Outcomes of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Identification and Selection Criteria
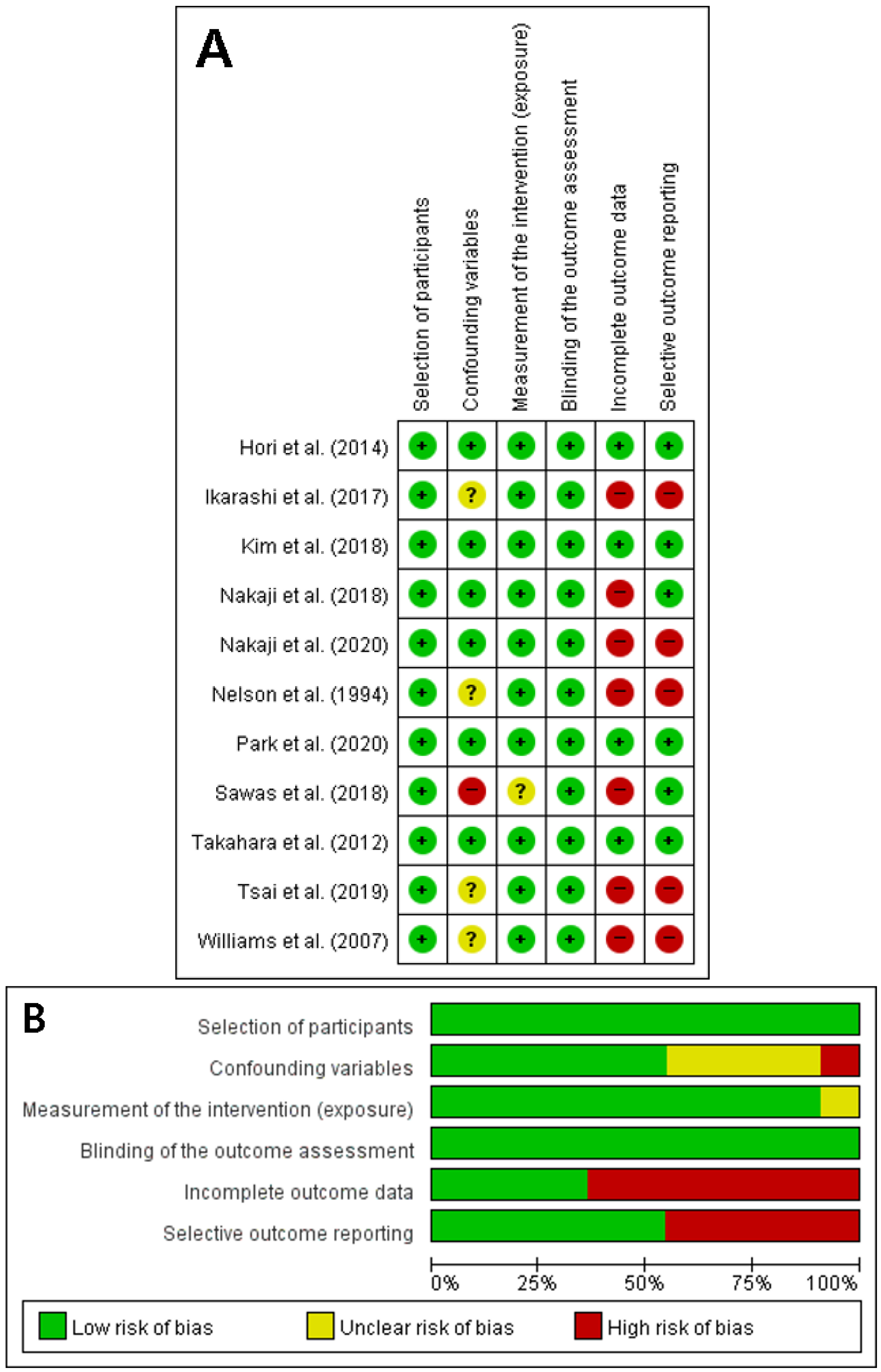
2.2. Study Selection, Quality Assessment, and Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
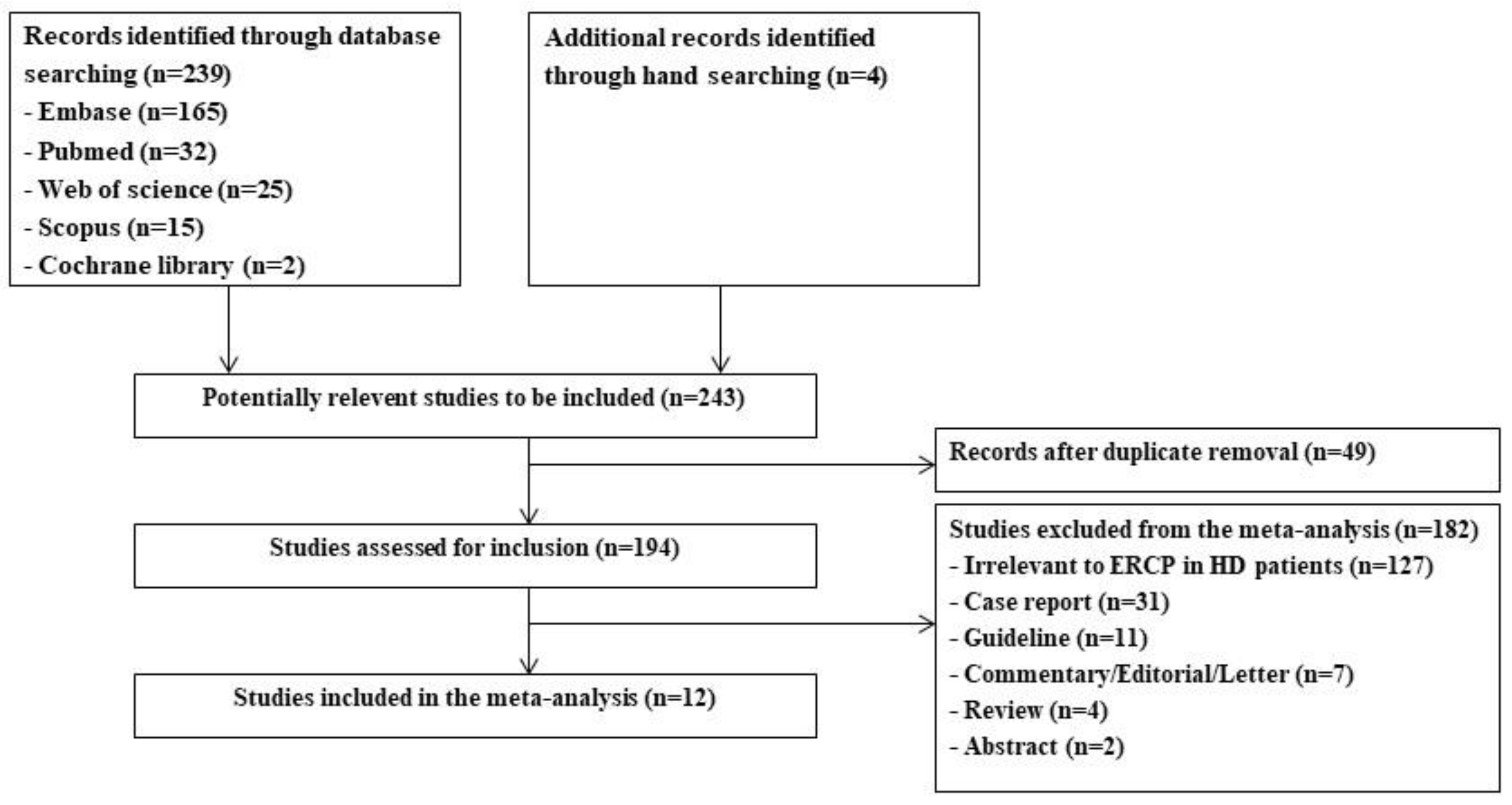
3.1. Identification of Relevant Studies
3.2. Characteristics of the Enrolled Publications
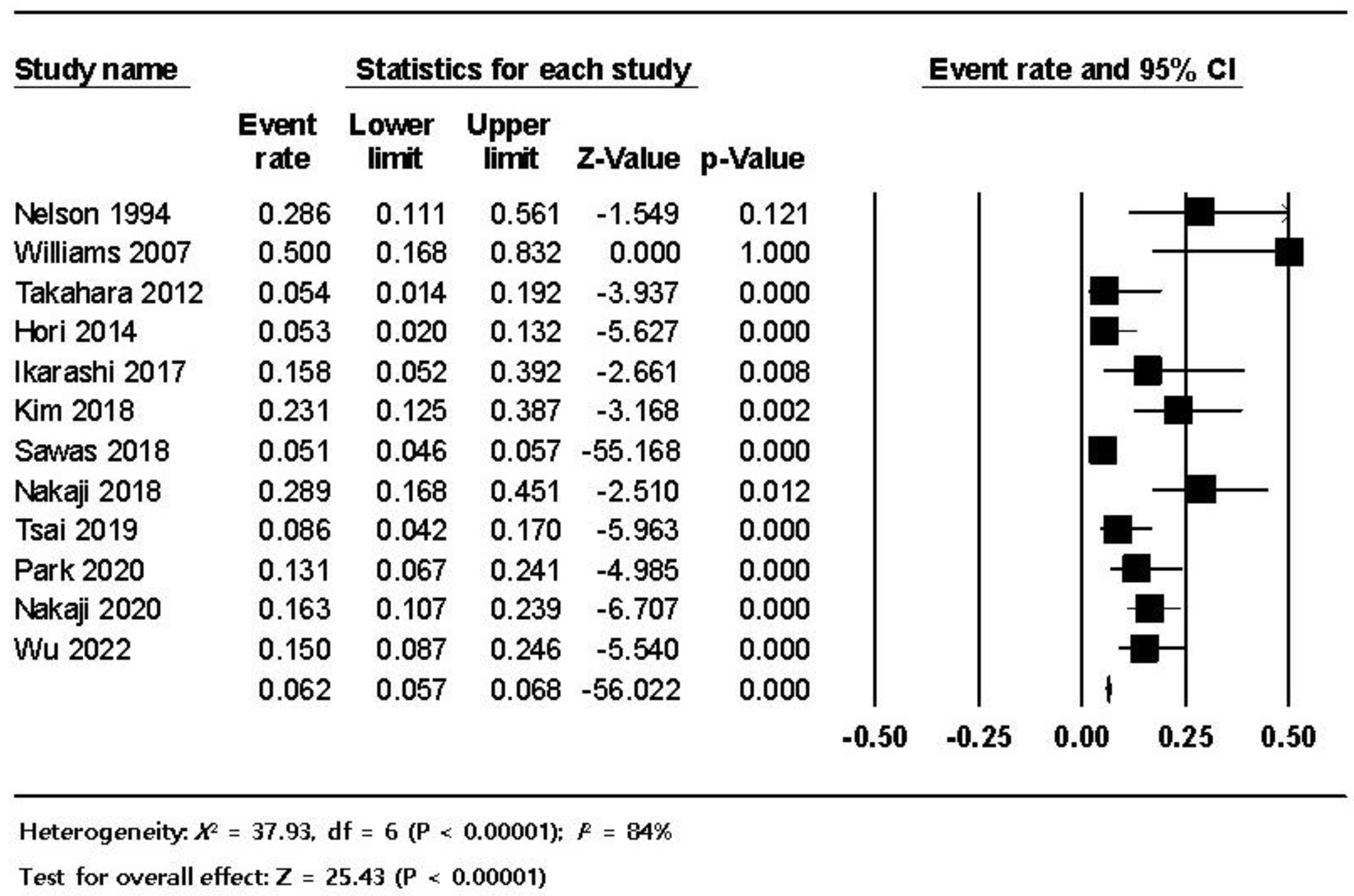
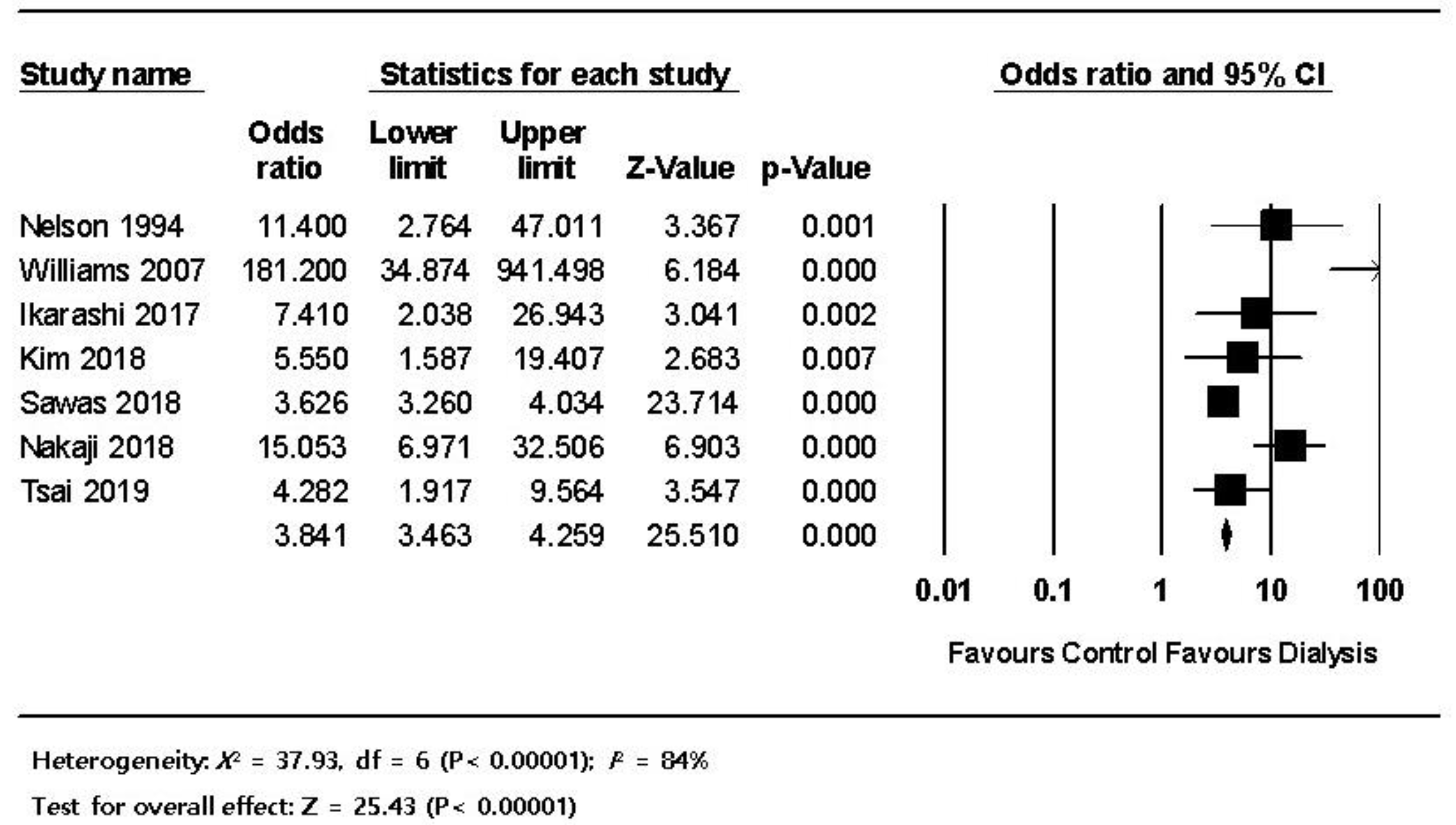
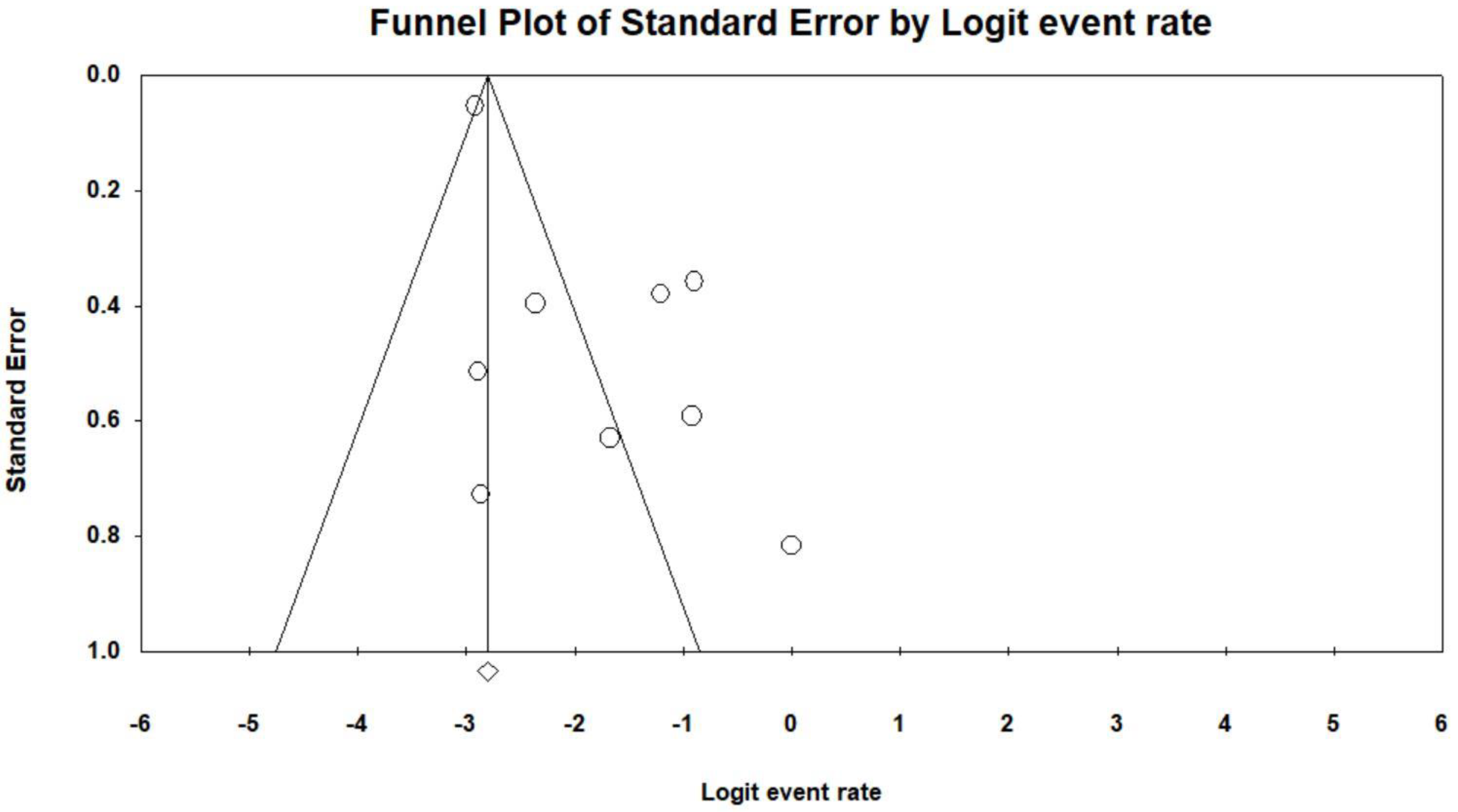
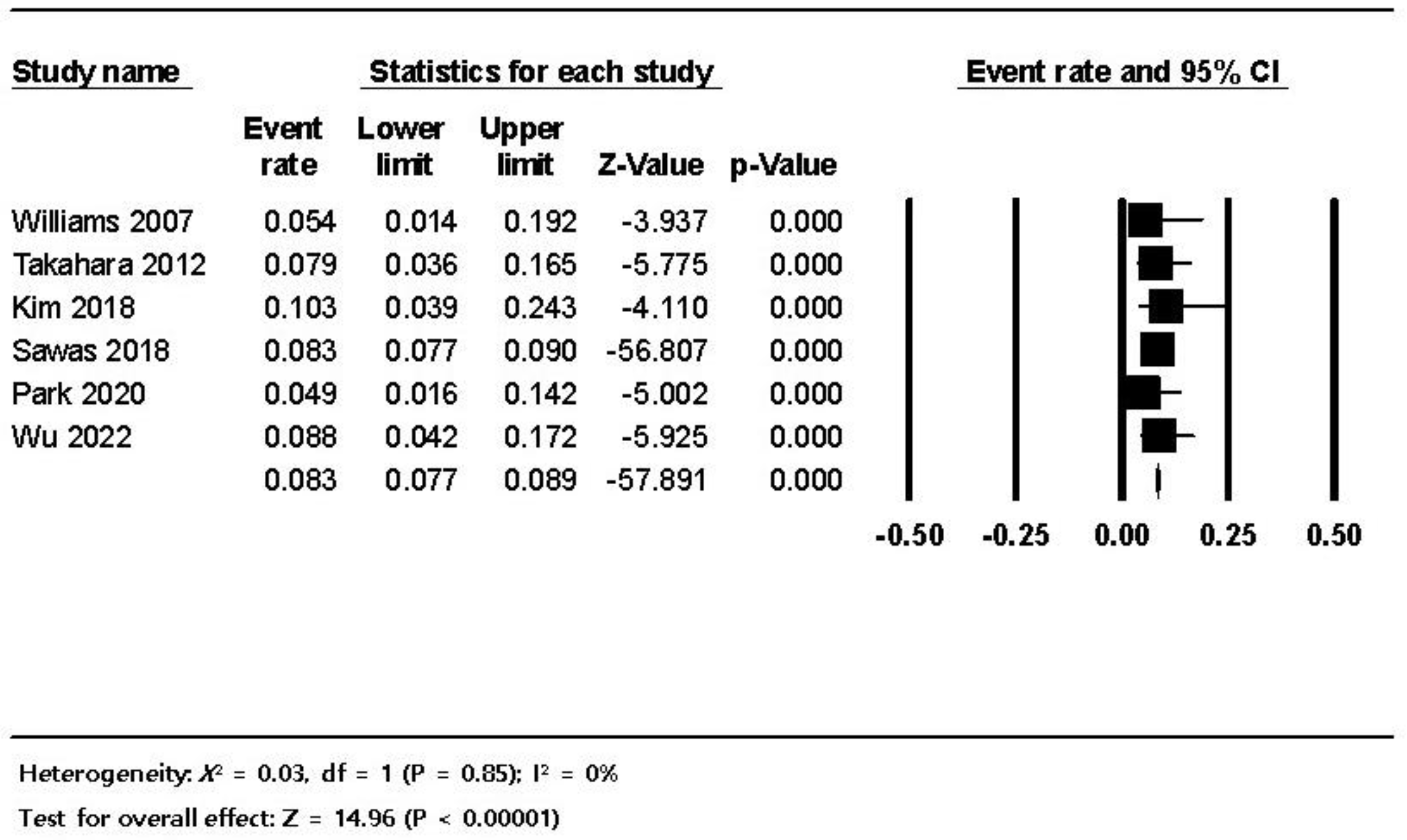
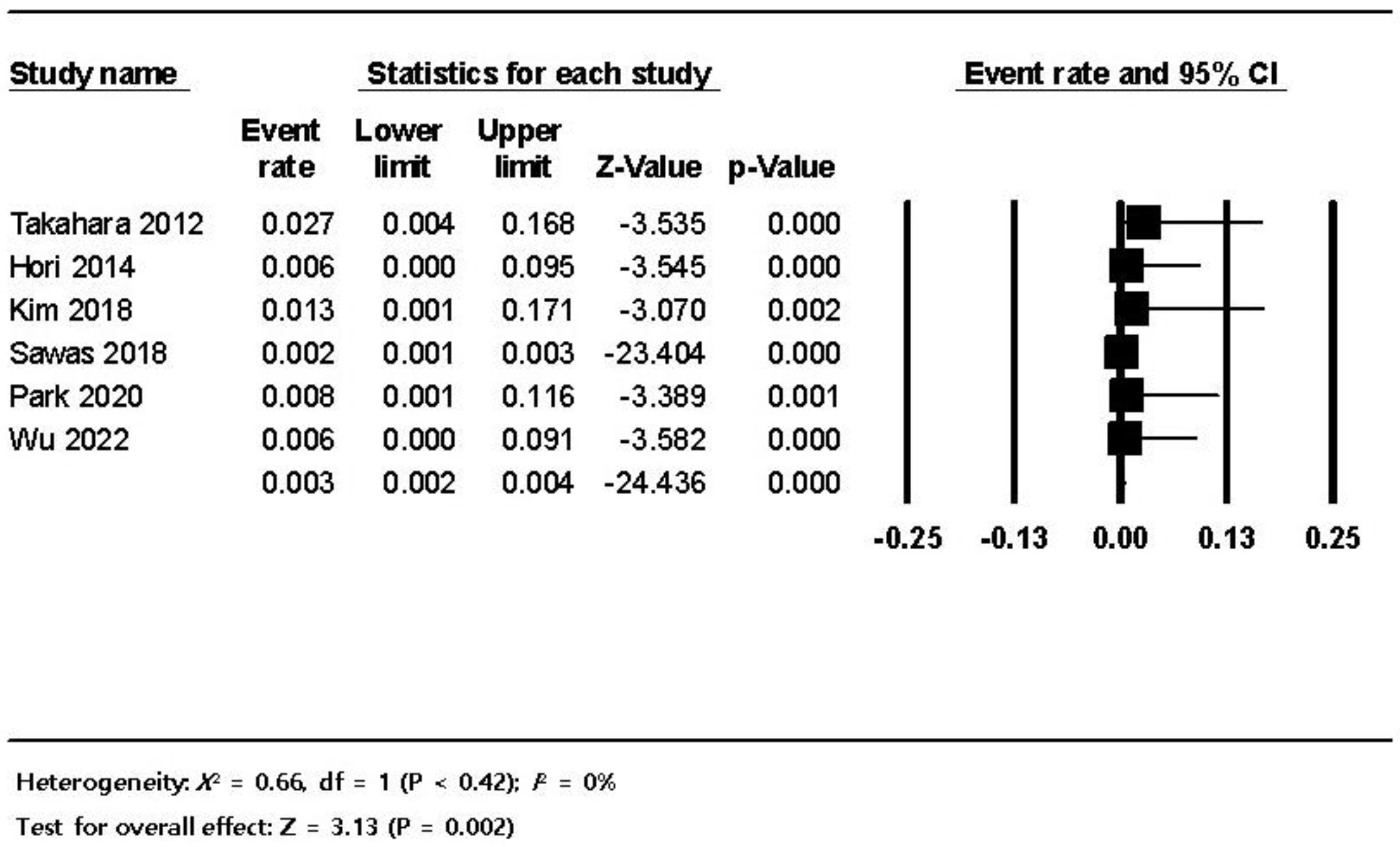
3.3. Pooled Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahm, J.S.; Lee, H.L.; Park, J.Y.; Eun, C.S.; Han, D.S.; Choi, H.S. Prevalence of gallstone disease in patients with end-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis in Korea. Hepatogastroenterology 2003, 50, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar]
- Badalamenti, S.; DeFazio, C.; Castelnovo, C.; SanGiovanni, A.; Como, G.; De Vecchi, A.; Graziani, G.; Colombo, M.; Ponticelli, C. High Prevalence of Silent Gallstone Disease in Dialysis Patients. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 1994, 66, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazama, J.J.; Kazama, S.; Koda, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Narita, I.; Gejyo, F. The Risk of Gallbladder Stone Formation Is Increased in Patients with Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease but Not Those Undergoing Chronic Hemodialysis Therapy. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 111, c167–c172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naitoh, I.; Hori, Y. Post-ERCP Complications in Dialysis Patients: Cutting One’s Losses or Expanding Possibilities? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2826–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, P.; Lehman, G.; Vennes, J.; Geenen, J.; Russell, R.; Meyers, W.; Liguory, C.; Nickl, N. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: An attempt at consensus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1991, 37, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.B.; Garrow, D.A.; Gallagher, J.; Romagnuolo, J. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: A multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabovic, M.; Salobir, B.; Zupan, I.P.; Bratina, P.; Bojec, V.; Ponikvar, J.B. The Influence of the Haemodialysis Procedure on Platelets, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberst, M.E.; Berkowitz, L.R. Hemostasis in renal disease: Pathophysiology and management. Am. J. Med. 1994, 96, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, G.R.; Cornette, G.L.; Clouse, R.E.; Harter, H.R. Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 102, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawas, T.; Bazerbachi, F.; Haffar, S.; Cho, W.K.; Levy, M.J.; A Martin, J.; Petersen, B.T.; Topazian, M.D.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K. End-stage renal disease is associated with increased post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography adverse events in hospitalized patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4691–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.J.; Sheen, S.S.; Hahn, S.; Jang, B.H.; Son, H.J. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.J.A.K.; Jones, D.R.; Sheldon, T.A.; Song, F. Methods for Meta-Analysis in Medical Research; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating Characteristics of a Rank Correlation Test for Publication Bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.G.S. Cochrane Handbook for Systemic Reviews of Interventions; Version 5.1.0; The Cochrane Collaboration: Chichester, UK, 2011; p. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.B.; Freeman, M.L. Major Hemorrhage from Endoscopic Sphincterotomy: Risk Factor Analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1994, 19, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Taylor, S.; Fairclough, P.; Hamlyn, A.; Logan, R.; Martin, D.; Riley, S.; Veitch, P.; Wilkinson, M.; Williamson, P.; et al. Risk factors for complication following ERCP; results of a large-scale, prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, N.; Isayama, H.; Sasaki, T.; Tsujino, T.; Toda, N.; Sasahira, N.; Mizuno, S.; Kawakubo, K.; Kogure, H.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation for bile duct stones in patients on hemodialysis. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Naitoh, I.; Nakazawa, T.; Hayashi, K.; Miyabe, K.; Shimizu, S.; Kondo, H.; Yoshida, M.; Yamashita, H.; Umemura, S.; et al. Feasibility of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography-related procedures in hemodialysis patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikarashi, S.; Katanuma, A.; Kin, T.; Takahashi, K.; Yane, K.; Sano, I.; Yamazaki, H.; Maguchi, H. Factors associated with delayed hemorrhage after endoscopic sphincterotomy: Japanese large single-center experience. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, T.N. Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography for Choledocholithiasis in Long-Term Dialysis: A Propensity Score Analysis. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 63, 3141–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaji, S.; Hirata, N.; Matsui, H.; Shiratori, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshimura, S.; Kanda, K.; Kawamitsu, N.; Harasawa, H. Hemodialysis is a strong risk factor for post-endoscopic sphincterotomy bleeding in patients with choledocholithiasis. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 06, E568–E574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Yang, T.W.; Chen, H.Y. Major bleeding risk of endoscopic sphincterotomy versus endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Jeong, S.; Cho, J.H.; Kwon, C.I.; Jang, S.I.; Lee, T.H.; Han, J.H.; Hwang, J.C.; Lee, D.H. Clinical outcome of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for