Personalized Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Cerebral Venous Hemodynamics in a Case of Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Imaging and Geometric Modeling
2.2. Computational Setup
2.3. Boundary Conditions and Blood Flow Parameters
2.4. Numerical Solution and Solver Setup
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Flow Distribution
3.2. Pressure and Wall Stress Distribution
3.3. Effect of Increased Flow (Hyperemia)
3.4. Comprehensive Cerebral Venous Network Analysis
3.5. Rheological Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemodynamic Adaptation Mechanism
4.2. Clinical Significance
4.3. Comparison to Prior Studies
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICVs | Internal Cerebral Veins |
| DCVT | Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis |
| ICP | Intracranial Pressure |
| IIH | Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| IJVs | Internal Jugular Veins |
| MRV | Magnetic Resonance Venography |
| SCVs | Superior Cerebral Veins |
| SSS | Superior Sagittal Sinus |
| STS | Straight Sinus |
| WSS | Wall Shear Stress |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
References
- Schaller, B. Physiology of cerebral venous blood flow: From experimental data in animals to normal function in humans. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 46, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousser, M.-G.; Ferro, J.M. Cerebral venous thrombosis: An update. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, T.; Akakin, A. Anatomy of cerebral veins and sinuses. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2008, 23, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, N.; Carare, R.O. Cerebral Vessels: An Overview of Anatomy, Physiology, and Role in the Drainage of Fluids and Solutes. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 611485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, J.M.; Canhão, P.; Stam, J.; Bousser, M.-G.; Barinagarrementeria, F. Prognosis of Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis. Stroke 2004, 35, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Meng, R.; Duan, J.; Zhou, C.; Ji, X. Anatomy, imaging and hemodynamics research on the cerebral vein and venous sinus among individuals without cranial sinus and jugular vein diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 999134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, J.-C.; Jianu, D.C.; Sadik, R.; Purcell, Y.; Novaes, N.; Saragoussi, E.; Obadia, M.; Lecler, A.; Savatovsky, J. Imaging of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Life 2022, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.R.; Bateman, G.A.; Barber, T. The relationship between cerebral blood flow and venous sinus pressure: Can hyperemia induce idiopathic intracranial hypertension? Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzmitcheva, E.; Andrade, A.; Muthusami, P.; Shroff, M.; MacGregor, D.L.; deVeber, G.; Dlamini, N.; Moharir, M. Anatomical Venous Variants in Children With Cerebral Sinovenous Thrombosis. Stroke 2019, 50, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Bokkers, R.P.H.; Uyttenboogaart, M.; Van Dijk, J.M.C. Patient-Specific Cerebral Blood Flow Simulation Based on Commonly Available Clinical Datasets. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 835347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Ma, L.; Yan, D.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Han, H.; Yuan, K.; et al. Quantitative hemodynamics of draining veins in brain arteriovenous malformation: A preliminary study based on computational fluid dynamics. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1474857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, C.A.; Witter, T.L.; Nikoubashman, O.; Wiesmann, M.; Steinseifer, U.; Neidlin, M. Evaluating the accuracy of cerebrovascular computational fluid dynamics modeling through time-resolved experimental validation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandrelli, R.; Colò, F.; Broccolini, A.; Della Marca, G.; Frisullo, G.; Colosimo, C.; Pilato, F. Deep cerebral venous system involvement in patients with cerebral sinus thrombosis. A proposal of neuroradiological score systems useful for clinical assessment. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Northrup, H.; Le, H.; Cheung, A.K.; Berceli, S.A.; Shiu, Y.T. Medical Image-Based Computational Fluid Dynamics and Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis in Vascular Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 855791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saposnik, G.; Bushnell, C.; Coutinho, J.M.; Field, T.S.; Furie, K.L.; Galadanci, N.; Kam, W.; Kirkham, F.C.; McNair, N.D.; Singhal, A.B.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Stroke 2024, 55, e77–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoquart-Elsankari, S. A Phase-Contrast MRI Study of Physiologic Cerebral Venous Flow. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhu, T.; Fan, S.; Yuan, J. Cerebral sinus hemodynamics in adults revealed by 4D Flow MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambila-Solórzano, A.; Méndez-Lavielle, F.; Naude, J.L.; Martínez-Sánchez, G.J.; García-Rebolledo, A.; Hernández, B.; Escobar-del Pozo, C. Influence of Blood Rheology and Turbulence Models in the Numerical Simulation of Aneurysms. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taebi, A.; Berk, S.; Roncali, E. Realistic boundary conditions in SimVascular through inlet catheter modeling. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Imada, S.; Usui, R.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakamura, M.; Ihara, M. High Middle Cerebral Artery Wall Shear Stress in Branch Atheromatous Disease: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2025, 32, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, J.; Abou-Mrad, T.; Stone McGuire, L.; Janiga, G.; Saalfeld, S.; Alaraj, A.; Berg, P. Flow-based simulation in transverse sinus stenosis pre- and post-stenting: Pressure prediction accuracy, hemodynamic complexity, and relationship to pulsatile tinnitus. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-L.; Xin, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Feng, G.-G.; Wu, F.-Q.; Feng, Z.-P.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, X.-H.; Xin, H.-W.; Luo, W.-Y. Recent Advances on the Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Trials of Venous Thromboembolism. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 6167–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivard, A.; Parsons, M. Normal and Abnormal Physiology of Cerebral Blood Flow. Radiology Key. 2018. Available online: https://radiologykey.com/normal-and-abnormal-physiology-of-cerebral-blood-flow/ (accessed on 13 September 2025).
