Abstract
The Shapley Concentration (SC) is a galaxy supercluster (few tens of degrees) in the Local Universe (<z>∼0.048) which is currently undergoing cluster mergers and group accretion. It is a diversified environment, with cluster complexes in advanced evolutionary stage, groups of clusters in the very early stages of merger, fairly massive clusters with ongoing accretion activity, and smaller groups located in filaments. These features make the SC an ideal place to observe the signatures of the formation of large-scale structures in the Universe. As a matter of fact, the SC has been observed over a broad range of frequencies with the most important observatories, allowing for a unique multiband study. In this paper, we will present new results from an ongoing study of the Shapley Concentration Core, which is being carried out with the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT). Our work confirms the role played by radio observations in disentangling the details of the accretion and merging processes, and delivers a wealth of information in regions well outside the cluster cores. In particular, we will report on the discovery of a relic in the region between the two clusters A 3558 and A 3562, and of the radio properties of the brightest galaxy in the peripheral cluster A 3556.
1. Cluster Mergers and Diffuse Radio Emission
According to the hierarchical scenario, cluster mergers—the most energetic events in the Universe, with a total energy output of the order of 10–10 erg—are the natural way to account for mass assembly: galaxy clusters form as a consequence of merger trees, to reach and exceed masses on the order of 10 M. Cluster mergers deeply affect the dynamics of the galaxies, as well as the properties of the thermal intracluster medium and those of relativistic particles and magnetic field.
The close connection between the properties of the radio emission in galaxy clusters and their dynamical state is now an established result. Giant radio halos and relics—Mpc-scale steep spectrum synchrotron radio sources (see Feretti et al. [1] for a recent observational overview)—are thought to be the result of particle re-acceleration due to turbulence and shocks, respectively, induced in the cluster volume during mergers and accretion processes (see Brunetti and Jones [2] for a recent theoretical review). While the details of the microphysics of these processes are still a matter of investigation, the connection between radio halos, relics, and cluster mergers is supported by a number of observational results. In particular:
- (1)
- diffuse emission in the form of a radio halo may be or may be not present. When detected, it correlates with the cluster X-ray luminosity (Kale et al. [3] and references therein) and/or mass (Cassano et al. [4]);
- (2)
- a quantitative link exists between the presence of a radio halo and the cluster dynamical status, as derived by the substructure analysis of the X-ray emission (Buote [5]; Cassano et al. [6]);
- (3)
- the occurrence of radio halos is a steep function of the cluster mass; i.e., the number of radio halos increases considerably for masses M M (Cuciti et al. [7] and references therein), a result which is consistent with the expectations of the turbulent re-acceleration model;
- (4)
- giant radio halos with ultrasteep spectrum ( for S) have been found by means of deep observations at frequencies below 1 GHz (some remarkable examples are A 521, Brunetti et al. [8] and Dallacasa et al. [9]; A 697, Macario et al. [10]; RXCJ 1514.9-1523, Giacintucci et al. [11]). Such class of diffuse cluster sources is predicted by the re-acceleration model in the presence of minor mergers; i.e., less energetic and/or less massive ( M) merger events (Cassano [12]);
- (5)
- the connection between radio relics and cluster mergers is also well established (e.g., Ensslin et al. [13]; Hoeft & Brüggen [14]). They are found in the outskirts of galaxy clusters, and are thought to trace shock waves generated during merger events. The details of the re-acceleration in relics is still debated, and a clear association between relics and shocks has only been seen in few cases. As a matter of fact, the detection of shocks in galaxy clusters is challenging, partly because projection effects could hide temperature and density jumps, and partly because the strongest shocks are expected in the clusters outskirts, where the X-ray brightness is low. Remarkable examples of relics at merger shocks are A 754 (Macario et al. [15]), A 115 (Botteon et al. [16]), and CIZA J 2242.8+5301 (Ogrean et al. [17]). As for radio halos, scaling relations seem to hold for relics, too, though with high dispersion (de Gasperin et al. [18]).
