Planetary Nebulae Research: Past, Present, and Future
Abstract
1. Introduction
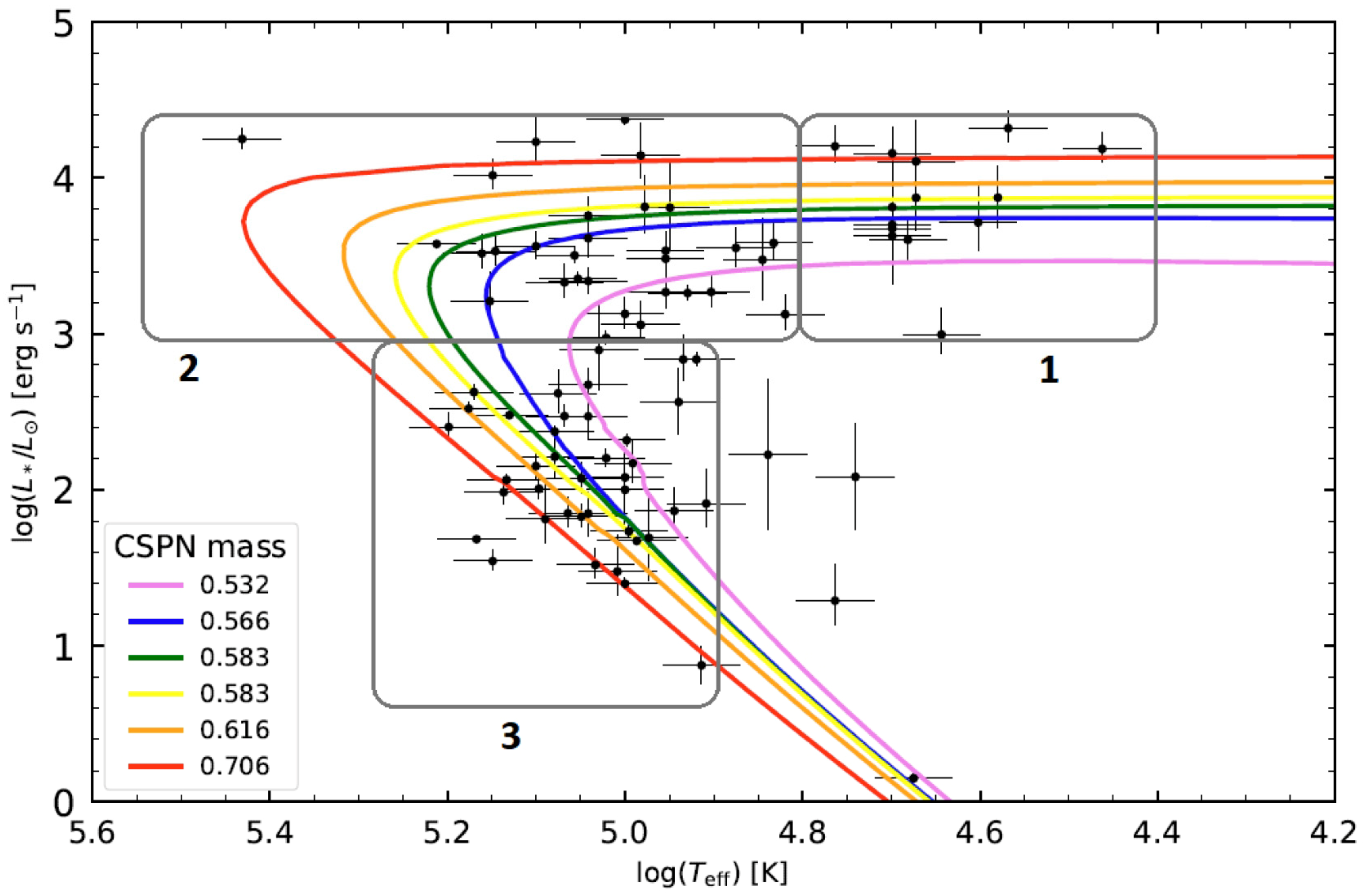
2. PN as a Phase of Stellar Evolution
3. Formation of the Nebula
3.1. Ejection of the Hydrogen Envelope
3.2. The Interacting Winds Theory
4. Missing Link between AGB and PN
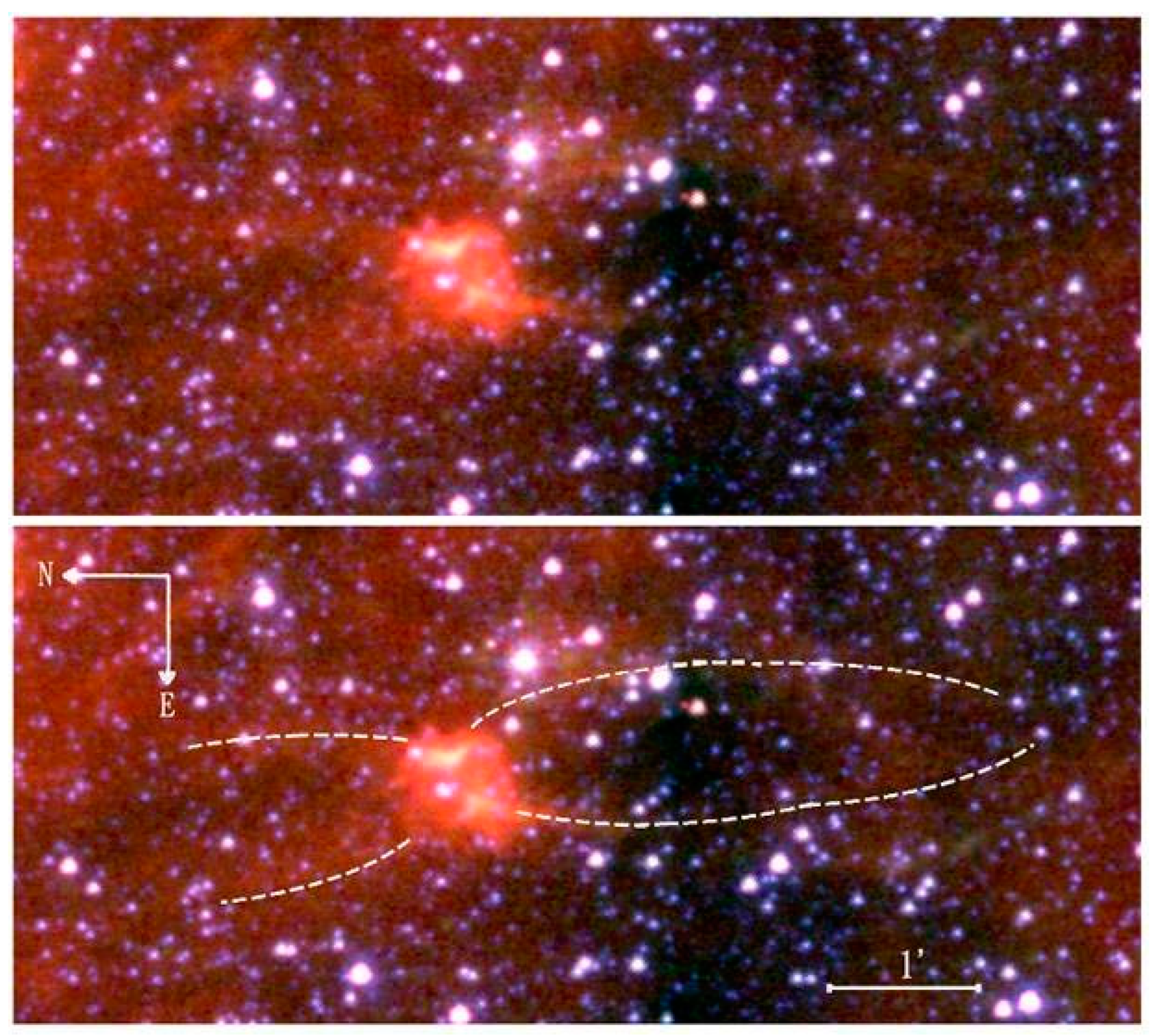
5. Binary Evolution
6. Observational and Evolutionary Definition of PN
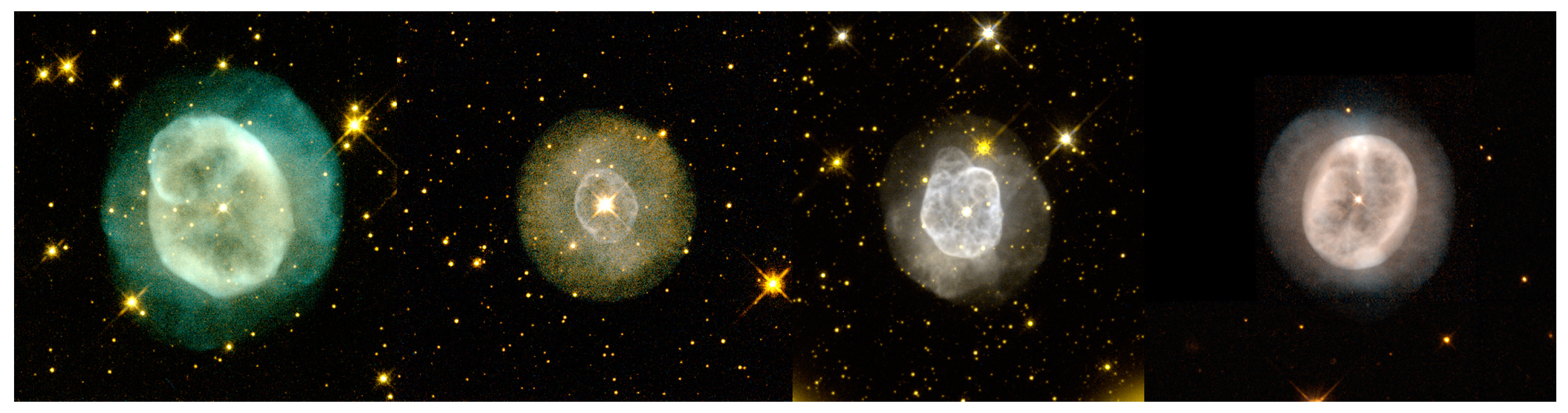
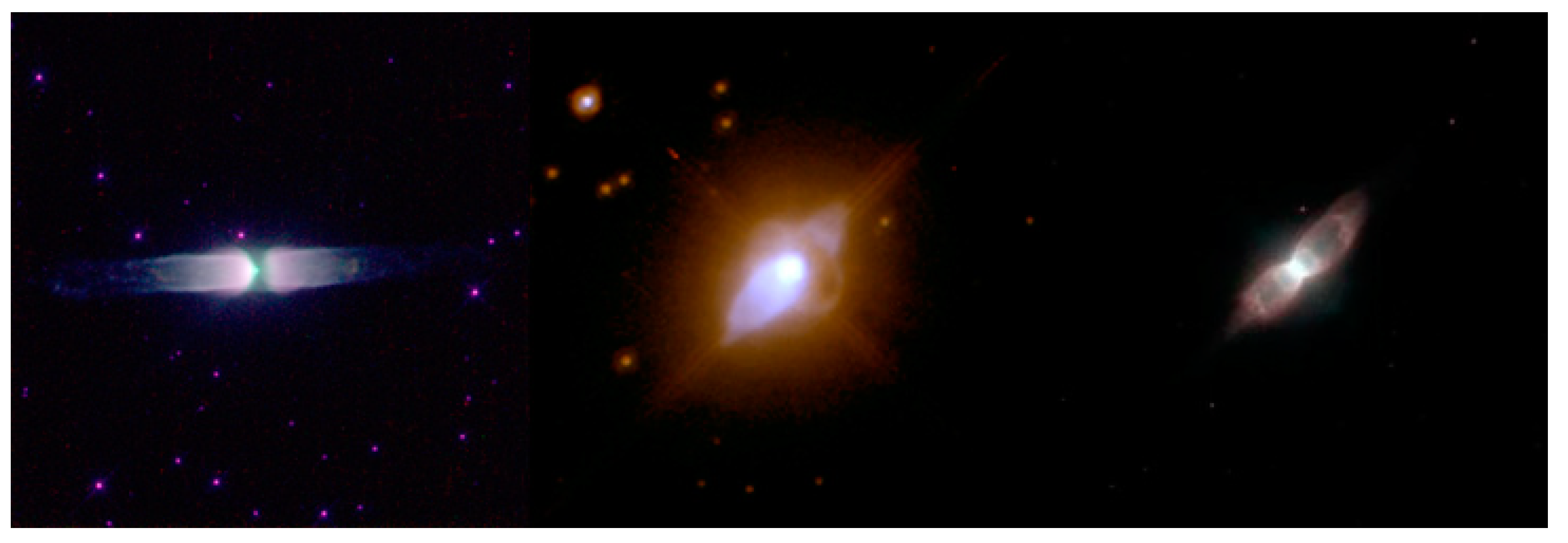
7. Morphological Classifications
- Images are sensitivity dependent, and a deeper image may reveal previously unseen faint features of different shapes;
- Images taken with narrow-band filters may show different structures, as ionic species are distributed differently based on the ionization structure of the nebulae;
- PNe are 3D objects and their apparent 2D morphology on the sky is dependent on the viewing angle;
- The morphological classification may change when the nebulae are observed with a larger field of view;
- Classifications are based on optical images and may not represent the distribution of the neutral (molecules and dust) component. The optical light distribution may not present an accurate picture of the actual matter distribution in the nebulae. Where we see light, does not mean that is where most of the matter is.

