Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographies
Abstract
1. Introduction
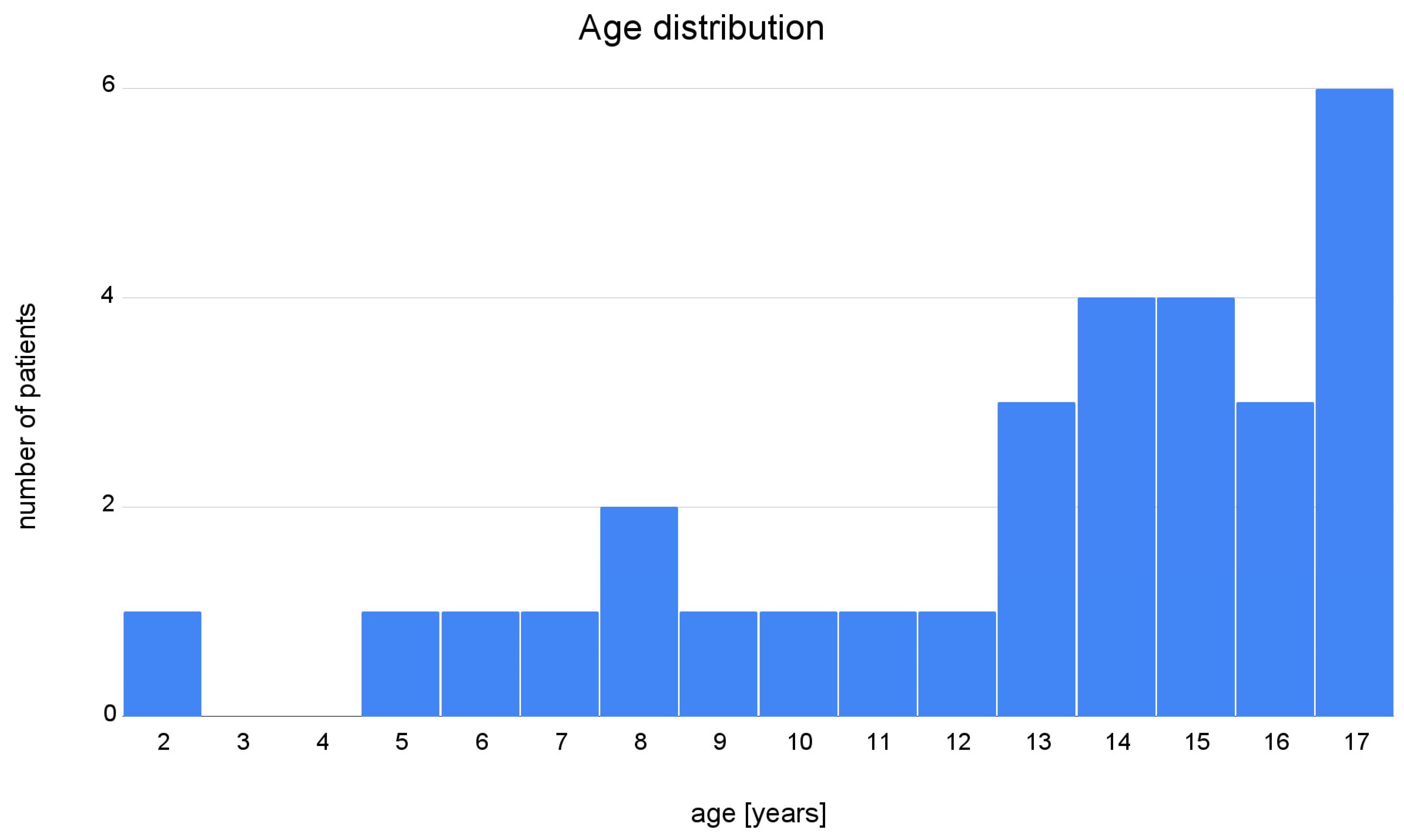
2. Materials and Methods
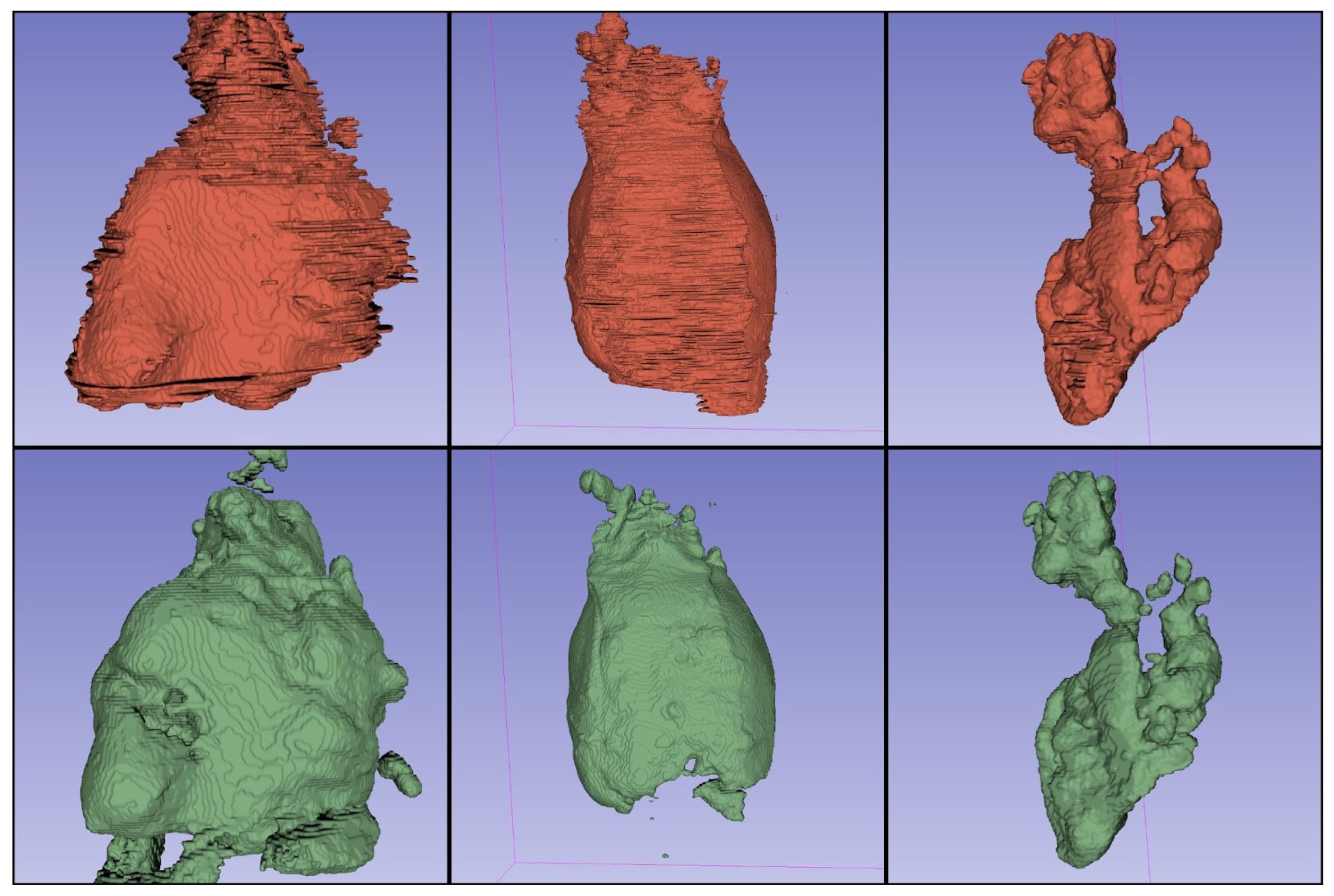
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, L.M.; Wang, S.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Hartge, P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Linet, M.S. Lymphoma Incidence Patterns by WHO Subtype in the United States, 1992–2001. Blood 2006, 107, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostakoglu, L.; Cheson, B.D. Current Role of FDG PET/CT in Lymphoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1004–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A.; Alliance, Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Consortium; et al. Recommendations for Initial Evaluation, Staging, and Response Assessment of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Lugano Classification. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, S.F.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Kostakoglu, L.; Meignan, M.; Hutchings, M.; Müeller, S.P.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Trotman, J.; et al. Role of Imaging in the Staging and Response Assessment of Lymphoma: Consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3048–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Hilden, P.; Coiffier, B.; Hagenbeek, A.; Salles, G.; Wilson, W.; Seymour, J.F.; Kelly, K.; Gribben, J.; Pfreunschuh, M.; et al. International Working Group Consensus Response Evaluation Criteria in Lymphoma (RECIL 2017). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, J.; Steyn, T.; Combrinck, N.; Joubert, G.; Sherriff, A.; Rensburg, J.J.V. Inter-Observer Variability Influences the Lugano Classification When Restaging Lymphoma. SA J. Radiol. 2018, 22, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girinsky, T.; Ghalibafian, M.; Bonniaud, G.; Bayla, A.; Magne, N.; Ferreira, I.; Lumbroso, J. Is FDG-PET Scan in Patients with Early Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma of Any Value in the Implementation of the Involved-Node Radiotherapy Concept and Dose Painting? Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 85, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlevi, C.L.; De Frank, S.; Stewart, C.; Hamlin, P.A.; Matasar, M.J.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Hamilton, A.M.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Drullinsky, P.; et al. Phase I/II Clinical Trial of Ibrutinib and Buparlisib in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Mantle Cell Lymphoma, and Follicular Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, W.; Terauchi, T.; Maruyama, D.; Nagai, H. Revised Staging System for Malignant Lymphoma Based on the Lugano Classification. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juweid, M.E. FDG-PET/CT in Lymphoma. In Positron Emission Tomography, 1st ed.; Juweid, M.E., Hoekstra, O.S., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–19. ISBN 978-1-61779-062-1. [Google Scholar]
