Exact Expressions for the Pericenter Precession Caused by Some Dark Matter Distributions and Constraints on Them from Orbital Motions in the Solar System, in the Double Pulsar and in the Galactic Center
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Orbital Precessions for Various DM Density Profiles
2.1. Exponential DM Density Profile
2.2. Power-Law DM Density Profile
3. Confrontation with the Observations
3.1. Planets of the Solar System
| Planet | (mas cty) | (mas cty) |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | ||
| Venus | ||
| Earth | ||
| Mars | ||
| Jupiter | ||
| Saturn |
3.1.1. Constraints for the Exponential Density Profile
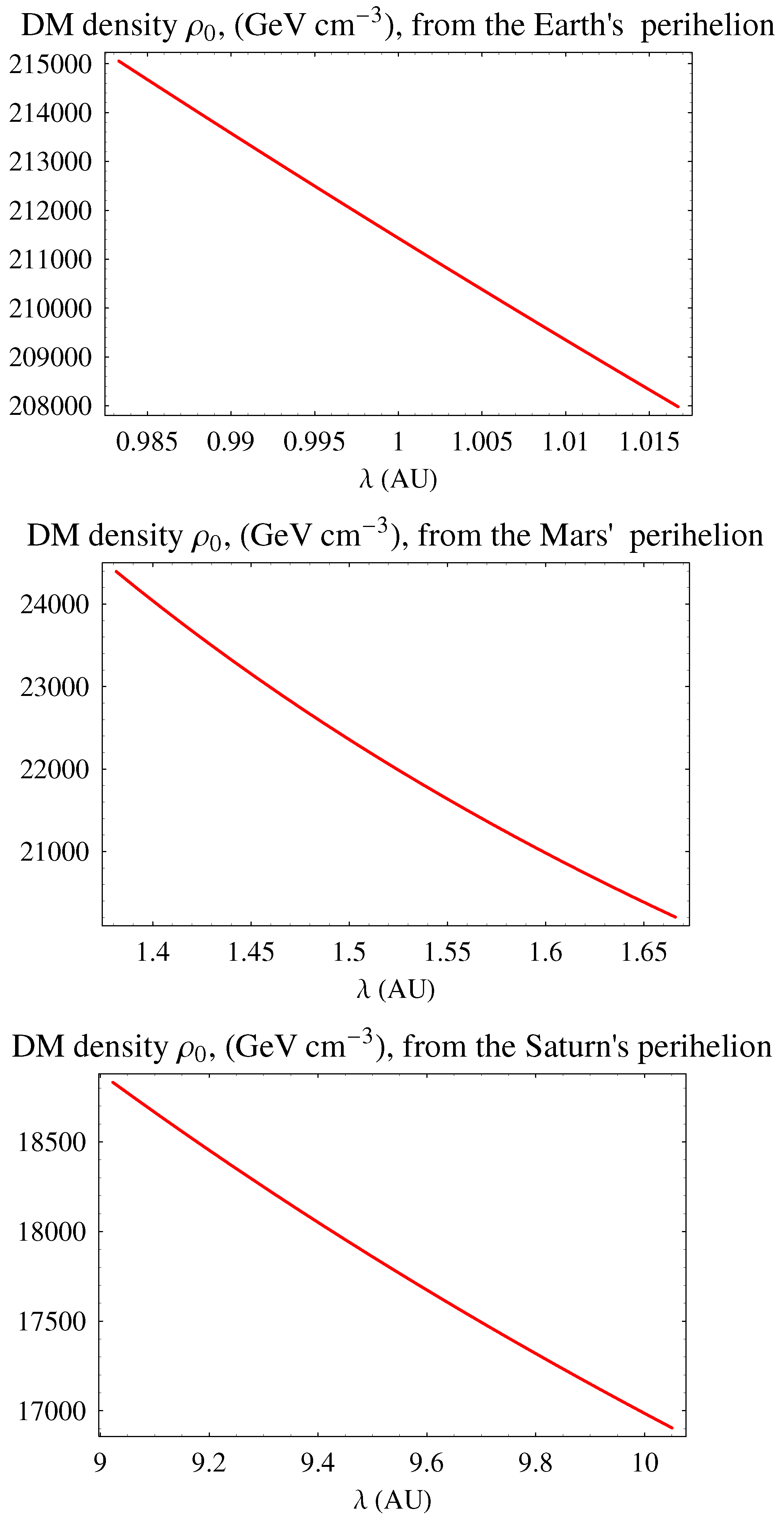
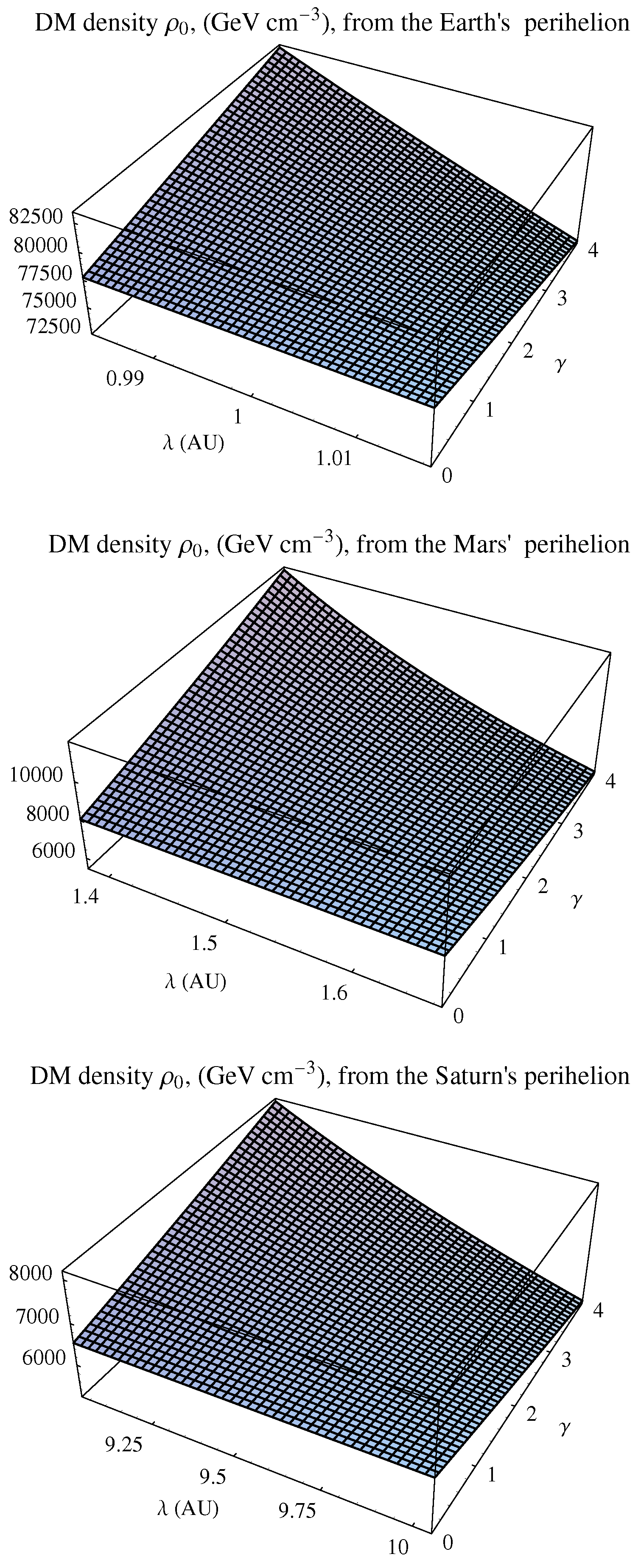
3.1.2. Constraints for the Power-Law Density Profile
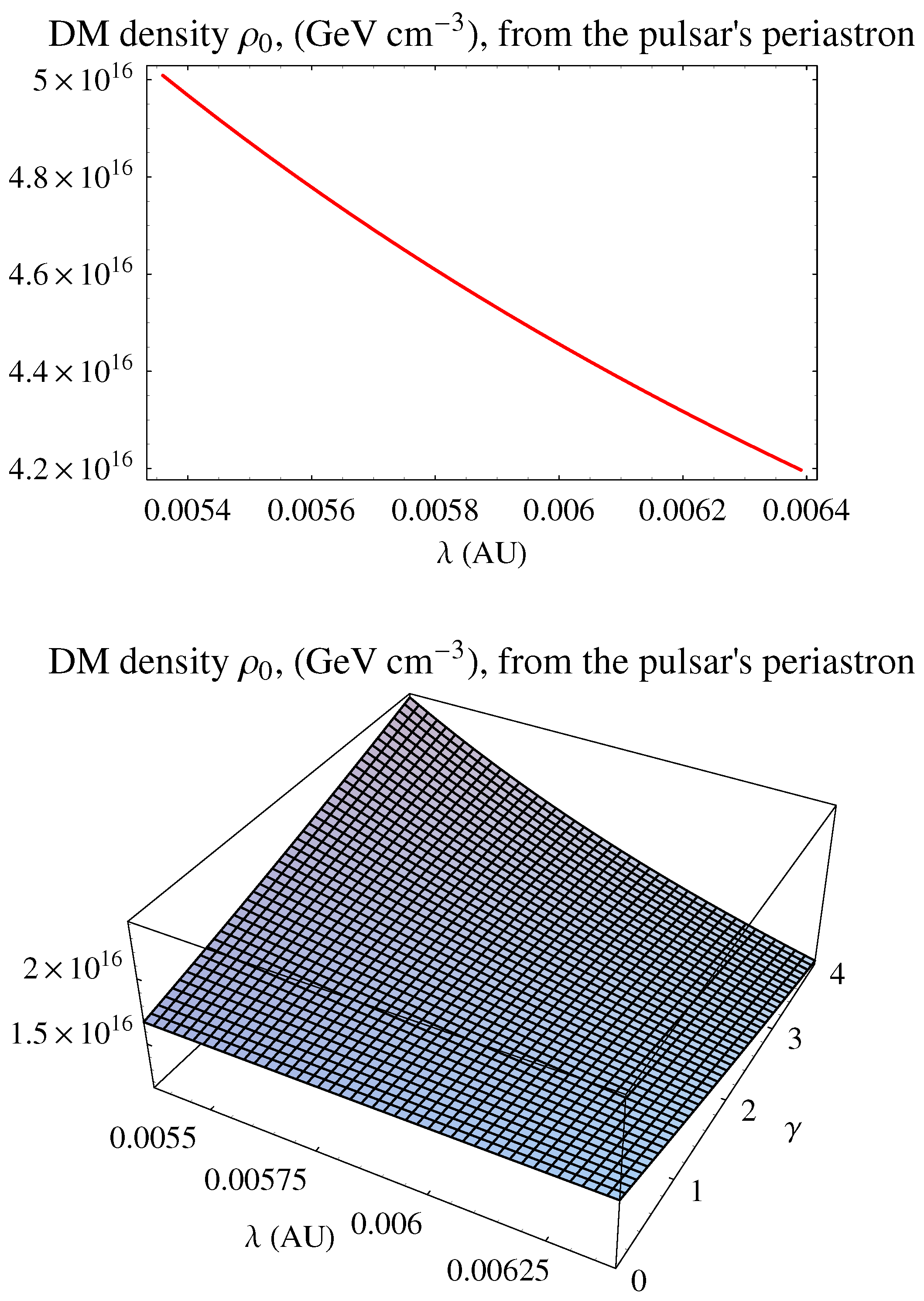
3.2. The Double Pulsar
3.3. The Stellar System Orbiting the Galactic Black Hole in Sgr A
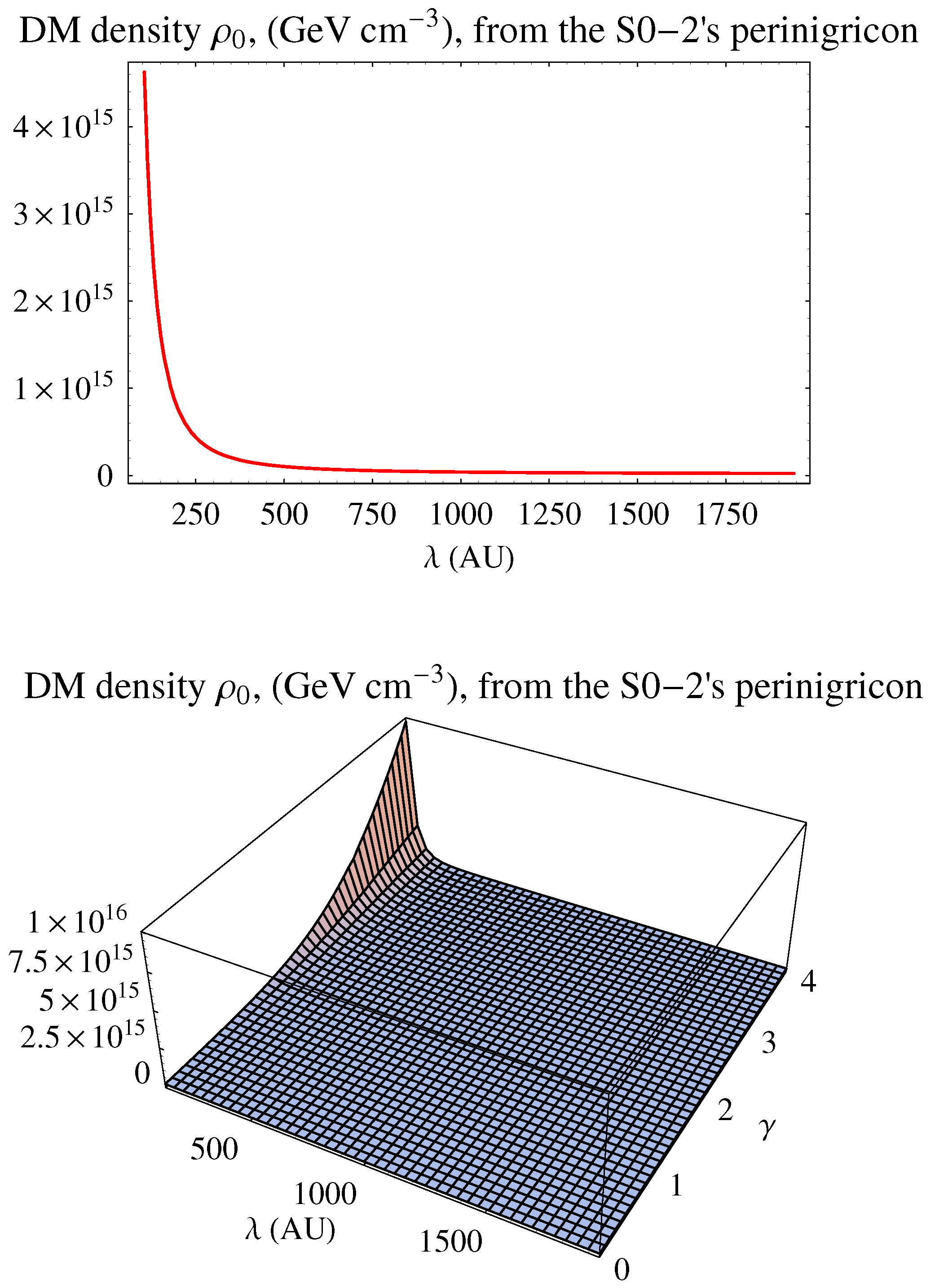
4. Summary and Conclusions
Appendix
A. The Coefficients of the Pericenter Precession due to the Power-Law Density
References
- Planck, C.; Ade, P.A.R.; Aghanim, N.; Armitage-Caplan, C.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; et al. Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters. ArXiv E-Prints 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Planck Collaboration; Ade, P.A.R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Baker, M.; Balbi, A.; Banday, A.J.; et al. Planck early results. I. The Planck mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 536, A1:1–A1:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, G.; Larson, D.; Komatsu, E.; Spergel, D.N.; Bennett, C.L.; Dunkley, J.; Nolta, M.R.; Halpern, M.; Hill, R.S.; Odegard, N.; et al. Nine-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Cosmological parameter results. ArXiv E-Prints 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann, T.; Huang, X.; Ibarra, A.; Vogl, S.; Weniger, C. Fermi LAT search for internal bremsstrahlung signatures from dark matter annihilation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weniger, C. A tentative gamma-ray line from Dark Matter annihilation at the Fermi Large Area Telescope. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempel, E.; Hektor, A.; Raidal, M. Fermi 130 GeV gamma-ray excess and dark matter annihilation in sub-haloes and in the Galactic Centre. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 032:1–032:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempel, E.; Hektor, A.; Raidal, M. Addendum: Fermi 130 GeV gamma-ray excess and dark matter annihilation in sub-haloes and in the Galactic Centre. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, A01:1–A01:2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hektor, A.; Raidal, M.; Tempel, E. Evidence for indirect detection of dark matter from galaxy clusters in fermi γ-ray data. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 762, L22:1–L22:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salucci, P.; Nesti, F.; Gentile, G.; Frigerio Martins, C. The dark matter density at the Sun’s location. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 523, A83:1–A83:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni Bidin, C.; Carraro, G.; Méndez, R.A.; Smith, R. Kinematical and chemical vertical structure of the galactic thick disk. II. A lack of dark matter in the solar neighborhood. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751, 30:1–30:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovy, J.; Tremaine, S. On the local dark matter density. Astrophys. J. 2012, 756, 89:1–89:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesti, F.; Salucci, P. The local dark matter density. ArXiv E-Prints 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akerib, D.S.; Alvaro-Dean, J.; Armel, M.S.; Attisha, M.J.; Baudis, L.; Bauer, D.A.; Bolozdynya, A.I.; Brink, P.L.; Bunker, R.; Cabrera, B.; et al. New results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search experiment. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 082002:1–082002:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDMS Collaboration; Ahmed, Z.; Akerib, D.S.; Arrenberg, S.; Bailey, C.N.; Balakishiyeva, D.; Baudis, L.; Bauer, D.A.; Brink, P.L.; Bruch, T.; et al. Dark matter search results from the CDMS II experiment. Science 2010, 327, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabei, R.; Belli, P.; Cappella, F.; Cerulli, R.; Montechia, F.; Nozzoli, F.; Incicchitti, A.; Prosperi, D.; Dai, C.J.; Kuang, H.H.; et al. Dark matter search. Riv. Nuovo Cimento 2003, 26, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabei, R.; Belli, P.; Bussolotti, A.; Cappella, F.; Cerulli, R.; Dai, C.J.; D’Angelo, A.; He, H.L.; Incicchitti, A.; Kuang, H.H.; et al. The DAMA/LIBRA apparatus. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2008, 592, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J.; Aprile, E.; Arneodo, F.; Baudis, L.; Bernstein, A.; Bolozdynya, A.; Coelho, L.C.C.; Dahl, C.E.; Deviveiros, L.; Ferella, A.D.; et al. Constraints on inelastic dark matter from XENON10. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 115005:1–115005:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, T.J. The ZEPLIN III dark matter project. New Astron. Rev. 2005, 49, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDMS Collaboration; Agnese, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Anderson, A.J.; Arrenberg, S.; Balakishiyeva, D.; Basu Thakur, R.; Bauer, D.A.; Billard, J.; Borgland, A.; et al. Dark matter search