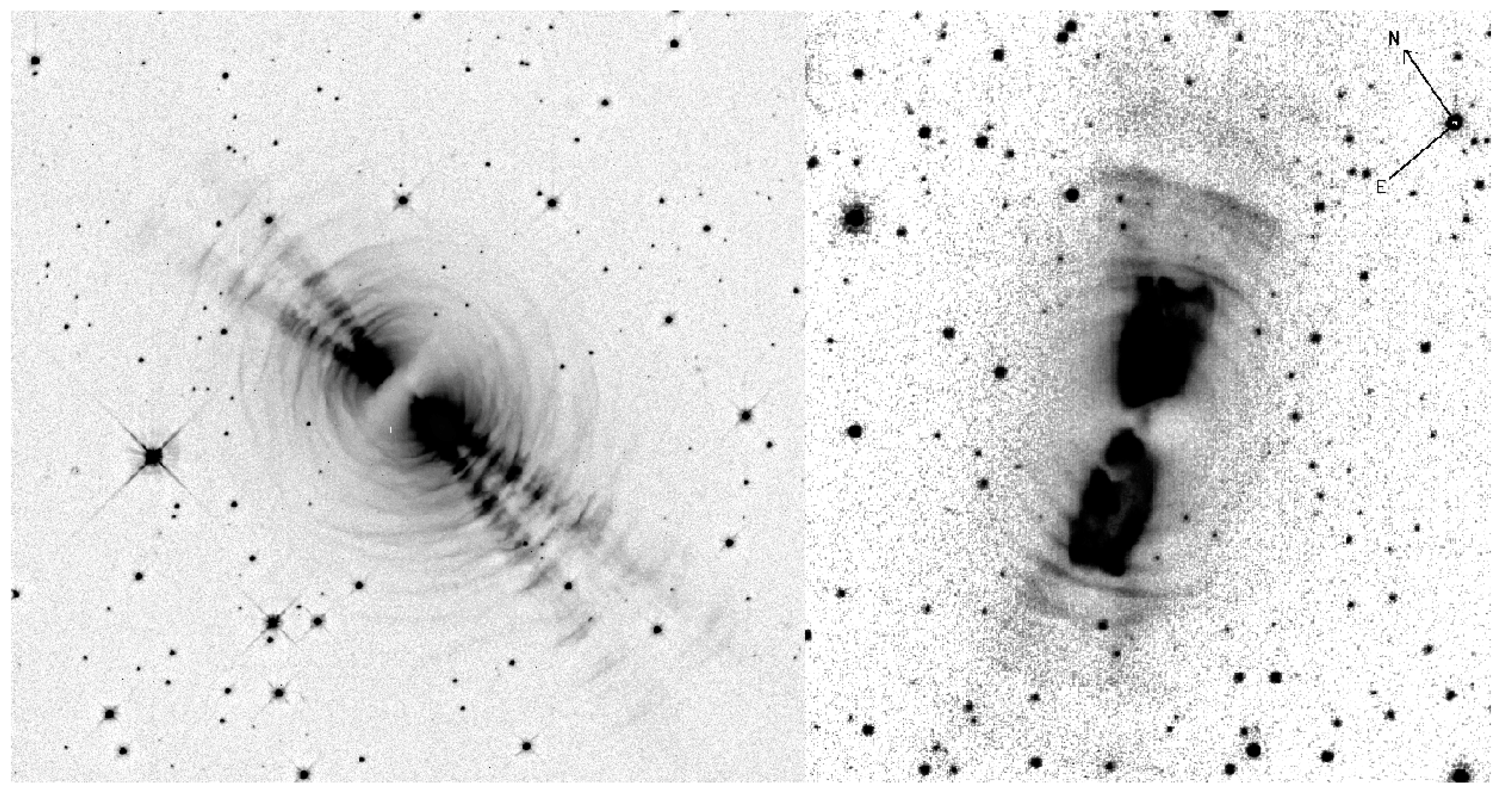
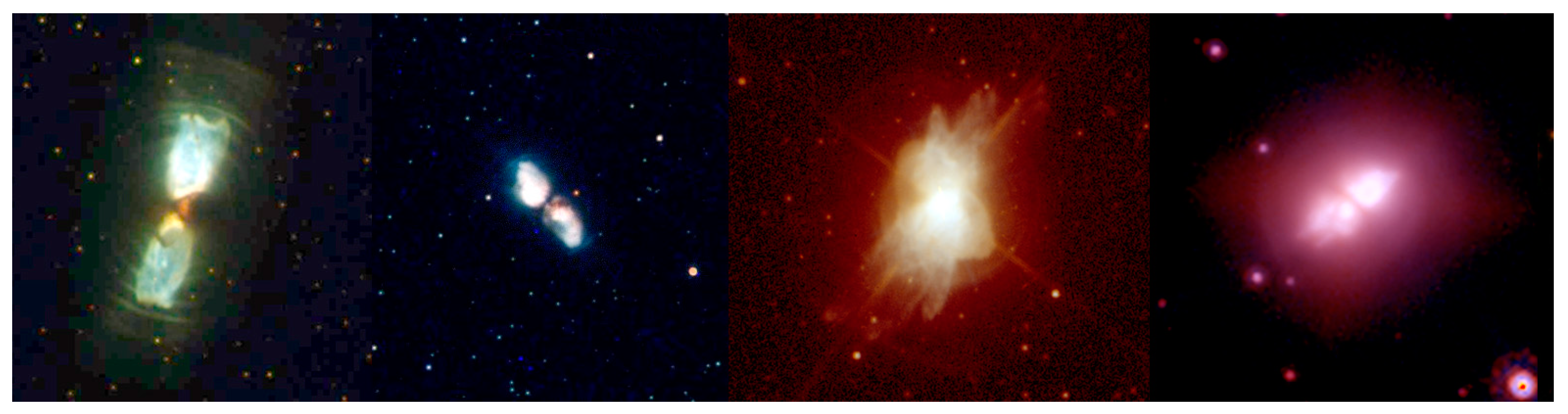
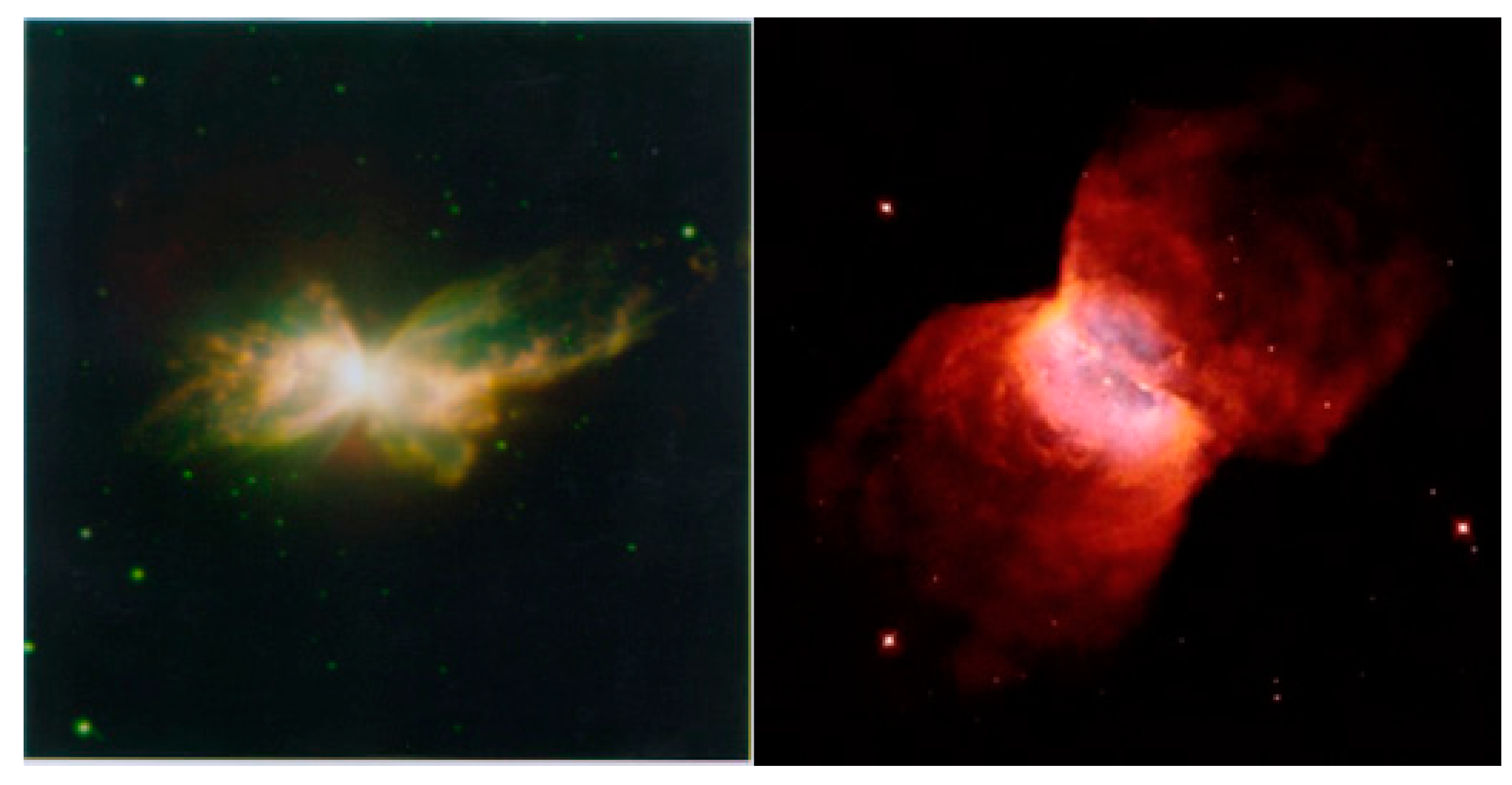
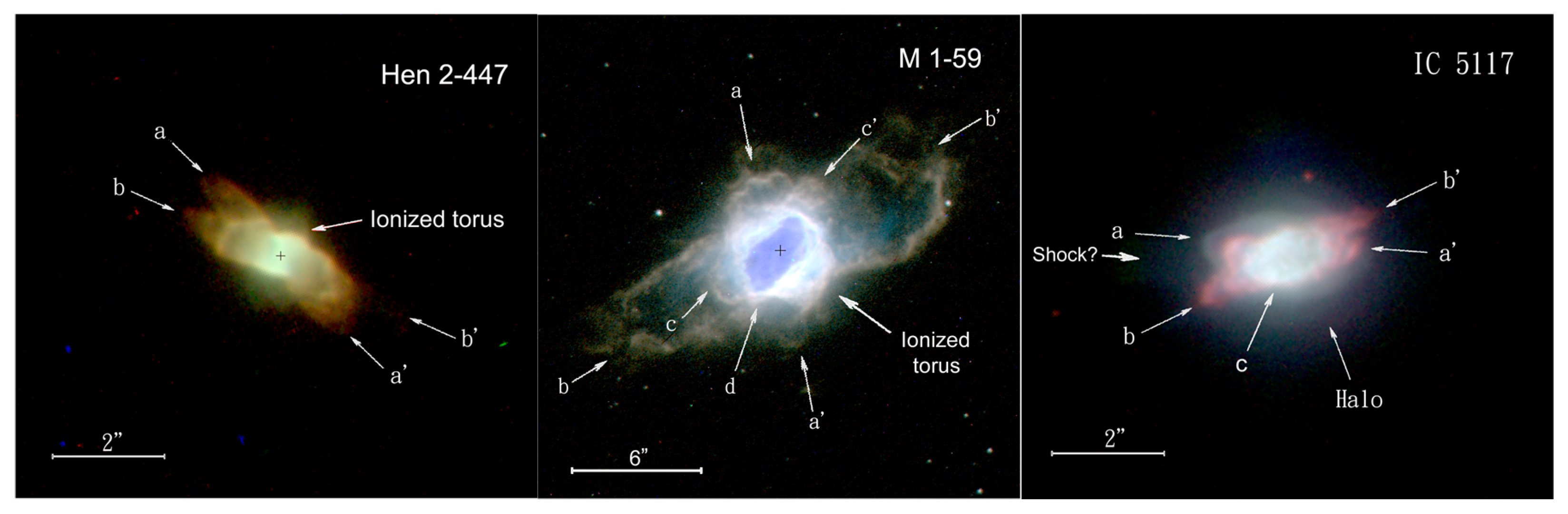
8. Multipolar Nebulae
9. The Role of Invisible Matter in Planetary Nebulae
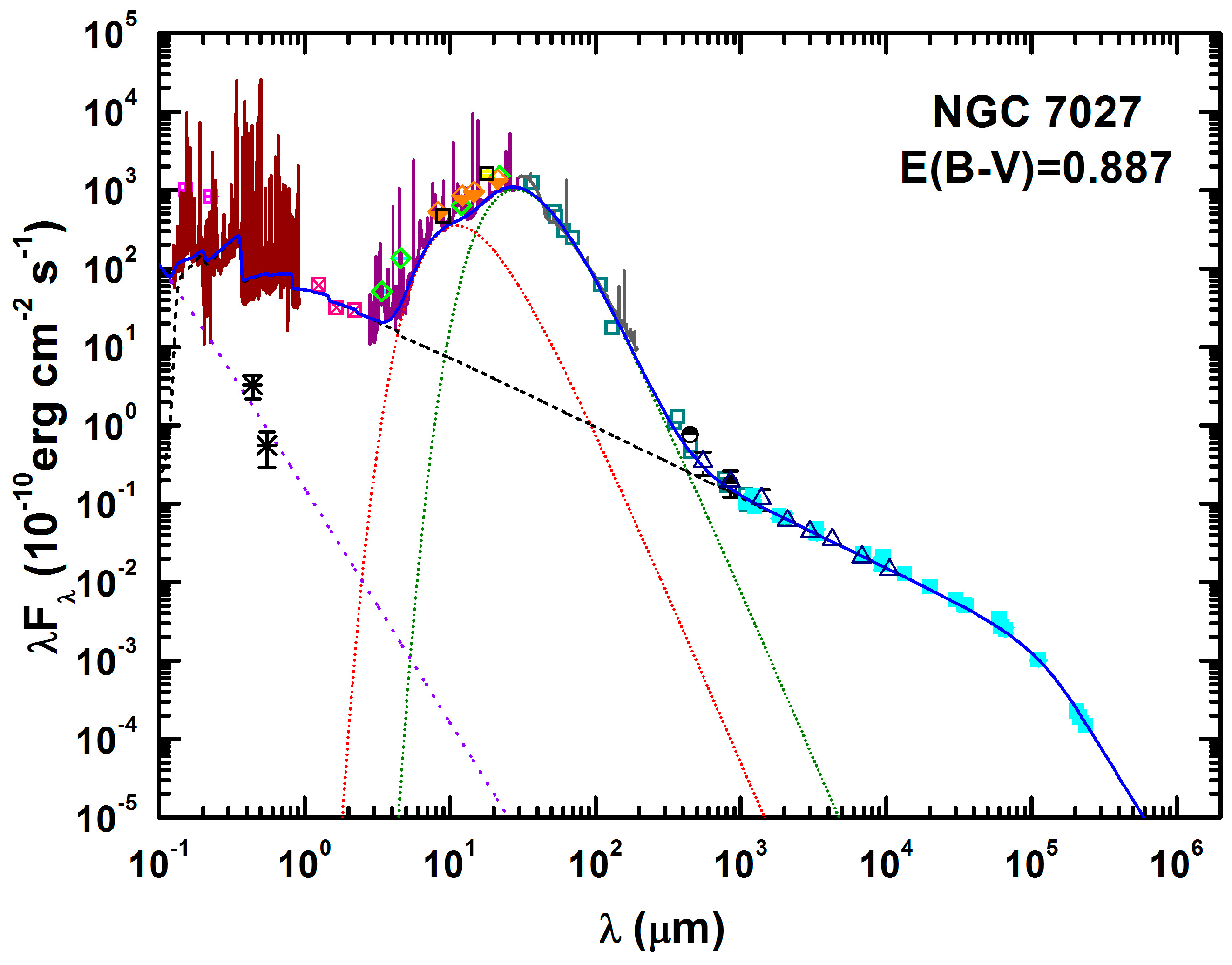
10. Recent Progress and Still Unsolved Problems in PN Research
11. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubble, E.P. The source of luminosity in galactic nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1922, 56, 400–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, D.H. The Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1926, 38, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanstra, H. An Application of the Quantum Theory to the Luminosity of Diffuse Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1927, 65, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, I.S. The origin of the nebular lines and the structure of the planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1928, 67, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, G.O. Properties of Some Old Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1966, 144, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkowski, R. The Sub-System of Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1964, 76, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henize, K.G. Observations of Southern Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1967, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perek, L.; Kohoutek, L. Catalogue of Galactic Planetary Nebulae; Academia: Praha, Czech Republic, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Acker, A.; Marcout, J.; Ochsenbein, F.; Stenholm, B.; Tylenda, R.; Schohn, C. The Strasbourg-ESO Catalogue of Galactic Planetary Nebulae. Parts I, II; ESO Publications: Garching, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, Q.A. Planetary nebulae and how to find them: A concise review. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 895287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, L.H. Gaseous Nebulae; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, H.D. The Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Lick Obs. 1918, 13, 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shklovsky, I.S. The nature of planetary nebulae and their nuclei. Astron. Zh. 1956, 33, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Abell, G.O.; Goldreich, P. On the Origin of Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1966, 78, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shklovskii, I.S. Once More on the Distances to Planetary Nebulae and the Evolution of Their Nuclei. Astron. Zh. 1957, 34, 403. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dell, C.R. The Evolution of the Central Stars of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1963, 138, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, R.F.; Seaton, M.J. The ionization structure of planetary nebulae, IV. Optical thickness of the nebulae and temperatures of the central stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1966, 132, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seaton, M.J. The ionization structure of planetary nebulae. V. Radii, luminosities and problems of evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1966, 132, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxburgh, I.W. Origin of Planetary Nebulae. Nature 1967, 215, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planetary Nebulae. Nature 1967, 215, 1438–1439. [CrossRef]
- Salpeter, E.E. Evolution of Central Stars of Planetary Nebulae Theory. In IAU Symposium 34: Planetary Nebulae; Kluwer: Dordrechet, The Netherlands, 1968; pp. 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Deinzer, W.; Hansen, C. On the Evolution of the Central Stars of Planetary Nebulae. Astron. J. Suppl. 1968, 73, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Kutter, G.S.; Savedoff, M.P.; Schuerman, D.W. A Mechanism for the Production of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1969, 3, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, G. Theory of evolution of the central star. In IAU Symposium 76: Planetary Nebulae; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S. On the distance of planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1985, 290, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczyński, B. Evolution of Single Stars. VI. Model Nuclei of Planetary Nebulae. Acta Astron. 1971, 21, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberner, D. Asymptotic giant branch evolution with steady mass loss. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 79, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberner, D. Late stages of stellar evolution: Central stars of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 103, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kovetz, A.; Harpaz, A. The central star of a planetary nebula. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 95, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Iben, I., Jr. On the frequency of planetary nebula nuclei powered by helium burningand on the frequency of white dwarfs with hydrogen-deficient atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 1984, 277, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.R.; Faulkner, D.J. Hydrostatic Evolutionary Sequences for the Nuclei of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1986, 307, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller Bertolami, M.M. New models for the evolution of post-asymptotic giant branch stars and central stars of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasińska, G.; Gorny, S.K.; Tylenda, R. On the mass distribution of planetary nebulae central stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 327, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann, W.A.; Mari, M.B.; Schmidt, E.O.; Gaspar, G.; Miller Bertolami, M.M.; Oio, G.A.; Gutiérrez-Soto, L.A.; Volpe, M.G.; Gamen, R.; Mast, D. Catalogue of the central stars of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 640, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L.B. Formation of Planetary Nebulae. Astron. J. 1967, 72, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczyński, B.; Ziółkowski, J. On the Origin of Planetary Nebulae and Mira Variables. Acta Astron. 