Predictive Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Lean Chinese Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Establishment and Evaluation of the Nomogram
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients
3.2. Selection of Predictive Factors
3.3. Development of Nomogram
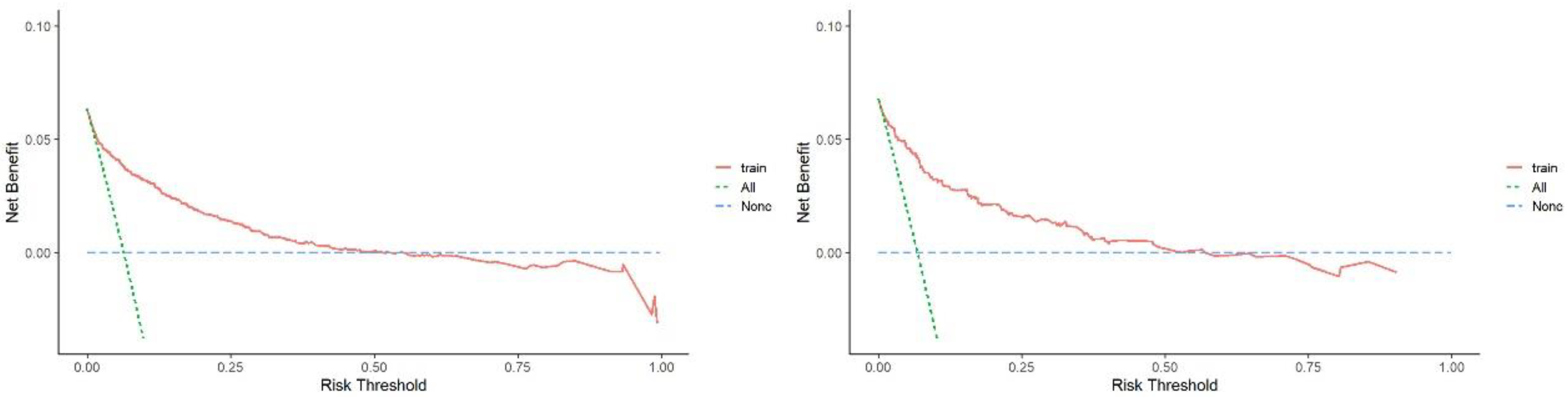
3.4. Evaluations of the Nomogram Performance
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouad, Y.; Waked, I.; Bollipo, S.; Gomaa, A.; Ajlouni, Y.; Attia, D. What’s in a name? Renaming ‘NAFLD’ to ‘MAFLD’. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diehl, A.M.; Day, C. Cause, Pathogenesis, and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariani, K.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Pathophysiology of NASH in endocrine diseases. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, R52–R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.T.; Kleiner, D.E. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalbantoglu, I.L.; Brunt, E.M. Role of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9026–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardullo, S.; Perseghin, G. Prevalence of elevated liver stiffness in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 190, 109981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardullo, S.; Monti, T.; Perseghin, G. High Prevalence of Advanced Liver Fibrosis Assessed by Transient Elastography among U.S. Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes. Care. 2021, 44, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Das, K.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Mridha, A.R.; Dhibar, T.; Bhattacharya, B.; Bhattacharya, D.; Manna, B.; et al. Nonobese population in a developing country has a high prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver and significant liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, R.; Govaere, O.; Petta, S.; Miele, L.; Tiniakos, D.; Burt, A.; David, E.; Vecchio, F.M.; Maggioni, M.; Cabibi, D.; et al. Caucasian lean subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease share long-term prognosis of non-lean: Time for reappraisal of BMI-driven approach? Gut 2022, 71, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niriella, M.A.; Kasturiratne, A.; Pathmeswaran, A.; De Silva, S.T.; Perera, K.R.; Subasinghe, S.; Kodisinghe, S.K.; Piyaratna, T.; Vithiya, K.; Dassanayaka, A.S.; et al. Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (lean NAFLD): Characteristics, metabolic outcomes and risk factors from a 7-year prospective, community cohort study from Sri Lanka. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.C.; Loong, T.C.; Wei, J.L.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, A.W.; Choi, P.C.; Shu, S.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Histological severity and clinical outcomes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese patients. Hepatology 2017, 65, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, M.H.; Yang, J.C.; Nien, C.K.; Yang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Yueh, S.K. Prevalence and risk factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in an adult population of taiwan: Metabolic significance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese adults. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.K.; Ahn, C.W.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, H.C.; Huh, K.B.; et al. Metabolic significance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese, nondiabetic adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, R.; Bugianesi, E. NASH in Lean Individuals. Semin. Liver. Dis. 2019, 39, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferraioli, G.; Soares Monteiro, L.B. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Kumar, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Rousson, V.; Lee, W.C.; Ferdynus, C.; Chen, M.; Qian, X.; Guo, Y. Decision curve analysis: A technical note. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A.J.; van Calster, B.; Steyerberg, E.W. A simple, step-by-step guide to interpreting decision curve analysis. Diagn. Progn. Res. 2019, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.T.; Noureddin, M.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update: Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Individuals: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 764–774.e761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertot, L.C.; Jeffrey, G.P.; Wallace, M.; MacQuillan, G.; Garas, G.; Ching, H.L.; Adams, L.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related cirrhosis is commonly unrecognized and associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Cholesterol metabolism and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2013, 52, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomita, K.; Teratani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sato, H.; Narimatsu, K.; Okada, Y.; Kurihara, C.; Irie, R.; Yokoyama, H.; et al. Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells: Mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Haigh, W.G.; Thorning, D.; Savard, C. Hepatic cholesterol crystals and crown-like structures distinguish NASH from simple steatosis. J. Lipid. Res. 2013, 54, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vendhan, R.; Amutha, A.; Anjana, R.M.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Deepa, M.; Mohan, V. Comparison of characteristics between nonobese and overweight/obese subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a South Indian population. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Cantero, J.; Martin-Rodriguez, J.L.; Gonzalez-Cantero, A.; Arrebola, J.P.; Gonzalez-Calvin, J.L. Insulin resistance in lean and overweight non-diabetic Caucasian adults: Study of its relationship with liver triglyceride content, waist circumference and BMI. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsuhaibani, K.A.; Althunayyan, F.S.; Alsudays, A.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Aljarallah, B.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean and obese patients in Saudi patients from a single center. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2021, 10, 3381–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuz, U.; Yesil, A.; Yilmaz, Y. Characterization of lean patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential role of high hemoglobin levels. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ren, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; Wu, G.; Yang, F.; Yuan, S.; Fang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Lean-NAFLD) and the development of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xin, Y. Proportion of NAFLD patients with normal ALT value in overall NAFLD patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Jensen, D.; Hart, J.; Mohanty, S.R. Predictive value of ALT levels for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Liver. Int. 2013, 33, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, I.; Bashmakov, Y.; Ikemoto, S.; Horton, J.D.