Abstract
Searching for very-high-energy photons arising from dark matter interactions in selected astrophysical environments is a promising strategy to probe the existence and particle nature of dark matter. Among the many particle candidates, motivated by the extensions of the Standard Model, Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are considered the most compelling candidate for the elusive dark matter in the universe. In this contribution, we report an overview of the important developments in the field of indirect searching for dark matter through cosmic gamma-ray observations. We mainly focus on the role of atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes in probing the dark matter. Finally, we emphasize the opportunities for the Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) situated in Hanle, India, to explore WIMPs in the mass range of 200 GeV to 10 TeV for Segue1 and Draco dwarf–spheroidal galaxies.
1. Introduction
In the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model of modern cosmology, approximately 85% of the total mass density of the universe is attributed to the contribution of dark matter [1,2]. This concordance model has been found to be extremely successful in explaining a number of astrophysical and cosmological measurements with high precision at different scales and epochs of the present universe, containing two significant components, namely dark energy () and CDM [3,4,5]. The standard CDM model assumes flat, homogeneous, and isotropic space-time to describe the large-scale geometry and dynamics of the universe with a positive cosmological constant ( 0) depending on the material content. However, it cannot explain key cosmological concepts such as the existence of dark energy [6], dark matter [7], and inflation [8] to fully understand the mysteries of the universe. These concepts form a dark sector in the universe and individually constitute independent fields in their own rights for active and dynamic research today.
Historically, the first dynamical estimate of the amount of matter in the Milky Way Galaxy was attempted by Lord Kelvin (https://archive.org/details/baltimorelecture00kelviala. (1 February 2025)) in early 1900 by applying a simple and powerful argument of the theory of gases to the galactic stellar population. An upper limit on the matter density within a sphere of the radius ∼3 × 10 km in the Milky Way was derived by establishing a relationship between the size of the system and velocity dispersion of the system. Impressed by these estimates, Henri Poincaré, in 1906, argued that the abundance of dark matter should be less than or same as that of ordinary matter [9]. In 1933, the Swiss–American astronomer Fritz Zwicky noticed a large scatter in the apparent velocity of eight galaxies within the Coma cluster during his investigation of redshifts of galaxy clusters, as published by Edwin Hubble [10]. Zwicky applied the famous virial theorem (from thermodynamics) to the galaxy cluster for estimating the mass of the Coma cluster. From his detailed calculation, he was able to conclude that ...if this would be confirmed, we would get the surprising result that dark matter is present in much greater amount than luminous matter. This statement is considered in the literature the first use of dark matter in a scientific publication by Fritz Zwicky. In his seminal work on galaxy clusters, published in 1937, Fritz Zwicky argued the possibility of deriving the masses of galaxies from their observed rotation curves (the circular velocity of stars in a galaxy as a function of their distance from the center of galaxy) without using any additional information [11]. In 1970, explicit statements started appearing to suggest the need for additional mass in outer regions of some galaxies to explain the peak position in the galaxy rotation curves predicted by a combination of theoretical models and 21 cm radio observations [12,13]. The importance of radio observations, extending beyond the optical radius of galaxies, was properly highlighted in 1974 for exploring the amount of dark matter in galaxies or galaxy clusters [14].
Over the past five decades or more, understanding pertaining to the existence of dark matter has evolved considerably and species accounting for the bulk of the matter density of universe are referred to as dark matter candidates. A large number of observations have firmly established the cosmic abundance of cold dark matter as ∼25% in the form of non-baryonic matter and that of normal matter (standard model particles) as ∼5% [2]. But, the origin and nature of dark matter remain a leading mystery of cosmology, astronomy, and particle physics. Well-motivated theoretical models propose various particle candidates for dark matter with their masses spanning nearly 50 orders of magnitude [15,16]. These candidates should comply with the requirements of dark matter measurements and provide minimal coupling to the standard model particles. A significantly popular and potential candidate for dark matter is considered a dynamical cold particle (in order to form the large-scale structures observed in the universe) with neutral charge and long life-time. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) with mass in the GeV-TeV range, naturally arising in some models beyond the standard model of particle physics, are considered to represent a dominant family of such species [17]. However, their exact cosmic origin and particle nature, mass, and coupling to standard model particles remain completely elusive as they have escaped all the theoretical and experimental studies that have been carried out until now on high-energy physics and cosmology. Here, we briefly review the physical properties of WIMPs and attempts to probe them using very-high-energy gamma-ray observations. We also discuss the potential of the MACE (Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment) telescope to investigate the WIMPs in the mass range 0.2–10 TeV.
2. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
WIMPs are thought to have been thermally produced in the early universe to account for the correct relic density of the present universe [18]. They are assumed to have been in chemical equilibrium (reaction between the particles was balanced by a reverse reaction), in addition to thermal equilibrium, during the initial state of universe after the Big Bang. This means that the annihilation of WIMPs is balanced by creation of WIMPs through the process of pair production. Local thermal equilibrium is provided by the elastic scattering of WIMPs with standard model particles. Thermal decoupling, which predicts the matter and radiation contents of the universe reasonably well, suggests that the dark matter particles should have a thermal history. WIMPs are characterized by masses and typical interaction strengths set by the physics at the electroweak scale. A pair annihilation cross-section naturally arises for WIMPs which can lead to a correct relic density (accounting for ∼25% of the total energy budget of the universe). In the standard scenario of cosmology, WIMPs couple to the thermal plasma of standard model particles with a typical coupling strength at the electroweak scale, attain thermal and chemical equilibrium, and eventually freeze out. Freeze-out might have occurred significantly after the end of reheating epoch, when the energy density of the universe was dominated by radiation. A velocity-averaged annihilation cross-section (<v>) of the order of is typically required to be consistent with the results from observations [19]. This value of <v> is expected to remain constant during the evolution of the universe and may be treated as a benchmark in the search for WIMPs as dark matter particles.
In general, WIMPs represent particles in the mass range from a few GeV to hundreds of TeV. Most exotic particle candidates for dark matter, like the neutralino, sneutrino, and gravitino from supersymmetry theory, the Kaluza–Klein particle from superstring theory, and other candidates from beyond the standard model and extra-dimensional theories, collectively form the WIMP family [17,20]. They are electrically neutral and interact with baryonic or normal matter particles mainly through the electroweak interaction coupling of the standard model in addition to the gravitational one in the dense regions of the universe [21,22]. WIMPs not only address the dark matter problem but are also a consequence of theoretical models proposed for the hierarchy problem [22,23]. Thus, they are appealing candidates for dark matter from the theoretical as well as the experimental point of view. Different types of experiments have been proposed and carried out for the direct or indirect detection of WIMPs [24]. Direct detection experiments rely on electronic or nuclear scatterings of WIMPs in targets like Xe, Na, Ar, O, Ge, W, etc., in the laboratory or the production of WIMPs in the colliders for high-energy physics research like the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Indirect searches for dark matter are based on astronomical efforts to detect standard model particles like neutrinos, electrons/positrons, protons/antiprotons, gamma rays, and others produced in WIMP interactions via annihilation or decay. Here, we concentrate on the most popular indirect search method for dark matter through the detection of high-energy gamma-ray photons produced during WIMP annihilation.
