Five-Year Survival After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—Do We Choose the Right Treatment for Each Patient? A Propensity Score Matched Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
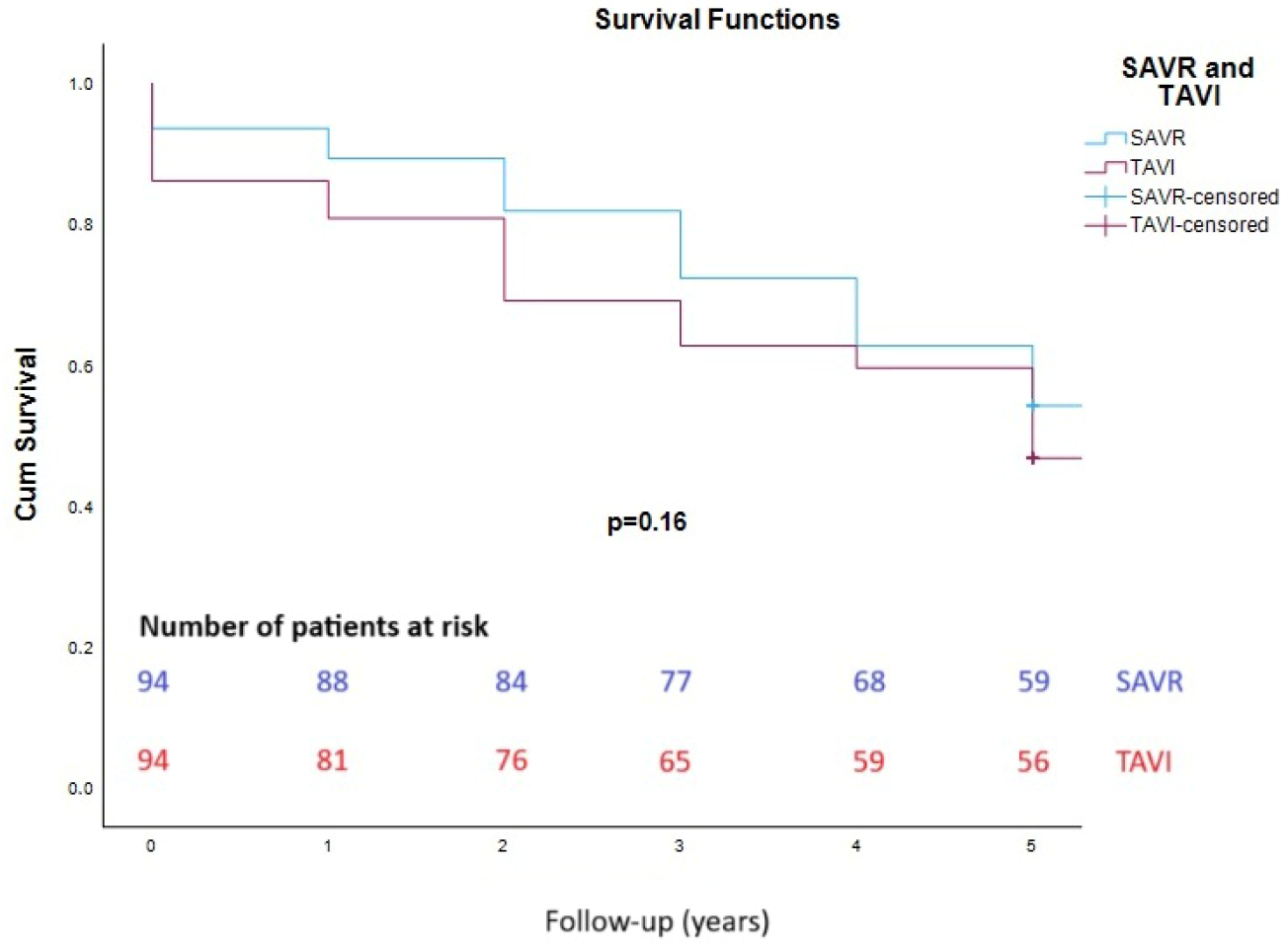
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubois, C.; Adriaenssens, T.; Annemans, L.; Bosmans, J.; Callebaut, B.; Candolfi, P.; Cornelis, K.; Delbaere, A.; Green, M.; Kefer, J.; et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in severe aortic stenosis patients at low surgical mortality risk: A cost-effectiveness analysis in Belgium. Acta Cardiol. 2024, 79, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkasaby, M.H.; Khalefa, B.B.; Yassin, M.N.A.; Alabdallat, Y.J.; Atia, A.; Altobaishat, O.; Omar, I.; Hussein, A. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement for pure aortic regurgitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 33,484 patients. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Blankenberg, S.; Seiffert, M.; Vonthein, R.; Baumgartner, H.; Bleiziffer, S.; Borger, M.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Clemmensen, P.; Cremer, J.; Czerny, M.; et al. Transcatheter or Surgical Treatment of Aortic-Valve Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.K.; Elder, D.; Nguyen, M.T.H.; Turner, L.; Doyle, M.; Woldendorp, K.; Seco, M.; Law, C.K.; Wilson, M.K.; Keech, A.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement for Aortic Stenosis (SAVR): A Cost-Comparison Study. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, S.J.; Salmasi, M.Y.; Zientara, A.; Roussin, I.; Quarto, C.; Asimakopoulos, G. Perceval sutureless bioprosthesis versus Perimount sutured bioprosthesis for aortic valve replacement in patients with aortic stenosis: A retrospective, propensity-matched study. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mack, M.J.; Leon, M.B.; Thourani, V.H.; Pibarot, P.; Hahn, R.T.; Genereux, P.; Kodali, S.K.; Kapadia, S.R.; Cohen, D.J.; Pocock, S.J.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement in Low-Risk Patients at Five Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyregod, H.G.H.; Jørgensen, T.H.; Ihlemann, N.; Steinbrüchel, D.A.; Nissen, H.; Kjeldsen, B.J.; Petursson, P.; De Backer, O.; Olsen, P.S.; Søndergaard, L. Transcatheter or surgical aortic valve implantation: 10-year outcomes of the NOTION trial. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barili, F.; Brophy, J.M.; Ronco, D.; Myers, P.O.; Uva, M.S.; Almeida, R.M.; Marin-Cuartas, M.; Anselmi, A.; Tomasi, J.; Verhoye, J.P.; et al. Risk of Bias in Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Transcatheter and Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open. 2023, 6, e2249321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Swift, S.L.; Puehler, T.; Misso, K.; Lang, S.H.; Forbes, C.; Kleijnen, J.; Danner, M.; Kuhn, C.; Haneya, A.; Seoudy, H.; et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e054222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Witberg, G.; Lador, A.; Yahav, D.; Kornowski, R. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients at low surgical risk: A meta-analysis of randomized trials and propensity score matched observational studies. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 92, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Hari, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Kuno, T.; Ando, T.; ALICE (All-Literature Investigation of Cardiovascular Evidence) Group. A meta-analysis of ≥5-year mortality after transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensminger, S.; Fujita, B.; Bauer, T.; Möllmann, H.; Beckmann, A.; Bekeredjian, R.; Bleiziffer, S.; Landwehr, S.; Hamm, C.W.; Mohr, F.W.; et al. Rapid Deployment Versus Conventional Bioprosthetic Valve Replacement for Aortic Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 727–800, Erratum in Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 61, 964; Erratum in Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Writing Committee Members; Otto, C.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P., 3rd; Gentile, F.; Jneid, H.; Krieger, E.V.; Mack, M.; et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021, 143, e72–e227, Erratum in Circulation 2021, 143, e229; Erratum in Circulation 2023, 148, e8; Erratum in Circulation 2023, 148, e185; Erratum in Circulation 2024, 150, e267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Sample (N = 667) | Propensity Score Matched Sample (N = 188) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI (N = 326) | SAVR (N = 341) | p | TAVI (N = 94) | SAVR (N = 94) | p | |
| Age, years old, (SD) | 81.0 (6.5) | 70.6 (10.0) | <0.001 ‡ | 77.5 (6.6) | 76.6 (6.5) | 0.35 ‡ |
| Sex, N (%) | ||||||
| Female | 146 (44.8) | 141 (41.3) | 0.37 + | 48 (51.1) | 48 (51.1) | 1.00 + |
| Male | 180 (55.2) | 200 (58.7) | 46 (48.9) | 46 (48.9) | ||
| Euroscore II, %, (SD) | 6.48 (4.86) | 1.68 (1.29) | <0.001 ‡ | 3.31 (1.88) | 3.0 (1.84) | 0.25 ‡ |
| Total Sample (N = 667) | Propensity Score Matched Sample (N = 188) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI (N = 326) | SAVR (N = 341) | p | TAVI (N = 94) | SAVR (N = 94) | p | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Weight, kgr, (SD) | 73.3 (13.6) | 80.7 (16.7) | <0.001 ‡ | 75.7 (15.7) | 76.6 (17) | 0.73 ‡ |
| Prosthetic aortic valve size, mm, (SD) | 27.5 (3.0) | 21.4 (5.6) | <0.001 ‡ | 27.1 (2.9) | 20.9 (2.1) | <0.001 ‡ |
| Preoperative LVEF, n (%) | ||||||
| >50% | 234 (71.7) | 267 (78.3) | 0.01 + | 85 (90.4) | 67 (71.3) | 0.004 ++ |
| 30–49% | 77 (23.6) | 70 (20.5) | 6 (6.4) | 25 (26.6) | ||
| <29% | 15 (4.7) | 4 (1.2) | 3 (3.2) | 2 (2.1) | ||
| Pulmonary artery hypertension, n (%) | 127 (39.0) | 26 (7.6) | <0.001 + | 28 (29.8) | 15 (16.0) | 0.02 + |
| Peripheral artery disease, n (%) | 88 (27.0) | 15 (4.4) | <0.001 + | 17 (18.1) | 6 (6.4) | 0.01 + |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, n (%) | 92 (28.2) | 89 (26.1) | 0.53 + | 25 (26.6) | 26 (27.7) | 0.87 + |
| Preoperative renal failure, n (%) | 38 (11.7) | 38 (11.1) | 0.83 + | 7 (7.4) | 15 (16) | 0.11 + |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 64 (19.6) | 77 (22.6) | 0.35 + | 16 (17.0) | 25 (26.6) | 0.11 + |
| Carotid disease (>70%), n (%) | 81 (25.2) | 6 (1.8) | <0.001 + | 16 (17.0) | 2 (2.1) | 0.001 + |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 226 (70.4) | 253 (74.2) | 0.27 + | 58 (61.7) | 69 (73.4) | 0.08 + |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 138 (43.0) | 191 (56.0) | 0.001 + | 33 (35.1) | 64 (68.1) | <0.001 + |
| Total Sample (N = 667) | Propensity Score Matched Sample (N = 188) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI (N = 326) | SAVR (N = 341) | p | TAVI (N = 94) | SAVR (N = 94) | p | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| Permanent cerebrovascular accident, n (%) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 1.00 ++ | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - ‡ |
| Transient ischemic attack, n (%) | 7 (2.1) | 2 (0.6) | 0.10 ++ | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - ‡ |