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Insulin selectively increases SREBP-1c mRNA in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13656–13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, H.; Takenoshita, M.; Sakurai, M.; Bruick, R.K.; Henzel, W.J.; Shillinglaw, W.; Arnot, D.; Uyeda, K. A glucose-responsive transcription factor that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9116–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoeckman, A.K.; Towle, H.C. The role of SREBP-1c in nutritional regulation of lipogenic enzyme gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27029–27035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foretz, M.; Guichard, C.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12737–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.I.; Shankaran, M.; Yoshino, M.; Schweitzer, G.G.; Chondronikola, M.; Beals, J.W.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; Nyangau, E.; Field, T.; et al. Insulin resistance drives hepatic de novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest 2020, 130, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Martínez-Montoro, J.I.; Choudhary, N.S.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Ramos-Molina, B. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean and Non-Obese Individuals: Current and Future Challenges. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cicerchi, C.; Kanbay, M.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Li, N.; Marek, G.; Duranay, M.; et al. Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: Potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40732–40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Xu, C.; Lin, Y.; Lu, C.; Li, D.; Sang, J.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, C. Uric acid regulates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through the NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent mechanism. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, T.; Oshida, N.; Suzuki, H.; Okada, K.; Watahiki, T.; Oh, S.; Kim, T.; Isobe, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ariizumi, S.I.; et al. Clinical and anthropometric characteristics of non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease subjects in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobari, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Taniai, M.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kodama, K.; Kogiso, T.; Tokushige, K.; Takayoshi, N.; Hashimoto, N. Characteristics of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis among lean patients in Japan: Not uncommon and not always benign. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, I.; Mets, T.; Bautmans, I. Chronic low-grade inflammation and age-related sarcopenia. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2012, 15, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatecola, A.M.; Paolisso, G.; Fattoretti, P.; Evans, W.J.; Fiore, V.; Dicioccio, L.; Lattanzio, F. Discovering pathways of sarcopenia in older adults: A role for insulin resistance on mitochondria dysfunction. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2011, 15, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.C.; Hwang, S.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; Choi, K.M. Relationship between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Perseghin, G. Statin use is associated with lower prevalence of advanced liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2021, 121, 154752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
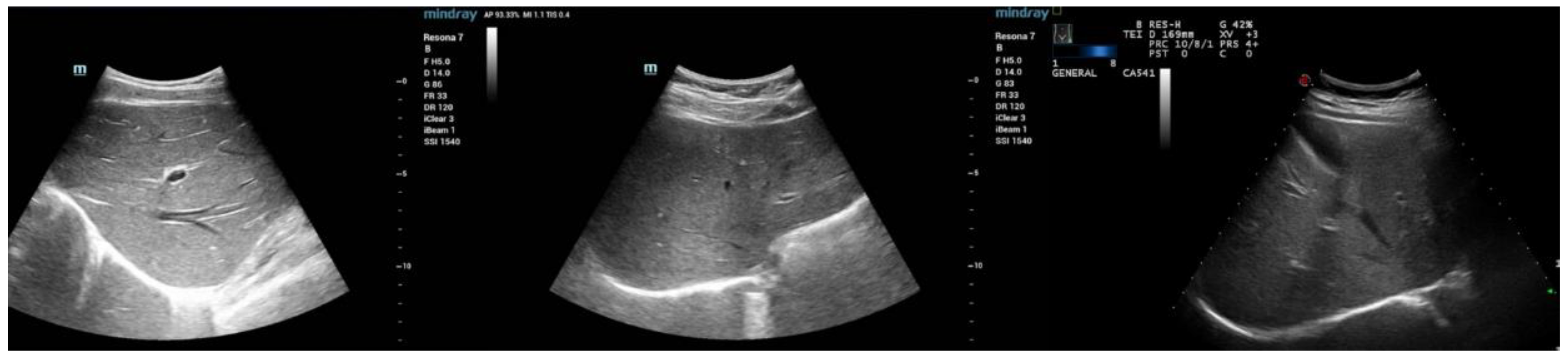