3. Gamma-Ray Signal from WIMPs
Under the reasonable assumption that WIMPs can decay or annihilate into standard model particles within the present age of the universe, it is possible to probe their presence and particle nature through the detection of different types of products of the above phenomena from astrophysical objects. This will greatly help in proposing a better hypothesis about the physical properties of dark matter particles. For kinematically possible interactions, WIMPs are expected to annihilate into all possible pairs of standard model particles like quarks, neutrinos, electrons, gamma rays, etc., with stable final states. Due to the possibility of detecting these standard model particles using astronomical instruments, gamma rays are the most interesting product among all. They can be produced in WIMP interactions via two pathways. The most obvious pathway for gamma ray production is the direct annihilation of WIMPs into gamma-ray photons. The energy of gamma-ray photons is proportional to the mass of WIMPs, and they can be observed as gamma-ray lines by telescopes. Alternatively, WIMPs can annihilate into quark–antiquark pairs, which hadronize and produce swarms of standard model particles including gamma-ray photons of different energies. The phenomena of quark–antiquark fragmentation is well known in high-energy physics. WIMP annihilation can be described as a 2 → 2 process ( SM + SM; SM indicates a standard model particle), and the energy spectrum of end products like gamma-ray photons or other standard model particles with stable final states is computed through decay, showers/jets, and hadronization. These processes are considered in Monte Carlo simulation tools like DarkSUSY [25], micrOMEGAs [26], DMFIT [27], PPPC4DMID [28] PYTHIA [29], MadDM [30], and HDMSpectra [31].
Gamma rays are generically the simplest among all possible final states of WIMP annihilation as they move straight from the production site to the detector and therefore can be used to easily locate the source in the universe. The differential energy spectrum of the gamma-ray photons yielded via WIMP annihilation (i.e., two WIMPs annihilate into a shower of standard model particles) is given by [32]
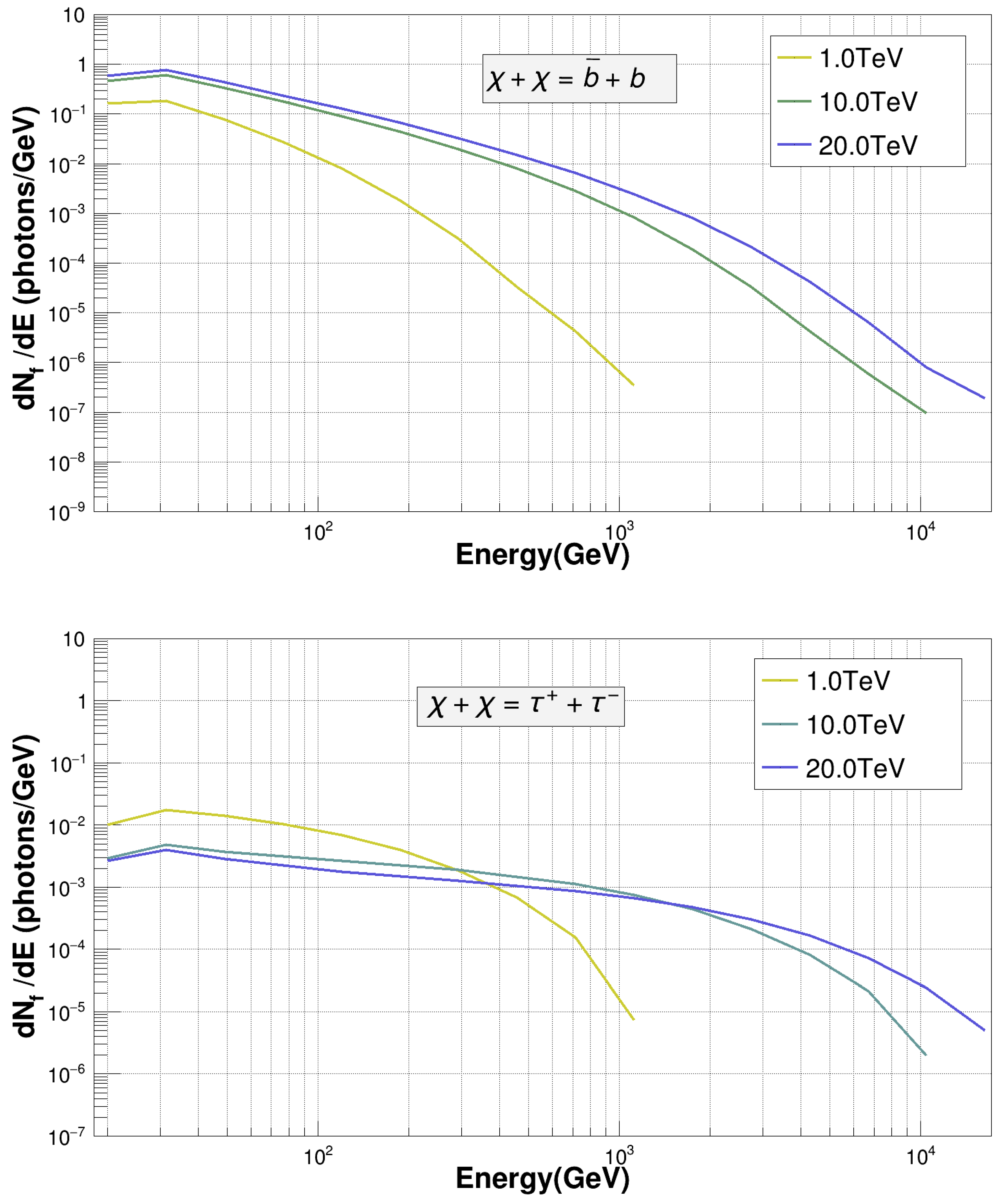
where <v> is the velocity-averaged annihilation cross-section, is the WIMP mass, and represents the gamma-ray spectra resulting from annihilation into the standard model particle of the type f with the branching ratio . The final spectrum is the weighted sum of various gamma-ray sub-spectra corresponding to different contributions specified by the fractional values of . The parameters and imply the particle types of WIMPs as Majorana (WIMPs are their own antiparticle) and Dirac (WIMPs have antiparticles like electrons–positrons), respectively. J is the Astrophysical Factor which takes into account the distribution of dark matter. A branching ratio of is assumed if WIMP annihilation into one particle species occurs with . For representation purposes, spectra for WIMP annihilation into and quarks with a 100% branching ratio for each channel are shown in Figure 1 corresponding to different values of . These spectra were computed using the PYTHIA simulation package [29]. It is evident from Figure 1 that the maximum energy of gamma rays produced in the WIMP annihilation for a given channel of a standard model particle can be same as the WIMP mass. The strength of the gamma-ray signal strongly depends on the value of the J-factor, which is defined as the integral of squared density of the dark matter/WIMP along the line of sight (los) over the solid angle and can be expressed as
where is the observing solid angle, is the dark matter density distribution parameterized as a function of the radial distance r from the center of an astrophysical source, and l is distance along the line of sight of the observer toward the source. For a spherically symmetric dark matter distribution, the solid angle reduces to an integral over the angular distance from the center of the source. For point-like sources, due to their large distances, the solid angle is the same as the angular resolution of the telescope. From the above discussions, it is evident that the expected gamma-ray signal from any astrophysical source due to WIMP annihilation can be easily characterized by a specific differential energy spectrum (, from particle physics) and a specific spatial shape (J or , from astrophysics). And, the overall strength of the gamma-ray signal is determined by the product of these two quantities in addition to <v> for a given WIMP mass. Thus, astrophysical sources with high dark matter density (i.e., large J-factor value) are the potential targets for searching for strong gamma-ray signals from WIMP annihilation using gamma-ray telescopes.
