Non-linear and Interaction Analyses of Biomarkers for Organ Dysfunctions as Predictive Markers for Sepsis: A Nationwide Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
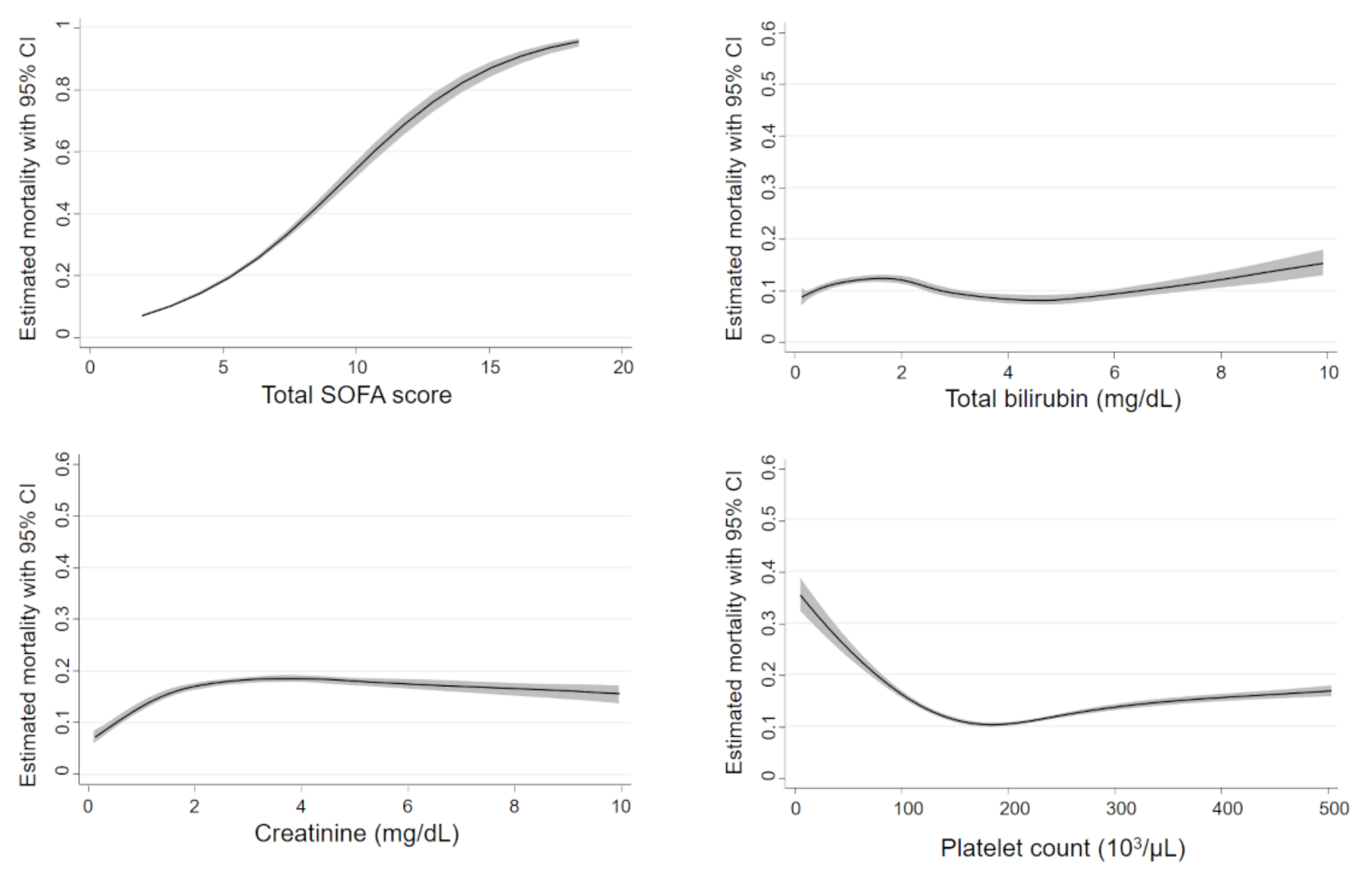
3.2. Non-linear Associations between Mortality and Biomarkers
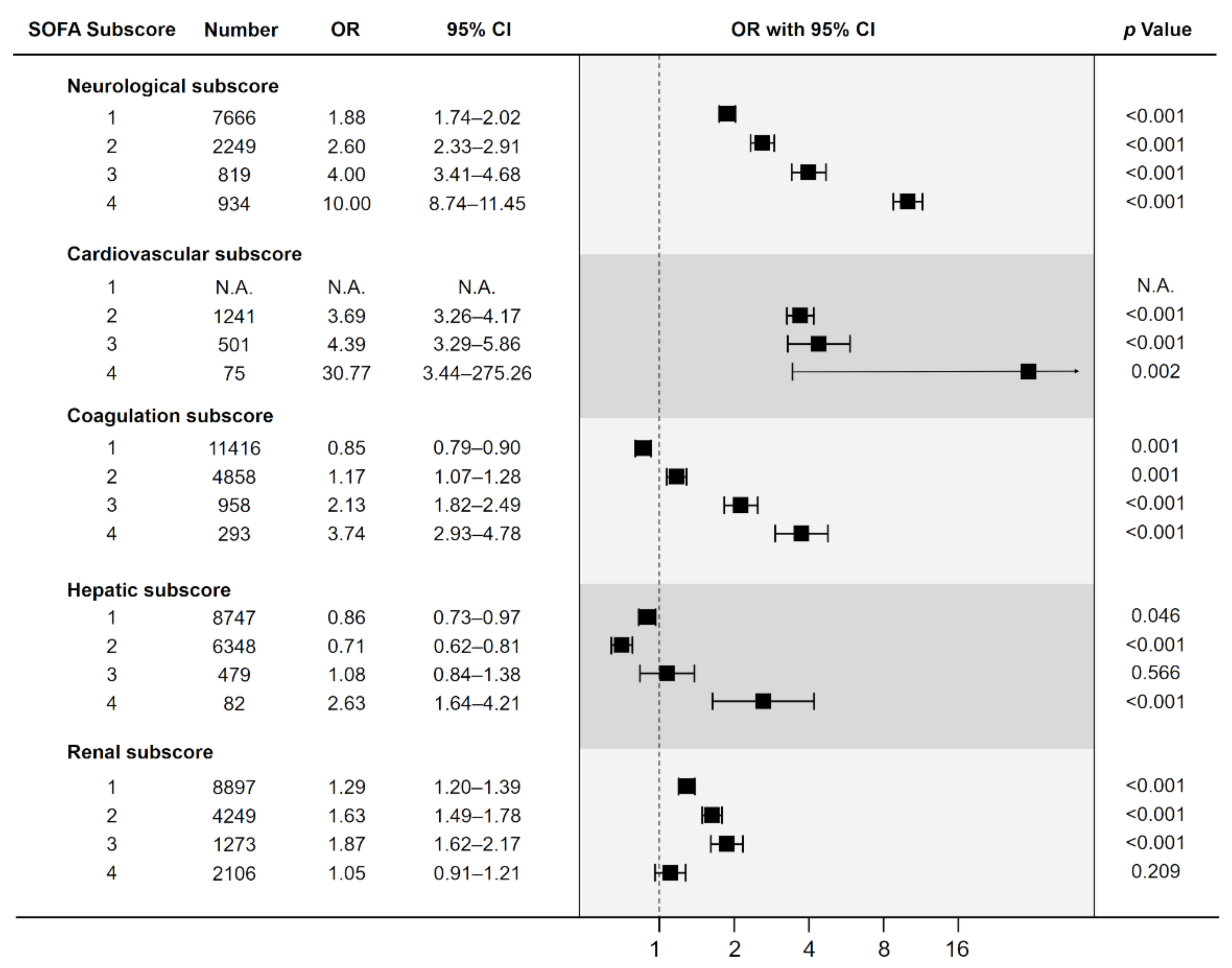
3.3. Risk of Death according to the Increase of SOFA Subscores
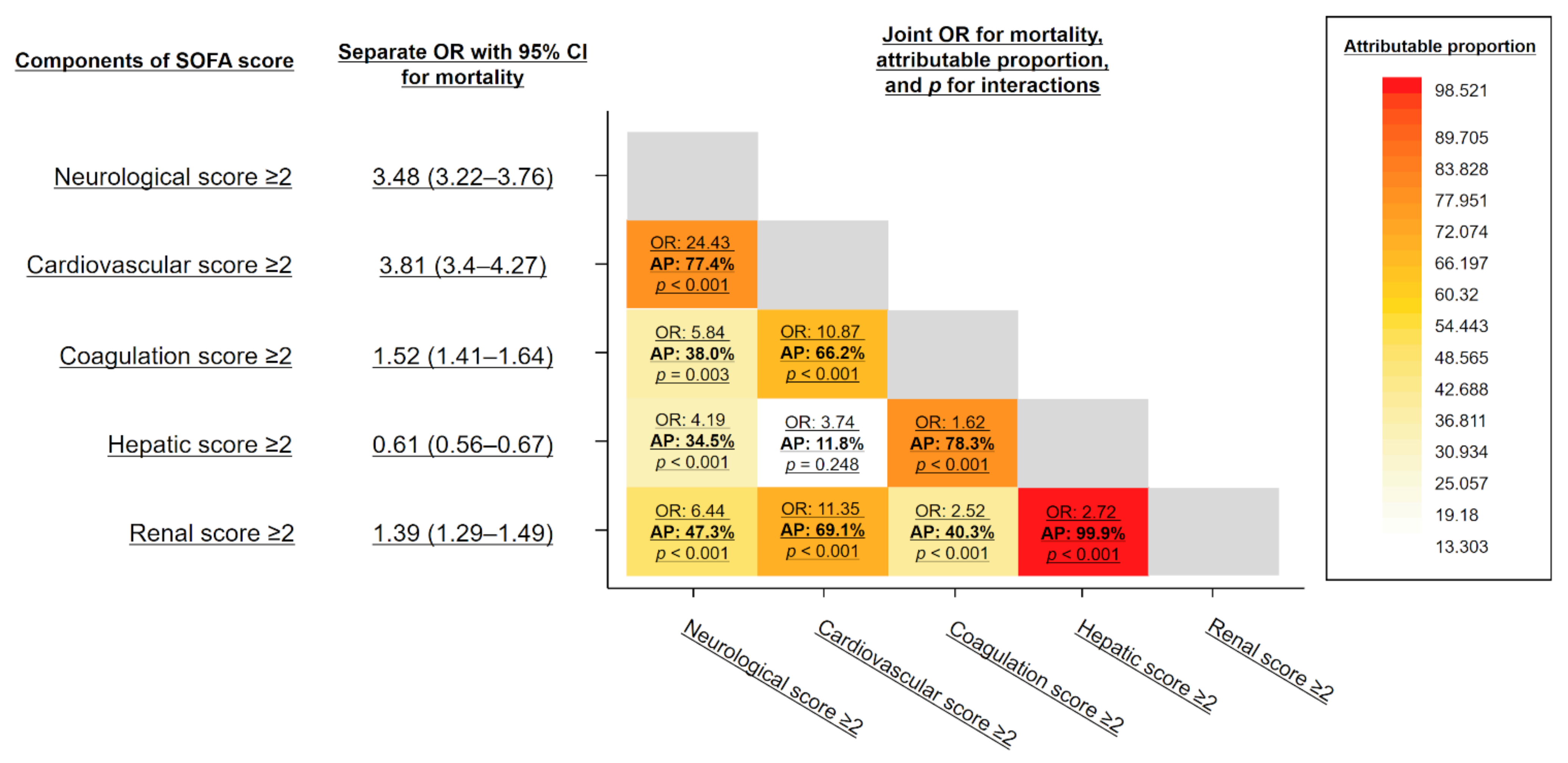
3.4. Interaction between SOFA Subscores
4. Discussion
4.1. Prognostic Association in SOFA Subscores
4.2. Interaction of Subscores
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar-Hari, M.; Phillips, G.S.; Levy, M.L.; Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Deutschman, C.S.; Angus, D.C.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Singer, M.; Sepsis Definitions Task Force. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: For the Third Interna-tional Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sep-sis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; de Mendonça, A.; Cantraine, F.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Suter, P.M.; Sprung, C.L.; Colardyn, F.; Blecher, S. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: Results of a multicenter, prospective study. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grooth, H.J.; Geenen, I.L.; Girbes, A.R.; Vincent, J.L.; Parienti, J.J.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M. SOFA and mortality endpoints in randomized controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raith, E.P.; Udy, A.A.; Bailey, M.; McGloughlin, S.; MacIsaac, C.; Bellomo, R.; Pilcher, D.V.; Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society (ANZICS) Centre for Outcomes and Resource Evaluation (CORE). Prognostic accuracy of the SOFA score, SIRS criteria, and qSOFA score for in-hospital mortality among adults with suspected infection admitted to the intensive care unit. JAMA 2017, 317, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Pool, R.