Association between Tonsillectomy and Cardiovascular Diseases in Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
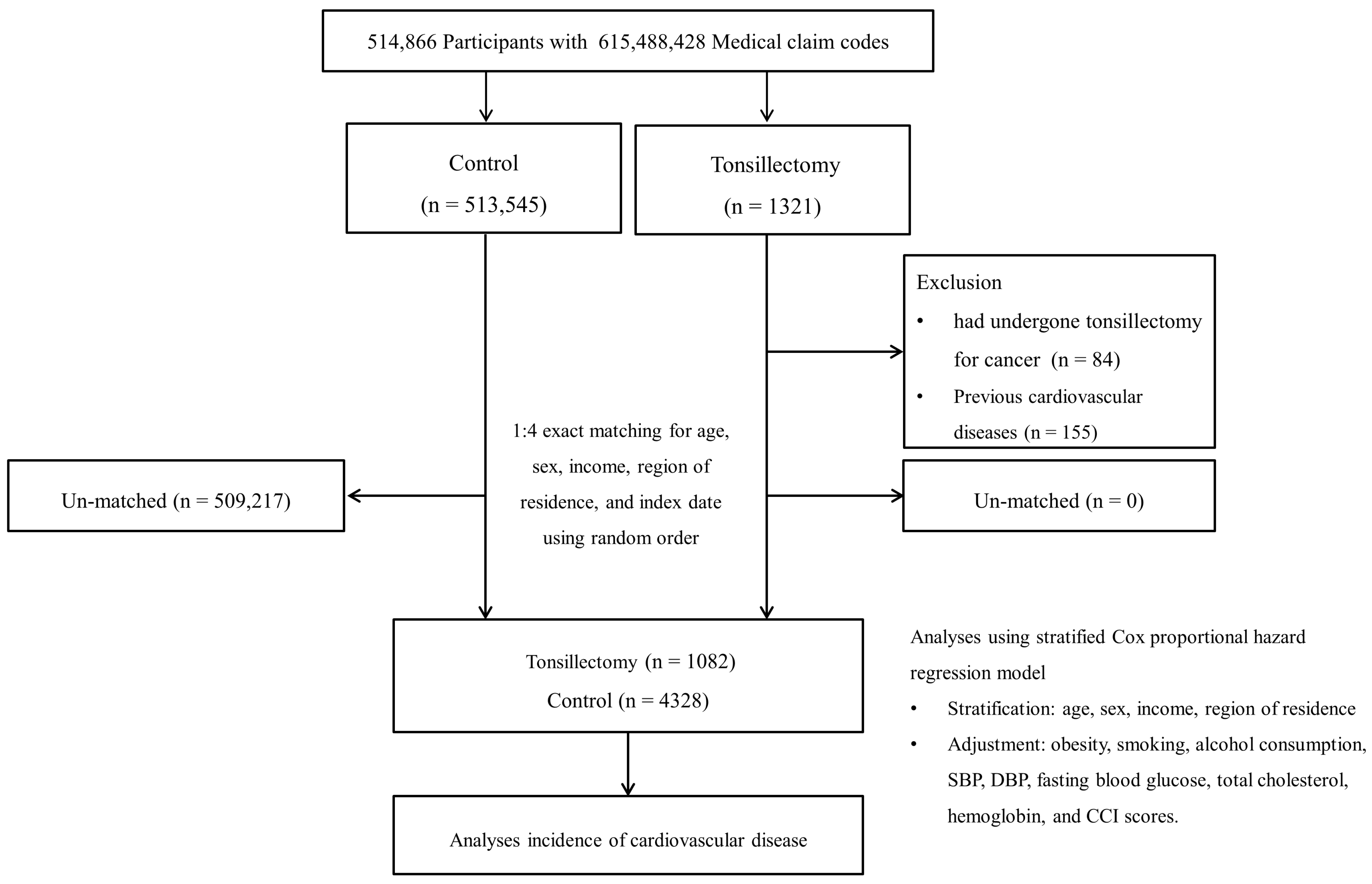
2.2. Participant Selection
2.3. Definition of Tonsillectomy (Independent Variable)
2.4. Definition of Cardiovascular Diseases
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
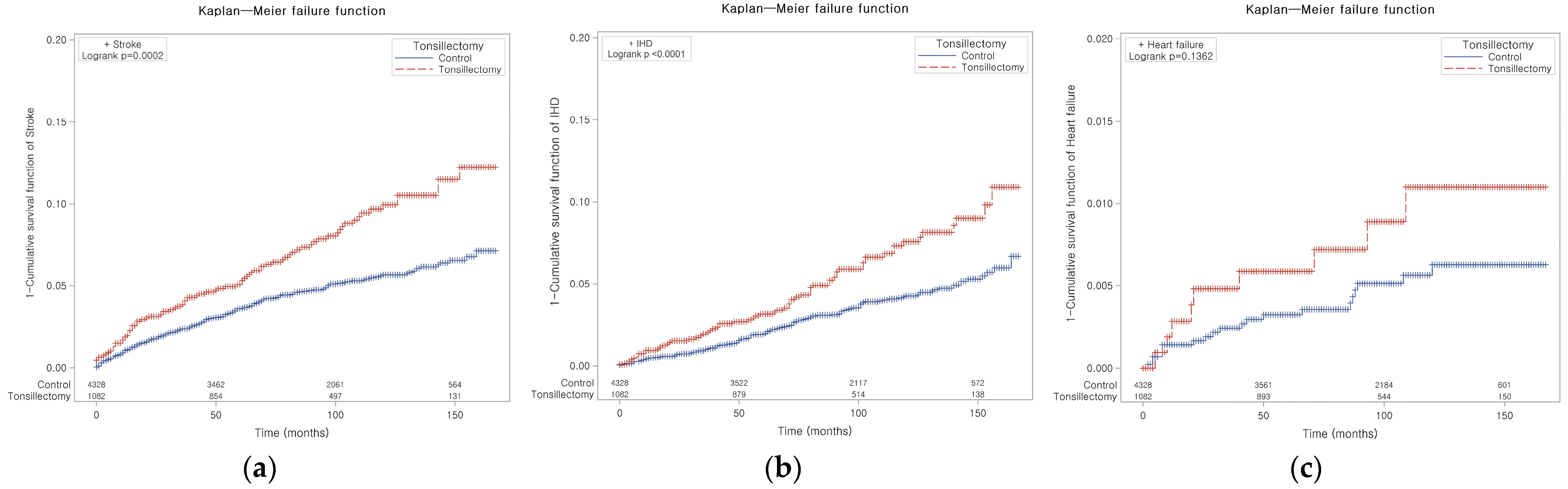
3.1. The Incidence of Stroke
3.2. The Incidence of IHD
3.3. The Incidence of HF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Cho, S.M.J.; Lee, H.; Baek, J.; Bae, J.H.; Chung, W.J.; Kim, H.C. Korea Heart Disease Fact Sheet 2020: Analysis of Nationwide Data. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, K.A.; Hall, M.J.; Golosinskiy, A. Ambulatory surgery in the United States, 2006. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2009, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, B.K.; Larson, D.R.; St Sauver, J.L.; Meverden, R.A.; Orvidas, L.J. Changes in incidence and indications of tonsillectomy and adenotonsillectomy, 1970–2005. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009, 140, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Yasuda, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Koike, K.; Maruyama, S.; Yokoo, T.; Matsuo, S.; Kawamura, T.; et al. Association between Tonsillectomy and Outcomes in Patients with Immunoglobulin a Nephropathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e194772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Increased risk of appendectomy due to appendicitis after tonsillectomy in women: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Medicine 2019, 98, e15579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Han, X.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Tonsillectomy and the risk of inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.S.; Wu, M.C.; Thota, E.; Wang, Y.H.; Alqaderi, H.E.; Wei, J.C. Tonsillectomy as a risk factor of periodontitis: A population-based cohort study. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Chen, H.J.; Li, T.C.; Sung, F.C.; Kao, C.H. A nationwide population-based cohort study on tonsillectomy and subsequent cancer incidence. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, D.T.; Mitchell, R.B. Systematic review of effects of adenotonsillectomy on cardiovascular parameters in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.T.; Chiu, S.N.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, M.T.; Hsu, W.C. Effect of adenotonsillectomy on blood pressure in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2021, 84, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janszky, I.; Mukamal, K.J.; Dalman, C.; Hammar, N.; Ahnve, S. Childhood appendectomy, tonsillectomy, and risk for premature acute myocardial infarction—A nationwide population-based cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Yenokyan, G.; Newman, A.B.; O’Connor, G.T.; Punjabi, N.M.; Quan, S.F.; Redline, S.; Resnick, H.E.; Tong, E.K.; Diener-West, M.; et al. Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: The sleep heart health study. Circulation 2010, 122, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; McEvoy, R.D. The epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, S.