The Impact of Hip Dysplasia on CAM Impingement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
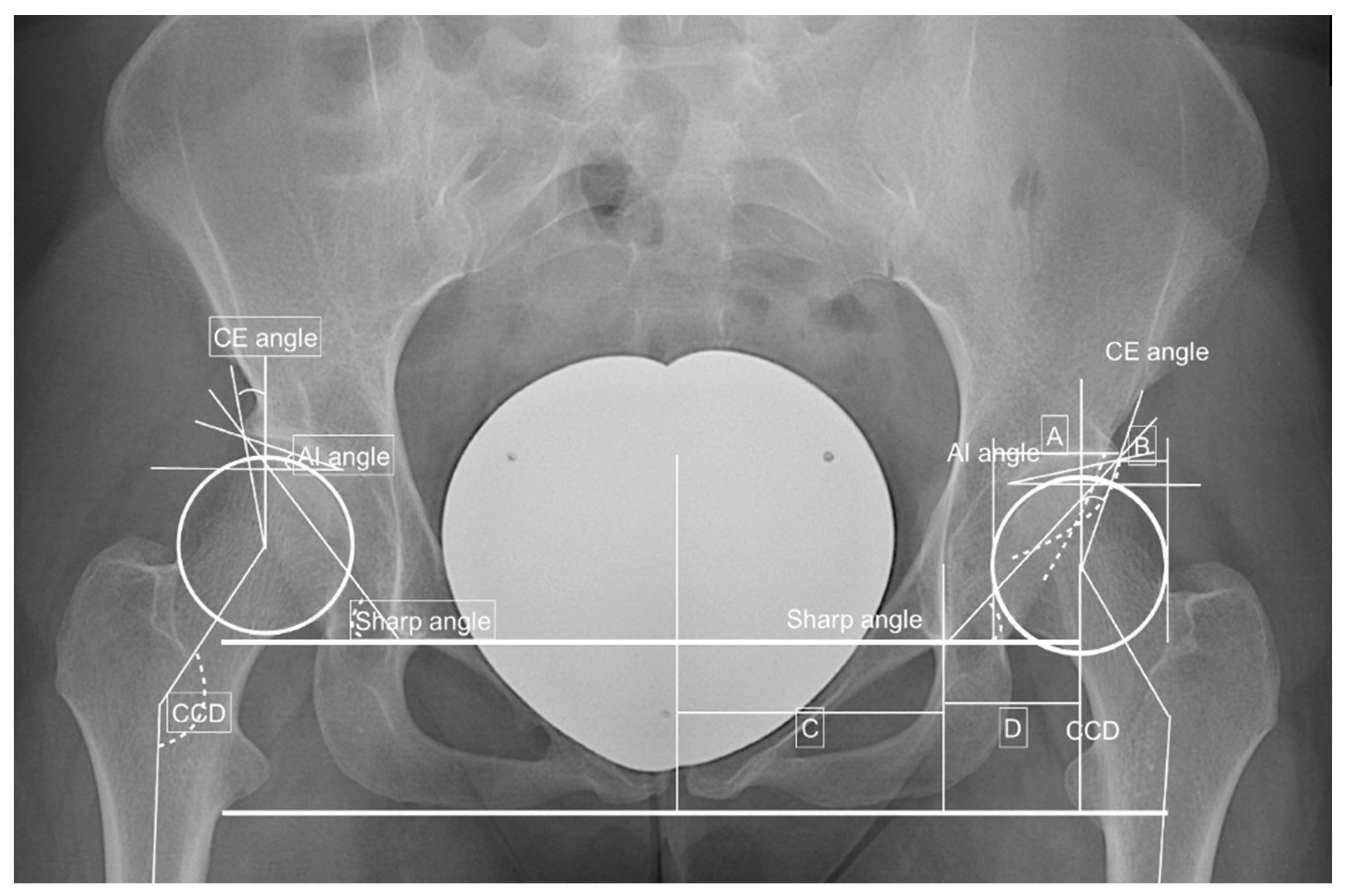
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerch, T.D.; Siegfried, M.; Schmaranzer, F.; Leibold, C.S.; Zurmühle, C.A.; Hanke, M.S.; Ryan, M.K.; Steppacher, S.D.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M. Location of Intra- and Extra-articular Hip Impingement Is Different in Patients with Pincer-Type and Mixed-Type Femoroacetabular Impingement Due to Acetabular Retroversion or Protrusio Acetabuli on 3D CT-Based Impingement Simulation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Hayes, M.; Royer, N.K. Relationship of acetabular dysplasia and femoroacetabular impingement to hip osteoarthritis: A focused review. PMR 2011, 3, 1055–1067.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganz, R.; Parvizi, J.; Beck, M.; Leunig, M.; Nötzli, H.; Siebenrock, K. Femoroacetabular impingement: A cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 417, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, M.; Kalhor, M.; Leunig, M.; Ganz, R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: Femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Br. Vol. 2005, 87, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, D.; Lucas, J.; Klaue, K. Retroversion of the acetabulum. A cause of hip pain. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Br. Vol. 1999, 81, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partenheimer, A.; Scheler-Hofmann, M.; Lange, J.; Kühl, R.; Follak, N.; Ebner, A.; Fusch, C.; Stenger, R.; Merk, H.; Haas, J.P. Correlation between sex, intrauterine position and familial predisposition and neonatal hip ultrasound results. Ultraschall Med. 2006, 27, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, L.S.; Rosenberg, Z.S.; Mayo, J.D.; De Tuesta, M.D.; Martin, O.; Neto, L.P.; Bencardino, J.T. Imaging evaluation of developmental hip dysplasia in the young adult. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannava, S.; Geeslin, A.G.; Frangiamore, S.J.; Cinque, M.E.; Geeslin, M.G.; Chahla, J.; Philippon, M.J. Comprehensive Clinical Evaluation of Femoroacetabular Impingement: Part 2, Plain Radiography. Arthrosc. Tech. 2017, 6, e2003–e2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henle, P.; Tannast, M.; Siebenrock, K.A. Imaging in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthopade 2008, 37, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, I.K. Acetabular Dysplasia—The Acetabular Angle. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Br. Vol. 1961, 43, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannast, M.; Hanke, M.S.; Zheng, G.; Steppacher, S.D.; Siebenrock, K.A. What are the radiographic reference values for acetabular under- and overcoverage? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonnis, D.; Heinecke, A. Acetabular and femoral anteversion: Relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Jt. Surg Am. 1999, 81, 1747–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidelich, H.A.; Strecker, W.; Schneider, E. Computed tomographic torsion-angle and length measurement of the lower extremity. The methods, normal values and radiation load. Rofo 1992, 157, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannast, M.