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Mechanisms of organ dysfunction in sepsis. Crit. Care Clin. 2018, 34, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, N.; Wang, Y. Penalized nonlinear mixed effects model to identify biomarkers that predict disease progression. Biometrics 2017, 73, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsubara, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Umemura, Y.; Gando, S.; Ogura, H.; Shiraishi, A.; Kushimoto, S.; Abe, T.; Tarui, T.; Hagiwara, A.; et al. Significance of plasma fibrinogen level and antithrombin activity in sepsis: A multicenter cohort study using a cubic spline model. Thromb. Res. 2019, 181, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.-C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med. Care 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; Linde-Zwirble, W.T.; Lidicker, J.; Clermont, G.; Carcillo, J.; Pinsky, M.R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.S.; Mannino, D.; Eaton, S.; Moss, M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamakawa, K.; Ohbe, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Matsui, H.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H. Time trends of the outcomes and treatment options for disseminated intravascular coagulation: A nationwide observational study in Japan. JMA J. 2020, 3, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic Regression, and Survival Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, G.G.; Griffiths, W.E.; Hill, R.C.; Lütkepohl, H.; Lee, T.C. The Theory and Practice of Econometrics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- VanderWeele, T.J. Reconsidering the denominator of the attributable proportion for interaction. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 28, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harell, F.E., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies. Package ‘rms’. 2018. Available online: https://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/rms/rms.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Ferreira, F.L.; Bota, D.P.; Bross, A.; Mélot, C.; Vincent, J.L. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA 2001, 286, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkata, C.; Kashyap, R.; Farmer, J.C.; Afessa, B. Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with sepsis: Incidence, risk factors, and its association with clinical outcome. J. Intensiv. Care 2013, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.J.; Taneja, A.; Niccum, D.; Kumar, G.; Jacobs, E.; Nanchal, R. The association of serum bilirubin levels on the outcomes of severe sepsis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 30, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivet, F.G.; Kleinknecht, D.J.; Loirat, P.; Landais, P.J. Acute renal failure in intensive care units--causes, outcome, and prognostic factors of hospital mortality; a prospective, multicenter study. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, G.M.; Levy, E.M.; E Hammermeister, K.; Grover, F.; Daley, J. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendonça, A.; Vincent, J.L.; Suter, P.M.; Moreno, R.; Dearden, N.M.; Antonelli, M.; Takala, J.; Sprung, C.; Cantraine, F. Acute renal failure in the ICU: Risk factors and outcome evaluated by the SOFA score. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhel, F.; Peters-Sengers, H.; Falahi, F.; Scicluna, B.P.; van Vught, L.A.; Bonten, M.J.; Cremer, O.L.; Schultz, M.J.; van der Poll, T. The MARS consortium. Mortality and host response aberrations associated with transient and persistent acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with sepsis: A prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickkers, P.; Mehta, R.L.; Murray, P.T.; Joannidis, M.; Molitoris, B.A.; Kellum, J.A.; Bachler, M.; Hoste, E.A.J.; Hoiting, O.; Krell, K.; et al. Effect of human recombinant alkaline phosphatase on 7-day creatinine clearance in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Workgroup. Acute renal failure—Definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The second international consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative (ADQI) group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Uchino, S. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, R.; Sheu, C.-C.; Su, L.; Gong, M.N.; Tejera, P.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Convery, M.P.; Thompson, B.T.; Christiani, D.C. Serum bilirubin levels on ICU admission are associated with ARDS development and mortality in sepsis. Thorax 2009, 64, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonetto, D.A.; Gines, P.; Kamath, P.S. Hepatorenal syndrome: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. BMJ 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rao, P.N. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Warkentin, T.E.; Thachil, J.; van der Poll, T.; Levi, M.; Scientific and Standardization Committee on DIC; The Scientific and Standardization Committee on Perioperative and Critical Care of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Patient Characteristics | Total | Survivors | Non-Survivors | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 38,869 | n = 34,088 | n = 4781 | ||
| Age, years | 80 (69–86) | 79 (68–86) | 84 (76–89) | <0.001 |
| Sex, male | 22,904 (58.9%) | 20,132 (59.1%) | 2772 (58%) | 0.155 |
| Height (cm) | 158 (150–165) | 158 (150–165) | 155 (148–163) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 53.5 (45–63) | 54.1 (45.8–63.6) | 47.8 (40–56.2) | <0.001 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 5 (2–9) | 5 (2–10) | 5 (2–9) | <0.001 |
| Anatomical site of infection | <0.001 | |||
| Respiratory | 16,608 (42.7%) | 13,640 (40%) | 2968 (62.1%) | |
| Abdominal | 8777 (22.6%) | 7965 (23.4%) | 812 (17%) | |
| Urinary tract | 6477 (16.7%) | 6046 (17.7%) | 431 (9%) | |
| Bone/soft tissue | 1754 (4.5%) | 1645 (4.8%) | 109 (2.3%) | |
| Central nervous system | 555 (1.4%) | 496 (1.5%) | 59 (1.2%) | |
| Cardiovascular | 420 (1.1%) | 376 (1.1%) | 44 (0.9%) | |
| Other/Unclassifiable | 4278 (11%) | 3920 (11.5%) | 358 (7.5%) | |
| White blood cell count (103/µL) | 99 (68–138.4) | 99 (68.5–137.7) | 100 (66–145) | 0.200 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 8.2 (2.8–16.1) | 7.9 (2.6–15.7) | 10.2 (4.4–18.3) | <0.001 |