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, S.K.; Khang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Cohort profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tonsillectomy does not reduce asthma in children: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, G.; Jeong, S.-M.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Son, J.S.; Yun, J.-M.; Park, S.M. Association of obesity or weight change with coronary heart disease among young adults in South Korea. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.M.; Lee, K. Weight gain after smoking cessation does not modify its protective effect on myocardial infarction and stroke: Evidence from a cohort study of men. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption are related to benign parotid tumor: A nested case-control study using a national health screening cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.; Sundararajan, V. Practice of epidemiology: Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med. Care 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Li, D.; Kawai, M.; Zaghi, S.; Teixeira, J.; Senchak, A.J.; Brietzke, S.E.; Frasier, S.; Certal, V. Tonsillectomy for adult obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, J.H.; Min, C.; Yoo, D.M.; Park, M.W.; Song, C.M.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G. Analyses of Weight/Blood Pressure Changes before and after Tonsillectomy in Adults: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, M.A.; Dowli, A.; Mourad, M. The effect of tonsillectomy on the immune system: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, H.G. Tonsillectomy increases the risk of retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscesses in adults, but not in children: A national cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhlin, K.; Gustafsson, A.; Ahnve, S.; Janszky, I.; Tabrizi, F.; Klinge, B. Oral health in women with coronary heart disease. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboldi, P.; Gerosa, M.; Luzzana, C.; Catelli, L. Cardiac involvement in systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 23, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.J.; Glasziou, P.P.; Chong, L.Y.; Venekamp, R.P. Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical treatment for chronic/recurrent acute tonsillitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD001802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Egea-Zorrilla, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Aragón-Vela, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Tercedor-Sánchez, L.; Abadia-Molina, F. The Gut Microbiota and Its Implication in the Development of Atherosclerosis and Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamura, S.; Del Pinto, R.; Pietropaoli, D.; Ferri, C. Oral health as a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2023; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, A.; Lampa, E.; Lind, L. Oral health and cardiovascular disease risk in a cohort of periodontitis patients. Atherosclerosis 2017, 262, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.C.; Ma, K.