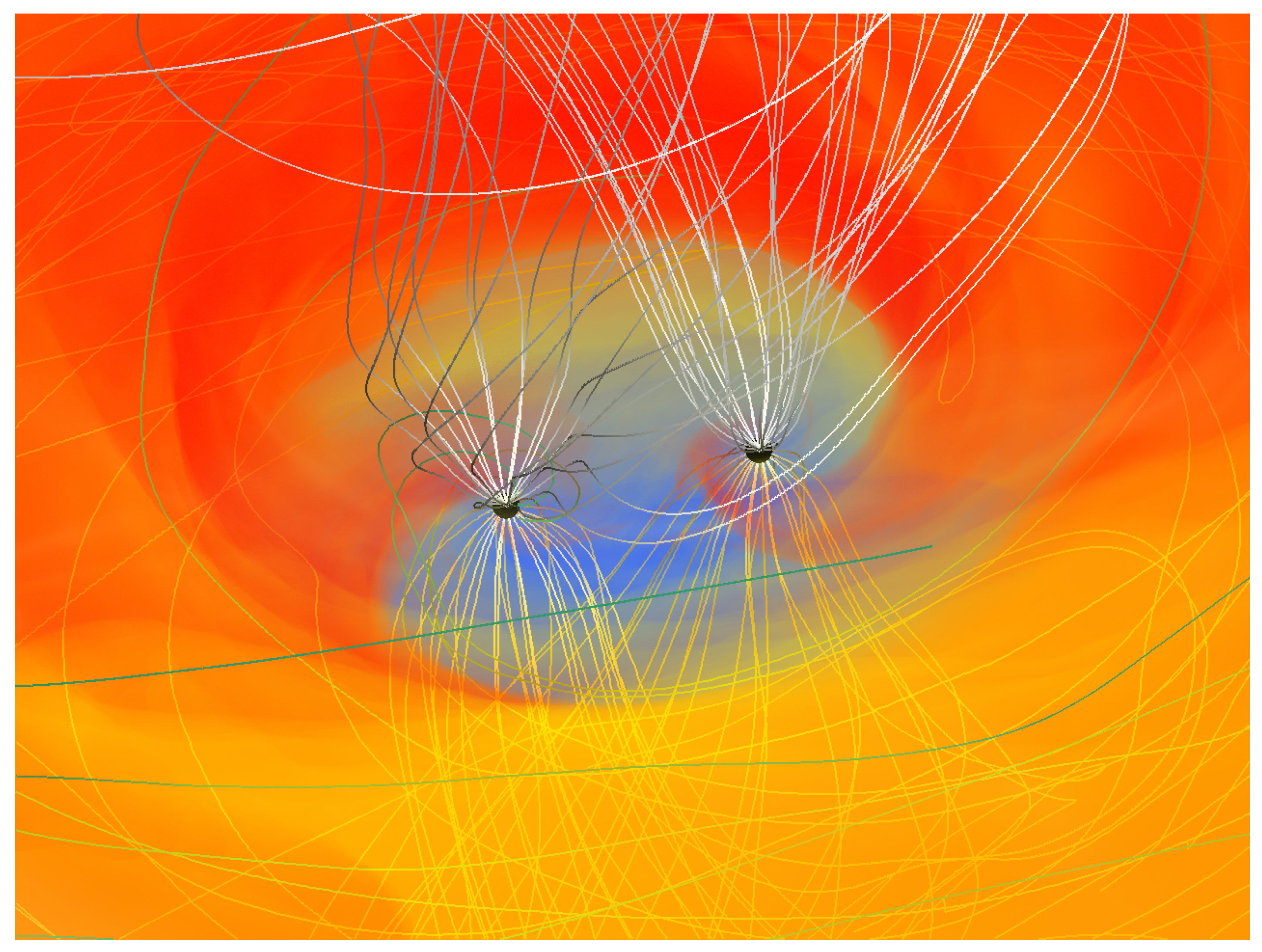
Figure 1.
Rest-mass density (linear color scale) from [55] a GRMHD simulation in a spacetime framework similar to [72]. A persistent non-axisymmetric overdensity termed a “lump” develops in the bulk of the disk.
2.1.3. Mini-Disks and Mass Sloshing
At large enough binary separations a region analogous to the Newtonian Hill-sphere in which gravity is dominated by the near-by binary component allows for mini-disks to form. This phenomenon was investigated in [62,69]. In total the system can therefore in principle feature three disks: (i) A mini disk around the primary, (ii) another mini disk around the secondary and (iii) the circumbinary disk. In general, these three disks are interacting with each other and lead to episodic dynamics that affect the accretion onto the black holes. Some qualitative conclusions can immediately be drawn. For instance, if there is a BH driven jet or a dual jet structure emerging from the system, it will be fueled by the material that is closest to the black hole horizon, i.e., the mini disks if present, not the circumbinary disk. The mini-disk-driven accretion flows around each black hole move at relativistic velocities with the binary orbit, which has great potential to leave clear smoking-gun signatures in observations.
One important relativistic aspect, is that mini disks cannot persist towards merger and in fact cannot last as long as one would expect from Newtonian estimates. While in Newtonian gravity test particles can orbit arbitrarily close to a central gravitating object forever, test particles around black holes in General Relativity can only do so outside a finite radius, the radius of the innermost stable circular orbit. The argument is strict for single BHs, but can be expected to at least qualitatively carry over for the binary case as well. As a result, mini disks can only exist when the extent of the Hill sphere extends beyond the innermost stable circular orbits around each BH. As the binary then shrinks due to the emission of gravitational waves, so do the Hill spheres (linearly with binary separation) until the Hill spheres are too small for matter to find stable trajectories around the near horizon regions. When this occurs the mini disks should be accreted on a comparatively short time scale. As first pointed out by [58], it is this mechanism that explains why in the full relativistic studies published so far [56,57,58] no persistent mini-disks were seen, while mini disks seem to be a generic feature in studies at larger binary separation, e.g., [55,69].