results using the silicon detectors of CDMS II. ArXiv E-Prints 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Coutu, S. Positrons galore. Phys. Online J. 2013, 6, 40:1–40:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Alberti, G.; Alpat, B.; Alvino, A.; Ambrosi, G.; Andeen, K.; Anderhub, H.; Arruda, L.; Azzarello, P.; Bachlechner, A.; et al. First result from the alpha magnetic spectrometer on the international space station: Precision measurement of the positron fraction in primary cosmic rays of 0.5–350 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 141102:1–141102:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.; Graham, A.W.; Moore, B.; Diemand, J.; Terzić, B. Empirical models for dark matter halos. I. Nonparametric construction of density profiles and comparison with parametric models. Astron. J. 2006, 132, 2685–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, B.; Farinella, P.; Vokrouhlický, D. Physics of the Solar System; Kluwer Academic Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.D.; Lau, E.L.; Taylor, A.H.; Dicus, D.A.; Teplitz, D.C.; Teplitz, V.L. Bounds on dark matter in solar orbit. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D.; Lau, E.L.; Krisher, T.P.; Dicus, D.A.; Rosenbaum, D.C.; Teplitz, V.L. Improved bounds on nonluminous matter in solar orbit. Astrophys. J. 1995, 448, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grø.n, Ø.; Soleng, H.H. Experimental limits on the density of dark matter in the solar system. Astrophys. J. 1996, 456, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sereno, M.; Jetzer, P. Dark matter versus modifications of the gravitational inverse-square law: Results from planetary motion in the Solar system. Mon. Notices R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 371, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, L. Solar system planetary orbital motions and dark matter. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 5, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khriplovich, I.B.; Pitjeva, E.V. Upper limits on density of dark matter in solar system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khriplovich, I.B. Density of dark matter in the solar system and perihelion precession of planets. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2007, 16, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.L. Planet-bound dark matter and the internal heat of Uranus, Neptune, and hot-Jupiter exoplanets. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 671, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frère, J.M.; Ling, F.S.; Vertongen, G. Bound on the dark matter density in the Solar System from planetary motions. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 083005:1–083005:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, L. Effect of sun and planet-bound dark matter on planet and satellite dynamics in the solar system. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 5, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, H.; Mousavi, S.N.; Saadat, M.; Saadat, N.; Saadat, A.M. The effect of dark matter on solar system and perihelion precession of earth planet. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2010, 49, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Risi, G.; Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S.N. Solar system constraints on local dark matter density. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 7, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitjev, N.; Pitjeva, E. Constraints on dark matter in the solar system. Astron. Lett. 2013, 39, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakida, H. Influence of dark matter on light propagation in solar system. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einasto, J. On the construction of a composite model for the galaxy and on the determination of the system of galactic parameters. Tr. Astrofiz. Inst. Alma Ata 1965, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gillessen, S.; Eisenhauer, F.; Trippe, S.; Alexander, T.; Genzel, R.; Martins, F.; Ott, T. Monitoring stellar orbits around the massive black hole in the galactic center. Astrophys. J. 2009, 692, 1075–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.F.; Nucita, A.A.; de Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G. Apoastron shift constraints on dark matter distribution at the Galactic Center. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 062001:1–062001:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.F.; de Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G.; Nucita, A.A. Constraints on parameters of dark matter and black hole in the Galactic Center. Phys. At. Nucl. 2010, 73, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; Novak, J. External field effect of modified Newtonian dynamics in the Solar System. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 412, 2530–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fienga, A.; Laskar, J.; Kuchynka, P.; Manche, H.; Desvignes, G.; Gastineau, M.; Cognard, I.; Theureau, G. The INPOP10a planetary ephemeris and its applications in fundamental physics. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 2011, 111, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hees, A.; Lamine, B.; Reynaud, S.; Jaekel, M.T.; Le Poncin-Lafitte, C.; Lainey, V.; Füzfa, A.; Courty, J.M.; Dehant, V.; Wolf, P. Radioscience simulations in general relativity and in alternative theories of gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2012, 29, 