A Way Out of the Bubble Trouble?—Upon Reconstructing the Origin of the Local Bubble and Loop I via Radioisotopic Signatures on Earth
Abstract
1. Introduction
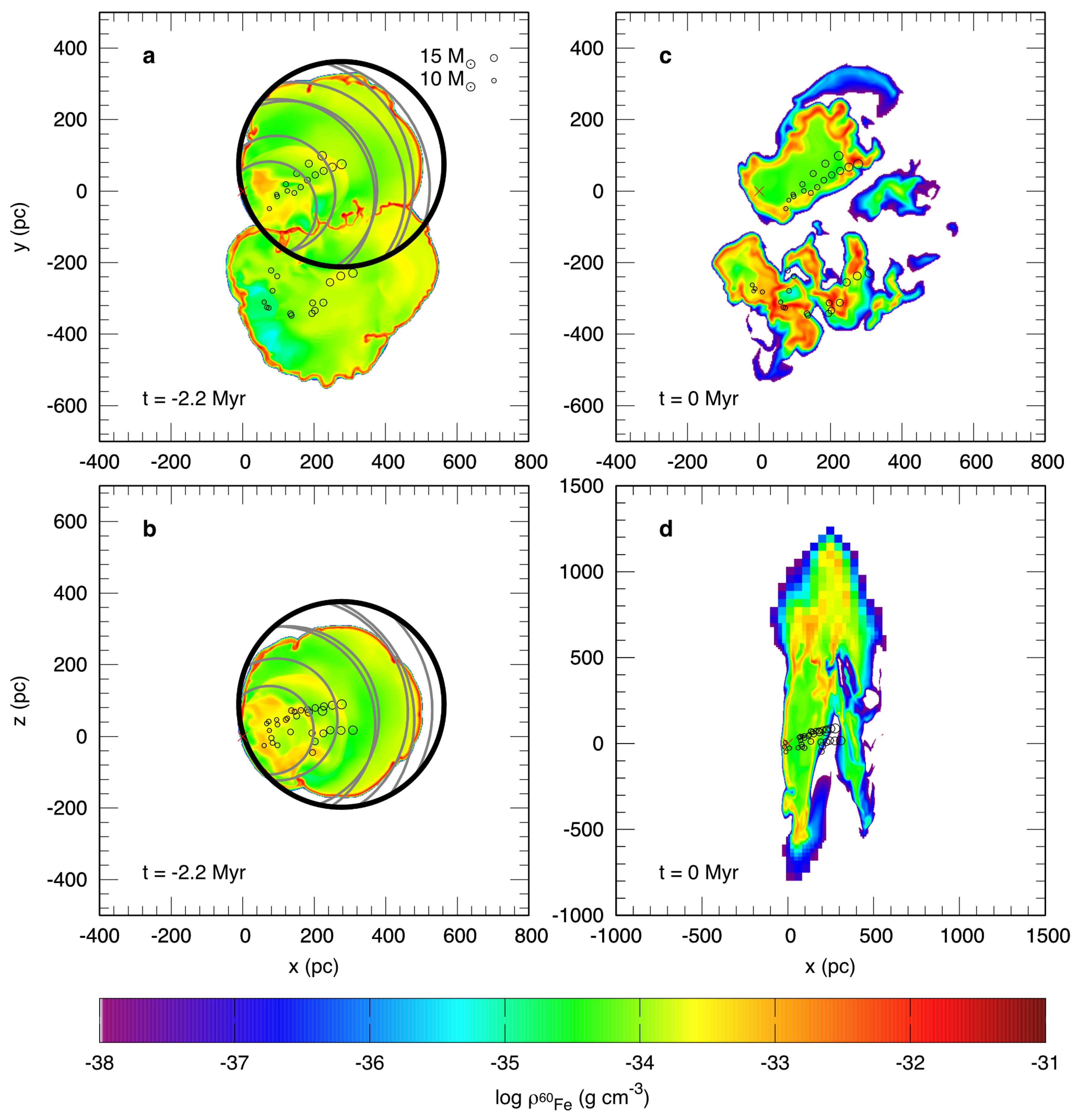
2. Numerically Modeling the 60Fe Transport to the Solar System
3. Discussion and Outlook
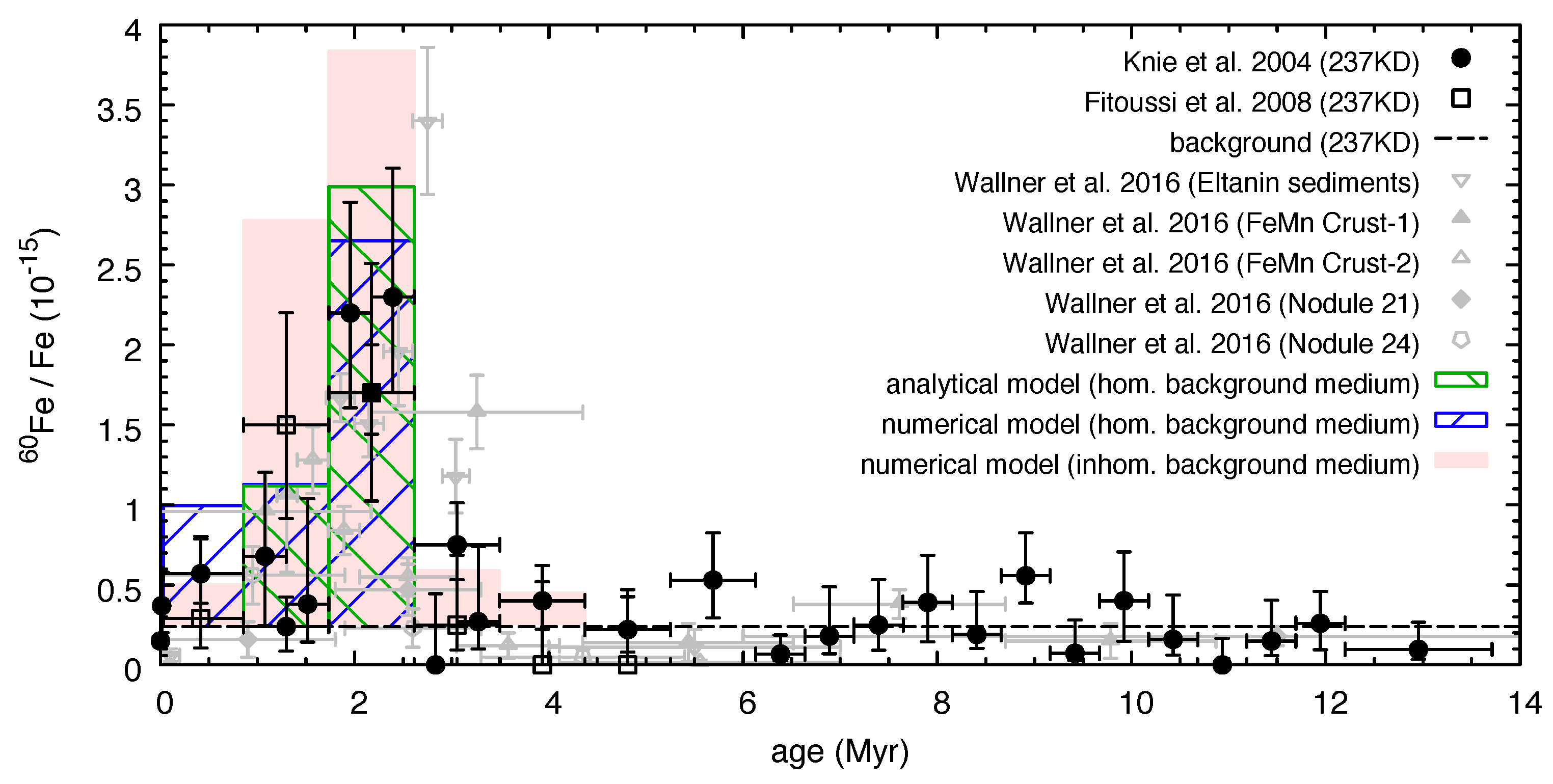
- Measurements in two independent Pacific Ocean sediment cores revealed elevated 60Fe levels in microfossils dated at 1.8–2.6 Myr [39]. These are the remains of so-called magnetotactic bacteria, which feed on iron to produce chains of magnetite (Fe3O4) crystals (so-called magnetosomes) for orientation at Earth’s magnetic field. When the bacteria population moves upward as the sediment grows, microfossils are left behind and the magnetite crystals get preserved in the corresponding sediment layers.