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Wei, J.C. Impact of tonsillectomy on irritable bowel syndrome: A nationwide population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riha, R.L.; Kotoulas, S.C.; Pataka, A.; Kvamme, J.A.; Joppa, P.; Hedner, J. Obstructive sleep apnoea in adult patients post-tonsillectomy. Sleep Med. 2021, 78, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchak, A.J.; McKinlay, A.J.; Acevedo, J.; Swain, B.; Tiu, M.C.; Chen, B.S.; Robitschek, J.; Ruhl, D.S.; Williams, L.L.; Camacho, M.; et al. The effect of tonsillectomy alone in adult obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignore, M.R. Obesity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 274, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillar, G.; Shehadeh, N. Abdominal fat and sleep apnea: The chicken or the egg? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S303–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tonsillectomy | Control | Standardized Difference | |
| Total number (n, %) | 1082 (100.0) | 4328 (100.0) | |
| Age (years old) (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 40–44 | 166 (15.3) | 664 (15.3) | |
| 45–49 | 287 (26.5) | 1148 (26.5) | |
| 50–54 | 293 (27.1) | 1172 (27.1) | |
| 55–59 | 207 (19.1) | 828 (19.1) | |
| 60–64 | 84 (7.8) | 336 (7.8) | |
| 65–69 | 35 (3.2) | 140 (3.2) | |
| 70–74 | 7 (0.7) | 28 (0.7) | |
| 75–79 | 2 (0.2) | 8 (0.2) | |
| 80–84 | 1 (0.1) | 4 (0.1) | |
| 85+ | 79 (1.0) | 316 (1.0) | |
| Sex (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Male | 755 (69.8) | 3020 (69.8) | |
| Female | 327 (30.2) | 1308 (30.2) | |
| Income (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 98 (9.1) | 392 (9.1) | |
| 2 | 119 (11.0) | 476 (11.0) | |
| 3 | 132 (12.2) | 528 (12.2) | |
| 4 | 223 (20.6) | 892 (20.6) | |
| 5 (highest) | 510 (47.1) | 2040 (47.1) | |
| Region of residence (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Urban | 526 (48.6) | 2104 (48.6) | |
| Rural | 556 (51.4) | 2224 (51.4) | |
| Obesity (n, %) * | 0.33 | ||
| Underweight | 5 (0.5) | 66 (1.5) | |
| Normal | 248 (22.9) | 1470 (34.0) | |
| Overweight | 295 (27.3) | 1229 (28.4) | |
| Obese I | 471 (43.5) | 1443 (33.3) | |
| Obese II | 63 (5.8) | 120 (2.8) | |
| Smoking status (n, %) | 0.1 | ||
| Nonsmoker | 634 (58.6) | 2548 (58.6) | |
| Past smoker | 189 (17.5) | 623 (17.5) | |
| Current smoker | 259 (23.9) | 1157 (23.9) | |
| Alcohol consumption (n, %) | 0.02 | ||
| <1 time a week | 649 (60.0) | 2555 (59.0) | |
| ≥1 time a week | 433 (40.0) | 1773 (41.0) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.04 | ||
| <120 mmHg | 336 (31.1) | 1425 (32.9) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 544 (50.3) | 2123 (49.1) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 202 (18.7) | 780 (18.0) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.05 | ||
| <80 mmHg | 456 (42.1) | 1931 (44.6) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 403 (37.3) | 1577 (36.4) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 223 (20.6) | 820 (19.0) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (n, %) | 0.08 | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 694 (64.1) | 2898 (67.0) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 313 (28.9) | 1108 (25.6) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 75 (6.9) | 322 (7.4) | |
