The Third Law of Galactic Rotation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Galaxy Rotation Curves
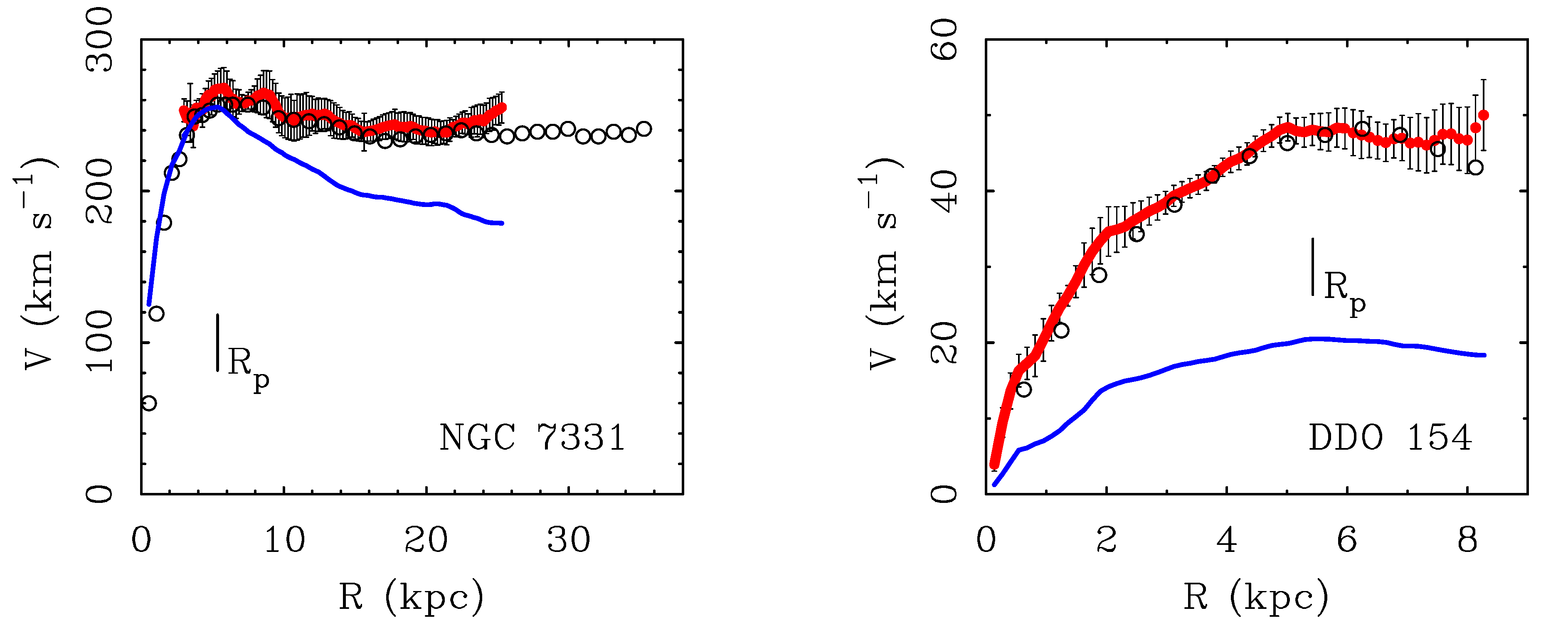
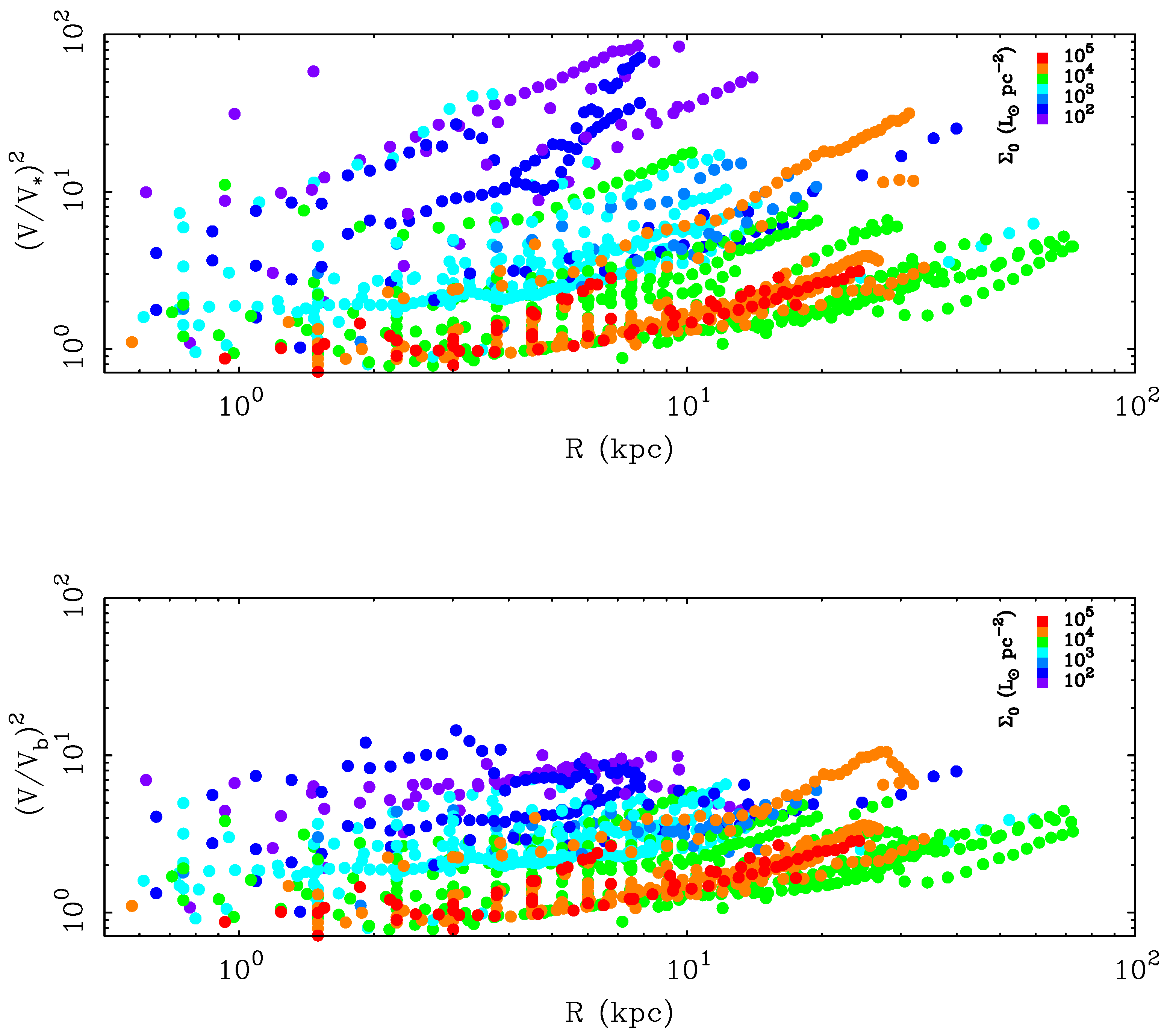
3. The Global Surface Brightness Dependence of the Mass Discrepancy

4. The Local Relation between Mass and Light
4.1. The Universal Rotation Curve

4.2. Renzo’s Rule