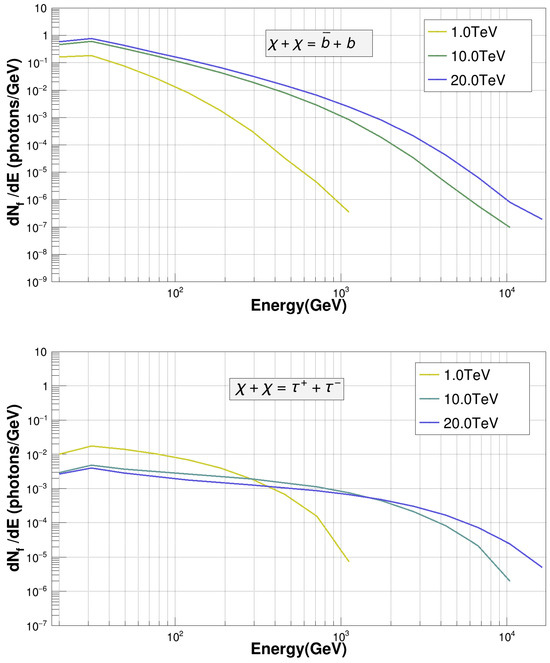
Figure 1.
Simulated gamma-ray spectra via WIMP annihilation into (upper) and (lower) quark species with 100% branching ratio for = 1 TeV, 10 TeV, and 20 TeV using PYTHIA 8.2 [29].
4. Opportunity for MACE
MACE (Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment) is the third-generation atmospheric Cherenkov telescope for ground-based, very-high-energy gamma-ray observations using imaging techniques. It has been operational at an altitude of ∼4.3 km above mean sea level in Hanle (32°46′46″ N, 78°58′35″ E) in the Ladakh region of India since 2021 [33,34]. Equipped with a quasi-parabolic reflector of a 21 m diameter and 25 m focal length, MACE belongs to class of state-of-the-art, extremely large imaging Cherenkov telescopes such as the prototype Large-Size Telescope (LST-1) for the upcoming Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) observatory ( https://www.ctao.org (5 February 2025)), the Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov (MAGIC) telescope (https://www.mpp.mpg.de/forschung/magic (5 February 2025)), and the High-Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S.-II) telescope ( https://www.mpi-hd.mpg.de/HESS/ (5 February 2025)) operating in the world. Located in the eastern region, MACE appropriately fills the important longitudinal gap among the major gamma-ray observatories and it can also be identified as the gamma-ray telescope operating at the highest level in its class across the globe at present. Over the short span of its operation, MACE has been able to produce significant scientific results by detecting very-high-energy signals from a number of astrophysical sources [35,36,37]. It is designed to probe the non-thermal universe in the energy range above ∼20 GeV with very high point-source flux sensitivity [38,39].
4.1. Expectations for MACE
The convolution of the instrument response function (e.g., effective area, point spread function) of MACE with a gamma-ray spectrum from a source for a given annihilation channel is used to estimate the number of observable events above the threshold energy of the telescope. This can be expressed as
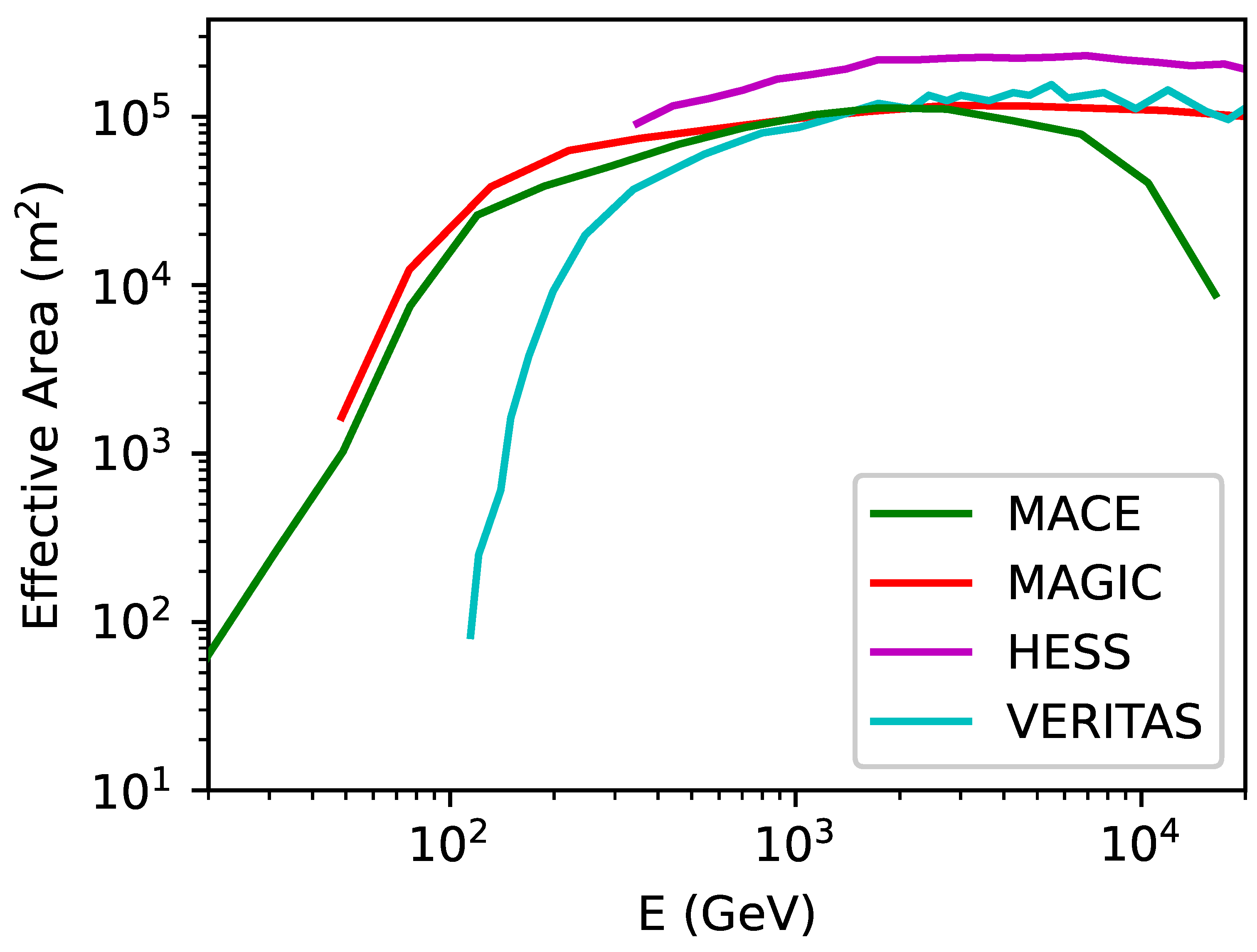
where is observation time of the source, and are the minimum and maximum energies of the gamma rays detected by the telescope, is the differential energy spectra of gamma rays corresponding to an assumed WIMP annihilation channel (given by Equation (1)), and (E) is the response function of the telescope which characterizes the effective area as a function of photon energy (E), the zenith angle of observation, and gamma-ray selection cuts. From the instrument response function, shown in Figure 2, it is evident that the MACE telescope has the capability of detecting high-energy gamma-rays with 20 GeV and above. Therefore, the potential of MACE can be exploited to probe the existence and properties of WIMPs in the GeV-TeV mass range.
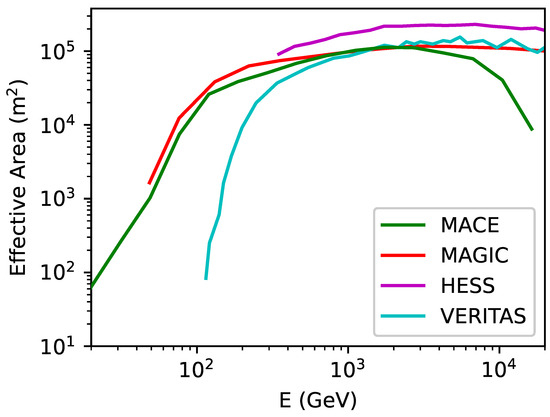
Figure 2.