Aside from these strong pieces of evidence in support of the connection between halos and relics and cluster mergers, a handful of giant radio halos have recently been found in clusters which do not show obvious signatures of major mergers (CL 1821+643, Bonafede et al. [19] and Kale & Parekh [20]; A 2142, Farnsworth et al. [21] and Venturi et al. [22]; A 2390 and A 2261, Sommer et al. [23]), a result which shows that our understanding is still incomplete.
Most of our current knowledge on the connection between cluster mergers and diffuse cluster radio sources builds on observations of samples of massive clusters (M M); at the same time, the dominant process of mass assembly in the Universe is the accretion of systems of smaller mass in less extreme processes—the so-called minor mergers. The steep relation between the cluster mass (or X-ray luminosity) and the radio power for radio halos (Cassano et al. [4]) and relics (de Gasperin et al. [18]) makes the detection of such sources in less massive systems an extremely challenging task for the current radio interferometers; hence, the observational signatures of minor mergers are still largely unexplored. In fact, the faint population of halos, relics, and mini-halos will be best targeted in the future by SKA and its precursors (Cassano et al. [24], Cassano et al. [25], and Gitti et al. [26]).
2. The Shapley Concentration in Context
An ideal place in the nearby Universe to study the mass assembly processes is the Shapley Concentration (SC, mean redshift z = 0.048, which implies a conversion factor of 0.928 kpc/arcsec and luminosity distance 210 Mpc for a ΛCDM cosmology with H = 70 km·s·Mpc, = 0.3), where a number of Abell clusters and groups are currently merging, with the fate of constituting a future single massive supercluster. The clusters and groups in the SC have low-to-intermediate individual masses ( to M, Reisenegger et al. [27]) and luminosities (from erg/s to L erg/s, de Filippis et al. [28]). Hence, deep radio observations of the SC are a unique chance to fill the gap in our knowledge of the observationals signatures of minor mergers on the radio emission properties, as the rate of occurrence of diffuse cluster sources in less energetic mergers is still unknown.
The central region of the SC is dominated by the A 3558 complex, a “chain” of clusters aligned in the East–West direction which includes A 3556, A 3558, A 3562, and the two SC groups SC 1329–313 and SC 1327–312 (see Figure 1), and by the A 3258 complex, which encompasses A 3528, A 3530, and A 3532. Due to its exceptional role, the SC core has been studied at all energy bands, from the X-ray (e.g., Ettori et al. [29], Gastaldello et al. [30], Rossetti et al. [31], Ursino et al. [32]) to the radio (e.g., Venturi et al. [33,34,35,36], Giacintucci et al. [37,38]), and has a wealth of data from Galex Spitzer and deep AAT spectroscopy from the ACCESS survey (e.g., Haines et al. [39], Merluzzi et al. [40,41]), which further highlight intense merging activity.
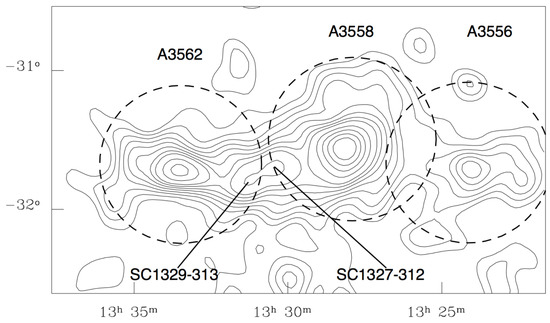
Figure 1.
Distribution of the optical galaxies in the A 3558 complex, shown as isodensity contours. The dashed circles represent the Abell radius for each cluster. The 325 MHz pointing is at the centre of A 3558.
