Longitudinal Follow-Up Using the Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (HEMRIS) Shows Minimal Changes in Heel Enthesitis Assessed in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriasis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Ankle-MRI Protocol and Scoring
2.3. Clinical Assessments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
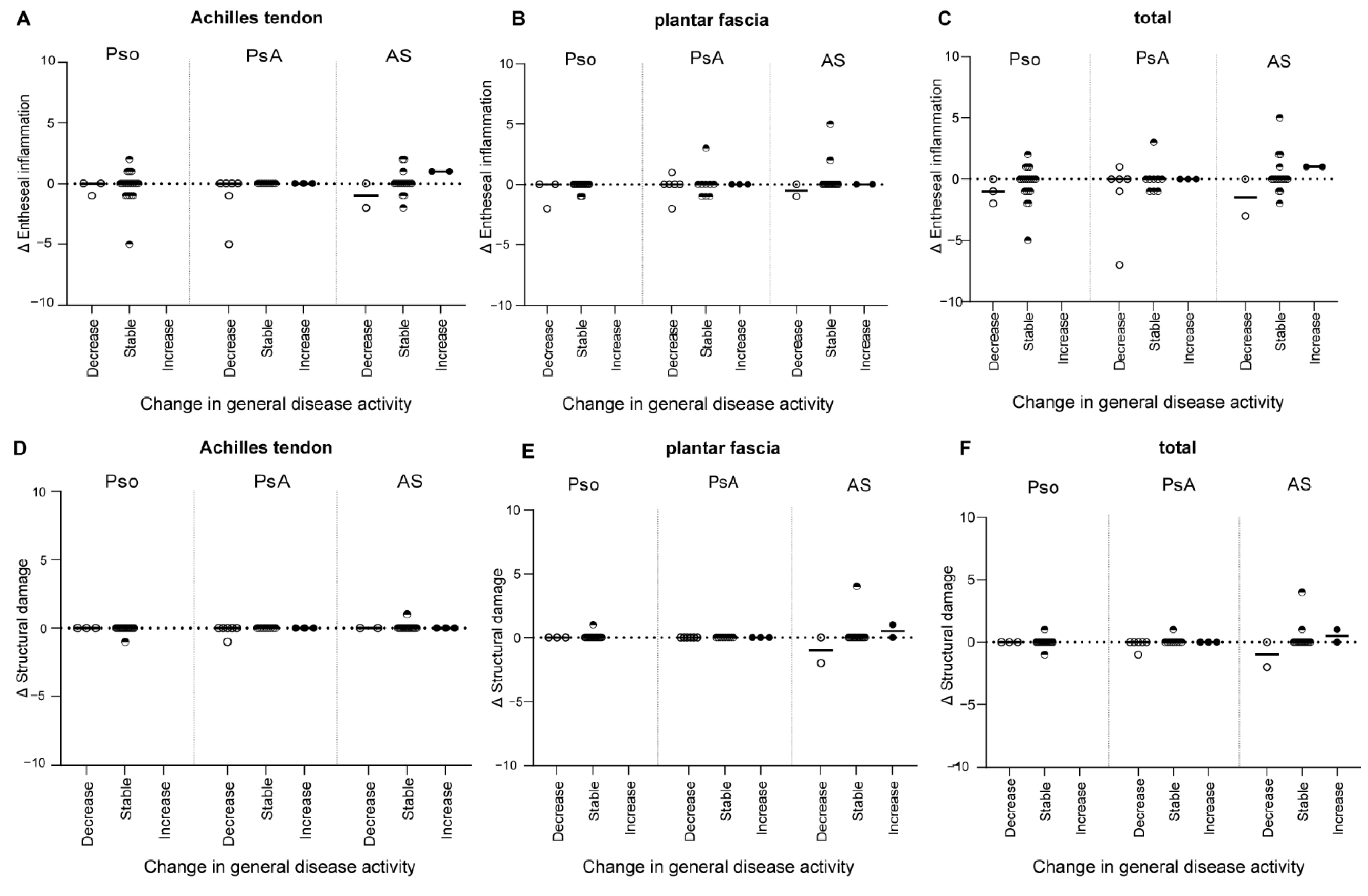
3.2. Change in Disease Activity during Follow-Up
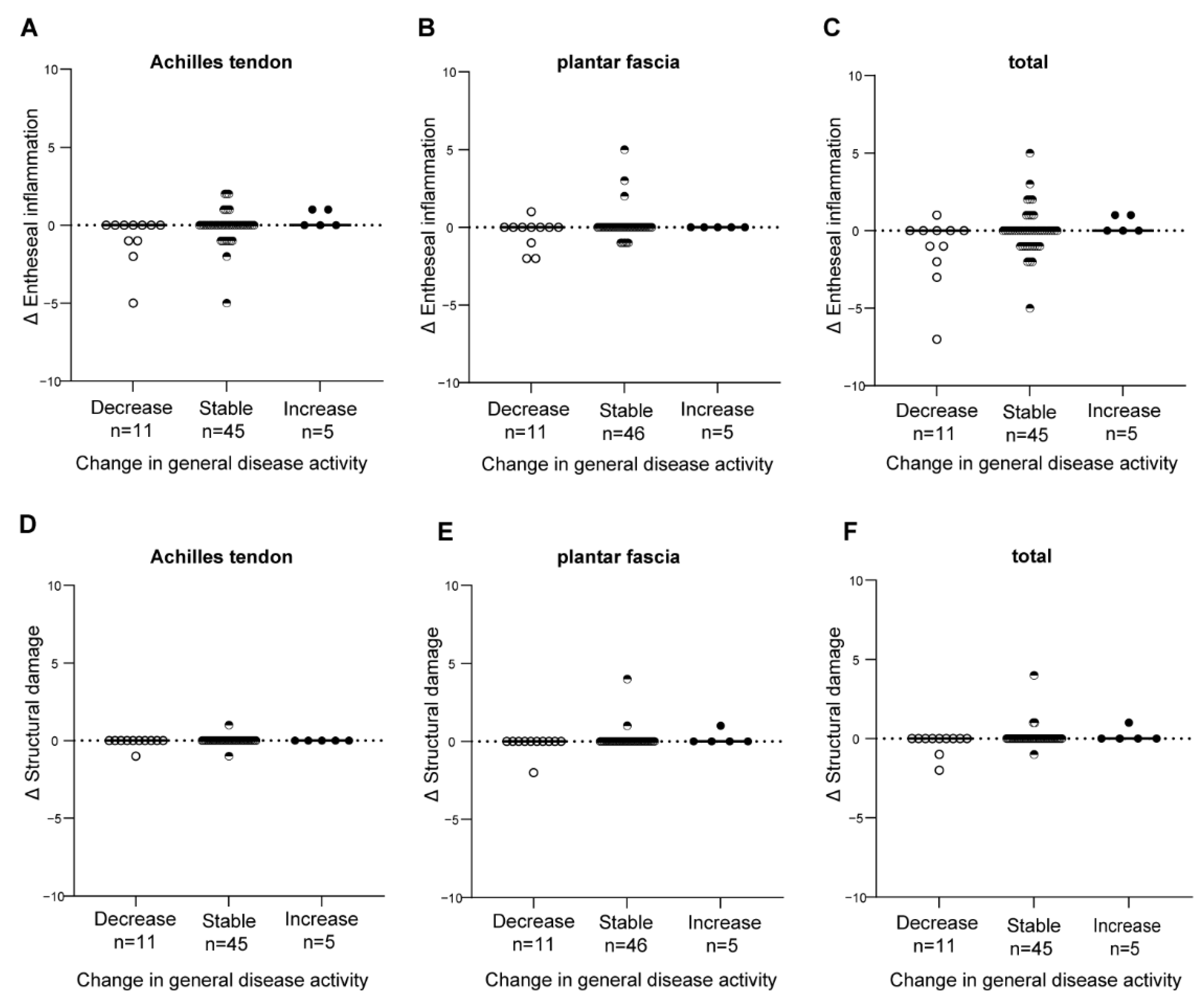
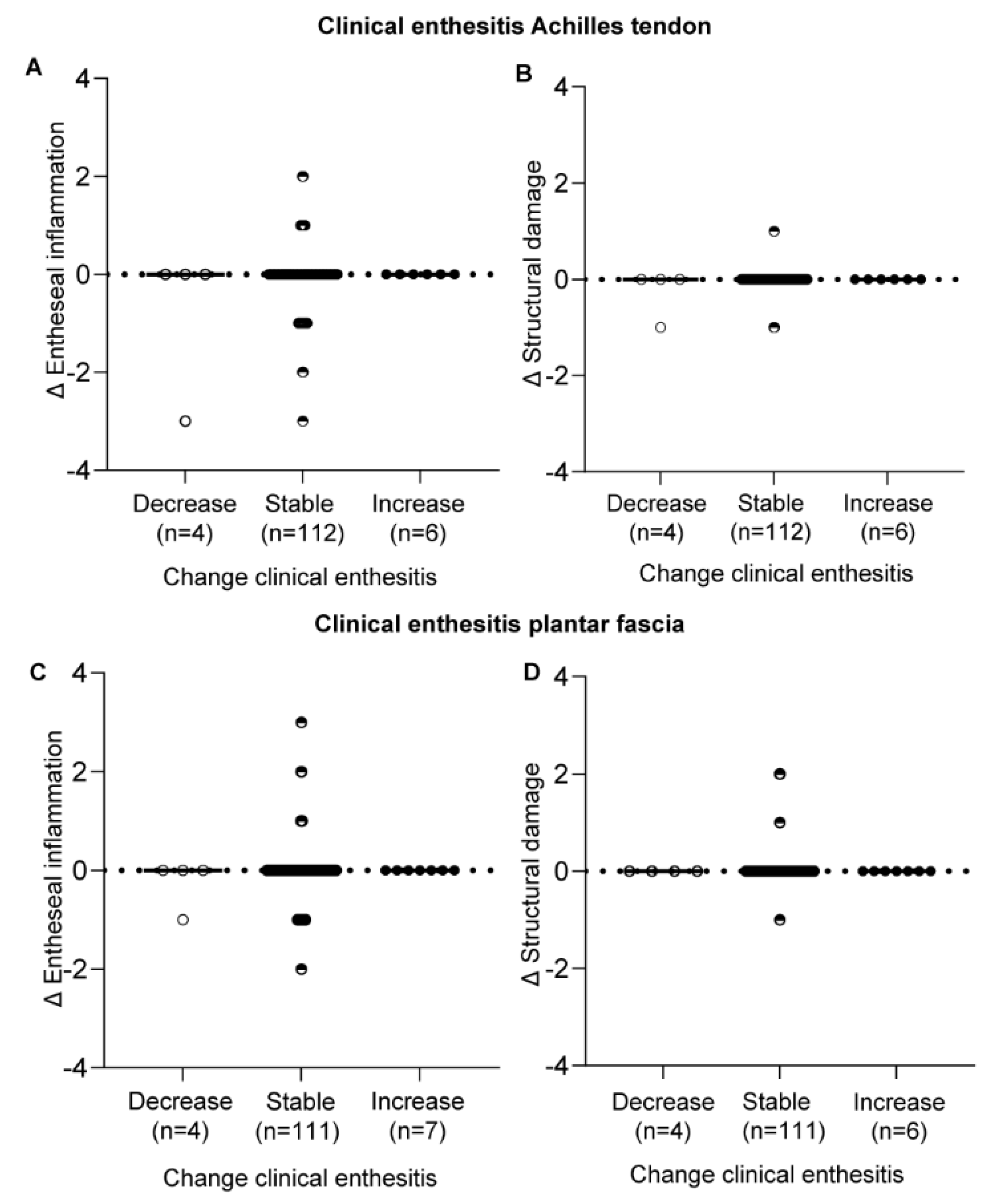
3.3. Change in the HEMRIS during Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schett, G.; Lories, R.J.; D’Agostino, M.-A.; Elewaut, D.; Kirkham, B.; Soriano, E.R.; McGonagle, D. Enthesitis: From pathophysiology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Stockwin, L.; Isaacs, J.; Emery, P. An enthesitis based model for the pathogenesis of spondyloarthropathy. Additive effects of microbial adjuvant and biomechanical factors at disease sites. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coates, L.C.; Ávila, D.G.F.; Fitzgerald, O.; Garg, A.; Gladman, D.D.; Lindsay, C. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): Updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Heijde, D.; Ramiro, S.; Landewé, R.; Baraliakos, X.; Van Den Bosch, F.; Sepriano, A.; Regel, A.; Ciurea, A.; Dagfinrud, H.; Dougados, M.; et al. 