The effective area () of MACE as a function of gamma-ray photon energy and its comparison with that of other telescopes. HESS and VERITAS (Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System) (https://veritas.sao.arizona.edu/ (20 April 2025)) are arrays of four 12m-diameter imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes for stereoscopic observations.
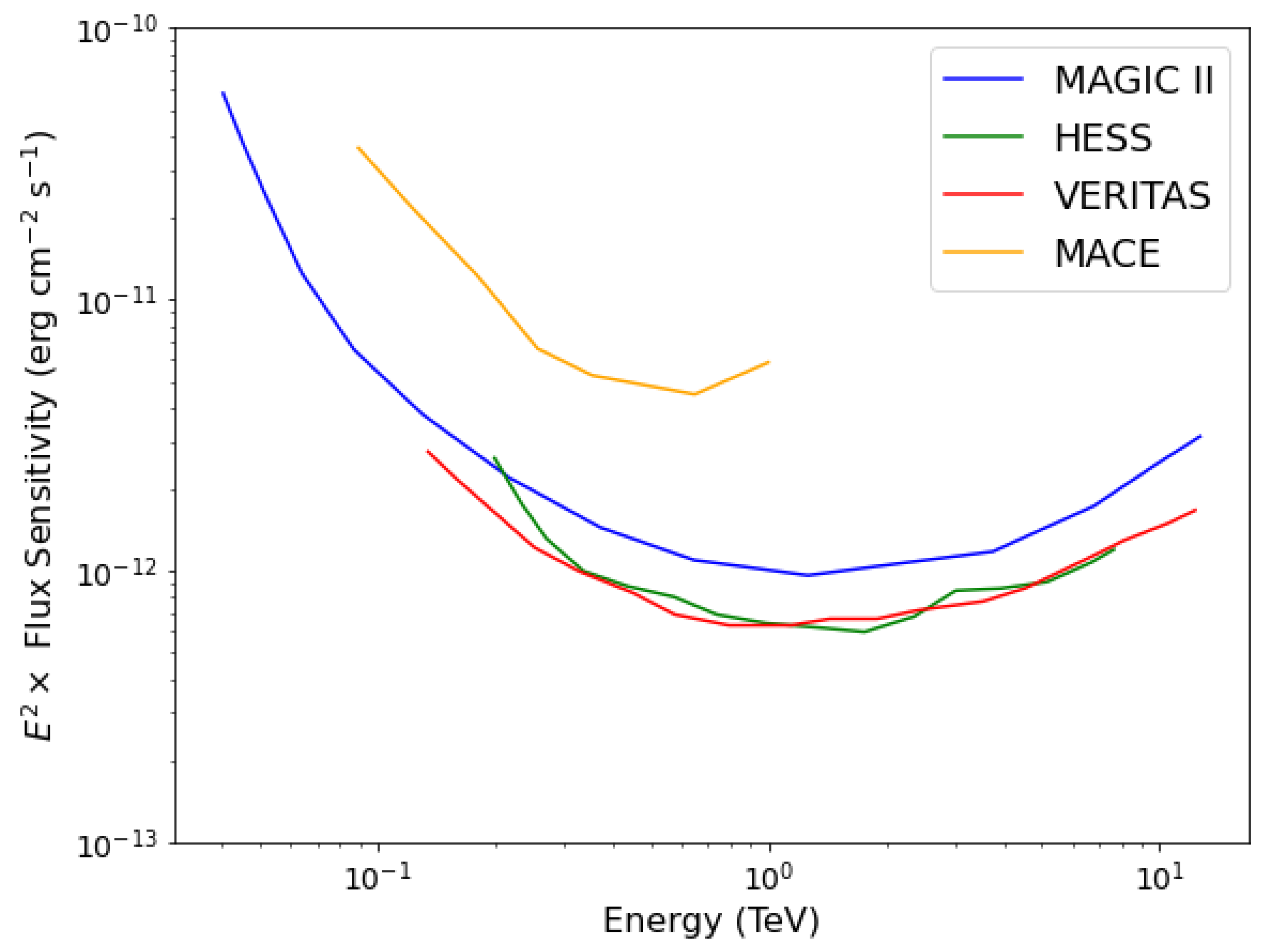
The contribution of the J-factor plays an important role in determining the expected strength of high-energy gamma-ray signals from an astrophysical source. Its value mainly depends on the dark matter density profile , the distance of the source, and the angular resolution of the telescope. For a given dark matter density profile, the J-factor is estimated within an angular region of a radius equal to the point spread function (PSF) or angular resolution (defined as the angular radius of the 68% containment of the reconstructed position of the reconstructed gamma-ray events) of the telescope using Equation (2). The imaging camera at the focal plane of the MACE telescope comprises 1088-photo multiplier tubes with a pixel resolution of 0.125 and provides an optical field of view of . This corresponds to a total solid angle of sr for MACE observations [40]. For point-like sources, the solid angle is same as the PSF of the telescope. The PSF of ground-based gamma-ray telescopes like MACE decreases from large values to small values as a function of increasing photon energy. For the MACE telescope, the PSF is for gamma-ray photons with 100 GeV of energy [35]. A comparison of the differential flux sensitivity of MACE with that of similar telescopes operating worldwide is shown in Figure 3. The better sensitivity of the MAGIC, H.E.S.S and VERITAS telescopes compared to that of MACE can be attributed to their stereoscopic observations of gamma-ray sources. However, the mono MACE system has potential to explore gamma-rays in space with a reasonably high sensitivity in the energy range from 200 GeV to ∼2 TeV. It is expected to improve further with the application of advanced machine learning techniques for signal extraction and the implementation of new tools in the data analysis chain for the MACE telescope [41].
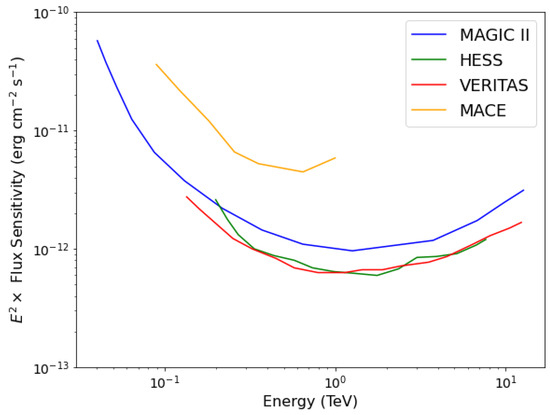
Figure 3.
The differential sensitivity of different observatories as a function of gamma-ray photon energy. The better flux sensitivity of other telescopes compared to that of the monoscopic MACE is due to their stereoscopic mode of observation.
In the case of null detection (statistical significance of gamma-ray signal is less than 5), upper limits on the integral flux of gamma rays above are derived at a given confidence level using information regarding the acceptance of the telescope, the mean zenith angle of observations, and signal selection cuts obtained from Monte Carlo simulations [35]. The upper-limit estimation is described in detail by Tolamatti et al. [37] for the MACE telescope. The value of the upper limit on integral flux, estimated using MACE observations, can be used to calculate the exclusion limits on <v> as a function of WIMP mass above 20 GeV for different final states of annihilation. As is custom in the indirect search of dark matter using high-energy gamma-ray observations, and <v> are considered free parameters by assuming single-channel annihilation spectra with (i.e., complete WIMP annihilation occurs in the specific channel each time) to derive the possible outcomes.
