Standardized Outcomes Measures in Physical Therapy Practice for Treatment and Rehabilitation of Cerebral PALSY: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
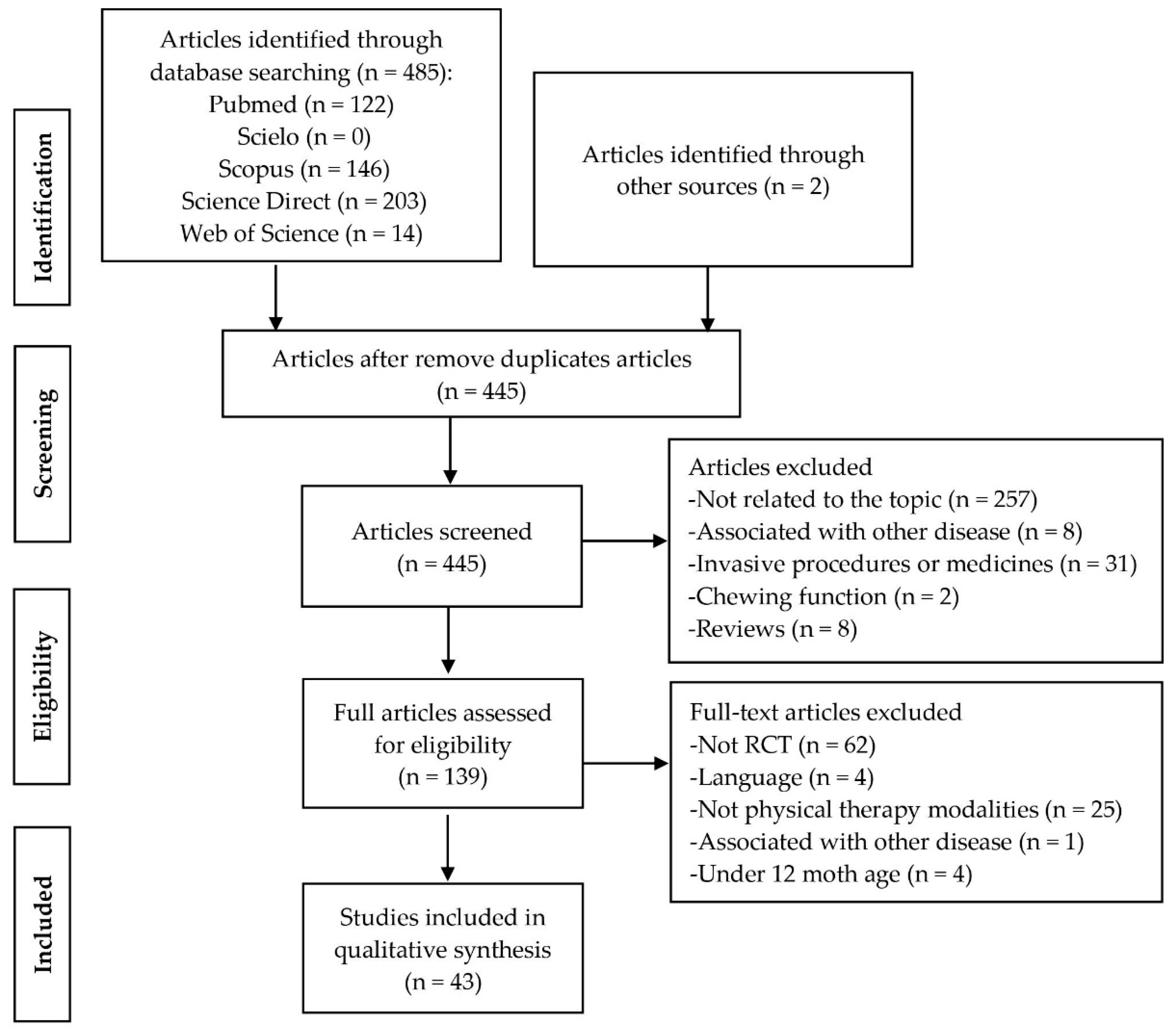
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Outcomes Measures
3.2.1. Variables
3.2.2. Instruments
3.3. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M. The Definition and Classification of Cerebral Palsy—A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral palsy: Current opinions on definition, epidemiology, risk factors, classification and treatment options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavsky, M.; Mor, O.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Greenbaum, S.; Than, N.G.; Erez, O. Cerebral palsy-trends in epidemiology and recent development in prenatal mechanisms of disease, treatment, and prevention. Front. Pediatrics 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Adde, L.; Blackman, J.; Boyd, R.N.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.; Darrah, J.; Eliasson, A.-C.; et al. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA 2017, 171, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imms, C.; Adair, B. Participation trajectories: Impact of school transitions on children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosa, M.; Marro, T.; Paolucci, S.; Morelli, D. Stability and harmony of gait in children with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Ali, A.; Kwon, M.; Lee, C.; Kim, Y.; Lee, G.; Kim, J. Effects of assisted aquatic movement and horseback riding therapies on emotion and brain activation in patients with cerebral palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 3283–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Obembe, A.O.; Dada, O.; Balogun, A.O.; Ojo, O.W.; Johnson, O.E. Standardized outcome measures for cerebral palsy among physiotherapists in southwestern Nigeria: Awareness, use, barriers, and facilitators. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2019, 35, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, F.; Neil, M.E.O. Cerebral Palsy; Springer: New York, 2006; p. 3145. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.P.; Ganesh, G.S. Evidence-based Approach to Physical Therapy in Cerebral Palsy. Indian J. Orthop. 2018, 52, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.E.; Fonner, V.A.; Armstrong, K.A.; Denison, J.A.; Yeh, P.T.; O’Reilly, K.R.; Sweat, M.D. The Evidence Project risk of bias tool: Assessing study rigor for both randomized and non-randomized intervention studies. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, R.D.; Politti, F.; Belina, S.F.; Collange Grecco, L.A.; Santos, C.A.; Dumont, A.J.L.; Lopes, J.B.P.; Cimolin, V.; Galli, M.; Santos Oliveira, C. Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined With Virtual Reality Training on Balance in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial. J. Mot. Behav. 2017, 49, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, C.; Herkenrath, P.; Hollmann, H.; Waltz, S.; Becker, I.; Hoebing, L.; Semler, O.; Hoyer-Kuhn, H.; Duran, I.; Hero, B.; et al. Early vibration assisted physiotherapy in toddlers with cerebral palsy—A randomized controlled pilot trial. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2016, 16, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, S.L.; Taylor, N.F.; Dodd, K.J.; Shields, N. An aerobic exercise program for young people with cerebral palsy in specialist schools: A phase I randomized controlled trial. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2017, 20, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilderley, A.J.; Fehlings, D.; Lee, G.W.; Wright, F.V. Comparison of a robotic-assisted gait training program with a program of functional gait training for children with cerebral palsy: Design and methods of a two group randomized controlled cross-over trial. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, D.J.; Woollacott, M.; Bencke, J.; Lauridsen, H.B.; Saavedra, S.; Bandholm, T.; Sonne-Holm, S. The functional effect of segmental trunk and head control training in moderate-to-severe cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2017, 21, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, N.; Chappell, A.; Blackmore, A.M.; Morris, S.; Williams, G.; Bear, N.; Allison, G. The effect of a running intervention on running ability and participation in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Yang, C.C.; Sun, S.H.; Chan, S.Y.; Wang, T.H.; Luo, H.J. Effects of hippotherapy on body functions, activities and participation in children with cerebral palsy based on ICF-CY assessments. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clutterbuck, G.L.; Auld, M.L.; Johnston, L.M. SPORTS STARS study protocol: A randomised, controlled trial of the effectiveness of a physiotherapist-led modified sport intervention for ambulant school-aged children with cerebral palsy. BMC Pediatrics 2018, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, L.E.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R.N. A randomized controlled trial of web-based training to increase activity in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Rao, B.K.; Senthil, K.D. Short-term balance training with computer-based feedback in children with cerebral palsy: A feasibility and pilot randomized trial. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2017, 20, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comans, T.; Mihala, G.; Sakzewski, L.; Boyd, R.N.; Scuffham, P. The cost-effectiveness of a web-based multimodal therapy for unilateral cerebral palsy: The Mitii randomized controlled trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-gohary, T.M.; Emara, H.A.; Al-Shenqiti, A.; Hegazy, F.A. Biodex balance training versus conventional balance training for children with spastic diplegia. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2017, 12, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, D.L.; Stanley, C.J.; Ohlrich, L.; Alter, K.E. Task-Specific and Functional Effects of Speed-Focused Elliptical or Motor-Assisted Cycle Training in Children with Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: Randomized Clinical Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shamy, S.M. Efficacy of Armeo® Robotic Therapy Versus Conventional Therapy on Upper Limb Function in Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatica-Rojas, V.; Méndez-Rebolledo, G.; Guzman-Muñoz, E.; Soto-Poblete, A.; Cartes-Velásquez, R.; Elgueta-Cancino, E.; Cofré Lizama, L.E. Does Nintendo Wii Balance Board improve standing balance? A randomized controlled trial in children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson, K.F.; Moreau, N.; Bodkin, A.W. Short-burst interval treadmill training walking capacity and performance in cerebral palsy: A pilot study. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2019, 22, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shamy, S.M. Effects of Antigravity Treadmill Training on Gait, Balance, and Fall Risk in Children With Diplegic Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hösl, M.; Böhm, H.; Eck, J.; Döderlein, L.; Arampatzis, A. Effects of backward-downhill treadmill training versus manual static plantarflexor stretching on muscle-joint pathology and function in children with spastic Cerebral Palsy. Gait Posture 2018, 65, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, Z.A.; Salem, I.A.; Ali, M.S. Effect of simultaneous proprioceptive-visual feedback on gait of children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2019, 19, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alwhaibi, R.; Alsakhawi, R.; ElKholi, S. Effects of auditovisual feedback on eye-hand coordination in children with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 101, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann-Reiffer, C.; Bastiaenen, C.H.G.G.; Meyer-Heim, A.D.; van Hedel, H.J.A.A. Effectiveness of robot-assisted gait training in children with cerebral palsy: A bicenter, pragmatic, randomized, cross-over trial (PeLoGAIT). BMC Pediatrics 2017, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassee, C.; Hunt, C.; Holmes, M.W.R.; Lloyd, M. Home-based Nintendo Wii training to improve upper-limb function in children ages 7 to 12 with spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy. J. Pediatric Rehabil. Med. 2017, 10, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pool, D.; Elliott, C.; Bear, N.; Donnelly, C.J.; Davis, C.; Stannage, K.; Valentine, J. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation-assisted gait increases muscle strength and volume in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-C.C.; Niu, X.-L.L.; Gao, Y.-R.R.; Wang, H.-B.B.; Hu, M.; Dong, L.-P.P.; Li, Y.-Z.Z. Therapeutic Effect Evaluation of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation With or Without Strengthening Exercise on Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Clin. Pediatrics 2018, 57, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusaini, A.A.; Fallatah, S.; Melam, G.R.; Buragadda, S. Efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation combined with therapeutic exercise on hand function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2019, 36, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inguaggiato, E.; Bolognini, N.; Fiori, S.; Cioni, G. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in unilateral cerebral palsy: A pilot study of motor effect. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 2184398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, R.C.F.; Santos, C.A.; Grecco, L.A.C.; Lazzari, R.D.; Dumont, A.J.L.; Duarte NC de, A.; Braun, L.A.; Lopes, J.B.P.; Santos, L.A.D.; Rodrigues, E.L.S.; et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation combined with upper limb functional training in children with spastic, hemiparetic cerebral palsy: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2016, 17, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Campos, M.E.; Rodriguez-Cervantes, N.; Reza-Lopez, S.; Avila-Esparza, M.; Chavez-Corral, D.V.; Levario-Carrillo, M. Body composition and newborn birthweight in pregnancies of adolescent and mature women. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 11, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, B. Rehabilitation treatment of spastic cerebral palsy with radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy and rehabilitation therapy. Medicine 2018, 97, e13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.V.; Lopes, J.B.P.; Duarte, N.A.C.; Galli, M.; Grecco, L.A.C.; Oliveira, C.S.; Villalta Santos, L.; Benite Palma Lopes, J.; Almeida Carvalho Duarte, N.; Galli, M.; et al. Effect of Anodic tDCS Over Motor Cortex Versus Cerebellum in Cerebral Palsy: A Study Protocol. Pediatric Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peungsuwan, P.; Parasin, P.; Siritaratiwat, W.; Prasertnu, J.; Yamauchi, J. Effects of Combined Exercise Training on Functional Performance in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized-Controlled Study. Pediatric Phys. Ther. 2017, 29, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schranz, C.; Kruse, A.; Belohlavek, T.; Steinwender, G.; Tilp, M.; Pieber, T.; Svehlik, M. Does Home-Based Progressive Resistance or High-Intensity Circuit Training Improve Strength, Function, Activity or Participation in Children With Cerebral Palsy? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 2457–2464.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillett, J.G.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Boyd, R.N.; Carty, C.P.; Barber, L.A. The effect of combined functional anaerobic and strength training on treadmill gait kinematics and kinetics in ambulatory young adults with cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 2019, 70, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.K.; Livanelioglu, A.; Yardimci, B.N.; Soylu, A.R.; Kaya Kara, O.; Livanelioglu, A.; Yardımcı, B.N.; Soylu, A.R. The Effects of Functional Progressive Strength and Power Training in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Pediatric Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.M.; Theis, N.; Kilbride, C.; Baltzopoulos, V.; Waugh, C.; Shortland, A.; Lavelle, G.; Noorkoiv, M.; Levin, W.; Korff, T. Strength Training for Adolescents with cerebral palsy (STAR): Study protocol of a randomised controlled trial to determine the feasibility, acceptability and efficacy of resistance training for adolescents with cerebral palsy. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutz, U.; Heussen, N.; Weigt-Usinger, K.; Leiz, S.; Raabe, C.; Polster, T.; Daniela, S.; Moll, C.; Lücke, T.