- Enhanced 60Fe signatures were detected in lunar soil samples recovered during the Apollo missions 12, 15, and 16 [40]. Unfortunately, the almost atmosphere-free Moon allows for no time-resolved measurements due to layer-mixing as a result of the continuous meteoritic bombardment (“gardening”). Solar and galactic cosmic rays (CRs) can also generate 60Fe (and 53Mn)—however, their contribution is less than 10% so that the bulk of 60Fe should be from SNe. We have shown in [31] that the lower limit of the detected integrated fluence (107 at cm−2) is compatible with our LB model.
- The ACE-CRIS experiment detected 15 60Fe atoms from a total of 3.55 × 105 CR particles during the time period 1997–2014 [41]. Since the CRIS energy range is ∼100 to 500 MeV/nuc, acceleration of nuclei must have been due to SN blast waves (i.e., first-oder Fermi process). By comparing the measured 60Fe/56Fe ratio with results from stellar evolution models, the authors concluded that the time between nucleosynthesis and acceleration is a few million years. Using a diffusive propagation model as a basis, the mean lifetime of 60Fe dictates the distance to the source to be less than 620 pc, which is easily fulfilled even by the farthest explosion in our LB model (300 pc). Moreover, it was shown that the whole set of known peculiar features of the locally observed CR spectrum can be explained in the framework of a single self-consistent model including the contribution to the CR flux of a SN that has injected CRs within a distance of about 100 pc from the Sun some 2–3 Myr ago [42]. Also this is consistent with the SNe derived from our model.
- Three-dimensional maps of the local interstellar dust, based on the inversion of color excess measurements for individual target stars, diffuse interstellar bands, and statistical methods using stellar surveys (including Gaia), showed four soft X-ray emitting cavities that are open toward the Sun. Strikingly, two of these potential SN relics match the sites of the two most recent SNe estimated in our LB model with respect to both distance and direction (within 3° and 7°, respectively) [43].
- There is some speculation as to whether the Tuc-Hor association rather than Sco-Cen could have hosted the SN(e) responsible for the 60Fe signal [44]. The masses of the current Tuc-Hor members as well as the fact that the group was at a similar distance (∼60 pc) 2.2 Myr ago indeed allow for this possibility. A suggestion by Fry et al. (2016) [45] to use the Moon as an “antenna” for pinning down the direction of incidence of 60Fe dust and thus the responsible stellar group, however, fails since the 60Fe concentrations of soil samples, scattered widely across the lunar surface, are barely different. Due to the huge spatial extent of Tuc-Hor, which appears to be rather an ensemble of evaporating subgroups than one large group [44], it could not be captured by our selection criterion based on compactness in both real and velocity space—one could say that in this case we did not see the forest for the trees. We plan to expand future model calculations in this regard.
- Provided that there had been one or more near-Earth SNe 2–3 Myr ago, it is quite likely that such an extremely bright stellar event—visible even in daylight—would had arisen the attention of the Australopithecus. Thomas et al. (2016) [46] modeled the impact of a SN occurring at a distance of 100 pc on the terrestrial atmosphere and biota. They found that it would only have “a small effect on terrestrial organisms from visible light and that chemical changes such as ozone depletion are weak. However, tropospheric ionization right down to the ground, due to the penetration of ≥TeV CRs, will increase by nearly an order of magnitude for thousands of years, and irradiation by muons on the ground and in the upper ocean will increase twentyfold, which will approximately triple the overall radiation load on terrestrial organisms. Such irradiation has been linked to possible changes in climate and increased cancer and mutation rates. This may be related to a minor mass extinction around the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary” [46] about 2.5 Myr ago.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CR | cosmic ray |
| FeMn | ferromanganese |
| IMF | initial mass function |
| ISM | interstellar medium |
| LB | Local Bubble |
| LIC | Local Interstellar Cloud |
| SB | superbubble |
| SN | supernova |
References
