Efficacy of an Online Educational Intervention in Reducing Body Weight in the Pre-Diabetic Population of 18–45 Years Old, a Randomized Trial Protocol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
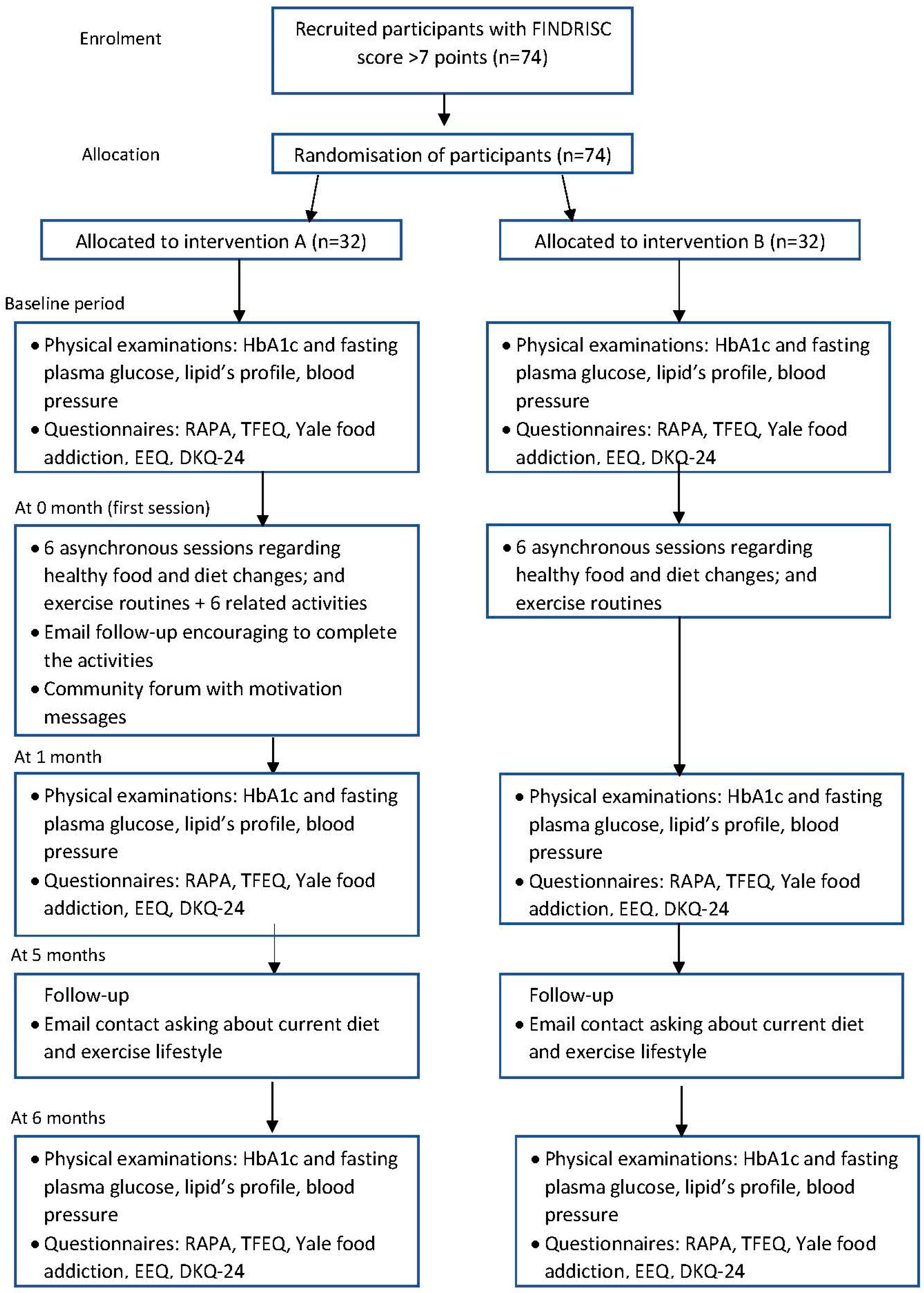
2.1. Study Design and Settings
2.2. Participants: Eligibility, Recruitment, and Allocation
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Recruitment
2.5. Allocation
2.6. Intervention
2.7. Outcomes of Interest
2.7.1. Primary Outcome
2.7.2. Secondary Outcomes
2.8. Data Analysis
2.8.1. Statistical Analysis
2.8.2. Data Management
2.8.3. Criteria for Discontinuation of Participation in the Study or of the Study
- If a participant withdraws consent for participation in the study.