1968, 18, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Kutter, G.S.; Sparks, W.M. Studies of Hydrodynamic Events in Stellar Evolution. III. Ejection of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1974, 192, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.R. Models of Asymptotic-Giant Stars. Astrophys. J. 1974, 190, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchman, Y.; Sack, N.; Barkat, Z. Miras and planetary nebula formation. Astrophys. J. 1979, 234, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Rose, W.K. Relaxation Oscillations in the Envelopes of Luminous Red Giants. Astrophys. J. 1972, 176, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.J. The Ejection of Planetary-Nebula Shells. Astrophys. J. 1970, 162, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, A.; Wolf, R.A. Ejection of Mass by Radiation Pressure in Planetary Nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1971, 11, 418. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, A.; Finzi, R.; Shaviv, G. The creation of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1974, 37, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Harm, R.; Schwarzschild, M. Transition from a Red Giant to a Blue Nucleus after Ejection of a Planetary Nebula. Astrophys. J. 1975, 200, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, V.; Sackmann, I.-J. Ejection of planetary nebulae by helium shell flashes and the planetary distance scale. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 182, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mathews, W.G. Model Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1966, 143, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.R. The structure and evolution of planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1973, 179, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferch, R.L.; Salpeter, E.E. Models of planetary nebulae with dust. Astrophys. J. 1975, 202, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzel, D.G. Dynamics of envelopes of planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1976, 204, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Purton, C.R.; Fitzgerald, P.M. On the origin of planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1978, 219, L125–L127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. From red giants to planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1982, 258, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. The Origin and Evolution of Planetary Nebulae; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, S.R.; Boggess, A.; Holm, A.; Klinglesmith, D.A.; Sparks, W.; West, D.; Wu, C.C.; Boksenberg, A.; Willis, A.; Wilson, R.; et al. IUE observations of hot stars—HZ43, BD +75 deg 325, NGC 6826, SS Cygni, Eta Carinae. Nature 1978, 275, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottasch, S.R.; Baud, B.; Beintema, D.; Emerson, J.; Habing, H.J.; Harris, S.; Houck, J.; Jennings, R.; Marsden, P. IRAS measurements of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 138, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Kwok, S. Spectral energy distribution of compact planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 250, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Jewitt, D.C.; Danielson, G.E.; Kupferman, P.N. Halos around planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1986, 302, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Jacoby, G.H.; Arendt, R. Multiple-shell planetary nebulae. I—Morphologies and frequency of occurrence. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1987, 64, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balick, B.; Gonzalez, G.; Frank, A.; Jacoby, G. Stellar Wind Paleontology. II. Faint Halos and Historical Mass Ejection in Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1992, 392, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, D.A.; Zhang, C.Y.; Kwok, S. Two-temperature X-ray emission from the planetary nebula NGC 7293. Astrophys. J. 1994, 422, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.M.; Chu, Y.-H. X-ray emission from Planetary Nebulae. In IAU Symposium 180: Planetary Nebulae; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 214–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, J.H.; Montez, R., Jr.; Balick, B.; Frew, D.J.; Miszalski, B.; Sahai, R.; Blackman, E.; Chu, Y.-H.; De Marco, O.; Frank, A.; et al. The Chandra X-ray Survey of Planetary Nebulae (ChanPlaNS): Probing Binarity, Magnetic Fields, and Wind Collisions. Astron. J. 2012, 144, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, K.; Kwok, S. Dynamical evolution of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 153, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Voigt, M.; Koeppen, J. Influence of stellar evolution on the evolution of planetary nebulae. I—Numerical method and hydrodynamical structures. II—Confrontation of models with observations. Astron. Astrophys. 1987, 174, 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- Marten, H.; Schoenberner, D. On the dynamical evolution of planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 248, 590–598. [Google Scholar]
- Perinotto, M.; Kifonidis, K.; Schonberner, D.; Marten, H. Hydrodynamical models of planetary nebulae and the problem of abundance determinations. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 332, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Marigo, P.; Girardi, L.; Groenewegen, M.A.T.; Weiss, A. Evolution of planetary nebulae—I. An improved synthetic model. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 378, 958–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, F.D.; West, K.A. Shapes of planetary nebulae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1985, 212, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balick, B. The evolution of planetary nebulae. I—Structures, ionizations, and morphological sequences. Astron. J. 1987, 94, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.; Mellema, G. A Radiation-Gasdynamical Method For Numerical Simulations Of Ionized Nebulae—Radiation-Gasdynamics Of PNE-I. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 289, 937–945. [Google Scholar]