The unique multiband coverage of the SC core suggests that:
- (1)
- the A 3558 complex is undergoing merging processes, as witnessed by the presence of a radio halo at the centre of A3562 (Venturi et al. [42] and Giacintucci et al. [38]), and gas stripping in a number of galaxies in the region between A 3562 and A 3558 (Merluzzi et al. [40,43]);
- (2)
- A 3558 itself is an intriguing cluster. On the basis of a deep analysis based on XMM–Newton and Chandra data, Rossetti et al. [31] classified it as an intermediate case between cool-core and non-cool-core cluster: a cold front is located at ∼100 kpc in the SE direction, and more recently, two new candidate cold fronts at ∼500 kpc and at ∼1 Mpc, respectively SE and NW of the cluster centre, have been found (Rossetti et al., in prep.). Rossetti et al. [31] concluded that the relaxation process of A 3558 has most likely been perturbed either by the passage of the small group SC 1327–312 or by an off-axis merger with a more massive cluster, whose debris are A 3562 and the two SC groups in the region between A 3558 and A 3562 (see Figure 1);
- (3)
- the clusters in the A 3528 complex are most likely in a pre-merger stage, as suggested by the X-ray properties (Gastaldello et al. [30]) and by the properties of the radio galaxies (Lakhchaura et al. [44], Di Gennaro et al. [45]): the radio emission from the BCGs (Brightest Cluster Galaxies) in A 3528 and A 3532 is typical of very relaxed systems; i.e., high radio power and extended morphology with tails and signs of restarted activity.
With the purpose of exploring the full field of the A 3558 complex and performing a comparison study between the A 3558 and the A 3528 complexes (extended emission on the cluster scale, radio study of the BCGs, and of the radio galaxy population as a whole), we started an observational campaign of both cluster complexes with the GMRT at 610 MHz, 325 MHz, and 240 MHz. Here we present new results for the A 3558 complex, while our study of the A 3528 complex will be published in Di Gennaro et al. [45].
3. Observations
We observed the A 3558 complex with the GMRT at 240 MHz, 325 MHz, and 610 MHz in several different observing runs. A study of the eastern part of the complex (i.e., A 3562) at these frequencies was published in Giacintucci et al. [38]. Here we report preliminary results from our observations at 325 MHz, pointed at the centre of A 3558 (i.e., RA, DEC). The field of view of the GMRT at this frequency is ; therefore our pointing covers the full A 3558 complex.
The raw data were first processed with the software flagcal (Prasad and Chengalur [46]) to remove radio frequency interferences and apply bandpass calibration; then, further editing, calibration, self-calibration, and imaging were performed with the NRAO AIPS software (Astronomical Imaging Processing System). To improve the image quality and correct for residual artifacts due to the presence of strong point sources in the field, direction-dependent calibration was carried out with the PEELR procedure in AIPS. The final rms in the full-resolution image () ranges from ∼75 Jy/b in regions void of radio sources to ∼0.1 mJy/b close to the pointing centre. A gray-scale version of the final image is given in Figure 2, where the the location of all clusters is reported.
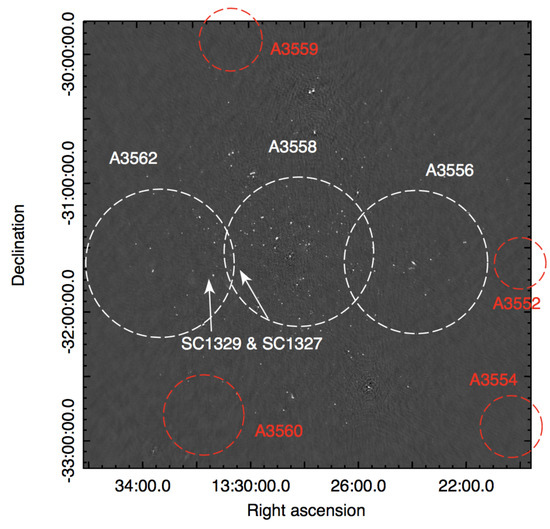
Figure 2.