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; et al. Impact of Hippotherapy on Gross Motor Function and Quality of Life in Children with Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Open-Label Crossover Study. Neuropediatrics 2018, 49, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Pazi, H.; Aran, A.; Pandyan, A.; Gelkop, N.; Ginsberg, G.; Pollak, Y.; Elnatan, D. Auditory stimulation improves motor function and caretaker burden in children with cerebral palsy—A randomized double blind study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrades-Caballero, E.; Santonja-Medina, C.S.; Sanz-Mengibar, J.M.; Santonja-Medina, F. Neurologic music therapy in upper-limb rehabilitation in children with severe bilateral cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziem, A.A.; El-Basatiny, H.M.Y. Effectiveness of backward walking training on walking ability in children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adar, S.; Dündar, Ü.; Demirda, Ü.S.; Ulaşlı, A.M.; Toktaş, H.; Solak, Ö. The effect of aquatic exercise on spasticity, quality of life, and motor function in cerebral palsy. Turk. Fiz. Tip Rehabil. Derg. 2017, 63, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, Y.-N.; Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Tankard, K.; Lee, J.; Song, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.-Q. Home-Based Versus Laboratory-Based Robotic Ankle Training for Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Randomized Comparative Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Q.; Habibullah, S.; Babur, M.N. The effects of traditional massage on spasticity of children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. JPMA 2020, 70, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Rha, D.; Park, E.S. Change in Pulmonary Function after Incentive Spirometer Exercise in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Study. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.; Whittingham, K.; Cunnington, R.; Boyd, R.N. Effect of mindfulness yoga programme MiYoga on attention, behaviour, and physical outcomes in cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Dev. Med. child Neurol. 2018, 60, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.L.; Silberstein, C.E.; Atkins, E.A.; Harryman, S.E.; Sponseller, P.D.; Hadley-Miller, N.A. Comparing reliability and validity of pediatric instruments for measuring health and well-being of children with spastic cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, B.J.; Allar, B.G.; Miller, P.E.; Matheney, T.H.; Snyder, B.D.; Fragala-Pinkham, M. Measuring the Reliability and Construct Validity of the Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory–Computer Adaptive Test (PEDI-CAT) in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.; Hickey, C.; Delahunt, E.; Walsh, M.; O’Brien, T. Six-minute walk test in children with spastic cerebral palsy and children developing typically. Pediatric Phys. Ther. 2016, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer-Henarejos, A.B.; Sǎnchez-Meca, J.; López-Pina, J.A.; Carles-Hernǎndez, R. Inter-and intra-rater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 576–590. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, M.; Long, T.; Kennedy, E.; Bavishi, S. The efficacy of GMFM-88 and GMFM-66 to detect changes in gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy (CP): A literature review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J. Sensitivity to functional improvements of GMFM-88, GMFM-66, and pedi mobility scores in young children with cerebral palsy. Percept. Mot. Skills 2014, 119, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebel, M.F.; Rodrigues, R.F.; Araújo AP de, Q.C.; Corrêa, C.L. Motor Prognosis and Current Perspectives in Cerebral Palsy. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2010, 20, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blair, E.; Langdon, K.; Mcintyre, S.; Lawrence, D.; Watson, L. Survival and Mortality in Cerebral Palsy: Observations to the Sixth Decade from a Data Linkage Study of a Total Population Register and National Death Index. BMC Neurology. 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Domain | Instrument | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body functions | b117—intellectual functions | German Bayley-II Mental Scale | Stark et al., 2016 |
