Simultaneous Evaluation of Shear Wave Elastography and C-Peptide Index for Predicting Need of Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
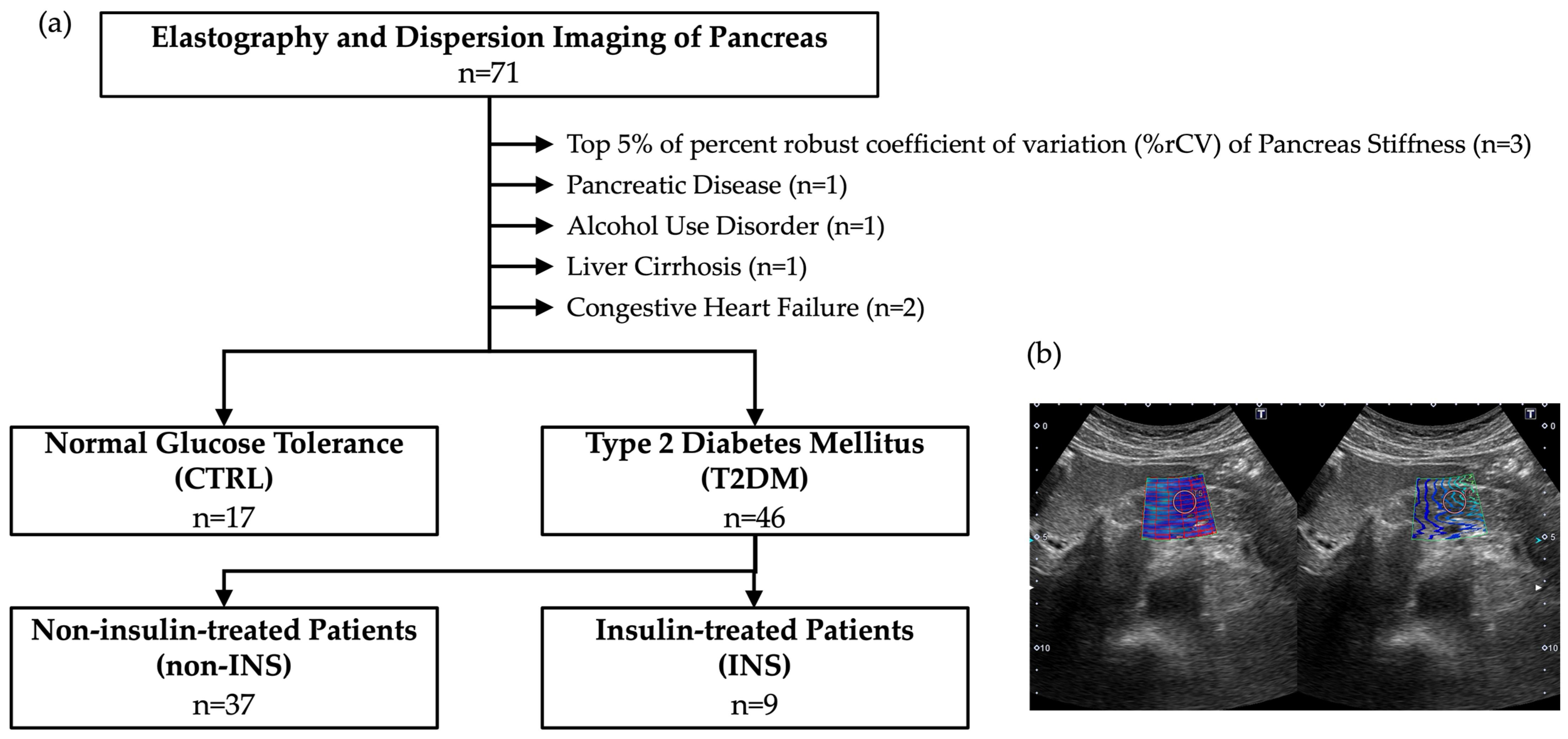
2. Methods and Datasets
3. Results
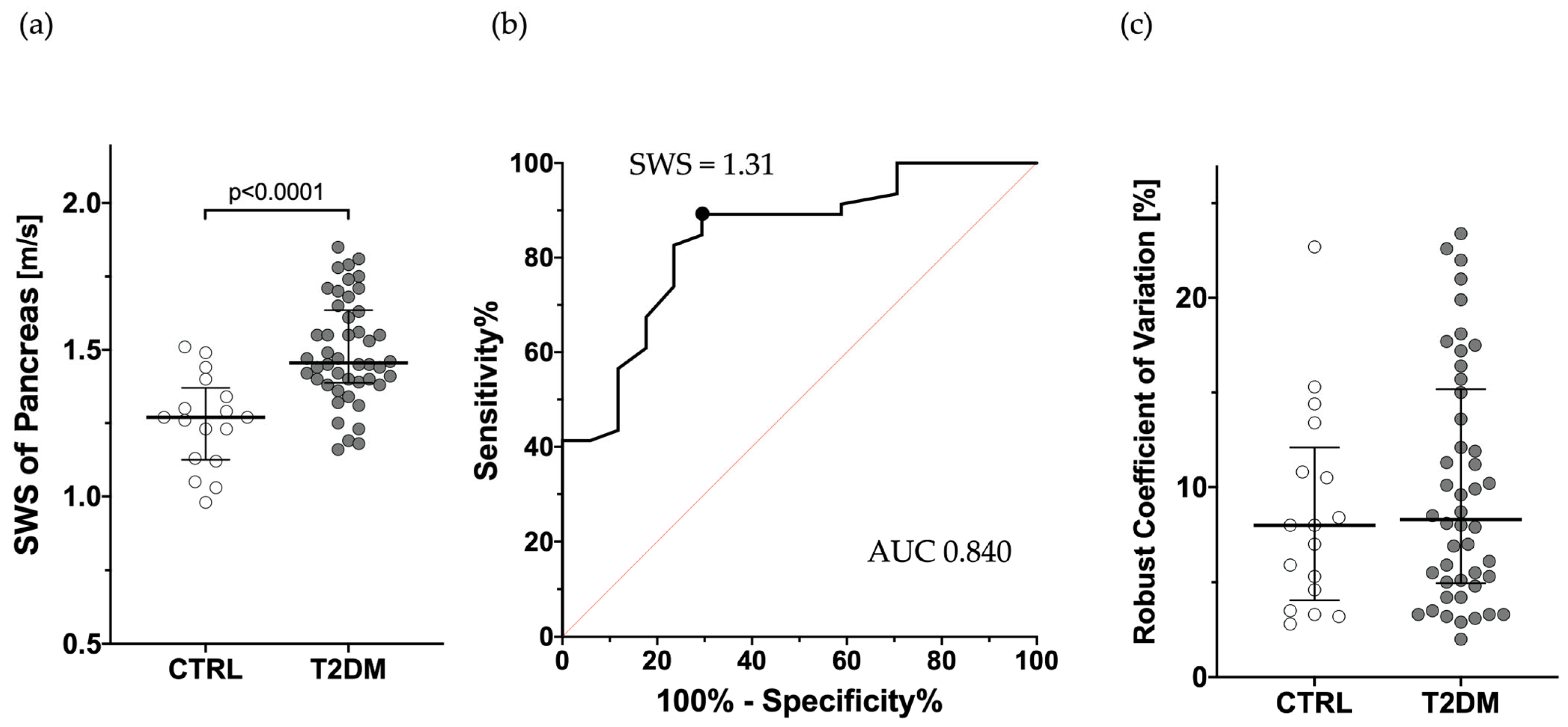
3.1. Comparison of SWS Between T2DM and CTRL
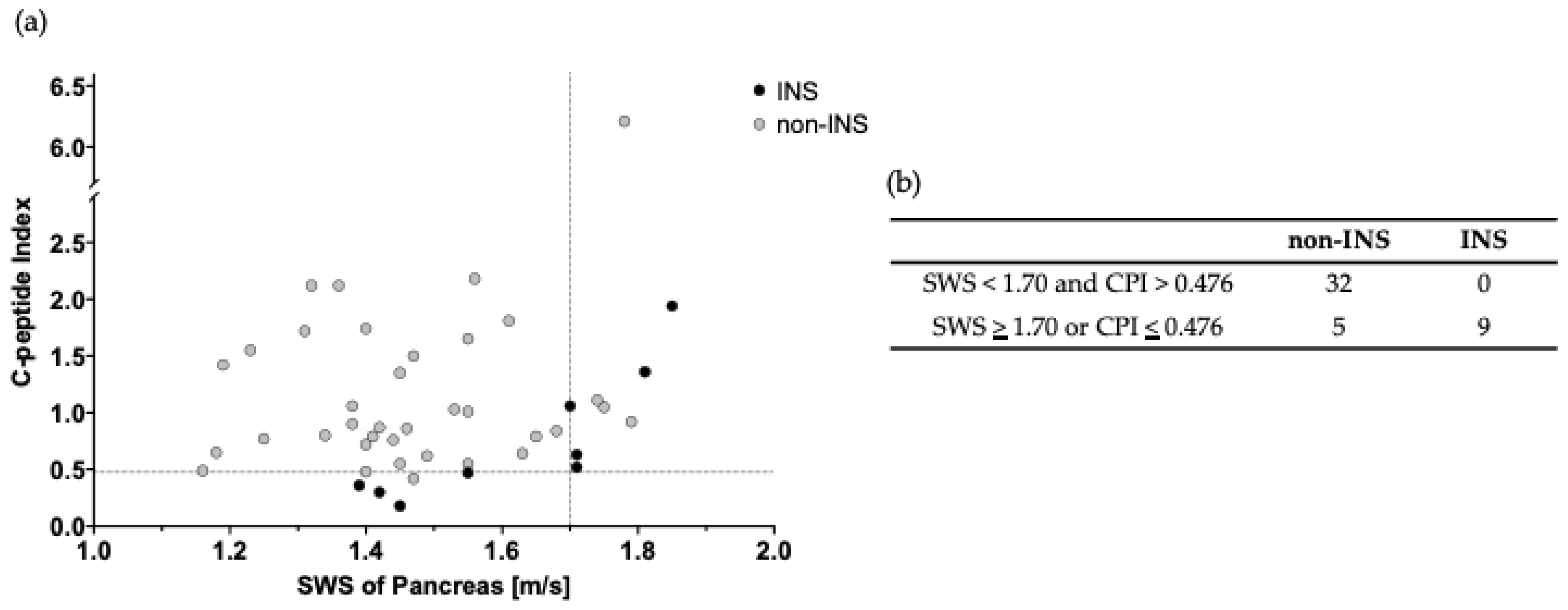
3.2. Comparison of SWS, DS, and CPI in Discriminating INS from Non-INS Patients
3.3. Usefulness of Combined Use of SWS and CPI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| CPI | C-peptide index |
| SWE | shear wave elastography |
| SWD | shear wave dispersion |
| SWS | shear wave speed |
| DS | dispersion slope |
| %rCV | robust coefficients of variation |
| CTRL | control subjects without impaired glucose tolerance |
| INS | patients receiving regular insulin |
| non-INS | patients not receiving regular insulin |
References
- Bouchi, R.; Kondo, T.; Ohta, Y.; Goto, A.; Tanaka, D.; Satoh, H.; Yabe, D.; Nishimura, R.; Harada, N.; Kamiya, H.; et al. A consensus statement from the Japan Diabetes Society (JDS): A proposed algorithm for pharmacotherapy in people with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, J.; Visentin, R.; Dalla Man, C. Smart Algorithms for Efficient Insulin Therapy Initiation in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: An in Silico Study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2024, 19322968241245930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kawamura, M.; Watanabe, T.; Abe, M.; Chin, R.; Miyazaki, S.; Hirata, Y. Indices of urinary and serum C-peptide corrected with fasting plasma glucose for decision-making of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes-validation and comparison. J. Jpn. Diabetes Soc. 2008, 51, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Enkaku, A.; Chujo, D.; Kamigishi, M.; Inagawa, S.; Matsukoshi, S.; Sakai, W.; Takikawa, A.; Fujisaka, S.; Tobe, K. Short-term recovery of insulin secretion in response to a meal is associated with future glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, Y.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Itoh, T.; Sasaki, T.; Mori, S.; Kubo, M.; Takenouchi, H.; et al. C-peptide index at 2 h post-meal is a useful predictor of endogenous insulin secretory capacity and withdrawal from insulin therapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, N.; Younes, N.; Ghosh, A.; Albu, J.; Cohen, R.M.