Epidermal Barrier Parameters in Psoriasis: Implications in Assessing Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
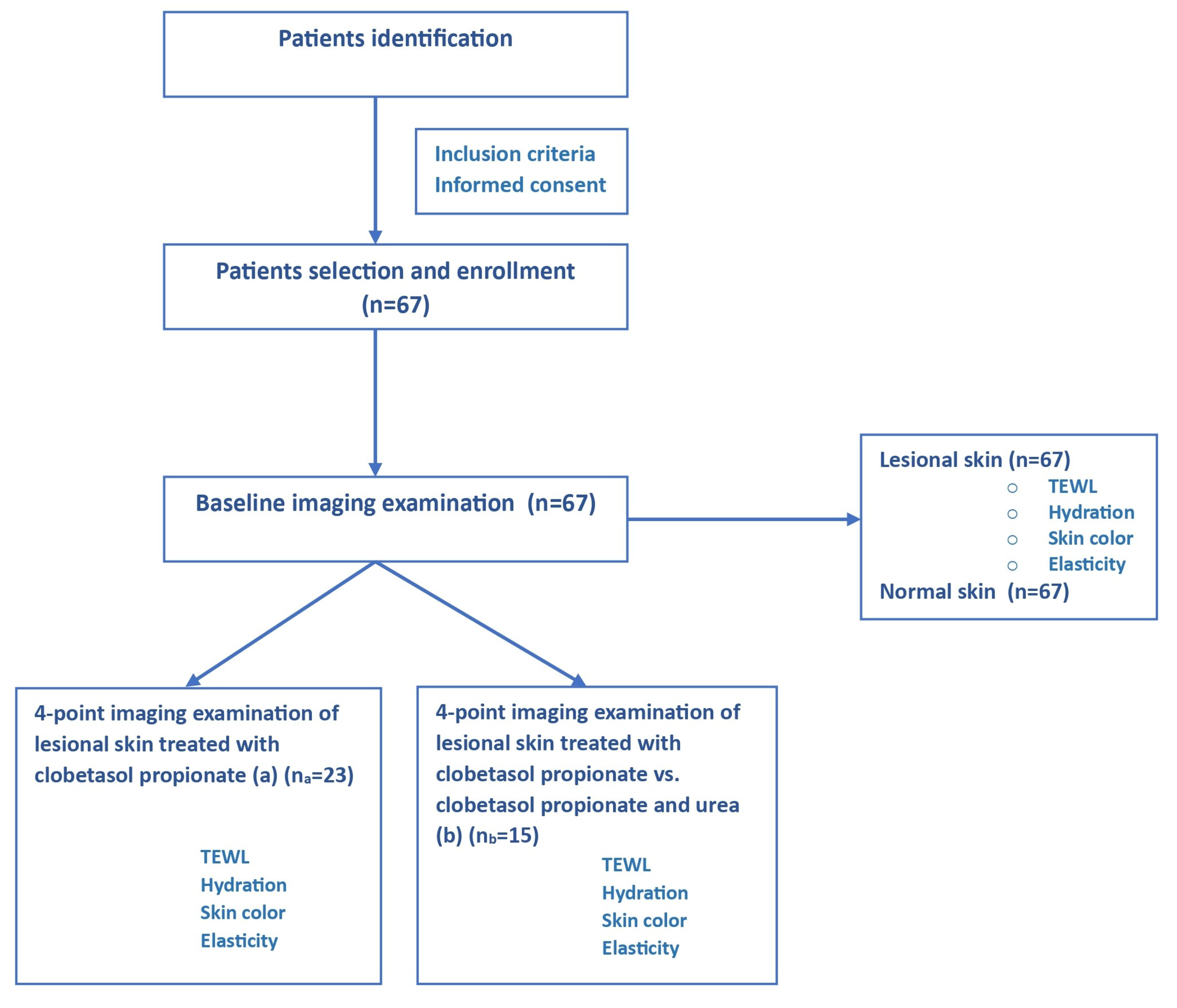
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Study Outcome
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Skin Parameters between Lesional and Non-Lesional Skin in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
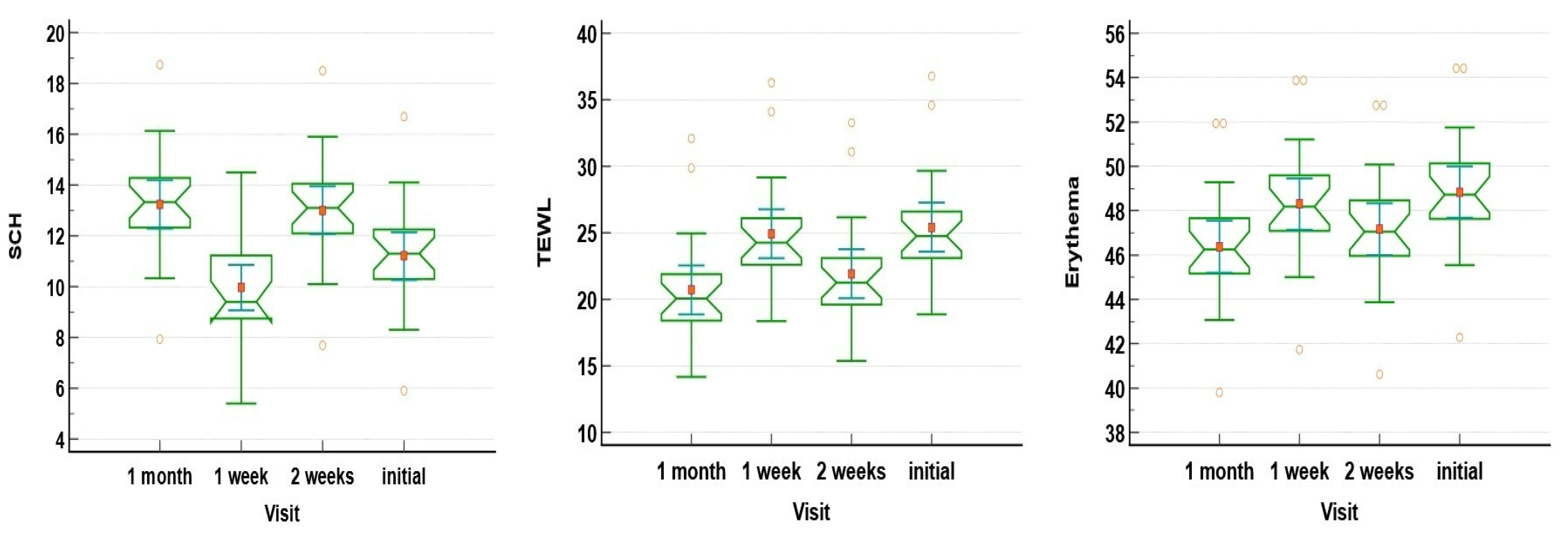
3.2. Lesional Skin Parameters Changes in Patients Undergoing Only Clobetasol Propionate 0.5% Ointment Treatment
3.3. Lesional Skin Parameters Variation in Patients Undergoing Clobetasol Propionate 0.5% Ointment Treatment vs. Patients Undergoing Clobetasol Propionate 0.5% Ointment with 10% Urea Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottlieb, A.B.; Chao, C.; Dann, F. Psoriasis comorbidities. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2008, 19, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strange, A.; Capon, F.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Knight, J.; Weale, M.E.; Allen, M.H.; Barton, A.; Band, G.; Bellenguez, C.; Bergboer, J.G.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Spain, S.L.; Knight, J.; Ellinghaus, E.; Stuart, P.E.; Capon, F.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Tejasvi, T.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Luo, S.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Q. Critical role of environmental factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.-I.; Mitran, C.-I.; Mitran, M.-I.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Advances in Understanding the Immunological Pathways in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nast, A.; Smith, C.; Spuls, P.; Valle, G.A.; Bata-Csörgö, Z.; Boonen, H.; De Jong, E.; Garcia-Doval, I.; Gisondi, P.; Kaur-Knudsen, D.; et al. EuroGuiDerm Guideline on the systemic treatment of Psoriasis vulgaris—Part 1: Treatment and monitoring recommendations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2461–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Ortiz-Lopez, L.; Choudhary, V.; Bollag, W.B. Updated Perspectives on Keratinocytes and Psoriasis: Keratinocytes are More Than Innocent Bystanders. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022, 12, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.A.; Dapavo, P.; Mastorino, L.; Roccuzzo, G.; Wolff, S.; Ribero, S.; Cassoni, P.; Senetta, R.; Quaglino, P. Exploring Psoriasis Inflammatory Microenvironment by NanoString Technologies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.e.m.; Christophers, E.; Barker, J.N.W.N.; Chalmers, R.; Chimenti, S.; Krueger, G.; Leonardi, C.; Menter, A.; Ortonne, J.