- If their physician determines that the continuation of the intervention is not preferable for an individual patient. At the moment, there is no reason that can be used to exclude a patient from the trial apart from the aforementioned exclusion criteria, which might minimize bias affecting the results of the study.
- If the study protocol cannot be followed.
2.9. Monitoring
2.9.1. Protocol Amendments
2.9.2. Follow-Up of Adverse Events
2.10. Ethics and Dissemination
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Extremadura Govern. Integral Diabetes Plan in Extremadura. 2020–2024. Available online: https://www.fadex.org/bddocumentos/QBDTB-PIDIA-2020-2024.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Extremadura Govern. Integral Diabetes Plan in Extremadura. 2014–2018. Available online: https://saludextremadura.ses.es/filescms/web/uploaded_files/CustomContentResources/PIDIA2014-2018.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Formiga, F.; Camafort, M.; Carrasco-Sánchez, F.J. Heart failure and diabetes: The confrontation of two major epidemics of the 21st century. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2020, 220, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2019, 9th ed.; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133352_2406-IDF-ATLAS-SPAN-BOOK.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Rosenbloom, A.L.; Joe, J.R.; Young, R.S.; Winter, W.E. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Association of Diabetes. Professional Practice Committee: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinero-Fort, M.A.; Carrillo-De Santa Pau, E.; Abánades-Herranz, J.C.; Dujovne-Kohan, I.; Cárdenas-Valladolid, J. Riesgo basal de Diabetes Mellitus en Atención Primaria según cuestionario FINDRISC, factores asociados y evolución clínica tras 18 meses de seguimiento. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2010, 210, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, J.; Tuomilehto, J. The Diabetes Risk Score: A practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Cases, M.; Artola, S.; Escalada, J.; Ezkurra-Loyola, P.; Ferrer-García, J.C.; Fornos, J.A.; Girbés, J.; Rica, I. Consensus on the detection and management of prediabetes. Consensus and Clinical Guidelines Working Group of the Spanish Diabetes Society. Aten. Primaria 2015, 47, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriguer, F.; Valdés, S.; Tapia, M.J.; Esteva, I.; Ruiz De Adana, M.S.; Almaraz, M.C.; Morcillo, S.; García Fuentes, E.; Rodríguez, F.; Rojo-Martínez, G. Validation of the FINDRISC (FINnish Diabetes RIsk SCore) for prediction of the risk of type 2 diabetes in a population of southern Spain. Pizarra Study. Med. Clin. 2012, 138, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; et al. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus By Changes in Lifestyle Among Subjects With Impaired Glucose Tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, D.J.; Talton, J.; Dabelea, D.; Divers, J.; Imperatore, G.; Lawrence, J.M.; Liese, A.D.; Linder, B.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Pihoker, C.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes in U.S. youth in 2009: The SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DECODE Study Group, the European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Glucose tolerance and cardiovascular mortality: Comparison of fasting and 2-hour diagnostic criteria. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, N.R.; Shyangdan, D.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Suri, G.; Hall, B. Screening for type 2 diabetes: A short report for the National Screening Committee. Health Technol. Assess. 2013, 17, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, A.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Schulze, J.; Bornstein, S.R.; Schwarz, P.E. A simplified Finnish diabetes risk score to predict type 2 diabetes risk and disease evolution in a German population. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, P.E.; Lindström, J.; Kissimova-Scarbeck, K.; Szybinski, Z.; Barengo, N.C.; Peltonen, M.; Tuomilehto, J. DE-PLAN project. The European perspective of type 2 diabetes prevention: Diabetes in Europe—Prevention using lifestyle, physical activity and nutritional intervention (DE-PLAN) project. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 116, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, P.E.; Gruhl, U.; Bornstein, S.R.; Landgraf, R.; Hall, M.; Tuomilehto, J. The European Perspective on Diabetes Prevention: Development and Implementation of An European Guideline and training standards for diabetes prevention (IMAGE). Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2007, 4, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, J.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Peltonen, M.; Aunola, S.; Eriksson, J.G.; Hemiö, K.; Hämäläinen, H.; Härkönen, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; et al. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: Follow-up of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet 2006, 368, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; An, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Morbidity and mortality after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance: 30-year results of the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renders, C.M.; Valk, G.D.; Griffin, S.J.; Wagner, E.; van Eijk, J.T.; Assendelft, W.J.J. Interventions to improve the management of diabetes mellitus in primary care, outpatient and community settings. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, 24, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.A.; Colagiuri, S.; Colagiuri, R. Individual patient education for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 1, CD005268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min-Hua, F.; Bing-Tong, H.; Ying-Chun, T.; Xiu-Hua, H.; Wei-Wei, D.; Le-Xin, W. Effect of individualized diabetes education for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A single-center randomized clinical trial. Afr. Health Sci. 2016, 16, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemcová, J.; Hlinková, E. The efficacy of diabetic foot care education. J. Clin. Nurs. 2013, 23, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Cuesta, T.; Cura-González, M.I.; del Azcoaga-Lorenzo, A.; González-González, A.I.; Tello-Bernabé, M.E.; Rodríguez-Gabriel, G.; Artola-Méndez, S.; Girbés-Fontana, M.; López, A. Systematic review of group educational interventions in type-2 diabetes patients. Aten. Primaria 2005, 36, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, J.L.; Andújar, I.; Páez, J. Evaluation of the assessment of diabetic patients and the diabetology education at the Servicio Andalud de Salud in Malaga (Spain). Rev. Int. De Cienc. Podol. 2012, 6, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, E.; Nooijer, J.; Schaper, N.C.; Schoonus-Spit, M.H.G.; Janssen, M.A.J.; Vries, N.K. Evaluation of the web-based Diabetes Interactive Education Programme (DIEP) for patients with type 2 diabetes. Patient Educ. Couns. 2012, 86, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavynejad, S.; Miladinia, M.; Jahangiri, M. A randomized trial of comparing video telecare education vs. in-person education on dietary regimen compliance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A support for clinical telehealth Providers. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Monro, J.; Venn, B.J. Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Altman, D.G.; Laupacis, A.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Krleža-Jerić, K.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Mann, H.; Dickersin, K.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. SPIRIT 2013 statement: Defining standard protocol items for clinical trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, E.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Collins, C.E.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Young, M.D.; Callister, R. Efficacy of the Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Using LifeStyle Education Program RCT. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 50, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Barrio, F.; Cabré, J.J.; Piñol, J.L.; Cos, X.; Solé, C.; Bolíbar, B.; Basora, J.; Castell, C.; Solà-Morales, O.; et al. Delaying progression to type 2 diabetes among high-risk Spanish individuals is feasible in real-life primary healthcare settings using intensive lifestyle intervention. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Barrio, F.; Piñol, J.L.; Cabré, J.J.; Mundet, X.; Sagarra, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Solà-Morales, O.; DE-PLAN-CAT/PREDICE Research Group. Shifting from glucose diagnosis to the new HbA1c diagnosis reduces the capability of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC) to screen for glucose abnormalities within a real-life primary healthcare preventive strategy. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, M.; De Berardis, G.; Rossi, M.C.; Sacco, M.; Belfiglio, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Tognoni, G.; Valentini, M.; Nicolucci, A. Use of the diabetes risk score for opportunistic screening of undiagnosed diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance: The IGLOO (Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Long-Term Outcomes Observational) study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrilakis, K.; Liatis, S.; Grammatikou, S.; Perrea, D.; Stathi, C.; Tsiligros, P.; Katsilambros, N. Validation of the Finnish diabetes risk score (FINDRISC) questionnaire for screening for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes, dysglycaemia and the metabolic syndrome in Greece. Diabetes Metab. 2011, 37, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirao i Goris, J.A. Development and Validation of the European Spanish Version of the Rapid Physical Activity Assessment Scale (RAPA). Thesis dissertation non published, University of Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jáuregui-Lobera, I.; García-Cruz, P.; Carbonero-Carreño, R.; Magallares, A.; Ruiz-Prieto, I. Psychometric Properties of Spanish Version of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R18 (Tfeq-Sp) and Its Relationship with Some Eating- and Body Image-Related Variables. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5619–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granero, R.; Hilker, I.; Agüera, Z.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Sauchelli, S.; Islam, M.A.; Fagundo, A.B.; Sánchez, I.; Riesco, N.; Dieguez, C.; et al. Food Addiction in a Spanish Sample of Eating Disorders: DSM-5 Diagnostic Subtype Differentiation and Validation Data. Eur. Eat Disord. Rev. 2014, 22, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabéu, E.; Marchena, C.; Iglesias, M.T. Factor Structure and Psychometric Properties of Emotional Eater Questionnaire (EEQ) in Spanish Colleges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.A.; Villagomez, E.T.; Brown, S.A.; Kouzekanani, K.; Hanis, C.L. The Starr County Diabetes Education Study Development of the Spanish-language diabetes knowledge questionnaire. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.K.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Weinhold, K.R. Early Weight-Loss Success Identifies nonresponders after a Lifestyle Intervention in a Worksite Diabetes Prevention Trial. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet 2015, 115, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendzerska, T.; Zhu, D.T.; Gershon, A.S.; Edwards, J.D.; Peixoto, C.; Robillard, R.; Kendall, C.E. The Effects of the Health System Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic on Chronic Disease Management: A Narrative Review. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Durán, M.d.V.; Basilio-Fernández, B.; Gómez-Luque, A.; Alfageme-García, P.; Clavijo-Chamorro, M.Z.; Jiménez-Cano, V.M.; Fabregat-Fernández, J.; Robles-Alonso, V.; Hidalgo-Ruiz, S. Efficacy of an Online Educational Intervention in Reducing Body Weight in the Pre-Diabetic Population of 18–45 Years Old, a Randomized Trial Protocol. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101669
Ramírez-Durán MdV, Basilio-Fernández B, Gómez-Luque A, Alfageme-García P, Clavijo-Chamorro MZ, Jiménez-Cano VM, Fabregat-Fernández J, Robles-Alonso V, Hidalgo-Ruiz S. Efficacy of an Online Educational Intervention in Reducing Body Weight in the Pre-Diabetic Population of 18–45 Years Old, a Randomized Trial Protocol. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(10):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101669
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Durán, María del Valle, Belinda Basilio-Fernández, Adela Gómez-Luque, Pilar Alfageme-García, María Zoraida Clavijo-Chamorro, Víctor Manuel Jiménez-Cano, Juan Fabregat-Fernández, Vicente Robles-Alonso, and Sonia Hidalgo-Ruiz. 2022. "Efficacy of an Online Educational Intervention in Reducing Body Weight in the Pre-Diabetic Population of 18–45 Years Old, a Randomized Trial Protocol" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 10: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101669
APA StyleRamírez-Durán, M. d. V., Basilio-Fernández, B., Gómez-Luque, A., Alfageme-García, P., Clavijo-Chamorro, M. Z., Jiménez-Cano, V. M., Fabregat-Fernández, J., Robles-Alonso, V., & Hidalgo-Ruiz, S. (2022). Efficacy of an Online Educational Intervention in Reducing Body Weight in the Pre-Diabetic Population of 18–45 Years Old, a Randomized Trial Protocol. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(10), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101669