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Diaz, E.; Sayyed Kassem, L.; Luchsinger, J.A.; McGill, J.B.; et al. Longitudinal Effects of Glucose-Lowering Medications on β-Cell Responses and Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes: The GRADE Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Bamber, J.; Berzigotti, A.; Bota, S.; Cantisani, V.; Castera, L.; Cosgrove, D.; Ferraioli, G.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Gilja, O.H.; et al. EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Liver Ultrasound Elastography, Update 2017 (Long Version). Ultraschall Med. 2017, 38, e16–e47. [Google Scholar]
- Saftoiu, A.; Gilja, O.H.; Sidhu, P.S.; Dietrich, C.F.; Cantisani, V.; Amy, D.; Bachmann-Nielsen, M.; Bob, F.; Bojunga, J.; Brock, M.; et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for the Clinical Practice of Elastography in Non-Hepatic Applications: Update 2018. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 40, 425–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzan, R.; Regev-Sadeh, T.; Dola, T.; Shemer-Shamay, H.; Umansky, A.; Zigmond, E.; Neeman, Z. Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography and Shear Wave Dispersion: Correlation with Histopathological Changes in Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2025, 51, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Mokuda, S.; Kawaoka, T.; Uchikawa, S.; Amioka, K.; Tsuge, M.; Asada, K.; Okada, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; et al. Influence of dispersion slope on the diagnosis of liver fibrosis by the shear wave in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 54, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ishigami, M.; Hirooka, Y.; Fujishiro, M. What is the role of measuring shear wave dispersion using shear wave elastography in pancreatic parenchyma? J. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 47, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, T.A. Value of Two-Dimensional Shear-Wave Elastography in Differentiating Pancreatic Steatosis From Pancreatic Fibrosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 43, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich-Treuenstätt, V.H.v.; Guenther, M.; Ilmer, M.; Knoblauch, M.M.; Koch, D.; Clevert, D.-A.; Ormanns, S.; Klauschen, F.; Niess, H.; D’Haese, J.; et al. Preoperative ultrasound elastography for postoperative pancreatic fistula prediction after pancreatoduodenectomy: A prospective study. Surgery 2024, 175, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Jin, C. Quantification of pancreatic elasticity in type 2 diabetes: A new potential imaging marker for evaluation of microangiopathy. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 124, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.P.; Zheng, J.J.; Jin, C.X. Pancreatic Elastography From Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging for Evaluation of Diabetic Microangiopathy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohno, E.; Iida, T.; Uetsuki, K.; Yashika, J.; Yamada, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Furukawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. An initial trial of quantitative evaluation of autoimmune pancreatitis using shear wave elastography and shear wave dispersion in transabdominal ultrasound. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaeza-del-Castillo, A.; Paz-Pineda, F.; Oviedo-Cárdenas, E.; Sánchez-Avila, F.; Vargas-Vorácková, F. AST to platelet ratio index (APRI) for the noninvasive evaluation of liver fibrosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2008, 7, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.A.; Baggio, L.L.; Cao, X.; Abdulla, T.; Campbell, J.E.; Secher, T.; Jelsing, J.; Larsen, B.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists increase pancreatic mass by induction of protein synthesis. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Kamiya, H.; Haneda, M.; Inagaki, N.; Tanizawa, Y.; Araki, E.; Ueki, K.; Nakayama, T. Causes of death in Japanese patients with diabetes based on the results of a survey of 45,708 cases during 2001-2010: Report of the Committee on Causes of Death in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Cooper, G.J.; Lewis, C.E.; Morris, J.F.; Willis, A.C.; Reid, K.B.; Turner, R.C. Islet amyloid formed from diabetes-associated peptide may be pathogenic in type-2 diabetes. Lancet 1987, 2, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, R.; Cao, P.; Noor, H.; Ridgway, Z.; Tu, L.H.; Wang, H.; Wong, A.G.; Zhang, X.; Abedini, A.; Schmidt, A.M.; et al. Islet Amyloid Polypeptide: Structure, Function, and Pathophysiology. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2798269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, R.L.; Westermark, G.T.; Westermark, P.; Kahn, S.E. Islet amyloid: A critical entity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3629–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, K.; Mizukami, H.; Inaba, W.; Tsuboi, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Yagihashi, S. Islet amyloid with macrophage migration correlates with augmented beta-cell deficits in type 2 diabetic patients. Amyloid 2014, 21, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, F.; Spahr, L.