Cochlear Implantation: The Volumetric Measurement of Vestibular Aqueduct and Gusher Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
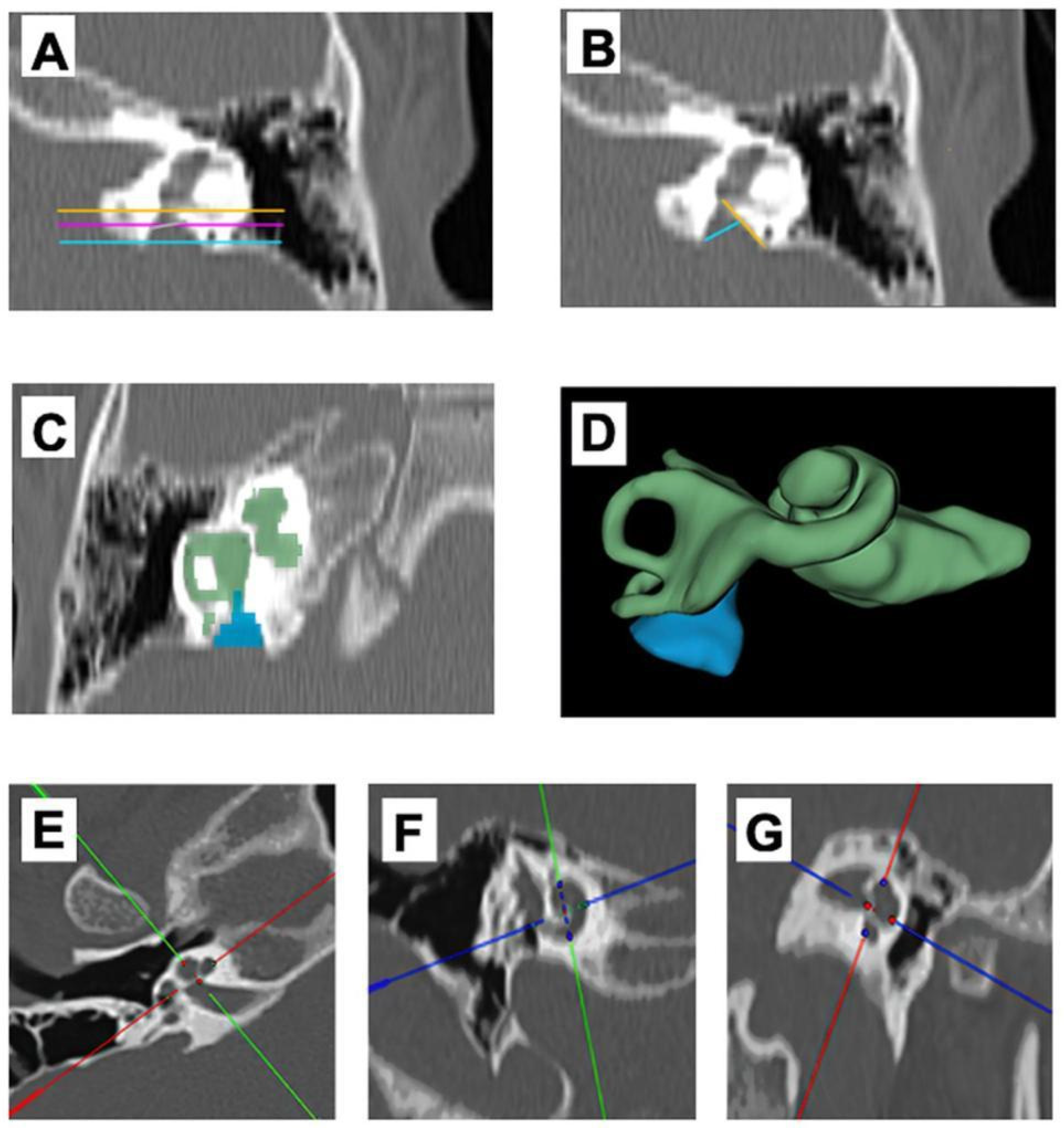
2.3. Assessment and Reliability of Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
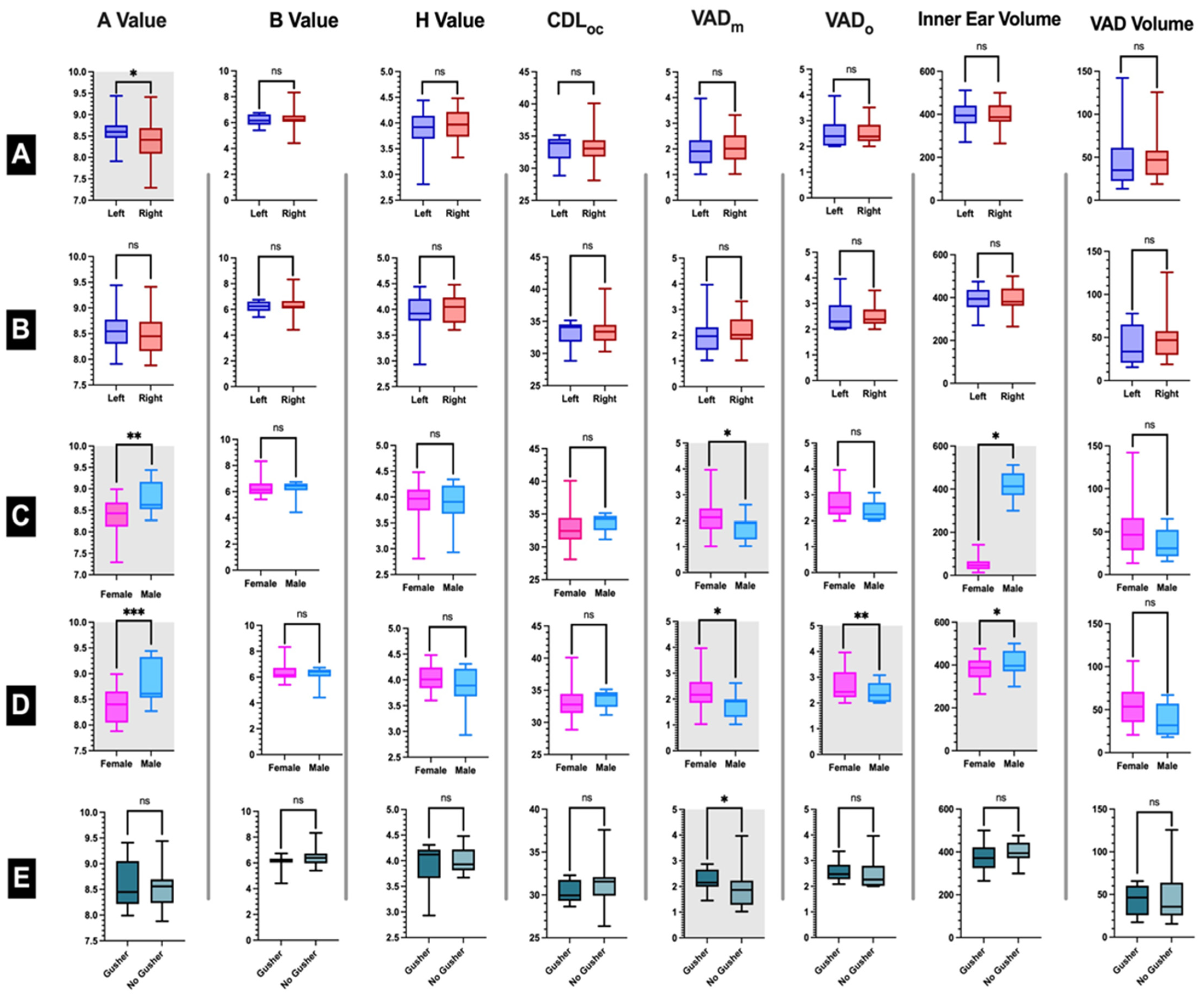
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Assessment and Reliability of Measurements
3.3. Correlations with CT VAD and Inner Ear Volumes
3.4. Regression Analysis
3.5. Risk Factors for Gusher
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Sheraz, S.; Malik, S.A.; Ahmed, N.R.; Malik, S.A.; Farooq, S. Frequency Of Congenital Hearing Loss In Neonates. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad JAMC 2018, 30, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korver, A.M.; Smith, R.J.; Camp, G.; Schleiss, M.R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.A.; Lustig, L.R. Congenital hearing loss. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 3, 16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.; Bamford, J.; Wilson, I.; Ramkalawan, T.; Forshaw, M.; Wright, S. A Critical Review of the Role of Neonatal Hearing Screening in the Detection of Congenital Hearing Impairment [Internet]. Vol. 1, HTA Health Technology Assessment NHS R&D HTA Programme Health Technology Assessment. 1997. Available online: www.hta.ac.uk/htacd.htm (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Pryor, S.P.; Madeo, A.C.; Reynolds, J.C.; Sarlis, N.J.; Arnos, K.S.; Nance, W.E. SLC26A4/PDS genotype-phenotype correlation in hearing loss with enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct (EVA): Evidence that Pendred syndrome and non-syndromic EVA are distinct clinical and genetic entities. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabionet, R.; Zelante, L.; López-Bigas, N.; D’Agruma, L.; Melchionda, S.; Restagno, G. Molecular basis of childhood deafness resulting from mutations in the GJB2 (connexin 26) gene. Hum. Genet. 2000, 106, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, S.A.; Saunders, K.; Osborn, A.H.; Arnold, A.; Wunderlich, J.; Kelly, T. High frequency hearing loss correlated with mutations in the GJB2 gene. Hum. Genet. 2000, 106, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, H.; Kupsch, P.; Sudendey, J.; Winterhager, E.; Jahnke, K.; Lautermann, J. Mutations in the connexin26/GJB2 gene are the most common event in non-syndromic hearing loss among the German population. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 17, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, A.; Yuge, I.; Kimura, S.; Namba, A.; Abe, S.; Laer, L. GJB2 deafness gene shows a specific spectrum of mutations in Japan, including a frequent founder mutation. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel-Friedrich, S. Congenital Auricular Malformations: Description of Anomalies and Syndromes. Facial. Plast. Surg. 2015, 31, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylanus, E.A.; Rotteveel, L.J.; Leeuw, R.L. Congenital malformation of the inner ear and pediatric cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Salamah, M.; Alenzi, S.; Badr, K.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Alsanosi, A. Cochlear Implantation in Adults and Pediatrics with Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct: A Systematic Review on the Surgical Findings and Patients’ Performance. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology [Internet]. 2022 Jun 30. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00405-022-07511-7 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Wu, C.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, P.J.; Hsu, C.J. Common clinical features of children with enlarged vestibular aqueduct and Mondini dysplasia. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopen, Q.; Zhou, G.; Whittemore, K.; Kenna, M. Enlarged vestibular aqueduct: Review of controversial aspects. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackler, R.K.; Cruz, A. The large vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Laryngoscope 1989, 99, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sun, C.; Shen, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q. Difference of SLC26A4 gene mutation frequency between patients with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome and/or Mondini dysplasia. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 35, 891–895. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.C.; Yeh, T.H.; Chen, P.J.; Hsu, C.J. Prevalent SLC26A4 mutations in patients with enlarged vestibular aqueduct and/or Mondini dysplasia: A unique spectrum of mutations in Taiwan, including a frequent founder mutation. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, S.; Rasp, G.; Sarikas, A.; Dossena, S. Genetic Determinants of Non-Syndromic Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct: A Review. Audiol. Res. 2021, 11, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, H.; Smouha, E.; Morgan, N. Multichannel cochlear implantation in a patient with bilateral Mondini deformities. Am. J. Otol. 1988, 9, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.; Kong, Y.; Xu, T.; Dong, R.