An AI Approach to Identifying Novel Therapeutics for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Limitations of Current Guidelines
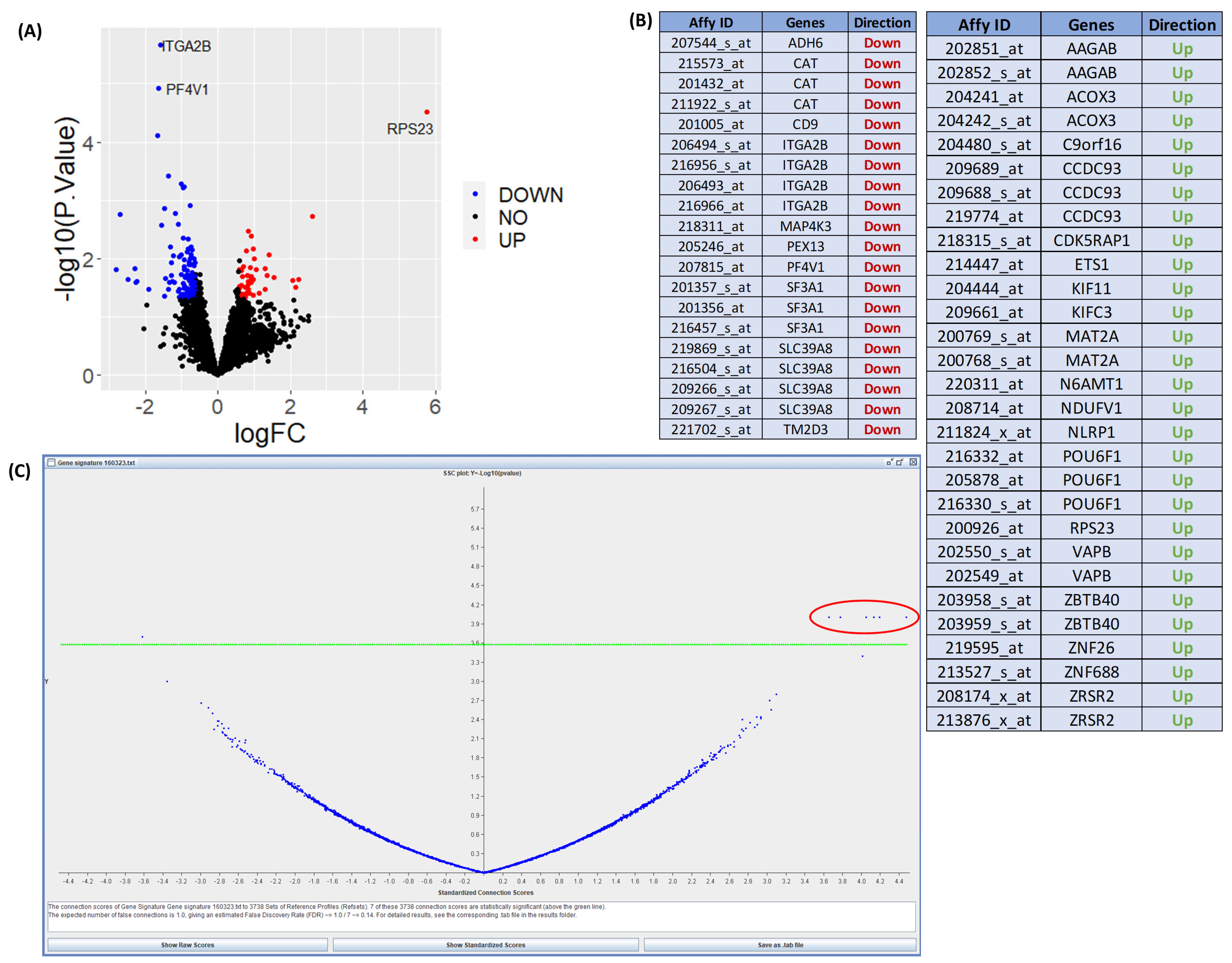
2.2. Connectivity Mapping
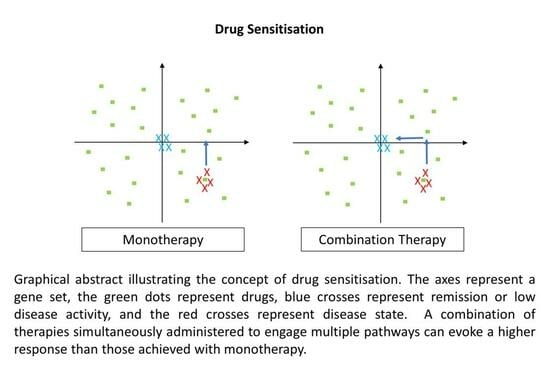
2.3. Drug Repurposing and Sensitisation
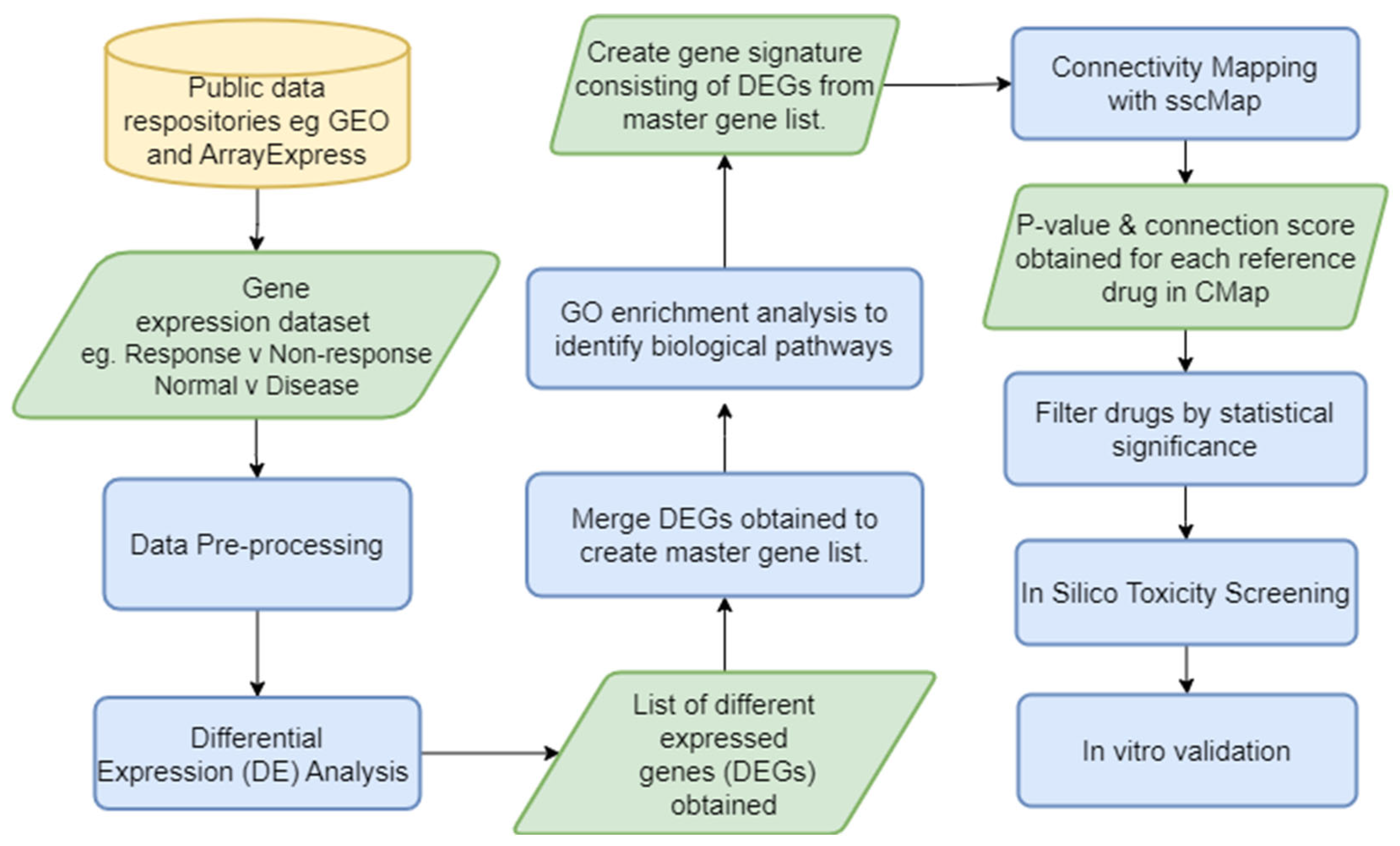
2.4. Bioinformatics Pipelines to Identify Potential Therapeutics
2.5. Application of Artificial Intelligence in RA
2.6. Challenges and Benefits
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.H.; Berman, J.R. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? JAMA 2022, 327, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figus, F.A.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.H.; Verstappen, S.M.M.; Hyrich, K.L.; Chipping, J.R.; Marshall, T.; Symmons, D.P.M. The incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in the UK: Comparisons using the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and the 1987 ACR classification criteria. Results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevalence and Incidence|Background Information|Rheumatoid Arthritis|CKS|NICE. Available online: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/rheumatoid-arthritis/background-information/prevalence-incidence/ (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Versus Arthritis. The State of Musculoskeletal Health 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.versusarthritis.org/media/25649/versus-arthritis-state-msk-musculoskeletal-health-2023.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Köhler, B.M.; Günther, J.; Kaudewitz, D.; Lorenz, H. Current Therapeutic Options in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, K.D.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Kelmenson, L.B.; Kuhn, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drongelen, V.; Holoshitz, J. HLA-Disease Associations in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 43, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedmon, L.E. The genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, S.; Yuan, X.; Shu, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H. Association between CTLA-4 gene polymorphism and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Aging 2021, 13, 19397–19414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimiyan, H.; Mostafaei, S.; Aslani, S.; Jamshidi, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Studying the association between STAT4 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis disease: An updated meta-analysis. Iran. J. Immunol. 2019, 16, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, C.; Chai, Z. Role of the PADI family in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers: A systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1115794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Woude, D.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and disease outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Best practice & research. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkova, M.; Petrovska, N.; Vencovsky, J.; Senolt, L.; Prajzlerova, K. The pre-clinical phase of rheumatoid arthritis: From risk factors to prevention of arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Jasemi, S.; Uras, G.; Erre, G.L.; Passiu, G.; Sechi, L.A. Role of Infections in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on Mycobacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising?: Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Alfredsson, L. Modifiable environmental exposure and risk of rheumatoid arthritis—Current evidence from genetic studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 1–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemtsova, M.V.; Zaletaev, D.V.; Bure, I.V.; Mikhaylenko, D.S.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Alekseeva, E.A.; Beloukhova, M.I.