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Giostra, E.; Bihl, F. Hepatic amyloidosis increases liver stiffness measured by transient elastography. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2010, 73, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bayramoglu, Z.; Akyol Sari, Z.N.; Koker, O.; Adaletli, I.; Eker Omeroglu, R. Shear wave elastography evaluation of liver, pancreas, spleen and kidneys in patients with familial mediterranean fever and amyloidosis. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Tan, Y.Q.; Teh, H.S.; Lee, P.J.; Khoo, R.N. Primary hepatic amyloidosis presenting as nodular masses on the background of diffuse infiltration and extreme liver stiffness on MR elastography. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2014, 23, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.B.; Cookson, L.M.; Barton, S.V.; Liefaard, L.; Lane, T.; Hutt, D.F.; Ritter, J.M.; Fontana, M.; Moon, J.C.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Repeat doses of antibody to serum amyloid P component clear amyloid deposits in patients with systemic amyloidosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loustaud-Ratti, V.R.; Cypierre, A.; Rousseau, A.; Yagoubi, F.; Abraham, J.; Fauchais, A.L.; Carrier, P.; Lefebvre, A.; Bordessoule, D.; Vidal, E.; et al. Non-invasive detection of hepatic amyloidosis: FibroScan, a new tool. Amyloid 2011, 18, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Hoodeshenas, S.; Venkatesh, S.H.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Torbenson, M.S.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic Resonance Elastography of Liver in Light Chain Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| T2DM (n = 46) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-INS (n = 37) | INS (n = 9) | p Value | ||
| Age [y.o.] | 68 (60–71) | 68 (60–71) | 65 (59–71) | not significant (n.s.) |
| M/F | 31/15 | 29/8 | 2/7 | 0.003 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 23.4 (21.1–26.6) | 23.5 (21.6–26.7) | 22.2 (19.7–24.0) | n.s. |
| AMY [U/L] | 78 (70–97) | 83 (70–106) | 70 (56–77) | n.s. |
| HbA1c [%] | 7.5 (7.0–8.1) | 7.3 (6.9–8.0) | 8.1 (7.9–8.6) | 0.003 |
| TC [mg/dL] | 200 (183–222) | 197 (183–215) | 207 (199–226) | n.s. |
| TG [mg/dL] | 114 (73–157) | 113 (78–149) | 134 (55–274) | n.s. |