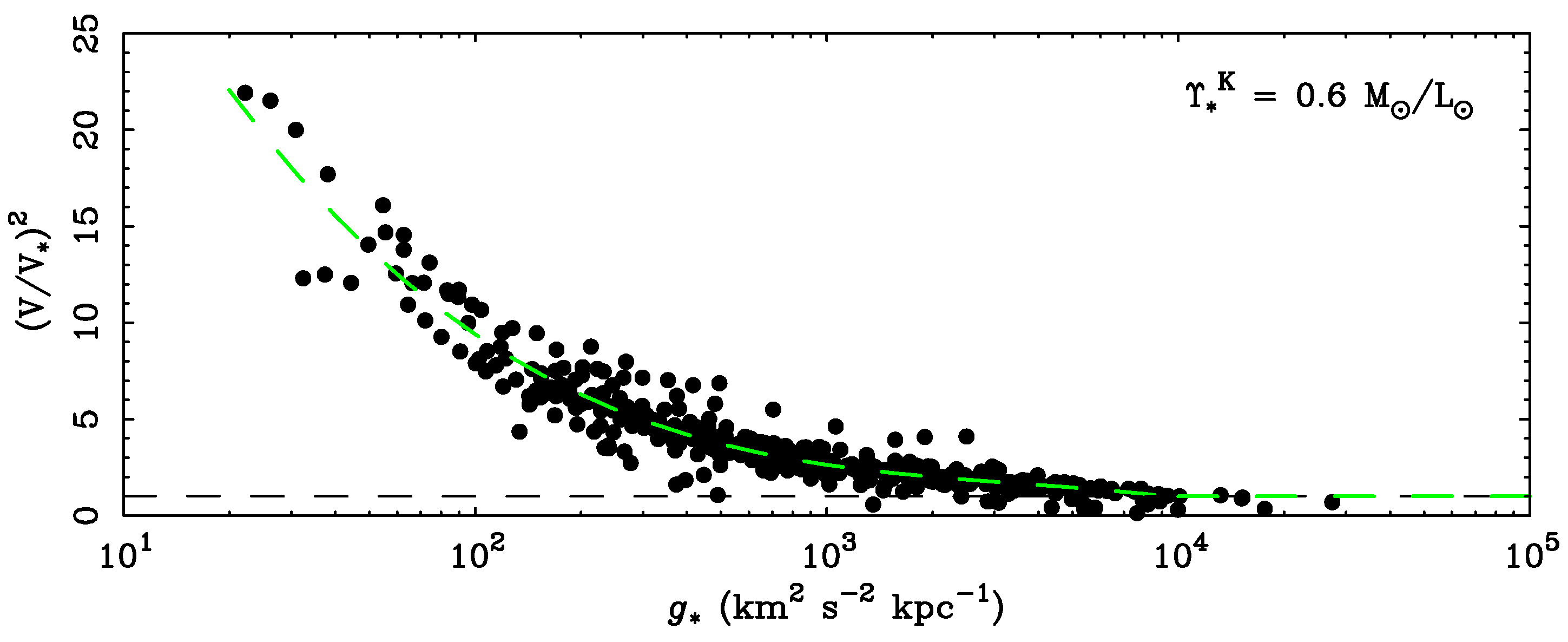
4.3. The Mass Discrepancy-Acceleration Relation
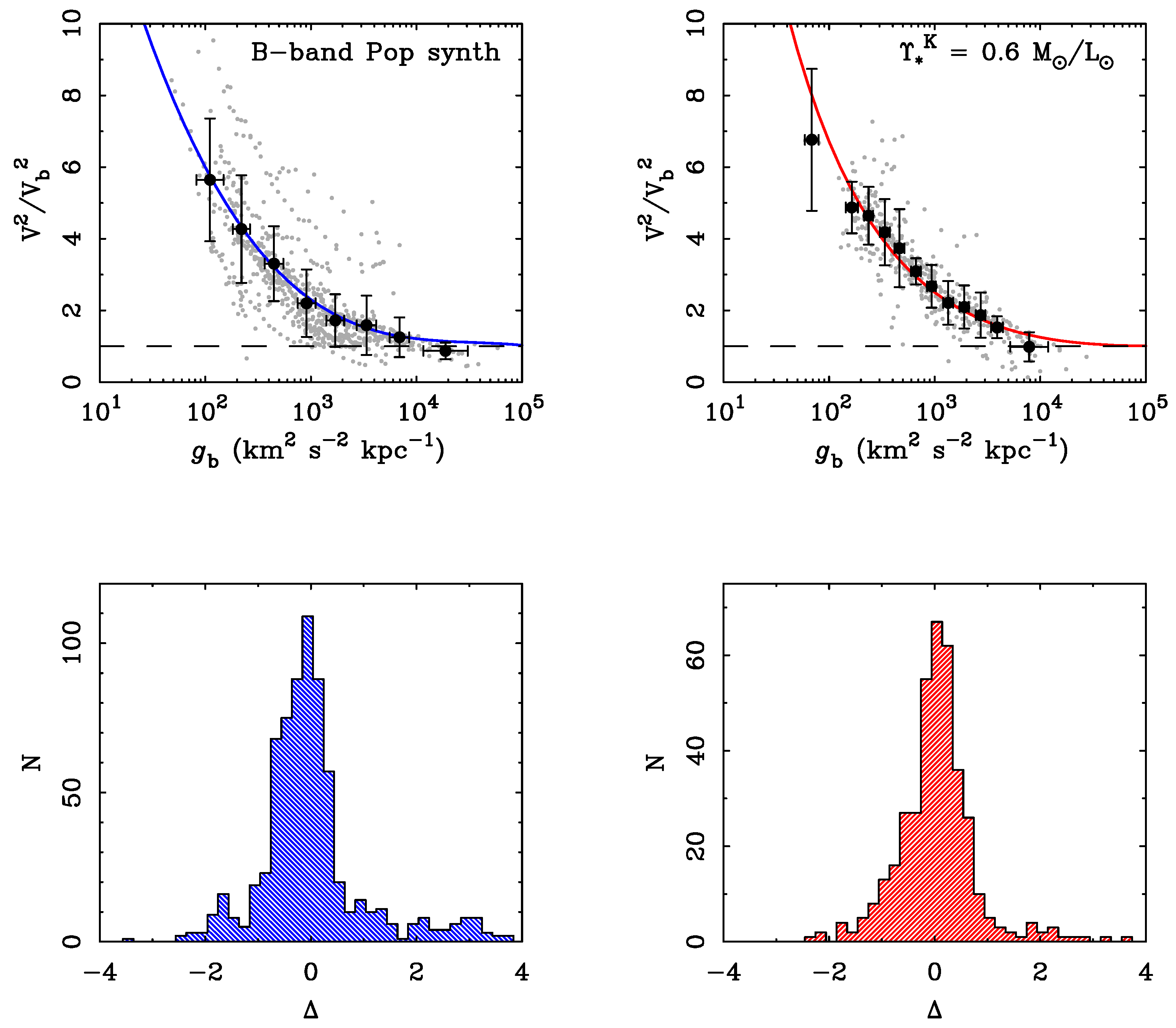
5. Discussion
5.1. The Dark Matter Distribution
5.2. Neither Cusps nor Cores
6. Broader Context
Renzo’s rule (Section 4.2; [3]) is an example of such a descriptive generalization.A descriptive generalization about how some aspect of the natural world behaves under stated circumstances.
- (1)
- Rotation curves attain an approximately constant velocity that persists indefinitely (flat rotation curves).
- (2)
- The observed (baryonic) mass scales as the fourth power of the amplitude of the flat rotation (the baryonic Tully–Fisher Relation).
- (3)
- There is a one-to-one correspondence between the radial force and the observed distribution of baryonic matter (the mass discrepancy-acceleration relation).
Everything happens in rotating galaxies as if the effective radial force law is MOND.
- (1)
- MOND represents a true modification of dynamical laws.
- (2)
- The laws of galactic rotation are a consequence of some process during galaxy formation.