- Liu, X.; Lan, L.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, J.; Cao, W.; Fan, Y.; Yang, X. Quantitative analysis of blood flow in cerebral venous sinus with stenosis by patient-specific CFD modeling. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 3848–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozy, S.; Orscelik, A.; Tolba, H.; Abdelghaffar, M.; Kobeissi, H.; Ghaith, H.S.; Abbas, A.S.; Kadirvel, R.; Brinjikji, W.; Kallmes, D.F. Endovascular thrombectomy for severe cerebral venous thrombosis: A comprehensive meta-analysis assessing safety and efficacy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2024, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xia, J.; Jin, L.; Qiao, A.; Su, T.; Li, Z.; Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Computational fluid dynamics study of the effect of transverse sinus stenosis on the blood flow pattern in the ipsilateral superior curve of the sigmoid sinus. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6286–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Deng, X. Hemodynamics of cerebral bridging veins connecting the superior sagittal sinus based on numerical simulation. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2018, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabannes, V.; Ismail, M.; Prud’homme, C.; Szopos, M. Hemodynamic simulations in the cerebral venous network: A study on the influence of different modeling assumptions. J. Coupled Syst. Multiscale Dyn. 2015, 3, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
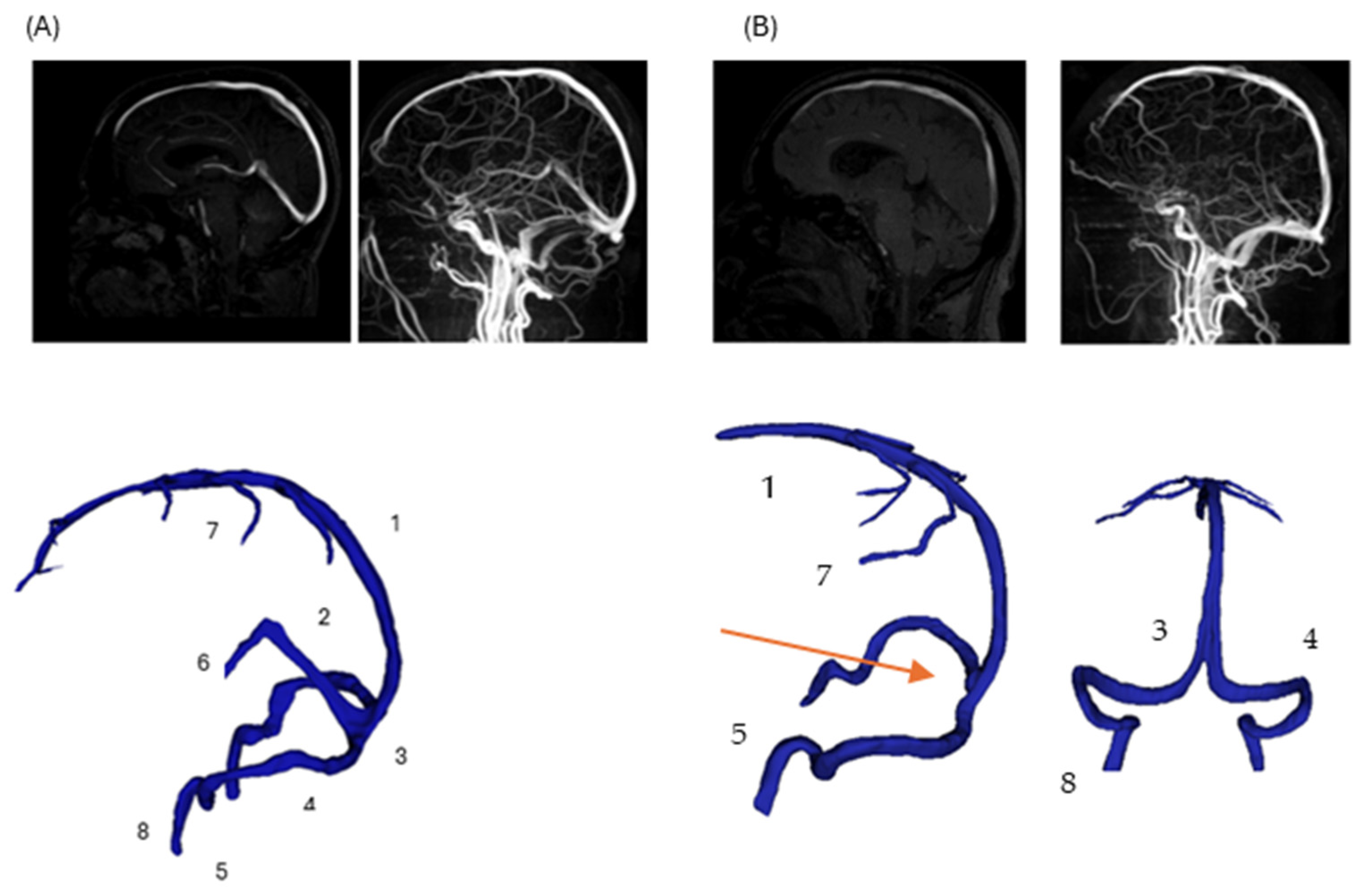
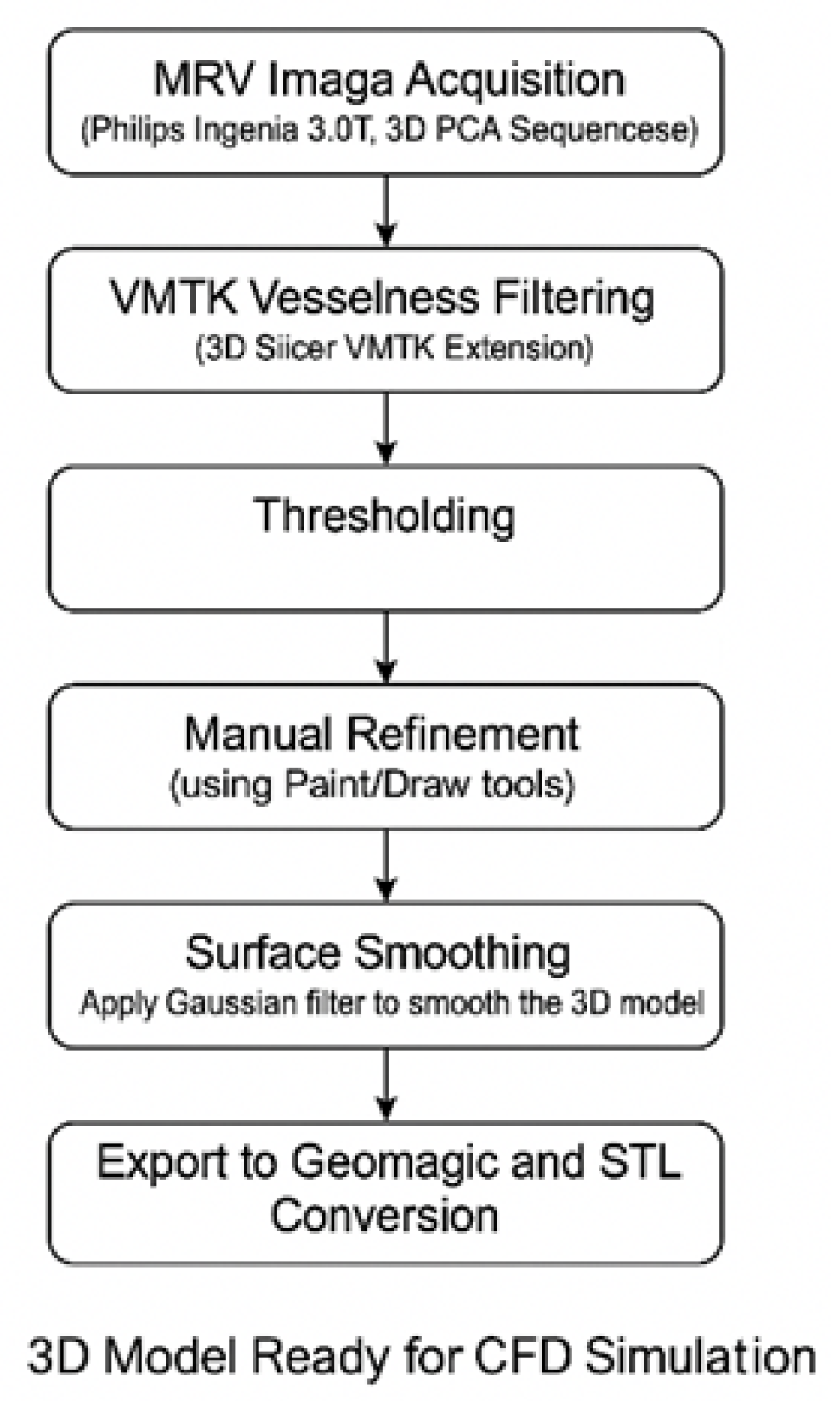
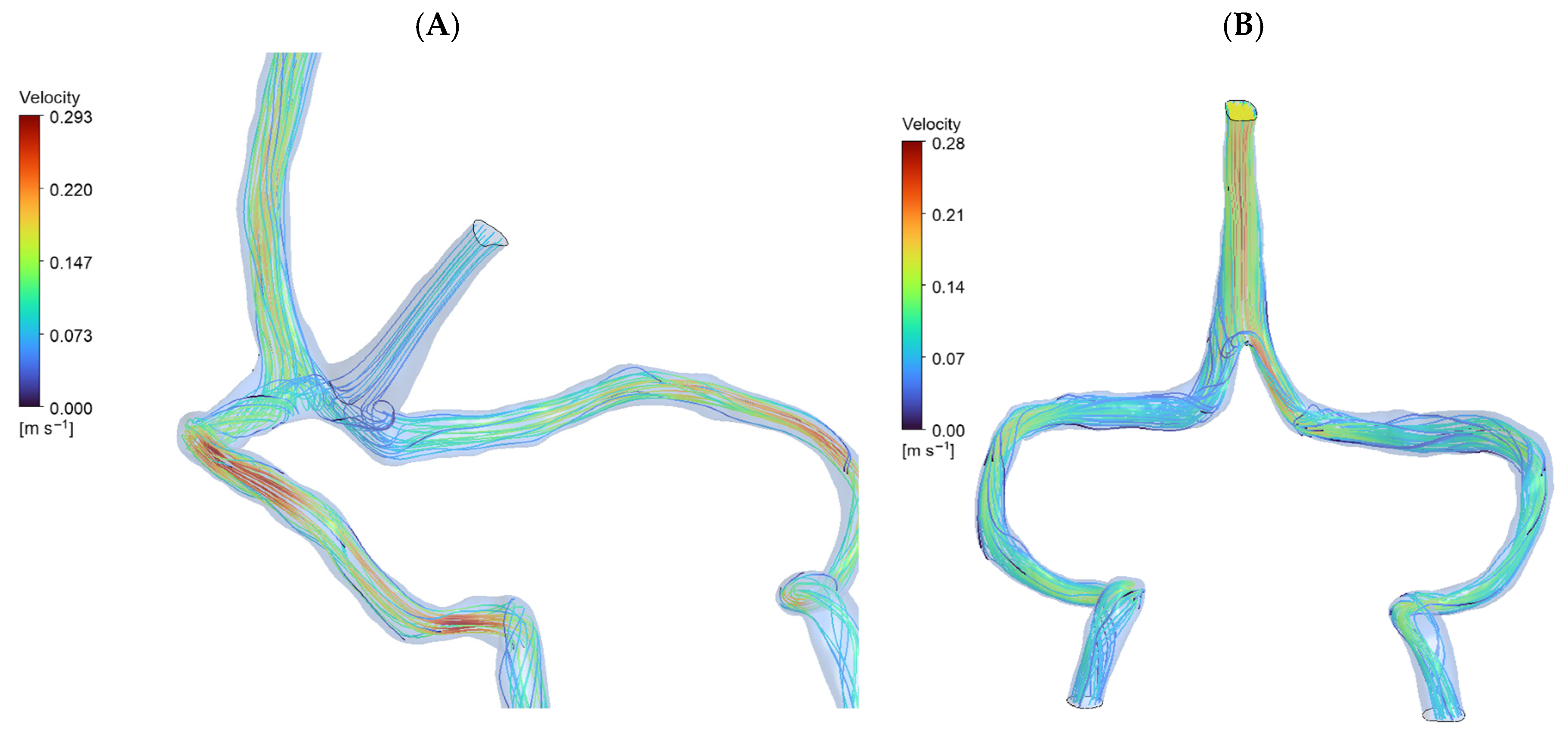
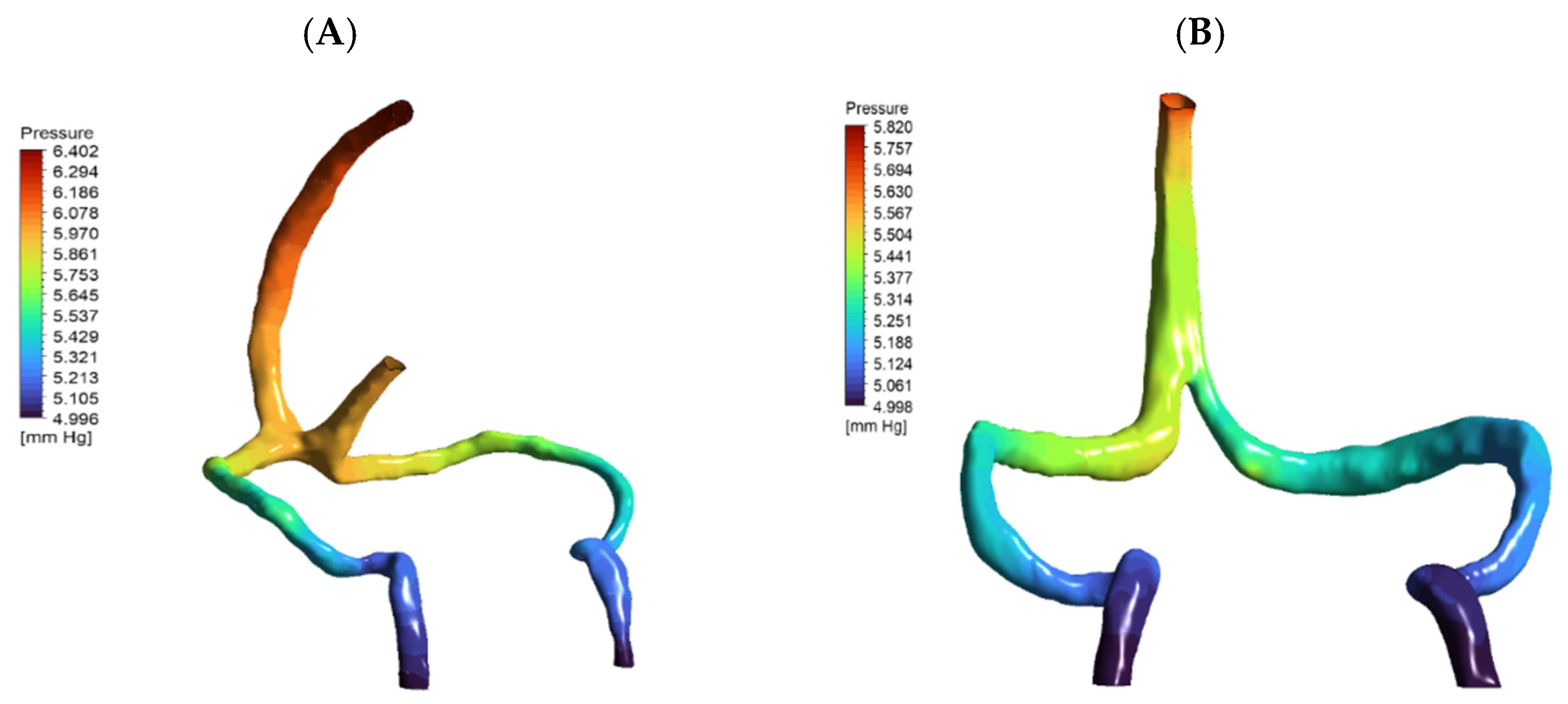
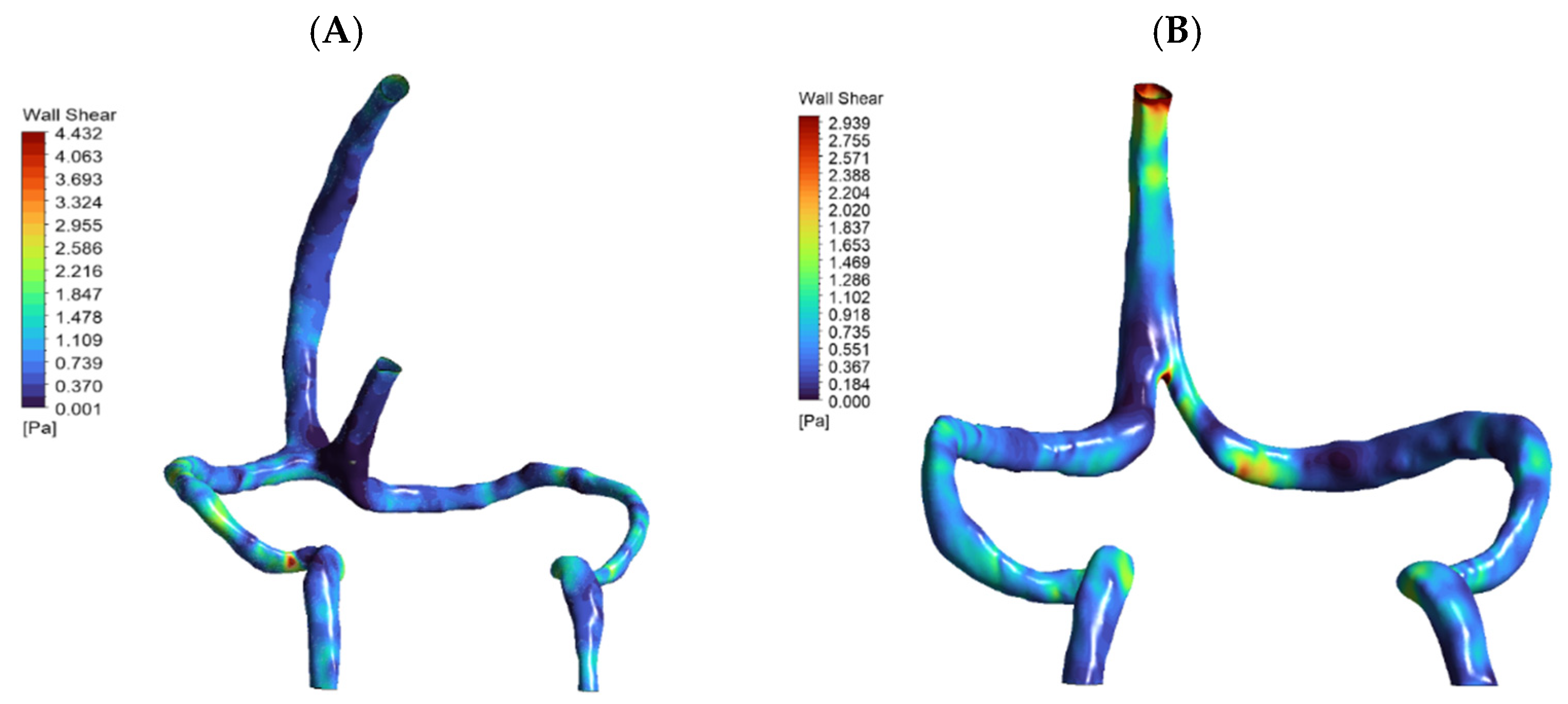
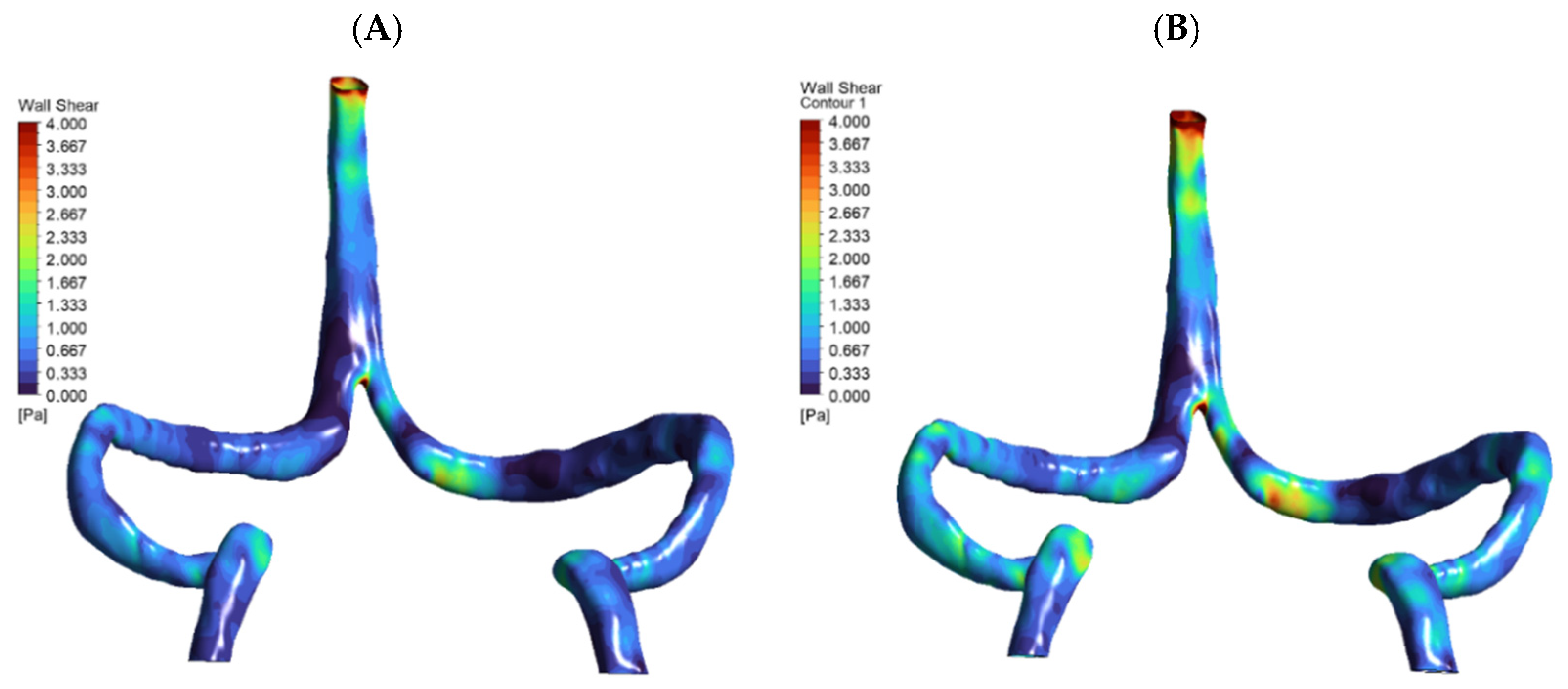

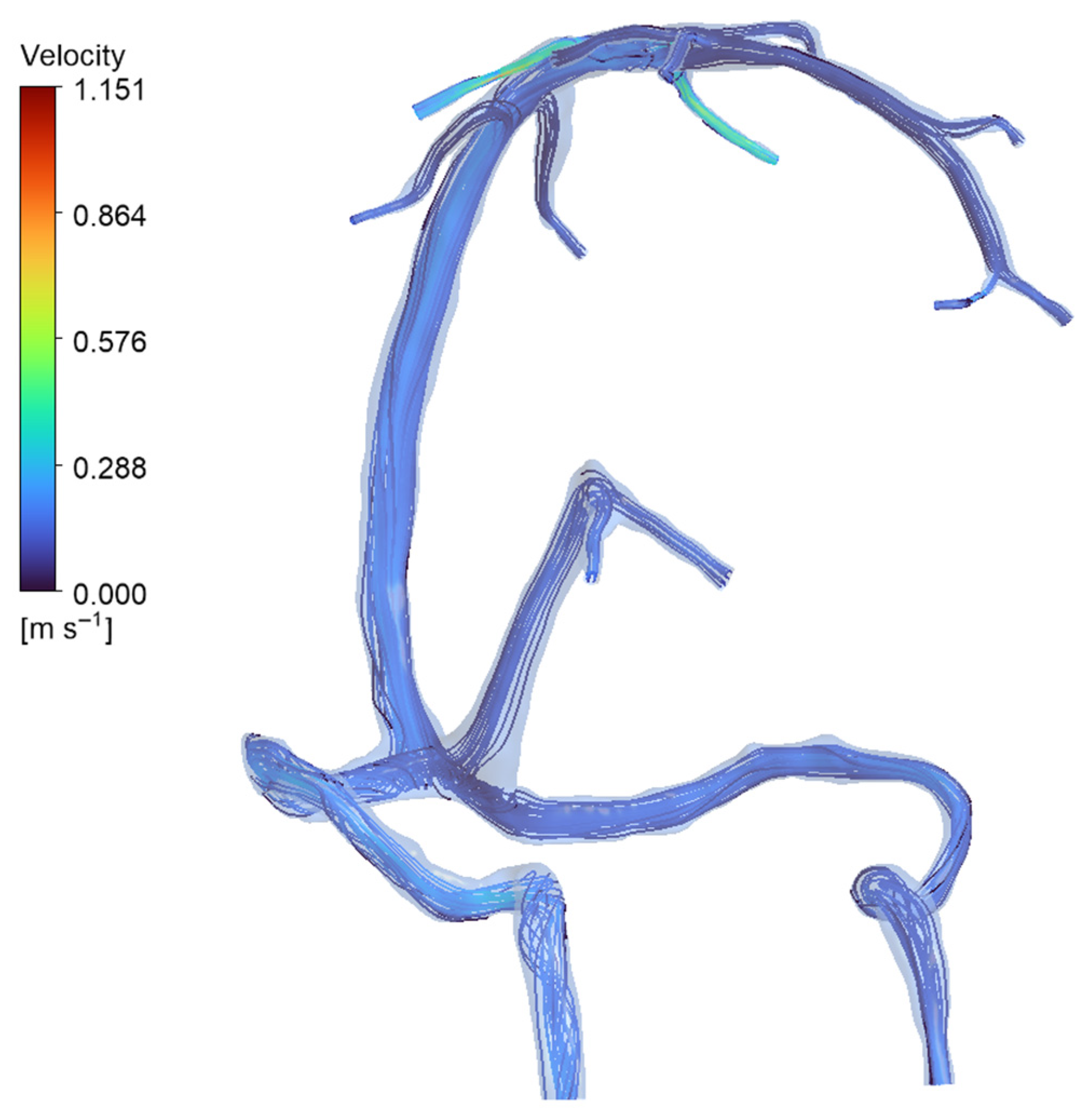
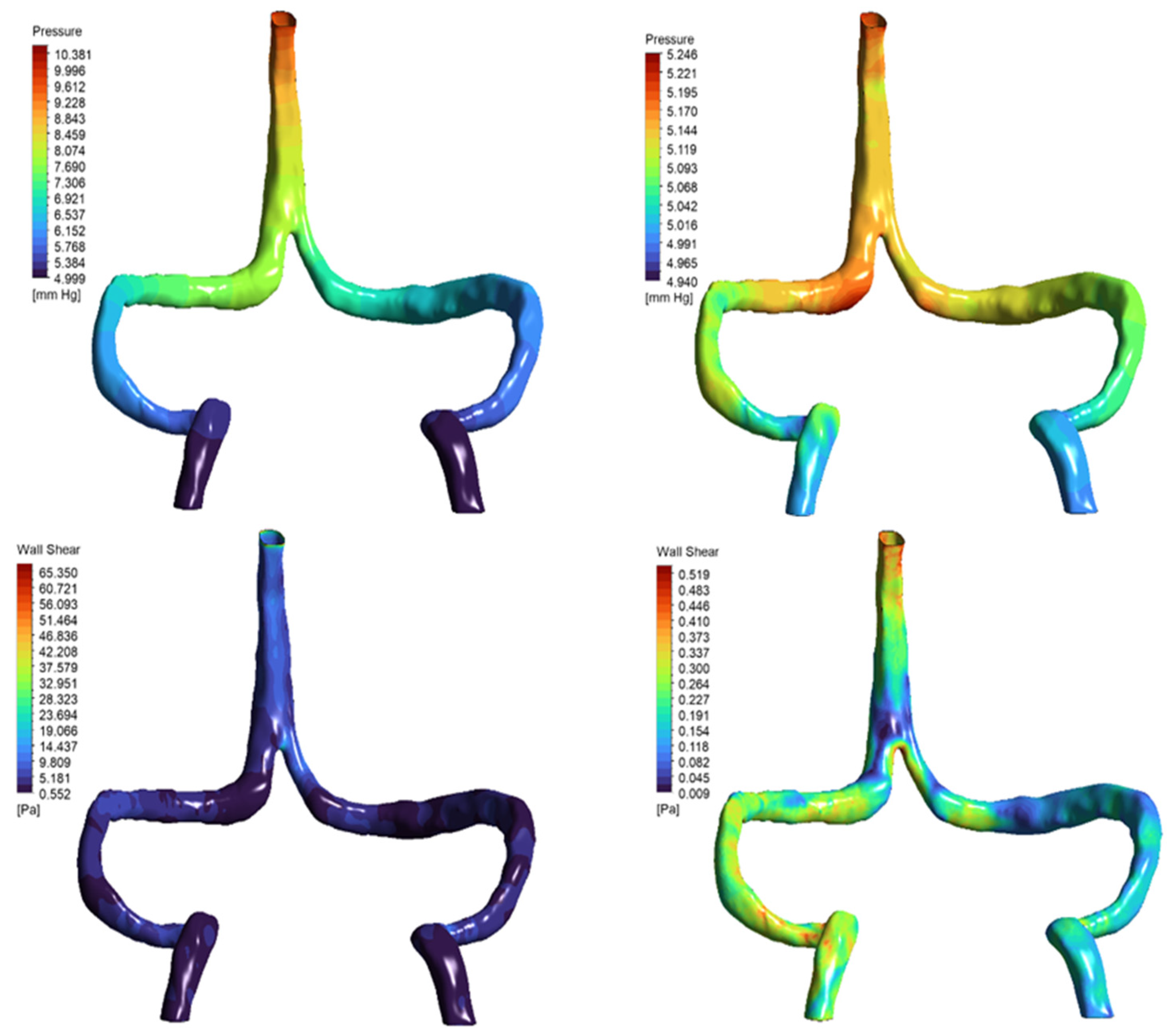
| Metric | Normal Anatomy | DCVT Anatomy |
|---|---|---|
| SSS vs. STS inflow split | ~70% SSS/30% STS | 100% SSS/0% STS |
| Jugular outflow split (right:left) | ~1.6:1 (right dominant) | ~0.8:1 (left dominant) |
| Peak velocity in sinuses | 0.11 m/s (SSS region) | 0.28 m/s (SSS region) |
| Pressure drop (SSS inlet to IJVs) | ~1.3 mmHg | ~0.67 mmHg |
