Ultra Light Axionic Dark Matter: Galactic Halos and Implications for Observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The -Dark Matter Halo
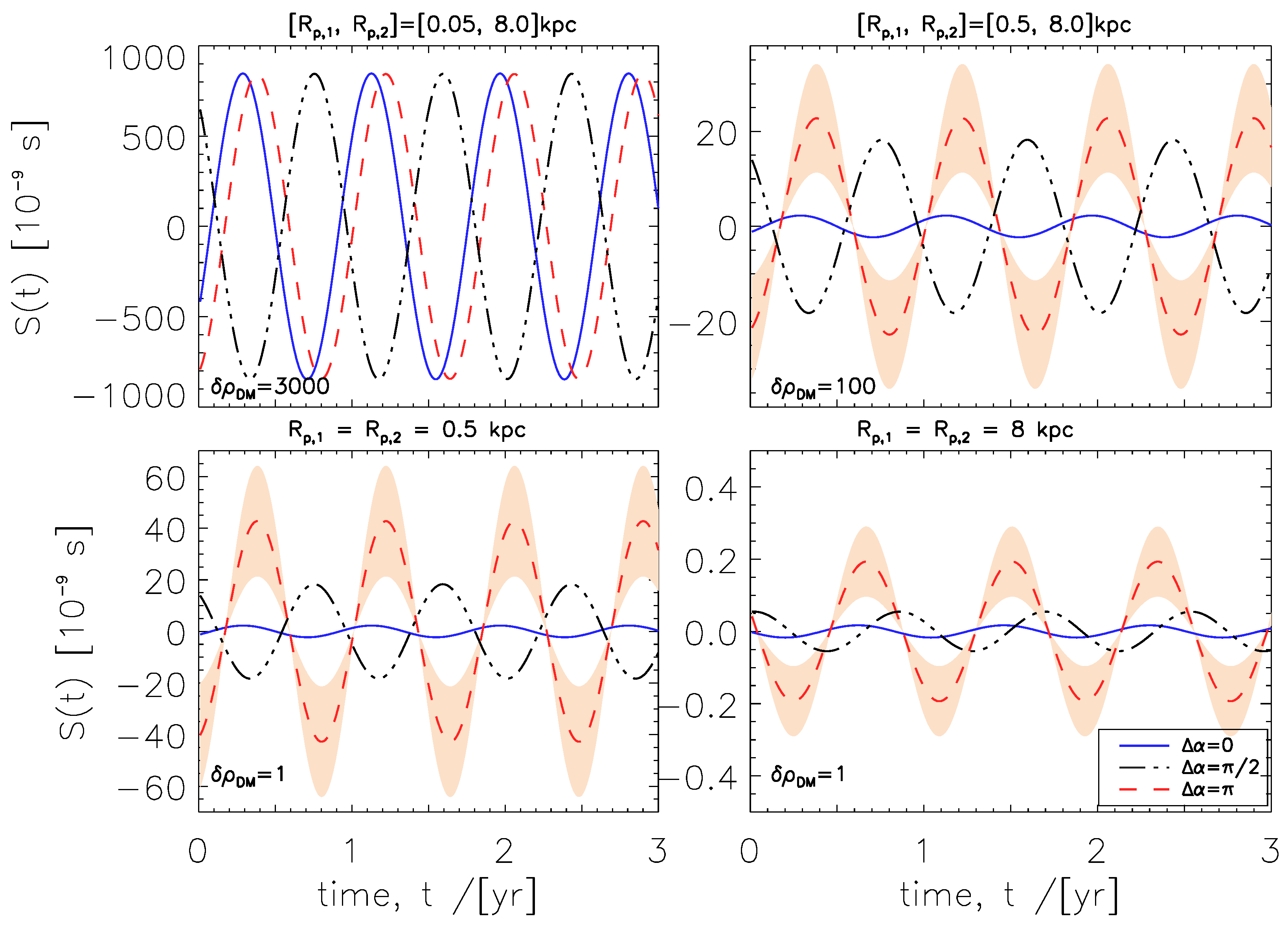
3. Shift of the Pulse Arrival Time
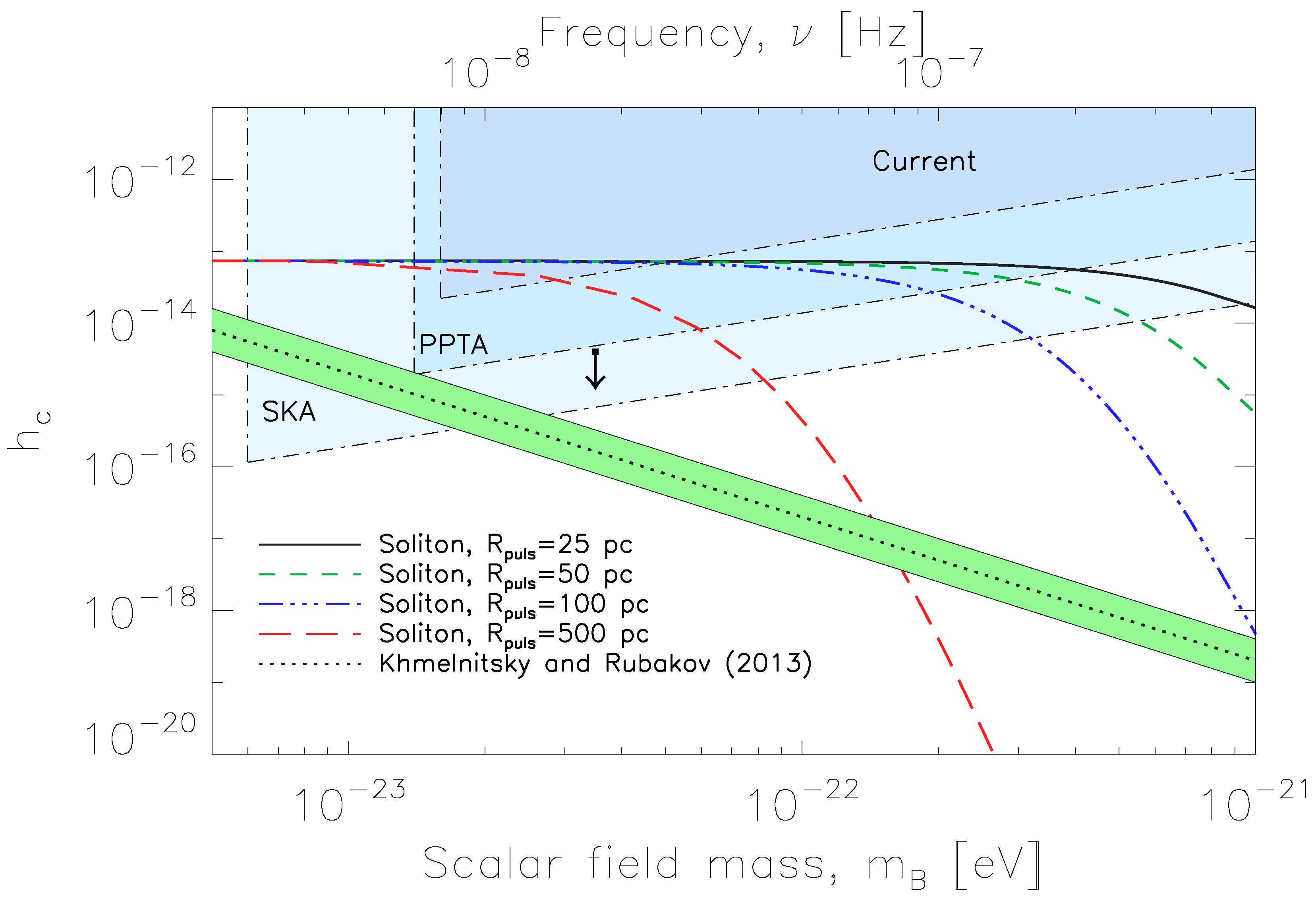
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertone, G.; Hooper, D.; Silk, J. Particle dark matter: Evidence, candidates and constraints. Phys. Rep. 2005, 405, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L. Dark Matter Candidates from Particle Physics and Methods of Detection. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 48, 495. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, J.S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M. Small-Scale Challenges to the Λ CDM Paradigm. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys 2017, 55, 343–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. The dark matter problem from f(R) gravity viewpoint. Ann. Phys. 2012, 524, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; De Laurentis, M.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Capozziello, S. Constraining f(R) gravity with Planck data on galaxy cluster profiles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; De Laurentis, M.; Capozziello, S. Constraining f(R) gravity by the Large Scale Structure. Universe 2015, 1, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I. f(R)-gravity model of the Sunyaev-Zeldovich profile of the Coma cluster compatible with Planck data. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 124043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; De Laraurentis, M. On the universality of MOG weak field approximation at galaxy cluster scale. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 770, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmology of spontaneously broken gauge family symmetry with axion solution of strong CP-problem. Z. Phys. C Part. Fields 1991, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial background of cosmological axions. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1992, 55, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. The nonhomogeneity problem for the primordial axion field. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1994, 57, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Sokoloff, D.D.; Khlopov, M.Y. Large scale modulation of the distribution of coherent oscillations of a primordial axion field in the Universe. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1996, 59, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Sakharov, A.S.; Sokoloff, D.D. The nonlinear modulation of the density distribution in standard axionic CDM and its cosmological impact. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 1999, 72, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, E.W.; Vélez Pérez, J.A. Toroidal halos in a nontopological soliton model of dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, E.W.; Vélez Pérez, J.A. Axion condensate as a model for dark matter halos. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 671, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A. Dark Matter and Dark Energy Induced by Condensates. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2016, 2016, 8089142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A. Quantum vacuum, dark matter, dark energy and spontaneous supersymmetry breaking. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.08769. [Google Scholar]
- Capolupo, A. Cosmological Effects of Quantum Vacuum Condensates. Galaxies 2017, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J.; Wise, M.B.; Wilczek, F. Cosmology of the Invisible Axion. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 120, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, L.F.; Sikivie, P. A Cosmological Bound on the Invisible Axion. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 120, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dine, M.; Fischler, W. The Not So Harmless Axion. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 120, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svrcek, P.; Witten, E. Axions In String Theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2006, 0606, 051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Barkana, R.; Gruzinov, A. Cold and Fuzzy Dark Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.; Ostriker, J.P.; Tremaine, S.; Witten, E. Ultralight scalars as cosmological dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 043541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, S.-H.; Wong, S.S.C. Linking Light Scalar Modes with A Small Positive Cosmological Constant in String Theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2017, 2017, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schive, H.-Y.; Chiueh, T.; Broadhurst, T. Cosmic structure as the quantum interference of a coherent dark wave. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schive, H.-Y.; Liao, M.-H.; Woo, T.-P.; Wong, S.-K.; Chiueh, T.; Broadhurst, T.; Pauchy Hwang, W.-Y. Understanding the Core-Halo Relation of Quantum Wave Dark Matter from 3D Simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 261302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khmelnitsky, A.; Rubakov, V. Pulsar timing signal from ultralight scalar dark matter. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; Broadhurst, T.; Tye, S.-H.H.; Chiueh, T.; Schive, H.