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Tan, A.L. The enthesis in psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kehl, A.S.; Corr, M.; Weisman, M.H. Review: Enthesitis: New Insights Into Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Modalities, and Treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, P. Enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis (Part 3): Clinical assessment and management. Rheumatology 2020, 59, i21–i28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakewell, C.; Aydin, S.Z.; Ranganath, V.K.; Eder, L.; Kaeley, G.S. Imaging Techniques: Options for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Treatment of Enthesitis in Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 47, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.J.; Krabbe, S.; Eshed, I.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Bird, P.; Pedersen, S.J.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Foltz, V.; Glinatsi, D.; Lambert, R.G.; et al. The OMERACT MRI in Enthesitis Initiative: Definitions of Key Pathologies, Suggested MRI Sequences and Novel Heel Enthesitis Scoring System (HEMRIS). J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.J.; Krabbe, S.; Eshed, I.; Lambert, R.G.; Laredo, J.-D.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Emad, Y.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Foltz, V.; et al. Atlas of the OMERACT Heel Enthesitis MRI Scoring System (HEMRIS). RMD Open 2020, 6, e001150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraliakos, X.; Sewerin, P.; de Miguel, E.; Pournara, E.; Kleinmond, C.; Shekhawat, A.; Jentzsch, C.; Wiedon, A.; Behrens, F. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics in patients with spondyloarthritis and clinical diagnosis of heel enthesitis: Post hoc analysis from the phase 3 ACHILLES trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.; Gladman, D.; Helliwell, P.; Marchesoni, A.; Mease, P.; Mielants, H. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: Development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudwaleit, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewe, R.; Listing, J.; Akkoc, N.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Chou, C.T.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Dougados, M.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): Validation and final selection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinrensink, N.J.; Foppen, W.; Ten Katen, I.; Van Der Veen, P.H.; De Klerk, B.; Diepstraten, S.C.E.