| Total cholesterol (n, %) | 0.05 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 558 (51.6) | 2271 (52.5) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 363 (33.5) | 1489 (34.4) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 161 (14.9) | 568 (13.1) | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.09 | ||
| ≥12 for men and ≥10 for women | 1077 (99.5) | 4274 (98.8) | |
| <12 for men and <10 for women | 5 (0.5) | 54 (1.3) | |
| CCI score † | 0.21 | ||
| 0 | 786 (72.6) | 3466 (80.1) | |
| 1 | 186 (17.2) | 439 (10.1) | |
| ≥2 | 110 (10.2) | 423 (9.8) | |
| Stroke | 64 (5.9) | 149 (3.4) | 0.12 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 3 (0.3) | 16 (0.4) | 0.02 |
| Ischemic stroke | 26 (2.4) | 59 (1.4) | 0.08 |
| Other stroke | 35 (3.2) | 74 (1.7) | 0.1 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 86 (8.0) | 204 (4.7) | 0.13 |
| Heart failure | 9 (0.8) | 20 (0.5) | 0.05 |
| Independent Variables | Stroke/Participants (n, %) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 10,000 (PY) | Hazard Ratios (95% CI) for Stroke | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude † | p-Value | Adjusted † ‡ | p-Value | ||||
| Total participants (n = 5410) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 64/1082 (5.9) | 7876 | 81.3 | 1.75 (1.30–2.35) | <0.001 * | 1.78 (1.32–2.42) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 149/4328 (3.4) | 31,966 | 46.6 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age < 50 years old (n = 2265) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 22/453 (4.9) | 4386 | 50.2 | 1.38 (0.85–2.24) | 0.196 | 1.42 (0.86–2.34) | 0.176 |
| Control | 64/1812 (3.5) | 17,644 | 36.3 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age ≥ 50 years old (n = 3145) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 42/629 (6.7) | 3490 | 120.3 | 2.04 (1.41–2.96) | <0.001 * | 2.10 (1.43–3.09) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 85/2516 (3.4) | 14,322 | 59.3 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Men (n = 3775) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 45/755 (6.0) | 5532 | 81.3 | 1.79 (1.26–2.55) | 0.001 * | 1.88 (1.31–2.71) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 103/3020 (3.4) | 22,473 | 45.8 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Women (n = 1635) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 19/327 (5.8) | 2344 | 81.1 | 1.66 (0.97–2.83) | 0.065 | 1.54 (0.87–2.70) | 0.137 |
| Control | 46/1308 (3.5) | 9493 | 48.5 | 1 | 1 | ||
| High income (n = 2860) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 37/572 (6.5) | 4180 | 88.5 | 1.87 (1.27–2.77) | 0.002 * | 1.95 (1.30–2.94) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 79/2288 (3.5) | 16,968 | 46.6 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Low income (n = 2550) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 27/510 (5.3) | 3696 | 73.1 | 1.61 (1.03–2.51) | 0.037 * | 1.61 (1.02–2.55) | 0.041 * |
