Exploring the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance, Liver Health, and Restrictive Lung Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Lung Function Testing and Metabolic Parameters
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
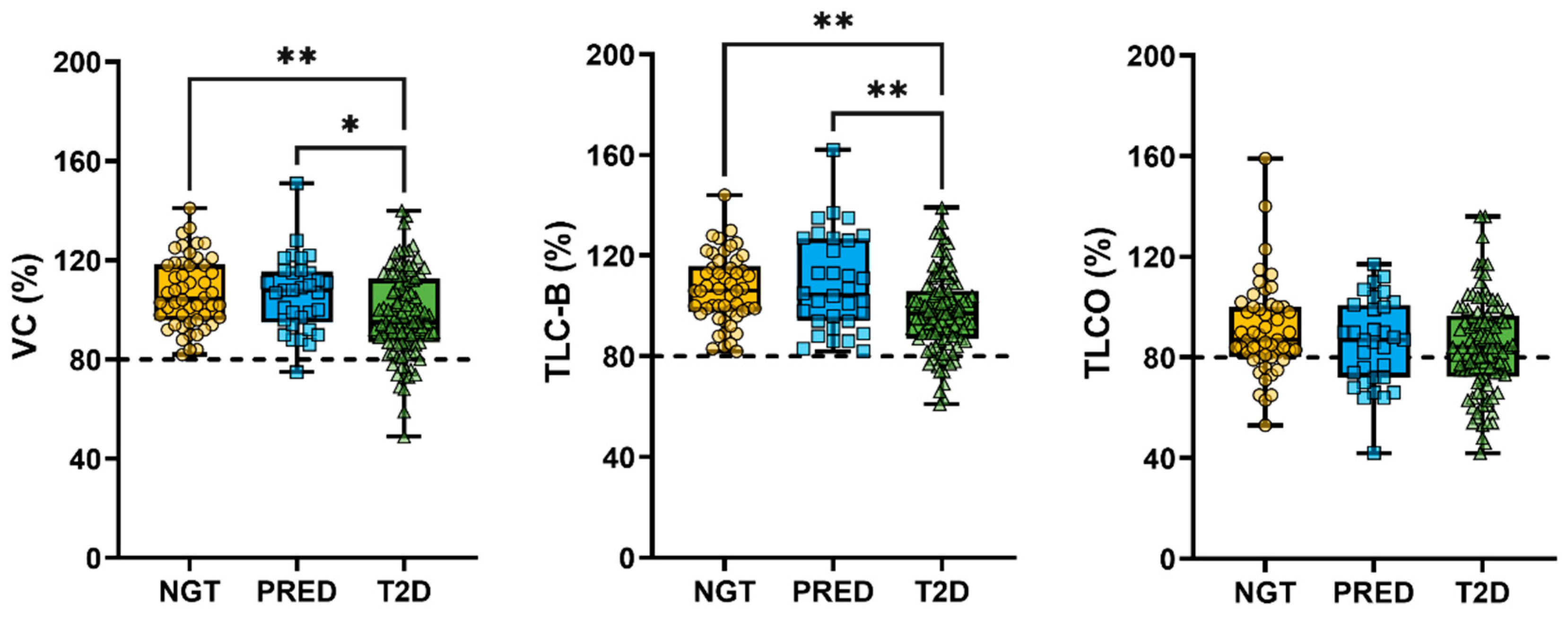
3.2. Association Between Metabolic Markers and Lung Function
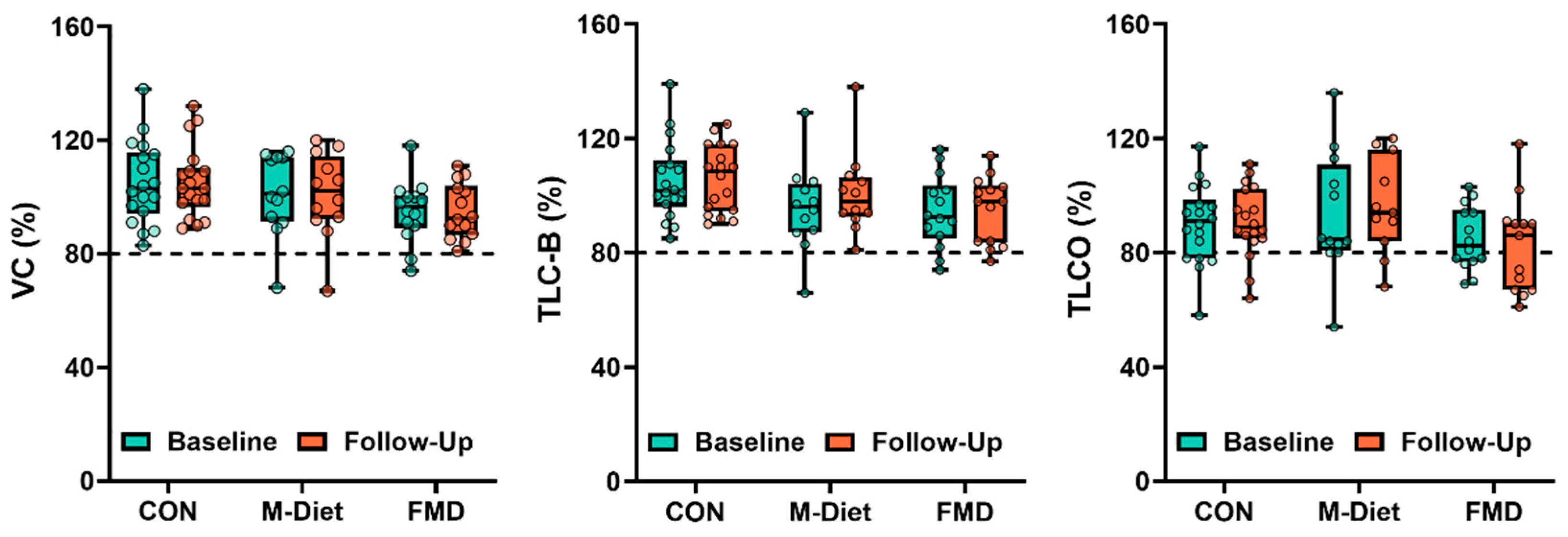
3.3. Effects of Dietary Intervention on RLD
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, O.L.; Krishnan, J.A.; Glick, S.; Smith, L.J. Systematic Review of the Association between Lung Function and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xue, Q.; Miao, L.; Cai, L. Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Possible Diabetic Complication. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, S.; Groener, J.B.; Kender, Z.; Fleming, T.; Brune, M.; Riedinger, C.; Volk, N.; Herpel, E.; Pesta, D.; Szendrödi, J.; et al. Breathlessness and Restrictive Lung Disease: An Important Diabetes-Related Feature in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Respiration 2018, 96, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowska, S.; Binienda, A.; Jabłkowski, M.; Szemraj, J.; Czarny, P. The Interplay between Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Base Excision Repair and Metabolic Syndrome in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyave-Ospina, J.C.; Wu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Moshage, H. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Implications for Prevention and Therapy. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Maranduca, M.A.; Ouatu, A.; Floria, M. The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3920196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Sehrawat, A.; Mishra, J.; Sidhu, I.S.; Navik, U.; Khullar, N.; Kumar, S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Oxidative Stress in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications: Current Therapeutics Strategies and Future Perspectives. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 184, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobârcă, D.; Cătoi, A.F.; Gavrilaș, L.; Banc, R.; Miere, D.; Filip, L. Natural Bioactive Compounds in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic (Dysfunction)-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.A.; Knuiman, M.; Kendall, P.; Grange, V.; Davis, T.M.E. Fremantle Diabetes Study Glycemic Exposure Is Associated with Reduced Pulmonary Function in Type 2 Diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgiarini, L.A.; Kretzmann, N.A.; Porawski, M.; Dias, A.S.; Marroni, N.A.P. Experimental Diabetes Mellitus: Oxidative Stress and Changes in Lung Structure. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, S.; Kumar, V.; Kender, Z.; Han, Z.; Fleming, T.; Herzig, S.; Nawroth, P.P. Diabetic Pneumopathy-A New Diabetes-Associated Complication: Mechanisms, Consequences and Treatment Considerations. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 765201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, K.R.; Panth, N.; Manandhar, B.; Singh, S.K.; Gupta, G.; Wich, P.R.; Nammi, S.; MacLoughlin, R.; Adams, J.; Warkiani, M.E.; et al. Attenuation of Cigarette-Smoke-Induced Oxidative Stress, Senescence, and Inflammation by Berberine-Loaded Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: In Vitro Study in 16HBE and RAW264.7 Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-S.; Park, J.