choledocholithiasis in end-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 31, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaji, S.; Okawa, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Itonaga, M.; Inase, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Suzuki, R.; Yamauchi, K.; Matsui, H.; Hirata, N.; et al. Predictive model of bleeding following endoscopic sphincterotomy for the treatment of choledocholithiasis in hemodialysis patients: A retrospective multicenter study. JGH Open 2020, 4, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Kang, J.W.; Wang, Y.S.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, C.Y. Comparison of Different Endoscopic Methods Used for Managing Choledocholithiasis in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease Undergoing Hemodialysis. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2022, 67, 5239–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhara, V.; Khashab, M.A.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Acosta, R.D.; Agrawal, D.; Bruining, D.H.; Eloubeidi, M.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Faulx, A.L.; Gurudu, S.R.; et al. Adverse events associated with ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 85, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, T.; Yasunaga, H.; Nakai, Y.; Isayama, H.; Matsui, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Fushimi, K.; Koike, K. Bleeding after endoscopic sphincterotomy or papillary balloon dilation among users of antithrombotic agents. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, K.; Fujishiro, M.; Kato, M.; Higuchi, K.; Iwakiri, R.; Sakamoto, C.; Uchiyama, S.; Kashiwagi, A.; Ogawa, H.; Murakami, K.; et al. Guidelines for gastroenterological endoscopy in patients undergoing antithrombotic treatment. Dig. Endosc. 2013, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Tada, M.; Toda, N.; Ohashi, M.; Shiratori, Y.; Omata, M. Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation in Cirrhotic Patients: Removal of Common Bile Duct Stones without Sphincterotomy. Endoscopy 1996, 28, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.L.; Nelson, D.B.; Sherman, S.; Haber, G.B.; Herman, M.E.; Dorsher, P.J.; Moore, J.P.; Fennerty, M.B.; Ryan, M.E.; Shaw, M.J.; et al. Complications of Endoscopic Biliary Sphincterotomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.L.; Guda, N.M. Prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: A comprehensive review. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 59, 845–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochar, B.; Akshintala, V.S.; Afghani, E.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Kim, K.J.; Lennon, A.M.; Khashab, M.A.; Kalloo, A.N.; Singh, V.K. Incidence, severity, and mortality of post-ERCP pancreatitis: A systematic review by using randomized, controlled trials. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 143–149.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.Y.; Oh, H.C.; Fogel, E.L.; Lehman, G.A. Prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis with rectal non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, E.; Toti, G.; Mariani, A.; Curioni, S.; Lomazzi, A.; Dinelli, M.; Minoli, G.; Crosta, C.; Comin, U.; Fertitta, A.; et al. Complications of diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: A prospective multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.C.; Yoo, B.M.; Moon, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.K.; Jeon, Y.S.; et al. Clinical course and proposed treatment strategy for ERCP-related duodenal perforation: A multicenter analysis. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie 2013, 45, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.S.; Solanki, N.; Mishra, P.K.; Sharma, B.C.; Saluja, S.S. ERCP-related perforation: An analysis of operative outcomes in a large series over 12 years. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 34, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtane, T.; Singhal, S. Endoscopic closure of iatrogenic duodenal perforation using dual over-the-scope clips. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 83, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Saverio, S.; Segalini, E.; Birindelli, A.; Todero, S.; Podda, M.; Rizzuto, A.; Tugnoli, G.; Biondi, A. Pancreas-sparing, ampulla-preserving duodenectomy for major duodenal (D1-D2) perforations. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Uemura, S.; Mita, N.; Iwata, K.; Yoshida, K.; Mukai, T.; Yasuda, I.; Shimizu, M. The Efficacy of Over-the-Scope Clip Closure for Gastrointestinal Iatrogenic Perforation During Endoscopic Ultrasound and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography for Pancreaticobiliary Diseases. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutaneous Tech. 2020, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Nation | Design | No. of Patients | Indications for ERCP, No. | Duration of Dialysis, Years | Anticoagulant Use, No. | Cirrhosis, No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nelson [22], 1994 | United States | Retrospective single arm | HD 14 Non-dialysis 177 | CBD stone 73 Cholangitis 41 Tumor/stricture 26 Gallstone pancreatitis 16 SOD/papillary stenosis 17 Bile leak 4 Others 4 | N/A | 5 | N/A |
| Williams [23], 2007 | United Kingdom | Prospective single arm | HD 6 Non-dialysis 4555 | CBD stone 2477 Malignancy 891 Pancreatitis 435 Gallstone pancreatitis 16 Cholangitis 245 Bile leak 100 SOD 69 Others 344 | N/A | N/A | 43 |
| Takahara [24], 2012 | Japan | Retrospective single arm | HD 37 | CBD stone 37 | 5.1 (0.03–14.8) * | 12 | 6 |
| Hori [25], 2014 | Japan | Retrospective single arm | HD 76 | CBD stone 43 Mucinous neoplasm 7 Pancreas cancer 6 Others 20 | 6 (1–35) * | 30 | 2 |
| Ikarashi [26], 2017 | Japan | Retrospective single arm | HD 19 Non-dialysis 1094 | CBD stone 801 Malignant biliary stricture 256 Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction 13 Acute cholecystitis 11 Benign biliary stricture 11 Other 21 | N/A | 56 | 16 |