| Control | 70/2040 (3.4) | 14,998 | 46.7 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Urban residents (n = 2630) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 29/526 (5.5) | 3776 | 76.8 | 2.14 (1.37–3.37) | 0.001 * | 2.30 (1.44–3.69) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 55/2104 (2.6) | 15,382 | 35.8 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Rural residents (n = 2780) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 35/556 (6.3) | 4100 | 85.4 | 1.52 (1.03–2.24) | 0.036 * | 1.56 (1.04–2.33) | 0.033 * |
| Control | 94/2224 (4.2) | 16,584 | 56.7 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Independent Variables | IHD/Participants (n, %) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 10,000 (PY) | Hazard Ratios (95% CI) for IHD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude † | p-Value | Adjusted † ‡ | p-Value | ||||
| Total participants (n = 5410) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 86/1082 (7.9) | 7661 | 112.3 | 1.73 (1.34–2.23) | <0.001 * | 1.60 (1.24–2.08) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 204/4328 (4.7) | 31,446 | 64.9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age < 50 years old (n = 2265) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 37/453 (8.2) | 4249 | 87.1 | 2.19 (1.47–3.27) | <0.001 * | 2.02 (1.34–3.05) | 0.001 * |
| Control | 68/1812 (3.8) | 17,509 | 38.8 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age ≥ 50 years old (n = 3145) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 49/629 (7.8) | 3412 | 143.6 | 1.49 (1.07–2.07) | 0.017 * | 1.39 (0.99–1.96) | 0.057 |
| Control | 136/2516 (5.4) | 13,937 | 97.6 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Men (n = 3775) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 62/755 (8.2) | 5396 | 114.9 | 1.76 (1.30–2.37) | <0.001 * | 1.57 (1.15–2.14) | 0.004 * |
| Control | 144/3020 (4.8) | 22,131 | 65.1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Women (n = 1635) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 24/327 (7.3) | 2265 | 106.0 | 1.66 (1.03–2.67) | 0.038 * | 1.66 (1.01–2.72) | 0.044 * |
| Control | 60/1308 (4.6) | 9315 | 64.4 | 1 | 1 | ||
| High income (n = 2860) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 51/572 (8.9) | 4040 | 126.2 | 2.14 (1.52–3.00) | <0.001 * | 2.03 (1.42–2.89) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 99/2288 (4.3) | 16,755 | 59.1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Low income (n = 2550) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 35/510 (6.9) | 3621 | 96.7 | 1.36 (0.92–1.99) | 0.120 | 1.28 (0.87–1.89) | 0.218 |
| Control | 105/2040 (5.1) | 14,691 | 71.5 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Urban residents (n = 2630) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 45/526 (8.6) | 3680 | 122.3 | 2.07 (1.45–2.97) | <0.001 * | 2.08 (1.43–3.02) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 89/2104 (4.2) | 15,103 | 58.9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Rural residents (n = 2780) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 41/556 (7.4) | 3981 | 103.0 | 1.46 (1.02–2.09) | 0.037 * | 1.31 (0.91–1.88) | 0.154 |
| Control | 115/2224 (5.2) | 16,343 | 70.4 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Independent Variables | Heart Failure/Participants (n, %) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 10,000 (PY) | Hazard Ratios (95% CI) for Heart Failure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude † | p-Value | Adjusted † ‡ | p-Value | ||||
