Comparison Between the Human-Sourced Ellipsoid Method and Kidney Volumetry Using Artificial Intelligence in Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Correlation Analysis
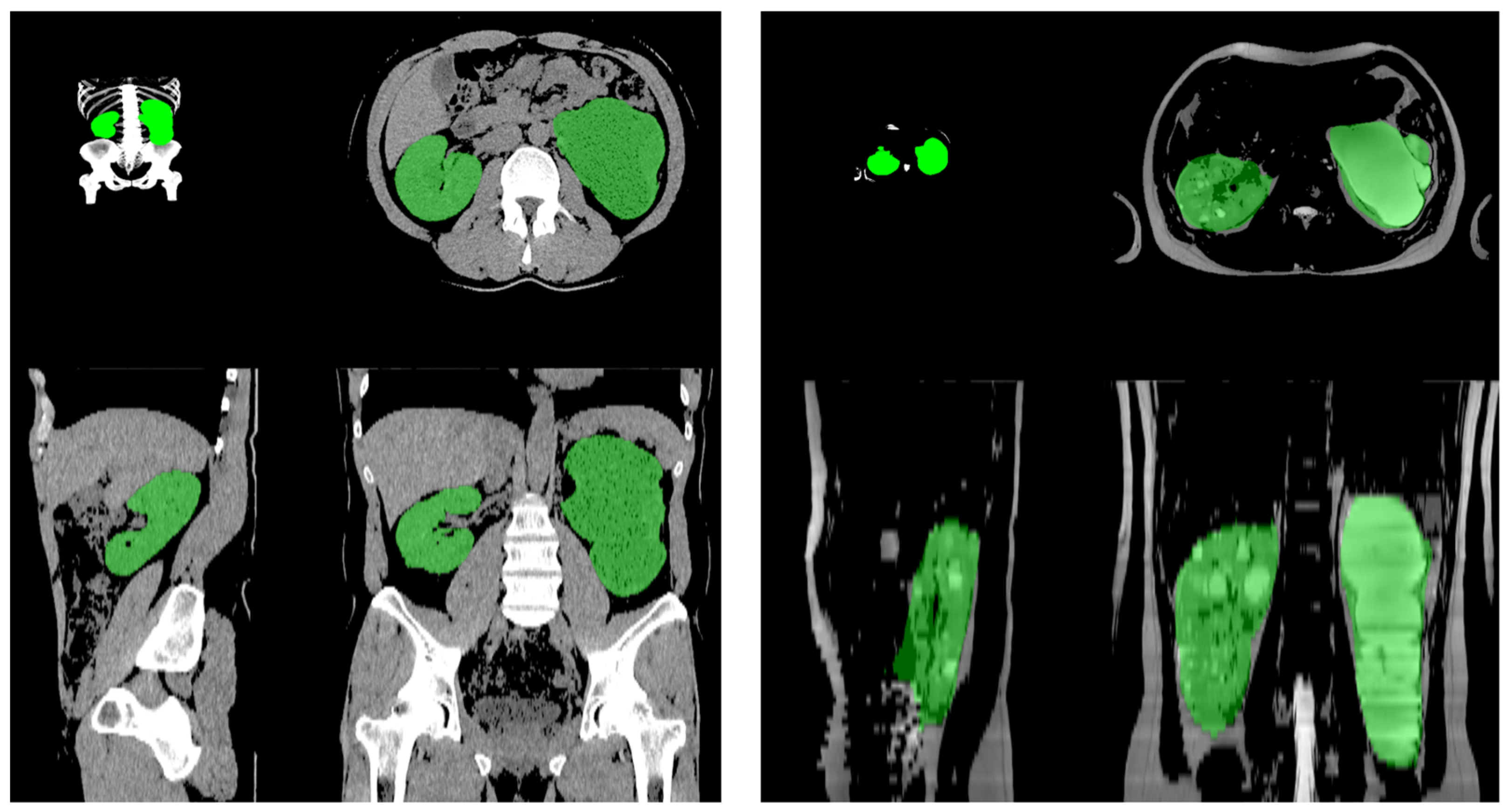
3.3. Performance of the AI-Based Volumetry
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIC | Mayo imaging classification |
| TKV | total kidney volume |
| PKD | polycystic kidney disease |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | computed tomography |
| ICC | intraclass correlation coefficient |
| ADPKD | autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
| htTKV | height-adjusted total kidney volume |
References
- Dalgaard, O.Z. Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys; a follow-up of two hundred and eighty-four patients and their families. AMA Arch Intern. Med. 1958, 102, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.T.; Bhandari, S.K.; Chen, Q.; Malik, F.T.; Willey, C.J.; Reynolds, K.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Sim, J.J. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Prevalence among a Racially Diverse United States Population, 2002 through 2018. Kidney360 2021, 2, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Torres, V.E.; Harris, P.C. Genetic Complexity of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney and Liver Diseases. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.E.; Ahn, C.; Barten, T.R.M.; Brosnahan, G.; Cadnapaphornchai, M.A.; Chapman, A.B.; Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Harris, P.C.; et al. KDIGO 2025 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation, management, and treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): Executive summary. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.K.; Park, H.C.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, K.H. Clinical and genetic characteristics of Korean autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.E.; Harris, P.C.; Pirson, Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 2007, 369, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, Y.; Duriseti, P.; Chebib, F.T. Management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in the era of disease-modifying treatment options. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.U.; Messchendorp, A.L.; Birn, H.; Capasso, G.; Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Devuyst, O.; van Eerde, A.; Guirchoun, P.; Harris, T.; Hoorn, E.J.; et al. An update on the use of tolvaptan for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Consensus statement on behalf of the ERA Working Group on Inherited Kidney Disorders, the European Rare Kidney Disease Reference Network and Polycystic Kidney Disease International. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.; Kline, T.L. Abdominal Imaging in ADPKD: Beyond Total Kidney Volume. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) ADPKD Work Group. KDIGO 2025 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation, Management, and Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD). Kidney Int. 2025, 107, S1–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, J.M.; Gregory, A.V.; Homes, H.L.; Wright, D.E.; Edwards, M.E.; Akkus, Z.; Erickson, B.J.; Kline, T.L. Automated measurement of total kidney volume from 3D ultrasound images of patients affected by polycystic kidney disease and comparison to MR measurements. Abdom. Imaging 2022, 47, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Thomas, R.; Metherall, P.; van Gastel, M.; Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Caroli, A.; Furlano, M.; Demoulin, N.; Devuyst, O.; Winterbottom, J.