PIK3CAMutations in Breast Cancer Subtypes Other Than HR-Positive/HER2-Negative
Abstract
1. Introduction
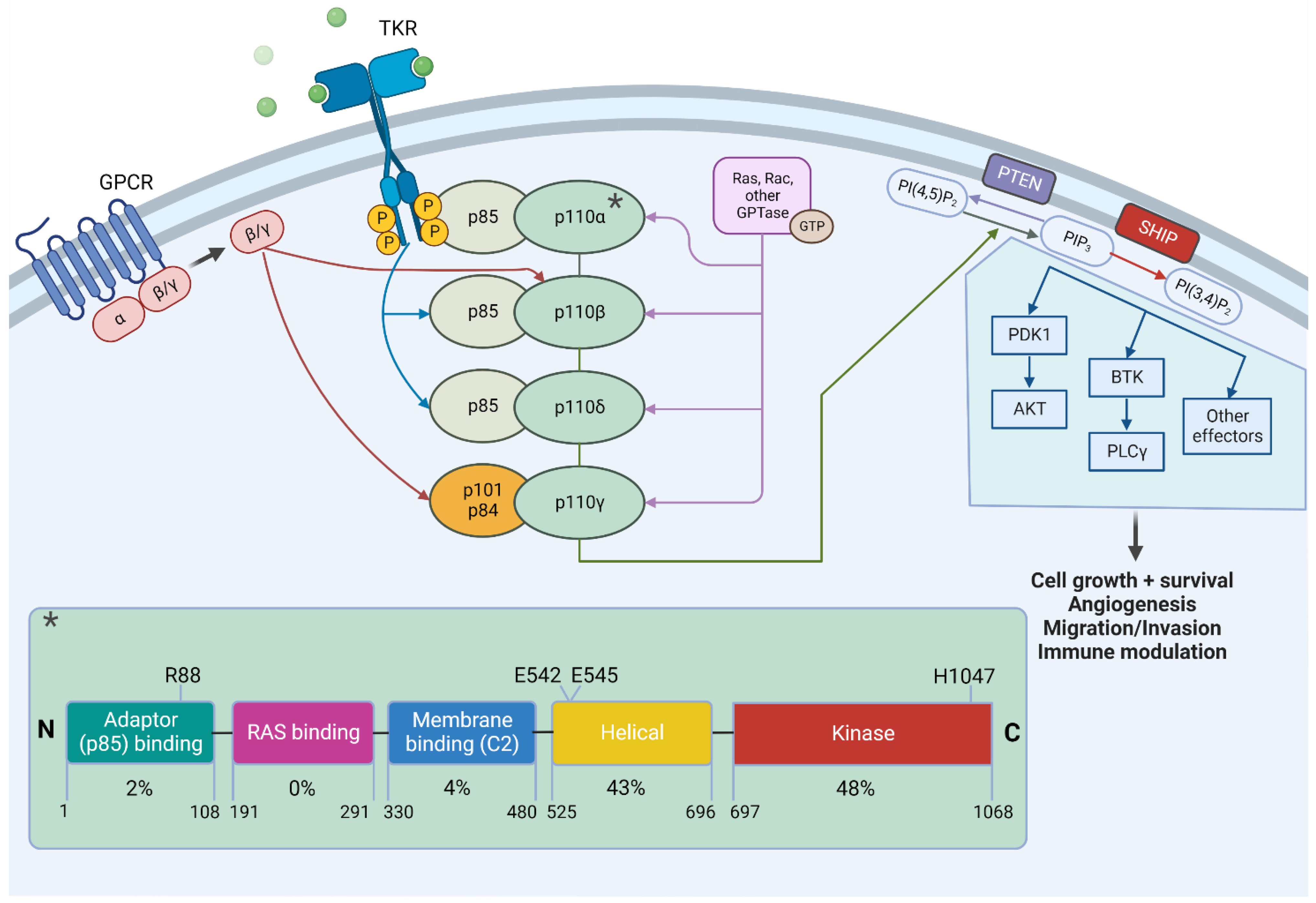
2. The PIK3CA/AKT/mTOR Pathway
3. PIK3CA Mutations and Their Detection
4. Targeting PI3K
5. Biological and Clinical Evidence of PIK3CA Mutations in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
6. Biological and Clinical Evidence of PIK3CA Mutations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verret, B.; Cortes, J.; Bachelot, T.; Andre, F.; Arnedos, M. Efficacy of PI3K inhibitors in advanced breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x12–x20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Ayesh, H.S.K.; Halawani, H. PIK3CA Gene Mutations in Solid Malignancies: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters and Prognosis. Cancers 2019, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; McLellan, M.D.; Schmidt, H.; Kalicki-Veizer, J.; McMichael, J.F.; Fulton, L.L.; Dooling, D.J.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.-M.; Liu, Y.-R.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Yu, K.-D.; Zuo, W.-J. OncoTargets and Therapy Dovepress PIK3CA mutations define favorable prognostic biomarkers in operable breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Stefanovska, B.; Lusque, A.; Dien, A.T.; Garberis, I.; Droin, N.; Le Tourneau, C.; Sablin, M.-P.; Lacroix, L.; Enrico, D.; et al. Outcome and molecular landscape of patients with PIK3CA-mutated metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Toska, E.; Scaltriti, M. Overview of the Relevance of PI3K Pathway in HR-Positive Breast Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x3–x11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W.; Balko, J.M.; Arteaga, C.L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase and Antiestrogen Resistance in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4452–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.; Cortés, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Gligorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T.; Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; et al. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Perry, M.W.D.; Brown, J.R.; André, F.; Okkenhaug, K. PI3K Inhibitors Are Finally Coming of Age. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 741–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, K.D.; Corcoran, R.B.; Engelman, J.A. The PI3K Pathway as Drug Target in Human Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xing, M.; Mambo, E.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Chatterjee, A.; Goldenberg, D.; Gollin, S.M.; Sukumar, S.; et al. Open Access Somatic mutation and gain of copy number of PIK3CA in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huw, L.-Y.; O’Brien, C.; Pandita, A.; Mohan, S.; Spoerke, J.M.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hampton, G.M.; Wilson, T.R.; Lackner, M.R. Acquired PIK3CA amplification causes resistance to selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors in breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e83–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, A.; Varadi, M.; Carrasco, D.; Li, H.; Luongo, L.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, E.Y.; Lewis, G.; Kehoe, S.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations in in situ and Invasive Breast Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5674–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukohara, T. PI3K mutations in breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Breast Cancer: Targets Ther. 2015, 7, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Mandelker, D.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Samuels, Y.; Velculescu, V.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Gabelli, S.B.; Amzel, L.M. The Structure of a Human P110a/P85a Complex Elucidates the Effects of Oncogenic PI3Ka Mutations. Science 2007, 318, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.S.; Koren, S.; Leroy, C.; Brinkhaus, H.; Müller, U.; Klebba, I.; Müller, M.; Cardiff, R.D.; Bentires-Alj, M. Expression of PIK3CA mutant E545K in the mammary gland induces heterogeneous tumors but is less potent than mutant H1047R. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3K and cancer: Lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimawi, M.F.; De Angelis, C.; Contreras, A.; Pareja, F.; Geyer, F.C.; Burke, K.A.; Herrera, S.; Wang, T.; Mayer, I.A.; Forero, A.; et al. Low PTEN levels and PIK3CA mutations predict resistance to neoadjuvant lapatinib and trastuzumab without chemotherapy in patients with HER2 over-expressing breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2018, 167, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, F.J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Santa-Maria, C.; Stone, S.; Lanchbury, J.S.; Sahin, A.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Yu, D. PTEN, PIK3CA, p-AKT, and p-p70S6K Status: Association with Trastuzumab Response and Survival in Patients with HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, M.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Fu, X.; Nardone, A.; Herrera, S.; Mao, S.; Contreras, A.; Gutierrez, C.; Wang, T.; et al. Upregulation of ER Signaling as an Adaptive Mechanism of Cell Survival in HER2-Positive Breast Tumors Treated with Anti-HER2 Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3995–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, N.; Malapelle, U.; Fassan, M.; Marchiò, C.; Buglioni, S.; Zupo, S.; Criscitiello, C.; Vigneri, P.; Tos, A.P.D.; Maiorano, E.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations as a Molecular Target for Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 644737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, C.; Marra, A.; Curigliano, G. PIK3CA Mutation Assessment in HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer: Overview for Oncology Clinical Practice. J. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 2, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves First PI3K Inhibitor for Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-pi3k-inhibitor-breast-cancer (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Martínez-Sáez, O.; Chic, N.; Pascual, T.; Adamo, B.; Vidal, M.; González-Farré, B.; Sanfeliu, E.; Schettini, F.; Conte, B.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; et al. Frequency and spectrum of PIK3CA somatic mutations in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, W.A.M.E.; Suijkerbuijk, K.P.M.; van Gils, C.H.; van der Wall, E.; Moelans, C.B.; van Diest, P.J. Receptor Conversion in Distant Breast Cancer Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, C.; Ranghiero, A.; Gandini, S.; Corso, F.; Taormina, S.; De Camilli, E.; Rappa, A.; Vacirca, D.; Viale, G.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; et al. Inter-tumor genomic heterogeneity of breast cancers: Comprehensive genomic profile of primary early breast cancers and relapses. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.D.; Laenkholm, A.-V.; Knoop, A.; Ewertz, M.; Bandaru, R.; Liu, W.; Hackl, W.; Barrett, J.C.; Gardner, H. Human Cancer Biology PIK3CA Mutations May Be Discordant between Primary and Corresponding Metastatic Disease in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Angulo, A.M.; Ferrer-Lozano, J.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Sahin, A.; Liu, S.; Barrera, J.A.; Burgues, O.; Lluch, A.M.; Chen, H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Molecular Medicine in Practice PI3K Pathway Mutations and PTEN Levels in Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thulin, A.; Andersson, C.; Rönnerman, E.W.; De Lara, S.; Chamalidou, C.; Schoenfeld, A.; Kovács, A.; Fagman, H.; Enlund, F.; Linderholm, B.K. Discordance of PIK3CA and TP53 mutations between breast cancer brain metastases and matched primary tumors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toppmeyer, D.L.; Press, M.F. Testing considerations for phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha as an emerging biomarker in advanced breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrava, E.; Call, S.; Huang, H.; Stuckett, A.; Madwani, K.; Adat, A.; Hong, D.; Piha-Paul, S.; Subbiah, V.; Karp, D.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in plasma circulating tumor DNA predict survival and treatment outcomes in patients with advanced cancers. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, P.; Toska, E.; Engelman, J.A.; Scaltriti, M. The present and future of PI3K inhibitors for cancer therapy. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.; Caparica, R.; Eiger, D.; de Azambuja, E. Biomarkers of Response and Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Patients and Combination Therapies Involving PI3K Inhibitors. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x27–x42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.J. Predictive biomarkers for molecularly targeted therapies and immunotherapies in breast cancer. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2022, 45, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, I.; Paoli, M.; Risi, E.; Biagioni, C.; Biganzoli, L.; Benelli, M.; Malorni, L. PIK3CA co-occurring mutations and copy-number gain in hormone receptor positive and HER2 negative breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Razavi, P.; Johnson, J.L.; Shao, H.; Shah, H.; Antoine, A.; Ladewig, E.; Gorelick, A.; Lin, T.-Y.; Toska, E.; et al. DoublePIK3CAmutations in cis increase oncogenicity and sensitivity to PI3Kα inhibitors. Science 2019, 366, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K Pathway in Cancer: Are We Making Headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnery, S.E.; Mayer, I.A. Management of Toxicity to Isoform α-Specific PI3K Inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x21–x26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, A.; Viale, G.; Curigliano, G. Safety, Tolerability, and Management of Toxic Effects of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitor Treatment in Patients with Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Jang, H.; Nussinov, R. PI3K inhibitors: Review and new strategies. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 5855–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gion, M.; Trapani, D.; Cortés, A.; Valenza, C.; Lin, N.; Cortés, J.; Curigliano, G. Systemic Therapy for HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Moving into a New Era. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, K.; Horlings, H.M.; Hennessy, B.T.; Madiredjo, M.; Hijmans, E.M.; Beelen, K.; Linn, S.C.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Hauptmann, M.; et al. A Functional Genetic Approach Identifies the PI3K Pathway as a Major Determinant of Trastuzumab Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Hurvitz, S.; Fasolo, A.; Tseng, L.-M.; Jerusalem, G.; Wilks, S.; O’Regan, R.; Isaacs, C.; Toi, M.; Burris, H.A.; et al. Molecular Alterations and Everolimus Efficacy in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Overexpressing Metastatic Breast Cancers: Combined Exploratory Biomarker Analysis From BOLERO-1 and BOLERO-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untch, M.; Rezai, M.; Loibl, S.; Fasching, P.A.; Huober, J.; Tesch, H.; Bauerfeind, I.; Hilfrich, J.; Eidtmann, H.; Gerber, B.; et al. Neoadjuvant Treatment with Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Results from the GeparQuattro Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untch, M.; Loibl, S.; Bischoff, J.; Eidtmann, H.; Kaufmann, M.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Hilfrich, J.; Strumberg, D.; Fasching, P.A.; Kreienberg, R.; et al. Lapatinib versus trastuzumab in combination with neoadjuvant anthracycline-taxane-based chemotherapy (GeparQuinto, GBG 44): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Minckwitz, G.; Schneeweiss, A.; Loibl, S.; Salat, C.; Denkert, C.; Rezai, M.; Blohmer, J.U.; Jackisch, C.; Paepke, S.; Gerber, B.; et al. Neoadjuvant carboplatin in patients with triple-negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer (GeparSixto; GBG 66): A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Bradbury, I.; Eidtmann, H.; Di Cosimo, S.; de Azambuja, E.; Aura, C.; Gómez, H.; Dinh, P.; Fauria, K.; Van Dooren, V.; et al. Lapatinib with trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer (NeoALTTO): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, V.; Frassoldati, A.; Bottini, A.; Cagossi, K.; Bisagni, G.; Sarti, S.; Ravaioli, A.; Cavanna, L.; Giardina, G.; Musolino, A.; et al. Preoperative Chemotherapy Plus Trastuzumab, Lapatinib, or Both in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive Operable Breast Cancer: Results of the Randomized Phase II CHER-LOB Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Majewski, I.; Guarneri, V.; Nekljudova, V.; Holmes, E.; Bria, E.; Denkert, C.; Schem, C.; Sotiriou, C.; Loi, S.; et al. PIK3CA mutations are associated with reduced pathological complete response rates in primary HER2-positive breast cancer: Pooled analysis of 967 patients from five prospective trials investigating lapatinib and trastuzumab. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Michiels, S.; Lambrechts, D.; Fumagalli, D.; Claes, B.