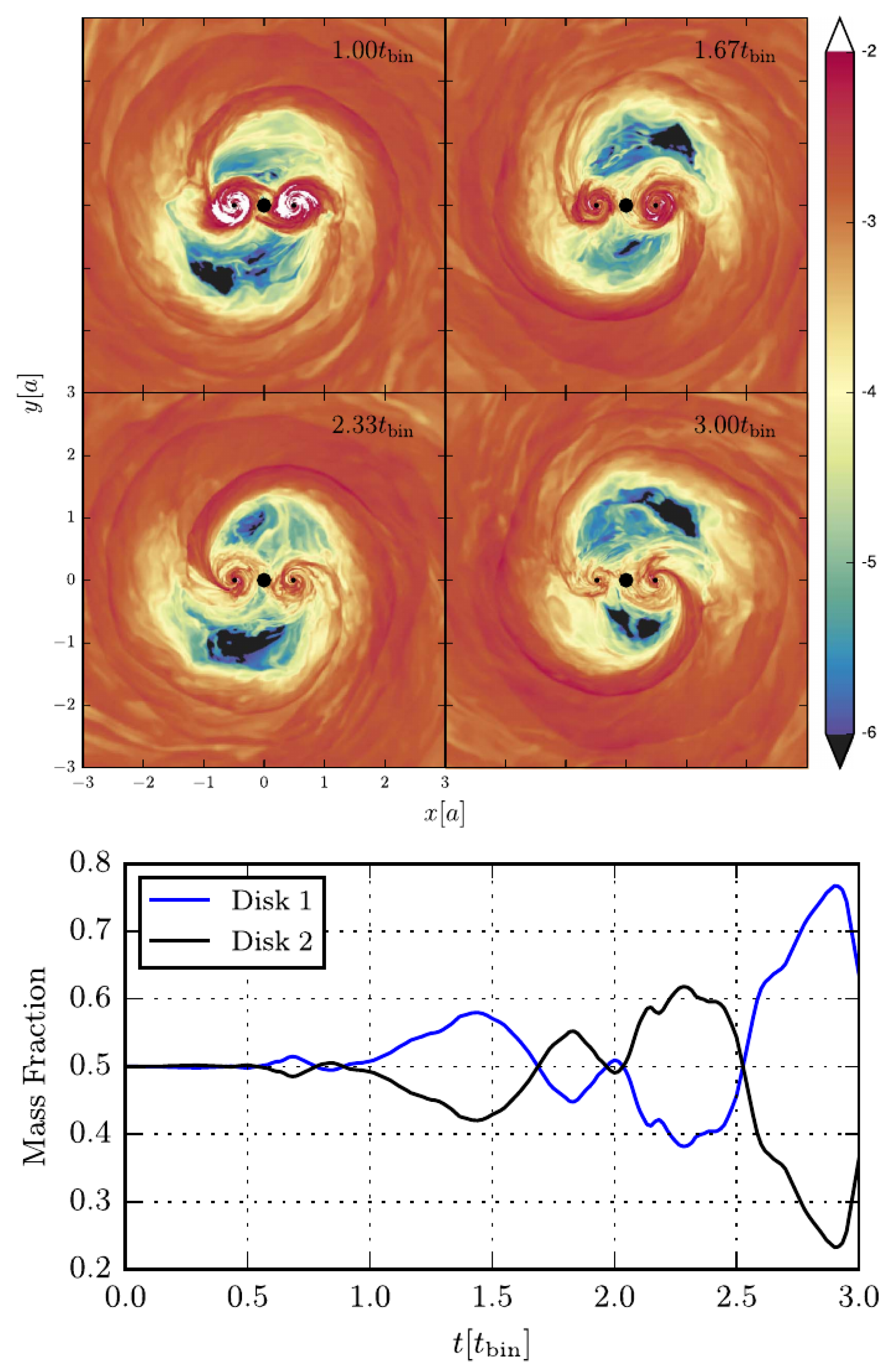
One particular process identified in these mini-disk systems is a mass sloshing from one mini-disk to the other with cycles of depletion and refilling of the mini disks that are fed by the circumbinary disk [62,69,70], see Figure 2.
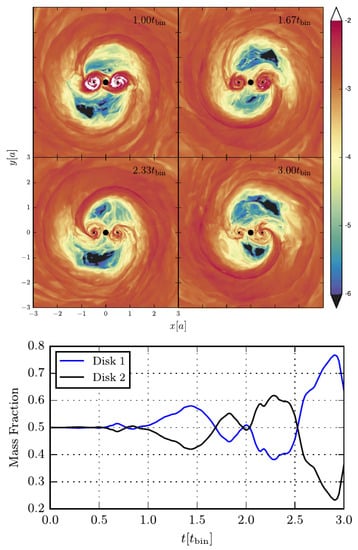
Figure 2.
Rest-mass density (linear color scale) from a GRMHD simulation in a spacetime framework similar to [69,72] (upper panel) and individual disk masses as a function of orbital phase (lower panel). One can clearly see in the lower panel, that mass is sloshing back and forth between the two mini disks. This effect is shown to persist over longer time scales in the follow-up work [70].
2.1.4. Enhanced Variability
Robust features in all theoretical models of circumbinary accretion onto SMBH binaries like accretion streams are promising candidates to produce coherent time dependent signatures in the electromagnetic output of the system.
Similarly, the resulting dynamical impact of a lump-like structure leads to periodic or quasi-periodic variability as the orbital period of the lump and its close passages with the accretion streams can beat against each other [69].
There are unambiguous findings of preferred time scales and quasi-periodic signatures in the mass accretion rate at binary separations where the orbital decay is noticable but slow, see e.g., in [62,69]. Such relatively clean frequencies in the matter dynamics and mass accretion rate are not seen in fully relativitistic regimes [57,58], most likely because no persistent mini-disks are formed. It is not fully clear whether or not further differences in the models, such as different matter configurations, see e.g., [73], thermodynamics, or something else, are responsible. However, the combined theoretical efforts by the community thus far, indicate that accreting BH binaries, at least those surrounded by puffy hot accretion flows, do reveal quasi-periodic behavior, but only up until some finite binary separation shortly before merger. This transition from quasi-periodic to generically variable (non-quasi-periodic) behavior could be one of the most robust EM precursors to the merger event.