- Im, H.-J.; Bradshaw, T.; Solaiyappan, M.; Cho, S.Y. Current Methods to Define Metabolic Tumor Volume in Positron Emission Tomography: Which One Is Better? Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 52, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasanelli, M.; Meignan, M.; Haioun, C.; Berriolo-Riedinger, A.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Biggi, A.; Gallamini, A.; Siegel, B.A.; Cashen, A.F.; Véra, P.; et al. Pretherapy Metabolic Tumour Volume Is an Independent Predictor of Outcome in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöder, H.; Moskowitz, C.H. Metabolic Tumor Volume in Lymphoma: Hype or Hope? J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3591–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Law, M.W.-M.; Khong, P.-L. Whole-Body PET/CT Scanning: Estimation of Radiation Dose and Cancer Risk. Radiology 2009, 251, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littooij, A.S.; Kwee, T.C.; Barber, I.; Granata, C.; Vermoolen, M.A.; Enríquez, G.; Zsíros, J.; Soh, S.Y.; de Keizer, B.; Beek, F.J.A.; et al. Whole-Body MRI for Initial Staging of Paediatric Lymphoma: Prospective Comparison to an FDG-PET/CT-Based Reference Standard. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baues, C.; Görgen, H.; Semrau, R.; Nast-Kolb, B.; Assenmacher, K.; Celik, E.; Morgenthaler, J.; Rosenbrock, J.; Trommer, M.; Houbois, C.; et al. Volumetric Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphoma Masses in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 3244–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri Devi, K.; Radhakrishnan, R. Automatic Segmentation of Colon in 3D CT Images and Removal of Opacified Fluid Using Cascade Feed Forward Neural Network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 670739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmanninger, J.; Prayer, F.; Pan, J.; Röhrich, S.; Prosch, H.; Langs, G. Automatic Lung Segmentation in Routine Imaging Is Primarily a Data Diversity Problem, Not a Methodology Problem. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserthal, J.; Meyer, M.; Breit, H.-C.; Cyriac, J.; Yang, S.; Segeroth, M. TotalSegmentator: Robust Segmentation of 104 Anatomical Structures in CT Images 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.05868. [Google Scholar]