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, M.-Y. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Formation: A Concise Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-S.; Park, K.-H.; Park, J.-M.; Jeong, H.; Kim, B.; Jeon, J.S.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, K.; Lee, M.-Y. Short-Term Inhalation Exposure to Cigarette Smoke Induces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Lungs without Systemic Oxidative Stress in Mice. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 40, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.-R.; Jang, J.; Park, S.-M.; Ryu, S.M.; Cho, S.-J.; Yang, S.-R. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Respiratory Response: Insights into Cellular Processes and Biomarkers. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, T.; Deng, Z.; Xie, J. Cigarette Smoke Promotes Interleukin-8 Production in Alveolar Macrophages Through the Reactive Oxygen Species/Stromal Interaction Molecule 1/Ca2+ Axis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 733650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celli, B.R.; Christenson, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Han, M.K.; van den Berge, M.; Criner, G.J.; Soler, X.; Djandji, M.; Radwan, A.; Rowe, P.J.; et al. Current Smoker: A Clinical COPD Phenotype Affecting Disease Progression and Response to Therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 211, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Jiang, X.; Qin, R.; Ding, Y.; Yu, C.; Xu, X.; Song, C. Effect of Smoking on Lung Function Decline in a Retrospective Study of a Health Examination Population in Chinese Males. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 843162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyunoya, T.; Mebratu, Y.; Contreras, A.; Delgado, M.; Chand, H.S.; Tesfaigzi, Y. Molecular Processes That Drive Cigarette Smoke-Induced Epithelial Cell Fate of the Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, I.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Park, J.-S. The Association of Normal Range Glycated Hemoglobin with Restrictive Lung Pattern in the General Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Wuyts, W.; Bonella, F.; Corte, T.J.; Kopf, S.; Weycker, D.; Kirchgaessler, K.-U.; Ryerson, C.J. Metformin Does Not Affect Clinically Relevant Outcomes in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respiration 2018, 96, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.-C.; Punjabi, N.M.; Wang, N.-Y.; Pankow, J.S.; Duncan, B.B.; Cox, C.E.; Selvin, E.; Brancati, F.L. Cross-Sectional and Prospective Study of Lung Function in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Borst, B.; Gosker, H.R.; Zeegers, M.P.; Schols, A.M.W.J. Pulmonary Function in Diabetes: A Metaanalysis. Chest 2010, 138, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Hong, N.; Kim, K.-W.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, M.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.-S.; Lee, B.-W. The Effectiveness of Intermittent Fasting to Reduce Body Mass Index and Glucose Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thodis, T.; Ward, G.; Trost, N.; Hofferberth, S.; O’Dea, K.; Desmond, P.V.; Johnson, N.A.; Wilson, A.M. The Mediterranean Diet Improves Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, S.A.; Hodson, L. Managing NAFLD in Type 2 Diabetes: The Effect of Lifestyle Interventions, a Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1381–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomah, S.; Salah, T.; Al-Badri, M.; Dhaver, S.; Gardner, H.; Tasabehji, M.W.; Hamdy, O. Multidisciplinary Intensive Lifestyle Intervention Improves Markers of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity: A Retrospective Matched-Cohort Study. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorell, E.; Otten, J.; Stomby, A.; Ryberg, M.; Waling, M.; Hauksson, J.; Svensson, M.; Olsson, T. Improved Peripheral and Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity after Lifestyle Interventions in Type 2 Diabetes Is Associated with Specific Metabolomic and Lipidomic Signatures in Skeletal Muscle and Plasma. Metabolites 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, E.; Negri, C.; Targher, G.; Faccioli, N.; Lanza, M.; Zoppini, G.; Zanolin, E.; Schena, F.; Bonora, E.; Moghetti, P. Both Resistance Training and Aerobic Training Reduce Hepatic Fat Content in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (the RAED2 Randomized Trial). Hepatology 2013, 58, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, S.; Choi, I.Y.; Wei, M.; Cheng, C.W.; Sedrakyan, S.; Navarrete, G.; Dubeau, L.; Yap, L.P.; Park, R.; Vinciguerra, M.; et al. A Periodic Diet That Mimics Fasting Promotes Multi-System Regeneration, Enhanced Cognitive Performance, and Healthspan. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaj, A.; Kopf, S.; von Rauchhaupt, E.; Kliemank, E.; Brune, M.; Kender, Z.; Bartl, H.; Cortizo, F.G.; Klepac, K.; Han, Z.; et al. Six-Month Periodic Fasting in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Burg, E.L.; Schoonakker, M.P.; van Peet, P.G.; le Cessie, S.; Numans, M.E.; Pijl, H.; Lamb, H.J. A Fasting-Mimicking Diet Programme Reduces Liver Fat and Liver Inflammation/Fibrosis Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 47, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kender, Z.; Groener, J.B.; Jende, J.M.E.; Kurz, F.T.; Fleming, T.; Sulaj, A.; Schuh-Hofer, S.; Treede, R.; Bendszus, M.; Szendroedi, J.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathy Is a Generalized Phenomenon with Impact on Hand Functional Performance and Quality of Life. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 3081–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kender, Z.; Jende, J.M.E.; Kurz, F.T.; Tsilingiris, D.; Schimpfle, L.; Sulaj, A.; von Rauchhaupt, E.; Bartl, H.; Mooshage, C.; Göpfert, J.; et al. Sciatic Nerve Fractional Anisotropy and Neurofilament Light Chain Protein Are Related to Sensorimotor Deficit of the Upper and Lower Limbs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol 2023, 14, 1046690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Stanojevic, S.; Cole, T.J.; Baur, X.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.H.; Enright, P.L.; Hankinson, J.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; et al. Multi-Ethnic Reference Values for Spirometry for the 3-95-Yr Age Range: The Global Lung Function 2012 Equations. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.D.; Latzin, P.; Verbanck, S.; Hall, G.L.; Horsley, A.; Gappa, M.; Thamrin, C.; Arets, H.G.M.; Aurora, P.; Fuchs, S.I.; et al. Consensus Statement for Inert Gas Washout Measurement Using Multiple- and Single- Breath Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Viegi, G.; Brusasco, V.; Crapo, R.O.