| Platelet count (103/µL) | 15.8 (11.8–21.9) | 15.8 (12–21.8) | 15.9 (10.7–23.2) | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1 (0.6–1.6) | 1 (0.6–1.7) | 0.8 (0.5–1.39) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.06 (0.74–1.69) | 1.04 (0.74–1.64) | 1.21 (0.77–2) | <0.001 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 76.3 (62–89) | 77.5 (64–90) | 67.8 (51.4–82.2) | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 130 (108–165) | 129 (109–163) | 133 (104–178) | 0.118 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.3 (2.8–3.8) | 3.4 (2.9–3.8) | 2.8 (2.3–3.3) | <0.001 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 23 (15.8–36.1) | 22 (15.2–34.1) | 32.4 (21.1–50) | <0.001 |
| Modified SOFA score total | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (3–6) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umemura, Y.; Yamakawa, K.; Murao, S.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Ogura, H.; Fujimi, S. Non-linear and Interaction Analyses of Biomarkers for Organ Dysfunctions as Predictive Markers for Sepsis: A Nationwide Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010044
Umemura Y, Yamakawa K, Murao S, Mitsuyama Y, Ogura H, Fujimi S. Non-linear and Interaction Analyses of Biomarkers for Organ Dysfunctions as Predictive Markers for Sepsis: A Nationwide Retrospective Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmemura, Yutaka, Kazuma Yamakawa, Shuhei Murao, Yumi Mitsuyama, Hiroshi Ogura, and Satoshi Fujimi. 2022. "Non-linear and Interaction Analyses of Biomarkers for Organ Dysfunctions as Predictive Markers for Sepsis: A Nationwide Retrospective Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010044
APA StyleUmemura, Y., Yamakawa, K., Murao, S., Mitsuyama, Y., Ogura, H., & Fujimi, S. (2022). Non-linear and Interaction Analyses of Biomarkers for Organ Dysfunctions as Predictive Markers for Sepsis: A Nationwide Retrospective Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010044