-P.; Fry, L. A classification of psoriasis vulgaris according to phenotype. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Tsai, T.-F. Anti-interleukin and interleukin therapies for psoriasis: Current evidence and clinical usefulness. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2017, 9, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwin, M.; Woźniacka, A. Interleukins 20 and 8–less widely known cytokinesin psoriasis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol./Postępy Dermatol. Alergol. 2023, 40, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Robaee, A.A.; Al-Zolibani, A.A.; Al-Shobili, H.A.; Kazamel, A.; Settin, A. IL-10 implications in psoriasis. Int. J. Health Sci. 2008, 2, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Orsmond, A.; Bereza-Malcolm, L.; Lynch, T.; March, L.; Xue, M. Skin Barrier Dysregulation in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczaj, W.; Wroński, A.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R.; Skrzydlewska, E. Lipidomic Analysis Reveals Specific Differences between Fibroblast and Keratinocyte Ceramide Profile of Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Molecules 2020, 25, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.; Lam, P.; Ng, W.; Kung, J.; Cheng, N.; Lin, Z.; Chow, C.; Leung, T. Age, sex, and disease status as determinants of skin hydration and transepidermal water loss among children with and without eczema. Hong Kong Med. J. 2020, 26, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdeniz, M.; Gabriel, S.; Lichterfeld-Kottner, A.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J. Transepidermal water loss in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis update. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroto-Morales, D.; Montero-Vilchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S. Study of Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis: The Impact of Emollients. Life 2021, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.-V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.C.; Nikam, V.N.; Dandakeri, S.; Bhat, R.M. Transepidermal water loss in psoriasis: A case-control study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 10, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Tsuji, H.; Minami-Hori, M.; Miyauchi, Y.; Iizuka, H. Defective barrier function accompanied by structural changes of psoriatic stratum corneum. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavò, S.P.; Guarneri, F.; Giuffrida, R.; Aragona, E.; Guarneri, C. Evaluation of cutaneous surface parameters in psoriatic patients. Ski. Res. Technol. 2017, 23, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Je, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-S.; Li, Z.J.; Choi, D.