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Qi, B.; Wang, S.; Yan, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Speech development in young children with Mondini dysplasia who had undergone cochlear implantation. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 116, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, F.; Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, S.; Han, D.; Zhang, L. The Development of Auditory Skills in Young Children with Mondini Dysplasia after Cochlear Implantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Arumugam, S.V.; Malik, V.; Goyal, S.; Kameswaran, M. Audiological and Surgical Outcomes of Pediatric Cochlear Implantation in Mondini’s Dysplasia: Our Experience. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, N.M.; Prasad, A.R.; Sayani, R.K.; Anand, A.; Jaychandran, G. Cochlear implantation in children with Mondini dysplasia: Our experience. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, N.E. Genetic Epidemiology of Hearing Impairment. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1991, 630, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondini, C. Anatomica surdi nati sectio; De Bononiensi scientarum et artium institute atque academia commentarii. Bononiae 1971, 7, 419–431. [Google Scholar]
- Mondini, C. Minor works of Carlo Mondini: The anatomical section of a boy born deaf. Am. J. Otol. 1997, 18, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, T.; Abu Rayan, A.; Abu Sa’ed, J.; Shahin, H.; Shepshelovich, J.; Lee, M.K. Genomic analysis of a heterogeneous Mendelian phenotype: Multiple novel alleles for inherited hearing loss in the Palestinian population. Hum. Genom. 2006, 2, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alenzi, S.; Dhanasingh, A.; Alanazi, H.; Alsanosi, A.; Hagr, A. Diagnostic Value of 3D Segmentation in Understanding the Anatomy of Human Inner Ear Including Malformation Types. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100 (Suppl. 5), 675S–683S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, R.; Stahl, M.; Hicks, K.; Murray, G.; Patel, N.; Gupta, A.; Otteson, T. Assessing the clinical utility of volumetric HRCT in pediatric enlarged vestibular aqueduct related hearing loss. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 155, 111067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthberg, J.; Ascha, M.S.; Kocharyan, A.; Gupta, A.; Murray, G.S.; Megerian, C.A.; Otteson, Y.D. Sex-specific enlarged vestibular aqueduct morphology and audiometry. Am. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Med. Surgery. 