| Conners’ Continuous Performance Test, Second Edition (CCPT) | Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| Communication Function Classification System (CFC) | Marrades-Caballero et al., 2018 | ||
| b440—respiration function | Spirometry | Choi et al., 2016 | |
| Peak flow meter | Choi et al., 2016 | ||
| b455—exercise tolerance | 6 Min Walk Test (6MWT) | Chen et al., 2016; Hilderley et al., 2016; Mitchell et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; Cleary et al., 2017; Peungsuwan et al., 2017; Mak et al., 2018; Schranz et al., 2018 | |
| Submaximal treadmill test | Cleary et al., 2017 | ||
| 10 m Shuttle Run Test (SRT) | Gibson et al., 2017 | ||
| 10 × 5 m Sprint Test | Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | ||
| b730—muscle power function | Muscle power sprint test | Cleary et al., 2017; Gibson et al., 2017; Clutterbuck et al., 2018; Schranz et al., 2018; Kara et al., 2019 | |
| Leg press | Kara et al., 2019 | ||
| Hand-held dynamometer | Pool et al., 2016; Kassee et al., 2017; El Shamy et al., 2018; Alhusaini et al., 2019; Inguaggiato et al., 2019; Kara et al., 2019 | ||
| Isokinetic dynamometer | Ryan et al., 2016; Damiano et al., 2017 | ||
| 30 s Sit-to-Stand Test (30sSTST) | Peungsuwan et al., 2017; Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| Lateral step-up test | Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| Half-kneel to stand | Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| Standing broad jump, vertical jump, and seated throw | Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | ||
| b735—muscle tone functions | Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) | Chen et al., 2016; Moura et al., 2016; Adar et al., 2017; El-Shamy et al., 2017; El Shamy et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2018; Mahmood et al., 2019 | |
| Ultrasonography | Adar et al., 2017 | ||
| Comprehensive Spasticity Scale (CSS) score | Qi et al., 2017 | ||
| Tardieu Scale | Hilderley et al., 2016 | ||
| b749—muscle function, other specified and unspecified | Ultrasonography | Hosl et al., 2018 | |
| Sit-and-reach test | Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| b755—involuntary movement reaction functions | Force plate | Lazzari et al., 2016; Gatica Rojas et al., 2017 | |
| Good balance system | Saxena et al., 2016 | ||
| Time Up and Go (TUG) | Chen et al., 2016; Hilderley et al., 2016; Lazzari et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; Adar et al., 2017; Peungsuwan et al., 2017; Bjornson et al., 2018; Clutterbuck et al., 2018; Hosl et al., 2018; Schranz et al., 2018; Kara et al., 2019 | ||
| Pediatric Balance Scale (PBS) | Chen et al., 2016; Lazzari et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; El-gohary et al., 2017 | ||
| Functional Reach Test (FRT) | Peungsuwan et al., 2017 | ||
| b760—control of voluntary movement functions | Segmental Assessment of Trunk Control (SATCo test) | Curtis et al., 2017 | |
| Chailey Levels of Ability | Marrades-Caballero et al., 2018 | ||
| Biodex Isokinetic Dynamometer | El-gohary et al., 2017 | ||
| Selective Control Assessment of the Lower Extremity (SCALE) | Chen et al., 2016; Pool et al., 2016; Ryan et al., 2016; Damiano et al., 2017 | ||
| Boyd and Graham’s ordinal scale | Pool et al., 2016 | ||
| b770—Gait pattern functions | 3D Gait Analysis (3DGA) | Abdel-aziem and El-Basatiny, 2016; Damiano et al., 2017; Hosl et al., 2018; Gillett et al., 2019 | |
| Gait Profile Score (GPS) | Schranz et al., 2018; Gillett et al., 2019 | ||
| Gait efficiency by Net nondimensional oxygen cost (NNcost) | Ryan et al., 2016 | ||
| Electronic walkway | Hilderley et al., 2016; Hussein et al., 2019 | ||
| Videography | Ryan et al., 2016; Hilderley et al., 2016 | ||
| b789—Movement functions, other specified and unspecified | Three dimensional analysis (3D) | Moura et al., 2016 | |
| Body structure | s770—additional musculoskeletal structures related to movement | Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Pool et al., 2016 |
| Electromyography | Moura et al., 2016 | ||
| Ultrasonography | Ryan et al., 2016; | ||
| Activities and participation | d420—transferring oneself/d469—walking and moving, other specified and unspecified | Gross Motor Function Classification System | Choi et al., 2016; Hilderley et al., 2016; Ryan et al., 2016; Adar et al., 2017; Kassee et al., 2017; Clutterbuck et al., 2018; Marrades-Caballero et al., 2018; Kara et al., 2019; Mahmood et al., 2019 |
