The Role of the Pharmacist in Selecting the Best Choice of Medication Formulation in Dysphagic Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Drug Formulations for Administration by Tube: The Pivotal Role of the Pharmacist
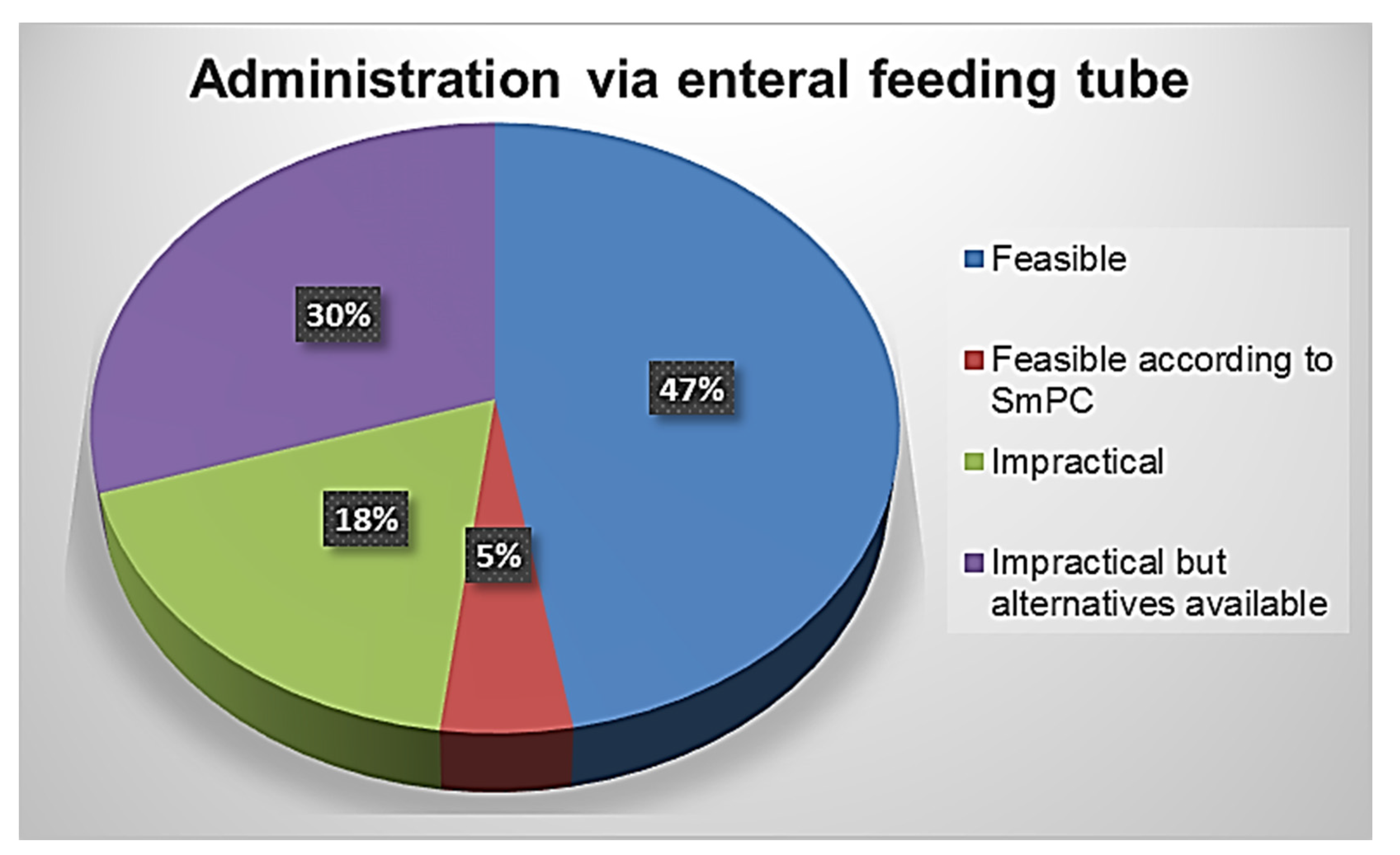
3.2. The Feasibility of Drug Administration by Enteral Feeding Tube
3.2.1. Liquid Formulations
3.2.2. Solid Formulations
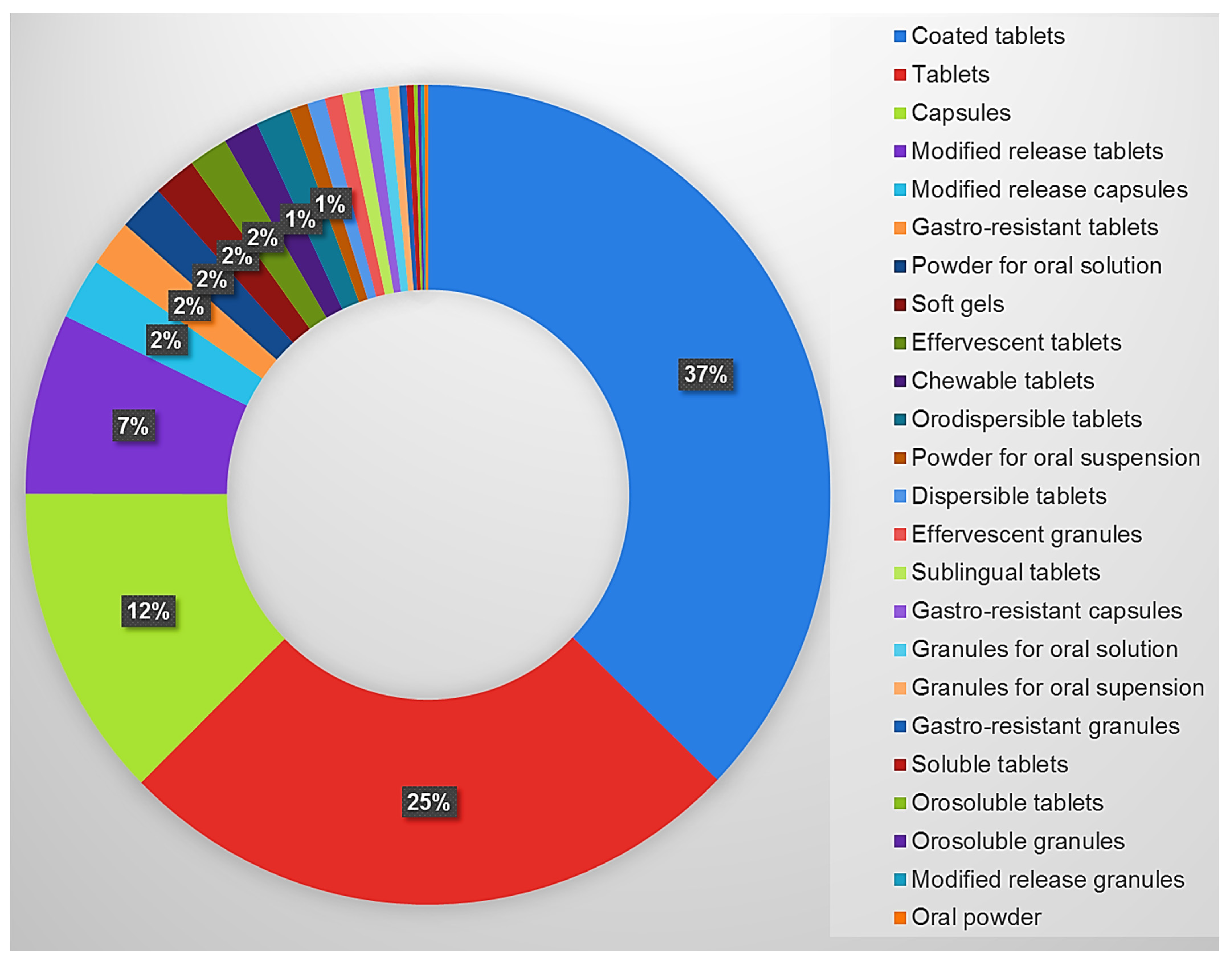
3.3. Analysis of the Solid Oral Formulations Present in the Hospital Formulary
3.4. Magistral Liquid Preparations
3.5. Instructions for the Nursing Staff Concerning Administration of Drugs via Tube
- if the patient is undergoing EN, temporarily stop the infusion;
- before administration, wash the probe with 30 mL of water;
- take, where necessary, a tablet crusher, wash it with water and dry it, then grind the tablet to a fine powder;
- put the powder or other pharmaceutical forms directly in a plastic cup, add 30 mL of water at room temperature, shake and dissolve (possibly with the help of a disposable plastic spoon);
- once a solution or a suspension is obtained, draw it with a 60 mL catheter cone syringe (dedicated syringe for EN). Make sure there are no drug residues left in the glass;
- check the correct positioning of the tube; insert the syringe cone into the tube connector and flush the medication dose down the feeding tube. If the medical prescription provides for the administration of several drugs at the same time, do not simultaneously grind several drugs and do not mix them in the same syringe, but it is necessary to rinse the tube between one drug and another with at least 5–10 mL of water to ensure that the tube is clean during the transition to the next drug;
- rinse the tube with at least 40 mL of water after the administration;
- restart the feed, unless a break is required.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowat, A. Enteral Tube Feeding for Dysphagic Stroke Patients. Br. J. Nurs. 2015, 24, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.; Duerksen, D. Enteral Nutrition in the Management of Pediatric and Adult Crohn’s Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffe, A.; Anton, N.; Lequier, L.; Vandermeer, B.; Tjosvold, L.; Larsen, B.; Hartling, L. Nutritional Support for Critically Ill Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, CD005144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochs, H.; Dejong, C.; Hammarqvist, F.; Hebuterne, X.; Leon-Sanz, M.; Schütz, T.; van Gemert, W.; van Gossum, A.; Valentini, L.; Lübke, H.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Gastroenterology. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorner, B.; Posthauer, M.E.; Friedrich, E.K.; Robinson, G.E. Enteral Nutrition for Older Adults in Nursing Facilities. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2011, 26, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gossum, A.; Cabre, E.; Hébuterne, X.; Jeppesen, P.; Krznaric, Z.; Messing, B.; Powell-Tuck, J.; Staun, M.; Nightingale, J. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Gastroenterology. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://farmaci.agenziafarmaco.gov.it/bancadatifarmaci/home (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Zanello, M. Linee Guida SINPE per la Nutrizione Artificiale Ospedaliera 2002-Parte Generale Rivista Italiana di Nutrizione Parenterale ed Enterale/Anno 20 S5; Wichtig Publishing S.r.l.: Milan, Italy, 2002; pp. S37–S43. Available online: https://www.simpe.it/documenti/campus2016/gastro/Linee_guida_sinpe_na_ospedaliera.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Bischoff, S.C.; Austin, P.; Boeykens, K.; Chourdakis, M.; Cuerda, C.; Jonkers-Schuitema, C.; Lichota, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Schneider, S.M.; Stanga, Z.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Home Enteral Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Bradnam, V. Hanbook of Drug Administration via Enteral Feeding Tubes, 3rd ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_675_allegato.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Wasylewicz, A.T.M.; van Grinsven, R.J.B.; Bikker, J.M.W.; Korsten, H.H.M.; Egberts, T.C.G.; Kerskes, C.H.M.; Grouls, R.J.E. Clinical Decision Support System-Assisted Pharmacy Intervention Reduces Feeding Tube-Related Medication Errors in Hospitalized Patients: A Focus on Medication Suitable for Feeding-Tube Administration. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckwith, M.C.; Feddema, S.S.; Barton, R.G.; Graves, C. A Guide to Drug Therapy in Patients with Enteral Feeding Tubes: Dosage Form Selection and Administration Methods. Hosp. Pharm. 2004, 39, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urashima, Y.; Urashima, K.; Ohnishi, M.; Matsushita, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kurachi, K.; Nishihara, M.; Katsumata, T.; Myotoku, M.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Interaction between Phenytoin and Enteral Nutrients and Its Influence on Gastrointestinal Absorption. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klang, M.; Graham, D.; McLymont, V. Warfarin Bioavailability with Feeding Tubes and Enteral Formula. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://farmaci.agenziafarmaco.gov.it/aifa/servlet/PdfDownloadServlet?pdfFileName=footer_000542_024447_RCP.pdf&retry=0&sys=m0b1l3 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Available online: https://farmaci.agenziafarmaco.gov.it/aifa/servlet/PdfDownloadServlet?pdfFileName=footer_001144_024989_FI.pdf&retry=0&sys=m0b1l3 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Available online: https://farmaci.agenziafarmaco.gov.it/aifa/servlet/PdfDownloadServlet?pdfFileName=footer_000813_028467_RCP.pdf&sys=m0b1l3 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Treleano, A.; Wolz, G.; Brandsch, R.; Welle, F. Investigation into the Sorption of Nitroglycerin and Diazepam into PVC Tubes and Alternative Tube Materials during Application. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 369, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark-Schmidt, A.L.; Garnett, W.R.; Lowe, D.R.; Karnes, H.T. Loss of carbamazepine suspension through nasogastric feeding tubes. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1990, 47, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
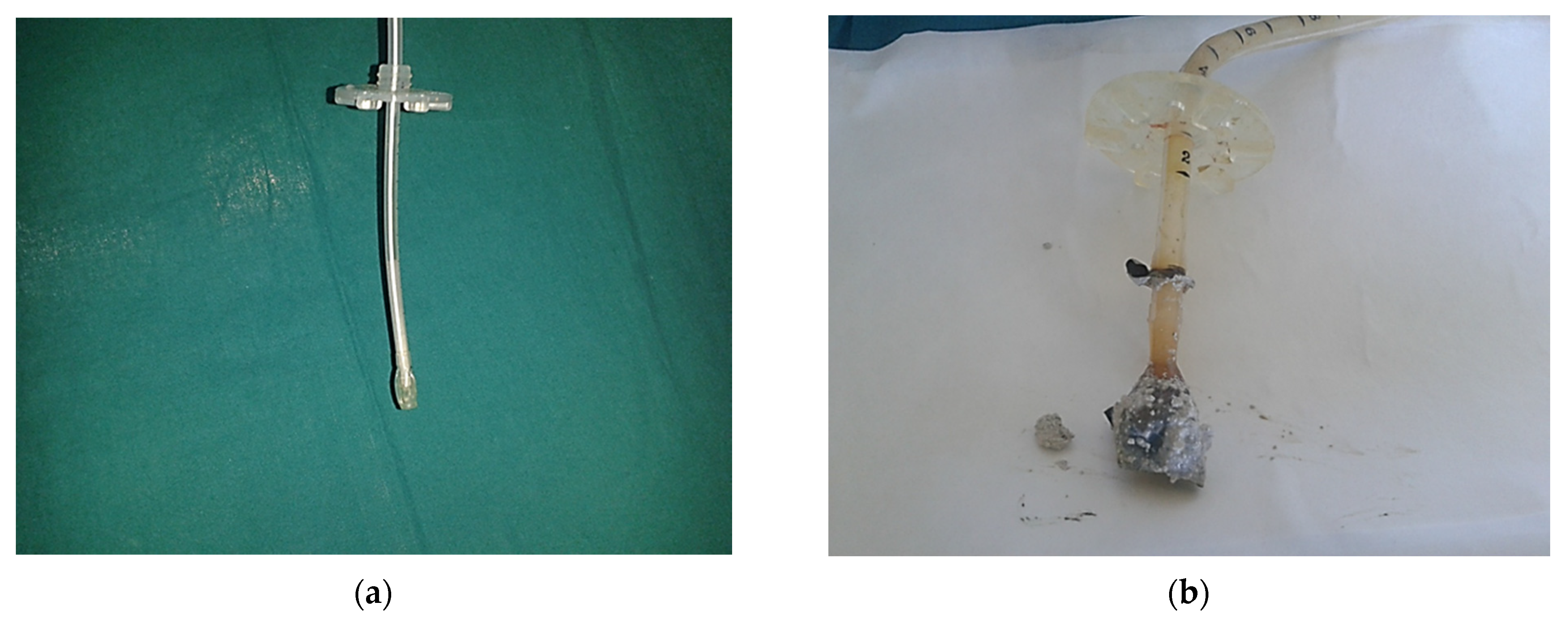
- Reece, G.; Kesarwani, V.; Ghelani, D. Enteral Feed Obstructing Its Own Way. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 14, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2892_allegato.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Ferreira Silva, R.; Rita Carvalho Garbi Novaes, M. Interactions between drugs and drug-nutrient in enteral nutrition: A review based on evidences. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, M.; McLymont, V.; Ng, N. Osmolality, PH, and Compatibility of Selected Oral Liquid Medications with an Enteral Nutrition Product. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziolek, M.; Alcaro, S.; Augustijns, P.; Basit, A.W.; Grimm, M.; Hens, B.; Hoad, C.L.; Jedamzik, P.; Madla, C.M.; Maliepaard, M.; et al. The Mechanisms of Pharmacokinetic Food-Drug Interactions–A Perspective from the UNGAP Group. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensel, T.M. Administration of proton pump inhibitors in patients requiring enteral nutrition. Pharm. Ther. 2009, 34, 143–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tousseeva, A.; Jackson, J.D.; Redell, M.; Henry, T.; Hui, M.; Capurso, S.; DeRyke, C.A. Stability and Recovery of DIFICID® (Fidaxomicin) 200-Mg Crushed Tablet Preparations from Three Delivery Vehicles, and Administration of an Aqueous Dispersion via Nasogastric Tube. Drugs R D 2014, 14, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

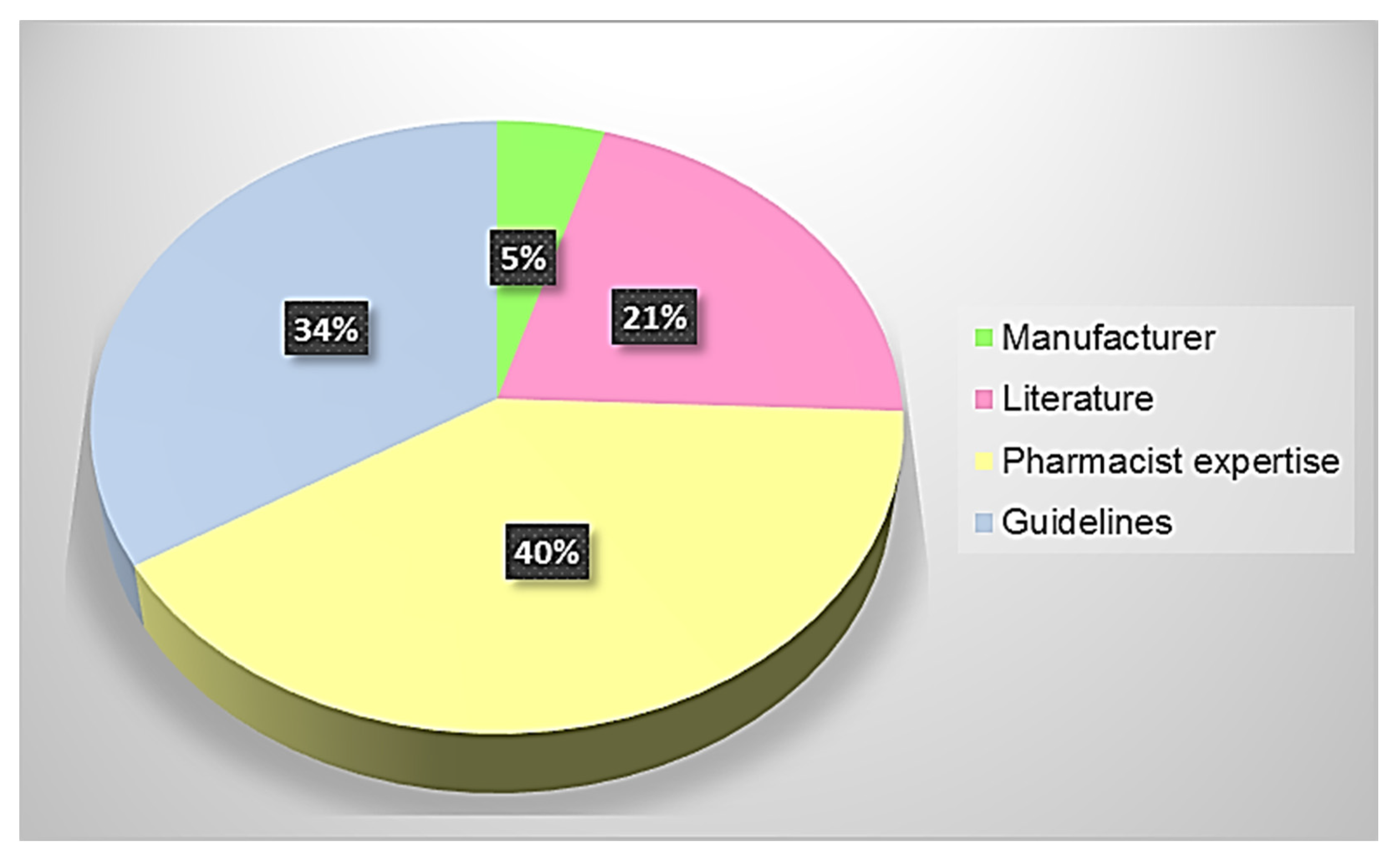
| Source | Level of Reliability |
|---|---|
| Summary of product characteristics | A |
| European and Italian guidelines on artificial nutrition | B |
| Research studies available in the literature | C |
| Hospital pharmacist know-how | D |
| Administration Route | API | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Intramuscular (i.m.) | Ampicillin/sulbactam Lorazepam Prednisolone | Expensive Invasive procedure Inappropriate in immunocompromised or bleeding-prone patients Only feasible with expert help |
| Intravenous (i.v.) | Dexamethasone Digoxin Phenytoin Hydromorphone Methotrexate Morphine Prometazin | Expensive Invasive procedure Only feasible with expert help |
| Inhalation | Salbutamolo Nicotina Zanamivir | Unavailable, not to be used if there is trauma to the upper airway |
| Rectal | Aspirin Bisacodil Caffeine/ergotamin Lactulose Morphine Prochloroperazine Prometazin Sodium polystyrene sulfonate | Low compliance Inappropriate in patients with heart disease, immunocompromised, rectal surgery or bleeding |
| Subcutaneous | Fentanyl Hydromorphone Morphine | Expensive Invasive procedure May cause local tissue damage Absorption of the drug may be slower than via i.v or i.m. Inappropriate in immunocompromised patients Only feasible with expert help |
| Transdermal | Estradiol Fentanyl Nicotine Nitroglycerin | Inappropriate in patients with cutaneous rush, dermatitis or open lesions Risk of skin irritation, itching, contact dermatitis |
| ATC | API (Strength) | Brand Name (Manufacturer) | Dosage Form | Via Tube | Operative Information | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A02AD01 | Aluminum hydroxide Magnesium hydroxide (800 mg) | MAALOX (SANOFI) | Chewable tablets | No | Interaction with dietary proteins Tube obstruction Use alternative medications | |
| A02AH | Sodium bicarbonate (500 mg) | SOD BIC NAR (NOVA ARGENTIA) | Tablets | No | Use other routes of administration | |
| A02BA02 | Ranitidine hydrochloride (150 mg) | RANIDIL (A.MENARINI) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | The tablet should be diluted with at least 75 mL of water (to be avoided in patients on a low sodium diet or with phenylketonuria) Alternatives: liquid formulation to be diluted with 60 mL of water (contains ethyl alcohol), or sugar-free galenic preparation | |
| A02BA02 | Ranitidine hydrochloride (150 mg) | ZANTAC (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | The effervescent tablets are the first choice (to be avoided in patients on a low sodium diet or with phenylketonuria) Alternatives: liquid formulation to be diluted with 60 mL of water (contains ethyl alcohol), or Ranitidine 15 mg/mL galenic preparation | [8,9] |
| ZANTAC SOLUB (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Effervescent tablets | |||||
| RANITIDINA MYL (MYLAN) | Coated tablets | |||||
| RANITIDINA RATIO (RATIOPHARM) | Coated tablets | |||||
| RANITIDINA TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | |||||
| A02BB01 | Misoprostol (200 µg) | CYTOTEC 200 (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet in a mortar, add 15 mL water, draw the suspension into the syringe and administer immediately Rinse the mortar with 15 mL water, draw this water into the syringe and administer Due to the poor stability of the API better an alternative therapy (Ranitidine or Lansoprazole) | [10] |
| A02BC01 | Omeprazole (20 mg) | ANTRA (ASTRAZENECA) | Gastro-resistant capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, suspend the granules contained therein with 20 mL water and then administer after 15–20 min in a tube >8 Fr The granules must not be crushed For children the galenic preparation of omeprazole suspension 2 mg/mL is required | [26] |
| Omeprazole (10 mg) | OMEPRAZOLO TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| A02BC02 | Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate (20, 40 mg) | PANTORC (TAKEDA) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Change route of administration or substitute API with Omeprazole or Lansoprazole | [8,9] |
| A02BC03 | Lansoprazole (15, 30 mg) | LANSOX (TAKEDA) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | Disperse in a small amount of water and administer through a nasogastric tube or oral syringe | SmPC |
| A02BC03 | Lansoprazole (15, 30 mg) | LANSOX (TAKEDA) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, suspend the granules with water and administer after 20 min Prefer orodispersible tablets | [26] |
| A02BC04 | Rabrepazole sodium (10, 20 mg) | PARIET (JANSSEN CILAG) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Do not grind gastro-resistant tablets Alternatives: esomeprazole, lansoprazole or omeprazole | [8,9] |
| A02BC05 | Esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate (10 mg) | NEXIUM (ASTRAZENECA) | Gastro-resistant granules | Yes | To a dose of 10 mg add 15 mL water, mix and leave to thicken for a few minutes Do not crush the granules, withdraw the suspension with a syringe and inject through the tube of 6 Fr caliber or greater for 30 min Rinse the tube with 15 mL water | SmPC |
| A02BC05 | Esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate (10 mg) | LUCEN (MALESCI) | Gastro-resistant granules | Yes | Mix the granules with 15 mL water, allow to thicken Pick up the suspension with a syringe and inject it into a tube of 6 Fr caliber or greater | SmPC |
| A02BX02 | Sucralfate (2 g) | SUCRALFIN (SANOFI) | Granules for oral suspension | No | Risk of tube occlusion, bezoar formations | [10,21] |
| SUCRAMAL (SCHARPER) | ||||||
| A02BX13 | Sodium alginate Sodium bicarbonate (250 + 133.5 mg) | GAVISCON (RECKITT BENCKISER) | Chewable tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A03AA05 | Trimebutine maleate (150 mg) | DEBRIDAT (SIGMA TAU) | Soft gels | No | Alternatives: solution for injection or suppositories | [8,9] |
| A03AA06 | Rociverin (10 mg) | RILATEN (LABORATORI GUIDOTTI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Tablet can be triturated and administered with water | |
| A03AX13 | Simethicone (40 mg) | MYLICONGAS (JOHNSON & JOHNSON) | Chewable tablets | No | Alternative: drops to be diluted with 50 mL water and given immediately | [8,9] |
| A03BB01 | Scopolamine methyl bromide (10 mg) | BUSCOPAN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Tablet can be triturated Alternative: solution for injection | |
| A03FA01 | Metoclopramide hydrochloride monohydrate (10 mg) | PLASIL (SANOFI) | Tablets | No | Alternative: syrup which must be diluted and given away from EN | [8,9] |
| A03FA03 | Domperidone maleate (10 mg) | DOMPERIDONE AGE (ANGENERICO) | Tablets | No | Alternatives: suppositories or oral suspension (to be diluted with water and administered at least 15 min before the start of EN) | [8,9] |