- Sanders, W.T.; Kraushaar, W.L.; Nousek, J.A.; Fried, P.M. Soft diffuse X-rays in the southern galactic hemisphere. Astrophys. J. 1977, 217, L87–L91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, D.E.; Hartquist, T.W. Are we in an old superbubble? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 209, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Breitschwerdt, D.; Schmutzler, T. Delayed recombination as a major source of the soft X-ray background. Nature 1994, 371, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.K.; Cox, D.P. Multiple Supernova Remnant Models of the Local Bubble and the Soft X-Ray Background. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 2001, 134, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, P.C.; Redfield, S.; Slavin, J.D. The Interstellar Medium Surrounding the Sun. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 49, 237–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghöfer, T.W.; Breitschwerdt, D. The origin of the young stellar population in the solar neighborhood—A link to the formation of the Local Bubble? Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 390, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maíz-Apellániz, J. Structural Properties of Massive Young Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2001, 563, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuchs, B.; Breitschwerdt, D.; de Avillez, M.A.; Dettbarn, C.; Flynn, C. The search for the origin of the Local Bubble redivivus. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 373, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, D.; Feige, J.; Schulreich, M.M.; de Avillez, M.A.; Dettbarn, C.; Fuchs, B. The locations of recent supernovae near the Sun from modelling 60Fe transport. Nature 2016, 532, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, P.; Johnson, K.E.; DeGioia-Eastwood, K. The Initial Mass Function and Massive Star Evolution in the OB Associations of the Northern Milky Way. Astrophys. J. 1995, 454, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.; Schaerer, D.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A. New grids of stellar models from 0.8 to 120 M⊙ at Z = 0.020 and Z = 0.001. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1992, 96, 269–331. [Google Scholar]
- Korschinek, G.; Faestermann, T.; Knie, K.; Schmidt, C. 60Fe, a promising AMS isotope for many applications. Radiocarbon 1996, 38, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.; Fields, B.D.; Schramm, D.N. Geological Isotope Anomalies as Signatures of Nearby Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1996, 470, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Weaver, T.A. The Evolution and Explosion of Massive Stars. II. Explosive Hydrodynamics and Nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1995, 101, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugel, G.; Faestermann, T.; Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Poutivtsev, M.; Schumann, D.; Kivel, N.; Günther-Leopold, I.; Weinreich, R.; Wohlmuther, M. New Measurement of the 60Fe Half-Life. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 072502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, A.; Bichler, M.; Buczak, K.; Dressler, R.; Fifield, L.K.; Schumann, D.; Sterba, J.H.; Tims, S.G.; Wallner, G.; Kutschera, W. Settling the half-life of 60Fe: Fundamental for a versatile astrophysical chronometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Harris, M.J.; Diehl, R.; Halloin, H.; Cordier, B.; Strong, A.W.; Kretschmer, K.; Knödlseder, J.; Jean, P.; Lichti, G.G.; et al. SPI observations of the diffuse 60Fe emission in the Galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Faestermann, T.; Wallner, C.; Scholten, J.; Hillebrandt, W. Indication for Supernova Produced 60Fe Activity on Earth. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J. Astronomie unter dem Meer. Phys. Unserer Zeit 2016, 47, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Faestermann, T.; Dorfi, E.; Rugel, G.; Wallner, A. F60e Anomaly in a Deep-Sea Manganese Crust and Implications for a Nearby Supernova Source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 171103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitoussi, C.; Raisbeck, G.; Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Faestermann, T.; Goriely, S.; Lunney, D.; Poutivtsev, M.; Rugel, G.; Waelbroeck, C.; et al. Search for Supernova-Produced 60Fe in a Marine Sediment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.J.; Fields, B.D.; Ellis, J.R. Astrophysical Shrapnel: Discriminating Among Extra-solar Sources of Live Radioactive Isotopes. Astrophys. J. 2015, 800, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J. The Connection Between the Local Bubble and the 60Fe Anomaly in the Deep Sea Hydrogenetic Ferromanganese Crust. Master’s Thesis, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, F.D. The Galactic Fountain. Lect. Notes Phys. 1998, 506, 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, R.; McCray, R.; Castor, J.; Shapiro, P.; Moore, R. Interstellar bubbles. II - Structure and evolution. Astrophys. J. 1977, 218, 377–395, Erratum in 1978, 220, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Heger, A.; Hoffman, R.D.; Woosley, S.E. Nucleosynthesis in Massive Stars with Improved Nuclear and Stellar Physics. Astrophys. J. 2002, 576, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, M.; Chieffi, A. The Nucleosynthesis of 26Al and 60Fe in Solar Metallicity Stars Extending in Mass from 11 to 120 M⊙: The Hydrostatic and Explosive Contributions. Astrophys. J. 2006, 647, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Heger, A. Nucleosynthesis and remnants in massive stars of solar metallicity. Phys. Rep. 2007, 442, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, D.; de Avillez, M.A. The history and future of the Local and Loop I bubbles. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 452, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitarini, L.; Lallement, R.; Vergely, J.L.; Snowden, S.L. Local ISM 3D distribution and soft X-ray background. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 566, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulreich, M.M.; Breitschwerdt, D.; Feige, J.; Dettbarn, C. Numerical studies on the link between radioisotopic signatures on Earth and the formation of the Local Bubble. I. 60Fe transport to the solar system by turbulent mixing of ejecta from nearby supernovae into a locally homogeneous ISM. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 604, A81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, R.J.; Aschenbach, B. Interaction of the Loop I supershell with the Local Hot Bubble. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 294, L25–L28. [Google Scholar]
- Teyssier, R. Cosmological hydrodynamics with adaptive mesh refinement. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 385, 337–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, E.F. Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Introduction, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, C.F.; Ostriker, J.P. A theory of the interstellar medium—Three components regulated by supernova explosions in an inhomogeneous substrate. Astrophys. J. 1977, 218, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Avillez, M.A.; Breitschwerdt, D. Volume filling factors of the ISM phases in star forming galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 425, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, A.; Feige, J.; Kinoshita, N.; Paul, M.; Fifield, L.K.; Golser, R.; Honda, M.; Linnemann, U.; Matsuzaki, H.; Merchel, S.; et al. Recent near-Earth supernovae probed by global deposition of interstellar radioactive 60Fe. Nature 2016, 532, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, K.A.; Vokrouhlický, D.; Bottke, W.F.; Nesvorný, D. A late Miocene dust shower from the break-up of an asteroid in the main belt. Nature 2006, 439, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, P.; Bishop, S.; Egli, R.; Chernenko, V.; Deneva, B.; Faestermann, T.; Famulok, N.; Fimiani, L.; Gómez-Guzmán, J.M.; Hain, K.; et al. Time-resolved 2-million-year-old supernova activity discovered in Earth’s microfossil record. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9232–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fimiani, L.; Cook, D.L.; Faestermann, T.; Gómez-Guzmán, J.M.; Hain, K.; Herzog, G.; Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Ludwig, P.; Park, J.; et al. Interstellar 60Fe on the Surface of the Moon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 151104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binns, W.R.; Israel, M.H.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, A.C.; de Nolfo, G.A.; Lave, K.A.; Leske, R.A.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Stone, E.C.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; et al. Observation of the 60Fe nucleosynthesis-clock isotope in galactic cosmic rays. Science 2016, 352, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachelrieß, M.; Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.V. Cosmic ray signatures of a 2-3 Myr old local supernova. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1710.02321. [Google Scholar]
- Capitanio, L.; Lallement, R.; Vergely, J.L.; Elyajouri, M.; Monreal-Ibero, A. Three-dimensional mapping of the local interstellar medium with composite data. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamajek, E.E. A Pre-Gaia Census of Nearby Stellar Groups. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2016, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.J.; Fields, B.D.; Ellis, J.R. Radioactive Iron Rain: Transporting 60Fe in Supernova Dust to the Ocean Floor. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.C.; Engler, E.E.; Kachelrieß, M.; Melott, A.L.; Overholt, A.C.; Semikoz, D.V. Terrestrial Effects of Nearby Supernovae in the Early Pleistocene. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 826, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schulreich, M.M.; Breitschwerdt, D.; Feige, J.; Dettbarn, C. A Way Out of the Bubble Trouble?—Upon Reconstructing the Origin of the Local Bubble and Loop I via Radioisotopic Signatures on Earth. Galaxies 2018, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010026
Schulreich MM, Breitschwerdt D, Feige J, Dettbarn C. A Way Out of the Bubble Trouble?—Upon Reconstructing the Origin of the Local Bubble and Loop I via Radioisotopic Signatures on Earth. Galaxies. 2018; 6(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchulreich, Michael Mathias, Dieter Breitschwerdt, Jenny Feige, and Christian Dettbarn. 2018. "A Way Out of the Bubble Trouble?—Upon Reconstructing the Origin of the Local Bubble and Loop I via Radioisotopic Signatures on Earth" Galaxies 6, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010026
APA StyleSchulreich, M. M., Breitschwerdt, D., Feige, J., & Dettbarn, C. (2018). A Way Out of the Bubble Trouble?—Upon Reconstructing the Origin of the Local Bubble and Loop I via Radioisotopic Signatures on Earth. Galaxies, 6(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010026