- (3)
- The properties of dark matter particles impose the observed phenomena.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, R.H. The Dark Matter Problem; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.H. Mass discrepancies in galaxies—Dark matter and alternatives. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 1990, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancisi, R. The visible matter—Dark matter coupling. In Dark Matter in Galaxies; Ryder, S., Pisano, D., Walker, M., Freeman, K., Eds.; IAU Symposium: Paris, France, 2004; Volume 220, p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S.S. The Mass Discrepancy-Acceleration Relation: Disk Mass and the Dark Matter Distribution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaters, R.A.; Sancisi, R.; van der Hulst, J.M.; van Albada, T.S. The link between the baryonic mass distribution and the rotation curve shape. Mon. Not. R. Ast. Soc. 2012, 425, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, V.C.; Thonnard, N.; Ford, W.K., Jr. Extended rotation curves of high-luminosity spiral galaxies. IV—Systematic dynamical properties, SA through SC. Astrophys. J. 1978, 225, L107–L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, A. 21-cm line studies of spiral galaxies. I—Observations of the galaxies NGC 5033, 3198, 5055, 2841, and 7331. II—The distribution and kinematics of neutral hydrogen in spiral galaxies of various morphological types. Astron. J. 1981, 86, 1791–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Fisher, J.R. A new method of determining distances to galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1977, 54, 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S.S.; Schombert, J.M.; Bothun, G.D.; de Blok, W.J.G. The Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 533, L99–L102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S. A Tale of Two Paradigms: The Mutual Incommensurability of LCDM and MOND. Can. J. Phys. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Binney, J.; Merrifield, M. Galactic Astronomy; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Binney, J.; Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Strigari, L.E. Kinematics of Milky Way Satellites: Mass Estimates, Rotation Limits, and Proper Motions. Adv. Astron. 2010, 2010, 407394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, G.W. Dwarf spheroidals in MOND. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 387, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.L.; Angus, G.W.; Diaferio, A. Implications for dwarf spheroidal mass content from interloper removal. 2009; arXiv:0907.3691. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; de Blok, W.J.G.; Walter, F.; Brinks, E.; Kennicutt, R.C. High-Resolution Dark Matter Density Profiles of THINGS Dwarf Galaxies: Correcting for Noncircular Motions. Astron. J. 2008, 136, 2761–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachternach, C.; de Blok, W.J.G.; Walter, F.; Brinks, E.; Kennicutt, R.C., Jr. Dynamical Centers and Noncircular Motions in THINGS Galaxies: Implications for Dark Matter Halos. Astron. J. 2008, 136, 2720–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzio de Naray, R.; McGaugh, S.S.; Mihos, J.C. Constraining the NFW Potential with Observations and Modeling of Low Surface Brightness Galaxy Velocity Fields. Astrophys. J. 2009, 692, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaman, R.; Venn, K.A.; Brooks, A.M.; Battaglia, G.; Cole, A.A.; Ibata, R.A.; Irwin, M.J.; McConnachie, A.W.; Mendel, J.T.; Tolstoy, E. The Resolved Structure and Dynamics of an Isolated Dwarf Galaxy: A VLT and Keck Spectroscopic Survey of WLM. Astrophys. J. 2012, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blok, W.J.G.; Walter, F.; Brinks, E.; Trachternach, C.; Oh, S.H.; Kennicutt, R.C. High-Resolution Rotation Curves and Galaxy Mass Models from THINGS. Astron. J. 2008, 136, 2648–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begeman, K.G.; Broeils, A.H.; Sanders, R.H. Extended rotation curves of spiral galaxies—Dark haloes and modified dynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 249, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carignan, C.; Purton, C. The “Total” Mass of DDO 154. Astrophys. J. 1998, 506, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, F.; Brinks, E.; de Blok, W.J.G.; Bigiel, F.; Kennicutt, R.C.; Thornley, M.D.; Leroy, A. THINGS: The H I Nearby Galaxy Survey. Astron. J. 2008, 136, 2563–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaritsky, D.; White, S.D.M. The massive halos of spiral galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1994, 435, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, F.; Vitvitska, M.; Klypin, A.; Holtzman, J.A.; Schlegel, D.J.; Grebel, E.K.; Rix, H.W.; Brinkmann, J.; McKay, T.A.; Csabai, I. Observing the Dark Matter Density Profile of Isolated Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2003, 598, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; McKay, T.A.; Sheldon, E.; Connolly, A.; Stebbins, A.; Frieman, J.A.; Jain, B.; Joffre, M.; Johnston, D.; Bernstein, G.; et al. Weak Lensing with Sloan Digital Sky Survey Commissioning Data: The Galaxy-Mass Correlation Function to 1 H–1 Mpc. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, R.; Mandelbaum, R.; Gunn, J.E.; Nakajima, R.; Seljak, U.; Hirata, C.M. Optical-to-virial velocity ratios of local disc galaxies from combined kinematics and galaxy-galaxy lensing. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 2610–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S.; de Blok, W.J.G. Testing the Dark Matter Hypothesis with Low Surface Brightness Galaxies and Other Evidence. Astrophys. J. 1998, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S. The Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation of Galaxies with Extended Rotation Curves and the Stellar Mass of Rotating Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2005, 632, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S. The Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation of Gas-rich Galaxies as a Test of ΛCDM and MOND. Astron. J. 2012, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, M.A.; van der Hulst, J.M.; de Blok, W.J.G.; McGaugh, S.S. The Tully-Fisher relation for low surface brightness galaxies: Implications for galaxy evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 273, L35–L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courteau, S.; Rix, H. Maximal Disks and the Tully-Fisher Relation. Astrophys. J. 1999, 513, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S. Balance of Dark and Luminous Mass in Rotating Galaxies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 171302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellwood, J.A. Dynamical Constraints on Disk Masses. In Galaxy Dynamics—A Rutgers Symposium; Merritt, D.R., Valluri, M., Sellwood, J.A., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series: San Francisco, USA, 1999; Volume 182, p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Palunas, P.; Williams, T.B. Maximum Disk Mass Models for Spiral Galaxies. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 2884–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, E.; van der Hulst, J.M.; Sancisi, R.; Swaters, R.S.; van Albada, T.S. The mass distribution in early-type disc galaxies: Declining rotation curves and correlations with optical properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 376, 1513–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, F.; Fraternali, F.; Verheijen, M. A scaling relation for disc galaxies: Circular-velocity gradient versus central surface brightness. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, L30–L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, F. The Inner Regions of Disk Galaxies: A Constant Baryonic Fraction? Galaxies 2014, 2, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blok, W.J.G.; McGaugh, S.S. Does Low Surface Brightness Mean Low Density? Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 469, L89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Verheijen, M.A.W. The Ursa Major Cluster of Galaxies. II. Bimodality of the Distribution of Central Surface Brightnesses. Astrophys. J. 1997, 484, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, E.; Verheijen, M.A.W. The high-mass end of the Tully-Fisher relation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.H.; Verheijen, M.A.W. Rotation Curves of Ursa Major Galaxies in the Context of Modified Newtonian Dynamics. Astrophys. J. 1998, 503, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, M.A.W. The Ursa Major Cluster of Galaxies. V. H I Rotation Curve Shapes and the Tully-Fisher Relations. Astrophys. J. 2001, 563, 694–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schombert, J.; McGaugh, S. Stellar Populations and the Star Formation Histories of LSB Galaxies: IV Spitzer Surface Photometry of LSB Galaxies. 2014; ArXiv:1401.0238. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, K.C. On the Disks of Spiral and so Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1970, 160, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hulst, J.M.; Terlouw, J.P.; Begeman, K.G.; Zwitser, W.; Roelfsema, P.R. The Groningen Image Processing SYstem, GIPSY. In Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems I; Worrall, D.M., Biemesderfer, C., Barnes, J., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series: San Francisco, USA, 1992; Volume 25, p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzio de Naray, R.; Arsenault, C.A.; Spekkens, K.; Sellwood, J.A.; McDonald, M.; Simon, J.D.; Teuben, P. DiskFit: Modeling Asymmetries in Disk Galaxies. Astrophysics Source Code Library, record ascl:1209.011. Available online: http://ascl.net/1209.011 (accessed on 10 December 2014).