- Mellema, G.; Frank, A. Radiation gasdynamics of planetary nebulae—V. Hot bubble and slow wind dynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 273, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellema, G. The formation of bipolar planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 321, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Cosmic Butterflies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, R.L.M.; Schönberner, D.; Steffen, M.; Perinotto, M. Ionized haloes in planetary nebulae: New discoveries, literature compilation and basic statistical properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 340, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frank, A.; Balick, B.; Riley, J. Stellar Wind Paleontology—Shells And Halos Of Planetary-Nebulae. Astron. J. 1990, 100, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öttl, S.; Kimeswenger, S.; Zijlstra, A.A. Ionization structure of multiple-shell planetary nebulae. I. NGC 2438. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 565, A87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.; Szczerba, R.; Schoenberner, D. Hydrodynamical models and synthetic spectra of circumstellar dust shells around AGB stars. II. Time-dependent simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 337, 149–177. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, R.L.M.; Schönberner, D.; Steffen, M.; Perinotto, M. A hydrodynamical study of multiple-shell planetaries. I. NGC 2438. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 354, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberner, D.; Jacob, R.; Lehmann, H.; Hildebrandt, G.; Steffen, M.; Zwanzig, A.; Sandin, C.; Corradi, R.L.M. A hydrodynamical study of multiple-shell planetary nebulae. III. Expansion properties and internal kinematics: Theory versus observation. Astron. Nachr. 2014, 335, 378–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, K.M.; Kwok, S. Evolution of Proto--planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. An infrared sequence in the late stages of stellar evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1990, 244, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hrivnak, B.J.; Kwok, S.; Volk, K.M. A study of several F and G supergiant-like stars with infrared excesses as candidates for proto-planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1989, 346, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Proto-planetary nebulae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Su, K.Y.L.; Hrivnak, B.J. Hubble Space Telescope V-Band Imaging of the Bipolar Proto-Planetary Nebula IRAS 17150-3224. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 501, L117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.Y.L.; Volk, K.; Kwok, S.; Hrivnak, B.J. Hubble Space Telescope Imaging of IRAS 17441-2411: A Case Study of a Bipolar Nebula with a Circumstellar Disk. Astrophys. J. 1998, 508, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hrivnak, B.J.; Kwok, S.; Su, K.Y.L. The Discovery of Two New Bipolar Proto-Planetary Nebulae: IRAS 16594-4656 and IRAS 17245-3951. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerba, R.; Siódmiak, N.; Stasińska, G.; Borkowski, J. An evolutionary catalogue of galactic post-AGB and related objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, T.; Meixner, M.; Bobrowsky, M. A Hubble Space Telescope Snapshot Survey of Proto-Planetary Nebula Candidates: Two Types of Axisymmetric Reflection Nebulosities. Astrophys. J. 2000, 528, 861–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, R.; Morris, M.; Sánchez Contreras, C.; Claussen, M. Preplanetary Nebulae: A Hubble Space Telescope Imaging Survey and a New Morphological Classification System. Astron. J. 2007, 134, 2200–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siódmiak, N.; Meixner, M.; Ueta, T.; Sugerman, B.E.K.; Van de Steene, G.C.; Szczerba, R. Hubble Space Telescope Snapshot Survey of Post-AGB Objects. Astrophys. J. 2008, 677, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.Y.L.; Hrivnak, B.J.; Kwok, S. High-Resolution Imaging of Proto-Planetary Nebulae: The Effects of Orientation. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Su, K.Y.L.; Stoesz, J.A. Circumstellar Arcs in AGB and Post-AGB Stars. In Proceedings of the Astrophysics and Space Science Library, Boston, MA, USA, 1 August 2001; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree, D.R.; Rogers, C. Circumstellar Envelopes Observed as Optical Haloes. In Proceedings of the European Southern Observatory Conference and Workshop Proceedings, La Serena, Chile, 1 January 1993; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Hrivnak, B.J.; Kwok, S.; Su, K.Y.L. The Discovery of Circumstellar Arcs around Two Bipolar Proto-planetary Nebulae. Astron. J. 2001, 121, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, R.; Trauger, J.T.; Watson, A.M.; Stapelfeldt, K.R.; Hester, J.J.; Burrows, C.J.; Ballister, G.E.; Clarke, J.T.; Crisp, D.; Evans, R.W.; et al. Imaging of the EGG Nebula (CRL 2688) with WFPC2/HST: A History of AGB/Post--AGB Giant Branch Mass Loss. Astrophys. J. 1998, 493, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Su, K.Y.L. Discovery of Multiple Coaxial Rings in the Quadrupolar Planetary Nebula NGC 6881. Astrophys. J. 2005, 635, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Hsia, C.H. Multiple Coaxial Rings in the Bipolar Nebula Hubble 12. Astrophys. J. 2007, 660, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koning, N.; Kwok, S.; Steffen, W. Morphology of the Red Rectangle Proto-planetary Nebula. Astrophys. J. 2011, 740, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.P. Binary Stars among Cataclysmic Variables. III. Ten Old Novae. Astrophys. J. 1964, 139, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, B. Cataclysmic Variable Stars; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Podsiadlowski, P. Binary Evolutionary Models. In IAU Symposium 252: The Art of Modeling Stars in the 21st Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Tutukov, A.V.; Yungelson, L.R. A Model for the Population of Binary Stars in the Galaxy. Astron. Rep. 2002, 46, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-W.; Ge, H.-W.; Chen, X.-F.; Chen, H.