| Kim [27], 2018 | Republic of Korea | Retrospective comparative | HD 28, PD 11 Non-dialysis 78 | CBD stone 117 | 8 (1–24) * | 13 12 | 1 2 |
| Sawas [10], 2018 | United States | Retrospective comparative | ESRD 7347 CKD 39,403 Non-dialysis 445,424 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Nakaji [28], 2018 | Japan | Retrospective comparative | HD 38 Non-dialysis 1480 | CBD stone 1518 | N/A | 25 1 | 12 |
| Tsai [29], 2019 | Taiwan | Retrospective comparative | HD 74 Non-dialysis 3487 | CBD stone 64 Malignancy 9 Pancreatitis 5 | N/A | None ** | None ** |
| Park [30], 2020 | Republic of Korea | Retrospective single arm | HD 61 | CBD stone 61 | 4.1 (4.7) † | 38 | N/A |
| Nakaji [31], 2020 | Japan | Retrospective single arm | HD 123 | CBD stone 123 | 5 (1–24) * | 8 | 0 |
| Wu [32], 2022 | Taiwan | Retrospective single arm | HD 80 | CBD stone 80 | N/A | 31 | N/A |
| Study | Groups | No. of Patients (Procedures) | Age, Years | Sex, M:F | Type of Sphincter Therapy | Bleeding, No. (%) | Post-ERCP Pancreatitis, No. (%) | Bowel Perforation, No. (%) | Mortality, No. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nelson [22], 1994 | Dialysis Control | 14 177 | 66 (19) | 108:69 | EST | 4/14 (28.6) 6/177 (3.4) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Williams [23], 2007 | Dialysis Control | 6 4555 | 65.0 (16.7) | 1970:2591 | EST | 3/6 (50) 25/4555 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Takahara [24], 2012 | Dialysis | 37 | 71 (49–88) * | 25:12 | EPBD | 2/37 (5.4) | 2/37 (5.4) | 1/37 (2.7) | 0/37 (0) |
| Hori [25], 2014 | Dialysis | 76 | 70 (33–87) * | 55:21 | EST ± EPBD | 4/76 (5.3) | 6/76 (7.9) | 0/76 (0) | 2/76 (2.9) |
| Ikarashi [26], 2017 | Dialysis Control | 19 1094 | 74 (14–101) * | 643:470 | EST | 3/19 (15.8) 27/1094 (2.5) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Kim [27], 2018 | Dialysis Control | 39 78 | 65.6 (12.6) † 65.6 (12.5) † | 22:17 46/32 | EST or EPBD ± NF | 9/39 (23.1) 4/78 (5.1) | 4/39 (10.3) 5/78 (6.4) | 0/39 (0) 1/78 (1.3) | 0/39 (0) 0/78 (0) |