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Bono, P.; Kataja, V.; Piccart, M.J.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Somatic Mutation Profiling and Associations with Prognosis and Trastuzumab Benefit in Early Breast Cancer. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogue-Geile, K.L.; Song, N.; Jeong, J.-H.; Gavin, P.G.; Kim, S.-R.; Blackmon, N.L.; Finnigan, M.; Rastogi, P.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Mamounas, E.P.; et al. Intrinsic Subtypes, PIK3CA Mutation, and the Degree of Benefit from Adjuvant Trastuzumab in the NSABP B-31 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Krop, I. PIK3CA mutations in HER2-positive breast cancer: An ongoing conundrum. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizkova, M.; Dujaric, M.-E.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Scott, V.; Tembo, O.; Asselain, B.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Marty, M.; De Cremoux, P.; Spyratos, F.; et al. Outcome impact of PIK3CA mutations in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1807–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.D.; Knoop, A.; Laenkholm, A.V.; Grauslund, M.; Jensen, M.B.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Andersson, M.; Ewertz, M. PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, and pHER2 expression and impact on outcome in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and trastuzumab. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 23, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Cortes, J.; Im, S.-A.; Clark, E.; Ross, G.; Kiermaier, A.; Swain, S. Biomarker Analyses in CLEOPATRA: A Phase III, Placebo-Controlled Study of Pertuzumab in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive, First-Line Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3753–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Phillips, G.D.L.; Verma, S.; Ro, J.; Huober, J.; Guardino, A.E.; Samant, M.K.; Olsen, S.; de Haas, S.L.; Pegram, M.D. Relationship between Tumor Biomarkers and Efficacy in EMILIA, a Phase III Study of Trastuzumab Emtansine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasti, A.R.; Guimaraes-Young, A.; Datko, F.; Borges, V.F.; Aisner, D.L.; Shagisultanova, E. PIK3CA Mutations Drive Therapeutic Resistance in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Positive Breast Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, C.; Bendell, J.; Jerusalem, G.; Su, S.; Ru, Q.; De Buck, S.; Mills, D.; Ruquet, S.; Bosch, A.; Urruticoechea, A.; et al. Cancer Therapy: Clinical Phase Ib Study of Buparlisib plus Trastuzumab in Patients with HER2-Positive Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer That Has Progressed on Trastuzumab-Based Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodón, J.; Bendell, J.; Abdul, R.A.; Homji, N.; Trandafir, L.; Quadt, C.; Graña-Suárez, B.; Siu, L.; Di Tomaso, E.; Demanse, D.; et al. P3-16-01: Safety Profile and Clinical Activity of Single-Agent BKM120, a Pan-Class I PI3K Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Breast Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, P3-16-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistilli, B.; Pluard, T.; Urruticoechea, A.; Farci, D.; Kong, A.; Bachelot, T.; Chan, S.; Han, H.S.; Jerusalem, G.; Urban, P.; et al. Phase II study of buparlisib (BKM120) and trastuzumab in patients with HER2+ locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer resistant to trastuzumab-based therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 168, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, M.; Rezai, K.; Isambert, N.; Campone, M.; Autret, A.; Pakradouni, J.; Provansal, M.; Camerlo, J.; Sabatier, R.; Bertucci, F.; et al. PIKHER2: A phase IB study evaluating buparlisib in combination with lapatinib in trastuzumab-resistant HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; de la Pena, L.; Nekljudova, V.; Zardavas, D.; Michiels, S.; Denkert, C.; Rezai, M.; Bermejo, B.; Untch, M.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Neoadjuvant buparlisib plus trastuzumab and paclitaxel for women with HER2+ primary breast cancer: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial (NeoPHOEBE). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 85, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.; Burris, H.; Gartner, E.; Mayer, I.A.; Saura, C.; Maurer, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Garcia, A.A.; Campana, F.; Wu, B.; et al. Phase I/II study of pilaralisib (SAR245408) in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab plus paclitaxel in trastuzumab-refractory HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 149, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.J.; Guan, J.; Prior, W.W.; Lee, L.B.; Berry, L.; Belmont, L.D.; Koeppen, H.; Belvin, M.; Friedman, L.S.; Sampath, D. GDC-0941, a Novel Class I Selective PI3K Inhibitor, Enhances the Efficacy of Docetaxel in Human Breast Cancer Models by Increasing Cell Death In Vitro and In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3901–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondesire, W.H.; Jian, W.; Zhang, H.; Ensor, J.; Hung, M.-C.; Mills, G.B.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Synergistically Enhances Chemotherapy-Induced Cytotoxicity in Breast Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7031–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, N.M.; Furney, S.J.; Walshe, J.M.; Gullo, G.; Kennedy, M.J.; Smith, D.; McCaffrey, J.; Kelly, C.M.; Egan, K.; Kerr, J.; et al. Phase Ib Trial of Copanlisib, A Phosphoinositide-3 Kinase (PI3K) Inhibitor, with Trastuzumab in Advanced Pre-Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer “PantHER”. Cancers 2021, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Shah, A.N.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Siziopikou, K.; Rademaker, A.; Helenowski, I.; Cristofanilli, M.; Gradishar, W.J. Phase I study of alpelisib (BYL-719) and trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC) after trastuzumab and taxane therapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, F.W.; Barker, H.R.; Lipert, B.; Rothé, F.; Gebhart, G.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Sotiriou, C.; Jamieson, S.M.F. Mechanisms of resistance to trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in HER2-positive breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, K.; Drago, J.Z.; Shah, P.D.; Wang, R.; Pareja, F.; Ratzon, F.; Iasonos, A.; Patil, S.; Rosen, N.; Fornier, M.N.; et al. A Phase I Study of Alpelisib in Combination with Trastuzumab and LJM716 in Patients with PIK3CA-Mutated HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, V.; Scaltriti, M.; Prudkin, L.; Eichhorn, P.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Markman, B.; Rodriguez, O.; Guzman, M.; Gili, M.; et al. PI3K inhibition results in enhanced HER signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; De Angelis, C.; Licata, L.; Gianni, L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer—Expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 19, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagami, P.; Carey, L.A. Triple negative breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves First Targeted Therapy for HER2-Low Breast Cancer|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-targeted-therapy-her2-low-breast-cancer (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Pascual, J.; Turner, N.C. Targeting the PI3-kinase pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, F.; Lavigne, M.; De Koning, L.; EL Botty, R.; Nemati, F.; Naguez, A.; Bataillon, G.; Ouine, B.; Dahmani, A.; Montaudon, E.; et al. Response to mTOR and PI3K inhibitors in enzalutamide-resistant luminal androgen receptor triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenografts. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Schafer, J.M.; Pendleton, C.S.; Tang, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Chen, X.; Balko, J.M.; Gómez, H.; Arteaga, C.L.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations in Androgen Receptor-Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Confer Sensitivity to the Combination of PI3K and Androgen Receptor Inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, U.S.; Barr, A.R.; Cutts, R.; Beaney, M.; Babina, I.; Sampath, D.; Giltnane, J.; Lacap, J.A.; Crocker, L.; Young, A.; et al. Cancer Therapy: Preclinical Single-Cell Dynamics Determines Response to CDK4/6 Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5561–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.S.; SelviMiralles, M.; Ameratunga, M.; Minchom, A.; Pascual, J.; Banerji, U.; Bye, H.; Raynaud, F.; Swales, K.E.; Malia, J.; et al. PIPA: A phase Ib study of selective ß-isoform sparing phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor taselisib (T) plus palbociclib (P) in patients (pts) with advanced solid cancers—Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic (PK), and pharmacodynamic (PD) analysis of the doublet combination. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3087–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Geng, R.; Ji, Y.; Guan, Q.; Hong, C.; Wei, Y.; Min, N.; Qi, A.; et al. PIK3CA mutation confers resistance to chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting apoptosis and activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 410–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfgen, C.; Reeve, K.; Moskovszky, L.; Güth, U.; Bjelic-Radisic, V.; Fleisch, M.; Tausch, C.; Varga, Z. Prognostic impact of PIK3CA protein expression in triple negative breast cancer and its subtypes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinsky, K.; Jacks, L.M.; Heguy, A.; Patil, S.; Drobnjak, M.; Bhanot, U.K.; Hedvat, C.V.; Traina, T.A.; Solit, D.; Gerald, W.; et al. PIK3CA Mutation Associates with Improved Outcome in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5049–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Inao, T.; Sueta, A.; Fujiwara, S.; Omoto, Y.; Iwase, H. Prognostic role of PIK 3 CA mutations of cell-free DNA in early-stage triple negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Loibl, S.; Von Minckwitz, G.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Lederer, B.; Denkert, C. PIK3CA H1047R Mutation Associated with a Lower Pathological Complete Response Rate in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Anthracycline-Taxane–Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Saura, C.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Guo, H.; Ciruelos, E.; Bermejo, B.; Gavilá, J.; Serra, V.; Prat, A.; Paré, L.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Buparlisib (BKM120), a Pan-Class I PI3K Inhibitor, in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lin, N.U.; Maurer, M.A.; Chen, H.; Mahvash, A.; Sahin, A.; Akcakanat, A.; Li, Y.; Abramson, V.; Litton, J.; et al. Phase II trial of AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in patients with advanced breast cancer who have tumors with PIK3CA or AKT mutations, and/or PTEN loss/PTEN mutation. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Inada-Inoue, M.; Mitsuma, A.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Suenaga, N.; Sato, M.; Kakizume, T.; Robson, M.; Quadt, C.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of buparlisib (BKM 120), an oral pan-class I PI 3K inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.; Chan, A.; Dirix, L.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Hegg, R.; Manikhas, A.; Shtivelband, M.; Krivorotko, P.; Batista López, N.; Campone, M.; et al. A randomized adaptive phase II/III study of buparlisib, a pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, combined with paclitaxel for the treatment of HER2– advanced breast cancer (BELLE-4). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodon, J.; Curigliano, G.; Delord, J.-P.; Harb, W.; Azaro, A.; Han, Y.; Wilke, C.; Donnet, V.; Sellami, D.; Beck, T. A Phase Ib, open-label, dose-finding study of alpelisib in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31709–31718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Abramson, V.G.; O’Dea, A.; Nye, L.; Mayer, I.; Pathak, H.B.; Hoffmann, M.; Stecklein, S.R.; Elia, M.; Lewis, S.; et al. Clinical and Biomarker Results from Phase I/II Study of PI3K Inhibitor Alpelisib plus Nab-paclitaxel in HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvekar, A.; Burga, L.N.; Hu, H.; Lunsford, E.P.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Balmañà, J.; Rajendran, A.; Papa, A.; Spencer, K.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; et al. Combining a PI3K Inhibitor with a PARP Inhibitor Provides an Effective Therapy for BRCA1-Related Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1048–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.H.; García-García, C.; Serra, V.; He, L.; Torres-Lockhart, K.; Prat, A.; Anton, P.; Cozar, P.; Guzmán, M.; Grueso, J.; et al. PI3K Inhibition Impairs BRCA1/2 Expression and Sensitizes BRCA-Proficient Triple-Negative Breast Cancer to PARP Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulonis, U.A.; Wulf, G.M.; Barry, W.T.; Birrer, M.; Westin, S.N.; Farooq, S.