Reducing Tolerance for SABA and OCS towards the Extreme Ends of Asthma Severity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
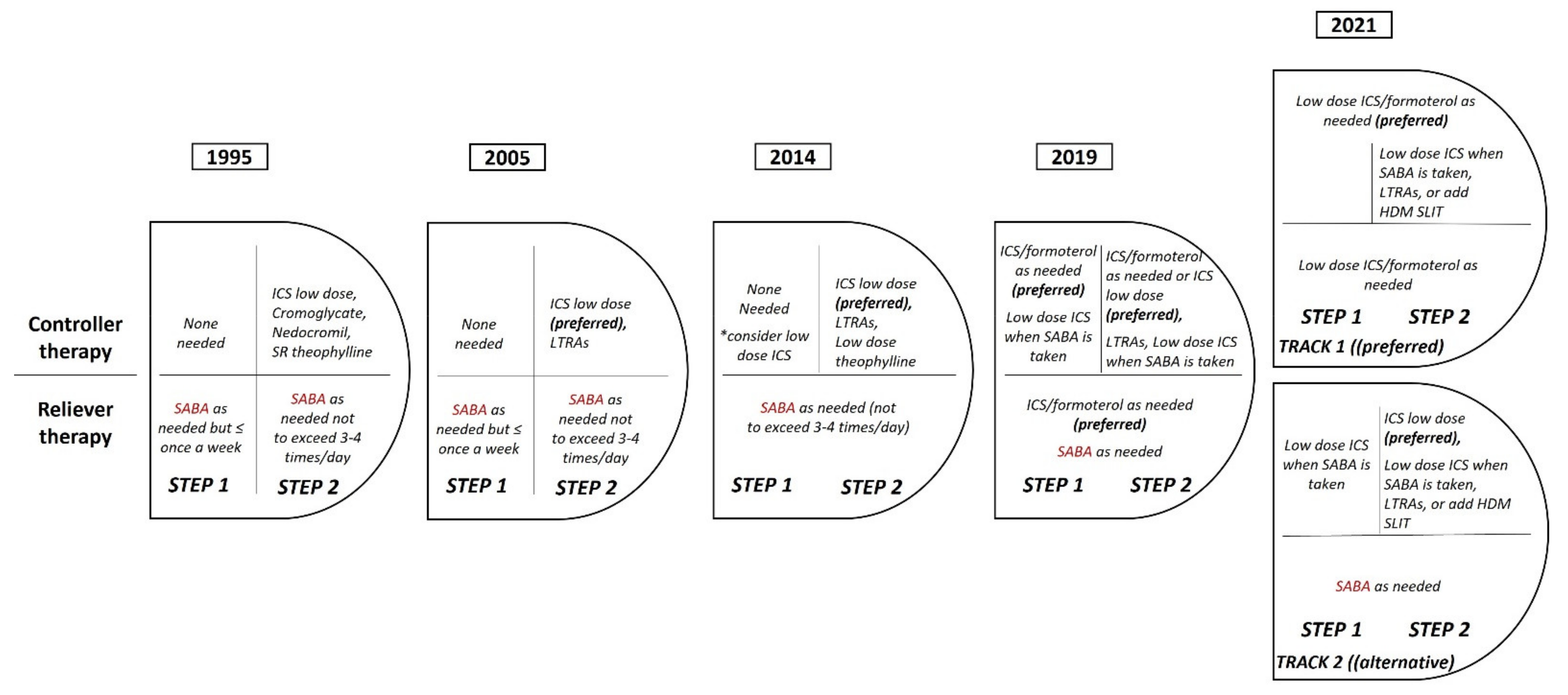
2. Reducing Inappropriate Use of SABA in Mild Asthma
2.1. The Use of SABA in Asthma—The Story so Far
2.2. The Body of Evidence That Led the Change of Treatment Strategy in Mild Asthma
2.3. New Recommendations from the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA): The Revolution in Mild Asthma Treatment
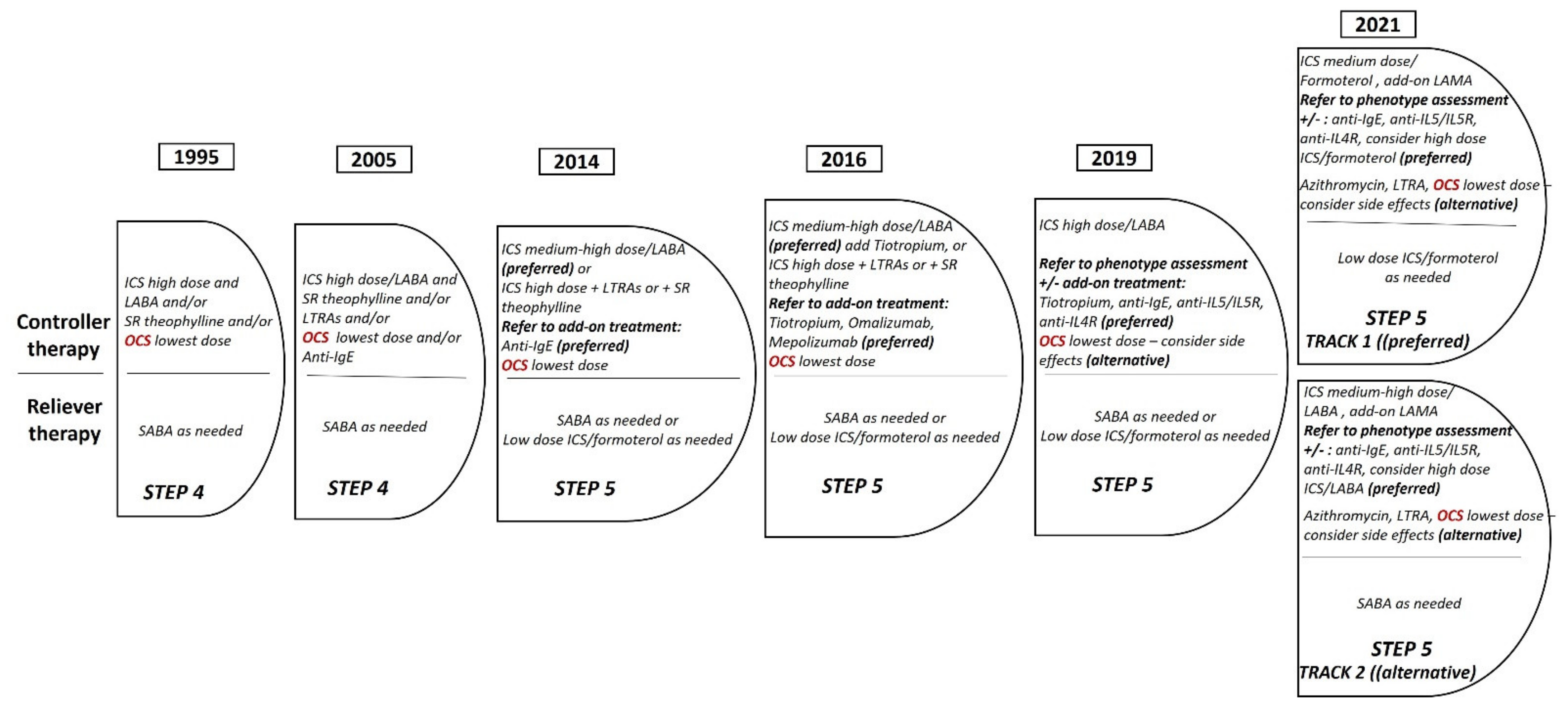
3. Towards the Minimization of Use of OCS in Severe Asthma
3.1. OCS in Severe Asthma: Effectiveness and Safety
3.2. Steroid Sparing Effect of Biologics and New Concept of GINA Guidelines for OCS
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agustí, A.; Bafadhel, M.; Beasley, R.; Bel, E.H.; Faner, R.; Gibson, P.G.; Louis, R.; McDonald, V.M.; Sterk, P.J.; Thomas, M.; et al. Precision medicine in airway diseases: Moving to clinical practice. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ish, P.; Malhotra, N.; Gupta, N. GINA 2020: What’s new and why? J. Asthma 2021, 58, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.; van Boven, J.F.M.; Ryan, D.; Tsiligianni, I.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Group REGAW. GINA 2020: Potential Impacts, Opportunities, and Challenges for Primary Care. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Reddel, H.K.; Beasley, R. The management of mild asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volmer, T.; Effenberger, T.; Trautner, C.; Buhl, R. Consequences of long-term oral corticosteroid therapy and its side-effects in severe asthma in adults: A focused review of the impact data in the literature. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzetta, L.; Aiello, M.; Frizzelli, A.; Bertorelli, G.; Rogliani, P.; Chetta, A. Oral Corticosteroids Dependence and Biologic Drugs in Severe Asthma: Myths or Facts? A Systematic Review of Real-World Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehs, C.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Price, D.; Bleecker, E.R.; Canonica, G.W.; Gurnell, M.; Bourdin, A.; Oral Corticosteroids Tapering Delphi Expert Panel. Expert Consensus on the Tapering of Oral Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Asthma. A Delphi Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieraj, D.M.; Weeda, E.R.; Nguyen, E.; Coleman, C.I.; White, C.M.; Lazarus, S.C.; Blake, K.V.; Lang, J.E.; Baker, W.L. Association of Inhaled Corticosteroids and Long-Acting beta-Agonists as Controller and Quick Relief Therapy with Exacerbations and Symptom Control in Persistent Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2018, 319, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beasley, R.; Holliday, M.; Reddel, H.K.; Braithwaite, I.; Ebmeier, S.; Hancox, R.J.; Harrison, T.; Houghton, C.; Oldfield, K.; Papi, A.; et al. Controlled Trial of Budesonide-Formoterol as Needed for Mild Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Canonica, G.W.; Maestrelli, P.; Paggiaro, P.; Olivieri, D.; Pozzi, E.; Crimi, N.; Vignola, A.M.; Morelli, P.; Nicolini, G.; et al. Rescue Use of Beclomethasone and Albuterol in a Single Inhaler for Mild Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2040–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelkonen, M.K.; Notkola, I.