| Average SSS wall shear stress (WSS) | ~1.5 Pa | ~1.8 Pa |
| Peak WSS | ~3.9 Pa (near sigmoid) | ~2.5 Pa (near SSS outlet) |
| Flow Rate (mL/s) | Pressure Drop (mmHg) | Flow Condition |
|---|---|---|
| 5.4 | 0.674 | Baseline |
| 5.94 | 0.766 | +10% Flow |
| 6.21 | 0.81 | +15% Flow |
| 6.48 | 0.862 | +20% Flow |
| 6.75 | 0.911 | +25% Flow |
| 7.02 | 0.96 | +30% Flow |
| 7.25 | 1.00 | +34% Flow |
| 7.5 | 1.051 | +39% Flow |
| Vessel | Pressure (Pa) | Pressure (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Cerebral Vein (Left) | 837.71 | 6.28 |
| Internal Cerebral Vein (Right) | 846.98 | 6.35 |
| Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein (Left) | 1452.61 | 10.90 |
| Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein (Right) | 1444.07 | 10.84 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Midline) | 951.33 | 7.14 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Left) | 952.90 | 7.15 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Left) | 1074.52 | 8.06 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Left) | 882.33 | 6.62 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Right) | 1277.22 | 9.60 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Right) | 991.76 | 7.44 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Right) | 934.26 | 7.01 |
| Superior Cerebral Vein (Right) | 907.20 | 6.81 |
| Quantity | Newtonian | Carreau-Yasuda | Cross | % Diff (vs. CY) | % Diff (vs. Cross) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Velocity (SSS, m/s) | 0.1658 | 0.1658 | 0.1658 | 0% | 0% |
| Peak Velocity (fluid, m/s) | 0.2830 | 0.349 | 0.225 | +23.3% | −20.5% |
| Area-Averaged WSS (Pa) | 1.80 | 4.04 | 0.204 | +124.4% | −88.7% |
| Pressure Drop (mmHg) | 0.679 | 4.725 | 0.2 | +595.6% | −70.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assefa, A.M.; Palaiodimou, L.; Bourantas, G.; Sakellarios, A. Personalized Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Cerebral Venous Hemodynamics in a Case of Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120570
Assefa AM, Palaiodimou L, Bourantas G, Sakellarios A. Personalized Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Cerebral Venous Hemodynamics in a Case of Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(12):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120570
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssefa, Adisu Mengesha, Lina Palaiodimou, George Bourantas, and Antonis Sakellarios. 2025. "Personalized Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Cerebral Venous Hemodynamics in a Case of Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 12: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120570
APA StyleAssefa, A. M., Palaiodimou, L., Bourantas, G., & Sakellarios, A. (2025). Personalized Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Cerebral Venous Hemodynamics in a Case of Deep Cerebral Vein Thrombosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(12), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120570