- Klimont, M.; Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak, A.; Flieger, M.; Rzeszutek, J.; Jończyk-Potoczna, K. Pediatric Chest Lymphoma with Segmentation. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimont, M.; Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak, A.; Flieger, M.; Rzeszutek, J.; Jończyk-Potoczna, K. Pretrained Model for Pediatric Chest Lymphoma Segmentation. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma as an Alternative for Staging and Monitoring. Available online: https://github.com/fast-radiology/lymphoma (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–10 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Theory and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. NnU-Net: A Self-Configuring Method for Deep Learning-Based Biomedical Image Segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fastai. Available online: https://docs.fast.ai/index.html (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A. Metrics for Evaluating 3D Medical Image Segmentation: Analysis, Selection, and Tool. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.S.W.; Makmur, A.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, A.J.L.; Sia, D.S.Y.; Eide, S.E.; Ong, H.Y.; Jagmohan, P.; Tan, W.C.; et al. Improved Productivity Using Deep Learning–Assisted Reporting for Lumbar Spine MRI. Radiology 2022, 305, 220076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingelhoff, K.; Eichhorn, K.W.G.; Wagner, I.; Kunkel, M.E.; Moral, A.I.; Rilk, M.E.; Wahl, F.M.; Bootz, F. Analysis of Manual Segmentation in Paranasal CT Images. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 265, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, H.; Lu, L.; Seff, A.; Cherry, K.M.; Hoffman, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Turkbey, E.; Summers, R.M. A New 2.5 D Representation for Lymph Node Detection in CT. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2014, 17, 520–527. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, D.M.; Singer, A.A.; Chilcote, W.A.; Desai, R.K. Abdominal Lymphadenopathy: Spectrum of CT Findings. Radiographics 1991, 11, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornheim, J.; Seim, H.; Preim, B.; Hertel, I.; Strauss, G. Segmentation of Neck Lymph Nodes in CT Datasets with Stable 3D Mass-Spring Models: Segmentation of Neck Lymph Nodes. Acad. Radiol. 2007, 14, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feulner, J.; Kevin Zhou, S.; Hammon, M.; Hornegger, J.; Comaniciu, D. Lymph Node Detection and Segmentation in Chest CT Data Using Discriminative Learning and a Spatial Prior. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuga, A.-I.; Carolus, H.; Höink, A.J.; Brosch, T.; Klinder, T.; Maintz, D.; Persigehl, T.; Baeßler, B.; Püsken, M. Automated Detection and Segmentation of Thoracic Lymph Nodes from CT Using 3D Foveal Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoquaux, G.; Cheplygina, V. Machine Learning for Medical Imaging: Methodological Failures and Recommendations for the Future. Npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Region/Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Cervical lymph nodes not always distinguishable from surrounding tissues | Include cervical lymph nodes whenever possible |