| A03FA03 | Domperidone (10 mg) | PERIDON (ITALCHIMICI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: suppositories or oral suspension (to be diluted with water and administered at least 15 min before the start of EN) | [8,9] |
| A04AA01 | Ondansetron hydrochloride dihydrate (4 mg) | ZOFRAN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | Prefer orodispersible tablets, syrup or solution for injection | [8,9] |
| A04AA01 | Ondansetron (8 mg) | ZOFRAN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | ||
| A04AA01 | Ondansetron hydrochloride (4, 8 mg) | ONDANSETRONE TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Zofran syrup | [8,9] |
| A04AA02 | Granisetron hydrochloride (2 mg) | KYTRIL (ROCHE) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| A04AD12 | Aprepitant (125, 80 mg) | EMEND (MSD) | Capsules | No | Open the capsule and administer the granules with water without crushing Preferred alternative: Ivemend solution for injection | |
| A05AA02 | Ursodeoxycholic acid (450, 150 mg) | DEURSIL (CHEPLAPHARM ARZNEIMITTEL) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternatives: granules for oral suspension, capsules | [8,9] |
| A05AA02 | Ursodeoxycholic acid (450, 150 mg) | URSILON (I.B.I.GIOVANNI LORENZINI) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule and suspend the granules in 20 mL water then administer immediately | [10] |
| A05BA03 | Sylimarin (70 mg) | LEGALON (MEDA PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| A06AB06 | Senna leaves (12 mg) | PURSENNID (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | Prefer other laxatives in syrups | [10] |
| A06AB58 | Sodium picosulfate Magnesium oxide Anhydrous citric acid | PICOPREP (FERRING) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dissolve the powder in 150 mL of water | |
| A06AD11 | Lactulose (10 g) | LAEVOLAC EPS (ROCHE) | Granules for oral solution | Yes | Dilute with at least 60 mL water Avoid high doses, risk of diarrhea and malabsorption of dietary nutrients | |
| A06AD15 | Macrogol 4000 (4, 9.7, 10 g) | PAXABEL (IPSEN) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dissolve the powder in 125 mL water and administer immediately Seek dietary advice in case of chronic constipation | |
| REGOLINT (LABORATORI BALDACCI) | ||||||
| LAXIPEG (ZAMBON) | ||||||
| A06AD65 | Macrogol 4000 Sodium sulfate Sodium bicarbonate Sodium chloride Potassium chloride (17.4, 34.8 g) | ISOCOLAN (GIULIANI) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dissolve the powder in 250 mL water then shake and administer immediately | SmPC |
| A06AD65 | Macrogol 3350 Sodium bicarbonate Sodium chloride Potassium chloride (13.8 g) | MOVICOL (NORGINE) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dissolve the powder in 125 mL water, shake and administer immediately Seek dietary advice in case of chronic constipation | |
| A06AD65 | Macrogol 3350 Sodium sulfate Sodium bicarbonate Sodium chloride Potassium chloride Ascorbic Acid Sodium Ascorbate (112 g) | MOVIPREP (NORGINE) | ||||
| A07AA06 | Paromomycin sulfate (250 mg) | HUMATIN (PFIZER) | Capsules | No | Alternative: syrup to be diluted in at least 60 mL water and then given immediately | [8,9] |
| A07AA09 | Vancomycin hydrochloride (250 mg) | MAXIVANIL (GENETIC) | Capsules | No | Alternatives: powder for oral solution or for infusion | [10] |
| A07AA11 | Rifaximin (200 mg) | NORMIX (ALFA WASSERMANN) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension | [8,9] |
| A07AA12 | Fidaxomicin (200 mg) | DIFICLIR (ASTELLAS) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, suspend the powder in water and administer immediately | [27] |
| A07BC05 | Diosmectite (3 g) | DIOSMECTAL (MALESCI) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dissolve the powder in half a glass of water and then administer | |
| A07DA03 | Loperamide hydrochloride (2 mg) | LOPERAMIDE HEX (SANDOZ) | Capsules | No | Use other dosage form | |
| A07DA03 | Loperamide hydrochloride (2 mg) | DISSENTEN (SOC.PRO.ANTIBIOTICI) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| A07EA06 | Budesonide (3 mg) | ENTOCIR (ASTRAZENECA) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternative: suppositories | [8,9] |
| A07EA07 | Beclomethasone dipropionate (5 mg) | CLIPPER (CHIESI FARMACEUTIC)I | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Alternative: rectal preparations for distal ulcerative colitis | [8,9] |
| A07EC01 | Sulfasalazine (500 mg) | SALAZOPYRIN EN (PFIZER) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A07EC02 | Mesalazine (400, 500, 800, 1200 mg) | PENTASA (FERRING) | Modified release tablets | Yes | Break the tablet and let it disintegrate in water. Alternatives: suppositories or rectal suspension | SmPC |
| A07EC02 | Mesalazine (400, 500, 800, 1200 mg) | MESAVANCOL (GIULIANI) | Modified release tablets | No | Do not crush Alternatives: rectal suspension or suppositories | [8,9] |
| PENTACOL (SOFAR) | ||||||
| A07FA02 | Saccharomyces boulardii (5 bn) | CODEX (ZAMBON) | Capsules | No | ||
| CODEX (ZAMBON) | Powder for oral suspension | |||||
| A09AA02 | Pancrelipase (150, 300 mg) | CREON 25000 (BGP PRODUCTS) | Modified release capsules | Yes | Open the capsule without grinding the granules, suspend them in 20 mL water or in liquids, with a pH <5.5 such as apple, pineapple juice or yogurt, then administer immediately | |
| A10BA02 | Metformin hydrochloride (500, 850, 1000 mg) | GLUCOPHAGE (BRUNO FARMACEUTICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, suspend the powder in 20 mL water, and administer immediately | [10] |
| A10BA02 | Metformin hydrochloride (500, 850, 1000 mg) | ZUGLIMET (ZENTIVA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, suspend the powder in 20 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| A10BB01 | Glibenclamide (5 mg) | DAONIL (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, suspend the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN at least 30 min before drug administration | |
| A10BB09 | Gliclazide (30, 60 mg) | DIAMICRON (SERVIER) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A10BB09 | Gliclazide (80 mg) | GLICLAZIDE (ZENTIVA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and suspend the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN at least 30 min before drug administration Divisible tablet. | [10] |
| A10BB12 | Glimepiride (2 mg) | GLIMEPIRIDE ACC (ACCORD HEALTHCARE) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water until a fine dispersion is created Administer before the main meal | [10] |
| Glimepiride (3 mg) | GLIMEPIRIDE SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| Glimepiride(1, 2, 3, 4 mg) | AMARYL(SANOFI) | |||||
| A10BD02 | Metformin hydrochloride Glibenclamide (500 + 5 mg) | GLICONORM (ABIOGEN PHARMA) | Coated tablets | No | Administer the two drugs separately Flush with 10 mL water between each one | [8,9] |
| Metformin hydrochloride Glibenclamide (400 + 2.5/500 + 5 mg) | GLIBOMET (LABORATORI GUIDOTTI) | |||||
| Metformin hydrochloride Glibenclamide (400 + 2.5 mg) | SUGUAN (SANOFI) | |||||
| A10BD05 | Pioglitazone Metformin hydrochloride (15 + 850 mg) | COMPETACT (TAKEDA) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A10BD07 | Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate Metformin hydrochloride (50 + 850 mg) | JANUMET (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| A10BD08 | Vildagliptin Metformin (50 + 1000 mg) | EUCREAS (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A10BD10 | Saxagliptin hydrochloride Metformin hydrochloride (2.5 + 850 mg) | KOMBOGLYZE (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A10BF01 | Acarbose (50, 100 mg) | GLUCOBAY (BAYER) | Tablets | Yes | The tablets do not disperse easily in water but require gentle stirring for 5 min. A fine suspension is obtained which must be administered immediately, then continue with EN | [10] |
| A10BG03 | Pioglitazone hydrochloride (15, 30 mg) | PIOGLITAZONE ACV (ACTAVIS) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| ACTOS (TAKEDA) | ||||||
| A10BH01 | Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate (100 mg) | TESAVEL (ADDENDA) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| A10BH01 | Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate (50, 100 mg) | JANUVIA (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | Check the glycemia | |
| A10BH02 | Vildagliptin (50 mg) | GALVUS (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | No | ||
| A10BH03 | Saxagliptin hydrochloride (5 mg) | ONGLYZA (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| A10BX02 | Repaglinide (0.5, 1 mg) | REPAGLINIDE EG (EG) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| Repaglinide (1, 2 mg) | REPAGLINIDE SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| A11AA03 | Vitamins Mineral salts | SUPRADYN (BAYER) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve in water and administer at the end of the effervescence | |
| A11CC04 | Calcitriol (0.25 µg) | DIFIX (PROMEDICA) | Soft gels | No | Drug adheres to the walls of the tube, risk of loss | [8,9] |
| ROCALTROL (ROCHE) | ||||||
| CALCITRIOLO TEV (TEVA) | ||||||
| A11DA01 | Thiamine hydrochloride (300 mg) | BENERVA (TEOFARMA) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| A11DB | Thiamine hydrochloride Cyanocobalamin Pyridoxine hydrochloride | BENEXOL B12 (BAYER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| A11DB | Thiamine hydrochloride Cyanocobalamin Pyridoxine hydrochloride | TRINEVRINA B6 (LABORATORI GUIDOTTI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| A11HA02 | Pyridoxine hydrochloride (300 mg) | BENADON (BAYER) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| A11HA03 | Alpha-Tocopherol (400 IU) | RIGENTEX (BRACCO) | Soft gels | No | [8,9] | |
| A11JB | Sodium Citrate Potassium Citrate Thiamine diphosphate Riblofavin-5 monophosphate monosodium Pyridoxine hydrochloride Citric acid | BIOCHETASI (SIGMS TAU) | Effervescent granules | Yes | ||
| A12AA04 | Calcium Carbonate (1000 mg) | CALCIODIE (SPA) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve in 20 mL water and administer at the end of the effervescence at least 1 h before or 2 h after the NE | |
| A12AX | Calcium Carbonate Cholecalciferol | IDEOS (MEDA PHARMA) | Chewable tablets | Yes | ||
| METOCAL VIT.D3 (MEDA PHARMA) | ||||||
| A12BA01 | Potassium Chloride (600 mg) | KCL-RETARD (ASTELLAS) | Modified release tablets | No | Change route of administration | [8,9] |
| A12BA30 | Potassium Citrate Potassium Succinate Potassium Malate Potassium Tartrate Potassium Bicarbonate | POTASSION (ACARPIA) | Effervescent granules | Yes | Dissolve in water, and administer at the end of the effervescence | |
| A16AA02 | Ademetionine Butanedisulfonate (400 mg) | SAMYR 400 (BGP PRODUCTS) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| B01AA03 | Warfarin sodium (5 mg) | COUMADIN (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and suspend the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop feeding at least 1 h before and 2 h after drug administration Avoid supplementation with vitamin K Warning: drug-EN interaction, continuous monitoring and dosage adjustment. If possible administer low molecular weight heparins | [10] |
| B01AA07 | Acenocumarol (1, 4 mg) | SINTROM (MERUS LABS LUXCO II SARL) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve in 10 mL water and administer immediately Trituration can alter bioavailability Check for clotting and prothrombin time | [10] |
| B01AB11 | Sulodexide (250 LSU) | VESSEL (ALFA WASSERMANN) | Soft gels | No | Oily excipients do not guarantee correct administration Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| B01AC04 | Clopidogrel besylate (75 mg) | CLOPIDOGREL AURO (ACTAVIS) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Plavix | |
| B01AC04 | Clopidogrel besylate (75, 300 mg) | PLAVIX (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water Administer by an 8 Fr tube | [10] |
| B01AC05 | Ticlopidine hydrochloride (250 mg) | TIKLID (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 20 mL water, and administer immediately preferably concurrently with EN to avoid gastrointestinal adverse effects | |
| B01AC06 | Acetylsalicylic Acid (100 mg) | ACIDO ACETILSALICILICO SAN (SANDOZ) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | The tablet must not be crushed to avoid irritating effects on the intestine Alternatives: effervescent tablets, chewable tablets, granules for oral solution | [8,9] |
| B01AC06 | Acetylsalicylic Acid Magnesium Hydroxide Algedrate | ASCRIPTIN (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, and administer immediately concurrently with EN | |
| B01AC06 | Lysine Acetylsalicylate (75, 100, 160 mg) | CARDIRENE (SANOFI) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | Dilute with at least 60 mL of water and administer immediately in conjunction with EN | |
| B01AC07 | Dipyridamole (75, 200 mg) | PERSANTIN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Coated tablets | Yes | [10] | |
| B01AC07 | Dipyridamole (75 mg) | PERSANTIN R (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Modified release capsules | No | [8,9] | |
| B01AC10 | Indobufen (200 mg) | IBUSTRIN (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| B01AC22 | Prasugrel hydrochloride (100 mg) | EFIENT (DAIICHI SANKYO) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and administer immediately Highly photosensitive hygroscopic drug | |
| B01AC24 | Ticagrerol (90 mg) | BRILIQUE (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet to a fine powder, transfer it in half a glass of water and administer Rinse the tube with water | SmPC |
| B01AC30 | Dipyridamole Acetylsalicylic Acid (200 + 25 mg) | AGGRENOX (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Modified release capsules | No | The granules can block the tube Alternatives: change dosage form or route of administration | |
| B01AE07 | Dabigatran etexilate mesylate (75, 110, 150 mg) | PRADAXA (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Capsules | No | The opening of the capsule increases drug bioavailability by 75% Bleeding risk Switch to another anticoagulant | |
| B01AF01 | Rivaroxaban (10, 15, 10 mg) | XARELTO (BAYER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet, dissolve the powder in water, then administer immediately Rinse the tube with water The drug administration should be followed immediately by EN | SmPC |
| B01AF02 | Apixaban (2.5, 5 mg) | ELIQUIS (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet and suspend the powder in 60 mL water or 5% dextrose water solution, then administer immediately The crushed tablets are stable up to 4 h when stored at 30 °C | SmPC |