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; Hankinson, J.; et al. Interpretative Strategies for Lung Function Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 948–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, T.; Jubran, A.; Tobin, M.J. Dyspnea and Decreased Variability of Breathing in Patients with Restrictive Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R.; Hermans, M.P. Correct Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) Evaluation Uses the Computer Program. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 2191–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinson, T.; Buchanan, R.M.; Byrne, C.D. Noninvasive Serum Biomarkers for Liver Fibrosis in NAFLD: Current and Future. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S157–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.-F.; Chan, M.K.-K.; Li, J.S.-F.; Chan, A.S.-W.; Tang, P.C.-T.; Leung, K.-T.; To, K.-F.; Lan, H.-Y.; Tang, P.M.-K. TGF-β Signaling: From Tissue Fibrosis to Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungratanawanich, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Essa, M.M.; Song, B.-J. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) and Other Adducts in Aging-Related Diseases and Alcohol-Mediated Tissue Injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Aragón-Herrera, A.; Moraña-Fernández, S.; Anido-Varela, L.; Tarazón, E.; Roselló-Lletí, E.; Portolés, M.; Moscoso, I.; Gualillo, O.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; et al. Adipokines and Inflammation: Focus on Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, K.; Zoltan, K.; Alba, S.; Manuel, B.; Elisabeth, K.; Dimitrios, T.; Jan, B.G.; Maik, B.; Khurrum, S.; Berend, I.; et al. Elevated Markers of DNA Damage and Senescence Are Associated with the Progression of Albuminuria and Restrictive Lung Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, R.; Johnston, K.L.; Collins, A.L.; Robertson, M.D. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgat-Seon, Y.; Peters, C.M.; Sheel, A.W. Sex-Differences in the Human Respiratory System and Their Impact on Resting Pulmonary Function and the Integrative Response to Exercise. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2018, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, T.M.; Muiser, S.; Kraft, M.; Siddiqui, S.; Fabbri, L.M.; Rabe, K.F.; Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Singh, D.; van der Molen, T.; et al. Sex Differences in Asthma Control, Lung Function and Exacerbations: The ATLANTIS Study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2024, 11, e002316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beulens, J.W.J.; Reichelt, F.; Remmelzwaal, S.; Rutters, F.; Strooij, B.; Harms, P.; de Vries, R.; Blom, M.T.; Stronks, K.; Muilwijk, M. Type 2 Diabetes Complications in Ethnic Minority Compared with European Host Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e004345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | NGT | PRED | T2D | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants | 50 | 33 | 101 | |
| Age (years) | 51.2 ± 7.4 | 59.9 ± 11.8 | 66.8 ± 8.0 ****/°°° | #### |
| Sex (male/female) | 21/29 | 18/15 | 68/33 | # |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.6 (24.1–30.8) | 27.8 (24.7–33.6) | 29.5 (26.0–32.9) * | # |
| Smoking (%) | 3 (6.0%) | 2 (6.1%) | 6 (5.9%) | |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | – | – | 13.0 (8.0–20.0) | |
| Metabolic Markers | ||||
| HbA1c (%) | 5.4 (4.2–5.7) | 5.7 (5.3–6.0) | 7.0 (6.5–8.1) ****/°°°° | #### |