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Generated Automated Algorithm to Measure Total Kidney Volume in ADPKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irazabal, M.V.; Rangel, L.J.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Osborn, S.L.; Harmon, A.J.; Sundsbak, J.L.; Bae, K.T.; Chapman, A.B.; Grantham, J.J.; Mrug, M.; et al. Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Caroli, A.; Quach, L.V.; Petzold, K.; Bozzetto, M.; Serra, A.L.; Remuzzi, G.; Remuzzi, A. Kidney volume measurement methods for clinical studies on autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, T.L.; Korfiatis, P.; Edwards, M.E.; Warner, J.D.; Irazabal, M.V.; King, B.F.; Torres, V.E.; Erickson, B.J. Automatic total kidney volume measurement on follow-up magnetic resonance images to facilitate monitoring of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease progression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sharbatdaran, A.; He, X.; Zhu, C.; Blumenfeld, J.D.; Rennert, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ramnauth, A.; Shimonov, D.; Chevalier, J.M.; et al. Improved predictions of total kidney volume growth rate in ADPKD using two-parameter least squares fitting. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, S.; Torcitto, A.G.; Marcantoni, C.; Giordano, G.; Campisi, C.; Failla, G.; Saporito, L.; Giunta, R.; Veroux, M.; Foti, P.V.; et al. Calculation of Kidney Volumes with Magnetic Resonance in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Comparison between Methods. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gastel, M.D.A.; Edwards, M.E.; Torres, V.E.; Erickson, B.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Kline, T.L. Automatic Measurement of Kidney and Liver Volumes from MR Images of Patients Affected by Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, M.K.; Min, H.S.; Cho, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, T.Y. Feasibility of artificial intelligence-based decision supporting system in tolvaptan prescription for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2023, 64, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Hong, Y.; Yeon, J.H.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Chae, D.W.; Chung, W.; Ahn, C.; et al. Mayo imaging classification is a good predictor of rapid progress among Korean patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Results from the KNOW-CKD study. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashihara, E.; Nutahara, K.; Okegawa, T.; Tanbo, M.; Hara, H.; Miyazaki, I.; Kobayasi, K.; Nitatori, T. Kidney volume estimations with ellipsoid equations by magnetic resonance imaging in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephron 2015, 129, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allmer, D.M.; Parada Rodriguez, D.; Aigner, C.; Laccone, F.; Nagel, M.; Metz-Schimmerl, S.; Sunder-Plassmann, G. Progression to kidney failure in ADPKD: The PROPKD score underestimates the risk assessed by the Mayo imaging classification. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1470309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckscher, S.; Ihlo, N.A.; Schueler, J.; Kellermeier, F.; Werner, J.M.; Nuebel, B.; Gross, V.; May, M.; Wullich, B.; Kammerl, M.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of renal cyst fluid in advanced ADPKD: Insights from dialysis and transplantation cohorts. Metabolomics 2025, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Akbari, P.; Pourafkari, M.; Iliuta, I.A.; Guiard, E.; Quist, C.F.; Song, X.; Hillier, D.; Khalili, K.; Pei, Y. Prognostic Performance of Kidney Volume Measurement for Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Comparative Study of Ellipsoid vs. Manual Segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoulin, N.; Nicola, V.; Michoux, N.; Gillion, V.; Ho, T.A.; Clerckx, C.; Pirson, Y.; Annet, L. Limited Performance of Estimated Total Kidney Volume for Follow-up of ADPKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Category (Numbers = 32) | Number or Median (min–max) |
|---|---|
| Sex (male) | 18 (56.25%) |
| Age (years) | 56 (31–95) |
| Heights (cm) | 169 (152–186) |
| Weights (kg) | 69 (45–109) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.16 (0.57–4.77) |
| Mayo imaging classification (MIC) (using the ellipsoid method, nephrology professor) (%) | |
| 1A | 4 (12.5%) |
| 1B | 10 (31.25%) |
| 1C | 12 (37.5%) |
| 1D | 5 (15.63%) |
| 1E | 1 (3.13%) |
| Total kidney volume (mL) | 1200.24 (432.19–6984.2) |
| MIC | Nephrology Professor n, (%) | AI Volumetry n, (%) | Trained Clinician n, (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 4 (12.5%) | 3 (9.38%) | 5 (15.6%) |
| 1B | 10 (31.25%) | 10 (31.25%) | 8 (25%) |
| 1C | 12 (37.5%) | 16 (50%) | 10 (31.25%) |
| 1D | 5 (15.63%) | 1 (3.13%) | 7 (21.88%) |
| 1E | 1 (3.13%) | 2 (6.25%) | 2 (6.25%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Lee, Y.R.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, T.Y.; Lee, K.-B. Comparison Between the Human-Sourced Ellipsoid Method and Kidney Volumetry Using Artificial Intelligence in Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080392
Yang J, Lee YR, Hyun YY, Kim HJ, Shin TY, Lee K-B. Comparison Between the Human-Sourced Ellipsoid Method and Kidney Volumetry Using Artificial Intelligence in Polycystic Kidney Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(8):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080392
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jihyun, Young Rae Lee, Young Youl Hyun, Hyun Jung Kim, Tae Young Shin, and Kyu-Beck Lee. 2025. "Comparison Between the Human-Sourced Ellipsoid Method and Kidney Volumetry Using Artificial Intelligence in Polycystic Kidney Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 8: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080392
APA StyleYang, J., Lee, Y. R., Hyun, Y. Y., Kim, H. J., Shin, T. Y., & Lee, K.-B. (2025). Comparison Between the Human-Sourced Ellipsoid Method and Kidney Volumetry Using Artificial Intelligence in Polycystic Kidney Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(8), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080392






