Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale
Abstract
1. Introduction
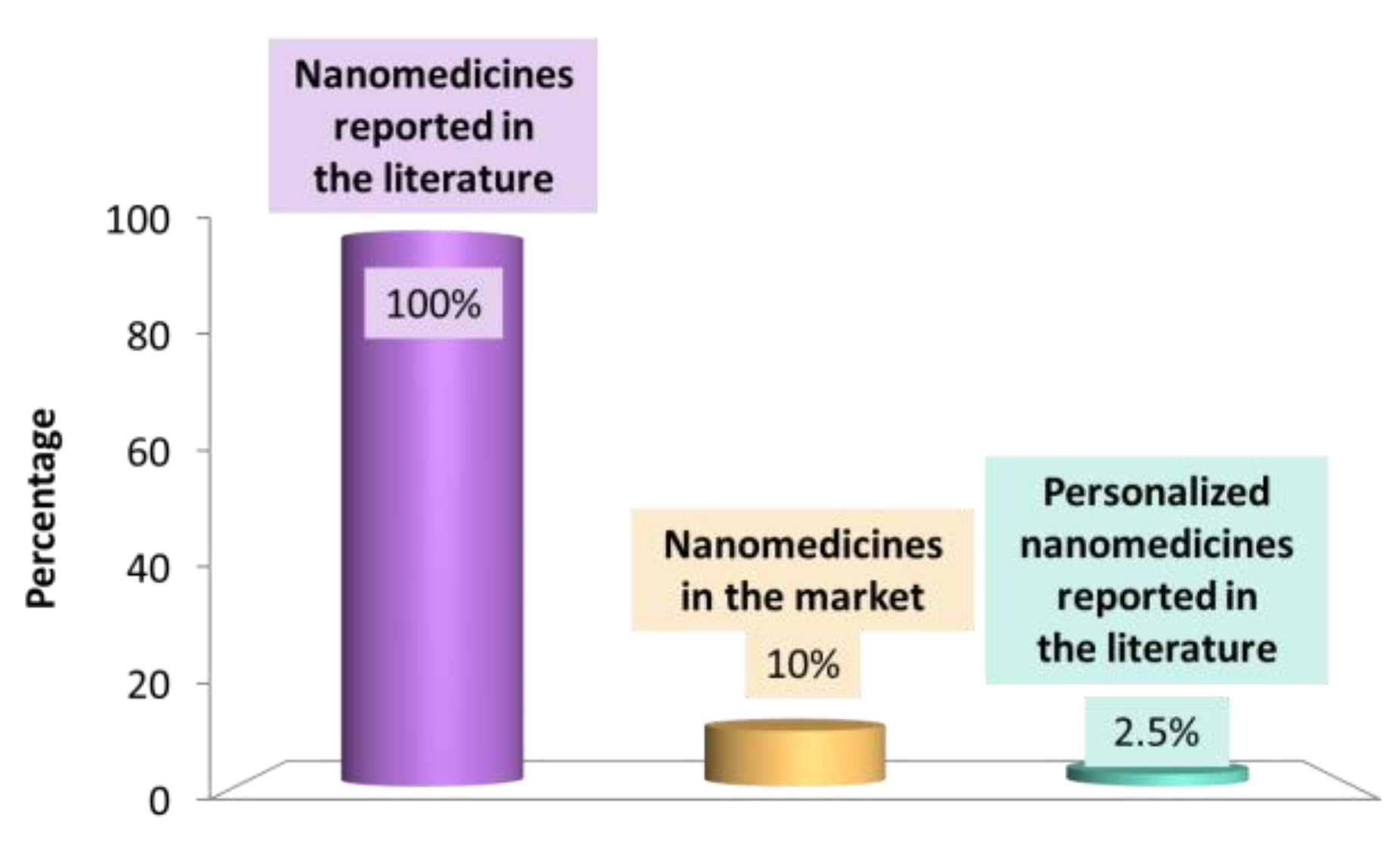
1.1. Nanomedicines in Pre-Clinical and Clinical Development: An Overview
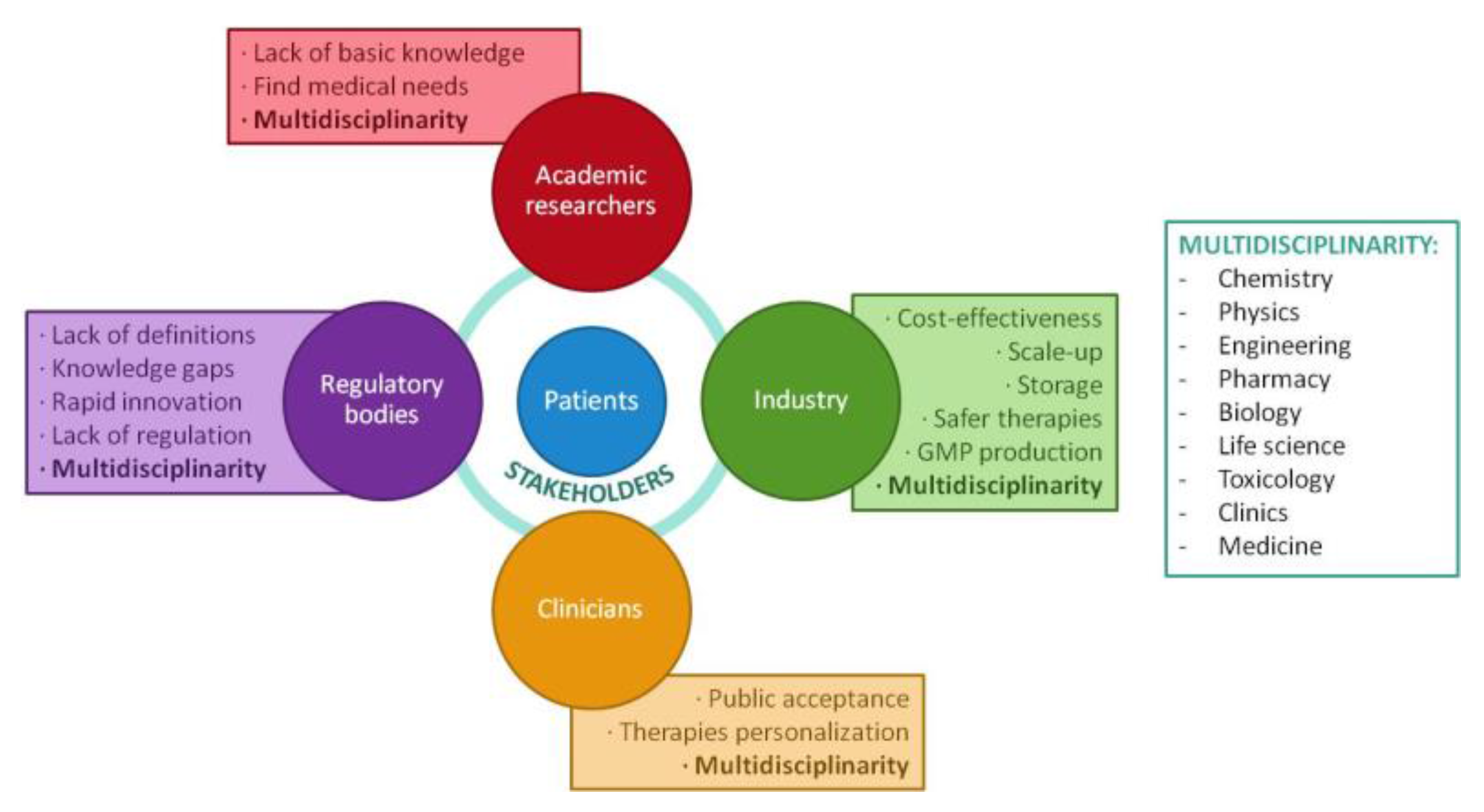
1.2. Challenges in Personalized Medicine
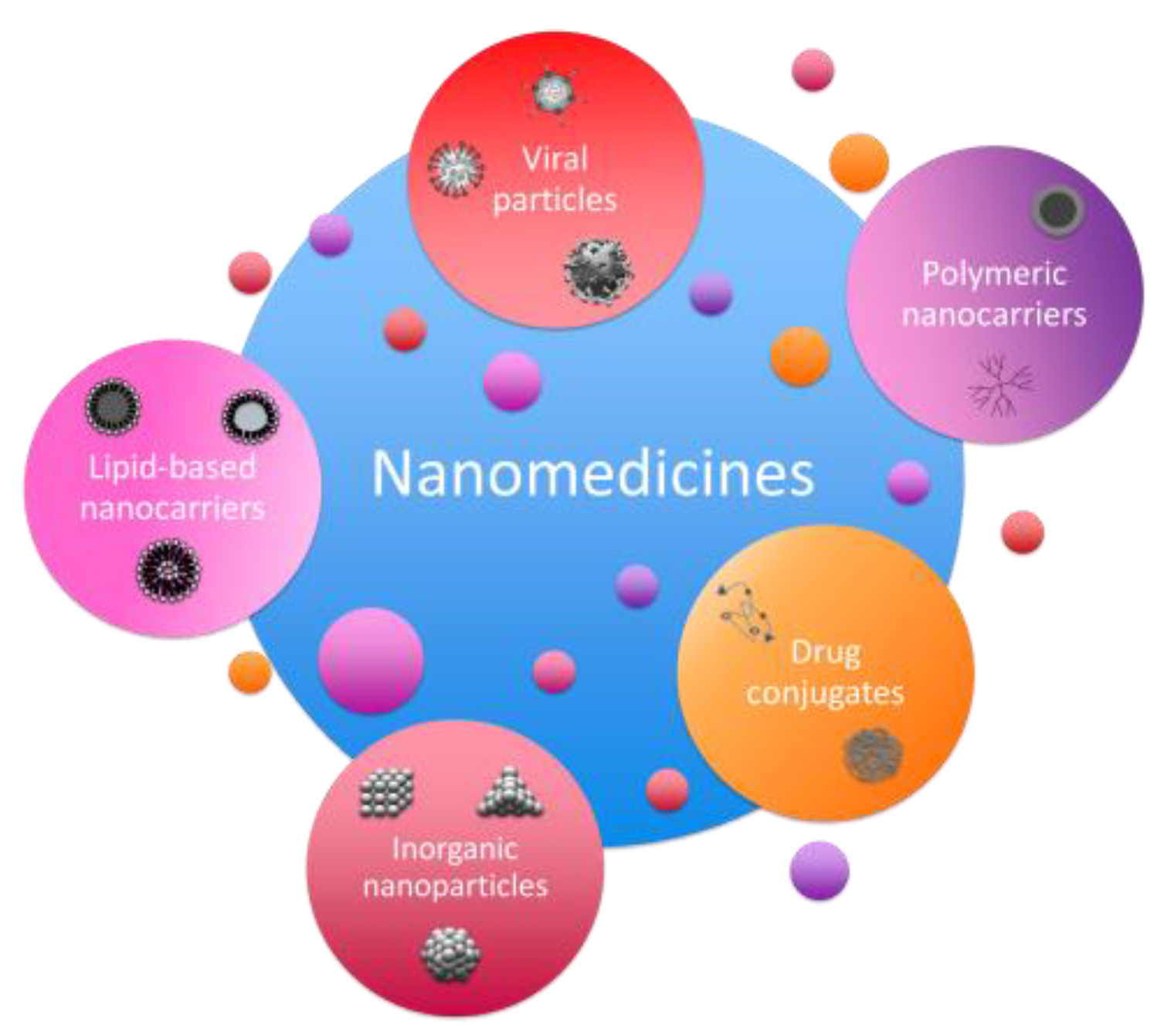
2. Development of Novel Nanomedicines
2.1. Design of Nanomedicines in Research Labs
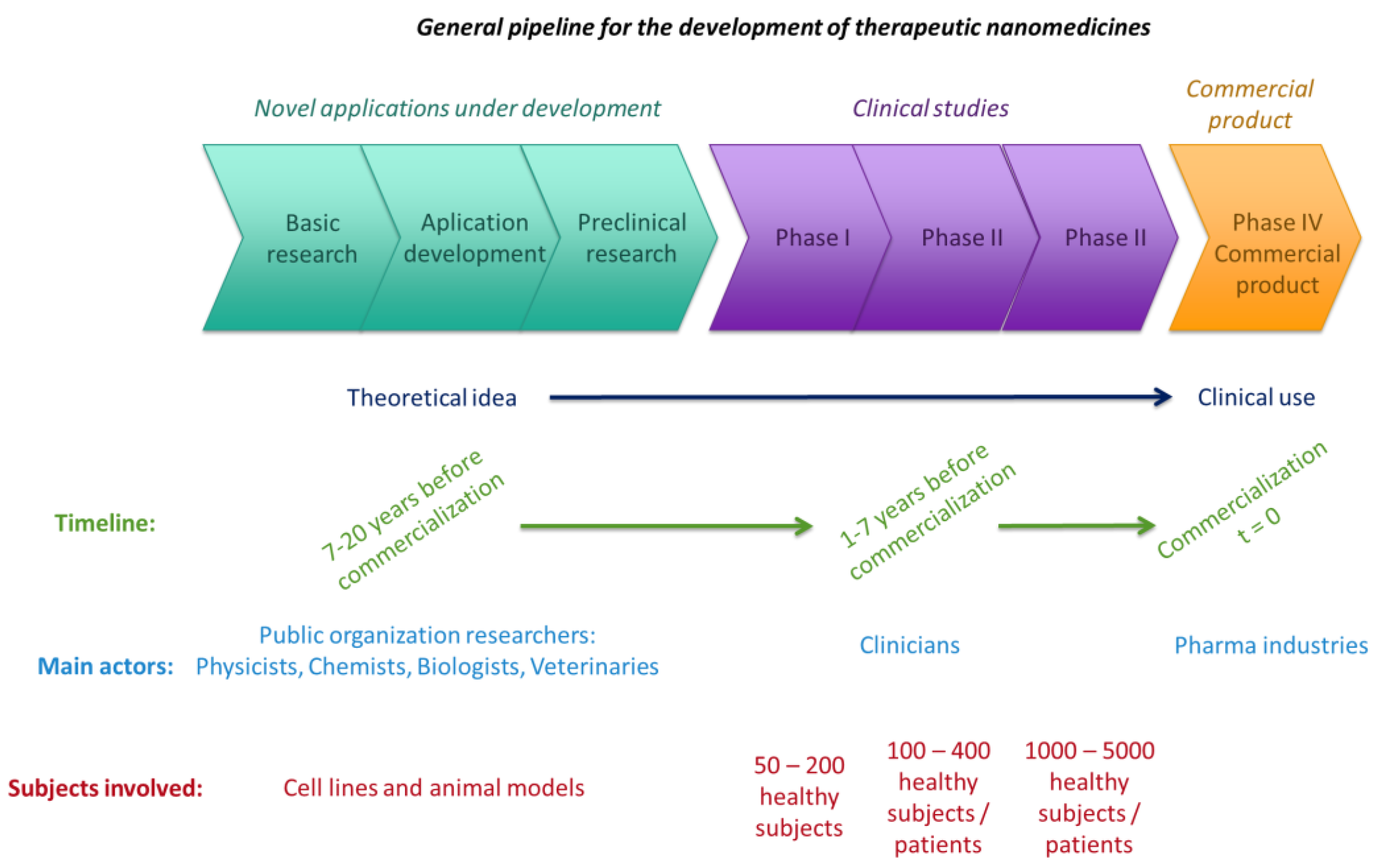
2.2. From Lab to Market
3. Pharmaceutical Industry Opportunities
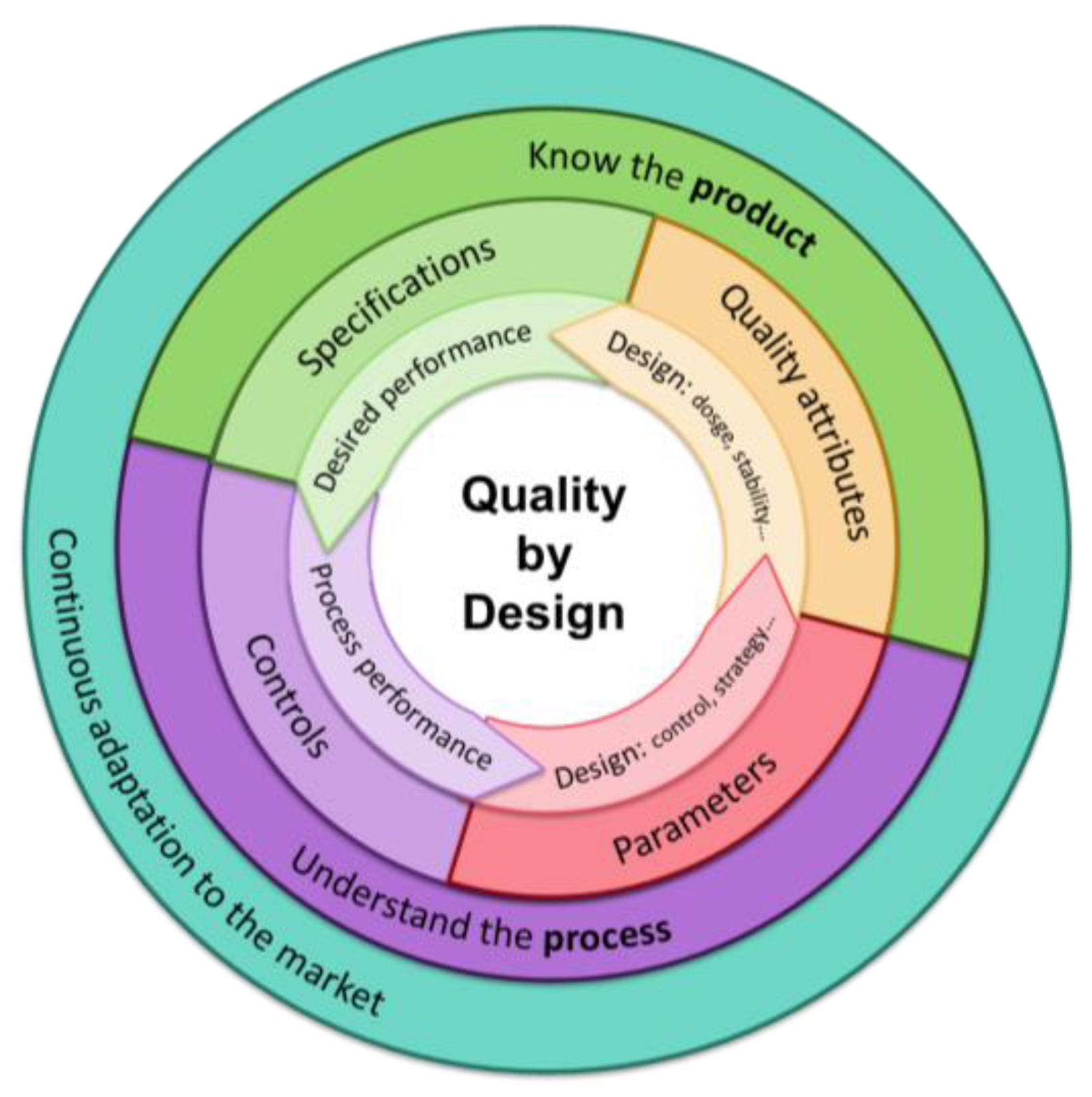
3.1. Regulations of Nanomedicines
3.2. The Specific Case of Personalized Nanomedicine
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duncan, R.; Gaspar, R. Nanomedicine(s) under the microscope. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2101–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudin, A.; Andrieux, K.; Couvreur, P. Nanomedicines and stroke: Toward translational research. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, K.S.; Yang, M.; Mao, C. Phage-Enabled Nanomedicine: From Probes to Therapeutics in Precision Medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1964–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Moore, R. Nanomedicine; Nanostruct; Springer: Otawa, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissig, V.; Guzman-Villanueva, D. Nanopharmaceuticals (Part 2): Products in the pipeline. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazile, D.V. Nanotechnologies in drug delivery—An industrial perspective. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etheridge, M.L.; Campbell, S.A.; Erdman, A.G.; Haynes, C.L.; Wolf, S.M.; McCullough, J. The big picture on nanomedicine: The state of investigational and approved nanomedicine products, Nanomedicine Nanotechnology. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, B.B.S.; Lasham, A.; Shelling, A.N.; Al-Kassas, R. Nanoparticle therapeutics: Technologies and methods for overcoming cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bregoli, L.; Movia, D.; Gavigan-Imedio, J.D.; Lysaght, J.; Reynolds, J.; Prina-Mello, A. Nanomedicine applied to translational oncology: A future perspective on cancer treatment, Nanomedicine Nanotechnology. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Patel, P.R. Nanomedicine: A pharma perspective, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X.; Bertrand, N.; Pridgen, E.; Swami, A.; Farokhzad, O.C. Interactions of nanomaterials and biological systems: Implications to personalized nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1363–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissig, V.; Pettinger, T.K.; Murdock, N. Nanopharmaceuticals (part 1): Products on the market. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4357–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornaguera, C.; Solans, C. Methods for the In Vitro Characterization of Nanomedicines—Biological Component Interaction. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Patri, A.K.; McNeil, S.E. Characterization of nanoparticles for therapeutics. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2007, 2, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.P.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F. Nanoencapsulation I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, Nanomedicine Nanotechnology. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, Y.; Thassu, D. Drug Delivery Nanoparticles Formulation and Characterization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Ho, W.; Zhang, X.; Bertrand, N.; Farokhzad, O. Cancer nanomedicine: From targeted delivery to combination therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Harford, J.B.; Eaton, M.A.W.; Boisseau, P.M.; Dube, A.; Hayeshi, R.; Swai, H.; Lee, D.S. Nanomedicine: Past, present and future—A global perspective, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, G.; Havel, H.; Analoui, M.; Barton, R.W.; Diwan, A.R.; Hennessy, M.; Reddy, V.; Sadrieh, N.; Tamarkin, L.; Wolfgang, M.; et al. Nanomedicine drug development: A scientific symposium entitled “Charting a roadmap to commercialization”. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, S. Has nanomedicine lived up to its promise? Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 372501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehmann, F.; Sakai-Kato, K.; Duncan, R.; de la Ossa, D.H.P.; Pita, R.; Vidal, J.-M.; Kohli, A.; Tothfalusi, L.; Sanh, A.; Tinton, S.; et al. Next-generation nanomedicines and nanosimilars: EU Regulators’ initiatives relating to the development and evaluation of nanomedicines. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2013, 8, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arachchige, M.C.M.; Reshetnyak, Y.K.; Andreev, O.A. Advanced targeted nanomedicine. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 202, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchilin, V. Drug Targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, A.; Lemmer, Y.; Hayeshi, R.; Balogun, M.; Labuschagne, P.; Swai, H.; Kalombo, L. State of the art and future directions in nanomedicine for tuberculosis. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, J. Drug delivery to the central nervous system by polymeric nanoparticles: What do we know? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, G.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Ruozi, B. Nanomedicine and neurodegenerative disorders: So close yet so far. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditto, V.J.; Szoka, F.C. Cancer nanomedicines: So many papers and so few drugs! Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, J.I.; Lammers, T.; Ashford, M.B.; Puri, S.; Storm, G.; Barry, S.T. Challenges and strategies in anti-cancer nanomedicine development: An industry perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 108, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; von Roemeling, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Qie, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Kim, B.Y.S. Designing nanomedicine for immuno-oncology. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Chen, X.; Chow, E.K.; Ho, D.; Kabanov, A.V.; Karp, J.M.; Kataoka, K.; Mirkin, C.A.; Petrosko, S.H.; et al. Accelerating the Translation of Nanomaterials in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6644–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidczyk, C.M.; Kim, C.; Park, J.H.; Russell, L.M.; Lee, K.H.; Pomper, M.G.; Searson, P.C. State-of-the-Art in Design Rules for Drug Delivery Platforms: Lessons from FDA-approved Nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawa, R.; Audette, G.F.; Reese, B.E. Clinical Nanomedicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, S. Regulating nanomedicine. IEEE Pulse 2014, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KHoward, A.; Vorup-jensen, T.; Peer, D. Nanomedicine; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The smart drug delivery system and its clinical potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicki, A.; Witzigmann, D.; Balasubramanian, V.; Huwyler, J. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: Challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J. Control. Release 2015, 200, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Mathew, L.; Burney, M.; Nyshadham, P.; Coleman, R.L. Equivalency challenge: Evaluation of Lipodox? as the generic equivalent for Doxil? in a human ovarian cancer orthotropic mouse model. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, M.; Farhangrazi, S. Defining and characterizing non-biological complex drugs (NBCDs)—Is size enough? The case for liposomal doxorubicin generics (“liposomal nanosimilars”) for injection. GaBI J. 2014, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölükbas, D.A.; Meiners, S. Lung cancer nanomedicine: Potentials and pitfalls. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2015, 10, 3203–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.A.; Shim, M.S.; Heo, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.J. “Combo” nanomedicine: Co-delivery of multi-modal therapeutics for efficient, targeted, and safe cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 98, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the Clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, S. What nanomedicine in the clinic right now really forms nanoparticles? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 6, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, T.; Rizzo, L.Y.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F. Personalized nanomedicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4889–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiseh, O.; Tang, B.C.; Whitehead, K.A.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: Challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. 2017. Available online: https://ncats.nih.gov/ (accessed on 11 October 2017).
- Parveen, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanomedicine: Clinical applications of polyethylene glycol conjugated proteins and drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamvakas, S.; Martinalbo, J.; Pita, R.; Isaac, M. On the edge of new technologies (advanced therapies, nanomedicines). Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2011, 8, e21–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, W.J.; Stoessel, P.R.; Wohlleben, W.; Hafner, A. Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 98, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, A.; Lovrić, J.; Lakoš, G.P.; Pepić, I. Nanotherapeutics in the EU: An overview on current state and future directions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1005–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodson, T.S. Public private partnerships and emerging technologies: A look at nanomedicine for diseases of poverty. Res. Policy 2015, 45, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islan, G.A.; Durán, M.; Cacicedo, M.L.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Castro, G.R.; Durán, N. Nanopharmaceuticals as a solution to neglected diseases: Is it possible? Acta Trop. 2017, 170, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, R. Cost-effectiveness of nanomedicine: The path to a future successful and dominant market? Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1851–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béduneau, A.; Hindré, F.; Clavreul, A.; Leroux, J.C.; Saulnier, P.; Benoit, J.P. Brain targeting using novel lipid nanovectors. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato-Berciano, A.; Raimondi, G.; Maliandi, M.V.; Alemany, R.; Montoliu, L.; Fillat, C. A NOTCH-sensitive uPAR-regulated oncolytic adenovirus effectively suppresses pancreatic tumor growth and triggers synergistic anticancer effects with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22700–22715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straussman, R.; Morikawa, T.; Shee, K.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Du, J.; Davis, A.; Mongare, M.M.; Gould, J.; Frederick, D.T.; et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012, 487, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegh, A.H. Toward personalized cancer nanomedicine—past, present, and future. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Mita, M.M.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Weiss, G.J.; Mita, A.C.; Lorusso, P.M.; Burris, H.A.; Hart, L.L.; Low, S.C.; Parsons, D.M.; et al. Phase I study of PSMA-targeted docetaxel-containing nanoparticle BIND-014 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3157–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, M.W.; Dawson, K.A.; Åberg, C. Nanoparticle