| Total participants (n = 5410) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 9/1082 (0.8) | 8121 | 11.1 | 1.79 (0.81–3.93) | 0.148 | 1.35 (0.55–3.27) | 0.513 |
| Control | 20/4328 (0.5) | 32,556 | 6.1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age < 50 years old (n = 2265) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 3/453 (0.7) | 4458 | 6.7 | 2.00 (0.50–8.01) | 0.326 | 2.79 (0.63–12.39) | 0.177 |
| Control | 6/1812 (0.3) | 17,909 | 3.4 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age ≥ 50 years old (n = 3145) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 6/629 (1.0) | 3663 | 16.4 | 1.70 (0.65–4.42) | 0.279 | 3.25 (0.96–11.04) | 0.059 |
| Control | 14/2516 (0.6) | 14,647 | 9.6 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Men (n = 3775) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 7/755 (0.9) | 5702 | 12.3 | 3.51 (1.27–9.67) | 0.015 * | 1.70 (0.65–4.42) | 0.278 |
| Control | 8/3020 (0.3) | 22,910 | 3.5 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Women (n = 1635) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 2/327 (0.6) | 2419 | 8.3 | 0.66 (0.15–2.93) | 0.580 | 0.74 (0.13–4.25) | 0.732 |
| Control | 12/1308 (0.9) | 9646 | 12.4 | 1 | 1 | ||
| High income (n = 2860) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 6/572 (1.0) | 4309 | 13.9 | 1.70 (0.65–4.42) | 0.278 | 1.38 (0.47–4.07) | 0.555 |
| Control | 14/2288 (0.6) | 17,255 | 8.1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Low income (n = 2550) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 3/510 (0.6) | 3812 | 7.9 | 2.00 (0.50–7.99) | 0.328 | 2.23 (0.39–12.87) | 0.369 |
| Control | 6/2040 (0.3) | 15,301 | 3.9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Urbal residents (n = 2630) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 4/526 (0.8) | 3911 | 10.2 | 5.16 (1.16–23.07) | 0.032 * | 1.18 (0.43–3.20) | 0.748 |
| Control | 3/2104 (0.1) | 15,613 | 1.9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Rural residents (n = 2780) | |||||||
| Tonsillectomy | 5/556 (0.9) | 4210 | 11.9 | 7.31 (1.05–50.94) | 0.045 * | 0.81 (0.24–2.73) | 0.734 |
| Control | 17/2224 (0.8) | 16,943 | 10.0 | 1 | 1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Park, M.W.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, H.; Wee, J.H. Association between Tonsillectomy and Cardiovascular Diseases in Adults. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010016
Park SJ, Lee SY, Jung HJ, Park MW, Choi HG, Kim H, Wee JH. Association between Tonsillectomy and Cardiovascular Diseases in Adults. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010016
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sung Joon, Sei Young Lee, Hahn Jin Jung, Min Woo Park, Hyo Geun Choi, Heejin Kim, and Jee Hye Wee. 2024. "Association between Tonsillectomy and Cardiovascular Diseases in Adults" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010016
APA StylePark, S. J., Lee, S. Y., Jung, H. J., Park, M. W., Choi, H. G., Kim, H., & Wee, J. H. (2024). Association between Tonsillectomy and Cardiovascular Diseases in Adults. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010016