| B02BX05 | Eltrombopag olamine (25, 50 mg) | REVOLADE (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| B03AA01 | Ferrous (II) glycine sulphate (100 mg) | NIFEREX (UCB PHARMA) | Capsules | No | Risk of tube occlusion | |
| B03AA03 | Ferrous (II) gluconate (80 mg) | PRONTOFERRO (IBSA FARMACEUTICI) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in water, administer before EN Alternatives: ampoules or syrup | SmPC |
| B03AA07 | Ferrous (II) sulfate (105 mg) | FERROGRAD (TEOFARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: ampoules | [8,9] |
| B03BB01 | Folic Acid (5 mg) | FOLINA (TEOFARMA) | Capsules | No | Alternative: liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| B06AA | Promelase (30 mg) | FLAMINASE (GRUNENTHAL) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| C01AA05 | Digoxin (0.0625, 0.125 mg) | LANOXIN (ASPEN PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 10 mL of water, administer immediately. Stop NE 2 h before and 2 h after the drug administration. Inaccurate dosage, change in bioavailability: monitor the patient Preferably give liquid formulation | [10] |
| C01AA05 | Digoxin (0.1, 0.2 mg) | EUDIGOX (TEOFARMA) | Soft gels | No | Alternative: liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| C01AA08 | Methyl Digoxin (0.1 mg) | LANITOP (RIEMSER PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 10 mL water and administer immediately Preferably give drops | |
| C01BA | Dihydroquinidine hydrochloride (250 mg) | IDROCHINIDINA R (TEOFARMA) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, suspend the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| C01BC03 | Propafenone hydrochloride (325 mg) | RYTMONORM (BGP PRODUCTS) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternatives: Rytmonorm coated tablets or solution for injection | [8,9] |
| C01BC03 | Propafenone hydrochloride (150, 300 mg) | RYTMONORM (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Interaction with EN: the effect can be enhanced by the presence of food Alternative: solution for injection | |
| C01BC04 | Flecanide Acetate (100 mg) | ALMARYTM (MEDA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water for 2 min The suspension must be administered immediately | [10] |
| C01BC04 | Flecainide Acetate (100 mg) | FLECAINIDE TEV (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets | |
| C01BD01 | Amiodarone hydrochloride (200 mg) | CORDARONE (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets | |
| C01BD07 | Dronedarone hydrochloride (400 mg) | MULTAQ (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| C01DA08 | Isosorbide dinitrate (5 mg) | CARVASIN (TEOFARMA) | Sublingual tablets | No | Do not grind Reduction of the absorption of the drug due to the hepatic first pass effect Administer sublingually only if the patient is conscious | [8,9] |
| C01DA14 | Isosorbide mononitrate (60 mg) | DURONITRIN (ASTRAZENECA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Nitroglycerine transdermal formulation | [8,9] |
| Isosorbide mononitrate (60 mg) | MONOKET MULTITAB (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Modified release tablets | ||||
| Isosorbide mononitrate (20 mg) | MONOKET (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Modified release tablets | ||||
| Isosorbide mononitrate (50 mg) | MONOKET RETARD (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Modified release capsules | ||||
| Isosorbide mononitrate (20, 40, 50, 80 mg) | MONOCINQUE R (IST.LUSOFARMACOI) | Modified release capsules | ||||
| C01EB17 | Ivabradine hydrochloride | PROCORALAN (SERVIER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet, suspend in water and administer immediately | |
| Ivabradine hydrochloride | CORLENTOR (STRODER) | |||||
| C01EB18 | Ranolazine (375, 500, 750 mg) | RANEXA (A.MENARINI) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| C02AB01 | Methyldopa (250 mg) | ALDOMET (IROKO PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | No | Change antihypertensive drug | |
| C02AC01 | Clonidine hydrochloride | CATAPRESAN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| C02CA04 | Doxazosin mesylate (2, 4 mg) | CARDURA (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder with 10 mL sterile water and administer immediately Monitor the patient and adjust the therapy | [10] |
| C02DC01 | Loniten (5 mg) | MINOXIDIL (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | The tablet is dispersed in water to give a fine suspension which must be administered immediately | [10] |
| C02KX01 | Bosentan monohydrate (62.5, 125 mg) | TRACLEER (ACTELION PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet and dissolve it in at least 50 mL water, it is not very soluble Use individual protections for handling Dispersible tablets (Tracleer 32 mg) for pediatrics | |
| C02KX02 | Ambriesentan (5 mg) | VOLIBRIS (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| C02KX04 | Macitentan (10 mg) | OPSUMIT (ACTELION PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crush the tablet into a fine powder and add water, to have a suspension (drug not soluble) Rinse the tube several times after administration Use individual protections for handling Teratogen drug | |
| C02KX05 | Riociguat (2.5 mg) | ADEMPAS (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | The tablet can be crushed and mixed with water | SmPC |
| C03AA03 | Hydrochlorothiazide (25 mg) | ESIDREX (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| C03BA04 | Chlorthalidone (25 mg) | IGROTON (AMDIPHARM) | Tablets | Yes | The tablet disperses in water within 2 min | [10] |
| C03BA08 | Metolazone (5, 10 mg) | ZAROXOLYN (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it with 10 mL water and administer immediately Monitor the patient, drug bioavailability variable | [10] |
| C03CA01 | Furosemide (25 mg) | FUROSEMIDE (LAB.FARMACOLOGICO MILANESE) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 10 mL water and administer immediately preferably concomitantly with EN to minimize gastrointestinal effects It is recommended to use the liquid form | |
| Furosemide (25, 500 mg) | LASIX (SANOFI) | |||||
| Furosemide (500 mg) | FUROSEMIDE TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| C03CA04 | Torasemide (10 mg) | TORASEMIDE TEV (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablet | |
| C03DA01 | Spironolactone (100 mg) | ALDACTONE (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately Pay attention to concomitant administration with potassium. | [10] |
| Spironolactone (25 mg) | ALDACTONE (SANOFI) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, dissolve in 10 mL of water and administer immediately Pay attention to concomitant administration with potassium. | ||
| C03DA01 | Spironolactone (25 mg) | URACTONE SPA (SOC.PRO.ANTIBIOTICI) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| C03DA03 | Canrenone (50, 100 mg) | LUVION (THERABEL GIENNE PHARMA) | Tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | |
| C03EA01 | Amiloride hydrochloride Hydrochlorothiazide (5 + 50 mg) | MODURETIC (MSD) | Tablets | Yes | Grind, dissolve in 10 mL of water and administer immediately. | [10] |
| C03EA14 | Potassium Canrenoate Butizide (5 + 50 mg) | KADIUR (THERABEL GIENNE PHARMA) | Tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| C03EB01 | Furosemide Spironolactone (25 + 37 mg) | LASITONE (SANOFI) | Capsules | No | Administer the two drugs separately Flush with 10 mL water between each one | [8,9] |
| C04AD03 | Pentoxifylline (400 mg) | TRENTAL (SANOFI) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| C05CA53 | Diosmin Hesperidin (500 mg) | DAFLON (SERVIER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL of water and administer it immediately | |
| C05CX | Escin (40 mg) | EDEVEXIN (I.B.I.GIOVANNI LORENZINI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: solution for injection or cutaneous gel | |
| C07AA05 | Propranolol hydrochloride (40 mg) | INDERAL (ASTRAZENECA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately Alternative: galenic preparation (Propranolol 2 or 5 mg/mL oral suspension) | |
| C07AA07 | Sotalol hydrochloride (80 mg) | RYTMOBETA (BGP PRODUCTS) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water by shaking for 5 min, then administer immediately Stop EN 2 h before and 2 h after drug administration Follow the same administration schedule | [10] |
| C07AA12 | Nadolol (80 mg) | NADOLOLO SFV (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately If possible, use another beta blocker available in liquid form | |
| C07AB02 | Metoprolol tartrate (100 mg) | LOPRESOR (DAIICHI SANKYO) | Coated tablets | Yes | It is recommended to use a beta blocker liquid preparation If Metoprolol is non-replaceable, prepare an extemporaneous suspension of Metoprolol 10 mg/mL with simple syrup, or grind the tablet and dissolve it in 10 mL of water. | [10] |
| METOPROLOLO HEX (SANDOZ) | Tablets | |||||
| C07AB03 | Atenolol (100 mg) | ATENOLOLO RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water under shaking for 5 min, then administer immediately Stop EN 30 min before and 30 min after drug administration Divisible tablets | [10] |
| ATENOLOLO HEX (SANDOZ) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN 30 min before and 30 min after drug administration | [10] | ||||
| C07AB07 | Bisoprolol fumarate (10 mg) | CONCOR (BRACCO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water under shaking for 5 min, then administer immediately preferably in the morning after EN | [10] |
| Bisoprolol hemifumarate (2.5 mg) | CONGESCOR (DAIICHI SANKYO) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water under shaking for 5 min, then administer immediately preferably in the morning after EN | [10] | |
| Bisoprolol hemifumarate (1.25, 2.5, 3.75, 5, 10 mg) | CARDICOR (RECORDATI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water under shaking for 5 min, then administer immediately preferably in the morning after EN Divisible tablet | [10] | |
| C07AB12 | Nebivolol hydrochloride (5 mg) | NEBIVOLOLO SAN (SANDOZ) | Tablets | No | Alternative: Atenolol | |
| C07AG01 | Labetalol hydrochloride (100 mg) | TRANDATE (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | No | ||
| C07AG02 | Carvedilol (6.25 mg) | OMERIA (MEDIOLANUM FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind and dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water Administer with EN to reduce the risk of orthostatic hypotension | [10] |
| C07AG02 | Carvedilol (25 mg) | Carvedilol ZTV (ZENTIVA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind and dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water Administer with EN to reduce the risk of orthostatic hypotension | [10] |
| C08CA01 | Amlodipine besylate (5, 10 mg) | NORVASC (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately concurrently with EN to minimize the gastrointestinal side effects | [10] |
| Amlodipine maleate (10 mg) | AMLODIPINA WIN (ZENTIVA) | |||||
| C08CA02 | Felodipine (5 mg) | FELODIPINA WPI (ZENTIVA) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| C08CA05 | Nifedipine (20,30,60 mg) | ADALAT CRONO (BAYER) | Modified release tablets | No | Do not grind, use the liquid formulation (Nifedicor 20 mg/mL drops) to be diluted with 60 mL water and administer immediately | [8,9] |
| Nifedipine (10 mg) | ADALAT (BAYER) | Soft gels | No | Alternative: Nifedicor 20 mg/mL drop solution to be diluted with 60 mL of water | ||
| Nifedipine (30 mg) | CORAL (SO.SE.PHARM) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Nifedicor 20 mg/mL drop solution to be diluted with 60 mL of water | ||
| C08CA06 | Nimodipine (30 mg) | NIMOTOP (BAYER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Photosensitive drug, use amber syringe Not compatible with PVC tube | |
| C08CA09 | Lacipidine (4 mg) | LACIPIL (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | Drug poorly soluble in water and photosensitive Divisible tablets Alternative: Amlodipine formulations | |
| C08CA11 | Manidipine hydrochloride (20 mg) | IPERTEN (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | No | ||
| MANIDIPINA MYL (MYLAN) | Yes | |||||
| MANIDIPINA TEV (TEVA) | Yes | Divisible tablets | ||||
| C08CA13 | Lecardipine hydrochloride (10 mg) | ZANEDIP (RECORDATI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Administer away from EN Alternative: Amlodipine formulations | |
| C08DA01 | Verapamil hydrochloride (40, 80, 180 mg) | ISOPTIN (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | Yes | [10] | |
| C08DA01 | Verapamil hydrochloride (120 mg) | ISOPTIN R (BGP PRODUCTS) | Modified release tablets | No | Do not grind Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| VERAPAMIL HEX (SANDOZ) | ||||||
| C08DB01 | Diltiazem hydrochloride (120 mg) | ALTIAZEM (IST.LUSOFARMACO) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: 60 mg Diltiazem divisible tablets dosage form | [8,9] |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride (300 mg) | ALTIAZEM (IST.LUSOFARMACO) | Modified release capsules | ||||
| Diltiazem hydrochloride (200, 300 mg) | TILDIEM (SANOFI) | Modified release tablets | ||||
| Diltiazem Hydrochloride (60, 120 mg) | TILDIEM (SANOFI) | Modified release tablets | ||||
| C09AA01 | Captopril (25, 50 mg) | CAPTOPRIL RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Tablets | Yes | Grind, dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately Stop EN at least two h before drug administration. Divisible tablets | [10] |
| C09AA02 | Enalapril maleate (5, 20 mg) | ENAPREN (MSD) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL sterile water and administer immediately | [10] |
| C09AA03 | Lisinopril dehydrate (5, 20 mg) | ZESTRIL (ASTRAZENECA) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets It is possible to prepare an extemporaneous galenic solution/suspension: stable for 30 days at 2–8 °C | [10] |
| C09AA03 | Lisinopril dehydrate (20 mg) | LISINOPRIL WPI (ZENTIVA) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| C09AA04 | Perindopril arginine (5 mg) | COVERSYL (SERVIER) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| C09AA04 | Perindopril tosilate (5 mg) | PERINDOPRIL TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | No | Switch to another ACE inhibitor | |
| C09AA05 | Ramipril (10 mg) | QUARK (POLIFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 20 mL water and administer immediately Divisible tablets | [10] |
| Ramipril (2.5, 5, 10 mg) | TRIATEC (SANOFI) | |||||
| C09AA13 | Moexipril hydrochloride (15 mg) | FEMIPRES (UCB PHARMA) | Coated tablets | No | [10] | |