Gray-scale version of the 325 MHz Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) image. The full field of view—centered on A 3558—is shown. The Abell clusters and groups are indicated. The restoring beam is .
4. Results
The full analysis of the 325 MHz image is still in progress. Here we report on the discovery of diffuse radio emission in the A 3558 complex between A 3558 and A 3562, where the two SC groups are located (Figure 1 and Figure 2), and on new features of the radio emission associated with the BCG in A 3556, at the western end of the chain.
4.1. The Relic
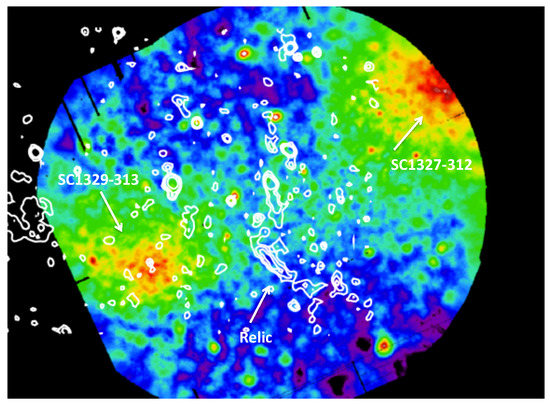
We found a radio relic in the region between the two SC groups SC 1327–312 and SC 1329–313, at a distance of and , respectively (note that the Abell radius in the Shapley Concentration core is ). Figure 3 shows the 325 MHz contours overlaid in the Digitized Sky Survey Red plate (DSS2), and highlights the lack of a clear (or even candidate) counterpart to the radio emission. The size of the relic in our image is ∼ 350 kpc, which is small but not unusual. Its radio power is low (P W Hz), and it is at least qualitatively consistent with the scaling relation between the radio power of relics and the mass of the host cluster (see de Gasperin et al. [18]), considering that the mass estimated for SC 1329–313 from Beppo–SAX observations is approximately M (Bardelli et al. [47]). The relic is overlaid on the XMM–Newton X-ray image in Figure 4, which clearly shows the location between the two SC groups.
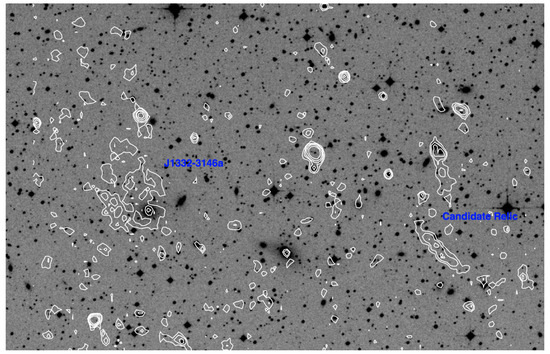
Figure 3.
Radio contours at 325 MHz overlaid on the Digitized Sky Survey (DSS2) –red optical frame of the region between A 3558 and A 3562, where the two Shapley Concentration (SC) groups are located. The radio image is primary beam corrected. The contours start at 0.4 mJy/b and are drawn as powers of two. The resolution of the image is . The two extended radio sources discussed here are labelled.
Hints of the presence of this relic have been unveiled “a posteriori” in the images published in Giacintucci et al. [38], but the sensitivity of those images is too low to derive an estimate of its spectral index. The relic is undetected at 150 MHz in the First Alternative Data Release (ADR1) of the TGSS (TIFR GMRT Sky Survey) (Intema et al. [48]), most likely due to sensitivity limitations.
4.2. Restarted Radio Emission in J 1332–3146a?
Figure 3 shows the 325 MHz emission of J 1332–3146a, surrounding a bright galaxy in SC1329–313. Comparison with earlier imaging with the Very Large Array at 1.4 GHz (Giacintucci et al. [38]) suggests a very steep spectrum for this emission, (S). At the same time, the compact component embedded in the extended radio emission and associated with a cluster member (z = 0.043) m = 15.3 galaxy suggests that its nucleus could be active. The nature of this radio emission, and the connection with the radio activity cycles of the bright galaxy and with the location within the A 3558 complex will be clarified with new 240 MHz and 610 MHz observations currently in the reduction stage.
