Ultra-High-Energy Particles at the Border of Kerr Black Holes Triggered by Magnetocentrifugal Winds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Kerr Black Holes as Particle Accelerators?
3. The Accretion Mechanism
3.1. Accretion Fluid Dynamics
3.2. Mass Accretion Rate and Radiative Phenomena
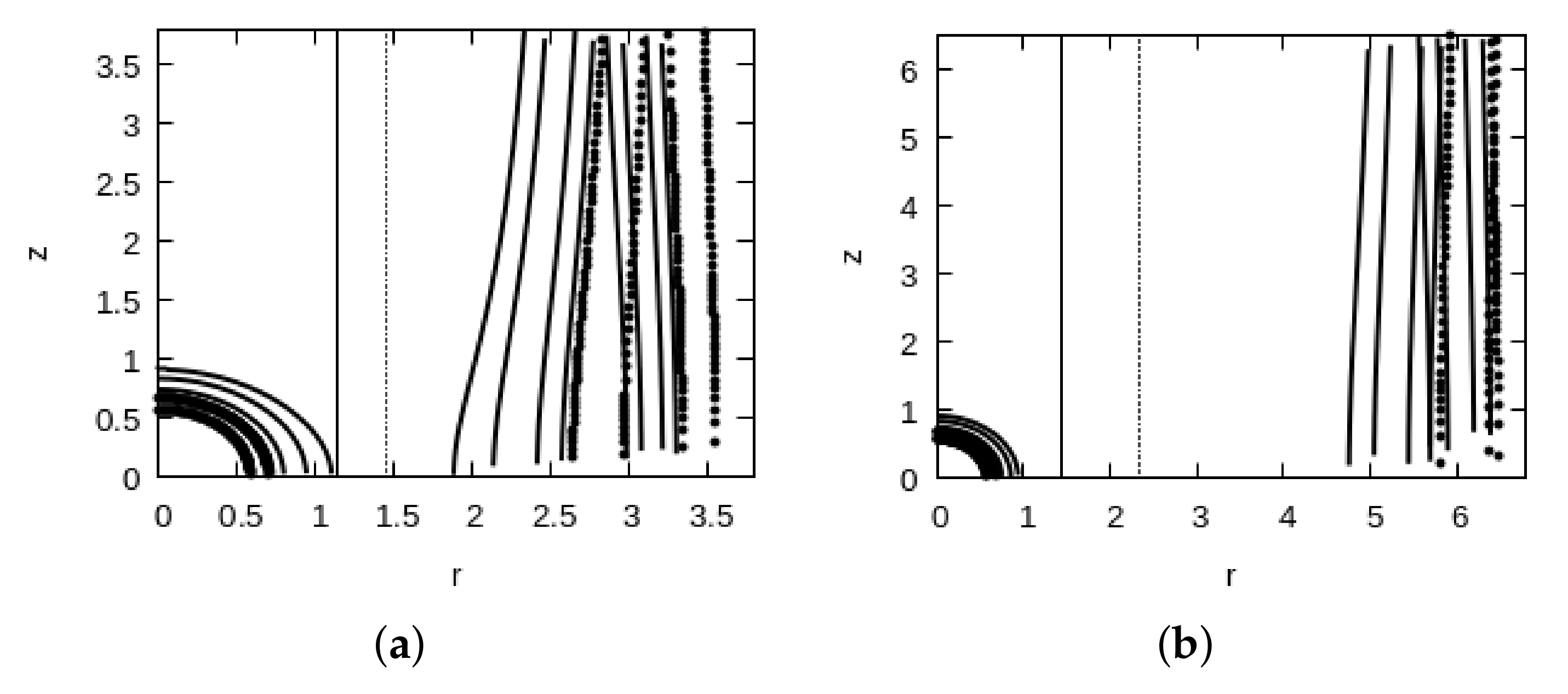
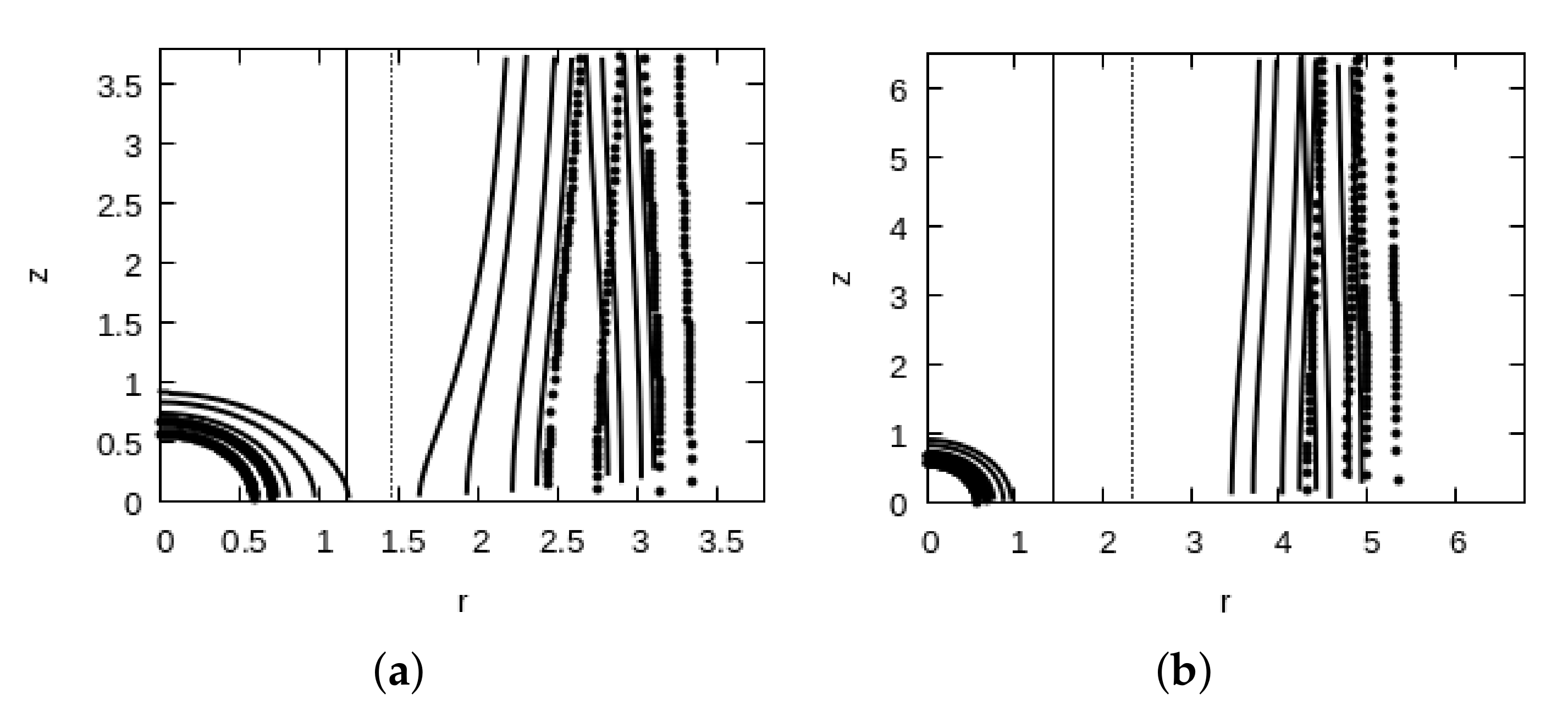
4. Magnetocentrifugal Winds
5. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zakharov, A.F.; Kardashev, N.S.; Lukash, V.N.; Repin, S.V. Magnetic fields in active galactic nuclei and microquasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 342, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cremaschini, C.; Kovář, J.; Slaný, P.; Stuchlík, Z.; Karas, V. Kinetic Theory of Equilibrium Axisymmetric Collisionless Plasmas in Off-equatorial Tori around Compact Objects. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2013, 209, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kološ, M.; Tursunov, A.; Stuchlík, Z. Possible signature of the magnetic fields related to quasi-periodic oscillations observed in microquasars. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.J.; Babul, A. Maximum spin of black holes driving jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambi, C. Astrophysical Black Holes: A Compact Pedagogical Review. Annal. Phys. 2018, 530, 1700430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, J.E.; Boksenberg, A. Optical spectroscop of two broad absorption line QSOs and implications for spherical-symmetric absorbing wind models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 211, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vitello, P.A.J.; Shlosman, I. Line-driven winds from accretion disks. I-Effects of the ionization structure. Astrophys. J. 1988, 327, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Payne, D.G. Hydromagnetic flows from accretion discs and the production of radio jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1982, 199, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proga, D.; Stone, J.M.; Drew, J.E. Radiation-driven winds from luminous accretion discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 295, 595–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proga, D.; Stone, J.M.; Kallman, T.R. Dynamics of line-driven disk winds in active galactic nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2000, 543, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, N.A.; Owocki, S.P.; Hillier, D.J.; Turnshek, D.A. On the steady nature of line-driven disk winds. Astrophys. J. 2004, 608, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.E. Radiative transfer and acceleration in magnetocentrifugal winds. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Raymond, J.; Fabian, A.; Steeghs, D.; Homan, J.; Reynolds, C.; van der Klis, M.; Wijnands, R. The magnetic nature of disk accretion onto black holes. Nature 2006, 441, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proga, D. Dynamics of accretion flows irradiated by a quasar. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elitzur, M.; Ho, L.C.; Trump, J.R. Evolution of broad-line emission from active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 3340–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Neutrino emission from the direction of the blazar TXS 0506+056 prior to the IceCube-170922A alert. Science 2018, 361, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, K.; Olinto, A.V. The Astrophysics of Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Rays. Ann. Rev. Astronom. Astrophys. 2011, 49, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banados, M.; Silk, J.; West, S.M. Kerr Black Holes as Particle Accelerators to Arbitrarily High Energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.; Sotiriou, T.P. Spinning Black Holes as Particle Accelerators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, E.; Cardoso, V.; Gualtieri, L.; Pretorius, F.; Sperhake, U. Comment on “Kerr Black Holes as Particle Accelerators to Arbitrarily High Energy”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 239001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambi, C. Testing black hole candidates with electromagnetic radiation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammie, C.F.; Shapiro, S.L.; McKinney, J.C. Black Hole Spin Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 602, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, E.; Volonteri, M. Cosmological black hole spin evolution by mergers and accretion. Astrophys. J. 2008, 684, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.U.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Al-Seady, M.; Allen, M.; Amman, J.F.; Anderson, R.J.; Archbold, G.; Belov, K.; Belz, J.W.; Bergman, D.R.; et al. Indications of Proton-Dominated Cosmic-Ray Composition above 1.6 EeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.U.; Abe, M.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Allen, M.; Azuma, R.; Barcikowski, E.; Belz, J.W.; Bergman, D.R.; Blake, S.A.; Cady, R. The Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum between 2 PeV and 2 EeV Observed with the TALE Detector in Monocular Mode. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aab, A.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Samarai, I.A.; Albuquerque, I.F.; Allekotte, I.; Almela, A.; Castillo, J.; Alvarez-Muniz, J.; Anastasi, G.A.; et al. Combined fit of spectrum and composition data as measured by the Pierre Auger Observatory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 1704, 038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra-Araújo, C.H.; Anjos, R.C. Acceleration of charged particles from near-extremal rotating black holes embedded in magnetic fields. Class. Quant. Grav. 2020, 38, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursunov, A.; Stuchlík, Z.; Kološ, M.; Dadhich, N.; Ahmedov, B. Supermassive Black Holes as Possible Sources of Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. 