-K.; Kwon, Y.-B.; Sohn, K.-C.; Im, M.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. Changes in Transepidermal Water Loss and Skin Hydration according to Expression of Aquaporin-3 in Psoriasis. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellemère, G.; Von Stetten, O.; Oddos, T. Retinoic Acid Increases Aquaporin 3 Expression in Normal Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodén, M. Role of Topical Emollients and Moisturizers in the Treatment of Dry Skin Barrier Disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, S.; Sesana, S.; Ghidoni, R.; Monti, M. Content of the different lipid classes in psoriatic scale. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1995, 287, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Shon, J.C.; Seo, H.S.; Liu, K.; Lee, J.W.; Ahn, S.K.; Hong, S.P. Decrease of ceramides with long-chain fatty acids in psoriasis: Possible inhibitory effect of interferon gamma on chain elongation. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uva, L.; Miguel, D.; Pinheiro, C.; Antunes, J.; Cruz, D.; Ferreira, J.; Filipe, P. Mechanisms of Action of Topical Corticosteroids in Psoriasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 561018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero-Casals, J.; Morgado-Carrasco, D.; Granger, C.; Trullàs, C.; Jesús-Silva, A.; Krutmann, J. Urea in Dermatology: A Review of its Emollient, Moisturizing, Keratolytic, Skin Barrier Enhancing and Antimicrobial Properties. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D. Moisturizing cream ameliorates dryness and desquamation in participants not receiving topical psoriasis treatment. Cutis 2008, 82, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, I.; Proksch, E. Topical treatment by urea reduces epidermal hyperproliferation and induces differentiation in psoriasis. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 1996, 76, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlrab, W. DNA synthesis in the epidermis after contact with urea (author’s transl). Dermatologica 1974, 149, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, L.M.; Pérez, P. Roles of the Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptors in Skin Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, T.S.-R.; Barlow, R.; Mohandas, P.; Bewley, A. Topical steroid withdrawal: An emerging clinical problem. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 48, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadially, R.; Reed, J.T.; Elias, P.M. Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Correlates with Phenotype in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | All Patients (n = 67) | Mild Psoriasis (n = 15) | Moderate Psoriasis (n = 23) | Severe Psoriasis (n = 29) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 37 | 12 | 14 | 11 |