| Sawas [10], 2018 | Dialysis Control | 7347 445,424 | 65.5 (0.42) † 58 (0.12) † | 3870:3477 174,124:271,300 | N/A | 377/7347 (5.1) 6546/445,424 (1.5) | 611/7347 (8.3) 20,315/445,424 (4.6) | 14/7347 (0.2) 340/445,424 (0.07) | 526/7347 (7.1) 5138/445,424 (1.15) |
| Nakaji [28], 2018 | Dialysis Control | 38 1480 | 70.7 (9.3) † 74.8 (12.9) † | 22:16 791:689 | EST ± EPLBD | 11/38 (29.0) 39/1480 (2.6) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Tsai [29], 2019 | Dialysis Control | 74 (81) 3487 (4025) | 67 (33–86) ** | 32:42 | EST or EPBD | ** 7/81 (8.64) ** 87/4025 (2.16) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Park [30], 2020 | Dialysis | 61 | 69.7 (10.7) † | 36: 25 | EST 30 EPBD 23 EST + EPBD 8 | 8/61(13.1) | 3/61 (4.9) | 0/61 (0) | 0/61 (0) |
| Nakaji [31], 2020 | Dialysis | 123 | 71(47–101) * | 79:44 | EST ± EPLBD | 20/123 (16.3) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Wu [32], 2022 | Dialysis | 80 | N/A | 36:44 | EST 21 EPBD 28 EST + EPBD 31 | 12/80 (15.0) | 7/80 (8.8) | 0/80 (0) | 0/80 (0) |
| Adverse Events | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Post-ERCP pancreatitis * | 633 (8.3) |
| Mortality * | 528 (7.1) |
| Bleeding | 460 (5.8) |
| Bowel perforation * | 15 (0.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, T.Y.; Bang, C.S.; Do, J.H.; Oh, H.C. Outcomes of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111883
Park TY, Bang CS, Do JH, Oh HC. Outcomes of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111883
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Tae Young, Chang Seok Bang, Jae Hyuk Do, and Hyoung Chul Oh. 2022. "Outcomes of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111883
APA StylePark, T. Y., Bang, C. S., Do, J. H., & Oh, H. C. (2022). Outcomes of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111883