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; De Jong, P.A.; Leijten, E.F.A.A. Comparison of the Heel Enthesitis MRI Scoring System (HEMRIS) with clinical enthesitis and local metabolic activity on PET-CT. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, T.; Pettersson, U. Severe psoriasis--oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica 1978, 157, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowietz, U.; Kragballe, K.; Reich, K.; Spuls, P.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Nast, A.; Franke, J.; Antoniou, C.; Arenberger, P.; Balieva, F.; et al. Definition of treatment goals for moderate to severe psoriasis: A European consensus. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, L.C.; Fransen, J.; Helliwell, P.S. Defining minimal disease activity in psoriatic arthritis: A proposed objective target for treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, P.J.; Helliwell, P.S. Measuring clinical enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis: Assessment of existing measures and development of an instrument specific to psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2008, 59, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, S.; Jenkinson, T.; Kennedy, L.G.; Whitelock, H.; Gaisford, P.; Calin, A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krabbe, S.; Eshed, I.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Pedersen, S.J.; Bird, P.; Mathew, A.J.; Lambert, R.G.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Glinatsi, D.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; et al. Development and validation of an OMERACT MRI whole-body score for inflammation in peripheral joints and entheses in inflammatory arthritis (MRI-WIPE). J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

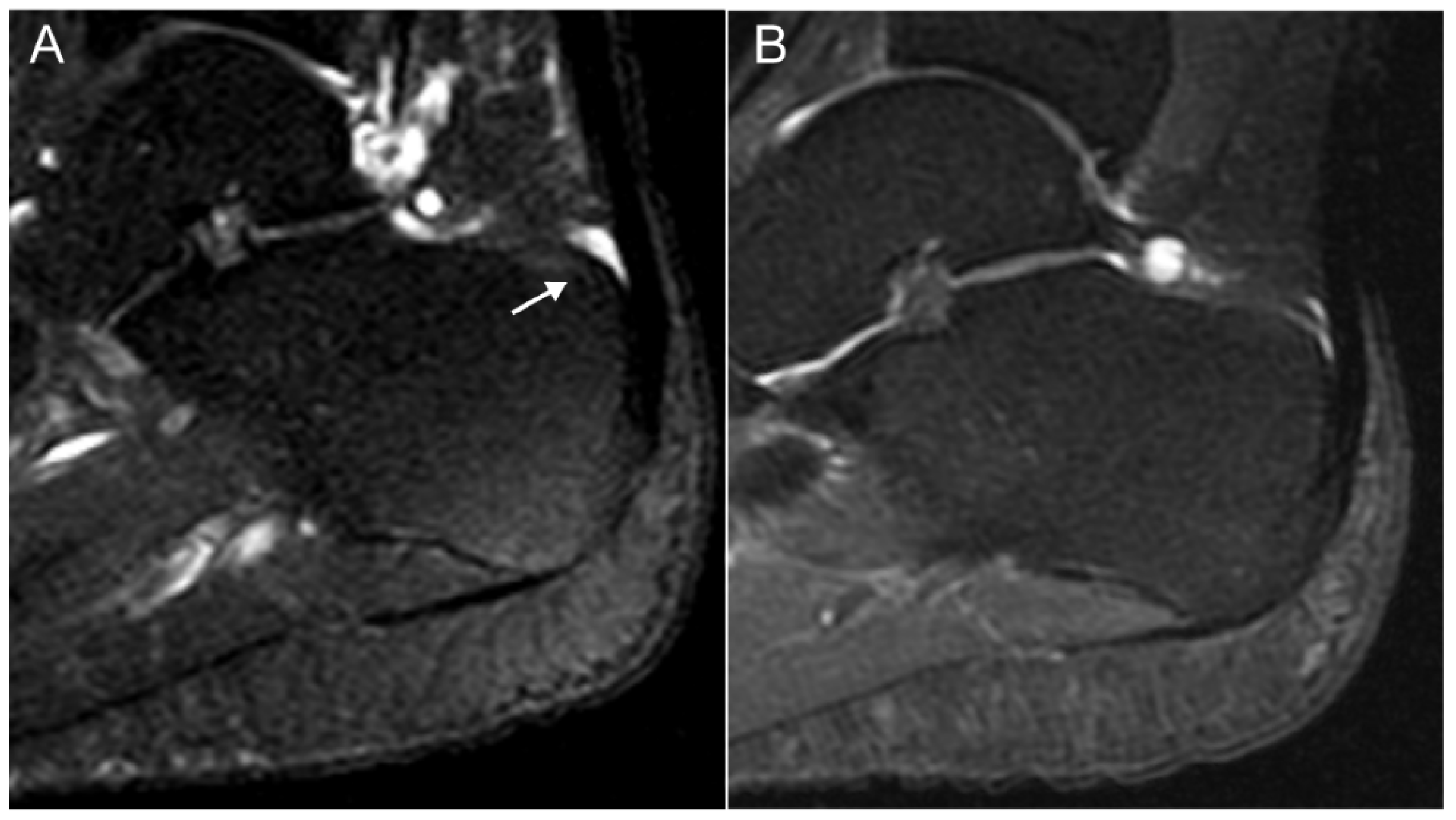
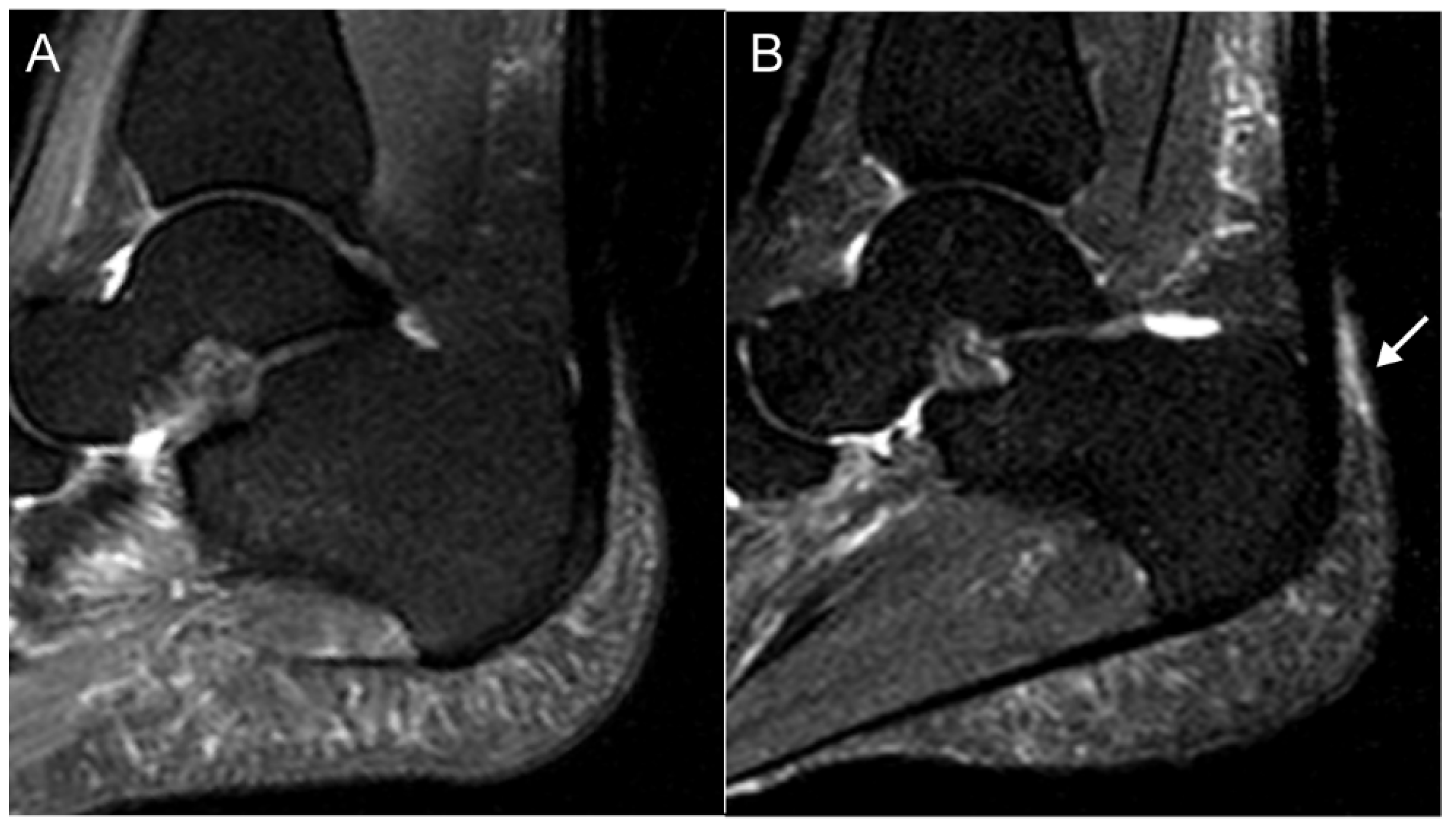
| Disease Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pso | PsA | AS | All | |
| Total one year intervals, N | 24 | 24 | 24 | 72 |
| Demographics | ||||
| Male gender, n (%): | 12 (50.0) | 18 (75.0) | 18 (75.0) | 48 (66.7) |
| Age, median (IQR): | 42.2 (34.7–53.4) | 50.9 (40.6–52.9) | 49.1 (38.8–52.2) | 49.2 (36.8–52.8) |
| Disease duration in years, median (IQR) | 22.5 (14.4–42.2) | 7.8 (0.9–12.6) | 8.7 (3.4–17.2) | NA |
| General disease activity: | ||||
| Pso: moderate-severe psoriasis, n (%) | 5 (20.8) | NA | NA | NA |
| PsA: MDA, n (%) | NA | 11 (45.8) | NA | NA |
| Missing, n (%) | NA | 3 (12.5) | NA | NA |
| AS: BASDAI score ≥ 4, n (%) | NA | NA | 22 (91.7) | NA |