| Female | 30 | 3 | 9 | 18 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Employed | 45 | 15 | 14 | 16 |
| Unemployed/retired | 22 | 0 | 9 | 13 |
| BMI values (kg/m2) | 27.46 ± 7.32 | 24.56 ± 4.34 | 25.6 ± 7.34 | 30.6 ± 6.85 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 35 | 6 | 12 | 17 |
| Diabetes | 18 | 2 | 6 | 12 |
| Dyslipidemia | 27 | 3 | 6 | 18 |
| Joint involvement (psoriatic arthritis) | 21 | 1 | 6 | 14 |
| Eye involvement (uveitis) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Special sites | ||||
| Scalp involvement | 32 | 2 | 12 | 18 |
| Nail involvement | 30 | 3 | 11 | 16 |
| Genital involvement | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Parameter | Normal Skin | Psoriatic Plaque | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCH | 33.4 [28.90–37.38] | 9.3 [7.9–10.59] | <0.0001 |
| TEWL | 10.3 [9.70–10.79] | 25.71 [24.76–27.03] | <0.0001 |
| Elasticity | 7.71 [7.36–8.27] | 6.7 [6.40–7.19] | <0.0001 |
| Erythema | 28.16 [27.78–28.44] | 50.30 [49.12–51.26] | <0.0001 |
| Melanin | 26 [25.73–27.34] | 19.4 [18.90–20.09] | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Mild Psoriasis (n = 15) | Moderate Psoriasis (n = 23) | Severe Psoriasis (n = 29) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCH | 12.10 [11.10–13.12] | 7.90 [6.60–9.23] | 5.3 [4.25–6] | <0.001 |
| TEWL | 23.5 [21.49–27.64] | 24.76 [23.29–26.14] | 27.29 [25.32–30.77] | 0.032 |
| Elasticity | 7.2 [6.13–7.4] | 6.4 [5.70–6.76] | 7.1 [6.58–7.52] | 0.370 |
| Erythema | 48.72 [47.66–49.68] | 49.34 [48.21–53.39] | 51.67 [50.96–52.71] | 0.002 |
| Melanin | 18.4 [17.40–19.77] | 19.4 [18.9–20.66] | 19.4 [18.78–20.91] | 0.217 |
| Parameter | Initial Visit | 1-Week Visit | 2-Weeks Visit | 1-Month Visit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCH | 11.21 ± 2.18 | 9.96 ± 2.06 | 13.01 ± 2.18 | 13.23 ± 2.18 | <0.01 |
| TEWL | 25.41 ± 4.24 | 24.91 ± 4.24 | 21.91 ± 4.24 | 20.71 ± 4.24 | <0.001 |
| Elasticity | 6.60 ± 1.15 | 6.95 ± 1.15 | 6.80 ± 1.15 | 7.25 ± 1.15 | 0.284 |
| Erythema | 48.83 ± 2.69 | 48.29 ± 2.69 | 47.16 ± 2.69 | 46.36 ± 2.69 | 0.011 |
| Melanin | 19.87 ± 1.84 | 20.12 ± 1.84 | 20.16 ± 1.84 | 20.41 ± 1.84 | 0.804 |
| PASI | 7.53 ± 1.61 | 6.78 ± 1.42 | 6.17 ± 1.62 | 3.73 ± 1.65 | <0.001 |
| Parameter | Initial Visit | 1-Week Visit | 2-Weeks Visit | 1-Month Visit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clobetasol propionate 0.5% | |||||
| SCH | 11.2 [10.15–12.10] | 9.2 [8.55–10.04] | 12.6 [12.10–13.90] | 14.13 [12.03–14.27] | <0.001 |
| TEWL | 23.5 [21.49–27.64] | 24.25 [22.05–25.66] | 22.01 [18.97–26.74] | 20.05 [18.40–22.56] | 0.014 |