4.2. Plausible Targets
The strategy of selecting astronomical regions for the search for gamma-ray signals from WIMP interactions includes regions with a high density of dark matter, high mass-to-light ratios, and the minimum possibility of hosting astrophysical gamma-ray emitters (or the minimum possible contamination of background gamma-ray photons of astrophysical origin). This implies that quiescent galaxies without any ongoing star-formation activities are the most likely targets to probe the dark matter properties through high-energy gamma-ray observations using ground-based telescopes such as MACE. Also, the angular size of the target source or galaxy should be less than or equal to the PSF of the telescope so that the source can be considered point-like in the high-energy gamma-ray band. A detailed description pertaining to the source selection for observations with MACE can be found in [42]. A high mass-to-light ratio is also a key consideration for selecting astrophysical targets. A large content of baryonic matter in a given target can have major drawbacks as it reduces the expected gamma-ray flux from dark matter interactions.
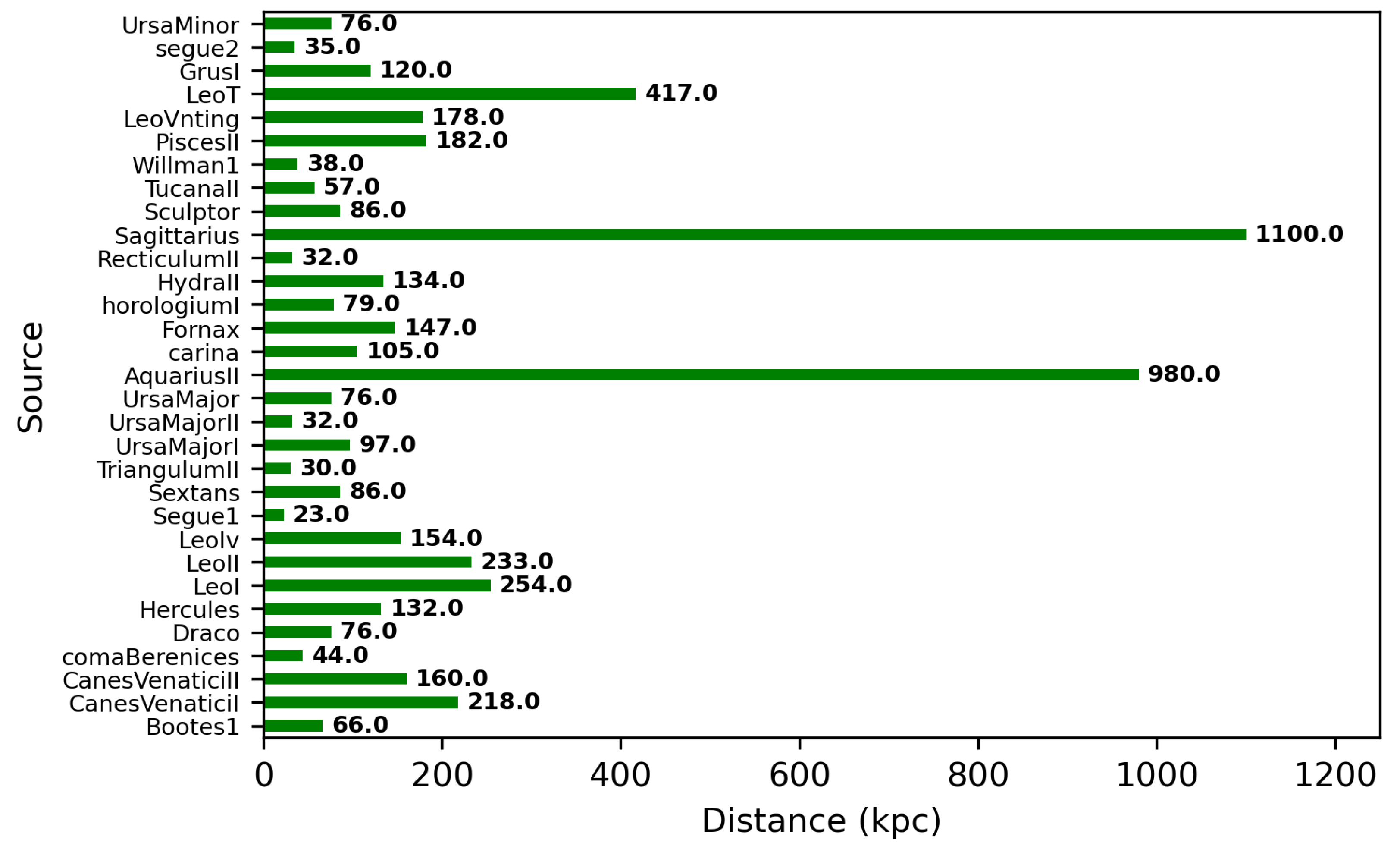
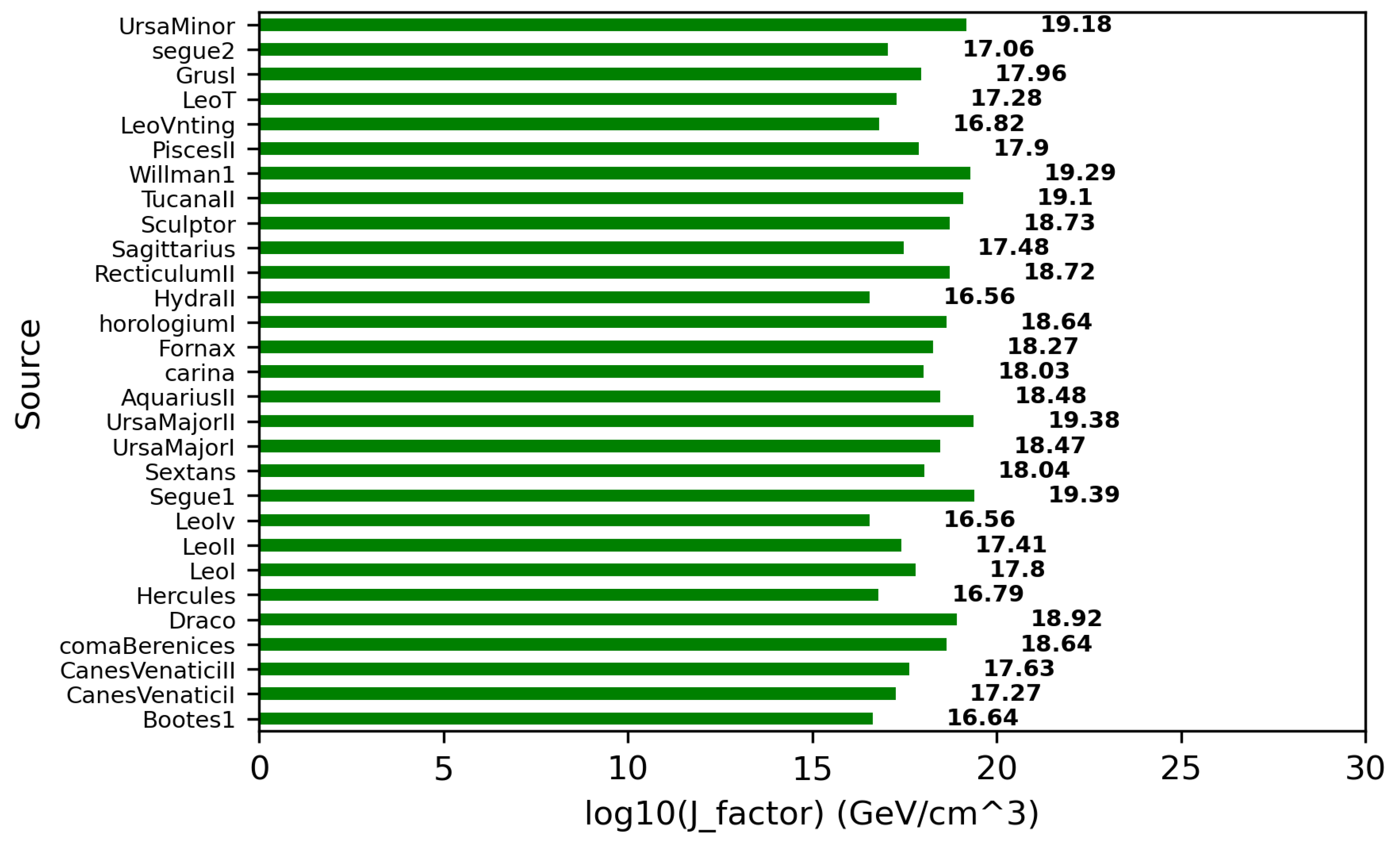
The prominent targets for the indirect search for WIMPs through gamma-ray observations are the Galactic Center [43], dwarf spheroidal galaxies [44], and galaxy clusters [45]. Among these targets, dwarf spheroidal galaxies are the most promising due to their large dark matter content, small spatial extension, very large dynamical mass-to-light ratio (up to 1000 times that of the Sun) and close proximity (distance < 100 kpc) to Earth. Being satellite galaxies of the Milky Way, dwarf spheroidal galaxies are observed to be dark matter-dominated (containing 1000 times more mass as dark matter than that as visible/baryonic matter) astrophysical systems without known a gas content or history of active star formation [46]. Thus, the absence of gas and stars in the dwarf spheroidal galaxies provides strong evidence of the negligible gamma-ray background produced by known astrophysical processes [47]. This also reduces the chances of diffuse gamma-ray background for searching for high-energy signals from WIMP interaction. The distance distribution of known dwarf spheroidal galaxies is presented in Figure 4. It is observed that most of the dwarf spheroidal galaxies are relatively near to Earth. Therefore, individual stars around them are easily resolved and their dark matter content can be better determined using stellar kinematic data. This is important for predicting the relative strength