-L. Binary Population Synthesis. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.S., III; Code, A.D. Ultraviolet photometry from the Orbiting Astronomical Observatory. X. Nova FH Serpentis 1970. Astrophys. J. 1974, 189, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Common Envelope Binaries In IAU Symposium 73: Structure and Evolution of Close Binary Systems; Reidel: Dredrecht, The Netherlands, 1976; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Webbink, R.F. The Formation of White Dwarfs in Close Binary Systems. In IAU Colloq. 53: White Dwarfs and Variable Degenerate Stars; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1979; p. 426. [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel, E.P.J. Late Stages of Close Binary Systems. In IAU Symposium 73: Structure and Evolution of Close Binary Systems; Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1976; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Iben, I., Jr.; Tutukov, A.V. On the evolution of close binaries with components of initial mass between 3 solar masses and 12 solar masses. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1985, 58, 661–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iben, I., Jr.; Tutukov, A.V. Binary stars and planetary nebulae. In IAU Symposium 131: Planetary Nebulae; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 505–522. [Google Scholar]
- de Kool, M. Common Envelope Evolution and Double Cores of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1990, 358, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, H.E.; Livio, M. Morphologies of Planetary Nebulae Ejected by Close-Binary Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 1990, 355, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, O. The Origin and Shaping of Planetary Nebulae: Putting the Binary Hypothesis to the Test. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2009, 121, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Boffin, H.M.J. Binary stars as the key to understanding planetary nebulae. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 0117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutek, L. New and misclassified planetary nebulae. In IAU Symposium 131 Planetary Nebulae; Kluwe: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Frew, D.J.; Parker, Q.A. Planetary Nebulae: Observational Properties, Mimics and Diagnostics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2010, 27, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.A. A catalogue of symbiotic stars. Astron. Soc. Aust. Proc. 1984, 5, 369–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D. Allen, D. A Perspective on the Symbiotic Stars. In IAU Colloq. 103: The Symbiotic Phenomenon; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Feast, M.W.; Catchpole, R.M.; Whitelock, P.A.; Carter, B.S.; Roberts, G. The infrared variability and nature of symbiotic stars. V. Seven more systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1983, 203, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paczynski, B.; Rudak, B. Symbiotic Stars—Evolutionary Considerations. Astron. Astrophys. 1980, 82, 349–351. [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini, L.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Schwarz, H.E. The correlations between planetary nebula morphology and central star evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 279, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, Q.A.; Acker, A.; Frew, D.J.; Hartley, M.; Peyaud, A.E.J.; Ochsenbein, F.; Phillipps, S.; Russeil, D.; Beaulieu, S.F.; Cohen, M.; et al. The Macquarie/AAO/Strasbourg Hα Planetary Nebula Catalogue: MASH. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 373, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, M.; Balick, B.; Meaburn, J. Investigating the Haloes of Planetary Nebulae—Part Four—NGC6720 the Ring Nebula. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 266, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Chong, S.-N.; Koning, N.; Hua, T.; Yan, C.-H. The True Shapes of the Dumbbell and the Ring. Astrophys. J. 2008, 689, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; López, J.A.; Koning, N.; Kwok, S.; Riesgo, H.; Richer, M.G.; Morisset, C. The 3D structure of the Ring Nebula. In Proceedings of the Asymmetrical Planetary Nebulae IV, La Palma, Spain, 1 June 2007; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn, J.; Clayton, C.A.; Bryce, M.; Walsh, J.R.; Holloway, A.J.; Steffen, W. The nature of the cometary knots in the Helix planetary nebula (NGC7293). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 294, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaburn, J.; Boumis, P.; López, J.A.; Harman, D.J.; Bryce, M.; Redman, M.P.; Mavromatakis, F. The creation of the Helix planetary nebula (NGC 7293) by multiple events. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, H.; Schwarz, H.E.; Gruenwald, R.; Heathcote, S. Three-Dimensional Photoionization Structure and Distances of Planetary Nebulae. I. NGC 6369. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; López, J.A. Morpho-Kinematic Modeling of Gaseous Nebulae with SHAPE. Rev. Mexicana Astron. Astros. 2006, 42, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Larios, G.; Guerrero, M.A.; Vázquez, R.; Phillips, J.P. Optical and infrared imaging and spectroscopy of the multiple-shell planetary nebula NGC 6369. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W. 3-D structures of planetary nebulae. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 728, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hsia, C.-H.; Kwok, S. Planetary Nebulae Detected in the Spitzer Space Telescope GLIMPSE 3D Legacy Survey. Astrophys. J. 2012, 745, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hsia, C.-H.; Kwok, S. Discovery of a Halo around the Helix Nebula NGC 7293 in the WISE All-sky Survey. Astrophys. J. 2012, 755, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampaso, A.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Viironen, K.; Leisy, P.; Greimel, R.; Drew, J.E.; Barlow, M.J.; Frew, D.J.; Irwin, J.; Morris, R.A.H.; et al. The “Príncipes de Asturias” nebula: A new quadrupolar planetary nebula from the IPHAS survey. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 458, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. Planetary Nebulae Detected in the Spitzer Space Telescope GLIMPSE II Legacy Survey. Astrophys. J. 2009, 706, 252–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchado, A.; Stanghellini, L.; Guerrero, M.A. Quadrupolar Planetary Nebulae: A New Morphological Class. Astrophys. J. 1996, 466, L95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A.; Meaburn, J.; Bryce, M.; Holloway, A.J. The Morphology and Kinematics of the Complex Polypolar Planetary Nebula NGC 2440. Astrophys. J. 1998, 493, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, R. The Starfish Twins: Two Young Planetary Nebulae with Extreme Multipolar Morphology. Astrophys. J. 2000, 537, L43–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.-H.; Chau, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. Hubble Space Telescope Observations and Geometric Models of Compact Multipolar Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.A.; Vazquez, R.; Rodriguez, L.F. The Discovery of a Bipolar, Rotating, Episodic Jet (BRET) in the Planetary Nebula KjPn 8. Astrophys. J. 1995, 455, L63–L66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, R. Bipolar and Multipolar Jets in Protoplanetary and Planetary Nebulae. Rev. Mex. Astron. Y Astrofis. Conf. Ser. 2002, 13, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Khromov, G.S.; Kohoutek, L. Morphological Study of Planetary Nebulae. In IAU Symposium 34: Planetary Nebulae; Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1968; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Masson, C.R. On The Structure Of Ionization-Bounded Planetary-Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1990, 348, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Kwok, S. A Morphological Study of Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1998, 117, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.-N.; Kwok, S.; Imai, H.; Tafoya, D.; Chibueze, J. Multipolar Planetary Nebulae: Not as Geometrically Diversified as Thought. Astrophys. J. 2012, 760, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, K.; Kwok, S. A Self-consistent Photoionization-Dust Continuum-Molecular Line Transfer Model of NGC 7027. Astrophys. J. 1997, 477, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mufson, S.L.; Lyon, J.; Marionni, P.A. The detection of carbon monoxide emission in planetary nebulae. Astrophys. J. 1975, 201, L85–L89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santander-García, M.; Jones, D.; Alcolea, J.; Bujarrabal, V.; Wesson, R. Lessons from the Ionised and Molecular Mass of Post-CE PNe. Galaxies 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh-V-Trung; Bujarrabal, V.; Castro-Carrizo, A.; Lim, J.; Kwok, S. Massive Expanding Torus and Fast Outflow in Planetary Nebula NGC 6302. Astrophys. J. 2008, 673, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Y.; Hasegawa, T.I.; Kwok, S. The Detection of a Molecular Bipolar Flow in the Multipolar Planetary Nebula NGC 2440. Astrophys. J. 2008, 673, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santander-García, M.; Bujarrabal, V.; Alcolea, J.; Castro-Carrizo, A.; Sánchez Contreras, C.; Quintana-Lacaci, G.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Neri, R. ALMA high spatial resolution observations of the dense molecular region of NGC 6302. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga Baez, P.; Kastner, J.H.; Bublitz, J.; Alcolea, J.; Santander-Garcia, M.; Forveille, T.; Hily-Blant, P.; Balick, B.; Montez, R., Jr.; Gieser, C. ALMA Observations of Molecular Line Emission from High-excitation Bipolar Planetary Nebulae. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.08961. [Google Scholar]
- Andriantsaralaza, M.; Zijlstra, A.; Avison, A. CO in the C1 globule of the Helix nebula with ALMA. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, K.; Hrivnak, B.J.; Su, K.Y.L.; Kwok, S. An Infrared Imaging Study of the Bipolar Proto-Planetary Nebula IRAS 16594-4656. Astrophys. J. 2006, 651, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumariappan, C.; Kwok, S.; Volk, K. Subarcsecond Mid-Infrared Imaging of Dust in the Bipolar Nebula Hen 3-401. Astrophys. J. 2006, 640, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadec, E.; Verhoelst, T.; Mékarnia, D.; Suáeez, O.; Zijlstra, A.A.; Bendjoya, P.; Szczerba, R.; Chesneau, O.; van Winckel, H.; Barlow, M.J.; et al. A mid-infrared imaging catalogue of post-asymptotic giant branch stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 417, 32–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.Y.L.; Kelly, D.M.; Latter, W.B.; Misselt, K.A.; Frank, A.; Volk, K.; Engelbracht, C.W.; Gordon, K.D.; Hines, D.C.; Morrison, J.E.; et al. High spatial resolution mid- and far-infrared imaging study of NGC 2346. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2004, 154, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, T. Spitzer MIPS Imaging of NGC 650: Probing the History of Mass Loss on the Asymptotic Giant Branch. Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoof, P.A.M.; Van de Steene, G.C.; Exter, K.M.; Barlow, M.J.; Ueta, T.; Groenewegen, M.A.T.; Gear, W.K.; Gomez, H.L.; Hargrave, P.C.; Ivison, R.J.; et al. A Herschel study of NGC 650. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 560, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Steene, G.C.; van Hoof, P.A.M.; Exter, K.M.; Barlow, M.J.; Cernicharo, J.; Etxaluze, M.; Gear, W.K.; Goicoechea, J.R.; Gomez, H.L.; Groenewegen, M.A.T.; et al. Herschel imaging of the dust in the Helix nebula (NGC 7293). Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 574, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, T.; Torres, A.J.; Izumiura, H.; Yamamura, I.; Takita, S.; Tomasino, R.L. AKARI mission program: Excavating Mass Loss History in extended dust shells of Evolved Stars (MLHES). I. Far-IR photometry. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 71, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.W.; Sahai, R.; Davis, J.; Livingston, J.; Lykou, F.; DE Buizer, J.; Morris, M.R.; Keller, L.; Adams, J.; Gull, G.; et al. Mid-infrared Imaging of the Bipolar Planetary Nebula M2-9 from SOFIA. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, R.M.; Werner, M.; Sahai, R.; Ressler, M.E. Evidence from SOFIA Imaging of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Formation along a Recent Outflow in NGC 7027. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Physics and Chemistry of the Interstellar Medium; University Science Books: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S. Morphological Structures of Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2010, 27, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwok, S.; Hrivnak, B.J.; Su, K.Y.L. Discovery of a Disk-collimated Bipolar Outflow in the Proto-Planetary Nebula IRAS 17106-3046. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, L149–L152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujarrabal, V.; Alcolea, J.; Sahai, R.; Zamorano, J.; Zijlstra, A.A. The shock structure in the protoplanetary nebula M 1-92: Imaging of atomic and H-2 line emission. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 331, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Alcolea, J.; Neri, R.; Bujarrabal, V. Minkowski’s footprint revisited. Planetary nebula formation from a single sudden event? Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 468, L41–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Contreras, C.; Sahai, R.; Gil de Paz, A. Physical Structure of the Proto-Planetary Nebula CRL 618. I. Optical Long-Slit Spectroscopy and Imaging. Astrophys. J. 2002, 578, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bujarrabal, V.; Alcolea, J.; Soria-Ruiz, R.; Planesas, P.; Teyssier, D.; Marston, A.P.; Cernicharo, J.; Decin, L.; Dominik, C.; Justtanont, K.; et al. Herschel/HIFI observations of high-J CO transitions in the protoplanetary nebula CRL 618. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 521, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, N.; Kwok, S.; Steffen, W. Post Asymptotic Giant Branch Bipolar Reflection Nebulae: Result of Dynamical Ejection or Selective Illumination? Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, R.H.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Herrero, A. On central star luminosities and optical thicknesses in planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 260, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberner, D.; Balick, B.; Jacob, R. Expansion patterns and parallaxes for planetary nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimeswenger, S.; Barría, D. Planetary nebula distances in Gaia DR2. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santamaría, I.; Manteiga, M.; Manchado, A.; Ulla, A.; Dafonte, C. Gaia DR2 Distances to Planetary Nebulae. Galaxies 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemann, V. Mass loss towards the white dwarf stage. Astron. Astrophys. 1977, 59, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.D.; Kalirai, J.S.; Tremblay, P.-E.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Choi, J. The White Dwarf Initial-Final Mass Relation for Progenitor Stars from 0.85 to 7.5 M⊙. Astrophys. J. 2018, 866, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decin, L.; Montargès, M.; Richards, A.M.S.; Gottlieb, C.A.; Homan, W.; McDonald, I.; El Mellah, I.; Danilovich, T.; Wallström, S.H.J.; Zijlstra, A.; et al. (Sub)stellar companions shape the winds of evolved stars. Science 2020, 369, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. The synthesis of organic and inorganic compounds in evolved stars. Nature 2004, 430, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziurys, L.M. The chemistry in circumstellar envelopes of evolved stars: Following the origin of the elements to the origin of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12274–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicharo, J.; Agúndez, M.; Guélin, M.; Bachiller, R. Spectral Line Surveys of Evolved Stars. In IAU Symposium 280: The Molecular Universe; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S. Planetary Nebulae as Sources of Chemical Enrichment of the Galaxy. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 893061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. The mystery of unidentified infrared emission bands. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2022, 367, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilker, J.S.; Phadke, K.A.; Aravena, M.; Archipley, M.; Bayliss, M.B.; Birkin, J.E.; Béthermin, M.; Burgoyne, J.; Cathey, J.; Chapman, S.C.; et al. Spatial variations in aromatic hydrocarbon emission in a dust-rich galaxy. Nature 2023, 618, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartke, J.; Arnaboldi, M.; Longobardi, A.; Gerhard, O.; Freeman, K.C.; Okamura, S.; Nakata, F. The halo of M 49 and its environment as traced by planetary nebulae populations. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.H.; Branch, D.; Ciardullo, R.; Davies, R.L.; Harris, W.E.; Pierce, M.J.; Pritchet, C.J.; Tonry, J.L.; Welch, D.L. A Critical Review of Selected Techniques for Measuring Extragalactic Distances. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1992, 104, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meatheringham, S.J.; Dopita, M.A.; Ford, H.C.; Webster, B.L. The Kinematics of the Planetary Nebulae in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys. J. 1988, 327, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccato, L. Planetary nebulae as kinematic tracers of galaxy stellar halos. In IAU Symposium 323: Planetary Nebulae: Multi-Wavelength Probes of Stellar and Galactic Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S. Delivery of Complex Organic Compounds from Evolved Stars to the Solar System. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2011, 41, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwok, S. Planetary Nebulae Research: Past, Present, and Future. Galaxies 2024, 12, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12040039
Kwok S. Planetary Nebulae Research: Past, Present, and Future. Galaxies. 2024; 12(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwok, Sun. 2024. "Planetary Nebulae Research: Past, Present, and Future" Galaxies 12, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12040039
APA StyleKwok, S. (2024). Planetary Nebulae Research: Past, Present, and Future. Galaxies, 12(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12040039