adhesion to the cell membrane and its effect on nanoparticle uptake efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauthier, C.; Ponchel, G. Polymeric Nanoparticles on Nanomedicines: A Guide for Their Design, Preparation and Development; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.; Trieu, V.; Damascelli, B.; Soon-Shiong, P. SPARC Expression Correlates with Tumor Response to Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kaminski, M.D.; Chen, H.; Torno, M.; Taylor, L.; Rosengart, A.J. Synthesis and characterization of highly-magnetic biodegradable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okassa, L.N.; Marchais, H.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Hervé, K.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Munnier, E.; Soucé, M.; Linassier, C.; Dubois, P.; Chourpa, I. Optimization of iron oxide nanoparticles encapsulation within poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) sub-micron particles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkansah, M.K.; Thakral, D.; Shapiro, E.M. Magnetic poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and cellulose particles for MRI-based cell tracking. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ran, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Krupka, T.M.; Li, A.; Li, P.; et al. Superparamagnetic PLGA-iron oxide microcapsules for dual-modality US/MR imaging and high intensity focused US breast cancer ablation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5854–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. A microenvironmental model of carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 182, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamonte, G.; Tang, X.; Chen, J.L.; Wu, J.; Ding, C.C.; Keenan, M.M.; Sangokoya, C.; Kung, H.; Ilkayeva, O.; Boros, L.G.; et al. Acidosis induces reprogramming of cellular metabolism to mitigate oxidative stress. Cancer Metab. 2013, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, B.P.; Raghunand, N.; Baggett, B.; Gillies, R.J. Tumor acidity, ion trapping and chemotherapeutics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtkowiak, J.W.; Verduzco, D.; Schramm, K.J.; Gillies, R.J. Drug resistance and cellular adaptation to tumor acidic pH microenvironment. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2032–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanth, H.; Murthy, R.S.R. pH-Sensitive liposomes—Principle and application in cancer therapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormehr, M.; Schrörs, B.; Boegel, S.; Löwer, M.; Türeci, Ö.; Sahin, U. Mutanome Engineered RNA Immunotherapy: Towards Patient-Centered Tumor Vaccination. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloke, B.-P.; Britten, C.M.; Loquai, C.; Löwer, M.; Attig, S.; Bukur, V.; Bidmon, N.; Derhovanessian, E.; Diekmann, J.; Diken, M.; et al. Abstract CT202: IVAC MUTANOME: Individualized vaccines for the treatment of cancer. In Proceedings of the AACR 106th Annunal Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 18–22 April 2015; Volume 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielin, O.; Coukos, G. Immuno-Oncology; Progress I; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Würmseher, M.; Firmin, L. Nanobiotech in big pharma: A business perspective. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2017, 12, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, E.; Murphy, F.; Poland, C.A.; Mullins, M.; Costa, A.L.; Mcalea, E.; Tran, L.; Tofail, S.A.M. Impact and effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies on the insurability of nanomaterial production: Evidences from industrial case studies, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Tran, C.L. Nanotoxicology: Progress toward Nanomedicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, J.; Godman, B.; Ofierska-Sujkowska, G.; Osińska, B.; Herholz, H.; Wendykowska, K.; Laius, O.; Jan, S.; Sermet, C.; Zara, C.; et al. Risk sharing arrangements for pharmaceuticals: Potential considerations and recommendations for European payers. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2010, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.K.; Rath, B. Real-World Data Analytics in Global Pharmaceutical Marketing. IUP J. Knowl. Manag. 2016, XIV, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory. Assay Cascade Protocols; Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory from National Cancer Institute: Frederick, MD, USA, 2017.
- Nasr, M. Implementation of Quality by Design (QbD): Status, Challenges and Next Steps; Office of New Drug Quality Assessment: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2006.