| Gross Motor Function Measure Challenge Module (GMFM Challenge) | Hilderley et al., 2016; Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | ||
| GMFM-88 | Abdel-aziem and El-Basatiny, 2016; Adar et al., 2017; El-gohary et al., 2017; Reiffer et al., 2017; Ben-Pazi et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2018; Kara et al., 2019; Mahmood et al., 2019 | ||
| GMFM-66 | Choi et al., 2016; Hilderley et al., 2016; Ryan et al., 2016; Stark et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; Curtis et al., 2017; Qi et al., 2017; Deutz et al., 2018; Hosl et al., 2018 | ||
| 1 Min Walk Test (1MWT) | Bjornson et al., 2018; Kara et al., 2019 | ||
| 10 m Walk Test (10 mWT) | Santos et al., 2016; Peungsuwan et al., 2017; Reiffer et al., 2017; Bjornson et al., 2018 | ||
| Test of Gross Motor Development-2 (TGMD-2) | Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | ||
| Peabody Developmental Motor Scales, Second Edition (PDMS-2) | El Shamy et al., 2018; Alwhaibi et al., 2020 | ||
| d445—hand and arm use | ABILHAND–kid’s questionnaire | Kassee et al., 2017 | |
| Quality of Upper Extremity Skills Test (QUEST) | Moura et al., 2016; El-Shamy et al., 2017; Ben-Pazi et al., 2018 | ||
| Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) | Kassee et al., 2017; Kara et al., 2019; Marrades-Caballero et al., 2018 | ||
| Melbourne Assessment of Unilateral Upper Limb Function-2 (Melbourne-2) | Kassee et al., 2017 | ||
| Goal Attainment Scaling (GAS) | Gibson et al., 2017 | ||
| High Level Mobility Assessment Tool (HiMAT) | Gibson et al., 2017 | ||
| Jebsen–Taylor Hand Function Test (JTHFT) | Alhusaini et al., 2019 | ||
| Box and Block Test (BBT) | Inguaggiato et al., 2019 | ||
| d450—walk | Accelerometer | Mitchell et al., 2016; Ryan et al., 2016; Cleary et al., 2017; Bjornson et al., 2018 | |
| Energy Expenditure Index | Schranz et al., 2018 | ||
| d920—recreation and leisure | Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE) | Hilderley et al., 2016; Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | |
| Preferences of Activities for Children (PAC) | Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | ||
| Personal factors | Quality of life | Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL)-CP | Adar et al., 2017 |
| Cerebral Palsy Quality of Life Questionnaire for Children (CP QOL Child) | Cleary et al., 2017; Clutterbuck et al., 2018; Mak et al., 2018 | ||
| Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ 28) | Deutz et al., 2018 | ||
| KIDSCREEN-27 parental version | Hilderley et al., 2016; Deutz et al., 2018 | ||
| Cerebral Palsy Quality of Life Questionnaire for Adolescents | Mak et al., 2018 |
| Variable | Instrument | Authors |
|---|---|---|
| Functioning and disability | International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health-Children and Youth (ICF-CY) checklist | Hsieh et al., 2016; Pool et al., 2016; Curtis et al., 2017 |
| 28-Item Mobility Questionnaire | Mitchell et al., 2016; Mak et al., 2018 | |
| Activity Scale for Kids (ASK) | Hilderley et al., 2016; Bjornson et al., 2018 | |
| Assessment of Life Habits (LIFE-H) | Mitchell et al., 2016; Ryan et al., 2016; Bjornson et al., 2018 | |
| Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) | Comans et al., 2017 | |
| Canadian Occupational Performance Measure (COPM) | Hilderley et al., 2016; Comans et al., 2017; Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | |
| Functional Mobility Scale (FMS) | Clutterbuck et al., 2018 | |
| Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI-G; PEDI; PEDI-CAT) | Hilderley et al., 2016; Stark et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; Curtis et al., 2017; Damiano et al., 2017 | |
| Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instrument (POCCI) | Damiano et al., 2017 | |
| Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) | Bjornson et al., 2018 | |
| Timed Stairs Test (TST) | Schranz et al., 2018 | |
| Wee Functional Independence Measure (WeeFIM) | Adar et al., 2017 |
| Study | Item 1 | Item 2 | Item 3 | Item 4 | Item 5 | Item 6 | Item 7 | Item 8 | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Participant Representativeness | Equivalence of Comparison Groups | |||||||
