RETRACTED: Brevilin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis and Reduces Th17 Differentiation in Psoriasis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
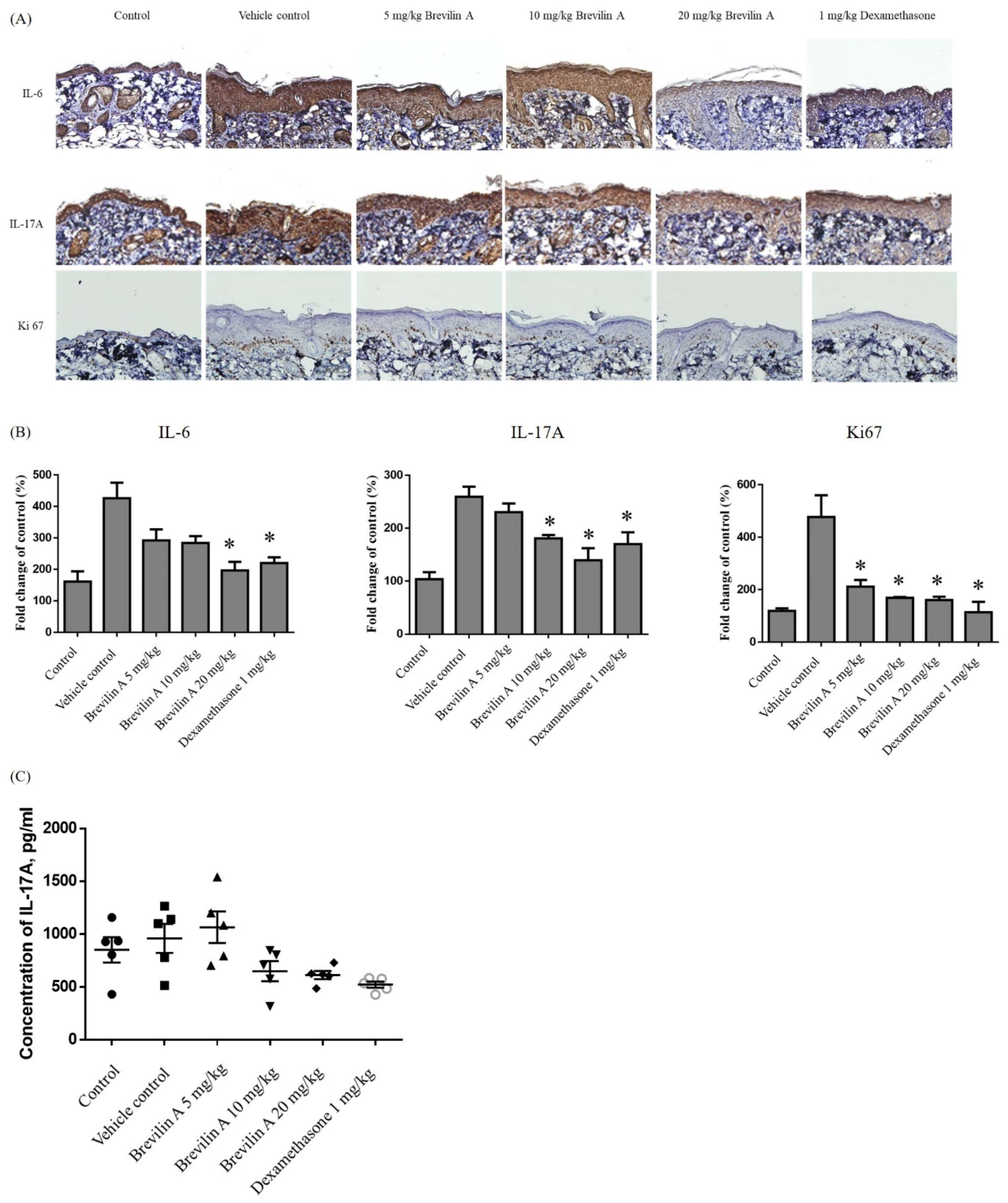
3.1. Brevilin A Ameliorated IMQ-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis
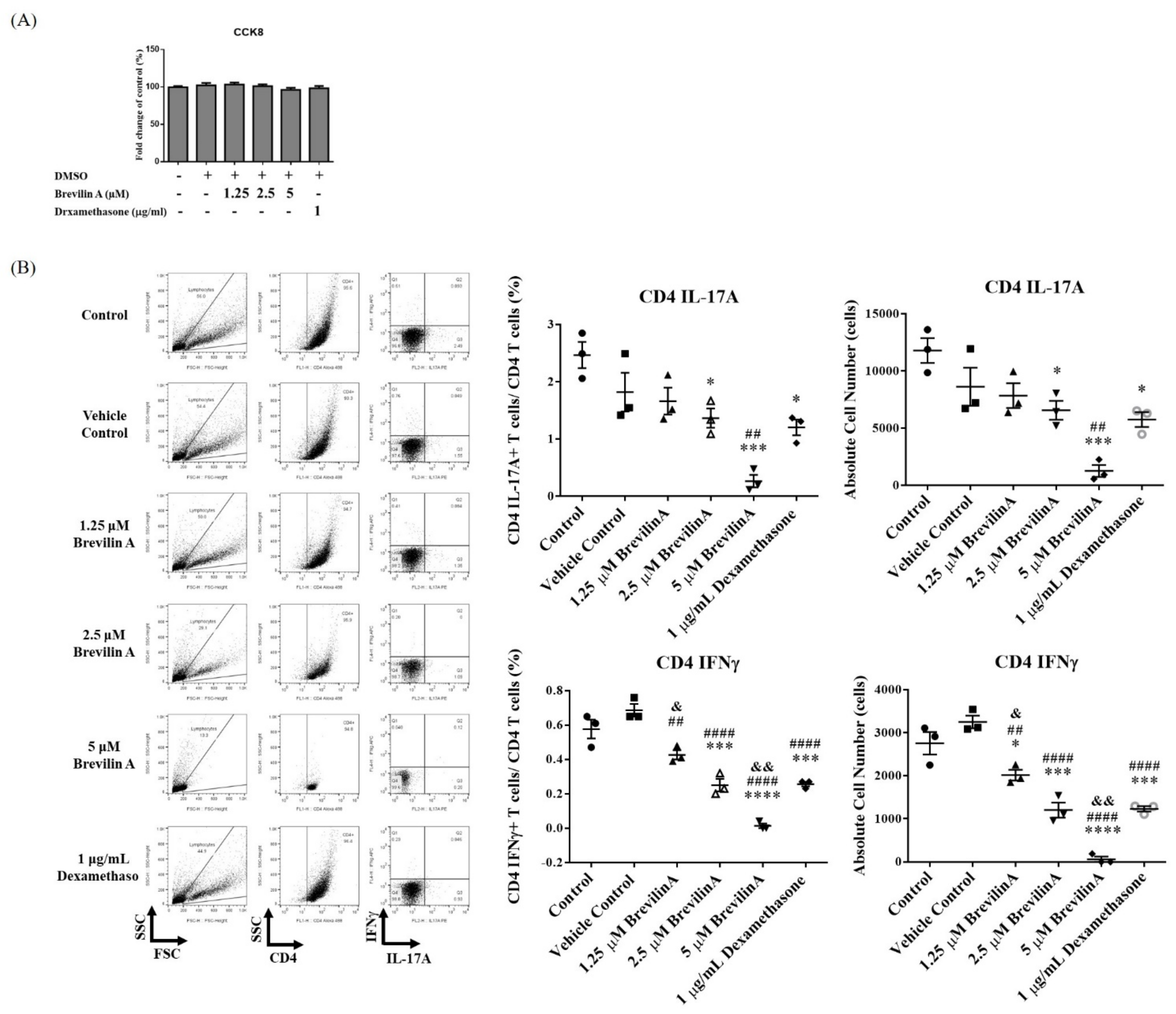
3.2. Brevilin A Could Inhibit Th17 Cell Differentiation
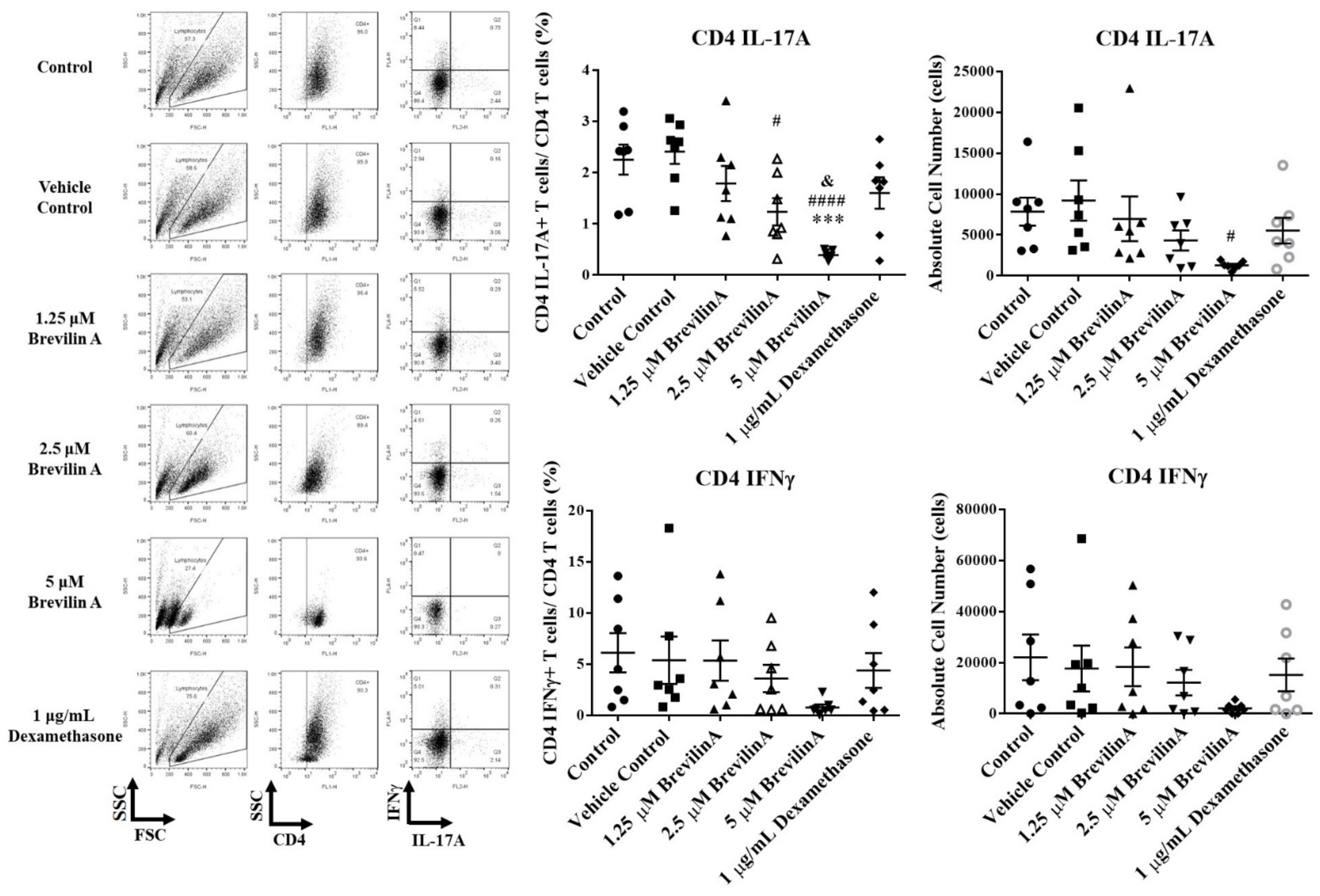
3.3. Effects of Brevilin A on PBMCs Isolated from Psoriasis Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.; Griffiths, C.E.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickoloff, B.J.; Wrone-Smith, T. Injection of pre-psoriatic skin with CD4+ T cells induces psoriasis. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Yan, B.Y.; Chan, T.C.; Krueger, J.G. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 Signaling Pathway and the Treatment of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.G.; Brunner, P.M. Interleukin-17 alters the biology of many cell types involved in the genesis of psoriasis, systemic inflammation and associated comorbidities. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, S.; Narang, T.; Joshi, N.; Goel, S.; Sawatkar, G.; Saikia, B.; Dogra, S.; Bansal, F.; Minz, R. Circulating T-helper 17 cells and associated cytokines in psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Derm. 2016, 41, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.I.; McKenzie, B.S.; Zhou, L.; Tadokoro, C.E.; Lepelley, A.; Lafaille, J.J.; Cua, D.J.; Littman, D.R. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 2006, 126, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Bao, F.; Dong, X.; Tan, R.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, Y. Antibacterial thymol derivatives isolated from Centipeda minima. Molecules 2007, 12, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.O.; Jin, D.P.; Dong, N.P.; Chen, S.B.; Mok, D.K. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of chemical constituents of Centipeda minima by HPLC-QTOF-MS & HPLC-DAD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.; Wu, H.; Deng, M.; Peng, J.; Li, F.; Yang, Y. Brevilin A induces apoptosis and autophagy of colon adenocarcinoma cell CT26 via mitochondrial pathway and PI3K/AKT/mTOR inactivation. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 98, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Chiu, C.S.; Lin, T.H.; Lee, M.M.; Lee, C.Y.; Chang, S.J.; Hou, W.C.; Huang, G.J.; Deng, J.S. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract of Centipeda minima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghantous, A.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Vuorela, H.; Saliba, N.A.; Darwiche, N. What made sesquiterpene lactones reach cancer clinical trials? Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Nan, J.; Zhang, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J. Brevilin A, a novel natural product, inhibits janus kinase activity and blocks STAT3 signaling in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, C.L.; Yen, L.J.; Lu, L.Y.; Huang, H.S.; Liao, E.C.; Yu, S.J. Forsythoside A Alleviates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice by Regulating Th17 Cells and IL-17A Expression. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Yang, L.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, C. Brevilin A, a Sesquiterpene Lactone, Inhibits the Replication of Influenza A Virus In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2019, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Mok, D.K.; Bian, Q.; Tai, W.C.; Chen, S. Brevilin A, a Natural Sesquiterpene Lactone Inhibited the Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via Akt/mTOR and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5363–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Jeon, M.