2.2. Connecting Theoretical Models and Observational Data
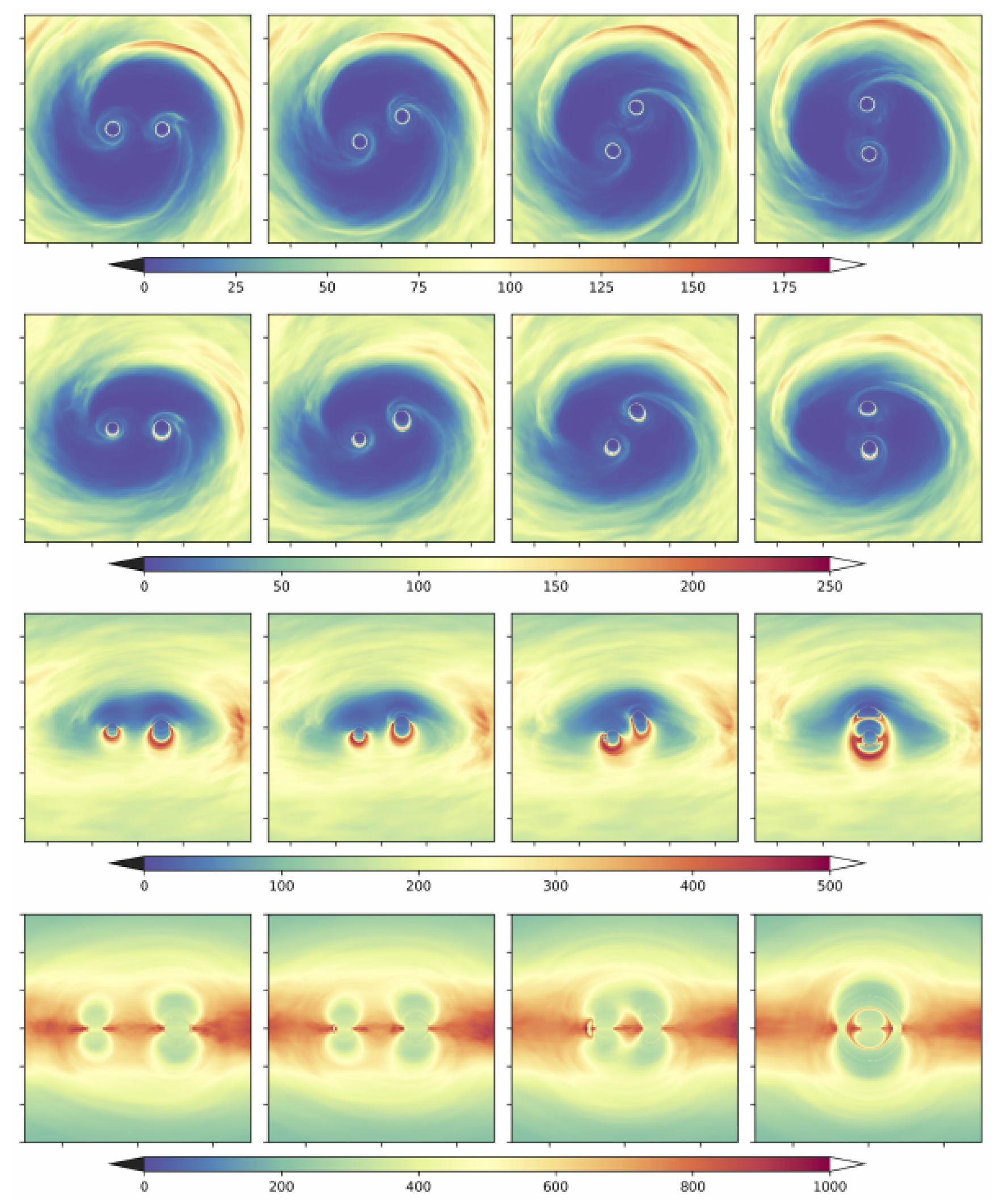
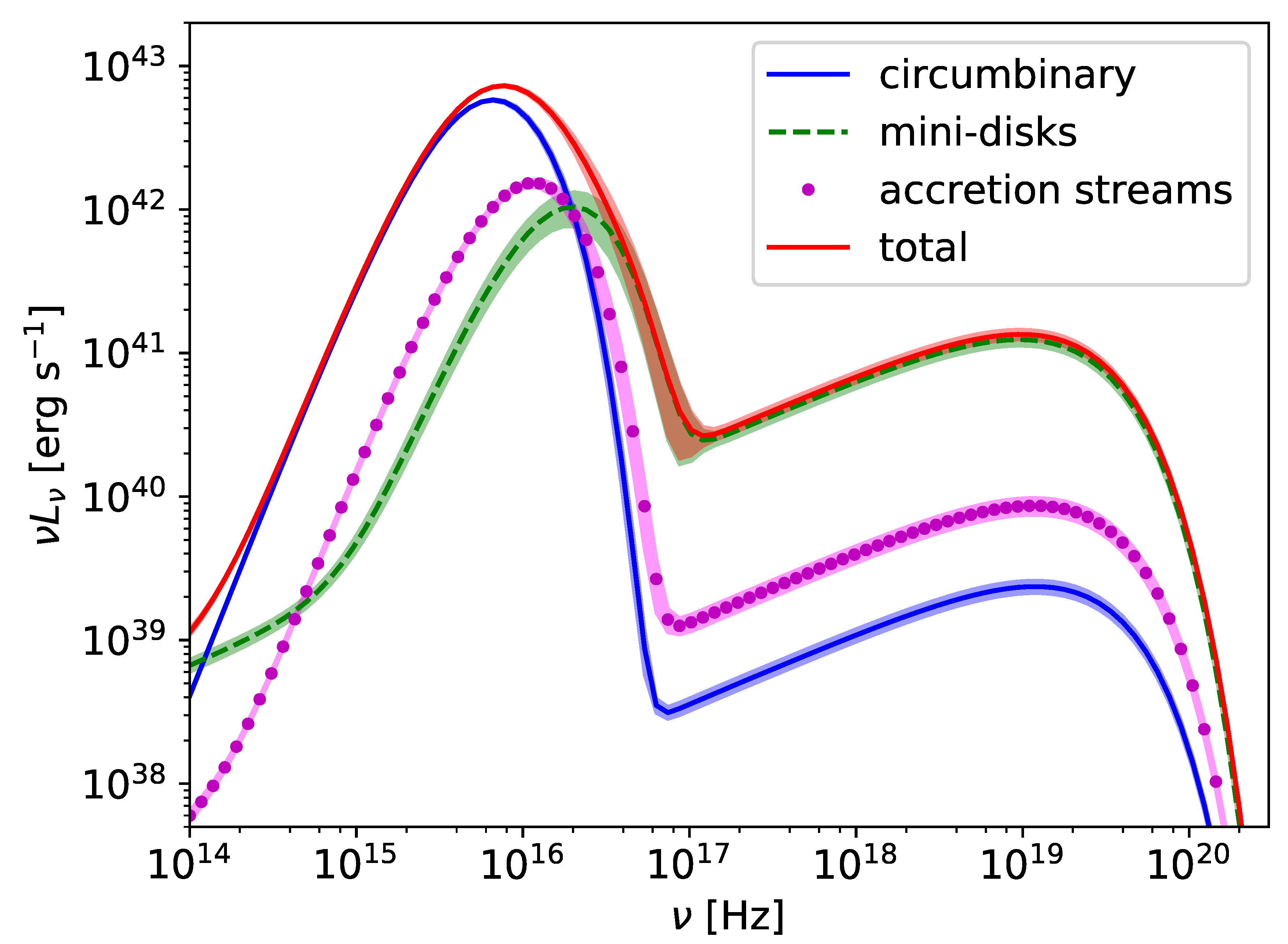
It is generally extremely important to distinguish between the behavior of intrinsic, dynamic quantities such as the fluid density and the observational appearance in a given EM waveband. A first and substantial advancement in this direction was given in [74]. This study was carried out at a larger binary separations of , which is in the predecoupling regime, adopting a treatment for the spacetime metric based on [72], which is particularly relevant for potential Pulsar Timing Array sources This study incorporates, for the first time, direct information from radiative transfer effects. These studies constitute the best basis yet for judging electromagnetic emission from supermassive black hole binaries embedded in a magnetized, gaseous environment in the GW-driven regime. Figure 3 shows several ray-traced images of the system. One can nicely see how the strong lensing effects lead to major distortions in the images compared to a flat space treatment. In Figure 4 one can further see theoretical spectra computed from the GRMHD simulations used in [74]. One can clearly see the different contributing components to the broad band spectral energy distribution (SED). The thermal emission from the mini disks dominate over the streams and circumbinary disk emission at high-energy emission. The accretion streams and circumbinary disk on the other hand dominate at lower frequencies and appear to be difficult to distinguish at least based on spectral grounds and for the cases considered.