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Lukashev, A.N.; Zamyatnin, J.; et al. Epigenetic Changes in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.; Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.; Ahmed, S.; Do, D.; Ansari, R.; Ahmed, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med. Princ. Pract. 2019, 27, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, L.; Buch, M. The ‘therapeutic window’ and treating to target in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Med. 2013, 13, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Kwon, E.; Lee, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weddell, J.; Hider, S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Prescriber 2021, 32, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiel, M.H. Treat to target strategy in rheumatoid arthritis: Real benefits. Reumatol. Clin. 2013, 9, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; Vollenhoven, R.F.v.; Wit, M.d.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE Rheumatoid Arthritis Guideline. Available online: https://www.guidelines.co.uk/musculoskeletal-and-joints-/nice-rheumatoid-arthritis-guideline/454370.article (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grossi Moura, M.; Cruz Lopes, L.; Silva, M.T.; Barberato-Filho, S.; Motta, R.H.L.; Bergamaschi, C.d.C. Use of steroid and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Robson, J. The dangers of NSAIDs: Look both ways. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2016, 66, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Combe, B. Glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis: Current status and future studies. RMD Open 2020, 6, e000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoui, Y.; Guillot, X.; Sélambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Ralandison, S.; Gasque, P. Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, X.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, H.; Cui, H. Leflunomide Reduces Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Neuroblastoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, S.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigating the safety and compliance of using csDMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis treatment through face-to-face interviews: A cross-sectional study in China. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, B.; Cronstein, B. Methotrexate mechanism in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine Rev. Rhum. 2019, 86, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xie, D.; He, D.; Lu, A.; Liang, C. Toward Overcoming Treatment Failure in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 755844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482425/?report=classic (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Scott, L.J. Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, O.; Goyal, A.; Lappin, S.L. Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARD); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Luo, Y.; O’Shea, J.J.; Nakayamada, S. Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: A mechanisms-based approach. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.S.; Taylor, P.C.; Choy, E.H.; Sebba, A.; Quebe, A.; Knopp, K.L.; Porreca, F. The Jak/STAT pathway: A focus on pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, R.; Al Nokhatha, S.A.; Conway, R. JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence-Based Review on the Emerging Clinical Data. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior-Español, A.; Sánchez-Piedra, C.; Campos, J.; Manero, F.J.; Pérez-García, C.; Bohórquez, C.; Busquets-Pérez, N.; Blanco-Madrigal, J.M.; Díaz-Torne, C.; Sánchez-Alonso, F.; et al. Clinical factors associated with discontinuation of ts/bDMARDs in rheumatic patients from the BIOBADASER III registry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Gonçalves, D.; Bernardes, M.; Costa, L. Quality of life and functional capacity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—Cross-sectional study. Reumatol. Clin. 2018, 14, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versus Arthritis. The State of Musculoskeletal Health 2019. Versus Arthritis 2019, 91, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xie, W.; Geng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. Towards a Better Implementation of Treat-to-Target Strategy in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of Two Real-World Cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vollenhoven, R. Treat-to-target in rheumatoid arthritis—Are we there yet? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, B.; Agosti, J.; Bitton, A.; Corrigan, C.; Fraenkel, L.; Harrold, L.R.; Losina, E.; Katz, J.N.; Solomon, D.H. Implementation of Treat to Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US: Analysis of Baseline Data from the TRACTION Trial. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupatini, E.d.O.; Zimmermann, I.R.; Barreto, J.O.M.; da Silva, E.N. How long does it take to translate research findings into routine healthcare practice?—The case of biological drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in Brazil. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.; Pangan, A.L.; Song, I.; Mysler, E.; Bessette, L.; Peterfy, C.; Durez, P.; Ostor, A.J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Upadacitinib Versus Placebo or Adalimumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: Results of a Phase III, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, D.B. Factors associated with clinical trials that fail and opportunities for improving the likelihood of success: A review. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2018, 11, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. The Cost of Drug Development. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, A.; Ghoraie, L.S.; Zhang, S.; Glazko, G.; Yli-Harja, O.; Dehmer, M.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Emmert-Streib, F. A review of connectivity map and computational approaches in pharmacogenomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 506–523. [Google Scholar]
- Fortney, K.; Griesman, J.; Kotlyar, M.; Pastrello, C.; Angeli, M.; Sound-Tsao, M.; Jurisica, I. Prioritizing Therapeutics for Lung Cancer: An Integrative Meta-analysis of Cancer Gene Signatures and Chemogenomic Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; O’Reilly, P.; Dunne, P.D.; Lawler, M.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Hamilton, P.; Zhang, S. Connectivity mapping using a combined gene signature from multiple colorectal cancer datasets identified candidate drugs including existing chemotherapies. BMC Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcomson, B.; Wilson, H.; Veglia, E.; Thillaiyampalam, G.; Barsden, R.; Donegan, S.; El Banna, A.; Elborn, J.S.; Ennis, M.; Kelly, C.; et al. Connectivity mapping (ssCMap) to predict A20-inducing drugs and their antiinflammatory action in cystic fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3725–E3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.; Zhang, X. Identification of breast cancer hub genes and analysis of prognostic values using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2017, 21, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, W.; Lu, X.; Ma, S.; Dong, L.; Zou, B. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis and connectivity map identifies lovastatin as a treatment option of gastric cancer by inhibiting HDAC2. Gene 2019, 681, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Choi, M.; Kim, S. Bioinformatics and Connectivity Map Analysis Suggest Viral Infection as a Critical Causative Factor of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Rang, X.; Hong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C.; Fu, J. Immune cells transcriptome-based drug repositioning for multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1020721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, J.L.; Breda, C.; Mason, R.P.; Kooner, G.; Luthi-Carter, R.; Gant, T.W.; Giorgini, F. Connectivity mapping uncovers small molecules that modulate neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease models. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Lee, S. The Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Clinical Trials Provide Very Effective Therapeutic Combinations: Lessons Learned from Major Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehàr, J.; Krueger, A.S.; Avery, W.; Heilbut, A.M.; Johansen, L.M.; Price, E.R.; Rickles, R.J.; Short, G.F.; Staunton, J.E.; Jin, X.; et al. Synergistic drug combinations improve therapeutic selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X. Mechanisms of drug combinations: Interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.M.; Baker, J. Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: Methotrexate and beyond. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 64, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, D.P.; Cannon, G.W.; Teng, C.; Mikuls, T.R.; Curtis, J.R.; Sauer, B.C. Low Persistence Rates in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Triple Therapy and Adverse Drug Events Associated with Sulfasalazine. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pers, Y.; Padern, G. Revisiting the cardiovascular risk of hydroxychloroquine in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooller, S.K.; Benstead-Hume, G.; Chen, X.; Ali, Y.; Pearl, F.M.G. Bioinformatics in Translational Drug Discovery. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X. Bioinformatics and Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1709–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Smith, E.; Stegmaier, P.; Bergey, F.; Morris, L.; Kittner, M.; England, H.; Spiller, D.; White, M.H.R.; et al. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis. Models Mech. 2020, 13, dmm044040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, J.; Yang, M.; Dong, B.R.; Wu, H.M. Macrolides for diffuse panbronchiolitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD007716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, B.; Maślińska, M. Macrolide Therapy in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 636157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.P.H.; Thomas, P.R.S.; Tizard, M.L.V.; Lake, J.; Sanderson, J.D.; Hermon-Taylor, J. Two-year-outcomes analysis of Crohn’s disease treated with rifabutin and macrolide antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puniya, B.L.; Amin, R.; Lichter, B.; Moore, R.; Ciurej, A.; Bennett, S.J.; Shah, A.R.; Barberis, M.; Helikar, T. Integrative computational approach identifies drug targets in CD4+ T-cell-mediated immune disorders. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Q. A genomics-based systems approach towards drug repositioning for rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Cheng, W.; Ke, L.; Sun, A.R.; Jia, Q.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, P. Repurposing of Pirfenidone (Anti-Pulmonary Fibrosis Drug) for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 631891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, U.; Comertpay, B.; Demirtas, T.Y.; Gov, E. Drug repurposing for rheumatoid arthritis: Identification of new drug candidates via bioinformatics and text mining analysis. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Nowroozi, A.; Rezaei, N. Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Status and Future Perspectives: A State-of-the-Art Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 1249–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wu, H.; Wu, L.; Cui, C.; Shi, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, F. A deep learning classification of metacarpophalangeal joints synovial proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis by ultrasound images. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2022, 50, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steunebrink, L.M.M.; Versteeg, G.A.; Vonkeman, H.E.; Klooster, P.M.T.; Kuper, H.H.; Zijlstra, T.R.; van Riel, P.L.C.M. Initial combination therapy versus step-up therapy in treatment to the target of remission in daily clinical practice in early rheumatoid arthritis patients: Results from the DREAM registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Gant, T.W. sscMap: An extensible Java application for connecting small-molecule drugs using gene-expression signatures. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zou, L.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, J. Transcriptome based drug repositioning identifies TPCA 1 as a potential selective inhibitor of esophagus squamous carcinoma cell viability. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Teng, S.; Bao, X.; Lu, Z.J.; Wang, D. A comprehensive evaluation of connectivity methods for L1000 data. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhu, Y. The Challenges of Data Quality and Data Quality Assessment in the Big Data Era. Data Sci. J. 2015, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Gonzalez, A.; Cabezon, A.; Seco-Gonzalez, A.; Conde-Torres, D.; Antelo-Riveiro, P.; Pineiro, A.; Garcia-Fandino, R. The Role of AI in Drug Discovery: Challenges, Opportunities, and Strategies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoseri, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.M. Re-Thinking Data Strategy and Integration for Artificial Intelligence: Concepts, Opportunities, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Xiang, Y.; Lin, D.; Yan, A.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Lai, W.; Wu, X.; Wan, C.; et al. Expert recommendation on collection, storage, annotation, and management of data related to medical artificial intelligence. Intell. Med. 2023, 3, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippman, C.; Nislow, C. Pharmacogenomic testing: Clinical evidence and implementation challenges. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virelli, C.R.; Mohiuddin, A.G.; Kennedy, J.L. Barriers to clinical adoption of pharmacogenomic testing in psychiatry: A critical analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabbani, D.; Akika, R.; Wahid, A.; Daly, A.K.; Cascorbi, I.; Zgheib, N.K. Pharmacogenomics in practice: A review and implementation guide. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1189976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajan, J.R.; McDonald, S.; Bjourson, A.J.; Zhang, S.-D.; Gibson, D.S. An AI Approach to Identifying Novel Therapeutics for Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13121633
Rajan JR, McDonald S, Bjourson AJ, Zhang S-D, Gibson DS. An AI Approach to Identifying Novel Therapeutics for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(12):1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13121633
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajan, Jency R., Stephen McDonald, Anthony J. Bjourson, Shu-Dong Zhang, and David S. Gibson. 2023. "An AI Approach to Identifying Novel Therapeutics for Rheumatoid Arthritis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 12: 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13121633
APA StyleRajan, J. R., McDonald, S., Bjourson, A. J., Zhang, S.-D., & Gibson, D. S. (2023). An AI Approach to Identifying Novel Therapeutics for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(12), 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13121633