-L.K.; Laatikainen, T.; Jousilahti, P. 30-year trends in asthma and the trends in relation to hospitalization and mortality. Respir. Med. 2018, 142, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.; Fletcher, M.; van der Molen, T. Asthma control and management in 8000 European patients: The REcognise Asthma and LInk to Symptoms and Experience (REALISE) survey. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2014, 24, 14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Jenkins, C.; Bateman, E.D. The paradoxes of asthma management: Time for a new approach? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suissa, S.; Ernst, P.; Boivin, J.F.; Horwitz, R.I.; Habbick, B.; Cockroft, D.; Blais, L.; McNutt, M.; Buist, A.S.; Spitzer, W.O. A cohort analysis of excess mortality in asthma and the use of inhaled beta-agonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149 Pt 1, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suissa, S.; Ernst, P.; Benayoun, S.; Baltzan, M.; Cai, B. Low-Dose Inhaled Corticosteroids and the Prevention of Death from Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W.; Tan, W.C.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Ohlsson, S.V.; Ullman, A.; Lamm, C.J.; O’Byrne, P. Early intervention with budesonide in mild persistent asthma: A randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal College of Physicians. Why Asthma Still Kills: The National Review of Asthma Deaths (NRAD) Confidential Enquiry Report. Available online: https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/national-review-asthma-deaths (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- Reddel, H.K.; Ampon, R.D.; Sawyer, S.M.; Peters, M. Risks associated with managing asthma without a preventer: Urgent healthcare, poor asthma control and over-the-counter reliever use in a cross-sectional population survey. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Barnes, P.J.; Zhong, N.; Keen, C.; Jorup, C.; Lamarca, R.; Ivanov, S.; Reddel, H. Inhaled Combined Budesonide-Formoterol as Needed in Mild Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, E.D.; Reddel, H.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Zhong, N.; Keen, C.; Jorup, C.; Lamarca, R.; Siwek-Posluszna, A.; FitzGerald, J.M. As-Needed Budesonide-Formoterol versus Maintenance Budesonide in Mild Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Baggott, C.; Fingleton, J.; Reddel, H.; Hancox, R.J.; Harwood, M.; Corin, A.; Sparks, J.; Hall, D.; Sabbagh, D.; et al. Budesonide-formoterol reliever therapy versus maintenance budesonide plus terbutaline reliever therapy in adults with mild to moderate asthma (PRACTICAL): A 52-week, open-label, multicentre, superiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Pocket Guide for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2019. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/pocket-guide-for-asthma-management-and-prevention (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Reddel, H.K.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bacharier, L.B.; Becker, A.; Brusselle, G.; Buhl, R.; Cruz, A.A.; Fleming, L.; Inoue, H.; et al. GINA 2019: A fundamental change in asthma management: Treatment of asthma with short-acting bronchodilators alone is no longer recommended for adults and adolescents. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1901046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuprys-Lipinska, I.; Kolacinska-Flont, M.; Kuna, P. New approach to intermittent and mild asthma therapy: Evolution or revolution in the GINA guidelines? Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GINA. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2021. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GINA-Main-Report-2021-V2-WMS.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Christie, L.; Scadding, J.; Boyd, J. Controlled trial of effects of cortisone acetate in status asthmaticus. Report to the Medical Research Council by the subcommittee on clinical trials in asthma. Lancet 1956, 2, 803–806. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, E.K.; Drazen, J.M. Asthma: One hundred years of treatment and onward. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.J. Effect of beclomethasone dipropionate delivered by aerosol in patients with asthma. Lancet 1972, 1, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdin, A.; Adcock, I.; Berger, P.; Bonniaud, P.; Chanson, P.; Chenivesse, C.; de Blic, J.; Deschildre, A.; Devillier, P.; Devouassoux, G. How can we minimise the use of regular oral corticosteroids in asthma? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 190085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, H.B.; Saag, K.G. Glucocorticoid use in rheumatoid arthritis: Benefits, mechanisms, and risks. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22 (Suppl. 35), S77–S82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chang, S.-M.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Wu, A.C.; Huang, J.-L.; Tsai, H.-J. Association of Oral Corticosteroid Bursts with Severe Adverse Events in Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, A.A.; Duh, M.S.; Gozalo, L.; Robitaille, M.-N.; Albers, F.; Yancey, S.; Ortega, H.; Forshag, M.; Lin, X.; Lefebvre, P. Dose-Response Relationship Between Long-Term Systemic Corticosteroid Use and Related Complications in Patients with Severe Asthma. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2016, 22, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalitsios, C.V.; Shaw, D.E.; McKeever, T.M. Risk of osteoporosis and fragility fractures in asthma due to oral and inhaled corticosteroids: Two population-based nested case-control studies. Thorax 2021, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Efraij, K.; Johnson, K.M.; Wiebe, D.; Sadatsafavi, M.; FitzGerald, J.M. A systematic review of the adverse events and economic impact associated with oral corticosteroids in asthma. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.W.; Ghushchyan, V.H.; Globe, G.; Schatz, M. Oral corticosteroid exposure and adverse effects in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 110–116.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, D.B.; Trudo, F.; Voorham, J.; Xu, X.; Kerkhof, M.; Jie, J.L.Z.; Tran, T.N. Adverse outcomes from initiation of systemic corticosteroids for asthma: Long-term observational study. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, D.J.; Busby, J.