- Verheijen, M.; de Blok, E. The HSB/LSB Galaxies NGC 2403 and UGC 128. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1999, 269, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, V.C.; Burstein, D.; Thonnard, N. A new relation for estimating the intrinsic luminosities of spiral galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1980, 242, L149–L152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persic, M.; Salucci, P. The universal galaxy rotation curve. Astrophys. J. 1991, 368, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persic, M.; Salucci, P.; Stel, F. The universal rotation curve of spiral galaxies—I. The dark matter connection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 281, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomsma, R.; Oosterloo, T.A.; Fraternali, F.; van der Hulst, J.M.; Sancisi, R. HI holes and high-velocity clouds in the spiral galaxy NGC 6946. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 490, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais-Ouellette, S.; Amram, P.; Carignan, C.; Swaters, R. Accurate determination of the mass distribution in spiral galaxies. III. Fabry-Perot imaging spectroscopy of 6 spiral galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 420, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, O.; Carignan, C.; Amram, P.; Hernandez, O.; Chemin, L.; Balkowski, C.; Kennicutt, R. Hαkinematics of the SINGS nearby galaxies survey—I*. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 367, 469–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeils, A.H. The mass distribution of the dwarf spiral NGC 1560. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 256, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, G.; Baes, M.; Famaey, B.; van Acoleyen, K. Mass models from high-resolution HI data of the dwarf galaxy NGC 1560. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blok, W.J.G.; McGaugh, S.S. Testing Modified Newtonian Dynamics with Low Surface Brightness Galaxies: Rotation Curve FITS. Astrophys. J. 1998, 508, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famaey, B.; McGaugh, S.S. Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND): Observational Phenomenology and Relativistic Extensions. Living Rev. Relativ. 2012, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.F.; McIntosh, D.H.; Katz, N.; Weinberg, M.D. The Optical and Near-Infrared Properties of Galaxies. I. Luminosity and Stellar Mass Functions. Astrophys. J. Supp. 2003, 149, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.; Schombert, J. Color–Mass-to-Light Ratio Relations for Disk Galaxies. Astron. J. 2014, 148, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S. Milky Way Mass Models and MOND. Astrophys. J. 2008, 683, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A Universal Density Profile from Hierarchical Clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Hayashi, E.; Power, C.; Jenkins, A.R.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Stadel, J.; Quinn, T.R. The inner structure of ΛCDM haloes—III. Universality and asymptotic slopes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 349, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baushev, A.N. The real and apparent convergence of N-body simulations of the dark matter structures: Is the Navarro-Frenk-White profile real? Astropart. Phys. 2015, 62, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brada, R.; Milgrom, M. The Modified Newtonian Dynamics Predicts an Absolute Maximum to the Acceleration Produced by “Dark Halos”. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 512, L17–L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S.; de Blok, W.J.G.; Schombert, J.M.; Kuzio de Naray, R.; Kim, J.H. The Rotation Velocity Attributable to Dark Matter at Intermediate Radii in Disk Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2007, 659, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.G.; McGaugh, S.S.; Mateo, M.; Olszewski, E.W.; Kuzio de Naray, R. Comparing the Dark Matter Halos of Spiral, Low Surface Brightness, and Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 717, L87–L91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, G.; Famaey, B.; Zhao, H.; Salucci, P. Universality of galactic surface densities within one dark halo scale-length. Nature 2009, 461, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, F.; Gentile, G.; Salucci, P.; Frigerio Martins, C.; Wilkinson, M.I.; Gilmore, G.; Grebel, E.K.; Koch, A.; Wyse, R. A constant dark matter halo surface density in galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.G.; Loeb, A. Is the Universe Simpler than LCDM? 2014; arXiv:1401.1146. [Google Scholar]