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Anderson, S.E. Femoroacetabular impingement: Radiographic diagnosis--what the radiologist should know. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1540–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heimer, C.Y.W.; Göhler, F.; Vosseller, J.T.; Hardt, S.; Perka, C.; Bäcker, H.C. Rotation abnormalities in dysplastic hips and how to predict acetabular torsion. Eur Radiol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Heimer, C.Y.W.; Wu, C.H.; Perka, C.; Hardt, S.; Göhler, F.; Bäcker, H.C. The impact of the Laterality on Radiographic Outcomes of the Bernese Periacetabular Osteotomy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Tannast, M.; Anderegg, C.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Langlotz, F. Hip2Norm: An object-oriented cross-platform program for 3D analysis of hip joint morphology using 2D pelvic radiographs. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2007, 87, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannast, M.; Mistry, S.; Steppacher, S.D.; Reichenbach, S.; Langlotz, F.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Zheng, G. Radiographic analysis of femoroacetabular impingement with Hip2Norm-reliable and validated. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannast, M.; Kubiak-Langer, M.; Langlotz, F.; Puls, M.; Murphy, S.B.; Siebenrock, K.A. Noninvasive three-dimensional assessment of femoroacetabular impingement. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.E.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M. Femoroacetabular impingement. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3740–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfirrmann, C.W.; Mengiardi, B.; Dora, C.; Kalberer, F.; Zanetti, M.; Hodler, J. Cam and pincer femoroacetabular impingement: Characteristic MR arthrographic findings in 50 patients. Radiology 2006, 240, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerch, T.D.; Boschung, A.; Todorski, I.A.; Steppacher, S.D.; Schmaranzer, F.; Zheng, G.; Ryan, M.K.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M. Femoroacetabular Impingement Patients With Decreased Femoral Version Have Different Impingement Locations and Intra- and Extraarticular Anterior Subspine FAI on 3D-CT-Based Impingement Simulation: Implications for Hip Arthroscopy. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 3120–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetsroni, I.; Poultsides, L.; Bedi, A.; Larson, C.M.; Kelly, B.T. Anterior inferior iliac spine morphology correlates with hip range of motion: A classification system and dynamic model. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lerch, T.D.; Schmaranzer, F.; Hanke, M.S.; Leibold, C.; Steppacher, S.D.