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Brown, T.; Gore, R.; Doherty, M.; Mansur, A.H.; Message, S.; Niven, R.; et al. Characterisation of patients with severe asthma in the UK Severe Asthma Registry in the biologic era. Thorax 2021, 76, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Tran, T.N.; Heaney, L.G.; Jones, R.C.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Busby, J.; Jackson, D.J.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Rhee, C.K. Characterization of Severe Asthma Worldwide: Data from the International Severe Asthma Registry. Chest 2020, 157, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffler, E.; Blasi, F.; Latorre, M.; Menzella, F.; Paggiaro, P.; Pelaia, G.; Senna, G.; Canonica, G.W.; SANI Network. The Severe Asthma Network in Italy: Findings and Perspectives. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleich, F.; Brusselle, G.; Louis, R.; Vandenplas, O.; Michils, A.; Pilette, C.; Peche, R.; Manise, M.; Joos, G. Heterogeneity of phenotypes in severe asthmatics. The Belgian Severe Asthma Registry (BSAR). Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taube, C.; Bramlage, P.; Hofer, A.; Anderson, D. Prevalence of oral corticosteroid use in the German severe asthma population. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00092-2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.; Patterson, C.C.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Niven, R.M.; Mansur, A.H.; Bucknall, C.; Chaudhuri, R.; Price, D.; Brightling, C.E.; Heaney, L.G.; et al. Comorbidity in severe asthma requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy: Cross-sectional data from the Optimum Patient Care Research Database and the British Thoracic Difficult Asthma Registry. Thorax 2016, 71, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hew, M.; McDonald, V.M.; Bardin, P.G.; Chung, L.P.; Farah, C.S.; Barnard, A.; Cooper, M.S.; Gibson, P.G.; Upham, J.W. Cumulative dispensing of high oral corticosteroid doses for treating asthma in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 213, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, A.I.; Mplizou, M.; Porpodis, K.; Fouka, E.; Zervas, E.; Samitas, K.; Markatos, M.; Bakakos, P.; Papiris, S.; Gaga, M.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with allergic asthma: A real-life study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunstahl, G.J.; Chen, C.W.; Maykut, R.; Georgiou, P.; Peachey, G.; Bruceet, J. The eXpeRience registry: The ‘real-world’ effectiveness of omalizumab in allergic asthma. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siergiejko, Z.; Świebocka, E.; Smith, N.; Peckitt, C.; Leo, J.; Peachey, G.; Maykut, R. Oral corticosteroid sparing with omalizumab in severe allergic (IgE-mediated) asthma patients. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Pizzichini, M.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Inman, M.D.; Efthimiadis, A.; Pizzichini, E.; Hargreave, F.E.; O’Byrne, P. Mepolizumab for Prednisone-Dependent Asthma with Sputum Eosinophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel, E.H.; Wenzel, S.; Thompson, P.J.; Prazma, C.M.; Keene, O.; Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G.; Pavord, I.; SIRIUS Investigators. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Bourdin, A.; Lugogo, N.L.; Kuna, P.