- Salucci, P.; Nesti, F.; Gentile, G.; Frigerio Martins, C. The dark matter density at the Sun’s location. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 523, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P.J. Mass models of the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 2446–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienaymé, O.; Famaey, B.; Siebert, A.; Freeman, K.C.; Gibson, B.K.; Grebel, E.K.; Kordopatis, G.; Munari, U.; Navarro, J.F.; Reid, W.; et al. Weighing the local dark matter with RAVE red clump stars. 2014; arXiv:1406.6896. [Google Scholar]
- Strigari, L.E.; Bullock, J.S.; Kaplinghat, M.; Simon, J.D.; Geha, M.; Willman, B.; Walker, M.G. A common mass scale for satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. Nature 2008, 454, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprayberry, D.; Bernstein, G.M.; Impey, C.D.; Bothun, G.D. The mass-to-light ratios of low surface brightness spiral galaxies: Clues from the Tully-Fisher relation. Astrophys. J. 1995, 438, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blok, W.J.G.; McGaugh, S.S. The dark and visible matter content of low surface brightness disc galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 290, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blok, W.J.G. The Core-Cusp Problem. Adv. Astron. 2010, 2010, 789293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, H.; McGaugh, S.S.; Sellwood, J.A.; de Blok, W.J.G. The formation of spiral galaxies: adiabatic compression with Young’s algorithm and the relation of dark matter haloes to their primordial antecedents. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzio de Naray, R.; McGaugh, S.S.; de Blok, W.J.G. Mass Models for Low Surface Brightness Galaxies with High-Resolution Optical Velocity Fields. Astrophys. J. 2008, 676, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzio de Naray, R.; Kaufmann, T. Recovering cores and cusps in dark matter haloes using mock velocity field observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 3617–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.J.; Simon, J.D.; Fabricius, M.H.; van den Bosch, R.C.E.; Barentine, J.C.; Bender, R.; Gebhardt, K.; Hill, G.J.; Murphy, J.D.; Swaters, R.A.; et al. Dwarf Galaxy Dark Matter Density Profiles Inferred from Stellar and Gas Kinematics. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, F.C.; Dalcanton, J.J. Semianalytical Models for the Formation of Disk Galaxies. II. Dark Matter versus Modified Newtonian Dynamics. Astrophys. J. 2000, 534, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, F.J.; Cicerone, R.J.; Clegg, M.T.; Dalrymple, G.B.; Dickerson, R.E.; Gould, S.J.; Herschbach, D.R.; Kennedy, D.; McInerney, J.D.; Moore, J.A.; et al. Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences, 2nd Ed. ed; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S.S. Novel Test of Modified Newtonian Dynamics with Gas Rich Galaxies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milgrom, M. A modification of the Newtonian dynamics—Implications for galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1983, 270, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.S.; de Blok, W.J.G. Testing the Hypothesis of Modified Dynamics with Low Surface Brightness Galaxies and Other Evidence. Astrophys. J. 1998, 499, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.H.; McGaugh, S.S. Modified Newtonian Dynamics as an Alternative to Dark Matter. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 40, 263–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.; Milgrom, M. Andromeda Dwarfs in Light of Modified Newtonian Dynamics. Astrophys. J. 2013, 766, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, S.; Milgrom, M. Andromeda Dwarfs in Light of MOND. II. Testing Prior Predictions. Astrophys. J. 2013, 775, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, M. MOND laws of galactic dynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; le Tiec, A. Dipolar dark matter and dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 023524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; Bernard, L. Phenomenology of MOND and gravitational polarization. 2014; arXiv:1403.5963. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R.H. A tensor-vector-scalar framework for modified dynamics and cosmic dark matter. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 363, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J. An Alternative to Particle Dark Matter. 2014; arXiv:hep-th/1409.0012. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGaugh, S.S. The Third Law of Galactic Rotation. Galaxies 2014, 2, 601-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies2040601
McGaugh SS. The Third Law of Galactic Rotation. Galaxies. 2014; 2(4):601-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies2040601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGaugh, Stacy S. 2014. "The Third Law of Galactic Rotation" Galaxies 2, no. 4: 601-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies2040601
APA StyleMcGaugh, S. S. (2014). The Third Law of Galactic Rotation. Galaxies, 2(4), 601-622. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies2040601