| HOMA2-IR | 1.3 (1.1–1.7) | 1.8 (1.4–2.7) ** | 2.4 (1.7–3.6) **** | #### |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 93.9 (88.1–99.4) | 90.2 (84.0–106.1) | 89.7 (74.2–97.8) | |
| uAlb/Cre (mg/g) | 5.6 (3.4–10.3) | 5.6 (3.3–11.3) | 17.7 (7.2–45.0) ****/°°°° | #### |
| Liver Markers | ||||
| NAFLD Score | –2.2 ± 1.0 | –1.0 ± 1.2 *** | –0.4 ± 1.2 ****/° | #### |
| Fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4) | 1.1 (0.8–1.4) | 1.0 (0.7–1.5) | 1.3 (1.0–1.7) * | ## |
| Fatty liver index (FLI) | 38.5 (20.8–71.0) | 62.3 (28.8–91.0) | 79.6 (52.9–93.3) **** | #### |
| Lung Function | ||||
| VC (% predicted) | 104.5 (95.8–118.3) | 108.0 (95.0–115.5) | 95.0 (87.0–112.5) ** | ## |
| TLC-B (% predicted) | 106.0 (97.8–115.8) | 104.5 (94.0–126.8) | 97.0 (87.0–106.0) **/° | ### |
| TLCO (% predicted) | 87.0 (80.0–100.0) | 87.0 (72.0–100.8) | 84.0 (72.3–96.8) | |
| RLD (%) | 13 (26.0%) | 12 (38.7%) | 48 (48.0%) | # |
| Pulmonary Conditions | ||||
| COPD (%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (3.0%) | 3 (3.0%) | |
| Asthma (%) | 9 (18.0%) | 6 (18.2%) | 9 (8.9%) | |
| OSAS (%) | 3 (6.0%) | 1 (3.0%) | 11 (10.9%) | |
| CPAP therapy (%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (9.9%) | |
| Diabetes-Related Complications | ||||
| Cardiovascular disease (%) | 12 (24.5%) | 14 (43.8%) | 86 (85.2%) | #### |
| Nephropathy (%) | 3 (6.1%) | 3 (9.1%) | 39 (38.6%) | #### |
| Neuropathy (%) | 2 (4.0%) | 6 (18.8%) | 50 (51.6%) | #### |
| Medication Use | ||||
| Statin (%) | 6 (12.0%) | 4 (12.1%) | 64 (63.4%) | #### |
| Oral antidiabetics (%) | – | – | 78 (77.2%) | |
| Insulin (%) | – | – | 28 (27.7%) | |
| Diet only/no meds (%) | – | – | 18 (17.8%) | |
| Beta-blocker (%) | 5 (10.2%) | 5 (16.1%) | 41 (41.0%) | #### |
| Anticholinergics (%) | 2 (4.1%) | 1 (3.1%) | 4 (4.1%) | |
| Beta2-antagonists (%) | 4 (8.2%) | 3 (9.4%) | 9 (9.2%) | |
| Corticoids (%) | 4 (8.2%) | 2 (6.3%) | 6 (6.1%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roshan, M.; Mudrack, C.; Sulaj, A.; von Rauchhaupt, E.; Fleming, T.; Schimpfle, L.; Seebauer, L.; Flegka, V.; Longo, V.D.; Kliemank, E.; et al. Exploring the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance, Liver Health, and Restrictive Lung Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080340
Roshan M, Mudrack C, Sulaj A, von Rauchhaupt E, Fleming T, Schimpfle L, Seebauer L, Flegka V, Longo VD, Kliemank E, et al. Exploring the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance, Liver Health, and Restrictive Lung Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(8):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080340
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoshan, Mani, Christian Mudrack, Alba Sulaj, Ekaterina von Rauchhaupt, Thomas Fleming, Lukas Schimpfle, Lukas Seebauer, Viktoria Flegka, Valter D. Longo, Elisabeth Kliemank, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance, Liver Health, and Restrictive Lung Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 8: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080340
APA StyleRoshan, M., Mudrack, C., Sulaj, A., von Rauchhaupt, E., Fleming, T., Schimpfle, L., Seebauer, L., Flegka, V., Longo, V. D., Kliemank, E., Herzig, S., Hohneck, A., Kender, Z., Szendroedi, J., & Kopf, S. (2025). Exploring the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance, Liver Health, and Restrictive Lung Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(8), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080340