Giacintucci et al. [38] proposed that the origin of the radio halo in A 3562 could be sloshing induced in the cluster core by the passage of SC 1329–313 in its infalling motion westwards towards A 3558, hence highlighting the merger/accretion processes at work here. The discovery of the radio relic and the very steep extended emission of J 1332-3146a are another piece of evidence in support of the dynamical activity in the A 3558 complex. Whether the relic originates from the interaction between A 3562 and SC 1329–313, or from the ongoing dynamical activity between A 3558 and SC 1327–312 (Rossetti et al. [31], Merluzzi et al. [43]) is currently under investigation.
4.3. The Western End of the A 3558 Complex: A 3556
Figure 5 shows the central region of A 3556, where the head–tail radio galaxies J 1324–3138 and J 1324–3140 are located. J 1324–3138 was studied in detail in a previous work (Venturi et al. [49]), while J 1324–3140 was classified as point-like on the basis of 13 and 22 cm performed with the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) (Venturi et al. [33]). Our observations reveal the presence of two symmetric lobes with very low surface brightness. A comparison with images at 610 MHz and 235 MHz shows that these features have very steep spectrum 2, while the compact component has a spectral index 0.8, typical of active radio galaxies (Di Gennaro et al. [45]),
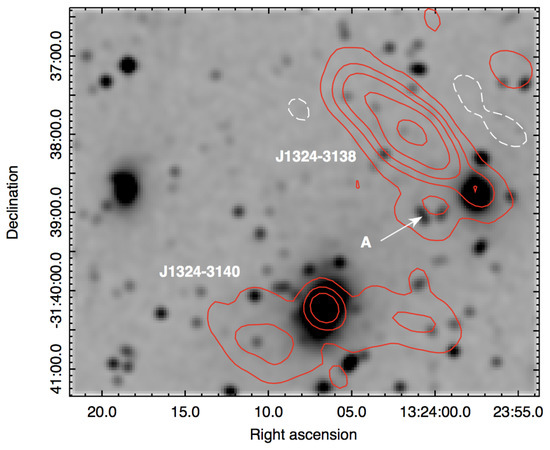
Figure 5.
325 MHz Contours of the central region of A 3556 overlaid on DSS2. Contour levels and resolution as in the previous figures.
The low frequency GMRT observations also reveal some emission between the head of J1324–3138 and J1324–3140 (undetected at the ATCA wavelengths), labelled A in Figure 5. The nature of this emission is still unclear, and is under investigation. Figure 5 shows the presence of some galaxies within the lowest radio contour, but it is not clear at this stage if A is a blend of radio emission from a number of cluster galaxies, or extended emission of different nature.
A study of the radio emission of the BCGs in the A 3558 and A 3528 complexes clearly shows that the radio properties of J1324–3140 are similar to those of the BCGs in relaxed/pre-merger environments, suggesting that A 3556 has not yet been involved in the merger ongoing activity in the A 3558 complex (Di Gennaro et al., [45]).
5. Conclusions
The preliminary results presented here cast light on the peripheral regions of the A 3558 complex in the Shapley Concentration core, and provide important information towards our understanding of the merger and accretion properties at play here.
We report on the discovery of a radio relic at the eastern periphery of A 3558, in the region between the two SC groups, where accretion processes are expected to be ongoing. The relic has a relatively small linear size ( kpc) and low radio power, qualitatively consistent with the scaling relations for the radio power of relics and the mass of the host cluster. Indeed, the masses of the clusters and groups in the Shapley Concentration core are low-to-intermediate (few times 10 to M). The merging event at the origin of the relic—in particular the accretion history of A 3558—is under investigation by us with a multiband approach.