2019, 40, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettman, S.; Sadeghi-Barzalighi, A.; Ambett, R.; Dowell, R.; Trotter, M.; Briggs, R. Cochlear implants in forty-eight children with cochlear and/or vestibular abnormality. Audiol. Neurotol. 2011, 16, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlms, L.A.; Edwards, M.S.; Mason, E.O.; Igarashi, M.; Alford, B.R.; Smith, R.J. Recurrent meningitis and Mondini dysplasia. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1990, 116, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.L.; Calderwood, S.B.; Weber, D.J.; Miller, S.I.; Southwick, F.S.; Caviness, V.S., Jr. Acute bacterial meningitis in adults. A review of 493 episodes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papsin, B.C. Cochlear Implantation in Children With Anomalous Cochleovestibular Anatomy. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.B.; Bozorgi, H.; Kazemi, T.; Babaei, A. Cerebrospinal fluid gusher in cochlear implant and its associated factors. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennaroglu, L. Histopathology of inner ear malformations: Do we have enough evidence to explain pathophysiology? Cochlear. Implants Int. 2016, 17, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennaroglu, L. Response to Letter Regarding ‘Another Evidence for Pressure Transfer Mechanism in Incomplete Partition Two Anomaly via Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct’; Cochlear Implants International; Taylor and Francis Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2021; Volume 22, pp. 183–185. [Google Scholar]
- King, K.A.; Choi, B.Y.; Zalewski, C.; Madeo, A.C.; Manichaikul, A.; Pryor, S.P.; Ferruggiaro, A.; Eisenman, D.; Kim, H.J.; Niparko, J.; et al. SLC26A4 genotype, but not cochlear radiologic structure, is correlated with hearing loss in ears with an enlarged vestibular aqueduct. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.; Muskett, J.A.; King, K.A.; Zalewski, C.K.; Chattaraj, P.; Butman, J.A.; Kenna, M.A.; Chien, W.W.; Brewer, C.C.; Griffith, A.J. Hearing loss associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct and zero or one mutant allele of SLC26A4. Laryngoscope 2016, 127, E238–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, M. Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct and Cochlear Anomalies: Just an Association or a Causal Relationship? Cochlear Implants International; Taylor and Francis Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2021; Volume 22, p. 182. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | CT Inner Volume | CT VAD Volume | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combined | Combined | |||