and spatial distribution of the gamma-ray signal expected from each dwarf spheroidal galaxy. Recent studies suggest that dwarf spheroidal galaxies exhibit a variety of dark matter densities, despite large uncertainties stemming from the dynamical modelling of their density profiles due to the unavailability of sufficient observational data [48,49]. The distribution of the J-factor, within the PSF of MACE, estimated using the popular Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) density profile in Equation (2), is shown in Figure 5. The NFW radial density profile (r) of dark matter in dwarf spheroidal galaxies is defined as [50]
where and are the scale density and scale radius, respectively. The values of and are determined using the kinematical data of the sources. The potential targets for observations with ground-based gamma-ray telescopes like MACE are mainly selected on the basis of a smaller distance from Earth and highest J-factor value. Due to their small angular size and distance at the kpc scale, most dwarf spheroidal galaxies appear as a near point source for gamma-ray telescopes with the point spread function .
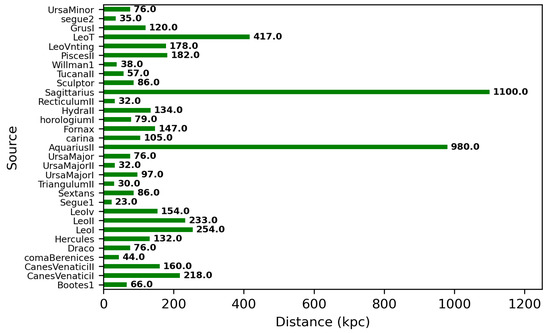
Figure 4.
Distance of the known dwarf spheroidal galaxies from Earth.
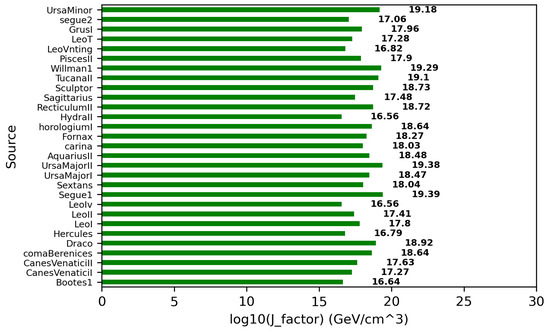
Figure 5.
Astrophysical J-factor of known dwarf spheroidal galaxies for NFW density profile of dark matter.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
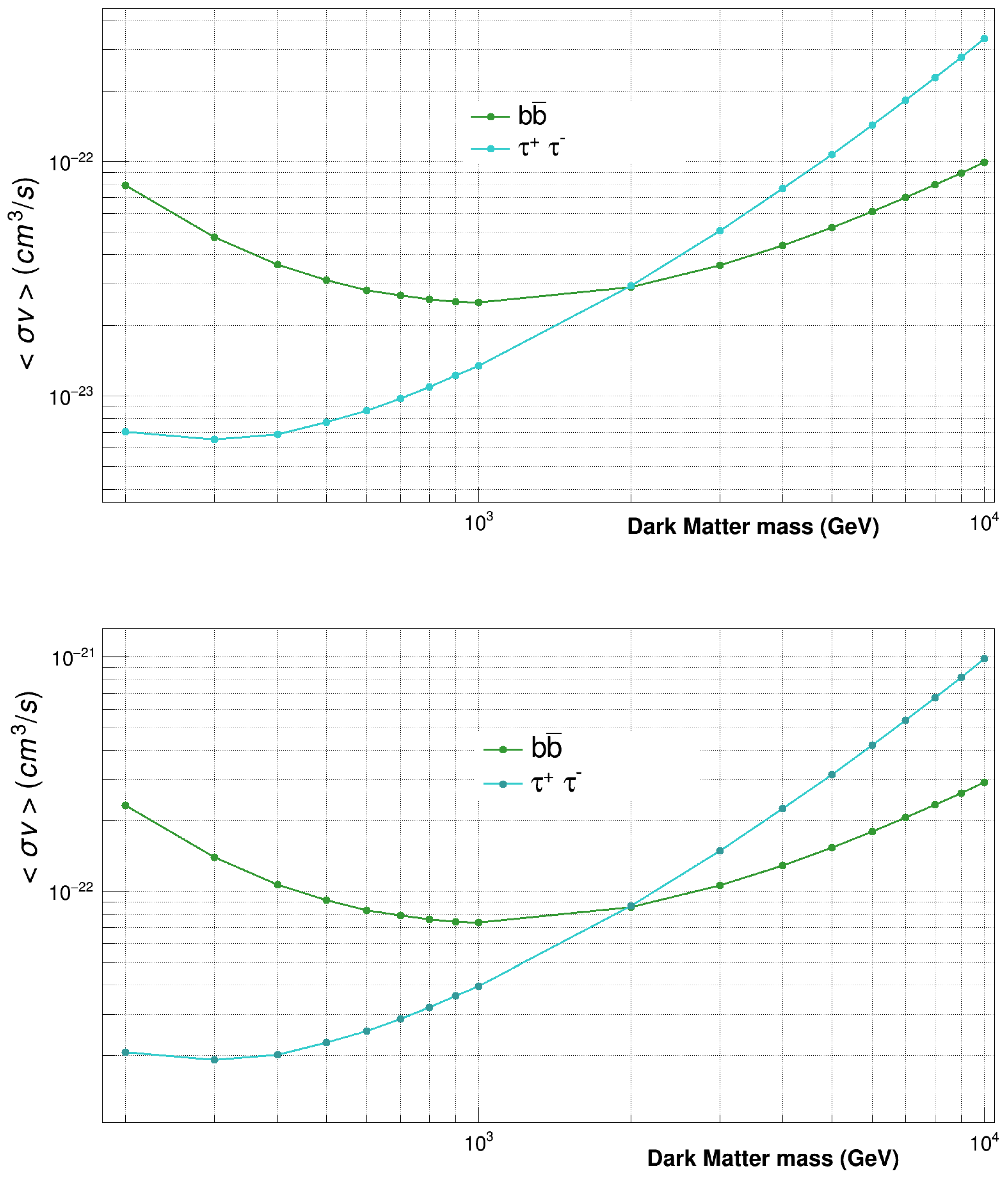
We selected two dwarf spheroidal galaxies, Segue 1 (distance ∼ 23 kpc; J-factor ) and Draco (distance ∼ 76 kpc; J-factor ), for searching for high-energy gamma-ray signals using the MACE telescope. From the visibility criteria of astronomical objects from a given ground-based observatory, Segue 1 and Draco can be monitored using MACE over the zenith angle range of 15°–70° and 25°–65°, respectively. Observations of these sources are ongoing, and stringent upper limits on the parameters of WIMPs in the mass range of 200 GeV to 10 TeV are expected to be derived with MACE data collected for more than 100 h from each source [51]. The upper limits on <v> at a 3 confidence level as a function of for WIMP annihilation into and quarks with a 100% branching ratio, expected from 100 h of MACE observations in the directions of Segue 1 and Draco, are presented in Figure 6. It is expected that dedicated MACE observations would be able to provide a 3 upper limit of the order of on <v> for WIMP annihilation of the mass 300 GeV into . A more stringent upper limit on <v> can be derived from longer observations of Segue 1 and Draco with MACE.