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M. Torsional deformities of the femur in patients with femoroacetabular impingement: Dynamic 3D impingement simulation can be helpful for the planning of surgical hip dislocation and hip arthroscopy. Orthopade 2020, 49, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, T.D.; Liechti, E.F.; Todorski, I.A.S.; Schmaranzer, F.; Steppacher, S.D.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M.; Klenke, F.M. Prevalence of combined abnormalities of tibial and femoral torsion in patients with symptomatic hip dysplasia and femoroacetabular impingement. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, A.G.; Siegal, D.S.; Scher, C.E.; Zaltz, I. Can femoral rotation be localized and quantified using standard CT measures? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.; Nepple, J.J.; Crook, K.; Ross, J.R.; Bedi, A.; Schoenecker, P.; Clohisy, J.C. Femoral Morphology in the Dysplastic Hip: Three-dimensional Characterizations With CT. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamborsky, R.; Kokavec, M.; Harsanyi, S.; Attia, D.; Danisovic, L. Developmental Dysplasia of Hip: Perspectives in Genetic Screening. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawadi, A.H.; Wakeel, A.; Tamimi, W.; Nasr, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Mashhour, A.; Fattah, M.A.; Alkhanein, N.; Abu Jaffal, A.S. Association analysis between four vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, H.O.; Schmidt, J.-P.; Haasters, F.; Bernstein, A.; Schmal, H.; Prall, W.C. Anteversion Angle Measurement in Suspected Torsional Malalignment of the Femur in 3-Dimensional EOS vs Computed Tomography-A Validation Study. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Coefficient | p-Value | CAM | nonCAM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | 52 | 19 (36.5%) | 33 (63.5%) | |||
| Female (%) | 46 (88.5) | −0.139 | 0.520 | 16 (84.2) | 30 (90.9) | 0.238 |
| Left hip (%) | 25 (48.1) | −0.078 | 0.573 | 8 (42.1) | 17 (51.5) | 0.261 |
| Age (years) | 28.8 ± 7.6 | 0.014 | 0.134 | 30.9 ± 6.6 | 27.6 ± 7.9 | 0.067 |
| Height (cm) | 169.7 ± 8.4 | 0.013 | 0.822 | 171.6 ± 9.1 | 168.6 ± 7.9 | 0.125 |
| Bodyweight (kg) | 68.1 ± 12.2 | −0.008 | 0.920 | 66.1 ± 9.7 | 69.4 ± 13.5 | 0.189 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 4.3 | −0.003 | 0.990 | 22.4 ± 2.6 | 24.5 ± 5.0 | 0.059 |
| Borderline DDH | 13 (25.0%) | 0.179 | 0.253 | 3 (15.8%) | 10 (30.3%) | |
| DDH | 39 (75.0%) | 0.179 | 0.253 | 16 (84.2%) | 23 (69.7%) |
| Coefficient | p-Value | Total | CAM | nonCAM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexion (°) | −0.011 | 0.120 | 130 ± 13.1 | 132.6 ± 12.8 | 128.5 ± 13.4 | 0.139 |
| Extension (°) | −0.026 | 0.111 | 2.1 ± 4.1 | 2.6 ± 4.5 | 1.8 ± 3.9 | 0.249 |
| External rotation (°) | 0.009 | 0.202 | 52.8 ± 11.5 | 54.5 ± 11.4 | 51.8 ± 11.6 | 0.214 |
| Internal rotation (°) | 0.006 | 0.280 | 41.4 ± 14.3 | 41.3 ± 14.8 | 41.4 ± 14.2 | 0.495 |
| Abduction (°) | 0.010 | 0.139 | 51.8 ± 15.2 | 51.8 ± 15.9 | 51.8 ± 15.1 | 0.498 |
| Adduction (°) | −0.007 | 0.467 | 26.9 ± 10.0 | 29.0 ± 11.5 | 25.8 ± 9.0 | 0.136 |