| Major bleeding (VARC-2), n (%) | 54 (16.6) | 166 (48.7) | <0.001 + | 14 (14.9) | 44 (46.8) | <0.001 + |
| Surgical intervention, n (%) | 14 (4.3) | N/A | - ‡ | 3 (3.2) | N/A | - ‡ |
| PPM implantation, n (%) | 61 (18.7) | 7 (2.1) | <0.001 + | 20 (21.3) | 1 (1.1) | <0.001 + |
| Other complications | 95 (29.1) | 144 (42.2) | <0.001 + | 23 (24.5) | 34 (36.2) | 0.08 + |
| Total Sample (N = 667) | Propensity Score Matched Sample (N = 188) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI (N = 326) | SAVR (N = 341) | p | TAVI (N = 94) | SAVR (N = 94) | p | |
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |||
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 7 (2.1) | 4 (1.2) | 0.32 + | 0 (0) | 2(2.1) | 0.49 ++ |
| Degree of postoperative prosthetic aortic valve regurgitation, n (%) | ||||||
| 0 | 49 (24.9) | 338 (99.1) | <0.001 ++ | 14 (28.6) | 91 (96.8) | <0.001 ++ |
| 1 | 120 (60.9) | 3 (0.9) | 28 (57.1) | 3 (3.2) | ||
| 2 | 27 (13.7) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 3 | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 4 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Degree of postoperative prosthetic aortic valve regurgitation, n (%) | ||||||
| 0–1 | 169 (85.9) | 341 (100.0) | <0.001 + | 42 (85.7) | 94 (100.0) | <0.001 + |
| 2–4 | 28 (14.1) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Total Sample (N = 667) | Propensity Score Matched Sample (N = 188) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI (N = 326) | SAVR (N = 341) | p ‡‡ | TAVI (N = 94) | SAVR (N = 94) | p ‡‡ | |
| Length of ICU stay, days, (IQR) | 2 (2–3) | 1.3 (1.3–2.0) | <0.001 | 2 (2–3) | 1.7 (1.3–3.0) | 0.08 |
| Length of in-hospital stay, days, (IQR) | 7 (6–9) | 6 (6–7) | <0.001 | 7 (6–9) | 7 (6–8) | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samanidis, G.; Roussakis, A.; Katsaridis, S.; Liaretidou, E.; Kefalidi, E.; Falara, A.; Koziakas, I.G.; Nenekidis, I.; Kosmas, I.; Leontiadis, E.; et al. Five-Year Survival After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—Do We Choose the Right Treatment for Each Patient? A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080391
Samanidis G, Roussakis A, Katsaridis S, Liaretidou E, Kefalidi E, Falara A, Koziakas IG, Nenekidis I, Kosmas I, Leontiadis E, et al. Five-Year Survival After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—Do We Choose the Right Treatment for Each Patient? A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(8):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080391
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamanidis, George, Antonios Roussakis, Sotirios Katsaridis, Efthymia Liaretidou, Eirini Kefalidi, Areti Falara, Ilias Georgios Koziakas, Ioannis Nenekidis, Ilias Kosmas, Evangelos Leontiadis, and et al. 2025. "Five-Year Survival After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—Do We Choose the Right Treatment for Each Patient? A Propensity Score Matched Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 8: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080391
APA StyleSamanidis, G., Roussakis, A., Katsaridis, S., Liaretidou, E., Kefalidi, E., Falara, A., Koziakas, I. G., Nenekidis, I., Kosmas, I., Leontiadis, E., Voudris, V., Iakovou, I., & Perreas, K. (2025). Five-Year Survival After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—Do We Choose the Right Treatment for Each Patient? A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(8), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080391