235027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, I.; Nussinov, S. Weakly interacting massive particles and neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 1989, 40, 3221–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, A.; Draine, B.T.; Romani, R.W.; Nussinov, S. Neutron stars: Graveyard of charged dark matter. Phys. Lett. B 1990, 238, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laarakkers, W.G.; Poisson, E. Quadrupole moments of rotating neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 1999, 512, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, G.; Fairbairn, M. Compact stars as dark matter probes. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 043515:1–043515:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaris, C. WIMP annihilation and cooling of neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 023006:1–023006:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaris, C.; Tinyakov, P. Can neutron stars constrain dark matter? Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 063531:1–063531:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lavallaz, A.; Fairbairn, M. Neutron stars as dark matter probes. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 123521:1–123521:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Reisenegger, A. Internal heating of old neutron stars: contrasting different mechanisms. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 522, A16:1–A16:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarcelluti, P.; Sandin, F. Have neutron stars a dark matter core? Phys. Lett. B 2011, 695, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, B.C. Gravitationally focused dark matter around compact stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2011, 197, 37:1–37:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Fan, Y.Z.; Waldman, R.; Chang, J. Dark matter mini-halo around the compact objects: the formation, evolution and possible contribution to the cosmic ray electrons/positrons. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, H.E.; Kane, G.L. The search for supersymmetry: Probing physics beyond the standard model. Phys. Rep. 1985, 117, 75–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalza, V.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Aharonian, F.; Khangulyan, D. Unraveling the high-energy emission components of gamma-ray binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 551, A17:1–A17:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, L.; Kramer, M.; Johnson, T.J.; Craig, H.A.; Romani, R.W.; Venter, C.; Harding, A.K.; Ferdman, R.D.; Stairs, I.H.; Kerr, M. Fermi LAT pulsed detection of PSR J0737-3039A in the double pulsar system. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 169:1–169:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgay, M.; D’Amico, N.; Possenti, A.; Manchester, R.N.; Lyne, A.G.; Joshi, B.C.