| Variables | Training Dataset (n = 4068) | Validation Dataset (n = 969) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Non-NAFLD | NAFLD | p-Value | Non-NAFLD | NAFLD | p-Value | |
| Sex (%) | Male | 2714 (71.2) | 104 (40.3) | <0.001 | 632 (70.0) | 33 (50.0) | <0.001 |
| Female | 1096 (28.8) | 154 (59.7) | 271 (30.0) | 33 (50.0) | |||
| Age (Years) (mean (SD)) | 40.00 (13.00) | 48.00 (13.00) | <0.001 | 40.00 (12.00) | 48.00 (13.00) | <0.001 | |
| SBP (mmHg) (mean (SD)) | 119.00 (16.00) | 128.00 (19.00) | <0.001 | 119.00 (16.00) | 126.00 (14.00) | <0.001 | |
| DBP (mmHg) (mean (SD)) | 72.00 (10.00) | 77.00 (10.00) | <0.001 | 72.00 (10.00) | 77.00 (8.00) | <0.001 | |
| Urea (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 4.80 (1.31) | 5.01 (1.19) | 0.012 | 4.79 (1.24) | 4.88 (1.11) | <0.001 | |
| Cr (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 59.17 (17.05) | 63.68 (14.08) | <0.001 | 59.05 (20.90) | 62.00 (12.03) | <0.001 | |
| UA (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 300.40 (71.74) | 366.35 (76.41) | <0.001 | 299.82 (71.51) | 347.69 (72.24) | <0.001 | |
| TP (g/L) (mean (SD)) | 72.26 (3.57) | 73.48 (3.64) | <0.001 | 72.40 (3.55) | 73.68 (3.56) | 0.003 | |
| Albumin (g/L) (mean (SD)) | 45.16 (2.39) | 45.55 (2.59) | 0.012 | 45.26 (2.46) | 45.59 (2.25) | 0.279 | |
| TB (μmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 15.17 (5.76) | 15.08 (5.28) | 0.811 | 15.11 (5.86) | 14.10 (5.26) | 0.151 | |
| DiB (μmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 4.26 (1.72) | 4.15 (1.60) | 0.296 | 4.24 (1.77) | 3.75 (1.38) | 0.02 | |
| IndiB (μmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 10.90 (4.22) | 10.93 (3.90) | 0.921 | 10.87 (4.33) | 10.35 (4.03) | 0.32 | |
| ALT (U/L) (mean (SD)) | 14.53 (9.58) | 26.10 (20.39) | <0.001 | 15.24 (23.46) | 24.13 (12.06) | 0.001 | |
| AST (U/L) (mean (SD)) | 19.17 (6.12) | 22.62 (8.58) | <0.001 | 19.49 (13.06) | 21.28 (5.59) | 0.247 | |
| GGT (U/L) (mean (SD)) | 16.46 (17.28) | 35.15 (52.91) | <0.001 | 17.45 (34.62) | 34.63 (24.76) | <0.001 | |
| ALP (U/L) (mean (SD)) | 56.87 (18.01) | 69.51 (19.55) | <0.001 | 57.07 (19.94) | 68.12 (16.70) | <0.001 | |
| TCh (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 4.75 (0.84) | 5.01 (0.88) | <0.001 | 4.77 (0.87) | 5.03 (0.89) | 0.017 | |
| TG (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 1.03 (0.57) | 1.91 (1.28) | <0.001 | 1.04 (0.54) | 1.93 (0.88) | <0.001 | |
| HDL (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 1.52 (0.35) | 1.23 (0.28) | <0.001 | 1.50 (0.35) | 1.24 (0.26) | <0.001 | |
| LDL (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 2.74 (0.76) | 3.08 (0.81) | <0.001 | 2.78 (0.78) | 3.10 (0.82) | 0.001 | |
| WBC (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 5.72 (1.37) | 6.36 (1.50) | <0.001 | 5.73 (1.38) | 6.53 (1.27) | <0.001 | |
| RBC (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 4.57 (0.44) | 4.86 (0.46) | <0.001 | 4.56 (0.44) | 4.93 (0.45) | <0.001 | |
| PLT (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 231.55 (55.65) | 241.08 (61.24) | 0.009 | 233.15 (53.29) | 240.47 (61.14) | 0.262 | |
| L (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 1.98 (0.54) | 2.12 (0.63) | <0.001 | 2.00 (0.56) | 2.22 (0.53) | 0.002 | |
| M (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 0.38 (0.12) | 0.43 (0.13) | <0.001 | 0.38 (0.12) | 0.43 (0.13) | 0.002 | |
| N (×109/L) (mean (SD)) | 3.20 (1.04) | 3.62 (1.14) | <0.001 | 3.19 (1.06) | 3.69 (0.97) | <0.001 | |
| glucose (mmol/L) (mean (SD)) | 5.04 (0.69) | 5.74 (1.66) | <0.001 | 5.04 (0.68) | 5.62 (1.32) | <0.001 | |