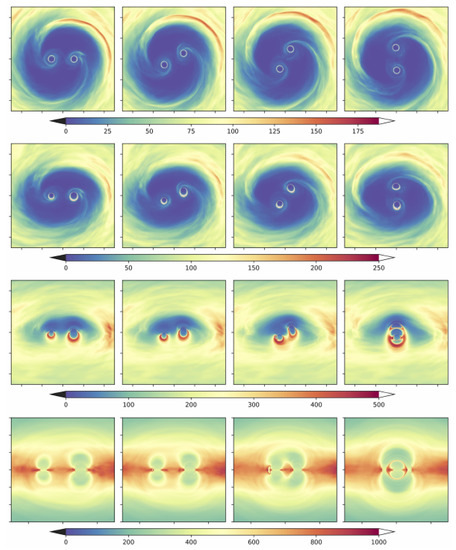
Figure 3.
Images of optical depth obtained by properly tracing light rays through the spacetime for different times (columns) from circumbinary accretion around supermassive black holes from [74] for inclination angles 0, 39, 71, 90 (from top to bottom row). Strong lensing effects introducing complicated image distortions are clearly visible.
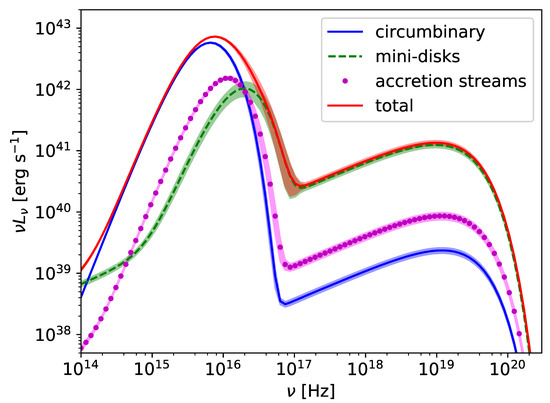
Figure 4.
Different components from the various disks present in the system of [74] contributing to the spectrum. Mini disks reveal their emission at higher energies whereas emission from the circumbinary disk at larger radii contributes more at lower frequency. Emission from the accretion streams falls in the middle of these two regimes and based on this analysis may be difficult to distinguish from the other contributions.
If system parameters and EM waveband lead to a situation where the flow is too optically thick, then information on the binary motion will at best be smeared out when viewed from outside the system. For optically thin cases, on the other hand, outgoing radiation can probe directly the binary orbital motion. It may still be possible to detect binary imprints like periodic features in light curves, non-axisymmetric structures, pile-ups etc. However the most desirable regime to gain information on the binary motion is a regime where the source is optically thin. One practical consideration is that optically thin emission is less efficient and typically produces dimmer sources which are then rarer due to an observational bias.
Also, specific features, such as mini-disks, although seen in GRMHD studies, need not necessarily shine strong enough to contribute to the EM output. At least in some accretion regimes with certain thermodynamical properties of the gas it is conceivable that jet emission may dominate over disk emission.
2.3. GRMHD in Dynamic Spacetime
Full GR studies [56,57,58,73,75] incorporate dynamic spacetime evolution with spatially resolved black hole horizons. These ingredients are not only appropriate, but in fact essential to enable any prediction for the emergence of magnetized, incipient jets resulting from twisting the magnetic field lines that are anchored both in the accretion flow and the orbiting and (potentially also) spinning black hole horizons, see Figure 5. The formation of jets in these systems is one of many purely relativistic aspects of this problem, see also the force-free study in GR [75]. These studies focus on the accretion flow and jet dynamics in the dynamic spacetime. Solving the full set of Einstein’s equations on non-uniform grids along with the equations of ideal MHD is a challenging task especially for long computational times as is required for accreting systems. Long term stability was achieved in [56] using an innovative approach to evolve the magnetic vector potential with a new gauge condition, the damped Lorenz gauge. This gauge condition damps EM gauge waves towards zero, thereby minimizing spurious amplifications of magnetic field strength at AMR boundaries. Only indirect diagnostics such as Poynting flux or approximative thermal luminosity based on an artificial emissivity prescriptions were given.
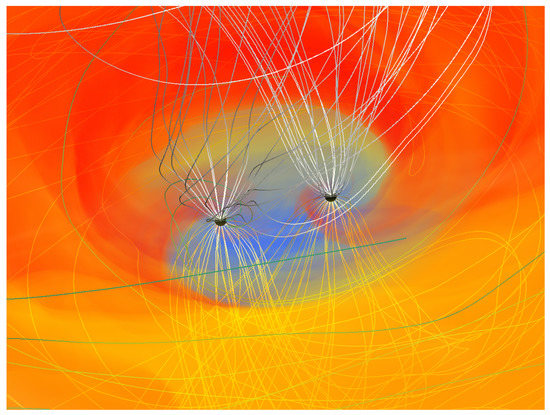
Figure 5.