| Unsharp border between lymphoma and thymic tissue | Exclude thymus from segmentation only when a clear border between lymphoma and thymus is visible; include thymus in segmentation when no clear border is visible |
| Unsharp borders between lymphoma/liquefactive necrosis and fluid in pericardium and pleural cavities | Try to exclude any pericardial and pleural effusion and include liquefactive necrosis in the segmentation (difficult in some cases) |
| Abdominal lymph nodes | Do not include in the segmentation |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 2D: 12 |
| 3D: 2 | |
| Float precision 16-bit | Yes |
| Max number of epochs * | 1000 |
| Number of batches per epoch * | 250 |
| Number of input channels | 1 |
| Initial learning rate * | 0.01 |
| Momentum * | 0.99 |
| Optimizer * | SGD |
| Patch size | 2D: 512 × 512 |
| 3D: 96 × 160 × 160 | |
| Weight decay * | 0.00003 |
| Model | Average Dice Coefficient |
|---|---|
| 2D U-Net | 0.7065 |
| 3D U-Net | 0.7262 |
| 3D U-Net Cascade | 0.7024 |
| 2D U-Net + 3D U-Net | 0.7221 |
| 2D U-Net + 3D U-Net Cascade | 0.7203 |
| 3D U-Net + 3D U-Net Cascade | 0.7148 |
| Patient | Dice | Manual Segmentation [cm3] | Automatic Segmentation [cm3] | Volume Difference [cm3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 0.88 | 288.79 | 257.68 | 31.11 |
| Patient 2 | 0.73 | 631.34 | 865.01 | −233.67 |
| Patient 3 | 0.92 | 776.99 | 686.14 | 90.85 |
| Patient 4 | 0.55 | 146.19 | 331.21 | −185.02 |
| Patient 5 | 0.95 | 354.63 | 352.09 | 2.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klimont, M.; Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak, A.; Flieger, M.; Rzeszutek, J.; Juszkat, R.; Jończyk-Potoczna, K. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographies. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020184
Klimont M, Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak A, Flieger M, Rzeszutek J, Juszkat R, Jończyk-Potoczna K. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographies. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlimont, Michał, Agnieszka Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak, Mateusz Flieger, Jacek Rzeszutek, Robert Juszkat, and Katarzyna Jończyk-Potoczna. 2023. "Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographies" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020184
APA StyleKlimont, M., Oronowicz-Jaśkowiak, A., Flieger, M., Rzeszutek, J., Juszkat, R., & Jończyk-Potoczna, K. (2023). Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Volume Calculation of Pediatric Lymphoma on Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomographies. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020184