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Ponnarambil, S.; Goldman, M. Oral Glucocorticoid-Sparing Effect of Benralizumab in Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, K.F.; Nair, P.; Brusselle, G.; Maspero, J.F.; Castro, M.; Sher, L.; Zhu, H.; Hamilton, J.D.; Swanson, B.N.; Khan, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Glucocorticoid-Dependent Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, F.; Graff, S.; Nekoee, H.; Moermans, C.; Henket, M.; Sanchez, C.; Paulus, V.; Guissard, F.; Donneau, A.F.; Louis, R. Real-word experience with mepolizumab: Does it deliver what it has promised? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillé, C.; Chanez, P.; Devouassoux, G.; Didier, A.; Pison, C.; Garcia, G.; Charriot, J.; Bouée, S.; Gruber, A.; Pribil, C.; et al. Mepolizumab in a population with severe eosinophilic asthma and corticosteroid dependence: Results from a French early access programme. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Toor, J.J.; van der Mark, S.C.; Kappen, J.H.; In’t Veen, J.C.C.M.; Braunstahl, G.J. Mepolizumab add-on therapy in a real world cohort of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: Response rate, effectiveness, and safety. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Difficult-to-Treat and Severe Asthma in Adolescent and Adult Patients; A GINA Pocket Guide for Health Professionals; V2.0 April 2019; Global Initiative for Asthma: Fontana, WI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bel, E.H.; Maspero, J.; Heaney, L.G.; Gurnell, M.; Wessman, P.; Martin, U.J.; Siddiqui, S.; Gil, E.G. Corticosteroid tapering with benralizumab treatment for eosinophilic asthma: PONENTE Trial. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00009-2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Gurnell, M.; Heaney, L.; Corren, J.; Bel, E.; Maspero, J.; Harrison, T.; Jackson, D.; Price, D.; Lugogo, N.; et al. Elimination of Oral Corticosteroids (OCS) with Benralizumab Treatment in OCS-Dependent Asthmatics Using a Rapid, Personalized Algorithm: The PONENTE Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Szefler, S.J.; Reddel, H.K.; Chipps, B.E. Symptoms and perception of airway obstruction in asthmatic patients: Clinical implications for use of reliever medications. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Study | Comparators | Patients | Duration | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O’ Byrne PM et al. | Budesonide–Formoterol as needed vs. | 3849 | 52 weeks | Superior efficacy, reduced severe asthma exacerbations, and more weeks of well-controlled asthma in Budesonide–Formoterol group vs. Terbutaline group; with lower FEV1 and higher ACQ-5 score in Budesonide–Formoterol group vs. Budesonide group without important clinical significance |
| (SYGMA I study) | Terbutaline as needed vs. | |||
| Randomized, double-blind, phase III study, multicenter | Budesonide maintenance plus Terbutaline as needed | |||
| Bateman ED et al. | Budesonide–Formoterol as needed | 4215 | 52 weeks | Non-inferior results in reducing severe asthma exacerbations between the two groups; higher ACQ-5 score and lower FEV1 values (without important clinical significance) in Budesonide–Formoterol group vs. Budesonide group |
| (SYGMA II study) | vs. | |||
| Randomized, double-blind, phase III study, multicenter | Budesonide maintenance plus Terbutaline as needed | |||