| Personalized Nanomedicines |
|---|
| Nanometric scale dimensions |
| Tunability/versatility |
| Use of labile compounds (e.g., siRNA) |
| Active principles: encapsulation and protection |
| Modification of actives pharmacokinetics |
| Specific organ targeting moieties |
| Arrival to specific cellular compartments |
| Adaptation to the requirements of a cohort of patients |
| Adaptation of therapy patterns to each patient (e.g., dosage, frequency, etc.) |
| Drug Name (Tradename/Active Principle) | Company | Type of Nanoformulation | Indication/Route of Administration | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abraxane/Paclitaxel | Abraxis (Warminster, Penn State, USA) and Celgene (Summit, New Jersey, USA) | Albumin nanoparticles | Various cancers/IV | Marketed |
| Adcetris/Brentuximab | Seattle Genetics (Bothell, Washington, USA) | Antibody-drug conjugate | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma/IV | Marketed |
| ALN-TTR02 (Patisiran)/siRNA | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, Massachussets, USA) | Liposome | Transthyretin amyloidosis/IV | Phase II |
| AmBisome/Amphotericine B | Astellas Pharma (Chuo, Tokio, Japan) | Liposomes | Fungal infections/IV | Marketed |
| Aurimune/--- | Cytimmune sciences (Rockville, MD, USA) | Colloidal gold | Solid tumors/IV | Phase I/II |
| Auroshell/--- | Nanospectra Biosciences (Houston, Texas, USA) | Gold-silica nanoshells | Lung cancer/IV | Phase I |
| BIND-014/Docetaxel | Bind Therapeutics (Cambridge, Massachussets, USA) | Polymeric NPs | Solid tumors/IV | Phase II |
| Caelyx/Doxorubicin | Janssen (Beerse, Belgium) | PEGylated liposome | Solid tumors/IV | Marketed |
| DaunoXome/Daunorubicin | Galen Limited (Portadown, United Kingdom) | Liposome | Solid tumors/IV | Marketed |
| Diprivan/Propofol | AstraZeneca (London, United Kingdom) | Nano-emulsion | Anesthetic/IV | Marketed |
| Doxil/Doxorubicin | Janssen (Beerse, Belgium) | PEGylated liposomes | Various cancers/IV | Marketed |
| Eligard/Leuprorelina | Tolmar (Fort Collins, Colorado, USA) | PEGylated polymeric NPs | Prostate cancer/IV | Marketed |
| Emend/Aprepitant | Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) | Nanocrystal | Anti-emetic/Oral | Marketed |
| Genexol-PM/Paclitaxel | Samyang Biopharm (Seongnam, South Korea) | PEG-PLA polymeric micelles | Various cancers/IV | Marketed |
| Invega sustenna/Paliperidone palmitate | Janssen (Beerse, Belgium) | Nanocrystal | Schizophrenia/IM | Marketed |
| Ivac-MUTANOME/specific mRNAs | BioNTech (Mainz, Germany) | mRNA vaccine | Breast cancer and melanoma/Intranodal | Phase I |
| L-490/Insulin | Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) | Polymeric nanoparticles | Diabetes type I/SC | Phase I |
| Lipotecan/Camptotethin | Taiwan liposome (Taipei, Taiwan) | Polymeric micelles | Various cancers/IV | Phase I/II |
| Marqibo/Vincristine | Talon therapeuticals (Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) | Sphingomyelin -based liposomes | Leukemia and melanoma/IV | Marketed |
| Megace ES/Megestrol | Par Pharmaceuticals (Woodcliff Lake, New Jersey, USA) | Nanocrystal | Anti-anorexic/Oral | Marketed |
| Myocet/Doxorubicin | Teva Pharmaceuticals (Pétah Tiqvà, Israel) | Liposome | Various tumors/IV | Marketed |
| NC-6004/Cisplatine | NanoCarrier Co. (Kashiwa, Chilba, Japan) | Micelle | Lung cancer/IV | Phase I/II |
| Oncaspar/Pegaspargase | Enzon Pharmaceuticals (Farmingdale, New York, USA) | Polymer-protein conjugate | Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)/IM or IV | Marketed |
| Oncoprex/pDNA TUSC2 | GenPrex (Austin, Texas, USA) | Liposomes | Lung cancer/IV | Phase II |
| Onivyde/Irinotecan | Merrimack Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, Massachussets, USA) | PEGylated liposomes | Pancreatic metastatic cancer/IV | Marketed |
| Ontak/Denileukin diftitox | Seragen (Madrid, Spain) | Protein NPs | Various tumors/IV | Marketed |
| Rapamune/Rapamycin | Wyeth/Pfizer (Philadelphia, Penn State, USA) | Nanocrystal | Immunosuppressive/Oral | Marketed |
| Tocosol/Paclitaxel | Oncogenex Technologies (Bothell, Washington, USA) | Nano-emulsion | Various tumors/IV | Marketed |
| Tricor/Fenofibrate | Abbott (Chicago, Illinois, USA) | Nanocrystal | Hypercholesterolemia/Oral | Marketed |
| ---/siRNA PCSK9 synthesis inhibitor | Alnylam/Tekmira (Cambridge, Massachussets, USA) | Lipid NPs | Hypercholesterolemia/IV | Phase I |
| ---/siRNA transthyretin inhibitor | Alnylam/Tekmira (Cambridge, Massachussets, USA) | Lipid NPs | Amyloidosis/IV | Phase II |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fornaguera, C.; García-Celma, M.J. Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm7040012
Fornaguera C, García-Celma MJ. Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2017; 7(4):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm7040012
Chicago/Turabian StyleFornaguera, Cristina, and Maria José García-Celma. 2017. "Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale" Journal of Personalized Medicine 7, no. 4: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm7040012
APA StyleFornaguera, C., & García-Celma, M. J. (2017). Personalized Nanomedicine: A Revolution at the Nanoscale. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 7(4), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm7040012