| C09AA15 | Zofenopril calcium (30 mg) | BIFRIL (IST.LUSOFARMACO) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| C09BA04 | Perindopril arginine Indapamide (2.5 + 0.625/5 + 1.25 mg) | PRETERAX (SERVIER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind, dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | |
| Perindopril arginine Indapamide (5 + 1.25 mg) | PRELECTAL (STRODER) | |||||
| C09BA05 | Ramipril Piretanide (5 + 6 mg) | PRILACE (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | No | Divisible tablets | [8,9] |
| C09BA06 | Quinapril hydrochloride hydrochlorothiazide (20 + 12.5 mg) | ACEQUIDE (RECORDATI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crushable and divisible tablets | |
| C09BA09 | Fosinopril sodium Hydrochlorothiazide (20 + 12.5 mg) | FOSICOMBI (A.MENARINI) | Tablets | No | Switch to another ACE inhibitor | [8,9] |
| C09CA01 | Losartan Potassium (50 mg) | LORTAAN (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind, dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| C09CA03 | Valsatrtan (40 mg) | TAREG (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| Valsatrtan (80, 160 mg) | NOVARTIS | Capsules | ||||
| C09CA04 | Ibersartan (150, 300 mg) | APROVEL (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | The tablet is dispersed in 10 mL water under stirring for 5–10 min No blockage risk with an 8 Fr tube | |
| Ibersartan (150 mg) | KARVEA (SANOFI) | Stirring to disperse the tablet | ||||
| C09CA06 | Candesartan Cilexetil (8 mg) | RATACAND (ASTRAZENECA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| Candesartan Cilexetil (16 mg) | BLOPRESS (TAKEDA) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately. Alternative: Ibersartan | ||||
| Candesartan Cilexetil (8, 16 mg) | CANDESARTAN TEV (TEVA) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately Divisible tablets. | ||||
| C09CA07 | Telmisartan (20, 80 mg) | PRITOR (BAYER) | Tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 5 mL water under stirring and administer immediately Hygroscopic drug | [10] |
| Telmisartan (20, 40, 80 mg) | MICARDIS (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | |||||
| C09CA08 | Olmesartan medoxomil (10, 20 mg) | OLPRESS (MENARINI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Ibersartan | |
| Olmesartan medoxomil (10, 20, 40 mg) | PLAUNAC (MENARINI) | |||||
| C09DA08 | Olmesartan medoxomil Hydrochlorothiazide (20 + 12.5 mg) | PLAUNAZIDE (MENARINI) | Coated tablets | No | Administer the two drugs separately Flush with 10 mL water between each one | [8,9] |
| Olmesartan medoxomil Hydrochlorothiazide (20 + 25/40 + 25 mg) | OLPREZIDE (MENARINI) | |||||
| C09DB02 | Olmesartan medoxomil Amlodipine besylate (40 + 5 mg) | SEVIKAR (IST.LUSOFARMACO) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: administer separately another angiotensin II antagonist drug (eg Irbesartan) and the calcium channel blocker | [8,9] |
| C09XA02 | Aliskiren hemifumarate (150, 300 mg) | RASILEZ (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| C10AA01 | Simvastatin (10, 20 mg) | SINVACOR (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately, preferably together with the last course of EN | [10] |
| Simvastatin (10, 20 mg) | SIMVASTAT.RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately, preferably together with the last course of EN Divisible tablets | ||||
| Simvastatin (10 mg) | SIMVASTAT.TEV (TEVA) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately, preferably together with the last course of EN Divisible tablets | ||||
| Simvastatin (40 mg) | SIMVASTAT.ZTV (ZENTIVA) | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water and administer immediately, preferably together with the last course of EN. | ||||
| C10AA03 | Pravastatin sodium (20 mg) | PRAVASTAT.RAT (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets | [10] |
| C10AA04 | Fluvastatin sodium (80 mg) | LESCOL (NOVARTIS) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Fluvastatin 20 or 40 mg capsules, or Atorvastatin or Pravastatin | [8,9] |
| C10AA05 | Atorvastatin calcium trihydrate (10, 20, 40 mg) | TORVAST (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | Yes | The tablet is dispersed within 2–5 min in 10 mL water Photosensitive drug Absorption not affected by the presence of food | |
| C10AA07 | Rosuvastatin calcium (5, 10, 20 mg) | CRESTOR (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in water, after 5 min a milky pink dispersion is obtained, then administer immediately Better to use Atorvastatin | [10] |
| C10AB04 | Gemfibrozil (600, 900 mg) | LOPID (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crushable tablets | |
| C10AB05 | Fenofibrate (145 mg) | FULCROSUPRA (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| Fenofibrate (200 mg) | FENOFIBRATO SAN (SANDOZ) | Capsules | No | |||
| C10AC01 | Cholestyramine hydrochloride (4 g) | QUESTRAN (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Powder for oral suspension | No | Risk of occlusion of the tube due to the formation of a semi-solid mass Possible interference with the absorption of other drugs | |
| C10AX06 | Polyenoic Omega (ethyl esters of polyunsaturated fatty acids) (1000 mg) | SEACOR (SOC.PRO.ANTIBIOTICI) | Soft gels | No | [8,9] | |
| C10AX09 | Ezetimibe (10 mg) | EZETROL (MERCK SHARP & DOHME) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water under stirring Administer the suspension immediately | |
| C10BA02 | Ezetimibe Simvastatin (10 + 10 mg) | INEGY (MERCK SHARP & DOHME) | Tablets | No | Administer the two drugs separately Flush with 10 mL water between each one | [8,9] |
| Ezetimibe Simvastatin (10 + 20 mg) | VYTORIN (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | |||||
| D01BA02 | Terbinafine hydrochloride (250 mg) | TERBINAFINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet under stirring in 10 mL water for 5 min, to give a fine dispersion that must be immediately administered Divisible tablets Be careful when handling | [10] |
| D05BB02 | Acitretin (10, 25 mg) | NEOTIGASON (AUROBINDO) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in water and administer immediately together with EN If possible change the drug | |
| D10BA01 | Isotretinoin (10 mg) | ISOTRETINOINA DIF (DIFA COOPER) | Soft gels | No | [8,9] | |
| D11AH04 | Alitretinoin (30 mg) | TOCTINO GLAXOSMITHKLINE | Soft gels | No | [8,9] | |
| G02AB01 | Methylergometrine maleate (0.125 mg) | METHERGIN (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | |
| G02CB01 | Bromocriptine mesylate (2.5 mg) | PARLODEL (MEDA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Administer together with EN | [10] |
| G02CB03 | Cabergoline (0.5 mg) | DOSTINEX (PFIZER) | Tablets | No | ||
| G03AA10 | Ethinylestradiol Gestodene | GINODEN (BAYER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: transdermal patches | [8,9] |
| ESTINETTE (EFFIK) | ||||||
| G03AD01 | Levonorgestrel (1.5 mg) | NORLEVO (LABORATOIRE HRA PHARMA) | Tablets | No | Alternative: transdermal patches | [8,9] |
| G03DA04 | Prgesterone (100, 200 mg) | PROGEFFIK (EFFIK) | Capslues | No | Alternatives: insert the capsule vaginally or use the solution for injection | [8,9] |
| G03DB04 | Nomegestrol acetate (5 mg) | LUTENYL (RATIOPHARM) | Tablets | No | ||
| G03DC02 | Norethisterone acetate (10 mg) | PRIMOLUT NOR (BAYER) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water under stirring for 5 min, to give a fine dispersion that must be immediately administered Be careful when handling | [10] |
| G03HA01 | Cyproterone acetate (50 mg) | ANDROCUR (BAYER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind, disperse the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately. Where possible switch to intramuscular administration | |
| G03XB01 | Mifepristone (200 mg) | MIFEGYNE (EXELGYN) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| G03XB02 | Ulipristal acetate (5 mg) | ESMYA (GEDEON RICHTER) | Tablets | Yes | Crushable tablets | |
| G04BD | Flavoxate Propyphenazone (200 + 30 mg) | CISTALGAN (MEDA PHARMA) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| G04BD04 | Oxybutynin hydrochloride (5 mg) | DITROPAN (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| G04BD08 | Solifenacin succinate (5 mg) | VESIKER (ASTELLAS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| G04BD12 | Mirabregon (50 mg) | BETMIGA (ASTELLAS) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| G04BE03 | Sildenafil citrate (20 mg) | REVATIO (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension | |
| Sildenafil citrate (50, 100 mg) | VIAGRA (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind, disperse the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | ||
| G04BE08 | Tadalafil (5, 10, 20 mg) | CIALIS (ELI LILLY) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| Tadalafil (20 mg) | ADCIRCA (ELI LILLY) | |||||
| G04CA01 | Alfuzosin hydrochloride (2.5 mg) | MITTOVAL (SANOFI) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Doxasozin | [8,9] |
| XATRAL (SANOFI) | ||||||
| G04CA01 | Alfuzosin hydrochloride (2.5 mg) | XATRAL (SANOFI | Coated tablets | Yes | Alternative: Doxasozin | |
| G04CA02 | Tamsulisin hydrochloride (0.4 mg) | PRADIF (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Capsules | No | Risk of blockage of the tube Alternative: Doxasozin | |
| G04CA03 | Terazosin hydrochloride (5 mg) | TERAPROST (MALESCI) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| Terazosin hydrochloride (2, 5 mg) | TERAZOSINA TEV (TEVA) | Tablets | No | |||
| G04CA04 | Silodosin (4, 8 mg) | UROREC (RECORDATI) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule and suspend the content in water | |
| G04CB01 | Finasteride (5 mg) | FINASTERIDE (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Crushable tablets Teratogen drug | [10] |
| G04CB02 | Dutasteride (0.5 mg) | AVODART (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Capsules | No | Content of the capsule liquid, irritant and teratogen | |
| H01BA02 | Desmopressin acetate (60, 120 µg) | MINIRIN/DDAVP (FERRING) | Sublingual tablets | No | Do not crush the tablet Reduction of the absorption of the drug due to the hepatic first pass effect | [8,9] |
| H02AB01 | Betamethasone sodium phosphate | BENTELAN (SIGMATAU) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | SmPC |
| H02AB04 | Methylprednisolone (4, 16 mg) | MEDROL (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| H02AB07 | Prednisone (5, 25 mg) | DELTACORTENE DELTACROTENE FTE (BRUNO FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| H02AB07 | Prednisone (5 mg) | LODOTRA (MUNDIPHARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Deltacortene 5 mg | [8,9] |
| H02AB09 | Hydrocortisone (5, 20 mg) | PLENADREN (SHIRE) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| H02AB10 | Cortisone acetate (25 mg) | CORTONE ACETATO (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| H03AA01 | Levothyroxine sodium (50, 100 µg) | TIROSINT (IBSA FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 10 mL water. Interaction with EN: suspend it 1 h before and resume it 2 h later drug administration Alternative: Tirosint oral solution which is not affected by simultaneous food intake | SmPC |
| H03AA01 | Levothyroxine sodium (25, 50, 75, 100 µg) | EUTIROX (MERCK SERONO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Suspend EN 1 h before and resume it 2 h later drug administration Monitor TSH levels Divisible tablets | [10] |
| Levothyroxine sodium (25 µg) | LEVOTIROXINA TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| H03BB02 | Thiamazole (Methimazole) (5 mg) | TAPAZOLE (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Divisible tablets | |
| H05BX01 | Cinacalcet hydrochloride (30, 60, 90 mg) | MIMPARA (AMGEN) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| H05BX02 | Paricalcitol (1 µg, 2 µg) | ZEMPLAR (ABBVIE) | Capsules | No | Alternative: Zemplar solution for injection | |
| J01AA02 | Doxycycline hyclate (100 mg) | BASSADO (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve it in 10 mL water. Administer immediately with plenty of water to prevent irritation | [10] |
| J01AA08 | Minocycline hydrochloride (100 mg) | MINOCIN (TEOFARMA) | Capsules | No | ||
| J01CA01 | Ampicillin (500 mg) | AMPLITAL (PFIZER) | Capsules | No | Alternative: powder for solution for injection | |
| J01CA04 | Amoxicillin trihydrate (1 g) | ZIMOX (PFIZER) | Tablets | No | Alternatives: switch to other formulations (drops, oral suspension, powder for oral suspension) | |
| J01CA04 | Amoxicillin trihydrate (1 g) | ZIMOX (PFIZER) | Chewable tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablets in a half glass of water | SmPC |
| J01CR02 | Amoxicillin trihydrate Clavulanate potassium (875 + 125 g) | ABBA (FIDIA FARMACEUTICI) | Powder for oral suspension | Yes | Dissolve the powder in 50 mL water Administer together with EN to minimize the gastrointestinal side effects | SmPC |
| AUGMENTIN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | ||||||
| J01CR02 | Amoxicillin trihydrate Clavulanate potassium (875 + 125 g) | NEODUPLAMOX (VALEAS) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: switch to other formulations (suspension, powder for oral suspension) | [8,9] |
| J01CR04 | Sultamicillin tosylate (750 mg) | UNASYN (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: powder for oral solution, or solution for injection | [8,9] |
| J01DB01 | Cephalexin monohydrate (1 g) | KEFORAL (CRINOS) | Tablets | No | Switch to another cephalosporin or use the oral suspension available on the market | [8,9] |
| Cephalexin (1 g) | CEPOREX (TEOFARMA) | Coated tablets | ||||
| J01DC02 | Cefuroxime acetoxyethyl (250 mg) | ZINNAT (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | Use the syrup which must be diluted with 60 mL water and administered immediately | [8,9] |
| J01DD08 | Cefixime (400 mg) | UNIXIME (F.I.R.M.A.) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: dispersible tablets or oral suspension. Stop the EN at least 1 h before and resume it 2 h after drug administration | [8,9] |
| J01DD13 | Cefpodoxime proxetil (100, 200 mg) | CEFODOX (SCHARPER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Better to switch to the oral suspension | [8,9] |
| J01EE01 | Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (160 + 800 mg) | BACTRIM (ROCHE) | Tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension | [8,9] |
| J01FA09 | Clarithromycin (250, 500 mg) | KLACID (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: oral suspension, solution for injection Photosensitive drug | [8,9] |
| Clarithromycin (500 mg) | CLARITROMICINA TEV (TEVA) | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted with 60 mL water and administered immediately | ||||