| Elasticity | 7.2 [6.12–7.40] | 6.65 [5.95–7.12] | 6.9 [6.01–7.69] | 7.35 [6.62–8.01] | 0.37 |
| Erythema | 49.34 [48.21–53.29] | 47.37 [46.60–48.92] | 47.53 [46.45–49.23] | 46.25 [45.18–47.08] | <0.001 |
| Melanin | 18.4 [17.40–19.76] | 20.05 [19.25–21.49] | 19.44 [18.85–20.75] | 22.32 [19.98–23.59] | 0.015 |
| Clobetasol propionate 0.5% and 10% urea | |||||
| SCH | 10.95 [9.90–11.75] | 11.55 [10.50–12.45] | 12.43 [11.97–14.04] | 14.73 [12.03–18.40] | <0.001 |
| TEWL | 23.35 [21.34–27.49] | 22.6 [20.59–26.74] | 21.25 [19.24–22.66] | 18.58 [16.97–22.44] | 0.027 |
| Elasticity | 7.4 [6.32–7.60] | 7.35 [6.26–7.55] | 6.9 [5.80–7.43] | 7.35 [6.56–8.21] | 0.54 |
| Erythema | 49.94 [48.81–53.89] | 48.44 [47.21–50.64] | 48.98 [46.28–49.91] | 47.21 [45.46–49.24] | 0.045 |
| Melanin | 17.62 [16.62–18.98] | 18.4 [17.40–19.76] | 20.03 [18.40–21.35] | 20.94 [19.98–21.59] | 0.002 |
| Parameter | Clobetasol Propionate 0.5% vs. Clobetasol Propionate 0.5% and 10% Urea | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 1 Month | |
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| SCH | 0.003 | 0.62 | 0.027 |
| TEWL | 0.804 | 0.043 | 0.07 |
| Elasticity | 0.569 | 0.224 | 0.499 |
| Erythema | 0.254 | 0.138 | 0.09 |
| Melanin | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morariu, S.-H.; Cotoi, O.S.; Tiucă, O.M.; Crișan, M.; Garaga, L.; Tiucă, R.A.; Mariean, C.R.; Buicu, F.C.; Nicolescu, A.C. Epidermal Barrier Parameters in Psoriasis: Implications in Assessing Disease Severity. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14070728
Morariu S-H, Cotoi OS, Tiucă OM, Crișan M, Garaga L, Tiucă RA, Mariean CR, Buicu FC, Nicolescu AC. Epidermal Barrier Parameters in Psoriasis: Implications in Assessing Disease Severity. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(7):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14070728
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorariu, Silviu-Horia, Ovidiu Simion Cotoi, Oana Mirela Tiucă, Maria Crișan, Liuba Garaga, Robert Aurelian Tiucă, Claudia Raluca Mariean, Florin Corneliu Buicu, and Alin Codrut Nicolescu. 2024. "Epidermal Barrier Parameters in Psoriasis: Implications in Assessing Disease Severity" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 7: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14070728
APA StyleMorariu, S.-H., Cotoi, O. S., Tiucă, O. M., Crișan, M., Garaga, L., Tiucă, R. A., Mariean, C. R., Buicu, F. C., & Nicolescu, A. C. (2024). Epidermal Barrier Parameters in Psoriasis: Implications in Assessing Disease Severity. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(7), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14070728