Rest-mass density (color scale) and magnetic field structure (white lines) of a fully relativistic GRMHD simulation in dynamical spacetime from [58].
Just like for single BHs the system has to be evolved for long enough such that the system can respond on a viscous time scale to settle into an inflow outflow quasi-equilibrium. Typically such an equilibration takes place “inside-out”, because the viscous time scale grows (steeply) with distance from the center. As a result, the longer a GRMHD simulation is run, the larger its inner region of validity where the flow has forgotten about its somewhat artificial initial state.
2.4. During and Post Merger
In the last few orbits and merger the directed GW emission is increasing sharply with time and does not average out over the course of an orbit. The linear momentum that was emitted in the form of GWs is compensated by a recoil on the merger remnant to conserve overall momentum [76,77,78]. The resulting kick velocity depends on the binary parameters, especially the magnitude and relative orientation of the BHs spin w.r.t. their orbital angular momentum and varies from a modest (but still impressively non-pedestrian) 200 km/s to 1800 km/s and perhaps as large as 4000 km/s for maximally spinning black holes [79]. This range of “kick” velocities exceeds typical galaxy escape velocities. Therefore, depending on the kick velocity attained, two qualitatively distinct possibilities arise: (i) For kick velocities lower than the escape velocity, the merger remnant will oscillate relative to the bulk of the disk dragging with it only the matter in the immediate vicinity of the BH. (ii) For kick velocities exceeding the escape velocity of the galaxy hosting the system, the black hole will take off into space again dragging only the material in its nearest vicinity with it and leaving behind the bulk of the disk without a central gravitating object. Which of those scenarios is more common is an interesting and still somewhat open topic that finally awaits observational data. Indications are that most mergers will lead to bound BH remnants [45,46,47,80]. Observationally such BH remnants that were kicked out of their host galaxy or have been displaced from the gravitational center could be detectable through spectral signatures, see e.g., [81] and by using HO megamasers [82].
The scenario following a merger with high kick velocities has been modeled [43,44] by Lorentz boosting the disk material but not the black hole. This treatment does not take into account the various remnant structures imparted in the system by the past binary system, but allows one to study the system under these idealized assumptions in a systematic and more efficient way.
After a typical merger with low (or even hardly any kick velocity) the accretion flow is substantially different from that around a single BH. Consequently, there will be a period of adjustment until the source transitions into the classical single BH accretion state on a few viscous time scales of the accretion flow. This phase is expected to lead to a slow brightening of the source over time as more matter diffuses into the cavity that was carved out by the past binary tidal torques. This phase has not been simulated yet and is different from increases in jet luminosity found in [58]. As discussed before the expected level of density decrease in the cavity has seen some variation recently, especially in the context of studies that include the dynamics of magnetic fields and the resulting strong effective viscosities. So, it is not clear how much of a rebrightening one truly expects and how the phenomenology scales with decoupling radius (dictated by disk height).
2.5. Distinguishability of Single vs. Binary AGN
In many respects current studies only scratch the surface of many important aspects of accretion onto binary black holes. For instance, one key development in the field will be to improve our general understanding on how different binary black hole systems are from single black hole systems. This is a complex question not only because of the already large spread in phenomenology even in single BH systems. So the differences for any given binary system to a corresponding single BH system will depend on many things including but not limited to, the mass supply, the thermodynamic regime of the gas and the EM waveband one observes in. Theoretical implications already point to clear differences between accreting single and binary black holes in the form of different density distributions or mass accretion rates, see [57] for a single vs binary black hole comparison with the same code and setup. The circumbinary disks used in various GRMHD studies differ greatly in their spatial extent and also in the amount of magnetic flux on the horizon at late times. It is well known that the magnetic flux is one key parameter in accreting single black holes [83,84,85]. Therefore, by extension understanding the influence of different levels of magnetic flux will have to be an important aspect of future studies also in the circumbinary disk case.
On the other hand, several discoveries such as the lump, the presence of a cavity, accretion streams, and mini disks along with characteristic variability are promising indications that such a distinction will be possible at least for some physical regimes. Key steps towards making theoretical predictions more relevant to what is actually observed [74,86] have been started and should constitute a solid foundation for future model building efforts to extract SMBH binary science out of observational data in the near future.
3. Discussion/Conclusions
The last few years have seen major progress in our understanding of accreting black hole binaries that are in the gravitational wave driven regime. Most importantly there is unanimous agreement among theoretical models from various groups that magnetically-driven effective viscosity dominates the angular momentum flux, causing accretion rates onto the binary that are very much comparable to rates encountered in single black hole systems with the same total mass. For the same reason, a decoupling of the supermassive black hole binary from the circumbinary disk long before merger as originally discussed in [21,64] can in fact occur only very few orbits prior to merger at least for disks with a sufficiently large scale height . In some respects, the sources share many similarities with and may in fact not always appear as different to single accreting BH sources as one would like. One key difference is that the mass inflow is not as axisymmetric near the black holes but instead very concentrated into the two dense accretion streams as well as the mini disks.
On the other hand there are equally clear and robust differences that are expected to yield distinct signatures that point to the binary nature of a source. The differences involve characteristic structural changes in the accretion flow (cavities, streams, lumps) which give rise to image, spectral (lack of emission due to cavity, enhanced emission due to overdensities) and time-dependent (periodicities, beating, sloshing) signatures. On top of these effects from the matter distributions and dynamics additional effects such as Doppler boosting will further enable us to extract scientific predictions by matching theory to observations. In [87] possible detection rates are estimated under the assumption of two variability models: Doppler boost related variations and periodic variability due to accretion flow dynamics. It is predicted that the Catalina Real-Time Survey (CRTS) [88] might see a few binary sources but 5 years of the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) [89] (first engineering light 2019, science runs in 2021) can detect tens to hundreds of them.
The first key steps towards first theoretical model predictions closer to observational data have been taken [74] with radiative transfer calculation. It will be a major undertaking in the field in the future to advance such calculations and at the same time start to cover the vast parameter space of these sources, which is even larger than the combined parameter sets known from binary black hole coalescences (in vacuum). In addition the phenomenology of just the accretion flows onto supermassive black hole binaries themselves is truly immense, the accretion flow structure being even more feature rich than for single BHs and radiation possibly originating from these separate regions and via distinct physical mechanisms. Aside from the emission from shocks other potential emission mechanisms are expected to operate. One main engine for (polarized) synchrotron emission has for a long time been, magnetic energy as provided by MHD turbulent dynamics [48,60,85] accompanied by dissipation effects e.g., magnetic reconnection at small scales of its turbulent cascade. Recently, however, indications for a more ordered larger scale magnetic field structure more akin to the magnetically arrested state [90,91,92] of accretion seems favored at least in Sgr A but [93,94] maybe also in other systems.
