The Synergistic Effects of Incobotulinum Toxin and Physiotherapy in a Rare Case of Paraparesis in a 7-Year-Old Affected by Klippel–Feil Syndrome Related to an MYH3 Gene Mutation: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
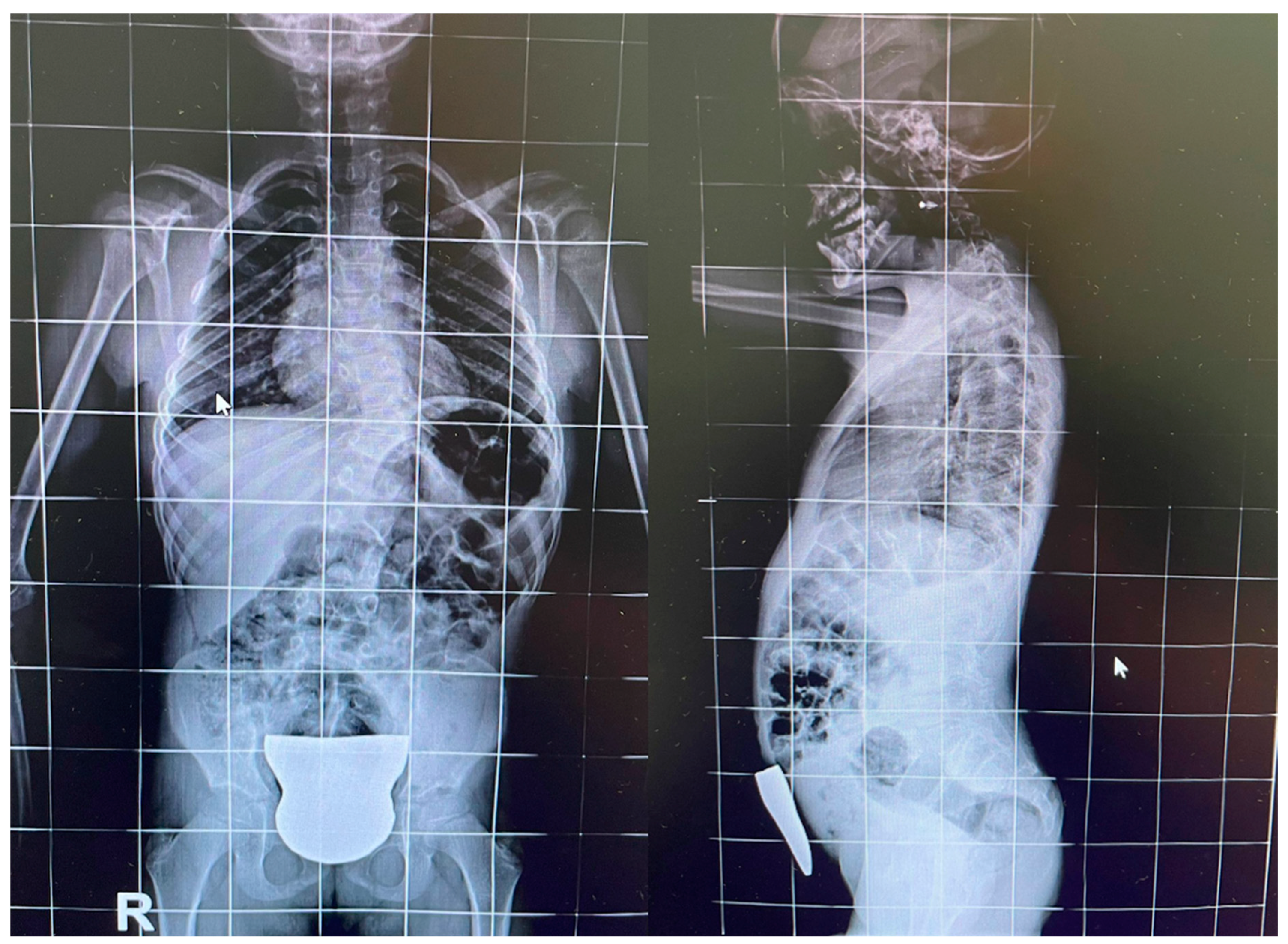
2. Case Report
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frikha, R. Klippel-Feil syndrome: A review of the literature. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2020, 29, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, A.; Patel, K.; Evans, H.; Saleh, M.; Kotter, M.R.N.; Heary, R.F.; Tessitore, E.; Fehlings, M.G.; Cheng, J.S. Demographics, presentation and symptoms of patients with Klippel-Feil syndrome: Analysis of a global patient-reported registry. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekin, E.E.; Altunrende, M.E. Klippel-Feil syndrome: Should additional examination be conducted? Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Saleh, A.; Bakhsh, W.; Rubery, P.T.; Mesfin, A. The Prevalence of Klippel-Feil Syndrome: A Computed Tomography-Based Analysis of 2917 Patients. Spine Deform. 2018, 6, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Bhattarai, A.; Bhandari, P.; Danai, A.; Singh, U.K. Klippel-Feil Syndrome Associated with Renal and Cardiac Anomalies in an Infant: A Case Report. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2023, 61, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonomura, H.; Nagae, M.; Ishibashi, H.; Hosoi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Mikami, Y.; Takahashi, K. Posterior Occipitocervical Fixation and Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy for the Treatment of Basilar Invagination with Klippel-Feil Syndrome: A Case Report. Medicina 2024, 60, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.; Talal Ashraf, M.; Khuzzaim Khan, M.; Admani, B.; Sam, S.J.; Imran, M.; Hameed, M. A Comprehensive Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Klippel Feil Syndrome. Arch. Razi Inst. 2023, 78, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seth, R.; Sinha, A.; Singla, N.; Chatterjee, D. Rare cause of paraparesis in a young man: Cervico-dorsal neurenteric cysts associated with Klippel-Feil syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e235327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litrenta, J.; Bi, A.S.; Dryer, J.W. Klippel-Feil Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hallgrimsdottir, S.; Zuo, Y.; Li, X.; Batkovskyte, D.; Liu, S.; Lindelöf, H.; Wang, S.; Hammarsjö, A.; et al. Expanding the mutation and phenotype spectrum of MYH3-associated skeletal disorders. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, M.; Accogli, A.; De Grandis, E.; Allegri, A.; Bagowski, C.P.; Shoukier, M.; Maghnie, M.; Capra, V. A novel pathogenic MYH3 mutation in a child with Sheldon-Hall syndrome and vertebral fusions. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.B.; Kong, L.C.; Zuo, R.T.; Kang, Q.L. Identification of a novel pathogenic mutation of the MYH3 gene in a family with distal arthrogryposis type 2B. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Bharadwaj, A.; Saini, M.; Kardon, G.; Mathew, S.J. Myosin heavy chain-embryonic regulates skeletal muscle differentiation during mammalian development. Development 2020, 147, dev184507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieba, J.; Zhang, W.; Chong, J.X.; Forlenza, K.N.; Martin, J.H.; Heard, K.; Grange, D.K.; Butler, M.G.; Kleefstra, T.; Lachman, R.S.; et al. A postnatal role for embryonic myosin revealed by MYH3 mutations that alter TGFβ signaling and cause autosomal dominant spondylocarpotarsal synostosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron-Christie, S.R.; Wells, C.F.; Simon, M.; Wessels, M.; Tang, C.Z.N.; Wei, W.; Takei, R.; Aarts-Tesselaar, C.; Sandaradura, S.; Sillence, D.O.; et al. Recessive Spondylocarpotarsal Synostosis Syndrome Due to Compound Heterozygosity for Variants in MYH3. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Shah, S.R.; Sankhla, C.S. Spastic Paraparesis—A Rare Cause. Neurol. India 2024, 72, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, M.; Marvulli, R.; D’Alesio, E.; Riccardi, M.; Raele, M.V.; Dell’Anna, L.; Fai, A.; Farì, G.; Megna, M. Effects of Intradermal Therapy (Mesotherapy) on Bilateral Cervicobrachial Pain. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashina, W.; Takahashi, T.; Sasanuma, H.; Saitsu, A.; Takeshita, K. Relationship Between Achilles Tendon Stiffness Using Myoton PRO and Translation Using a Tensile Testing Machine: A Biomechanical Study of a Porcine Model. Cureus 2023, 15, e49359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.P.; Detrembleur, C.; Fisette, P.; Selves, C.; Mahaudens, P. MyotonPro Is a Valid Device for Assessing Wrist Biome-chanical Stiffness in Healthy Young Adults. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 797975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvulli, R.; Raele, M.V.; Riccardi, M.; Farì, G.; Ranieri, M.; Megna, M. The Effectiveness of Combining Botulinum Toxin Type A and Therapeutic Exercise in Treating Spasticity in a Patient with Complicate. Stiff-Person Syndrome: A Case Report. Diseases 2024, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Aguilar, J.; Tizabi, Y. Botulinum Neurotoxin, an Example of Successful Translational Research. Clin. Pharmacol. Transl. Med. 2018, 2, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasyanju Carrero, L.M.; Ma, W.W.; Liu, H.F.; Yin, X.F.; Zhou, B.R. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids: Updated review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Johnson, E.A. Botulinum toxin therapy: Past, present and future developments. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2022, 129, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, S.; Cha, J. Botulinum toxin: Pharmacology and injectable administration for the treatment of primary hyperhidrosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.; Splevins, A.; Picaut, P.; van der Schans, M.; Langenberg, J.; Noort, D.; Snyder, D.; Foster, K. AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®), OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®), and IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) Neurotoxin Content and Potential Implications for Duration of Response in Patients. Toxins 2018, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, D.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum toxin for motor disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 196, 539–555. [Google Scholar]