| Beasley R et al. | Budesonide–Formoterol as needed vs. | 675 | 52 weeks | Lower asthma exacerbation rate in Budesonide–Formoterol group vs. Albuterol group; without important difference between Budesonide–Formoterol group and Budesonide group; ACQ-5 score better in Budesonide group |
| (NOVEL START study) | Albuterol (twice) as needed vs. | |||
| Randomized, open-label, parallel group study multicenter | Budesonide maintenance plus Albuterol (twice) as needed | |||
| Hardy et al. | Budesonide–Formoterol as needed | 890 | 52 weeks | Reduction in annual asthma exacerbation rate in Budesonide–Formoterol group vs. Budesonide group with increased time to first exacerbation appearance and same symptoms control |
| (PRACTICAL study) | vs. | |||
| Randomized, open-label, parallel group study, multicenter | Budesonide maintenance plus Terbutaline (twice) as needed |
| Study | Medication | Patients | Duration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bel et al. | Reduced oral corticosteroid dose (50%) and number of exacerbations (32%) | |||
| (SIRIUS study) | ||||
| Phase III | Mepolizumab | 135 | 20 weeks | |
| Nair et al. | Reduced oral corticosteroid dose (50%) and number of exacerbations (55%) | |||
| (ZONDA study) | ||||
| Phase III | Benralizumab | 220 | 28 weeks | |
| Rabe et al. | Reduced oral corticosteroid dose (50%), number of exacerbations (59%) and improved lung function (FEV1) | |||
| (VENTURE study) | ||||
| Phase III | Dupilumab | 210 | 24 weeks | |
| Schleich F et al. | Reduced dose of maintenance oral corticosteroids (50%) Reduced exacerbation rate (85%) | |||
| Real life | Mepolizumab | 116 | >18 months | |
| Taile C et al. | Reduced or stopped (58%) OCS dose | |||
| Real life | Mepolizumab | 146 | 24 months | |
| van Toor JJ et al. | Mepolizumab | 76 | 12 months | Reduced or stopped (36%) OCS |
| Real life | ||||
| Menzies Gow A et al. | Benralizumab | 598 | 52 weeks | Reduction (91%) or cessation (63%) of OCS Reduction in exacerbations |
| Open-label | ||||
| Single-arm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakakos, P.; Kostikas, K.; Loukides, S.; Makris, M.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Steiropoulos, P.; Tryfon, S.; Zervas, E. Reducing Tolerance for SABA and OCS towards the Extreme Ends of Asthma Severity. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030504
Bakakos P, Kostikas K, Loukides S, Makris M, Papadopoulos NG, Steiropoulos P, Tryfon S, Zervas E. Reducing Tolerance for SABA and OCS towards the Extreme Ends of Asthma Severity. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(3):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030504
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakakos, Petros, Konstantinos Kostikas, Stelios Loukides, Michael Makris, Nikolaos G. Papadopoulos, Paschalis Steiropoulos, Stavros Tryfon, and Eleftherios Zervas. 2022. "Reducing Tolerance for SABA and OCS towards the Extreme Ends of Asthma Severity" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 3: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030504
APA StyleBakakos, P., Kostikas, K., Loukides, S., Makris, M., Papadopoulos, N. G., Steiropoulos, P., Tryfon, S., & Zervas, E. (2022). Reducing Tolerance for SABA and OCS towards the Extreme Ends of Asthma Severity. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030504