These are fascinating times for understanding accretion physics in strong field gravity. Theoretical efforts to provide us with testable predictions as well as observational data that probe the relativistic regime around black holes are around the corner. Gravitational waves which have famously been observed in the stellar mass black hole case will be detected for supermassive black hole binaries eventually, either by PTAs or a space-based laser interferometer like LISA. In the meantime electromagnetic emission across several wavebands can be used to refine our understanding of black holes and how they feed in their natural habitat. In particular, the Event Horizon Telescope [85,95,96,97,98,99] has reached resolutions capable of spatially resolving not only the two largest black hole event horizons as seen on the sky (in Sgr A and M87) along with accretion flows governed by the physics of general relativistic magnetohydrodynamics but also sub- supermassive black hole binaries. Such resolved detections would not suffer from limitations of periodicity searches and be obtained even when the orbital period is large compared to the observational campaign. In fact, some binary candidate sources such as Ark 120, OJ-287 and others may already be spatially resolved. More generally, targeted very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) efforts will be able to resolve such binaries, see [100], see also a similar idea in [101]. At the current configuration of the Event Horizon Telescope any binary at a separation larger ≳ can be spatially resolved throughout the universe. This is possible thanks to recent technical improvements, the availability of very long baselines at 230 GHz (and 345 GHz in the near future), and the fact that angular separation projected on the sky is not a monotonic function of redshift in the universe we seem to live in. Obviously, the ability to spatially resolve a source is only one of the inherent challenges. The main technical challenge will therefore be to meet the sensitivity requirements for potentially very distant sources. Fortunately, this is an area where recent technical developments, such as bandwidth increases in the VLBI backends, have caused a surge in sensitivity improvements. From the theory side we can expect that radio emission from binary sources is comparable to single AGN sources which are successfully detected with radio VLBI routinely out to considerable distances.
Funding
This work is supported in part by the ERC synergy grant “BlackHoleCam: Imaging the Event Horizon of Black Holes” (Grant No. 610058).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Begelman, M.C.; Blandford, R.D.; Rees, M.J. Massive black hole binaries in active galactic nuclei. Nature 1980, 287, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, N. Galaxy mergers and active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 104, 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Y.H.; Reshetnikov, V.P. Interacting galaxies in deep fields of the Hubble Space Telescope. Astrophysics 2011, 54, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eracleous, M.; Boroson, T.A.; Halpern, J.P.; Liu, J. A Large Systematic Search for Close Supermassive Binary and Rapidly Recoiling Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2012, 201, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Observing black holes spin. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.A.; Craig, W.W.; Christensen, F.E.; Hailey, C.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Boggs, S.E.; Stern, D.; Cook, W.R.; Forster, K.; Giommi, P.; et al. The Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) High-energy X-ray Mission. Astrophys. J. 2013, 770, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, M.; Bavdaz, M.; Ferreira, I.; Wille, E.; Lumb, D.; Linder, M. ATHENA: System design and implementation for a next generation X-ray telescope. UV, X-Ray, and Gamma-Ray Space Instrumentation for Astronomy XIX. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9601, 96010L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarli, R.; Dotti, M.; Fumagalli, M.; Tsalmantza, P.; Montuori, C.; Lusso, E.; Hogg, D.W.; Prochaska, J.X. The nature of massive black hole binary candidates—I. Spectral properties and evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, B.; Ford, K.; Kocsis, B.; Haiman, Z. Ripple effects and oscillations in the broad FeKa line as a probe of massive black hole mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astrono. Soc. 2013, 32, 1468–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflueger, B.J.; Nguyen, K.; Bogdanović, T.; Eracleous, M.; Runnoe, J.C.; Sigurdsson, S.; Boroson, T. Likelihood for Detection of Subparsec Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in Spectroscopic Surveys. Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpaa, A.; Haarala, S.; Valtonen, M.J.; Sundelius, B.; Byrd, G.G. OJ 287—Binary pair of supermassive black holes. Astrophys. J. 1988, 325, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, H.J.; Valtonen, M.J. OJ 287 Outburst Structure and a Binary Black Hole Model. Astrophys. J. 1996, 460, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, M.J.; Lehto, H.J.; Nilsson, K.; Heidt, J.; Takalo, L.O.; Sillanpää, A.; Villforth, C.; Kidger, M.; Poyner, G.; Pursimo, T.; et al. A massive binary black-hole system in OJ287 and a test of general relativity. Nature 2008, 452, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtonen, M.; Ciprini, S. OJ 287 Binary Black Hole System. In Proceedings of the Multifrequency Behaviour of High Energy Cosmic Sources, Sicily, Italy, 23–28 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Britzen, S.; Fendt, C.; Witzel, G.; Qian, S.J.; Pashchenko, I.N.; Kurtanidze, O.; Zajacek, M.; Martinez, G.; Karas, V.; Aller, M.; et al. OJ287: Deciphering the ‘Rosetta stone of blazars’. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 3199–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.K.; Li, S.; Komossa, S. A Milliparsec Supermassive Black Hole Binary Candidate in the Galaxy SDSS J120136.02+300305.5. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.J.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Stern, D.; Glikman, E.; Drake, A.J.; Mahabal, A.A.; Donalek, C.; Larson, S.; Christensen, E. A possible close supermassive black-hole binary in a quasar with optical periodicity. Nature 2015, 518, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Gezari, S.; Heinis, S.; Magnier, E.A.; Burgett, W.S.; Chambers, K.; Flewelling, H.; Huber, M.; Hodapp, K.W.; Kaiser, N.; et al. A Periodically Varying Luminous Quasar at z = 2 from the Pan-STARRS1 Medium Deep Survey: A Candidate Supermassive Black Hole Binary in the Gravitational Wave-driven Regime. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 803, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisi, M.; Bartos, I.; Haiman, Z.; Price-Whelan, A.M.; Graham, M.J.; Bellm, E.C.; Laher, R.R.; Márka, S. A population of short-period variable quasars from PTF as supermassive black hole binary candidates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 2145–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnoe, J.C.; Eracleous, M.; Pennell, A.; Mathes, G.; Boroson, T.; Sigurdsson, S.; Bogdanović, T.; Halpern, J.P.; Liu, J.; Brown, S. A large systematic search for close supermassive binary and rapidly recoiling black holes—III. Radial velocity variations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 1683–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, M.; Merritt, D. Formation of Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2001, 563, 34–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, M.; Merritt, D. The Final Parsec Problem. AIP Conf. Proc. 2003, 686, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, M.; Merritt, D. Long-Term Evolution of Massive Black Hole Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2003, 596, 860–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodato, G.; Nayakshin, S.; King, A.R.; Pringle, J.E. Black hole mergers: Can gas discs solve the ‘final parsec’ problem? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadra, J.; Armitage, P.J.; Alexander, R.D.; Begelman, M.C. Massive black hole binary mergers within subparsec scale gas discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 393, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedig, C.; Dotti, M.; Sesana, A.; Cuadra, J.; Colpi, M. Limiting eccentricity of subparsec massive black hole binaries surrounded by self-gravitating gas discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 3033–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Holley-Bockelmann, K.; Berczik, P.; Just, A. Supermassive Black Hole Binary Evolution in Axisymmetric Galaxies: The Final Parsec Problem is Not a Problem. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Fiacconi, D.; Mayer, L.; Berczik, P.; Just, A. Swift Coalescence of Supermassive Black Holes in Cosmological Mergers of Massive Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2016, 828, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Perna, R.; Haiman, Z.; Ostriker, J.P.; Stone, N.C. Interactions between multiple supermassive black holes in galactic nuclei: A solution to the final parsec problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 3410–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzmann, K. LISA: Laser interferometer space antenna for gravitational wave measurements. Classical Quant. Grav. 1996, 13, A247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Seoane, P.; Audley, H.; Babak, S.; Baker, J.; Barausse, E.; Bender, P.; Berti, E.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M.; Bortoluzzi, D.; et al. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00786. [Google Scholar]
- Dotti, M.; Sesana, A.; Decarli, R. Massive black hole binaries: Dynamical evolution and observational signatures. Adv. Astron. 2012, 2012, 940568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.C.; Mathews, J. Gravitational radiation from point masses in a Keplerian orbit. Phys. Rev. 1963, 131, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.C. Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B1224–B1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G.; Archibald, A.; Arzoumanian, Z.; Backer, D.; Bailes, M.; Bhat, N.D.R.; Burgay, N.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Champion, D.; Cognard, I.; et al. The international pulsar timing array project: Using pulsars as a gravitational wave detector. Class. Quantum Grav. 2010, 27, 084013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, A.; Volonteri, M.; Haardt, F. LISA detection of massive black hole binaries: Imprint of seed populations and extreme recoils. Class. Quantum Grav. 2009, 26, 094033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiman, Z.; Kocsis, B.; Menou, K. The Population of Viscosity- and Gravitational Wave-Driven Supermassive Black Hole Binaries Among Luminous AGN. Astrophys. J. 2009, 700, 1952–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, A.; Roedig, C.; Reynolds, M.T.; Dotti, M. Multimessenger astronomy with pulsar timing and X-ray observations of massive black hole binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Haiman, Z.; Menou, K. Electromagnetic counterparts of supermassive black hole binaries resolved by pulsar timing arrays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komossa, S.; Baker, J.G.; Liu, F.K. Growth of Supermassive Black Holes, Galaxy Mergers and Supermassive Binary Black Holes. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2016, 29, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, A.; Haiman, Z.; Kocsis, B.; Kelley, L.Z. Testing the Binary Hypothesis: Pulsar Timing Constraints on Supermassive Black Hole Binary Candidates. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Haiman, Z.; Menou, K. Pre-Merger Localization of Gravitational-Wave Standard Sirens With LISA: Triggered Search for an Electromagnetic Counterpart. Astrophys. J. 2008, 684, 870–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.R.; Haiman, Z.; MacFadyen, A. Hydrodynamical response of a circumbinary gas disc to black hole recoil and mass loss. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 404, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, O.; Rezzolla, L.; Del Zanna, L.; Palenzuela, C. Electromagnetic counterparts of recoiling black holes: General relativistic simulations of non-Keplerian discs. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 523, A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousto, C.O.; Campanelli, M.; Zlochower, Y.; Nakano, H. Remnant masses, spins and recoils from the merger of generic black hole binaries. Classical Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittman, J.D.; Buonanno, A. The Distribution of Recoil Velocities from Merging Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 662, L63–L66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesden, M.; Sperhake, U.; Berti, E. Relativistic Suppression of Black Hole Recoils. Astrophys. J. 2010, 715, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Narayan, R. Hot Accretion Flows Around Black Holes. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 529–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Fragile, P.C. Foundations of Black Hole Accretion Disk Theory. Living Rev. Relat. 2013, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittman, J.D. Astrophysics of super-massive black hole mergers. Class. Quantum Grav. 2013, 30, 244007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, T.; Haas, R.; Bogdanovic, T.; Laguna, P.; Shoemaker, D. Relativistic Mergers of Supermassive Black Holes and their Electromagnetic Signatures. Astrophys. J. 2010, 715, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, B.D.; Liu, Y.T.; Shapiro, S.L. Binary black hole mergers in gaseous disks: Simulations in general relativity. Phys. Rev. 2011, D84, 024024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, T.; Bogdanovic, T.; Haas, R.; Healy, J.; Laguna, P.; Shoemaker, D. Mergers of Supermassive Black Holes in Astrophysical Environments. Astrophys. J. 2011, 744, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, T.; Bode, T.; Haas, R.; Laguna, P.; Shoemaker, D. Properties of accretion flows around coalescing supermassive black holes. Class. Quantum Grav. 2011, 28, 094020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noble, S.C.; Mundim, B.C.; Nakano, H.; Krolik, J.H.; Campanelli, M.; Zlochower, Y.; Yunes, N. Circumbinary MHD Accretion into Inspiraling Binary Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2012, 755, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, B.D.; Gold, R.; Paschalidis, V.; Etienne, Z.B.; Shapiro, S.L. Binary black hole mergers in magnetized disks: Simulations in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 221102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, R.; Paschalidis, V.; Etienne, Z.B.; Shapiro, S.L.; Pfeiffer, H.P. Accretion disks around binary black holes of unequal mass: General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations near decoupling. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 064060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, R.; Paschalidis, V.; Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L.; Etienne, Z.B.; Pfeiffer, H.P. Accretion disks around binary black holes of unequal mass: General relativistic MHD simulations of postdecoupling and merger. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbus, S.A.; Hawley, J.F. A powerful local shear instability in weakly magnetized disks. I—Linear analysis. II—Nonlinear evolution. Astrophys. J. 1991, 376, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbus, S.A.; Hawley, J.F. Instability, turbulence, and enhanced transport in accretion disks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.M.; Krolik, J.H.; Lubow, S.H.; Hawley, J.F. Three-dimensional Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Circumbinary Accretion Disks: Disk Structures and Angular Momentum Transport. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.B.; Campanelli, M.; Krolik, J.H.; Mewes, V.; Noble, S.C. Relativistic Dynamics and Mass Exchange in Binary Black Hole Mini-disks. Astrophys. J. 2017, 838, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Paschalidis, V.; Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L. Disks around merging binary black holes: From GW150914 to supermassive black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfadyen, A.I.; Milosavljevic, M. An Eccentric Circumbinary Accretion Disk and the Detection of Binary Massive Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2008, 672, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Haiman, Z.; Loeb, A. Gas pile-up, gap overflow, and Type 1.5 migration in circumbinary disks: Application to supermassive black hole binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 427, 2680–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.J. Physical processes in protoplanetary disks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.06382. [Google Scholar]