Moreover, our observations and preliminary spectral analysis of the radio galaxy J 1331–3146a—located in the same lively environment and detected in previous works—suggest that the radio emission consists of an active nucleus associated with the a bright galaxy surrounded by “dead” radio plasma. We also report on the discovery of two symmetric steep spectrum lobes associated with the BCG in A 3556, beyond the compact and active nucleus. A preliminary spectral analysis suggests restarted activity.
Neither the relic nor the lobes in J 1324-3140 were detected in relatively shallow all-sky surveys such as the Northern VLA SKy Survey (NVSS at 1.4 GHz), TGSS at 150 MHz, and SUMSS (Sydney Unversity Molonglo Sky Survey at 843 MHz), highlighting the need for deep pointed observations for the detection of cluster-scale diffuse radio emission in low-to-intermediate mass systems. We expect to considerably improve our knowledge of the radio properties of the Shapley Concentration in the near future, once the SKA precursors ASKAP and MeerKAT become operational.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff at the GMRT who have made these observations possible. GMRT is run by the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research. Basic research in radio astronomy at the Naval Research Laboratory is supported by 6.1 base funding.
Author Contributions
T. Venturi, G. Di Gennaro and D. Dallacasa performed the radio data reduction and analysis. F. Gastaldello and M. Rossetti provided the X–ray images. All authors contributed to the discussion and interpretation. This work is part of the MSc Thesis of G. Di Gennaro, University of Bologna (2016).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feretti, L.; Giovannini, G.; Govoni, F.; Murgia, M. Clusters of galaxies: Observational properties of the diffuse radio emission. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2012, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Jones, T.W. Cosmic Rays in Galaxy Clusters and Their Nonthermal Emission. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2014, 23, 1430007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.; Venturi, T.; Giacintucci, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Cassano, R.; Brunetti, G.; Cuciti, V.; Macario, G.; Athreya, R. The Extended GMRT Radio Halo Survey. II. Further results and analysis of the full sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 579, A92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R.; Ettori, S.; Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Pratt, G.W.; Venturi, T.; Kale, R.; Dolag, K.; Markevitch, M. Revisiting the Scaing Relations for Giant Radio Halos in Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2013, 777, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buote, D.A. On the Origin of Radio Halos in Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2001, 553, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R.; Ettori, S.; Giacintucci, S.; Brunetti, G.; Markevitch, M.; Venturi1, T.; Gitti, M. On the Connection Between Giant Radio Halos and Cluster Mergers. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 721, L82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuciti, V.; Cassano, R.; Brunetti, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Kale, R.; Ettori, S.; Venturi, T. Occurrence of radio halos in galaxy clusters. Insight from a mass-selected sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 580, A97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Cassano, R.; Lane, W.; Dallacasa, D.; Venturi, T.; Kassim, N.E.; Setti, G.; Cotton, W.D.; Markevitch, M. A low-frequency radio halo associated with a cluster of galaxies. Nature 2008, 455, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallacasa, D.; Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Cassano, R.; Venturi, T.; Macario, G.; Kassim, N.E.; Lane, W.; Setti, G. Deep 1.4 GHz Follow-up of the Steep Spectrim Radio Halo in A521. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, G.; Venturi, T.; Brunetti, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Giacintucci, S.; Cassano, R.; Bardelli, S.; Athreya, R. The very steep spectrum radio halo in Abell 697. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 517, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacintucci, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Venturi, T.; Brunetti, G.; Cassano, R.; Markevitch, M.; Athreya, R.M. An unlikely radio halo in the low X-ray lumoinous galaxy cluster RXC J1514.9-1523. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 534, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R. Radio halos, cluster mergers and the role of future LOFAR observations. Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 2011, 82, 531. [Google Scholar]