| Medication: | ||||
| Current DMARD use, n (%): | 0 | 4 (16.7) | 1 (4.2) | 5 (6.6) |
| Current NSAID use, n (%): | 2 (8.3) | 7(29.2) | 16 (66.7) | 25 (34.7) |
| Missing, n (%) | 1 (4.2) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.4) |
| Inflammatory markers: | ||||
| ESR, median (IQR): | 4.0 (2.0–10.0) | 4.0 (2.0–6.0) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 4.0 (2.0–6.5) |
| Missing, n (%) | 2 (8.0) | 0 | 1 | 2 (2.8) |
| CRP, median (IQR): | 2.5 (0.9–5.7) | 3.0 (1.6–4.6) | 1.6 (0.9–4.4) | 2.8 (1.2–4.5) |
| Missing, n (%) | 2 (8.0) | 0 | 1 | 3 (4.2) |
| Local disease activity at the enthesis: | ||||
| Achilles tendon, N enthesis | 48 | 48 | 48 | 144 |
| Clinical enthesitis, n (%) | 2 (4.2) | 1 (2.1) | 3 (6.3) | 6 (4.2) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 4 (8.3) | 6 (12.5) | 10 (6.9) |
| Plantar fascia, N enthesis | 48 | 48 | 48 | 144 |
| Clinical enthesitis, n (%) | 1 (2.1) | 4 (8.3) | 2 (4.2) | 7 (4.9) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 4 (8.3) | 6 (12.5) | 10 (6.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kleinrensink, N.J.; Foppen, W.; Katen, I.t.; Leijten, E.F.A.; de Jong, P.A.; Spierings, J. Longitudinal Follow-Up Using the Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (HEMRIS) Shows Minimal Changes in Heel Enthesitis Assessed in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriasis Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111765
Kleinrensink NJ, Foppen W, Katen It, Leijten EFA, de Jong PA, Spierings J. Longitudinal Follow-Up Using the Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (HEMRIS) Shows Minimal Changes in Heel Enthesitis Assessed in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriasis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111765
Chicago/Turabian StyleKleinrensink, Nienke J., Wouter Foppen, Iris ten Katen, Emmerik F. A. Leijten, Pim A. de Jong, and Julia Spierings. 2022. "Longitudinal Follow-Up Using the Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (HEMRIS) Shows Minimal Changes in Heel Enthesitis Assessed in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriasis Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111765
APA StyleKleinrensink, N. J., Foppen, W., Katen, I. t., Leijten, E. F. A., de Jong, P. A., & Spierings, J. (2022). Longitudinal Follow-Up Using the Heel Enthesitis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System (HEMRIS) Shows Minimal Changes in Heel Enthesitis Assessed in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriasis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111765