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Kramer, M.; Sarkissian, J.M.; Camilo, F.; et al. An increased estimate of the merger rate of double neutron stars from observations of a highly relativistic system. Nature 2003, 426, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyne, A.G.; Burgay, M.; Kramer, M.; Possenti, A.; Manchester, R.N.; Camilo, F.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lorimer, D.R.; D’Amico, N.; Joshi, B.C.; et al. A double-pulsar system: A rare laboratory for relativistic gravity and plasma physics. Science 2004, 303, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.; Stairs, I.H.; Manchester, R.N.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lyne, A.G.; Ferdman, R.D.; Burgay, M.; Lorimer, D.R.; Possenti, A.; D’Amico, N.; et al. Tests of general relativity from timing the double pulsar. Science 2006, 314, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, L. Constraining the cosmological constant and the DGP gravity with the double pulsar PSR J0737-3039. New Astron. 2009, 14, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondolo, P.; Silk, J. Dark matter annihilation at the galactic center. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Gondolo, P. Stellar orbit constraints on neutralino annihilation at the galactic center. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 063511:1–063511:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D. Dark Matter at the Centers of Galaxies. In Particle Dark Matter: Observations, Models and Searches; Bertone, G., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Chapter 5; pp. 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghian, L.; Ferrer, F.; Will, C.M. Dark matter distribution in the Schwarzschild geometry. APS April Meet. Abstr. 2012, 57. Abstract: X8.00003. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlen, M.; Guedes, J.; Pillepich, A.; Madau, P.; Mayer, L. An off-center density peak in the milky way’s dark matter halo? Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 10:1–10:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belikov, A.V.; Zaharijas, G.; Silk, J. Study of the gamma-ray spectrum from the Galactic Center in view of multi-TeV dark matter candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 083516:1–083516:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, R.; Ng, K.C.Y.; Dasgupta, B.; Horiuchi, S. Galactic Center radio constraints on gamma-ray lines from dark matter annihilation. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 043516:1–043516:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavalle, J.; Salati, P. Dark matter indirect signatures. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2012, 13, 740–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, T.; Weniger, C. Gamma ray signals from dark matter: Concepts, status and prospects. Phys. Dark Univ. 2012, 1, 194–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Eisenhauer, F.; Fritz, T.K.; Bartko, H.; Dodds-Eden, K.; Pfuhl, O.; Ott, T.; Genzel, R. The orbit of the star S2 around SGR A* from very large telescope and keck data. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 707, L114–L117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Ghez, A.M.; Schödel, R.; Yelda, S.; Boehle, A.; Lu, J.R.; Do, T.; Morris, M.R.; Becklin, E.E.; Matthews, K. The shortest-known-period star orbiting our galaxy’s supermassive black hole. Science 2012, 338, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melia, F. The Galactic Supermassive Black Hole; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bahcall, J.N.; Wolf, R.A. The star distribution around a massive black hole in a globular cluster. II. Unequal star masses. Astrophys. J. 1977, 216, 883–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P. Numerical models of star clusters with a central black hole. I—Adiabatic models. Astrophys. J. 1980, 242, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzel, R.; Schödel, R.; Ott, T.; Eisenhauer, F.; Hofmann, R.; Lehnert, M.; Eckart, A.; Alexander, T.; Sternberg, A.; Lenzen, R.; et al. The stellar cusp around the supermassive black hole in the galactic center. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, 812–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Iorio, L. Exact Expressions for the Pericenter Precession Caused by Some Dark Matter Distributions and Constraints on Them from Orbital Motions in the Solar System, in the Double Pulsar and in the Galactic Center. Galaxies 2013, 1, 6-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies1010006
Iorio L. Exact Expressions for the Pericenter Precession Caused by Some Dark Matter Distributions and Constraints on Them from Orbital Motions in the Solar System, in the Double Pulsar and in the Galactic Center. Galaxies. 2013; 1(1):6-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleIorio, Lorenzo. 2013. "Exact Expressions for the Pericenter Precession Caused by Some Dark Matter Distributions and Constraints on Them from Orbital Motions in the Solar System, in the Double Pulsar and in the Galactic Center" Galaxies 1, no. 1: 6-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies1010006
APA StyleIorio, L. (2013). Exact Expressions for the Pericenter Precession Caused by Some Dark Matter Distributions and Constraints on Them from Orbital Motions in the Solar System, in the Double Pulsar and in the Galactic Center. Galaxies, 1(1), 6-30. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies1010006