| Abdel-aziem (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Adar (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Alhusaini (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Benpazi (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Bjornson (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Kai Chen (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Choi (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Cleary (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Clutterbuck (2018) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Comans (2017) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 6/8 |
| Curtis (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Damiano (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Deutz (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| El-gohary (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| El-shamy (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| El-shamy (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Gatica Rojas (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Gibson (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Gillett (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Hilderley (2016) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 4/8 |
| Hosl (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | 6/8 |
| Hsieh (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Hussein (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Inguaggiato (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | 6/8 |
| Kassee (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Kayakara (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Lazzari (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Lin (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Mahmood (2019) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Mak (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | 6/8 |
| Marrades-caballero (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Mitchel (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Moura (2016) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | 3/8 |
| Peungsuwan (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Pool (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Qi (2017) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | 6/8 |
| Reem (2020) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Reiffer (2017) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | 3/8 |
| Ryan (2016) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | 3/8 |
| Saxena (2016) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Schranz (2018) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 5/8 |
| Stark 2016 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/8 |
| Villaltasantos (2019) | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | 3/8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apolo-Arenas, M.D.; Jerônimo, A.F.d.A.; Caña-Pino, A.; Fernandes, O.; Alegrete, J.; Parraca, J.A. Standardized Outcomes Measures in Physical Therapy Practice for Treatment and Rehabilitation of Cerebral PALSY: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070604
Apolo-Arenas MD, Jerônimo AFdA, Caña-Pino A, Fernandes O, Alegrete J, Parraca JA. Standardized Outcomes Measures in Physical Therapy Practice for Treatment and Rehabilitation of Cerebral PALSY: A Systematic Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(7):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070604
Chicago/Turabian StyleApolo-Arenas, Maria Dolores, Aline Ferreira de Araújo Jerônimo, Alejandro Caña-Pino, Orlando Fernandes, Joana Alegrete, and Jose Alberto Parraca. 2021. "Standardized Outcomes Measures in Physical Therapy Practice for Treatment and Rehabilitation of Cerebral PALSY: A Systematic Review" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 7: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070604
APA StyleApolo-Arenas, M. D., Jerônimo, A. F. d. A., Caña-Pino, A., Fernandes, O., Alegrete, J., & Parraca, J. A. (2021). Standardized Outcomes Measures in Physical Therapy Practice for Treatment and Rehabilitation of Cerebral PALSY: A Systematic Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(7), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070604