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Obermayer, E.; Whalen, C.; Spagnoletti, T.; et al. Phase I dose escalation study of the PI3kinase pathway inhibitor BKM120 and the oral poly (ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib for the treatment of high-grade serous ovarian and breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Keenan, T.E.; Pernas, S.; Exman, P.; Jain, E.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Hughes, M.; Bychkovsky, B.; Umeton, R.; Files, J.L.; et al. Tumor Mutational Burden and PTEN Alterations as Molecular Correlates of Response to PD-1/L1 Blockade in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, C.; Malu, S.; Creasy, C.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Xu, C.; McKenzie, J.A.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Loss of PTEN Promotes Resistance to T Cell–Mediated Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, G.; Wu, F.; Michelini, F.; Chan, C.; Qu, X.; Selenica, P.; Ladewig, E.; Castel, P.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Genomic Alterations in PIK3CA-Mutated Breast Cancer Result in mTORC1 Activation and Limit the Sensitivity to PI3Kα Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xie, X.; Ye, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, Z.; Yan, S.-M.; Yang, L.; Kong, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. N6-methyladenosine regulated FGFR4 attenuates ferroptotic cell death in recalcitrant HER2-positive breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, N.; Xue, Z.; Liu, L.-R.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Xie, X.; Zou, Y.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. Synergistic therapeutic effect of combined PDGFR and SGK1 inhibition in metastasis-initiating cells of breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, F.; Filleron, T.; Kamal, M.; Mosele, F.; Arnedos, M.; Dalenc, F.; Sablin, M.-P.; Campone, M.; Bonnefoi, H.; Lefeuvre-Plesse, C.; et al. Genomics to Select Treatment for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Check for Updates. Christophe Tourneau 2022, 610, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PI3K Inhibitor | Combined Treatment | Mutation on PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway Related Genes Required | Phase | Setting | NCT Number/Study Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpelisib α | +Trastuzumab + pertuzumab | Yes, in part 2 | III | Advanced HER2+ BC following induction with taxane | NCT04208178 |
| (EPIK-B2) | |||||
| Copanlisib ∞ | Trastuzumab + pertuzumab | Yes | I/II | Advanced HER2+ BC following induction with taxane | NCT04108858 |
| Taselisib β | Arm A: Taselisib with T-DM1 | No | I | mBC, HER2+ | NCT02390427 |
| Arm B: Taselisib with T-DM1 and pertuzumab | |||||
| Arm C: Taselisib with pertuzumab and trastuzumab | |||||
| Arm D: Taselisib with pertuzumab, trastuzumab and paclitaxel | |||||
| Copanlisib ∞ | Trastuzumab | No | I/II | mBC, HER2+ | NCT02705859 |
| ≥1 line with Trastuzumab or T-DM1 | (Panther) | ||||
| BEZ235 (Dactolisib) ¥ | + Trastuzumab | No | I/II | mBC, HER2+ after Trastuzumab | NCT01471847 |
| GDC-0084 × | + Trastuzumab | No | II | mBC, HER2+ | NCT03765983 |
| with brain mets | |||||
| MEN1611 * | Trastuzumab +/− fulvestrant (if HR+) | Yes | I | mBC, HER2+, | NCT03767335 (B-PRECISE-01) |
| >2 lines of anti-HER2 | |||||
| MK2206 γ | Trastuzumab and Lapatinib | No | I | Advanced HER2+ BC | NCT01705340 |
| MK2206 γ | Lapatinib | No | I | Advanced HER2+ BC | NCT01245205 |
| Ipatasertib γ | Trastuzumab + Pertuzumab + ET (if HR+) | Yes | I | Advanced HER2+ BC | NCT04253561 |
| Inavolisib α | Pertuzumab + Trastuzumab + Hyaluronidase + ET | Yes | II | Neoadjuvant HER2+, HR+ BC | NCT05306041 |
| (GeparPiPPa) | |||||
| Alpelisib α | Trastuzumab (+ET) vs chemotherapy + trastuzumab | Yes | III | mBC, HER2+/HR+ | NCT05063786 |
| 1 < line < 5 | (ALPHABET) | ||||
| Alpelisib α | T-DM1 | No | I | mBC, HER2+ after Trastuzumab-taxane regimen | NCT02038010 |
| Alpelisib α | + trastuzumab + pertuzumab + chemotherapy | Yes | I | Neoadjuvant HER2+ BC | NCT04215003 |
| XL147 (SAR245408, Pilaralisib) i | Trastuzumab (+/- paclitaxel) | No | I/II | mBC, HER2+ after Trastuzumab | NCT01042925 |
| Alpelisib α | Tucatinib + fulvestrant | Yes | I/II | Advacnced BC, HER2+, >2 lines | NCT05230810 |
| BKM120 (Buparlisib) i | Lapatinib | Yes | I/II | Trastuzumab-resistant | NCT01589861 (PIKHER2) |
| mBC, HER2+ | |||||
| BKM120 (Buparlisib) i | Trastuzumab + Paclitaxel | No | I II | Neoadjuvant HER2+ | NCT01816594 (NeoPHOEBE) |