| HbA1C (mg/dL) (mean (SD)) | 5.58 (0.47) | 6.04 (0.91) | <0.001 | 5.58 (0.48) | 5.99 (0.67) | <0.001 | |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR [95% CI] | p Value | OR [95% CI] | p Value | |
| Age (Years) | 1.037 [1.029, 1.044] | <0.001 | 1.039 [1.025, 1.052] | 0.000 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 3.341 [2.659, 4.208] | <0.001 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | 1.028 [1.022, 1.034] | <0.001 | 0.999 [.0987, 1.011] | 0.852 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 1.050 [1.038, 1.060] | <0.001 | 1.013 [.0995, 1.031] | 0.164 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 1.097 [1.017, 1.178] | <0.001 | 0.911 [0.807, 1.029] | 0.134 |
| Cr (mmol/L) | 1.006 [1.002, 1.011] | <0.001 | 0.975 [0.962, 0.988] | 0.000 |
| UA (mmol/L) | 1.010 [1.008, 1.011] | <0.001 | 1.007 [1.004, 1.009] | 0.000 |
| TP (g/L) | 1.099 [1.065, 1.134] | <0.001 | 1.025 [0.980, 1.073] | 0.281 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 1.067 [1.018, 1,118] | <0.001 | 1.049 [0.977, 1.127] | 0.187 |
| DiB (μmol/L) | 0.929 [0.864, 0.996] | <0.001 | 0.994 [0.907, 1.089] | 0.902 |
| ALT (U/L) | 1.037 [1.030, 1.045] | <0.001 | 1.056 [1.038, 1.074] | 0.000 |
| AST (U/L) | 1.032 [1.018, 1.046] | <0.001 | 0.923 [0.895, 0.951] | 0.000 |
| GGT (U/L) | 1.019 [1.015, 1.023] | <0.001 | 1.003 [0.997, 1.009] | 0.341 |
| ALP (U/L) | 1.025 [1.020, 1.030] | <0.001 | 1.004 [0.998, 1.011] | 0.214 |
| TCh (mmol/L) | 1.376 [1.219, 1.549] | <0.001 | 0.309 [0.175, 0.545] | 0.000 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.413 [2.963, 3.946] | <0.001 | 2.670 [2.027, 3.516] | 0.000 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.043 [0.028, 0.068] | <0.001 | 0.774 [0.344, 1.739] | 0.535 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 1.632 [1.435, 1.854] | <0.001 | 3.484 [2.051, 5.918] | 0.000 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 1.357 [1.263, 1.458] | <0.001 | 0.005 [0.000, 16.971] | 0.199 |
| RBC (×109/L) | 4.108 [3.242, 5.214] | <0.001 | 1.821 [1.163, 2.849] | 0.009 |
| PLT (×109/L) | 1.003 [1.001, 1.004] | <0.001 | 1.004 [1.002, 1.007] | 0.000 |
| L (×109/L) | 1.579 [1.316, 1.891] | <0.001 | 23.829 [0.062, 92.046] | 0.194 |
| M (×109/L) | 14.358 [6.467, 41.533] | <0.001 | 12.613 [0.028, 56.740] | 0.260 |
| N (×109/L) | 1.396 [1.273, 1.527] | <0.001 | 23.973 [0.063, 91,755] | 0.193 |
| glucose (mmol/L) | 1.786 [1.611, 1.986] | <0.001 | 1.067 [0.890, 1.279] | 0.484 |
| HbA1C (mg/dL) | 2.477 [2.110, 2.927] | <0.001 | 1.428 [1.096, 1.861] | 0.008 |
| TB (μmol/L) | 0.991 [0.970, 1.010] | 0.373 | - | - |
| IndiB (μmol/L) | 0.995 [0.967, 1.021] | 0.700 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Shi, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, X. Predictive Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Lean Chinese Population. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121958
Liu L, Shi X, Gao J, Xu C, Liu X. Predictive Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Lean Chinese Population. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121958
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Xiaolan Shi, Jingwen Gao, Chunfang Xu, and Xiaolin Liu. 2022. "Predictive Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Lean Chinese Population" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121958
APA StyleLiu, L., Shi, X., Gao, J., Xu, C., & Liu, X. (2022). Predictive Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Lean Chinese Population. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121958