| eGFR [mL/min/1.73 m2] | 69.70 (57.68–80.49) | 70.25 (58.55–80.34) | 65.72 (56.15–82.28) | n.s. |
| PLT [×104/μL] | 24.8 (21.3–27.5) | 24.7 (20.3–26.5) | 28.2 (22.1–28.9) | n.s. |
| AST [U/L] | 19 (17–22) | 19 (17–22) | 18 (15–20) | n.s. |
| ALT [U/L] | 17 (14–22) | 17 (14–21) | 17 (14–22) | n.s. |
| FIB-4 index | 1.20 (0.98–1.59) | 1.25 (1.02–1.60) | 1.02 (0.88–1.31) | n.s. |
| APRI | 0.27 (0.21–0.40) | 0.28 (0.22–0.43) | 0.24 (0.18–0.31) | n.s. |
| SWS of the Liver | 1.40 (1.32–1.53) | 1.44 (1.33–1.54) | 1.35 (1.29–1.45) | n.s. |
| Modality | Cut-off Value | Sensitivity [%] | Specificity [%] | Positive Predictive Value [%] | Negative Predictive Value [%] | Accuracy [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shear wave speed (SWS) | 1.70 | 55.6 | 89.2 | 55.6 | 89.2 | 82.6 |
| Dispersion slope (DS) | 12.38 | 88.9 | 56.8 | 33.3 | 95.5 | 63.0 |
| C-peptide index (CPI) | 0.63 | 66.7 | 83.3 | 50.0 | 91.2 | 80.4 |
| SWS and CPI | 1.69 & 0.48 | 100 | 86.5 | 64.3 | 100 | 89.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugita-Hamada, M.; Yokoo, T.; Nakajima, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Osaki, A.; Maruyama, M.; Takamura, M.; Waguri, N.; Isokawa, O.; Terai, S. Simultaneous Evaluation of Shear Wave Elastography and C-Peptide Index for Predicting Need of Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070277
Sugita-Hamada M, Yokoo T, Nakajima N, Takahashi Y, Osaki A, Maruyama M, Takamura M, Waguri N, Isokawa O, Terai S. Simultaneous Evaluation of Shear Wave Elastography and C-Peptide Index for Predicting Need of Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(7):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070277
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugita-Hamada, Moeno, Takeshi Yokoo, Nao Nakajima, Yoshifumi Takahashi, Akihiko Osaki, Masaki Maruyama, Masaaki Takamura, Nobuo Waguri, Osamu Isokawa, and Shuji Terai. 2025. "Simultaneous Evaluation of Shear Wave Elastography and C-Peptide Index for Predicting Need of Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 7: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070277
APA StyleSugita-Hamada, M., Yokoo, T., Nakajima, N., Takahashi, Y., Osaki, A., Maruyama, M., Takamura, M., Waguri, N., Isokawa, O., & Terai, S. (2025). Simultaneous Evaluation of Shear Wave Elastography and C-Peptide Index for Predicting Need of Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(7), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070277