| Rapamycin | Inetetamab + chemotherapy vs. pyrotenib + chemotherapy | Yes | III | mBC, HER2+ after Trastuzumab | NCT04736589 |
| Taselisibβ/Pictilisib i | Palbociclib | Yes | I | mBC, HER2+ >2 lines | NCT02389842 |
| mTNBC >1 line | |||||
| AZD5363 (Capivasertib) γ | / | Yes | I | mBC, ER+/HER2+ | NCT01226316 |
| Everolimus | Nab-paclitaxel | Yes | II | mTNBC | NCT04395989 |
| Alpelisib α | Nab-Paclitaxel | Yes or loss of function PTEN | II | Anthracycline refractory-TNBC, neoadjuvant | NCT04216472 |
| Alpelisib α | Sacituzumab govitecan | No | I | Advanced TNBC | NCT05143229 |
| Alpelisib α | Nab-paclitaxel | Yes or loss of function PTEN | III | Advanced TNBC, 2nd line | NCT04251533 (EPIK-B3) |
| Inavolisib α | / | Yes | I | mTNBC | NCT03006172 |
| CUDC907 (Fimepinostat) ç | / | No | I | mTNBC | NCT02307240 |
| Alpelisib α | Enzalutamide | AR-positive and PTEN-positive | I | mTNBC | NCT03207529 |
| Copanlisib ∞ | Eribulin | No | I/II | Advanced TNBC, | NCT04345913 |
| 1 < line ≤ 5 | |||||
| PF-05212384 (Gedatolisib) # | PTK-ADC | No | I | mTNBC, | NCT03243331 |
| ≥2nd line | |||||
| Taselisib β | / | Yes, without KRAS mutations or PTEN Loss | I | mTNBC | NCT04439175 |
| INCB050465 (Parsaclisib) ‡ | Pembrolizumab | No | I | mTNBC | NCT02646748 |
| PQR309 (Bimiralisib) ¥ | Eribulin | No | I | Advanced TNBC | NCT02723877 (PIQHASSO) |
| 1 < line ≤ 5 | |||||
| Everolimus | Anti-PD1 | No | I | mTNBC | NCT02890069 |
| AZD5363 (Capivasertib) γ | Paclitaxel | No | II | mTNBC | NCT02423603 |
| AZD2014 (Vistusertib) < | Selumetinib | Yes, or Ras/MEK pathway | II | mTNBC | NCT02583542 |
| Taselisib β | Enzalutamide | No | I/II | mTNBC, AR+ | NCT02457910 |
| Everolimus | AR-inhibitor | Yes and LAR subtype | I/II | mTNBC | NCT03805399 |
| Alpelisib α | / | Yes | II | mTNBC, ≥2nd line | NCT02506556 (PIKNIC) |
| Tenalisib ¤ | / | No | II | mTNBC | NCT05021900 |
| Ipatasertib γ | Paclitaxel vs. placebo + paclitaxel | Yes | III | mTNBC, 1st line | NCT03337724 |
| BKM120 (Buparlisib) i or Alpelisib α | Olaparib | No | I | mTNBC, >1st line | NCT01623349 |
| PF-05212384 (Gedatolisib) # | PTK7-ADC | No | I | mTNBC, >1st line | NCT03243331 |
| Ipatasertib γ | + paclitaxel +/-atezolizumab | No | III | mTNBC | NCT04177108 |
| Eganelisib ¶ | Atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel | No | II | mTNBC, 1st line | NCT03961698 (MARIO-3) |
| Eganelisib ¶ | Nivolumab | No | I | mTNBC | NCT02637531 |
| AZD8186 † | / | No | I | mTNBC | NCT01884285 |
| AZD8186 † | Docetaxel | Yes or loss of function PTEN | I | Advanced BC | NCT03218826 |
| Ipatasertib γ | / | Yes | II | mBC, ≤2 lines | NCT04591431 |
| LOXO-783 § | Alone or + paclitaxel | Yes, PIK3CA H1047R mutation | I | mBC, <5 lines | NCT05307705 |
| AZD8835 ∞ | / | Yes | I | mBC | NCT02260661 |
| Taselisib β/ Capivasertib γ/ Copanlisib ∞ | / | Yes, PIK3CA or AKT | I | mBC | NCT02465060 |
| MK2206 γ | Paclitaxel | No | I | mBC, ≤3 lines | NCT01263145 |
| Alpelisib α | / | Yes | I | mBC | NCT05238831 |
| Inavolisib α | / | Yes | II | mBC | NCT05332561 |
| BEZ235 (Dactolisib) ¥ | MEK162 | No | I | mBC | NCT01337765 |
| CYH33 α | Olaparib | Yes or on DDR gene | I | mBC | NCT04586335 |
| PF-05212384 (Gedatolisib) # | Paclitaxel and carboplatin | No | I | mBC | NCT02069158 |
| RLY-2608 α | / | Yes | I | Advanced solid tumors | NCT05216432 |
| Alpelisib α | / | Yes | I | Solid tumors | NCT01219699 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ascione, L.; Zagami, P.; Nicolò, E.; Crimini, E.; Curigliano, G.; Criscitiello, C. PIK3CAMutations in Breast Cancer Subtypes Other Than HR-Positive/HER2-Negative. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111793
Ascione L, Zagami P, Nicolò E, Crimini E, Curigliano G, Criscitiello C. PIK3CAMutations in Breast Cancer Subtypes Other Than HR-Positive/HER2-Negative. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111793
Chicago/Turabian StyleAscione, Liliana, Paola Zagami, Eleonora Nicolò, Edoardo Crimini, Giuseppe Curigliano, and Carmen Criscitiello. 2022. "PIK3CAMutations in Breast Cancer Subtypes Other Than HR-Positive/HER2-Negative" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111793
APA StyleAscione, L., Zagami, P., Nicolò, E., Crimini, E., Curigliano, G., & Criscitiello, C. (2022). PIK3CAMutations in Breast Cancer Subtypes Other Than HR-Positive/HER2-Negative. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111793