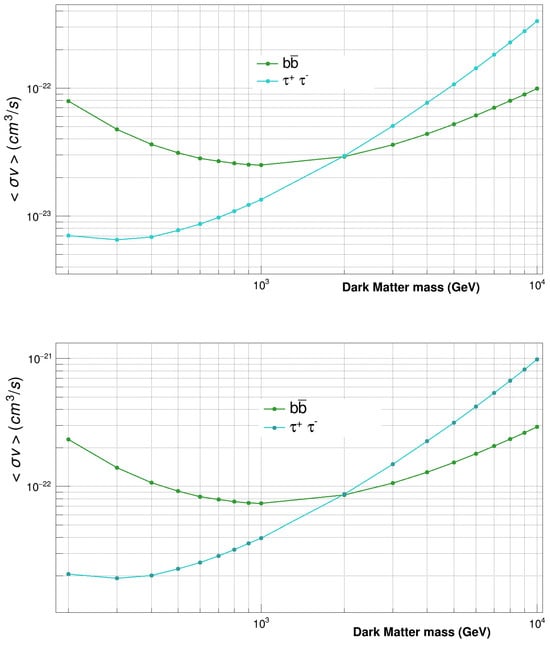
Figure 6.
MACE sensitivity for <v> as a function of WIMP mass expected from 100 h of observations of Segue 1 (up) and Draco (down). The sensitivity curves are derived for WIMP annihilation into and quarks with 100% branching.
For the first time, initial scientific data from the Fermi-LAT (Large-Area Telescope) recorded using a sample of eight dwarf spheroidal galaxies including Segue 1 and Draco during 2008–2010 were used to rule out models mostly with generic values of <v> up to 27 GeV and 37 GeV for the and channels, respectively [52]. Robust upper limits of and at a 95% confidence level at = 5 GeV and = 1 TeV, respectively, were placed on <v> for the channel without using any boosting for the J-factor value. A combined analysis of 6 years of data from the Fermi-LAT with a larger sample of 15 dwarf spheroidal galaxies including Segue 1 and Draco was used to derive the strongest constraints on <v> for 100 GeV annihilation via quark and -lepton channels [44]. A more recent study, using a larger dataset across 12 years from Fermi-LAT observations of 12 spheroidal galaxies including Segue 1, reported a very weak gamma-ray signal at a very low confidence level (less than 2) assuming WIMP annihilation into for = 14 GeV and 80 GeV [53]. The ground-based MAGIC telescope has also observed Segue 1 and Draco for ∼158 h and 52 h, respectively, during their multi-year observation program since 2011 in search for WIMPs, but no hint of high-energy gamma-ray signal has been detected [54]. Therefore, a stringent limit on the value of <v> of the order of at = 1 TeV has been derived. Another study, using a legacy dataset of 638 h of data collected on 17 dwarf spheroidal galaxies including about 127 h of data on Segue 1 with the VERITAS telescope, reported results from null detections for a broad dark matter particle mass range of 200 GeV to 30 PeV [55]. Observations of the Sculptor and Carina dwarf spheroidal galaxies with the H.E.S.S. telescope array, for a total of 11.8 h and 14.8 h, respectively, also provided upper limits on <v> in the range of to depending on the final state of dark matter annihilation [56]. The detection of no significant gamma signal from the monitoring of 16 dwarf spheroidal galaxies in 700 day of data at the Large High-Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) was also reported and the most stringent constraints on <v> for up to EeV were derived [57]. The above upper limits or constraints on <v>, derived from different observations of the dwarf spheroidal galaxies, are comparable to the results from a galactic halo with larger uncertainties [58]. Finally, we stress that the observational program of MACE with Segue 1 and Draco, after completing more than 100 h of monitoring of each source, will improve the exlusion limits of <v> in the largely unexplored WIMP mass range of 200 GeV to 10 TeV. Further, MACE observations will be combined with the Fermi -LAT to improve the results over a wide energy range as the dynamic energy range covered by MACE sufficiently overlaps with that of the Fermi -LAT below 200 GeV.
Author Contributions
M.K.—conceptualization, data curation, software; K.K.S.—conceptualization, original draft preparation; A.P.—data curation, software; P.K.N.—software; K.K.Y.—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study can be shared on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the three anonymous reviewers for their important comments and suggestions. We also thank our colleague Chinmay Borwankar for discussions related to the instrumenet response function simulations of the MACE telescope.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bennett, C.L.; Halpern, M.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Kogut, A.; Limon, M.; Meyer, S.S.; Page, L.; Spergel, D.N.; Tucker, G.S.; et al. First-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Preliminary Maps and Basic Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2003, 148, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.B.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.H.; Mortonson, M.J.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Hirata, C.; Riess, A.G.; Rozo, E. Observational probes of cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rep. 2013, 530, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, T.M.; Aguena, M.; Alarcon, A.; Allam, S.; Alves, O.; Amon, A.; Andrade-Oliveira, F.; Annis, J.; Avila, S.; Bacon, D.; et al. Dark Energy Survey Year 3 results: Cosmological constraints from galaxy clustering and weak lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 023520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, V. Existence and nature of dark matter in the universe. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1987, 25, 425–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, A.H. Inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poincare, H. The Milky Way and the Theory of Gases. Pop. Astron. 1906, 14, 475–488. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicky, F. The Redshift of Extragalactic Nebulae. Helv. Phys. Acta 1933, 6, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicky, F. On the Masses of Nebulae and of Clusters of Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1937, 86, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.C. On the Disks of Spiral and S0 Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1970, 160, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogstad, D.H.; Shostak, G.S. Gross Properties of Five Scd Galaxies as Determined from 21-CENTIMETER Observations. Astrophys. J. 1972, 1756, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.S. Radio Observations of Neutral Hydrogen in Galaxies. In Galaxies and the Universe; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL USA, 1975; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Boveia, A.; Doglioni, C. Dark Matter Searches at Colliders. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2018, 68, 429–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, R.L.; Burkert, V.D.; Crede, V.; Klempt, E.; Thoma, U.; Tiator, L.; Agashe, K.; Aielli, G.; Allanach, B.C.; Amsler, C.; et al. Review of Particle Physics. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 083C01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungman, G.; Kamionkowski, M.; Griest, K. Supersymmetric dark matter. Phys. Rep. 1996, 267, 195–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harigaya, K.; Mukaida, K.; Yamada, M. Dark matter production during the thermalization era. J. High Energy Phys. 2019, 2019, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigman, G.; Dasgupta, B.; Beacom, J.F. Precise relic WIMP abundance and its impact on searches for dark matter annihilation. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 023506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, G.; Hooper, D.; Silk, J. Particle dark matter: Evidence, candidates and constraints. Phys. Rep. 2005, 405, 279–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griest, K.; Kamionkowski, M. Unitarity limits on the mass and radius of dark-matter particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowski, L.; Sessolo, E.M.; Trojanowski, S. WIMP dark matter candidates and searches—Current status and future prospects. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 066201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, Y.; Kuflik, E.; Murayama, H. Twin Higgs model with strongly interacting massive particle dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskins, J.M. A review of indirect searches for particle dark matter. Contp. Phys. 2016, 57, 496–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondolo, P.; Edsjö, J.; Ullio, P.; Bergström, L.; Schelke, M.; Baltz, E.A. DarkSUSY: Computing supersymmetric dark matter properties numerically. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2004, 0407, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, G.; Boudjema, F.; Pukhov, A.; Semenov, A. micrOMEGAs: Version 1.3. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 174, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesla, E.J.; Stefano, P. Fitting the Gamma-Ray Spectrum from Dark Matter with DMFIT: GLAST and the Galactic Center Region. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2008, 0811, 003. [Google Scholar]
