Unique Polymorphisms at BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB and HBB Loci Associated with HbF in Kuwaiti Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genotype Determination
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. BCL11A Locus
3.3. HBS1L-MYB Intergenic Region
3.4. HBB Locus
3.5. Chromosome X Associations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menzel, S.; Jiang, J.; Silver, N.; Gallagher, J.; Cunningham, J.; Surdulescu, G.; Lathrop, M.; Farrall, M.; Spector, T.D.; Thein, S.L. The HBS1L-MYB intergenic region on chromosome 6q23.3 influences erythrocyte, platelet, and monocyte counts in humans. Blood 2007, 110, 3624–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, S.L.; Menzel, S. Discovering the genetics underlying foetal haemoglobin production in adults. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, M.; Galanello, R.; Sanna, S.; Lettre, G.; Sankaran, V.G.; Chen, W.; Usala, G.; Busonero, F.; Maschio, A.; Albai, G.; et al. Genome-wide association study shows BCL11A associated with persistent fetal hemoglobin and amelioration of the phenotype of beta-thalassemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekile, A.D.; Gu, L.H.; Baysal, E.; Haider, M.Z.; Al-Fuzae, L.; Aboobacker, K.C.; Al-Rashied, A.; Huisman, T.H. Molecular characterization of alpha-thalassemia determinants, beta-thalassemia alleles, and beta S haplotypes among Kuwaiti Arabs. Acta Haematol. 1994, 92, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekile, A.D.; Haider, M.Z. Morbidity, beta S haplotype and alpha-globin gene patterns among sickle cell anemia patients in Kuwait. Acta Haematol. 1996, 96, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, G.; Palmer, C.D.; Sankaran, V.G.; Orkin, S.H.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Lettre, G. Fine-mapping at three loci known to affect fetal hemoglobin levels explains additional genetic variation. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekile, A.; Menzel, S.; Gupta, R.; Al-Sharida, S.; Farag, A.; Haider, M.; Akbulut, N.; Mustafa, N.; Thein, S.L. Response to hydroxyurea among kuwaiti patients with sickle cell disease and elevated baseline HbF levels. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, E138–E139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.; Bae, H.; Steinberg, M.H.; Sebastiani, P.; Solovieff, N.; Baldwin, C.T.; Melista, E.; Safaya, S.; Farrer, L.A.; Al-Suliman, A.M.; et al. Fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia: Genetic studies of the Arab-Indian haplotype. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2013, 51, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikho, E.M.; Farrell, J.J.; Alsultan, A.; Sebastiani, P.; Steinberg, M.H. Genetic determinants of HbF in Saudi Arabian and African Benin haplotype sickle cell anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E555–E557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adekile, A. The Genetic and Clinical Significance of Fetal Hemoglobin Expression in Sickle Cell Disease. Med. Princ. Pr. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikho, E.M.; Farrell, J.J.; Alsultan, A.; Qutub, H.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Figueiredo, M.S.; Chui, D.H.; Farrer, L.; Murphy, G.J.; Mostoslavsky, G.; et al. A phased SNP-based classification of sickle cell anemia HBB haplotypes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, S.L.; Menzel, S.; Peng, X.; Best, S.; Jiang, J.; Close, J.; Silver, N.; Gerovasilli, A.; Ping, C.; Yamaguchi, M.; et al. Intergenic variants of HBS1L-MYB are responsible for a major quantitative trait locus on chromosome 6q23 influencing fetal hemoglobin levels in adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11346–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettre, G.; Sankaran, V.G.; Bezerra, M.A.; Araújo, A.S.; Uda, M.; Sanna, S.; Cao, A.; Schlessinger, D.; Costa, F.F.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; et al. DNA polymorphisms at the BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB, and beta-globin loci associate with fetal hemoglobin levels and pain crises in sickle cell disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11869–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanello, R.; Sanna, S.; Perseu, L.; Sollaino, M.C.; Satta, S.; Lai, M.E.; Barella, S.; Uda, M.; Usala, G.; Abecasis, G.R.; et al. Ame-lioration of Sardinian beta0 thalassemia by genetic modifiers. Blood 2009, 114, 3935–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieff, N.; Milton, J.N.; Hartley, S.W.; Sherva, R.; Sebastiani, P.; Dworkis, D.A.; Klings, E.S.; Farrer, L.A.; Garrett, M.E.; Ashley-Koch, A.; et al. Fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia: Genome-wide association studies suggest a regulatory region in the 5′ olfactory receptor gene cluster. Blood 2010, 115, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, S.; Garner, C.; Gut, I.; Matsuda, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; Heath, S.; Foglio, M.; Zelenika, D.; Boland, A.; Rooks, H.; et al. A QTL influencing F cell production maps to a gene encoding a zinc-finger protein on chro-mosome 2p15. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, V.G.; Menne, T.F.; Xu, J.; Akie, T.E.; Lettre, G.; Van Handel, B.; Mikkola, H.K.A.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Cantor, A.B.; Orkin, S.H. Human Fetal Hemoglobin Expression Is Regulated by the Developmental Stage-Specific Repressor BCL11A. Science 2008, 322, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, P.; Purvis, S.; Barron-Casella, E.; DeBaun, M.R.; Casella, J.F.; Arking, D.E.; Keefer, J.R. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic variants influencing F-cell levels in sickle-cell patients. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 56, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, D.E.; Kamran, S.C.; Lessard, S.; Xu, J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Lin, C.; Shao, Z.; Canver, M.C.; Smith, E.C.; Pinello, L.; et al. An Erythroid Enhancer of BCL11A Subject to Genetic Variation Determines Fetal Hemoglobin Level. Science 2013, 342, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, P.J.; Sebastiani, P.; Edward, H.; Baldwin, C.T.; Gladwin, M.T.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Chui, D.; Steinberg, M.H. The genetics of hemoglobin A2regulation in sickle cell anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Ding, L.-H.; Story, M.D.; Steinberg, M.H.; Sebastiani, P.; Hoppe, C.; Ballas, S.K.; Pace, B.S. Original Research: A case-control genome-wide association study identifies genetic modifiers of fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell disease. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, P.; Farrell, J.; Alsultan, A.; Wang, S.; Edward, H.L.; Shappell, H.; Bae, H.; Milton, J.N.; Baldwin, C.; Al-Rubaish, A.; et al. BCL11A enhancer haplotypes and fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 54, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.J.; Sherva, R.M.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Luo, H.-Y.; Chu, B.F.; Ha, S.Y.; Li, C.K.; Lee, A.C.W.; Li, R.C.H.; Yuen, H.L.; et al. A 3-bp deletion in the HBS1L-MYB intergenic region on chromosome 6q23 is associated with HbF expression. Blood 2011, 117, 4935–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadhouders, R.; Aktuna, S.; Thongjuea, S.; Aghajanirefah, A.; Pourfarzad, F.; van Ijcken, W.; Lenhard, B.; Rooks, H.; Best, S.; Menzel, S.; et al. HBS1L-MYB intergenic variants modulate fetal hemoglobin via long-range MYB enhancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canver, M.C.; Lessard, S.; Pinello, L.; Wu, Y.; Ilboudo, Y.; Stern, E.N.; Needleman, A.J.; Galactéros, F.; Brugnara, C.; Kutlar, A.; et al. Variant-aware saturating mutagenesis using multiple Cas9 nucleases identifies regulatory elements at trait-associated loci. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsheye, I.; Solovieff, N.; Ngo, D.; Malek, A.; Sebastiani, P.; Steinberg, M.H.; Chui, D.H.l. Fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia: Molecular characterization of the unusually high fetal hemoglobin phenotype in African Americans. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemo, T.A.; Ojewunmi, O.O.; Oyetunji, I.A.; Rooks, H.; Rees, D.C.; Akinsulie, A.O.; Akanmu, A.S.; Thein, S.L.; Menzel, S. A survey of genetic fetal-haemoglobin modifiers in Nigerian patients with sickle cell anaemia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Cong, P.; Ye, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Cai, W.; et al. LOVD–DASH: A comprehensive LOVD database coupled with diagnosis and an at-risk assessment system for hemoglobinopathies. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekile, A.; Al-Kandari, M.; Haider, M.; Rajaa, M.; D’Souza, M.; Sukumaran, J. Hemoglobin F Concentration as a Function of Age in Kuwaiti Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Med Princ. Pr. 2007, 16, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
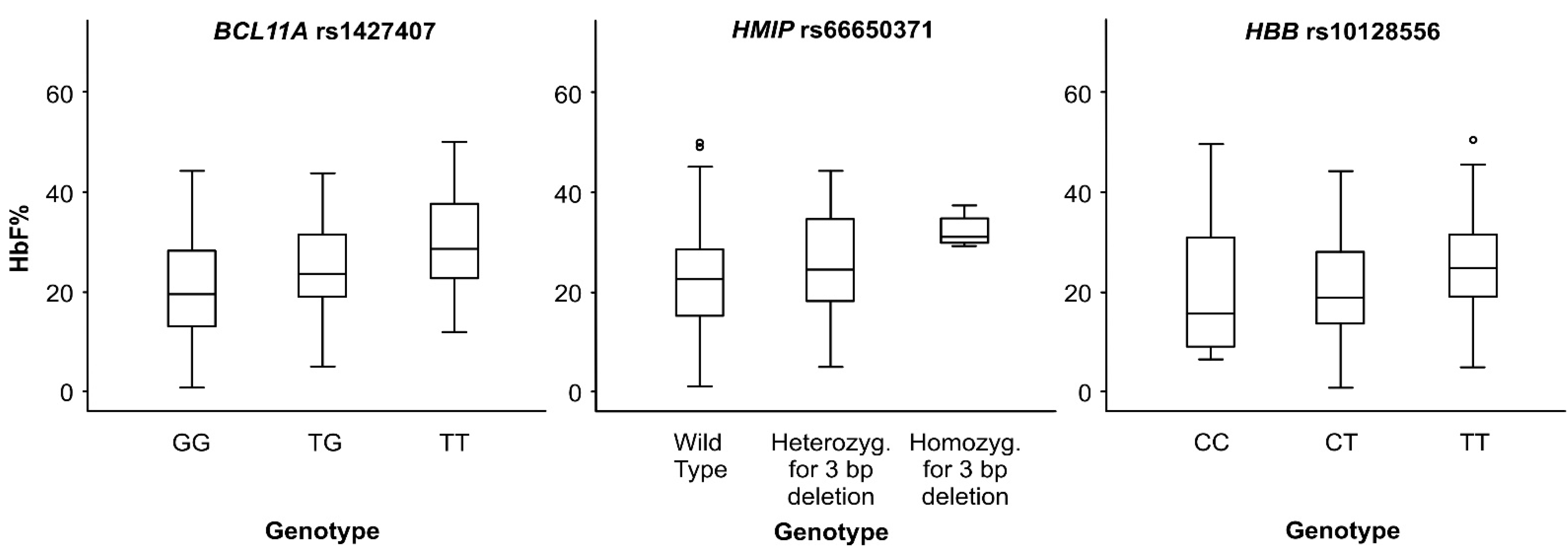
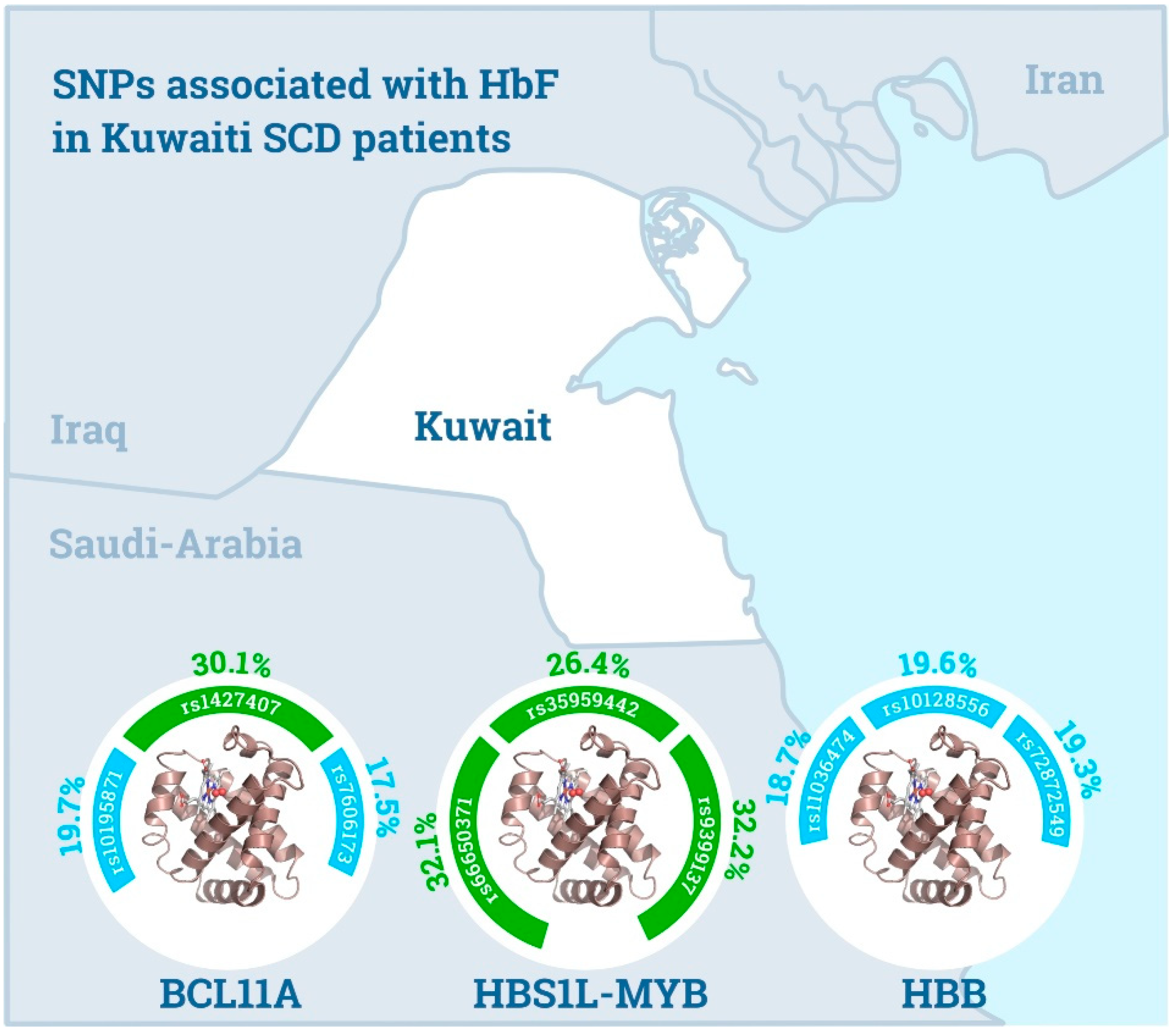
| Locus | SNP ID | BP | MAF | A1 | % R2 | HbF-1 | HbF-2 | HbF-3 | β | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | p | χ2 | p | χ2 | p | ||||||||
| BCL11A | rs1427407 | 60490908 | 0.2975 | T | 5.80 | 14.86 | 0.0003 | 17.31 | 3.32 × 10−5 | 9.97 | 0.0087 | 1.65 | 0.0023 |
| rs7606173 | 60498316 | 0.3249 | C | 1.70 | 16.46 | 6.13 × 10−5 | 9.99 | 0.0143 | 8.53 | 0.0103 | −1.27 | 9.17 × 10−5 | |
| rs10195871 | 60493454 | 0.4916 | G | 3.40 | 15.00 | 7.95 × 10−5 | 10.66 | 0.0234 | 6.22 | 0.0126 | −1.21 | 0.0003 | |
| rs7569946 | 60460824 | 0.3207 | A | 1.80 | 3.21 | 0.13169 | 0.80 | 0.4420 | 7.51 | 0.0061 | 0.59 | 0.0073 | |
| HBS1L-MYB | rs9399137 | 135097880 | 0.1181 | C | 0.10 | 3.33 | 0.1090 | 4.96 | 0.0259 | 9.49 | 0.0021 | 0.78 | 0.0056 |
| rs66650371 | 135097495 | 0.1181 | 2 * | 3.40 | 3.33 | 0.1090 | 5.33 | 0.0214 | 9.49 | 0.0021 | 0.78 | 0.0056 | |
| rs35786788 | 135097904 | 0.1181 | A | 0.20 | 3.33 | 0.1090 | 4.96 | 0.0259 | 9.17 | 0.0015 | 0.76 | 0.0043 | |
| rs35959442 | 135103041 | 0.1983 | G | 2.70 | 1.60 | 0.3053 | 2.77 | 0.0960 | 9.19 | 0.0025 | 0.76 | 0.0026 | |
| HBB | rs67385638 | 5269140 | 0.2089 | C | 1.70 | 19.22 | 1.65 × 10−5 | 19.82 | 9.96 × 10−6 | 3.65 | 0.1641 | −1.13 | 0.0002 |
| rs11036474 | 1253948 | 0.2131 | T | 1.50 | 18.13 | 2.65 × 10−5 | 18.22 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 3.43 | 0.0963 | −1.08 | 0.0002 | |
| rs10128556 | 5242453 | 0.2152 | C | 1.30 | 17.61 | 3.34 × 10−5 | 17.47 | 3.76 × 10−5 | 3.11 | 0.1849 | −1.07 | 0.0003 | |
| rs72872549 | 5268823 | 0.2152 | C | 1.70 | 16.48 | 4.95 × 10−5 | 15.45 | 0.0002 | 3.11 | 0.1849 | −1.07 | 0.0003 | |
| rs7482144 | 5254939 | 0.2574 | G | 1.20 | 15.25 | 0.0002 | 16.04 | 9.02 × 10−5 | 2.59 | 0.3364 | −1.08 | 0.0005 | |
| rs3759071 | 5270302 | 0.1160 | G | 0.20 | 1.45 | 0.2699 | 3.72 | 0.0804 | 8.55 | 0.0044 | 0.70 | 0.0100 | |