- Ensslin, T.A.; Biermann, P.L.; Klein, U.; Kohle, S. Cluster radio relics as a tracer of shock waves of the large-scale structure formation. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 332, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeft, M.; Brüggen, M. Radio signature of cosmological structure formation shocks. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 375, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, G.; Markevitch, M.; Giacintucci1, S.; Brunetti, G.; Venturi, T.; Murray, S.S. A Shock Front in the Merging Galaxy Cluster A754: X-ray and Radio Observations. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteon, A.; Gastaldello, F.; Brunetti, G.; Dallacasa, D. A shock at the radio relic position in Abell 115. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2016, 460, L84–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrean, G.A.; Brüggen, M.; van Weeren, R.; Röttgering, H.; Simionescu, A.; Hoeft, M.; Croston, J.H. Multiple density discontinuities in the merging galaxy cluster CIZA J2242.8+5301. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 3416–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gasperin, F.; van Weeren, R.J.; Brüggen, M.; Vazza, F.; Bonafede, A.; Intema, H.T. A new double radio relic in PSZ1 G096.89+24.17 and a radio relic mass-luminosity relation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 3130–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafede, A.; Intema, H.T.; Brüggen, M.; Russell, H.R.; Ogrean, G.; Basu, K.; Sommer, M.; van Weeren, R.J.; Cassano, R.; Fabian, A.C.; et al. A giant radio halo in the cool core cluster CL 1821+643. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2014, 444, L44–L48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.; Parekh, V. How unusual is the cool-core radio halo cluster CL 1821+643? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsnworth, D.; Rudnick, L.; Brown, S.; Brunetti, G. Discovery of Megaparsec-scale, Low Surface Brigthness Nonthermal Emission in Merging Galaxy Clusters Using the Green Bank Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2013, 779, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Venturi, T.; Rossetti, M.; Brunetti, G.; Farnsworth, D.; Gastaldello, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Lal, D.V.; Rudnick, L.; Shimwell, T.W.; Eckert, D.; et al. The two-component giant radio halo in the galaxy cluster A 2142. Astron. Astrophys. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, M.W.; Basu, K.; Intema, H.; Pacaud, F.; Bonafede, A.; Babul, A.; Bertoldi, F. Mpc-scale diffuse radio emission in two massive cool-core clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R.; Brunetti, G.; Norris, R.P.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; Trasatti, M. Radio halos in future surveys in the radio continuum. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 584, A100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, R.; Bernardi, G.; Brunetti, G.; Brüggen, M.; Clarke, T.; Dallacasa, D.; Dolag, K.; Ettori, S.; Giacintucci, S.; Giocoli, C.; et al. Cluster radio halos at the crossroad between astrophysics and cosmology in the SKA era. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the SKA (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; p. 73.
- Gitti, M.; Tozzi, P.; Brunetti, G.; Cassano, R.; Dallacasa, D.; Edge, A.; Ettori, S.; Feretti, L.; Ferrari, C.; Giacintucci, S. The SKA view of cool-core clusters: Evolution of radio mini-halos and AGN feedback. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the SKA (AASKA14), Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; p. 76.