| J01FA10 | Azithromycin monohydrate (500 mg) | AZITROMICINA EG (EG) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted with 60 mL water and administered immediately It does not interact with EN | [8,9] |
| Azithromycin monohydrate (500 mg) | AZITROMICINA MYL (MYLAN) | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted Administer 1 h before or 2 h after EN | ||||
| Azithromycin dihydrate (500 mg) | ZITROMAX (PFIZER) | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted Administer 1 h before or 2 h after EN | ||||
| Azithromycin dihydrate (500 mg) | AZITROMICINA PRG (PROGE FARM) | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted Administer 1 h before or 2 h after EN | ||||
| Azithromycin monohydrate (500 mg) | AZITROMICINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted Administer 1 h before or 2 h after EN | ||||
| J01FA10 | Azithromycin dihydrate (500 mg) | TROZAMIL (SO.SE.PHARM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Alternative: oral suspension which must be diluted Administer 1 h before or 2 h after EN | |
| J01FF01 | Clindamycin hydrochloride (150 mg) | DALACIN-C (PFIZER) | Capsules | Yes | Disperse the content in water and then administer Alternatives: solution for injection or other route of administration (cutaneous gel) | |
| J01MA02 | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (250, 500, 750, 1000 mg) | CIPROXIN (BAYER) | Coated tablets | No | EN-drug interaction: decreased absorption and therapeutic failure Alternatives: solution for infusion or granules for oral suspension (EN must be suspended 30 min before and 30 min after drug administration) | |
| Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride monohydrate (250 mg) | CIPROFLOXAC.RAT (RATIOPHARM) | |||||
| Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride monohydrate (750 mg) | CIPROFLOXAC.SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| J01MA12 | Levofloxacin hemihydrate (500 mg) | LEVOFLOXACINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: solution for injection or switch to more bioavailable Ofloxacin | |
| J01MA14 | Moxifloxacin hydrochloride (400 mg) | AVALOX (BAYER) | Coated tablets | Yes | The coating exerts only taste masking | |
| J01MA17 | Prulifloxacin (600 mg) | UNIDROX (ANGELINI) | Coated tablets | yes | Administer immediately after dissolution of the tablet in water | |
| J01XE01 | Nitrofurantoin macrocrystals (50 mg) | NEOFURADANTIN (GRUNENTHAL) | Capsules | No | Risk of tube blockage | |
| J01XX01 | Fosfomycin trometamol salt (3 g) | BERNY (SO.SE.PHARM) | Granules for oral solution | Yes | Administer away from the EN, usually at bedtime | |
| J01XX08 | Linezolid (600 mg) | ZYVOXID (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 20 mL water then administer immediately Prefer oral suspension or solution for infusion Any interaction with EN | [10] |
| J02AC01 | Fluconazole (100 g) | FLUCONAZOLO EG (EG) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately Prefer oral suspension or solution for injection If dietary product is rich in fiber, suspend EN 1 h before and 1 h after drug administration | [10] |
| DIFLUCAN (PFIZER) | ||||||
| FLUCONAZOLO SAN (SANDOZ) | ||||||
| FLUCONAZOLO HEX (SANDOZ) | ||||||
| FLUCONAZOLO RAT (TEVA) | ||||||
| J02AC02 | Itraconazole (100 g) | SPORANOX (JANSSEN CILAG) | Capsules | No | Alternatives: solution for infusion or oral solution to be diluted with water The absorption occurs at acidic pH Administer together with EN | |
| J02AC03 | Voriconazole (200 mg) | VFEND (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, disperse the powder in water and administer away from EN (1 h before or 2 h after EN) Alternatives: oral suspension or powder for solution for injection | [10] |
| J04AB02 | Rifampicin (300, 400 mg) | RIFADIN (SANOFI) | Capsules | No | Alternative: syrup to be diluted and administered away from EN | [8,9] |
| J04AC01 | Isoniazid (200 mg) | NICOZID (PIAM FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 20 mL water then administer immediately Stop EN 1 h before and 2 h after drug administration | [10] |
| J04AK01 | Pyrazinamide (500 mg) | PIRALDINA (BRACCO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water then administer immediately | [10] |
| J04AK02 | Ethambutol hydrochloride (400 mg) | ETAPIAM (PIAM FARMACEUTICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve the powder in 10 mL water then administer immediately 2 h after EN | [10] |
| J04AM02 | Rifampicin Isoniazid (300 + 150 mg) | RIFINAH 300 (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | No | Administer the two drugs separately Flush with 10 mL water between each one | [8,9] |
| J04AM05 | Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Rifampicin (50 + 300 +120 mg) | RIFATER (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Suspend EN 1 h before drug administration | |
| J05AB01 | Acyclovir (400 mg) | ACICLOVIR EG (EG) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, dissolve it in 30 mL water then administer immediately Alternatives: oral suspension or solution for injection | [10] |
| Acyclovir (800 mg) | ACICLIN (FIDIA FARMACEUTICI) | |||||
| Acyclovir (400 mg) | ACICLOVIR DRM (TEVA) | |||||
| J05AB04 | Ribavirin (200 mg) | REBETOL (MSD) | Capsules | No | Alternative: Ribavirin (Rebetol) oral solution | [8,9] |
| COPEGUS (ROCHE) | Coated tablets | |||||
| RIBAVIRINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Capsules | |||||
| RIBAVIRINA TEV (TEVA) | Capsules | |||||
| J05AB11 | Valacyclovir hydrochloride (1 g) | ZELITREX (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Better to switch to Acyclovir The tablets are difficult to crush and the powder does not suspend well Alternative: galenic suspension of Valaciclovir 50 mg/mL, by triturating the tablets and using simple syrup (good stability up to 21 days at 2–8 °C) | |
| VALACICLOVIR MYL (MYLAN) | ||||||
| J05AB14 | Valgancyclovir hydrochloride (450 mg) | DARILIN (ROCHE) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Valgancyclovir oral suspension (Novir) | [8,9] |
| J05AE03 | Ritonavir (100 mg) | NORVIR (ABBVIE) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Ritonavir oral suspension Tablets not crushable | [8,9] |
| J05AE07 | Fosamprenavir calcium (700 mg) | TELZIR (VIIV HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Fosamprenavir oral suspension (Telzir) | [8,9] |
| J05AE08 | Atazanavir sulfate (200, 300 mg) | REYATAZ (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, dissolve the content in water, administer it via tube, then continue with EN | |
| J05AE10 | Darunavir ethanolate (600, 800 mg) | PREZISTA (JANSSEN CILAG) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Darunavir ethanolate oral suspension | |
| J05AE11 | Telaprevir (375 mg) | INCIVO (JANSSEN CILAG) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| J05AE12 | Boceprevir (200 mg) | VICTRELIS (MSD) | Capsules | No | ||
| J05AE14 | Simeprevir (150 mg) | OLYSIO (JANSSEN CILAG) | Capsules | No | ||
| J05AF02 | Didanosine (250 mg) | VIDEX 250 (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Capsules | No | ||
| J05AF05 | Lamivudine (100 mg) | ZEFFIX (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water, a pale orange solution is obtained, then administer immediately Prefer: Lamivudine oral solution | [10] |
| J05AF05 | Lamivudine (100 mg) | LAMIVUDINA MYL (MYLAN) | Coated tablets | No | Prefer liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| J05AF07 | Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (245 mg) | VIREAD (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 100 mL water or orange juice and administer | SmPC |
| J05AF08 | Adefovir dipivoxil (10 mg) | HESPERA (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | No | Switch to Tenofovir | |
| J05AF09 | Emtricitabine (200 mg) | EMTRIVA (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Capsules | No | Alternative: Emtricitabine oral solution Increase the dose by 20% with respect to the tablets, due to reduced bioavailability of the oral solution | |
| J05AF10 | Entecavir (0.5, 1 mg) | BARACLUDE (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Coated tablets | No | Switch to oral solution | [8,9] |
| J05AG01 | Nevirapine (400 mg) | VIRAMUNE (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Tablets | No | Switch to oral suspension | [8,9] |
| Nevirapine (200 mg) | NEVIRAPINA TEV (TEVA) | Alternative: liquid formulation | ||||
| J05AG03 | Efavirenz (200 mg) | SUSTIVA (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Capsules | Yes | ||
| J05AG03 | Efavirenz (600 mg) | EFAVIRENZ MYL (MYLAN) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| J05AG04 | Etravirine (200 mg) | INTELENCE (JANSSEN CILAG) | Tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer | SmPC |
| J05AG05 | Rilpivirine hydrochloride (25 mg) | EDURANT (JANSSEN CILAG) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| J05AH02 | Oseltamivir phosphate (30, 45 mg) | TAMIFLU (ROCHE) | Capsules | No | Alternative: oral suspension | [8,9] |
| J05AR01 | Lamivudine Zidovidine (150 + 300 mg) | LAMIV+ZIDOV MYL (MYLAN) | Coated tablets | No | Administer the two drugs separately in liquid form | [8,9] |
| J05AR02 | Abacavir sulfate Lamivudine (600 + 300 mg) | KIVEXA (VIIV HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | Separate preparations of the two drugs are available in the form of oral suspension | [8,9] |
| J05AR03 | Emtricitabine Tenofovir disoproxil (200 + 245 mg) | TRUVADA (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | Yes | The tablets can be dissolved in about 100 mL of water, orange juice or grape juice and taken immediately | SmPC |
| J05AR04 | Abacavir sulfate Lamivudine Zidovudine (300 + 150 + 300 mg) | TRIZIVIR (VIIV HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | Separate preparations of the three drugs are available in the form of oral suspension | [8,9] |
| J05AR06 | Efavirenz Emtricitabine Tenofovir disoproxil (600 +200 +245 mg) | ATRIPLA (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| J05AR08 | Emtricitabine Rilpivirine hydrochloride Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (200 + 25 + 245 mg) | EVIPLERA (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| J05AR09 | Emtricitabine Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate Elvitegravir Cobicistat (200 + 300 + 150 + 150 mg) | STRIBILD (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| J05AR10 | Lopinavir Ritonavir (200 + 50 mg) | KALETRA (ABBVIE) | Coated tablets | No | Tablet crushing reduces AUC by approximately 40% Preferred alternative: Kaletra oral solution (slightly viscous, contains alcohol and propylene glycol) | [8,9] |
| J05AX08 | Raltegravir potassium (400 mg) | ISENTRESS (MSD) | Coated tablets | No | Drug insoluble in water | |
| J05AX09 | Maraviroc (150, 300 mg) | CELSENTRI (VIIV HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| J05AX12 | Dolutegravir sodium (50 mg) | TIVICAY (VIIV HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet, disperse it in water and administer away from EN (2 h before or 6 h after EN) | |
| J05AX14 | Daclatasvir dihydrochloride (60 mg) | DAKLINZA (BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB) | Coated tablets | Yes | The coating serves only to cover the drug bitter taste | |
| J05AX15 | Sofosbuvir (400 mg) | SOVALDI (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | Yes | The coating serves only to cover the drug bitter taste The tablets can be triturated and administered via tube concurrently with EN | |
| J05AX16 | Dasabuvir (250 mg) | EXVIERA (ABBVIE) | Coated tablets | No | Not crushable tablet | |
| J05AX65 | Ledipasvir Sofosbuvir (90 + 400 mg) | HARVONI (GILEAD SCIENCES) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| J05AX67 | Ombitasvir Paritaprevir Ritonavir (12.5 + 75 + 50 mg) | VIEKIRAX (ABBVIE) | Coated tablets | No | Not crushable tablet | [8,9] |
| L01AA01 | Cyclophosphamide (50 mg) | ENDOXAN (BAXTER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| L01AA02 | Chlorambucil (2 mg) | LEUKERAN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L01AA03 | Melfalan (25 mg) | ALKERAN (ASPEN PHARMA) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| L01AB01 | Busulfan (2 mg) | MYLERAN (ASPEN PHARMA) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: galenic suspension of Busulfan 2 mg/mL by triturating the tablet Shelf life 30 days if stored between 2–8 °C | |
| L01AX03 | Temozolomide (100 mg) | TEMODAL (MSD) | Capsules | No | ||
| Temozolomide (100 mg) | TEMOZOLOMIDE SUH (RANBAXY ITALIA) | |||||
| Temozolomide (5, 20, 140, 180, 250 mg) | TEMOZOLOMIDE SUH (SUN PHARMACEUTICALS) | |||||
| L01BA01 | Methotrexate (2.5 mg) | METHOTREXATE (PFIZER) | Tablets | No | Alternative: Methotrexate solution for injection Tablets are divisible but not crushable | [8,9] |
| L01BB05 | Fludarabine phosphate (10 mg) | FLUDARA (GENZYME) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| L01BC06 | Capecitabine (150, 500 mg) | CAPECITABINA ACC (ACCORD HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 200 mL warm water and then administer immediately Attention to handling, use individual protection measures | |
| CAPECITABINA MYL (MYLAN) | ||||||
| XELODA (ROCHE) | ||||||
| L01CA04 | Vinorelbine ditartrate(20, 30 mg) | NAVELBINE (PIERRE FABRE PHARMA) | Soft gels | No | Alternative: concentrate for solution for infusion | [8,9] |
| L01XE01 | Imatinib mesylate (100 mg) | GLIVEC (NOVARTIS) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, dilute the content in water or apple juice Attention to handling, use individual protection measures | SmPC |
| L01XE02 | Gefitinib (250 mg) | IRESSA (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in half glass water (it takes 20 min) Administer the suspension immediately | SmPC |
| L01XE03 | Erlotinib hydrochloride (100, 150 mg) | TARCEVA (ROCHE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L01XE04 | Sunitinib maleate (12.5, 25, 50 mg) | SUTENT (PFIZER) | Capsules | Yes | Attention to handling, use individual protection measures | |
| L01XE05 | Sorafenib tosilate (200 mg) | NEXAVAR (BAYER) | Coated tablets | No | No specific data are available | |
| L01XE06 | Dasatinib monohydrate (50, 100, 140 mg) | BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB | Coated tablets | No | No specific data are available Attention to handling, use individual protection measures | |
| L01XE07 | Lapatinib ditosylate monohydrate (250 mg) | TYVERB (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L01XE08 | Nilotinib hydrochloride (150, 200 mg) | TASIGNA (NOVARTIS) | Capsules | Yes | ||
| L01XE10 | Everolimus (5, 10 mg) | AFINITOR (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | No | ||