2020, 895, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teukolsky, S. The Kerr metric. Class. Quan. Grav. 2015, 32, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A. Rotating black holes: Locally nonrotating frames, energy extraction, and scalar synchrotron radiation. Astrophys. J. 1972, 178, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Kerr Metric Black Holes. Nature 1970, 226, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra-Araújo, C.H.; Anjos, R.C. Rotating black holes with magnetic fields as accelerators of charged particles. Proc. Sci. 2019, 329, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, K.S. Disk-accretion onto a black hole. II. Evolution of the hole. Astrophys. J. 1974, 191, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Czerny, B.; Lasota, J.P.; Szuszkiewicz, E. Slim accretion disks. Astrophys. J. 1988, 332, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.P.S.; Letelier, P.S. Exact general relativistic thin disks around black holes. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Fragile, P.C. Foundations of Black Hole Accretion Disk Theory. Liv. Rev. Relat. 2013, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, I.D.; Thorne, K.S. Astrophysics of Black Holes. In Black Holes, Proceedings of the Lectures Given at the 23rd Session of the Summer School of Les Houches, Paris, France, 23–28 July 1972; DeWitt, C., DeWitt, B.S., Eds.; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 343–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie, G.I. The non-linear fluid dynamics of a warped accretion disc. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 304, 557–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coimbra-Araújo, C.H.; dos Anjos, R.C. Ultra-High-Energy Particles at the Border of Kerr Black Holes Triggered by Magnetocentrifugal Winds. Galaxies 2022, 10, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040084
Coimbra-Araújo CH, dos Anjos RC. Ultra-High-Energy Particles at the Border of Kerr Black Holes Triggered by Magnetocentrifugal Winds. Galaxies. 2022; 10(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoimbra-Araújo, Carlos H., and Rita C. dos Anjos. 2022. "Ultra-High-Energy Particles at the Border of Kerr Black Holes Triggered by Magnetocentrifugal Winds" Galaxies 10, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040084
APA StyleCoimbra-Araújo, C. H., & dos Anjos, R. C. (2022). Ultra-High-Energy Particles at the Border of Kerr Black Holes Triggered by Magnetocentrifugal Winds. Galaxies, 10(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040084