- Cirelli, M.; Corcella, G.; Hektor, A.; Hütsi, G.; Kadastik, M.; Panci, P.; Raidal, M.; Sala, F.; Strumia, A. PPPC 4 DM ID: A Poor Particle Physicist Cookbook for Dark Matter Indirect Detection. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2011, 11032, 051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrand, T.; Ask, S.; Christiansen, J.R.; Corke, R.; Desai, N.; Ilten, P.; Mrenna, S.; Prestel, S.; Rasmussen, C.O.; Skands, P.Z. An Introduction to PYTHIA 8.2. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2015, 191, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, F.; Arina, C.; Backović, M.; Heisig, J.; Maltoni, F.; Mantani, L.; Mattelaer, O.; Mohlabeng, G. MadDM v.3.0: A comprehensive tool for dark matter studies. Phys. Dark Univ. 2019, 24, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.W.; Rodd, N.L.; Webber, B.R. Dark matter spectra from the electroweak to the Planck scale. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.W.; Ferrer, F.; Sarkar, S. A travel guide to the dark matter annihilation signal. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K. Gamma-ray astronomy with the imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes in India. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2022, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Chouhan, N.; Thubstan, R.; Norlha, S.; Hariharan, J.; Borwankar, C.; Chandra, P.; Dhar, V.K.; Mankuzhyil, N.; Godambe, S.; et al. Commissioning of the MACE gamma-ray telescope at Hanle, Ladakh, India. Curr. Sci. 2022, 123, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwankar, C.; Sharma, M.; Hariharan, J.; Venugopal, K.; Godambe, S.; Mankuzhyil, N.; Chandra, P.; Khurana, M.; Sarkar, D.; Dar, Z.A.; et al. Observations of the Crab Nebula with MACE (major atmospheric Cherenkov experiment). Astropart. Phys. 2024, 159, 102960. [Google Scholar]
- Godambe, S.; Mankuzhiyil, N.; Borwankar, C.; Ghosal, B.; Tolamatti, A.; Pal, M.; Chandra, P.; Khurana, M.; Pandey, P.; Dar, Z.A.; et al. Very High-energy Gamma-Ray Episodic Activity of Radio Galaxy NGC 1275 in 2022–2023 Measured with MACE. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 974, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolamatti, A.; Garg, A.; Pathania, A.; Singh, K.; Borwankar, C.; Khurana, M.; Chandra, P.; Shukla, A.; Godiyal, S.; Godambe, S.; et al. Search for very high energy gamma-ray emission from a sample of high redshift blazars with MACE. J. High Energy Phys. 2025, 45, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwankar, C.; Bhatt, N.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Rannot, R.; Tickoo, A.; Koul, R.; Thoudam, S. Simulation studies of MACE-I: Trigger rates and energy thresholds. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 84, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Yadav, K.K. 20 years of Indian gamma ray astronomy using imaging Cherenkov telescopes and road ahead. Universe 2021, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, M.; Singh, K.K.; Godiyal, S.; Yadav, K.K. Effects of the moonlight on the operating parameters of the MACE γ-ray telescope: A feasibility study. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2022, 43, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Chandra, P.; Singh, K.K.; Pathania, A.; Borwankar, C. PyMAP: Python-Based Data Analysis Package with a New Image Cleaning Method to Enhance the Sensitivity of MACE Telescope. Galaxies 2025, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolamatti, A.; Singh, K.K.; Yadav, K.K. Feasibility study of observing γ-ray emission from high redshift blazars using the MACE telescope. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2022, 43, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.; Milosavljević, M.; Verde, L.; Jimenez, R. Dark Matter Spikes and Annihilation Radiation from the Galactic Center. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 191301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Albert, A.; Anderson, B.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. Searching for Dark Matter Annihilation from Milky Way Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies with Six Years of Fermi Large Area Telescope Data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 231301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Conde, M.A.; Cannoni, M.; Zandanel, F.; Gómez, M.; Prada, F. Dark matter searches with Cherenkov telescopes: Nearby dwarf galaxies or local galaxy clusters? J. Cosmo. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 2011, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grcevich, J.; Putman, M.E. HI in Local Group Dwarf Galaxies and Stripping by the Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigari, L.E. Galactic Searches for Dark Matter. Phys. Rep. 2013, 531, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.I.; Walker, M.G.; Steger, P. Dark matter heats up in dwarf galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 1401–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Chiba, M.; Ishiyama, T. Diversity of Dark Matter Density Profiles in the Galactic Dwarf Spheroidal Satellites. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A Universal Density Profile from Hierarchical Clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, M.; Pathania, A.; Singh, K.K.; Borwankar, C.; Netrakanti, P.K.; Yadav, K.K. Prospects of detecting gamma-ray signal of dark matter interaction with the MACE telescope. Proc. Sci. 2023, ICRC2023, 1412. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. Constraining Dark Matter Models from a Combined Analysis of Milky Way Satellites with the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 241302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liang, Y.-F.; Fan, Y.-Z. Search for gamma-ray emission from the 12 nearby dwarf spheroidal galaxies with 12 years of Fermi-LAT data. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 083037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciari, V.A.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.; Engels, A.A.; Artero, M.; Asano, K.; Baack, D.; Babić, A.; Baquero, A.; de Almeida, U.B.; et al. Combined searches for dark matter in dwarf spheroidal galaxies observed with the MAGIC telescopes, including new data from Coma Berenices and Draco. Phys. Dark Universe 2022, 35, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, A.; Adams, C.B.; Bangale, P.; Bartkoske, J.T.; Batista, P.; Benbow, W.; Christiansen, J.L.; Chromey, A.J.; Duerr, A.; Errando, M.; et al. Indirect search for dark matter with a combined analysis of dwarf spheroidal galaxies from VERITAS. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 063034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowski, A.; Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Anton, G.; Barnacka, A.; de Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.; Becherini, Y.; Becker, J.; et al. H.E.S.S. constraints on dark matter annihilations towards the sculptor and carina dwarf galaxies. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 34, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Aharonian, F.; An, Q.; Axikegu; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; Cai, J.T.; et al. Constraints on Ultraheavy Dark Matter Properties from Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies with LHAASO Observations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 061001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Blandford, R.D.; Bloom, E.D.; et al. Constraints on the Galactic Halo Dark Matter from Fermi-LAT Diffuse Measurements. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).