| L01XE11 | Pazopanib hydrochloride (400 mg) | VOTRIENT (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L01XE13 | Afatinib dimaleate (40 mg) | GIOTRIF (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in water without breaking it, under stirring for 15 min until a fine dispersion is obtained, then administer immediately away from the EN Be careful when handling | SmPC |
| L01XE16 | Crizotinib (250 mg) | XALKORI (PFIZER) | Capsules | No | ||
| L01XE18 | Ruxolitinib phosphate (5, 15 mg) | JAKAVI (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | No | ||
| L01XE21 | Regorafenib (40 mg) | STIVARGA (BAYER) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L01XX05 | Hydroxycarbamide (500 mg) | ONCO CARBIDE (TEOFARMA) | Capsules | Yes | Attention to handling, use individual protection measures Antineoplastic drug | [10] |
| L01XX14 | Tretinoin (10 mg) | VESANOID (CHEPLAPHARM ARZNEIMITTEL) | Capsules | No | ||
| L01XX23 | Mitotane (500 mg) | LYSODREN (HRA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | The company confirms that the tablet can be crushed and the API dissolves in water Use gloves for handling Antineoplastic drug | Manufacturer upon request |
| L01XX35 | Anagrelide hydrochloride (0.5 mg) | XAGRID (SHIRE) | Capsules | No | ||
| L02AB01 | Megestrol acetate (160 mg) | GESTROLTEX (PHARMATEX) | Tablets | No | ||
| L02BA01 | Tamoxifen citrate (20 mg) | NOMAFEN (ITALIAN DEVICES) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| KESSAR (ORION) | Tablets | |||||
| L02BB01 | Flutamide (250 mg) | FLUTAMIDE FDI (FIDIA FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Tablet disaggregates slowly, maintain it under stirring in 10 mL water for 10 min Attention to handling | [10] |
| L02BB03 | Bicalutamide (50, 150 mg) | CASODEX (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | Yes | If possible use other antiandrogens administered as a subcutaneous implant Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in water Work in a closed system (disperse the tablet in the body of a syringe) Administer immediately after the EN Attention to handling | [10] |
| Bicalutamide (150 mg) | BICALUTAMIDE HIK (HIKMA FARMACEUTICA) | Coated tablets | No | If possible use other antiandrogens administered by subcutaneous implant | [10] | |
| L02BB03 | Bicalutamide (50, 150 mg) | BICALUTAMIDE TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | No | If possible use other antiandrogens administered by subcutaneous implant | |
| L02BG03 | Anastrozole (1 mg) | ANASTROZOLO ACC (ACCORD HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | Data not available | |
| ARIMIDEX (ASTRAZENECA) | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water in a closed system (disperse the tablet in the body of a syringe) Drug slightly soluble in water | ||||
| L02BG04 | Letrozole (2.5 g) | LETROZOLO ACC (ACCORD HEALTHCARE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| LETROZOLO SAN (SANDOZ) | ||||||
| L02BG06 | Exemestane (25 mg) | AROMASIN (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L02BX03 | Abiraterone acetate (25 mg) | ZYTIGA (JANSSEN CILAG) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L04AA06 | Mycophenolate sodium (180, 360 mg) | MYFORTIC (NOVARTIS) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Alternative: Mycofenolate mofetil (Cellept) oral solution | [8,9] |
| Mycofenolate mofetil (250, 500 mg) | CELLCEPT (ROCHE) | Capsules | ||||
| Mycofenolate mofetil (250, 500 mg) | MYFENAX (TEVA) | Coated tablets | ||||
| L04AA10 | Sirolimus (0.5, 1 mg) | RAPAMUNE (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Sirolimus (Rapamune) oral solution | [8,9] |
| L04AA13 | Leflunomide (20 mg) | ARAVA (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [10] |
| L04AA18 | Everolimus (0.25, 0.75 mg) | CERTICAN (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | No | Alternative: orosoluble tablets to be dissolved in 10 mL water Stop EN 1 h before and 2 h after drug administration | [8,9] |
| L04AA27 | Fingolimod hydrochloride (0.5 mg) | GILENYA (NOVARTIS) | Capsules | No | ||
| L04AA31 | Teriflunomide (14 mg) | AUBAGIO (GENZYME) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| L04AD01 | Cyclosporine (10, 25, 50, 100 mg) | SANDIMMUN NEORAL (NOVARTIS) | Capsules | No | Alternative: Cyclosporine oral solution | [8,9] |
| L04AD02 | Tacrolimus (1 mg) | TACROLIMUS ACC (ACCORD HEALTHCARE) | Capsules | No | Alternatives: Porgraf capsules or Tacni capsules | |
| Tacrolimus monohydrate (0, 5, 1, 3, 5 mg) | ADVAGRAF (ASTELLAS) | |||||
| Tacrolimus monohydrate (0, 5, 1, 5 mg) | PROGRAF (ASTELLAS) | Yes | Open the capsule and dissolve the content in water Administer through an 8 Fr caliber tube Do not use a PVC tube Beware of handling Take on an empty stomach or at least 1 h before or 2–3 h after eating | |||
| Tacrolimus (0.5 mg) | TACROLIMUS MYL (MYLAN) | No | Alternative: Porgraf capsules | |||
| Tacrolimus monohydrate (1 mg) | ADOPORT (SANDOZ) | No | Alternative: Porgraf capsules | |||
| L04AX01 | Azathioprine (50 mg) | AZATIOPRINA (ASPEN PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water in the body of a syringe (closed system) Cytotoxic drug Use personal protective equipment | [10] |
| L04AX02 | Thalidomide (50 mg) | THALIDOMIDE CELGENE (CELGENE) | Capsules | No | The capsules must not be opened Teratogen drug | |
| L04AX04 | Lenalomide (5, 10, 15, 25 mg) | REVLIMID (CELGENE) | Capsules | No | The capsules must not be opened Teratogen drug | |
| L04AX05 | Pirfenidone (267 mg) | ESBRIET (ROCHE) | Capsules | No | ||
| L04AX06 | Pomalidomide (4 mg) | IMNOVID (CELGENE) | Capsules | No | Not available data on drug manipulation | |
| M01AB01 | Indomethacin (25, 50 mg) | INDOXEN (SIGMATAU) | Capsules | No | Alternative: suppositories | [8,9] |
| M01AB05 | Diclofenac sodium (50, 150 mg) | FLOGOFENAC (A.MENARINI) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternatives: dispersible tablets, solution for injection, cutaneous formulations | [8,9] |
| M01AB05 | Diclofenac sodium (50, 150 mg) | DICLOREUM (ALFA WASSERMANN) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | Alternatives: dispersible tablets, solution for injection, cutaneous formulations | [8,9] |
| M01AB15 | Ketorolac tromethamine (10 mg) | TORADOL (RECORDATI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: drops, solution for injection | [8,9] |
| M01AC01 | Piroxicam (20 mg) | FELDENE SOL (PFIZER) | Soluble tablets | Yes | [8,9] | |
| M01AE01 | Ibuprofen (600 mg) | BRUFEN (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: effervescent granules, oral suspension to be diluted with the same water amount | [8,9] |
| Ibuprofen (600 mg) | BRUFEN (BGP PRODUCTS) | Effervescent granules | Yes | Dissolve the granules in plenty of water | ||
| Ibuprofen (200 mg) | NUROFEN (RECKITT BENCKISER) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension | ||
| Ibuprofen arginine salt (400 mg) | SPIDIDOL (ZAMBON) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: oral suspension | ||
| M01AE03 | Ketoprofen lysine salt (80 mg) | OKI (DOMPE’ FARMACEUTICI) | Granules for oral solution | Yes | Alternatives: solution for injection, suppositories, cutaneous gel | [8,9] |
| Ketoprofen (200 mg) | KETOPROFENE EG (EG) | Capsules | No | |||
| Ketoprofen lysine salt (80 mg) | KETOPROFENE MYL (MYLAN) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | |||
| Ketoprofen (200 mg) | ORUDIS RETARD (SANOFI) | Capsules | No | |||
| M01AH01 | Celecoxib (200 mg) | CELEBREX (PFIZER) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule and disperse the content in 10 mL water | [10] |
| M01AH05 | Etoricoxib (60, 90 mg) | TAUXIB (ADDENDA) | Coated tablets | Yes | The tablet immersed in 10 mL water, swells and then releases fine granules that must be administered in an 8 Fr caliber tube | [10] |
| Etoricoxib (60 mg) | ARCOXIA (MSD) | |||||
| Etoricoxib (60, 90 mg) | ALGIX (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | |||||
| M01AX17 | Nimesulide (100 mg) | AULIN (HELSINN BIREX PHARMAC.) | Granules for oral solution | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 30 mL water and then administer immediately Administer together with EN to reduce gastrointestinal side effects | |
| M03BX01 | Baclofen (10, 25 mg) | LIORESAL (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| M03BX03 | Pridinol mesilate (4 mg) | LYSEEN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Tablets | Yes | Alternative: solution for injection | |
| M03BX05 | Thiocolchicoside (4 mg) | MUSCORIL (SANOFI) | Capsules | No | Alternative: solution for injection | [8,9] |
| M04AA01 | Allopurinol (100, 300 mg) | ALLOPURINOLO TEV (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| M04AA03 | Febuxostat (80 mg) | ADENURIC (A.MENARINI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Allopurinol tablets | |
| M04AC01 | Colchicine (1 mg) | COLCHICINA LIRCA (PHARMAFAR) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| M05BA04 | Alendronate sodium (10 mg) | ALENDROS (ABIOGEN PHARMA) | Tablets | No | Interaction with EN Irritant for mucosal membranes If necessary grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 50 mL water, then administer 30 min before the first daily administration of EN keeping the patient in a semi-sitting position Rinse the tube with 100 mL water after administration | |
| Alendronate sodium trihydrate (70 mg) | ADRONAT (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | |||||
| Alendronate sodium (10 mg) | DRONAL (SIGMATAU) | |||||
| Alendronate sodium monohydrate (70 mg) | ALENDRONATO TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| M05BA06 | Ibandronate sodium monohydrate (150 mg) | BONVIVA (ROCHE) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| AC.IBANDR.TEV (TEVA) | ||||||
| M05BB03 | Alendronate sodium trihydrate Cholecalciferol (70 mg + 5600 IU) | FOSAVANCE (MSD) | Tablets | No | ||
| M05BX03 | Strontium ranelate (2 g) | PROTELOS (SERVIER) | Granules for oral suspension | Yes | ||
| N02AA01 | Morphine sulfate (10, 30 mg) | MS CONTIN (MUNDIPHARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: drops to be diluted with 50 mL water and administered immediately | [8,9] |
| N02AA03 | Hydromorphone hydrochloride (4, 8, 16 mg) | JURNISTA (JANSSEN CILAG) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N02AA05 | Oxycodone hydrochloride (5, 10, 20 mg) | OXYCONTIN (MUNDIPHARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| Oxycodone hydrochloride (40 mg) | OXICODONE SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| N02AA55 | Oxycodone hydrochloride Paracetamol (10 + 325/20 + 325 mg) | DEPALGOS (MOLTENI & C. F.LLI ALITTI) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N02AA55 | Oxycodone hydrochloride Naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate (10 + 325/20 + 325 mg) | TARGIN (MUNDIPHARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: switch to another analgesic opioid transdermal formulation | [8,9] |
| N02AA59 | Paracetamol Codeine phosphate (500 + 30 mg) | ANGELINI | Effervescent granules | Yes | Administer only after the end of the effervescence | |
| Coated tablets | The tablet can be triturated and dispersed in water | |||||
| N02AB03 | Fentanyl citrate (100, 200, 300, 400, 600 µg) | ABSTRAL (PROSTRAKAN) | Sublingual tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| Fentanyl citrate (100, 200, 300, 400 µg) | EFFENTORA (TEVA) | Orosoluble tablets | Yes | |||
| N02AX02 | Tramadol hydrochloride (100 mg) | CONTRAMAL (GRUNENTHAL) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternatives: suppositories, orosoluble tablets, suppositories, drops to be diluted with 50 mL water | [8,9] |
| N02AX06 | Tapentadol hydrochloride (50, 100 mg) | PALEXIA (GRUNENTHAL) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N02AX52 | Tramadol hydrochloride Paracetamol (37.5 + 325 mg) | PATROL (ALFA WASSERMANN) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: effervescent tablets to be dissolved in water and administered after the end of the effervescence | [8,9] |
| KOLIBRI (ALFA WASSERMANN) | ||||||
| N02BA01 | Acetylsalicylic acid (100 mg) | ASPIRINETTA (BAYER) | Tablets | Yes | Immerse directly the tablet in water Administer together with EN to reduce gastrointestinal side effects | SmPC |
| N02BE01 | Paracetamol (500 mg) | TACHIPIRINA (ANGELINI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Alternatives: orosoluble tablets, granules, suppositories, syrup or solution for injection | |
| Paracetamol (1000 mg) | Effervescent tablets | Dissolve the tablet in 30 mL water and administer only at the end of the effervescence Alternatives: orosoluble tablets, granules, suppositories or solution for injection | ||||
| N02BE01 | Paracetamol (250, 500 mg) | TACHIPIRINA FLASHTAB (ANGELINI) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | [8,9] | |
| Paracetamol (250, 1000 mg) | TACHIPIRINA OROS (ANGELINI) | Orosoluble granules | ||||
| N02CC01 | Sumatriptan succinate (50 mg) | SUMATRIPTAN DOC (DOC GENERICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Alternatives: solution for injection or nasal spray | [8,9] |
| N03AA02 | Phenobarbital (100 mg) | LUMINALE BRACCO (BRACCO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Administer together with EN to reduce gastrointestinal side effects Do not administer solution for injection via tube due to the presence of glycol | SmPC |
| N03AA02 | Phenobarbital (100 mg) | GARDENALE (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Administer together with EN to reduce gastrointestinal side effects Do not administer solution for injection via tube due to the presence of glycol | |
| N03AA03 | Primidone (250 mg) | MYSOLINE (SIT LABORATORIO FARMACEUTICO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| N03AB02 | Phenytoin sodium (100 mg) | DINTOINA (RECORDATI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN 2 h before and 2 h after drug administration Wash the tube with 50 mL water Alternative: solution for injection | [10] |
| N03AB52 | Phenytoin Methylphenobarbital (100 + 40 mg) | DINTOINALE (RECORDATI) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| N03AE01 | Clonazepam (2 mg) | RIVOTRIL (ROCHE) | Tablets | Yes | Alternative: Clonazepam drops to be diluted with 50 mL water and administered immediately | |
| N03AF01 | Carbamazepine (200, 400 mg) | CARBAMAZEPINA (EG) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL sterile water, then administer immediately Stop EN 1 h before and 2 h after drug administration Requires close monitoring, it interacts with the EN Can adhere to the walls of the tube and have a reduced absorption Better to use syrup | [10] |