- Louw, J.A.; Albertse, H. Traumatic quadriplegia after minor trauma in the Klippel-Feil syndrome. S. Afr. Med. J. 1987, 72, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhavana Chowdary, M.; Kumar, D.A. A Case Report of Klippel-Feil Syndrome Presenting as Tetraplegia. Cureus 2023, 15, e41241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jae-Min Park, A.; Nelson, S.E.; Mesfin, A. Klippel-Feil Syndrome: Clinical Presentation and Management. BJS Rev. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| T0 | T1 (30 Days) | T2 (90 Days) | T3 (120 Days) | T4 (150 Days) | T5 (180 Days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Knee | 20° (10°) | 15° (0°) | 5° (0°) | 5° (0°) | 7° (0°) | 10 (5°) |
| Left Knee | 20° (15°) | 10° (0°) | 10° (0°) | 10° (0°) | 10° (0°) | 15° (7°) |
| T0 | T1 (30 Days) | T2 (90 Days) | T3 (120 Days) | T4 (150 Days) | T5 (180 Days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Biceps Femoris | 3 | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 3 |
| Left Biceps Femoris | 3 | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 2 | 3 |
| T0 | T1 (30 Days) | T2 (90 Days) | T3 (120 Days) | T4 (150 Days) | T5 (180 Days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Biceps Femoris | 18.9 | 16.4 | 17.0 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 17.9 |
| Left Biceps Femoris | 20.4 | 17.0 | 17.3 | 17.5 | 18.6 | 19.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranieri, M.; Riccardi, M.; Raele, M.V.; Farì, G.; Megna, M.; Marvulli, R. The Synergistic Effects of Incobotulinum Toxin and Physiotherapy in a Rare Case of Paraparesis in a 7-Year-Old Affected by Klippel–Feil Syndrome Related to an MYH3 Gene Mutation: A Case Report. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14111073
Ranieri M, Riccardi M, Raele MV, Farì G, Megna M, Marvulli R. The Synergistic Effects of Incobotulinum Toxin and Physiotherapy in a Rare Case of Paraparesis in a 7-Year-Old Affected by Klippel–Feil Syndrome Related to an MYH3 Gene Mutation: A Case Report. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(11):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14111073
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanieri, Maurizio, Mariagrazia Riccardi, Maria Vittoria Raele, Giacomo Farì, Marisa Megna, and Riccardo Marvulli. 2024. "The Synergistic Effects of Incobotulinum Toxin and Physiotherapy in a Rare Case of Paraparesis in a 7-Year-Old Affected by Klippel–Feil Syndrome Related to an MYH3 Gene Mutation: A Case Report" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 11: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14111073
APA StyleRanieri, M., Riccardi, M., Raele, M. V., Farì, G., Megna, M., & Marvulli, R. (2024). The Synergistic Effects of Incobotulinum Toxin and Physiotherapy in a Rare Case of Paraparesis in a 7-Year-Old Affected by Klippel–Feil Syndrome Related to an MYH3 Gene Mutation: A Case Report. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(11), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14111073