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, T.S.; Chung, K.H.; Kim, K.H. Anti-fibrotic effects of brevilin A in hepatic fibrosis via inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 41, 127989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Sung, C.T.; Fang, J.Y. Murine models of psoriasis and their usefulness for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Yang, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Kao, H.C.; Fang, J.Y. Using Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin as a Model to Measure the Skin Penetration of Anti-Psoriatic Drugs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhorst, D.; Chelbi, R.; Wohn, C.; Malosse, C.; Tamoutounour, S.; Jorquera, A.; Bajenoff, M.; Dalod, M.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S. Dynamics and Transcriptomics of Skin Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in an Imiquimod-Induced, Biphasic Mouse Model of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4953–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Ogawa, E.; Okuyama, R. Role of Innate Immune Cells in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schon, M.P. Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, N.; Narisawa, Y.; Imafuku, S.; Ito, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Miyagi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Fukamatsu, H.; Morizane, S.; Koketsu, H.; et al. Cross-sectional multicenter observational study of psoriatic arthritis in Japanese patients: Relationship between skin and joint symptoms and results of treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. J. Derm. 2019, 46, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yao, Q.; Mariscal, A.G.; Wu, X.; Hülse, J.; Pedersen, E.; Helin, K.; Waisman, A.; Vinkel, C.; Thomsen, S.F.; et al. Epigenetic control of IL-23 expression in keratinocytes is important for chronic skin inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.; Chang, S.H.; Martinez, G.J.; Yang, X.O.; Nurieva, R.; Kang, H.S.; Ma, L.; Watowich, S.S.; Jetten, A.M.; Tian, Q.; et al. Critical regulation of early Th17 cell differentiation by interleukin-1 signaling. Immunity 2009, 30, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ivanov, I.I.; Spolski, R.; Min, R.; Shenderov, K.; Egawa, T.; Levy, D.E.; Leonard, W.J.; Littman, D.R. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.O.; Panopoulos, A.D.; Nurieva, R.; Chang, S.H.; Wang, D.; Watowich, S.S.; Dong, C. STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9358–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, M.; Ogura, H.; Ueda, N.; Tsuruoka, M.; Kitabayashi, C.; Tsuji, F.; Aono, H.; Ishihara, K.; Huseby, E.; Betz, U.A.; et al. IL-6-gp130-STAT3 in T cells directs the development of IL-17+ Th with a minimum effect on that of Treg in the steady state. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, L.-J.; Yen, C.-Y.; Li, C.-L.; Liao, E.-C.; Wang, K.-C.; Shih, M.-C.; Huang, H.-S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lu, L.-Y.; Yu, S.-J. RETRACTED: Brevilin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis and Reduces Th17 Differentiation in Psoriasis Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111888
Yen L-J, Yen C-Y, Li C-L, Liao E-C, Wang K-C, Shih M-C, Huang H-S, Chen Y-C, Lu L-Y, Yu S-J. RETRACTED: Brevilin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis and Reduces Th17 Differentiation in Psoriasis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111888
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Ling-Jung, Chung-Yang Yen, Chia-Ling Li, En-Chih Liao, Kai-Chun Wang, Meng-Chieh Shih, Hung-Sen Huang, Ying-Chin Chen, Ling-Ying Lu, and Sheng-Jie Yu. 2022. "RETRACTED: Brevilin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis and Reduces Th17 Differentiation in Psoriasis Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111888
APA StyleYen, L.-J., Yen, C.-Y., Li, C.-L., Liao, E.-C., Wang, K.-C., Shih, M.-C., Huang, H.-S., Chen, Y.-C., Lu, L.-Y., & Yu, S.-J. (2022). RETRACTED: Brevilin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis and Reduces Th17 Differentiation in Psoriasis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111888