| N03AF01 | Carbamazepine (400 mg) | TEGRETOL (NOVARTIS) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternatives: syrup or tablets | [8,9] |
| N03AF01 | Carbamazepine (400 mg) | TEGRETOL (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL sterile water, then administer immediately Stop EN at least 1 h before and 2 h after the dose Requires close monitoring, it interacts with the EN Can adhere to the walls of the tube and have a reduced absorption Better to use syrup | [10] |
| N03AF02 | Oxcarbazepine (300, 600 mg) | TOLEP (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| N03AG01 | Valproic acid Valproate sodium (300, 500 mg) | AC VAL/S.VALP.RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternatives: oral solution or drops to be diluted with 100 mL water | [8,9] |
| Valproic acid Valproate sodium (500 mg) | AC VALPROICO/SOD VALPR SAN (SANDOZ) | Modified release tablets | ||||
| Valproate sodium (200, 500 mg) | DEPAKIN (SANOFI) | Gastro-resistant tablets | ||||
| Valproic acid Valproate sodium (100, 250, 500, 750, 1000 mg) | DEPAKIN (SANOFI) | Modified release granules | ||||
| Valproate magnesium (500 mg) | DEPAMAG (SIGMATAU) | Gastro-resistant tablets | ||||
| N03AG02 | Valpromide (300 mg) | DEPAMIDE (SANOFI) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N03AG04 | Vugabatrin (500 mg) | SABRIL (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: granules | |
| N03AX09 | Lamotrigine (25, 200 mg) | LAMOTRIGINA EG (EG) | Dispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer the solution immediately | |
| N03AX09 | Lamotrigine (25, 50, 100, 200 mg) | LAMICTAL (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Dispersible tablets | Yes | SmPC | |
| N03AX11 | Topiramate (25 mg) | TOPIRAMATO DOC (DOC GENERICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | The tablet is not easily dispersed in water, due to the coating, but requires gentle stirring for 5 min A fine suspension is obtained which should be administered immediately Better to use capsules | [10] |
| Topiramate (25, 50, 100 mg) | TOPIRAMATO EG (EG) | |||||
| Topiramate (25, 50, 100 mg) | TOPAMAX (JANSSEN CILAG) | |||||
| Topiramate (25 mg) | TOPIRAMATO SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| N03AX11 | Topiramate (25 mg) | TOPAMAX (JANSSEN CILAG) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately | SmPC |
| N03AX12 | Gabapentin (400 mg) | DOC GENERICI | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| Gabapentin (100, 300, 400 mg) | GABAPENTIN TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| N03AX14 | Levetiracetam (500 mg) | LEVETIRACETAM DOC (DOC GENERICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 20 mL water, then administer immediately Better to use oral solution | [10] |
| Levetiracetam (500, 1000 mg) | LEVETIRACETAM SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| N03AX15 | Zonisamide (50, 100 mg) | ZONEGRAN (EISAI) | Capsules | Yes | ||
| N03AX16 | Pregabalin (25, 75, 150 mg) | LYRICA (PFIZER) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsules and dissolve the content in water Drug water soluble | |
| N03AX18 | Lacosamide (50, 100 mg) | VIMPAT (UCB PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Alternative: solution for injection | |
| N04AA02 | Biperiden hydrochloride (4 mg) | AKINETON (SIT LABORATORIO FARMACEUTICO) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Biperiden hydrochloride 2 mg | [8,9] |
| N04AA02 | Biperiden hydrochloride (2 mg) | AKINETON (SIT LABORATORIO FARMACEUTICO) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| N04AA11 | Bornaprine hydrochloride (4 mg) | SORMODREN (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Wash the tube with 50 mL water | |
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Carbidopa (100 + 25/200 + 50 mg) | SINEMET (MSD) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: dispersible tablets | [8,9] |
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Carbidopa (100 + 25/250 + 25 mg) | SINEMET (MSD) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN 2 h before and 2 h after drug administration Do not administer together with high-protein diets Photosensitive drug | [10] |
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Benserazide hydrochloride (100 + 25 mg) | MADOPAR (ROCHE) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternative: dispersible tablets | [8,9] |
| Levodopa Benserazide hydrochloride (100 + 25 mg) | MADOPAR (ROCHE) | Capsules | ||||
| Levodopa Benserazide hydrochloride (100 + 25 mg) | MADOPAR (ROCHE) | Tablets | ||||
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Benserazide hydrochloride (100 + 25 mg) | MADOPAR (ROCHE) | Dispersible tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 25–50 mL water until a fine opalescent suspension is obtained Stop EN 1 h before drug administration | SmPC |
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Carbidopa (200 + 50 mg) | LEVOD/CARB HEXAL (SANDOZ) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: dispersible tablets | [8,9] |
| N04BA02 | Levodopa Benserazide hydrochloride (200 + 50 mg) | LEVODOPA/BENSERAZIDE TEV (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Stop EN 2 h before and 2 h after drug administration Do not administer together with high-protein diets Splittable tablet | [10] |
| N04BA03 | Levodopa Carbidopa Entecapone (all dosages) | STALEVO (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N04BA05 | Melevodopa hydrochloride Carbidopa hydrate (12.5 + 125/25 + 100 mg) | SIRIO (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve in 150 mL water and wait until the end of the effervescence | |
| N04BB01 | Amantadine hydrochloride (100 mg) | MANTADAN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N04BC04 | Ropirinole hydrochloride (4, 8 mg) | REQUIP (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Requip tablets | [8,9] |
| N04BC04 | Ropirinole hydrochloride (0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 mg) | REQUIP (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Dissolve quickly the tablet in 10 mL water to obtain a fine dispersion to be administered immediately | [10] |
| N04BC04 | Ropirinole hydrochloride (4 mg) | ROPINIROLO SAN (SANDOZ) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Requip tablets | [8,9] |
| N04BC05 | Pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate (0.26, 0.52, 1.05, 2.1, 3.15 mg) | MIRAPEXIN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Pramipexol tablets | [8,9] |
| N04BC05 | Pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate (0.7 mg) | PRAMIPEXOLO EG (EG) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Photosensitive drug | |
| Pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate (0.18, 0.7 mg) | PRAMIPEXOLO (TEVA) | |||||
| N04BC06 | Cabergoline (2 mg) | CABASER (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N04BD01 | Selegiline hydrochloride (5, 10 mg) | JUMEX (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Administer in the morning before starting EN | |
| N04BD02 | Rasagiline mesylate (1 mg) | AZILECT (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| N04BX01 | Tolcapone (100 mg) | TASMAR (MEDA PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| N04BX02 | Entacapone (200 mg) | COMTAN (NOVARTIS) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 20 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N05AA01 | Chlorpromazine hydrochloride (100 mg) | PROZIN (IST.LUSOFARMACO) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: drops or oral solution | [8,9] |
| N05AA02 | Levomepromazine maleate (25, 100 mg) | NOZINAN (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| N05AB03 | Perfenazine (2, 4, 8 mg) | TRILAFON (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| N05AB06 | Trifluoperazine dihydrochloride (1 mg) | MODALINA (IST LABORATORIO FARMACEUTICO) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| N05AD01 | Haloperidol (1, 5 mg) | HALDOL (JANSSEN CILAG) | Tablets | Yes | Better to use drops diluted in 50 mL water and administered 1 h before or 2 h after EN | |
| N05AF05 | Zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride (10 mg) | CLOPIXOL (LUNDBECK) | Coated tablets | Yes | Immerse the tablet in water, after 10 min a fine suspension is obtained, then administer immediately Alternative: solution for injection | |
| N05AH02 | Clozapine (25 mg) | CLOZAPINA CHS (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| Clozapine (25, 100 mg) | LEPONEX (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | ||||
| Clozapine (100 mg) | CLOZAPINA (ORION) | Tablets | ||||
| N05AH03 | Olanzapine (5, 10 mg) | ZYPREXA VELOTAB (ELI LILLY) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve in 30 mL water, apple juice, orange juice, or milk Irritant drug Use personal protective equipment | SmPC |
| N05AH03 | Olanzapine (2.5 mg) | ZYPREXA (ELI LILLY) | Coated tablets | Yes | Better to use orodispersible tablets Irritant to mucous membranes and eyes | |
| Olanzapine (5, 10 mg) | OLANZAPINA SUN (SUN PHARMACEUTICALS) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in water and administer immediately | ||
| Olanzapine (2.5, 5, 10 mg) | OLANZAPINA TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | No | Better to use orodispersible tablets | ||
| N05AH03 | Olanzapine (5, 10 mg) | OLANZAPINA TEV (TEVA) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in water and administer immediately | SmPC |
| N05AH04 | Quetiapine fumarate (50, 150, 200, 300, 400 mg) | SEROQUEL (ASTRAZENECA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Seroquel coated tablets | [8,9] |
| N05AH04 | Quetiapine fumarate (100, 200, 300 mg) | SEROQUEL (ASTRAZENECA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 25 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| Quetiapine fumarate (50, 200, 300, 400 mg) | QUETIAPINA TEV (TEVA) | No | ||||
| N05AH04 | Quetiapine fumarate (50, 200, 300, 400 mg) | QUETIAPINA TEV (TEVA) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N05AH05 | Asenapine maleate (5, 10 mg) | SYCREST (LUNDBECK) | Sublingual tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N05AH06 | Clotiapine (40 mg) | ENTUMIN (LAB.JUVISE’ PHARMACEUTICALS) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Alternative: Entumin drops to be diluted with 50 mL water | |
| N05AL03 | Tiapride hydrochloride (100 mg) | SEREPRILE (SANOFI) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Administer at a fixed time | |
| N05AL05 | Amilsupride (50 mg) | AMISULPRIDE EG (EG) | Tablets | Yes | Alternative: oral solution | [10] |
| Amilsupride (50, 200, 400 mg) | AMISULPRIDE MYL (MYLAN) | Tablets | ||||
| Amilsupride (400 mg) | AMISULPRIDE SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | ||||
| Amilsupride (400 mg) | SOLIAN (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | ||||
| N05AL07 | Levosulpride (50, 100 mg) | LEVOPRAID (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N05AN01 | Lithium carbonate (300 mg) | LITIO CARBONATO (NOVA ARGENTIA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Attention drug with a narrow therapeutic index | |
| CARBOLITHIUM (TEVA) | Capsules | |||||
| N05AX08 | Risperidone (1, 2 mg) | RISPERIDONE SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| Risperidone (2, 3, 4 mg) | RISPERIDONE TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| N05AX12 | Aripripazole (5, 10, 15 mg) | ABILIFY (OTSUKA) | Tablets | Yes | Alternatives: orodispersible tablets or oral solution | [8,9] |
| Aripripazole (10, 15 mg) | ABILIFY (OTSUKA) | Orodispersible tablets | [8,9] | |||
| N05AX13 | Paliperidone (3, 6, 9 mg) | INVEGA (JANSSEN CILAG) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Xeplion modified release suspension for injection | [8,9] |
| N05BA | Delorazepam (0.5, 1, 2 mg) | DELORAZEPAM (AUROBINDO) | Tablets | No | Alternative: drops | [8,9] |
| Delorazepam (0.5, 1, 2 mg) | EN (BGP PRODUCTS) | |||||
| Delorazepam (2 mg) | DELORAZEPAM RAT (RATIOPHARM) | |||||
| Delorazepam (0.5, 1 mg) | DELORAZEPAM WPI (ZENTIVA) | |||||
| N05BA01 | Diazepam (2 mg) | VALIUM (ROCHE) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| Diazepam (5 mg) | VATRAN (VALEAS) | Tablets | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |||
| N05BA04 | Oxazepam (15 mg) | SERPAX (MEDA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Divisible tablet Better to use Diazepam or Lorazepam | [10] |
| N05BA06 | Lorazepam (1, 2.5 mg) | TAVOR (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Prefer liquid or the orosoluble formulation | [10] |
| N05BA08 | Bromazepam (1.5 mg) | COMPENDIUM (POLIFARMA) | Capsules | No | Alternative: drops | [8,9] |
| Bromazepam (3 mg) | BROMAZEPAM RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Tablets | ||||
| N05BA09 | Clobazam (10 mg) | FRISIUM (SANOFI) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N05BA11 | Prazepam (10 mg) | PRAZENE (PFIZER) | Tablets | No | Alternative: drops that must be diluted | [8,9] |
| N05BA12 | Alprazolam (0.25, 0.5 mg) | XANAX (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Better to use the drops | [10] |
| N05BB01 | Hydroxyzine hydrochloride (25 mg) | ATARAX (UCB PHARMA) | Coated tablets | Yes | Prefer Atarax syrup | [10] |
| N05CD01 | Flurazepam monohydrochloride (15, 30 mg) | VALDORM (VALEAS) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately Administer before the last EN | [10] |
| N05CD02 | Nitrazepam (5 mg) | MOGADON (MEDA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in a water glass and then administer immediately | SmPC |
| N05CD05 | Triazolam (250 µg) | HALCION (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| N05CD09 | Brotizolam (0.25 mg) | LENDORMIN (BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets | |
| N05CF02 | Zolpidem tartrate (10 mg) | ZOLPIDEM RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Better to administer at bedtime to have a hypnotic effect Divisible tablets | |
| N06AA04 | Clomipramine hydrochloride (75 mg) | ANAFRANIL (SIGMATAU) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N06AA04 | Clomipramine hydrochloride (10, 25 mg) | ANAFRANIL (SIGMATAU) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N06AA09 | Amitriptyline hydrochloride (10, 25 mg) | LAROXYL (TEOFARMA) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: drops that must be diluted with 50 mL water | [8,9] |
| N06AA10 | Nortriptyline hydrochloride (10, 25 mg) | NORITREN (LUNDBECK) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| N06AB03 | Fluoxetine hydrochloride (20 mg) | FLUOXETINA EG (EG) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately Prefer liquid formulation or orosoluble tablets The solution should not be administered in the fast due to the acidic pH | [10] |