-Y.; Lazkoz, R. Recognising Axionic Dark Matter by Compton and de-Broglie Scale Modulation of Pulsar Timing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 221103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widrow, L.M.; Kaiser, N. Using the Schroedinger Equation to Simulate Collisionless Matter. Astrophys. J. 1993, 416, L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, T.-P.; Chiueh, T. High-resolution simulation on structure formation with extremely light bosonic dark matter. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Cole, R.H.; Berry, C.P.L. Gravitational-wave sensitivity curves. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 015014. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, G.; Jenet, F.; Lee, K.J.; Verbiest, J.P.W.; Yardley, D.; Manchester, R.; Lommen, A.; Coles, W.; Edwards, R.; Shettigara, C. TEMPO2, a new pulsar timing package. III: Gravitational wave simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 394, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunov, D.S.; Rubakov, V.A. Introduction to the Theory of the Early Universe; World Scientific Pub. Co.: Singapore; Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Porayko, N.K.; Postnov, K.A. Constraints on ultralight scalar dark matter from pulsar timing. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 062008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, A.; Vecchio, A.; Colacino, C.N. The stochastic gravitational-wave background from massive black hole binary systems: Implications for observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 390, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Martino, I.; Broadhurst, T.; Tye, S.-H.H.; Chiueh, T.; Schive, H.-Y.; Lazkoz, R. Ultra Light Axionic Dark Matter: Galactic Halos and Implications for Observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Galaxies 2018, 6, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010010
De Martino I, Broadhurst T, Tye S-HH, Chiueh T, Schive H-Y, Lazkoz R. Ultra Light Axionic Dark Matter: Galactic Halos and Implications for Observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Galaxies. 2018; 6(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Martino, Ivan, Tom Broadhurst, S.-H. Henry Tye, Tzihong Chiueh, Hsi-Yu Schive, and Ruth Lazkoz. 2018. "Ultra Light Axionic Dark Matter: Galactic Halos and Implications for Observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays" Galaxies 6, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010010
APA StyleDe Martino, I., Broadhurst, T., Tye, S.-H. H., Chiueh, T., Schive, H.-Y., & Lazkoz, R. (2018). Ultra Light Axionic Dark Matter: Galactic Halos and Implications for Observations with Pulsar Timing Arrays. Galaxies, 6(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6010010