| R | p-Value | R | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.292 | 0.061 | 0.278 | 0.075 |
| A Value | −0.044 | 0.783 | 0.015 | 0.926 |
| B Value | 0.183 | 0.246 | 0.048 | 0.765 |
| H Value | −0.154 | 0.33 | 0.231 | 0.141 |
| CDL at the level of OC | 0.092 | 0.563 | 0.053 | 0.74 |
| VAD at midpoint (mm) | −0.158 | 0.318 | 0.471 | 0.002 |
| VAD at operculum (mm) | 0.019 | 0.903 | 0.416 | 0.006 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std Error | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT inner volume for combined data | ||||
| Constant | 527.203 | 163.229 | 3.23 | 0.003 * |
| Sex | 75.202 | 19.085 | 3.94 | <0.001 * |
| Age | 5.188 | 1.605 | 3.232 | 0.003 * |
| A Value | −46.35 | 20.618 | −2.248 | 0.031 * |
| VAD at Operculum (mm) | 35.474 | 15.356 | 2.31 | 0.027 * |
| CT VAD volume for combined data | ||||
| Constant | −145.593 | 44.320 | −3.285 | 0.002 * |
| Age | 2.744 | 0.683 | 4.016 | <0.001 * |
| H Value (Height) | 20.017 | 9.595 | 2.086 | 0.044 * |
| VAD at Midpoint (mm) | 13.609 | 6.296 | 2.161 | 0.037 * |
| VAD at Operculum (mm) | 19.039 | 7.364 | 2.585 | 0.014 * |
| Variable | Coefficient | OR | p-Value | 95%C.I. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Constant | −13.608 | 0 | 0.152 | ||
| Sex | −2.384 | 0.092 | 0.048 * | 0.009 | 0.982 |
| CDL at the level of OC | 0.64 | 1.897 | 0.074 | 0.939 | 3.833 |
| VAD at midpoint (mm) | −2.242 | 0.106 | 0.023 * | 0.015 | 0.735 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alahmadi, A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Almuhawas, F.; Hamed, N.; Salamah, M.; Alsanosi, A. Cochlear Implantation: The Volumetric Measurement of Vestibular Aqueduct and Gusher Prediction. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020171
Alahmadi A, Abdelsamad Y, Almuhawas F, Hamed N, Salamah M, Alsanosi A. Cochlear Implantation: The Volumetric Measurement of Vestibular Aqueduct and Gusher Prediction. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(2):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlahmadi, Asma, Yassin Abdelsamad, Fida Almuhawas, Nezar Hamed, Marzouqi Salamah, and Abdulrahman Alsanosi. 2023. "Cochlear Implantation: The Volumetric Measurement of Vestibular Aqueduct and Gusher Prediction" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 2: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020171
APA StyleAlahmadi, A., Abdelsamad, Y., Almuhawas, F., Hamed, N., Salamah, M., & Alsanosi, A. (2023). Cochlear Implantation: The Volumetric Measurement of Vestibular Aqueduct and Gusher Prediction. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020171