| Total | Coefficient | p-Value | CAM | nonCAM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE angle (°) | 22.7 ± 5.8 | 0.002 | 0.968 | 21.0 ± 5.4 | 23.7 ± 5.8 | 0.050 |
| AI angle (°) | 11.2 ± 5.2 | 0.006 | 0.781 | 12.6 ± 6.3 | 10.3 ± 4.3 | 0.065 |
| Sharp angle (°) | 42.5 ± 3.7 | −0.005 | 0.894 | 43.3 ± 3.5 | 42.1 ± 3.8 | 0.148 |
| Hip lateralization index | 0.56 ± 0.06 | 0.617 | 0.590 | 0.57 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.06 | 0.214 |
| AHI | 23.2 ± 7.0 | 0.017 | 0.524 | 25.6 ± 5.7 | 21.9 ± 7.3 | 0.031 |
| CCD (°) | 133.0 ± 5.7 | <0.005 | 0.994 | 133.3 ± 6.4 | 132.8 ± 5.4 | 0.378 |
| Crossing over sign | 17 (32.7) | −0.194 | 0.184 | 4 (21.1) | 13 (39.4) | 0.091 |
| Kellgren–Lawrence score | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.015 | 0.909 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.488 |
| Alpha angle (°) | 100.0 ± 10.9 | −0.001 | 0.922 | 101.5 ± 10.0 | 98.8 ± 11.6 | 0.235 |
| Beta angle (°) | 57.0 ± 7.5 | 0.015 | 0.288 | 58.8 ± 7.8 | 55.7 ± 7.2 | 0.111 |
| Total | Coefficient | p-Value | CAM | nonCAM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetabular torsion (°) | 18.9 ± 5.7 | −0.005 | 0.712 | 18.6 ± 6.5 | 19.1 ± 5.3 | 0.373 |
| Femoral neck torsion (°) | 15.4 ± 10.7 | 0.012 | 0.516 | 15.7 ± 8.3 | 15.2 ± 12.0 | 0.432 |
| Femoral condyle torsion (°) | −13.2 ± 9.8 | −0.048 | 0.277 | −12.4 ± 10.7 | −13.7 ± 9.4 | 0.328 |
| Femoral torsion (°) | 27.7 ± 12.6 | −0.014 | 0.469 | 26.5 ± 12.6 | 28.4 ± 12.7 | 0.305 |
| Tibial plateau torsion (°) | −7.5 ± 10.4 | 0.042 | 0.305 | −4.9 ± 9.4 | −9.0 ± 10.7 | 0.084 |
| Femorotibial torsion (°) | 6.3 ± 5.0 | −0.025 | 0.589 | 7.6 ± 6.5 | 5.5 ± 3.7 | 0.066 |
| Ankle torsion (°) | 28.9 ± 10.5 | 0.008 | 0.202 | 30.2 ± 11.2 | 27.9 ± 10.1 | 0.236 |
| Tibial torsion (°) | 37.0 ± 7.8 | −0.008 | 0.336 | 36.6 ± 9.6 | 37.3 ± 6.5 | 0.377 |
| Leg torsion (°) | −13.5 ± 14.0 | −0.002 | 0.674 | −14.5 ± 14.3 | −12.8 ± 14.0 | 0.337 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heimer, C.Y.W.; Wu, C.H.; Perka, C.; Hardt, S.; Göhler, F.; Winkler, T.; Bäcker, H.C. The Impact of Hip Dysplasia on CAM Impingement. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071129
Heimer CYW, Wu CH, Perka C, Hardt S, Göhler F, Winkler T, Bäcker HC. The Impact of Hip Dysplasia on CAM Impingement. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(7):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071129
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeimer, Carsten Y. W., Chia H. Wu, Carsten Perka, Sebastian Hardt, Friedemann Göhler, Tobias Winkler, and Henrik C. Bäcker. 2022. "The Impact of Hip Dysplasia on CAM Impingement" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 7: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071129
APA StyleHeimer, C. Y. W., Wu, C. H., Perka, C., Hardt, S., Göhler, F., Winkler, T., & Bäcker, H. C. (2022). The Impact of Hip Dysplasia on CAM Impingement. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(7), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071129