- Reisenegger, A.; Quintana1, H.; Carrasco, E.R.; Maze, J. The Shapey Supercluster. III. Collapse Dynamics and Mass of the Central Concentration. Astrophys. J. 2000, 120, 523. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, E.; Schindler, S.; Erben, T. The Shapley super-cluster. New X-ray detections and mass distribution. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 444, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettori, S.; Fabian, A.C.; White, D.A. On the mass distribution of the Shapley Supercluster inferred from X-ray observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 289, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldello, S.; Ettori, S.; Molendi, S.; Bardelli, S.; Venturi, T.; Zucca, E. XMM-Newton observations of the interacting cluster Abell 3528. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 411, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, M.; Ghizzardi, S.; Molendi, S.; Finoguenov, A. A cluster in a crowded environment: XMM-Newton and Chandra observations of A 3558. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 463, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, E.; Galeazzi, M.; Gupta, A.; Kelley, R.L.; Mitsuishi, I.; Ohashi, T.; Sato, K. Exploring the Bridge between A 3556 and A 3558 in the Shapley Supercluster. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Morganti, R.; Hunstead, R.W. Radio properties of the Shapley Concentration—I. The Abell cluster A 3556. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 285, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Morganti, R.; Hunstead, R.W. Radio properties of the Shapley Concentration—III. Merging clusters in the A 3558 complex. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 314, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Zambelli, G.; Morganti, R.; Hunstead, R.W. Radio properties of the Shapley Concentration—IV. The A 3528 cluster complex. Mon. Not. R. Aston. Soc. 2001, 324, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Rossetti, M.; Bardelli, S.; Giacintucci, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Cornacchia, M.; Kantharia, N.G. Radio emission at the centre of the galaxy cluster Abell 3560: Evidence for core sloshing? Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacintucci, S.; Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Zucca, E. AGN and starburst radio activity in the A 3558 cluster complex. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 419, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacintucci, S.; Venturi, T.; Brunetti, G.; Bardelli, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Ettori, S.; Finoguenov, A.; Rao, A.P.; Zucca, E. Spectral properties and origin of the radio halo in A 3562. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 440, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.P.; Busarello, G.; Merluzzi, P.; Smith, R.J.; Raychaudhury, S.; Mercurio, A.; Smith, G.P. ACCESS—II. A complete census of star formation in the Shapley supercluster. UV and IR luminosity functions. Mon. Not. R. Aston. Soc. 2011, 412, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merluzzi, P.; Busarello, G.; Dopita, M.A.; Haines, C.P.; Steinhauser, D.; Mercurio, A.; Rifatto, A.; Smith, R.J.; Schindler, S. ACCESS—V. Dissecting ram-pressure stripping through integral field spectroscopy and multiband imaging. Mon. Not. R. Aston. Soc. 2013, 429, 1747–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merluzzi, P.; Busarello, G.; Haines, C.P.; Mercurio, A.; Okabe, N.; Pimbblet, K.J.; Dopita, M.A.; Grado, A.; Limatola, L.; Bourdin, H.; et al. Shapley Supercluster Survey: Galaxy evolution from filaments to cluster cores. Mon. Not. R. Aston. Soc. 2015, 446, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Dallacasa, D.; Brunetti, G.; Giacintucci, S.; Hunstead, R.W.; Morganti, R. The radio halo in the merging cluster A 3562. Aston. Astrophys. 2003, 402, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merluzzi, P.; Busarello, G.; Dopita, M.A.; Haines, C.P.; Steinhauser, D.; Bourdin, H.; Mazzotta, P. Shapley Supercluster Survey: Ram-pressure stripping versus tidal interactions in the Shapley supercluster. Mon. Not. R. Aston. Soc. 2016, 460, 3345–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhchaura, K.; Singh, K.P.; Saikia, D.J.; Hunstead, R.W. A Cluster Pair: A 3532 and A 3530. ApJ 2013, 767, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, G.; Venturi, T.; Dallacasa, D.; Giacintucci, S. Cosmic Dance in the Shapley Concentration Core: radio emission from the BCGs and tailed radio galaxies. A&A 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, J.; Chengalur, J. FLAGCAL: A flagging and calibration package for radio interferometric data. Exp. Astron. 2012, 33, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, S.; De Grandi, S.; Ettori, S.; Molendi, S.; Zucca, E.; Colafrancesco, S. SC 1327-–312 & SC 1329-–313: Two galaxy groups in-between a major merging event observed with Beppo—SAX. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 382, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Intema, H.; Jagannathan, P.; Mooley, K.P.; Frail, D.A. The GMRT 150 MHz All-sky Radio Survey: First Alternative Data Release TGSS ADR1. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, T.; Venturi, T.; Bardelli, S.; Morganti, R.; Hunstead, R.W. Radio properties of the Shapley Concentration—II. J1324-3138: A remnant of a radio galaxy in the Abell cluster A3556? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 298, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).