| Locus | Haplotype | HbF % | β | % R2 | % Frequency | p | SNPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCL11A | TAG | 25.96 | 4.83 | 11.00 | 27.91 | 3.00 × 10−7 | rs1427407|rs10195871|rs7606173 |
| GGC | 15.30 | −4.94 | 10.00 | 30.12 | 9.59 × 10−7 | rs1427407|rs10195871|rs7606173 | |
| HBS1L-MYB | 22GT * | 26.35 | 3.80 | 3.40 | 11.14 | 0.0040 | rs66650371|rs34778774|rs35959442|rs4895440 |
| 11CA ** | 18.66 | −3.13 | 3.80 | 77.02 | 0.0030 | rs66650371|rs34778774|rs35959442|rs4895440 | |
| HBB | TCATG | 24.00 | 2.49 | 3.10 | 72.14 | 0.0010 | rs10128556|rs11036474|rs7482144|rs72872549|rs67385638 |
| CTGCC | 16.20 | −3.40 | 6.00 | 19.36 | 0.0110 | rs10128556|rs11036474|rs7482144|rs72872549|rs67385638 |
| Locus | SNP ID | BP | MAF | A1 | % R2 | HbF-1 | HbF-2 | HbF-3 | β | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | p | χ2 | p | χ2 | p | ||||||||
| HBS1L-MYB | rs13220662 | 135074410 | 0.3418 | A | 1.5 | 1.66 | 0.2857 | 2.82 | 0.0930 | 6.16 | 0.0303 | 0.45 | 0.0387 |
| rs1406811 | 135118989 | 0.4726 | A | 1.6 | 0.31 | 0.5904 | 0.18 | 0.6737 | 6.72 | 0.0096 | −0.51 | 0.0118 | |
| HBB | rs3813726 | 5234759 | 0.2574 | T | 0.8 | 10.20 | 0.0014 | 8.81 | 0.0041 | 0.95 | 0.5765 | −0.83 | 0.0033 |
| rs72872549 | 5268823 | 0.2152 | C | 1.7 | 16.48 | 4.95 × 10−5 | 15.45 | 0.0001 | 3.11 | 0.1849 | −1.07 | 0.0003 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbulut-Jeradi, N.; Fernandez, M.J.; Al Khaldi, R.; Sukumaran, J.; Adekile, A. Unique Polymorphisms at BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB and HBB Loci Associated with HbF in Kuwaiti Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060567
Akbulut-Jeradi N, Fernandez MJ, Al Khaldi R, Sukumaran J, Adekile A. Unique Polymorphisms at BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB and HBB Loci Associated with HbF in Kuwaiti Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(6):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060567
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbulut-Jeradi, Nagihan, Maria Jinky Fernandez, Rasha Al Khaldi, Jalaja Sukumaran, and Adekunle Adekile. 2021. "Unique Polymorphisms at BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB and HBB Loci Associated with HbF in Kuwaiti Patients with Sickle Cell Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 6: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060567
APA StyleAkbulut-Jeradi, N., Fernandez, M. J., Al Khaldi, R., Sukumaran, J., & Adekile, A. (2021). Unique Polymorphisms at BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB and HBB Loci Associated with HbF in Kuwaiti Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(6), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060567