| N06AB03 | Fluoxetine hydrochloride (20 mg) | FLUOXETINA FDI (FIDIA FARMACEUTICI) | Capsules | Yes | Preferably use the liquid form or the dispersible tablets | [8,9] |
| N06AB03 | Fluoxetine hydrochloride (20 mg) | FLUOXETINA RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Soluble tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 50 mL water and administer immediately | SmPC |
| N06AB03 | Fluoxetine hydrochloride (20 mg) | XEREDIEN (VALEAS) | Dispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in water and administer immediately | [8,9] |
| N06AB04 | Citalopram hydrobromide (20 mg) | CITALOPRAM RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse it in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Preferably use drops Incompatible with PVC tubes | [10] |
| CITALOPRAM HEX (SANDOZ) | [10] | |||||
| N06AB05 | Paroxetine hydrochloride (20 mg) | SEREUPIN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Alternatives: drops or oral suspension | [10] |
| N06AB06 | Sertraline hydrochloride (50 mg) | SERTRALINA MYL (MYLAN) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Rinse the tube well after administration Preferably switch to another selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | |
| ZOLOFT (PFIZER) | ||||||
| N06AB08 | Fluvoxamine maleate (50 mg) | FEVARIN (BGP PRODUCTS) | Coated tablets | No | Preferably switch to another selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in liquid formulation | [8,9] |
| MAVERAL (BGP PRODUCTS) | ||||||
| N06AB10 | Escitalopram oxalate (10, 20 mg) | CIPRALEX (LUNDBECK) | Coated tablets | Yes | Alternative: Cipralex drops Divisible tablets | [10] |
| Escitalopram oxalate (20 mg) | ENTACT (LUNDBECK) | |||||
| N06AX03 | Mianserin hydrochloride (30 mg) | LANTANON (MSD) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | |
| N06AX05 | Tradozone hydrochloride (75, 150 mg) | TRITTICO (ANGELINI) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternatives: coated tablets or drops | [8,9] |
| N06AX05 | Tradozone hydrochloride (75, 150 mg) | TRITTICO (ANGELINI) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately Divisible tablets | |
| N06AX11 | Mirtazapine (30 mg) | MIRTAZAPINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| N06AX12 | Bupropion hydrochloride (150 mg) | WELLBUTRIN (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N06AX16 | Venlafaxine hydrochloride (75, 150 mg) | ZARELIS (ITALFARMACO) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: oral solution | [8,9] |
| Venlafaxine hydrochloride (37.5, 75, 150 mg) | EFEXOR (PFIZER) | Modified release capsules | ||||
| Venlafaxine hydrochloride (37.5 mg) | VENLAFAX TEV (TEVA) | Modified release capsules | ||||
| N06AX21 | Duloxetine hydrochloride (30, 60 mg) | CYMBALTA (ELI LILLY) | Modified release capsules | No | Risk of probe occlusion | [8,9] |
| Duloxetine hydrochloride (60 mg) | XERISTAR (QUINTILES) | Gastro-resistant capsules | No | Do not grind the granules | [8,9] | |
| N06BA04 | Methylphenidate hydrochloride (10 mg) | RITALIN (NOVARTIS) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| N06BA04 | Methylphenidate hydrochloride (10, 20 mg) | EQUASYM (SHIRE) | Modified release capsules | No | [8,9] | |
| N06BA07 | Modafinil (100 mg) | PROVIGIL (TEVA) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in water, then administer immediately | [10] |
| N06BA09 | Atomoxetine hydrochloride (40, 60 mg) | STRATTERA (ELI LILLY) | Capsules | No | ||
| N06BX12 | Acetyl-L-carnitine (500 mg) | NICETILE (SIGMATAU) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N06BX12 | Acetyl-L-carnitine (500 mg) | NICETILE (SIGMATAU) | Powder for oral solution | Yes | ||
| N06CA01 | Amitriptyline Perphenazine (10 + 4 mg) | MUTABON MITE (NEOPHARMED GENTILI) | Coated tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| N06DA02 | Donepezil hydrochloride (10 mg) | ARICEPT 10 (PFIZER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 20 mL water, then administer within 15 min Preferably use Donezepil orodispersible tablets | [10] |
| Donepezil hydrochloride (5, 10 mg) | DONEPEZIL ACV (ACTAVIS) | |||||
| MEMAC (BRACCO) | ||||||
| DONEPEZIL EG (EG) | ||||||
| N06DA02 | Donepezil hydrochloride monohydrate (5 mg) | DONEPEZIL MYL (MYLAN) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer immediately | [8,9] |
| Donepezil hydrochloride (5, 10 mg) | DONEPEZIL TEV (TEVA) | |||||
| N06DA03 | Rivastigmine hydrogen tartrate (1.5, 3, 4.5 mg) | EXELON (NOVARTIS) | Capsules | No | Alternatives: transdermal patches or oral solution | [8,9] |
| Rivastigmine hydrogen tartrate (1.5, 3, 4.5, 6 mg) | RIVASTIGMINA SAN (SANDOZ) | |||||
| N06DA04 | Galantamine hydrobromide (8, 16, 24 mg) | REMINYL (JANSSEN CILAG) | Modified release capsules | No | Alternative: oral solution | [8,9] |
| N06DA04 | Galantamine hydrobromide (8, 16, 24 mg) | REMINYL (JANSSEN CILAG) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 10 mL water, then administer Preferably use Galantamine oral solution to be diluted before administration | [10] |
| N06DX01 | Memantine hydrochloride (10 mg) | EBIXA (LUNDBECK) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Ebixa oral solution | [8,9] |
| Memantine hydrochloride (10, 20 mg) | MEMANTINA MYL (MYLAN) | |||||
| N07AA02 | Pyridostigmine hydrobromide (180 mg) | MESTINON (MEDA PHARMA) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: Mestinton 60 mg | [8,9] |
| N07AA02 | Pyridostigmine hydrobromide (60 mg) | MESTINON (MEDA PHARMA) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible tablets | |
| N07AX01 | Pilocarpine hydrochloride (5 mg) | SALAGEN (MERUS LABS LUXCO II SARL) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| N07BB01 | Disulfiram (400 mg) | ANTABUSE DISPERGETTES (AUROBINDO) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in 10 mL water and administer at the end of the effervescence | |
| N07BB03 | Acamprosate calcium (333 mg) | CAMPRAL (BRUNO FARMACEUTICI) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| N07BC01 | Buprenorphine hydrochloride (2, 8 mg) | BUPRENORFINA MOL (MOLTENI & C. F.LLI ALITTI) | Sublingual tablets | No | Administer sublingually only if the patient is conscious | [8,9] |
| N07CA01 | Betahistine dihydrochloride (8 mg) | MICROSER (GRUNENTHAL) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in 20 mL water, then administer Preferably use drops | [10] |
| N07CA02 | Cinnarizine (75 mg) | STUGERON FTE (JANSSEN CILAG) | Capsules | No | Alternative: drops | [8,9] |
| STUGERON FTE (JANSSEN CILAG) | Tablets | |||||
| N07XX02 | Riluzole (50 mg) | RILUZOLO SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in water, then administer Preferably change therapy | [10] |
| N07XX06 | Tetrabenazine (25 mg) | XENAZINA (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Divisible and crushable tablet | |
| N07XX09 | Dimethyl fumarate (120, 240 mg) | TECFIDERA (BIOGEN ITALIA) | Gastro-resistant capsules | No | Do not grind the granules | [8,9] |
| P01AB01 | Metronidazole (250 mg) | VAGILEN (ALFA WASSERMANN) | Capsules | Yes | Open the capsule, disperse the content in 20 mL water, then administer immediately 1 h before EN Alternatives: solution for injection or vaginal ovules | |
| FLAGYL (ZAMBON) | Tablets | No | Alternatives: solution for injection or vaginal ovules | |||
| P01BA01 | Chloroquine diphosphate (250 mg) | CLOROCHINA (BAYER) | Coated tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately preferably after EN | [10] |
| P01BA02 | Hydroxychloroquine sulfate (200 mg) | PLAQUENIL (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | Yes | [10] | |
| P01BF05 | Piperaquine tetraphosphate Dihydroartemisinin (320 + 40 mg) | EURARTESIM (SIGMATAU) | Coated tablets | Yes | ||
| P02CA03 | Albendazole (400 mg) | ZENTEL (GLAXOSMITHKLINE) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer immediately | SmPC |
| P02DA01 | Niclosamide (500 mg) | YOMESAN (BAYER) | Chewable tablets | Yes | Dissolve the tablet in water and administer | SmPC |
| R03DA04 | Theophylline anhydrous (200, 300 mg) | THEO-DUR (RECORDATI) | Modified release tablets | No | Alternative: liquid formulation to be diluted with 20 mL water and administered 1 h after EN Monitor blood levels and adjust dosage | [8,9] |
| RESPICUR (TAKEDA) | Modified release capsules | |||||
| R03DA08 | Bamifylline hydrochloride (600 mg) | BAMIFIX (CHIESI FARMACEUTICI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: suppositories but only for pediatrics | |
| R03DA11 | Doxofylline (400 mg) | ANSIMAR (ABC FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Alternatives: Ansimar syrup or solution for injection | |
| R03DC03 | Montelukast sodium (5 mg) | SINGULAIR (MSD) | Chewable tablets | Yes | ||
| Montelukast sodium (10 mg) | SINGULAIR (MSD) | Coated tablets | Disperse the tablet in 10 mL water under gentle stirring, then administer immediately | |||
| Montelukast sodium (5 mg) | MONTELUKAST SAN (SANDOZ) | Chewable tablets | ||||
| Montelukast sodium (5 mg) | MONTELUKAST TEV (TEVA) | Coated tablets | Grind the tablet and disperse the powder in water, then administer away from EN Preferably use oral granules | |||
| R05CB01 | Acetylcysteine (600 mg) | ACETILCISTEINA RAT (RATIOPHARM) | Effervescent tablets | Yes | Administer at the end of the effervescence | |
| FLUIMUCIL (ZAMBON) | Granules for oral solution | Mix with water then administer | ||||
| FLUIMUCIL (ZAMBON) | Effervescent tablets | Administer at the end of the effervescence | ||||
| R06AE06 | Oxatomide (30 mg) | TINSET (GRUNENTHAL) | Tablets | No | Alternative: drops | [8,9] |
| R06AE07 | Cetirizine hydrochloride (10 mg) | CERCHIO (MEDIOLANUM FARMACEUTICI) | Tablets | Yes | Alternative: drops | |
| CETIRIZINA SAN (SANDOZ) | Coated tablets | |||||
| R06AX25 | Mizolastine (10 mg) | ZOLISTAM (SANOFI) | Modified release tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| R06AX26 | Fexofenadine hydrochloride (180 mg) | TELFAST (SANOFI) | Coated tablets | No | Alternatives: Cetirizine or Loratadine | |
| R06AX27 | Desloratadine (2.5 mg) | AERIUS (MSD) | Orodispersible tablets | Yes | ||
| S01EC01 | Acetazolamide (250 mg) | DIAMOX (TEOFARMA) | Tablets | Yes | ||
| V03AC03 | Deferasirox (125, 500 mg) | EXJADE (NOVARTIS) | Dispersible tablets | Yes | Disperse in 200 mL water until a suspension is obtained Take on an empty stomach before EN | SmPC |
| V03AE02 | Sevelamer hydrochloride (800 mg) | RENAGEL (GENZYME) | Coated tablets | No | Alternative: Renvela powder for oral suspension | [8,9] |
| RENVELA (GENZYME) | ||||||
| V03AE02 | Sevelamer carbonate (2.4 g mg) | RENVELA (GENZYME | Powder for oral suspension | Yes | Disperse the powder in 60 mL water and administer immediately Rinse well the tube | |
| V03AE03 | Lanthanum(III) carbonate hydrate (1 g) | FOZNOL (SHIRE) | Oral powder | No | ||
| Lanthanum(III) carbonate hydrate (1 g) | FOZNOL (SHIRE) | Chewable tablets | Yes | |||
| V03AE04 | Calcium acetate Magnesium carbonate (435 + 235 mg) | OSVAREN (VIFOR FRESENIUS) | Coated tablets | No | ||
| V03AF | Calcium mefolinate (15 mg) | PREFOLIC (ZAMBON) | Gastro-resistant tablets | No | [8,9] | |
| V03AF04 | Calcium levofolinate (7.5 mg) | LEDERFOLIN (PFIZER) | Tablets | Yes | Grind the tablet and dissolve the powder in 10 mL water, then administer Alternative: powder for reconstitution for injection | [10] |
| V03AF04 | Calcium levofolinate (2.5 mg) | LEDERFOLIN (PFIZER) | Granules for oral solution | Yes |
| Magistral Preparation | Ingredients | Storage/Expiration | Method of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Captopril 1 mg/mL Syrup | Captopril powder Pharm. Eur. Simple syrup | 5 °C in a well-closed amber glass jar for 10 days | Shake, withdraw the required portion of the liquid and dilute with water * |
| Carbamazepine 40 mg/mL Suspension | Carbamazepine powder Pharm. Eur. Simple syrup | ||
| Isoniazid 50 mg/mL Solution | Isoniazid powder Pharm. Eur. Distilled water | ||
| Midazolam 2.5 mg/mL Syrup | Midazolam powder Pharm. Eur. Simple syrup | ||
| Omeprazole 2 mg/mL Solution | Omeprazole powder Pharm. Eur. Sodium bicarbonate 8.4% | ||
| Ranitidine 15 mg/mL Solution | Omeprazole powder Pharm. Eur. Sorbitol Purified water | ||
| Spironolactone 10 mg/mL Suspension | Spironolactone powder Pharm. Eur. Simple syrup | ||
| Verapamil 50 mg/mL Suspension | Verapamil powder Pharm. Eur. Distilled water Simple syrup Glycerol |
| Pharmaceutical Form | Method of Administration |
|---|---|
| Liquid forms (drops, syrups, suspensions) | High osmolar or very viscous liquids must be suitably diluted before being administered If the osmolality is not known, it is advisable to dilute the drug with at least 30 mL of water to make it compatible with gastric administration and to prevent diarrheal phenomena from osmotic effect Shake and mix the solution or suspension well Administer directly by tube |
| Tablets Chewable tablets | The tablets must be crushed in the crusher until they are reduced to a fine and homogeneous powder to promote better absorption and avoid obstruction of the tube Transfer the powder to a plastic cup |
| Effervescent tablets | Put the tablet directly in a plastic cup |
| Dispersible/soluble tablets | Put the tablet directly in a plastic cup |
| Capsules | Open the capsule and insert the powder in a plastic cup, verifying the content first |
| Soft capsules | They cannot be administered |
| Modified-release tablets/capsules | |
| Gastroresistant tablets, enteric-coated tablets | |
| Sublingual tablets |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuccari, G.; Macis, S.; Alfei, S.; Marchitto, L.; Russo, E. The Role of the Pharmacist in Selecting the Best Choice of Medication Formulation in Dysphagic Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081307
Zuccari G, Macis S, Alfei S, Marchitto L, Russo E. The Role of the Pharmacist in Selecting the Best Choice of Medication Formulation in Dysphagic Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(8):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081307
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuccari, Guendalina, Sara Macis, Silvana Alfei, Leonardo Marchitto, and Eleonora Russo. 2022. "The Role of the Pharmacist in Selecting the Best Choice of Medication Formulation in Dysphagic Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 8: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081307
APA StyleZuccari, G., Macis, S., Alfei, S., Marchitto, L., & Russo, E. (2022). The Role of the Pharmacist in Selecting the Best Choice of Medication Formulation in Dysphagic Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(8), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081307