- Armitage, P.J.; Natarajan, P. Eccentricity of supermassive black hole binaries coalescing from gas rich mergers. Astrophys. J. 2005, 634, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.J.; Natarajan, P. Accretion during the merger of supermassive black holes. Astrophys. J. 2002, 567, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.B.; Mewes, V.; Campanelli, M.; Noble, S.C.; Krolik, J.H.; Zilhão, M. Quasi-periodic Behavior of Mini-disks in Binary Black Holes Approaching Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 853, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.B.; Mewes, V.; Noble, S.C.; Avara, M.; Campanelli, M.; Krolik, J.H. Quasi-Periodicity of Supermassive Binary Black Hole Accretion Approaching Merger. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.12048. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, G.; MacFadyen, A. Minidisks in Binary Black Hole Accretion. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, B.; Mundim, B.C.; Nakano, H.; Campanelli, M. Inspiralling, nonprecessing, spinning black hole binary spacetime via asymptotic matching. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzo, B.; Baker, J.G.; Miller, M.C.; Reynolds, C.S.; van Meter, J.R. General Relativistic Simulations of Magnetized Plasmas around Merging Supermassive Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2012, 752, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascoli, S.; Noble, S.C.; Bowen, D.B.; Campanelli, M.; Krolik, J.H.; Mewes, V. Electromagnetic Emission from Supermassive Binary Black Holes Approaching Merger. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzuela, C.; Lehner, L.; Liebling, S.L. Dual Jets from Binary Black Holes. Science 2010, 329, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperhake, U.; Berti, E.; Cardoso, V.; Pretorius, F.; Yunes, N. Superkicks in ultrarelativistic encounters of spinning black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 024037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousto, C.O.; Zlochower, Y. Hangup Kicks: Still Larger Recoils by Partial Spin-Orbit Alignment of Black-Hole Binaries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 231102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lousto, C.O.; Zlochower, Y. Nonlinear gravitational recoil from the mergers of precessing black-hole binaries. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 084027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Lousto, C.; Zlochower, Y.; Merritt, D. Large Merger Recoils and Spin Flips from Generic Black Hole Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 659, L5–L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, T.; Reynolds, C.S.; Miller, M.C. Alignment of the Spins of Supermassive Black Holes Prior to Coalescence. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, L147–L150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komossa, S. Recoiling Black Holes: Electromagnetic Signatures, Candidates, and Astrophysical Implications. Adv. Astron. 2012, 2012, 364973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, D.W.; Braatz, J.A.; Condon, J.J.; Greene, J.E. Measuring Supermassive Black Hole Peculiar Motion Using H2O Megamasers. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C. Efficient generation of jets from magnetically arrested accretion on a rapidly spinning black hole. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, L79–L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. V. Physical Origin of the Asymmetric Ring. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.J.; Baker, J.G.; Etienne, Z.B.; Giacomazzo, B.; Schnittman, J. Prompt electromagnetic transients from binary black hole mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisi, M.; Haiman, Z.; Schiminovich, D.; D’Orazio, D.J. Testing the relativistic Doppler boost hypothesis for supermassive black hole binary candidates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 4617–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, A.J.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Mahabal, A.; Prieto, J.L.; Beshore, E.; Graham, M.J.; Catalan, M.; Larson, S.; Christensen, E.; Donalek, C.; et al. The Catalina Real-time Transient Survey. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2011, 7, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LSST Science and LSST Project Collaborations. LSST Science Book, Version 2.0. 2009. Available online: https://www.lsst.org/scientists/scibook (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Narayan, R.; Igumenshchev, I.V.; Abramowicz, M.A. Magnetically Arrested Disk: An Energetically Efficient Accretion Flow. Publ. ASJ 2003, 55, L69–L72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Dai, L.; Avara, M.J. Efficiency of super-Eddington magnetically-arrested accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, L6–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.D.; Avara, M.J.; McKinney, J.C. Angular momentum transport in thin magnetically arrested discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Fish, V.L.; Doeleman, S.S.; Marrone, D.P.; Plambeck, R.L.; Wardle, J.F.C.; Akiyama, K.; Asada, K.; Beaudoin, C.; Blackburn, L.; et al. Resolved magnetic-field structure and variability near the event horizon of Sagittarius A*. Science 2015, 350, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, R.; McKinney, J.C.; Johnson, M.D.; Doeleman, S.S. Probing the Magnetic Field Structure in Sgr A* on Black Hole Horizon Scales with Polarized Radiative Transfer Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2017, 837, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. II. Array and Instrumentation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. III. Data Processing and Calibration. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. IV. Imaging the Central Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. VI. The Shadow and Mass of the Central Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke-Spolaor, S.; Blecha, L.; Bogdanovic, T.; Comerford, J.M.; Lazio, T.J.W.; Liu, X.; Maccarone, T.J.; Pesce, D.; Shen, Y.; Taylor, G. The Next-Generation Very Large Array: Supermassive Black Hole Pairs and Binaries. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04368. [Google Scholar]
- D’Orazio, D.J.; Loeb, A. Imaging Massive Black Hole Binaries with Millimeter Interferometry: Measuring black hole masses and the Hubble constant. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.02362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | We have normalized to a separation of as was used in studies with full general relativistic magnetohydrodynamics (GRMHD). This value is only slightly smaller than the decoupling radius in Equation (5). After all, these time scales only give crude estimates and due to the steep scaling of with a the resulting inspiral time scales can seem prohibitively large. |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).