Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subject Enrollment
2.2. Genomic DNA Isolation
2.3. Candidate Gene Sequencing of the DSPP Gene
2.4. Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.5. Haplotype Construction
3. Results
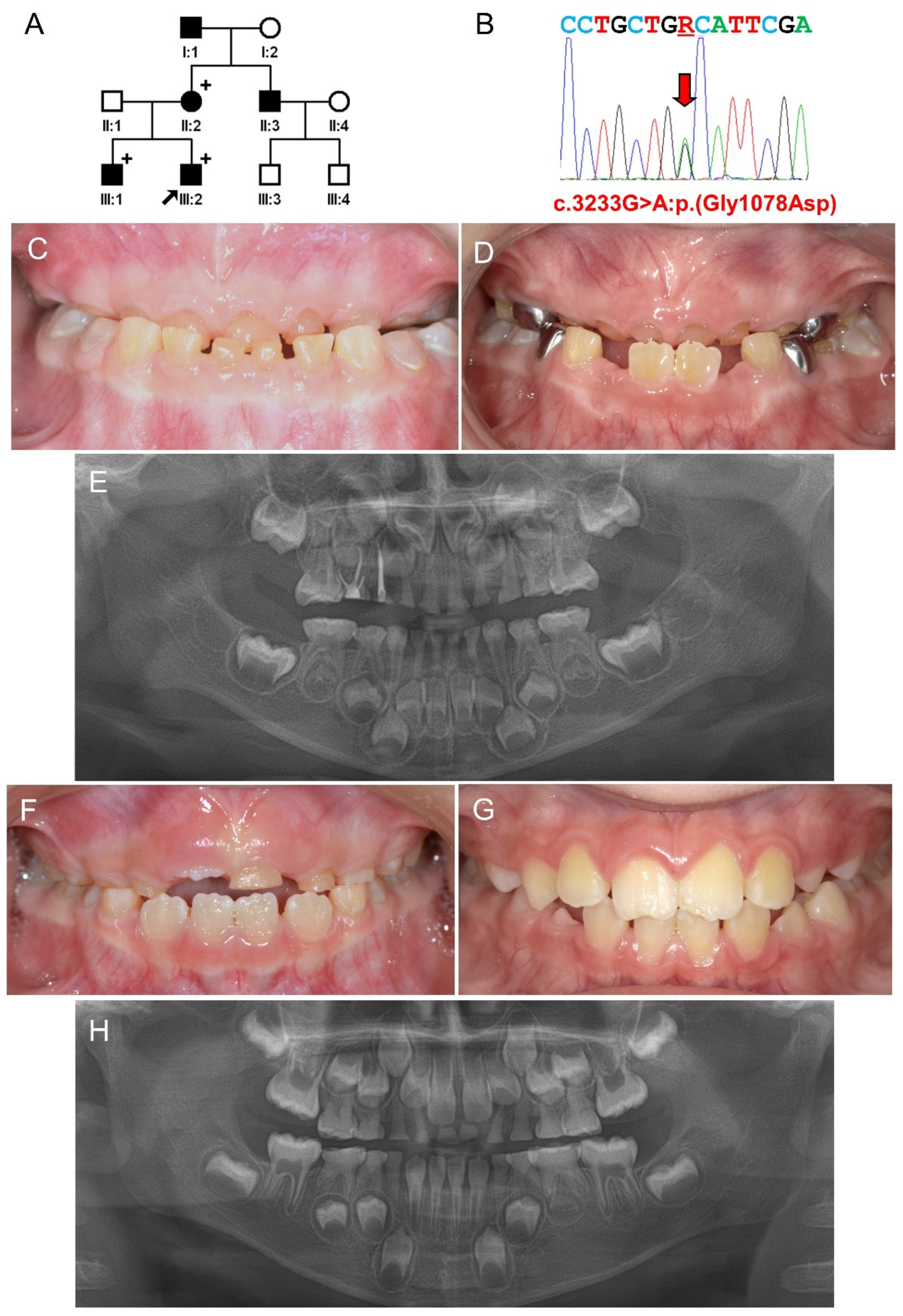
3.1. Family 1
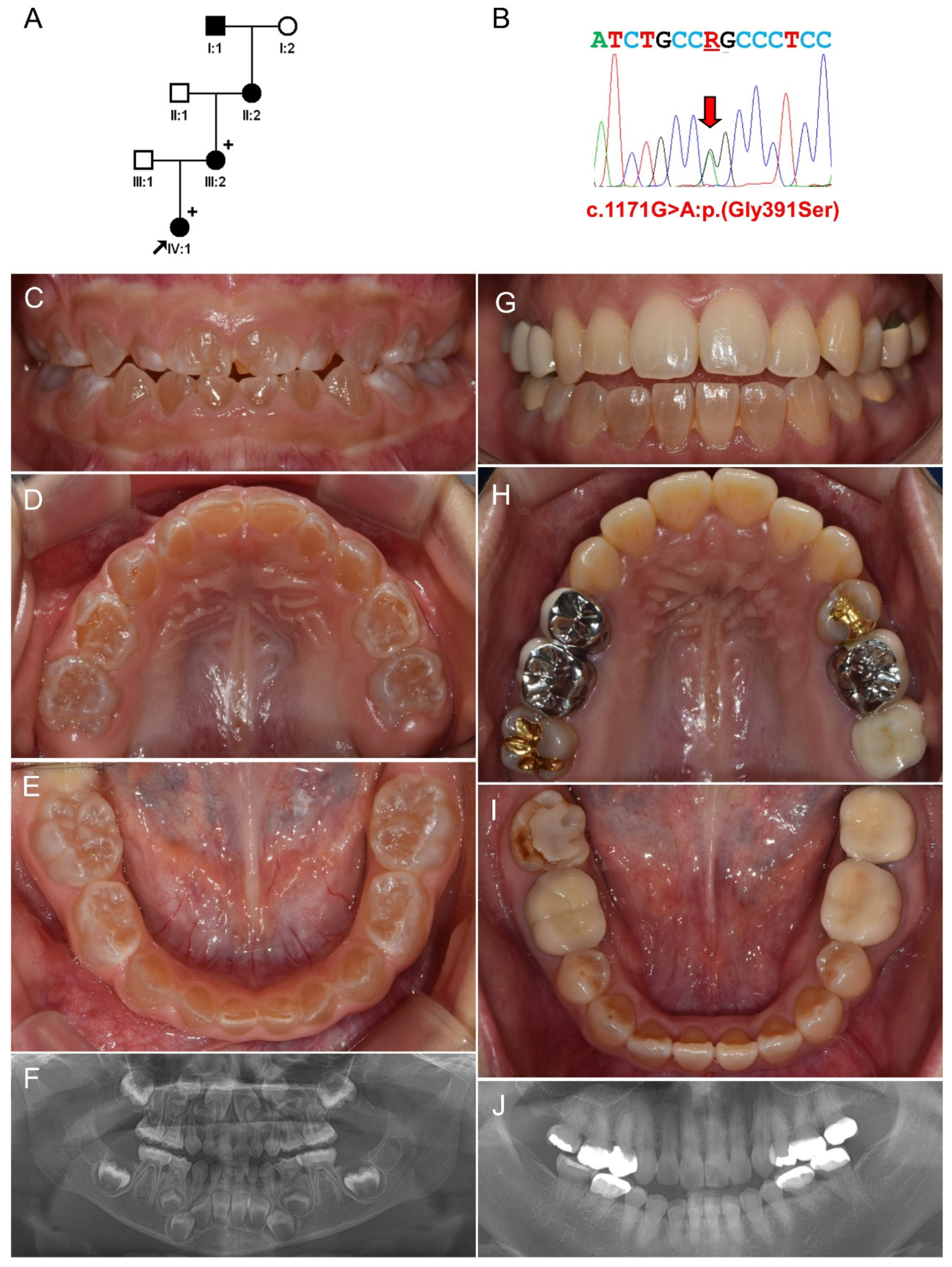
3.2. Family 2
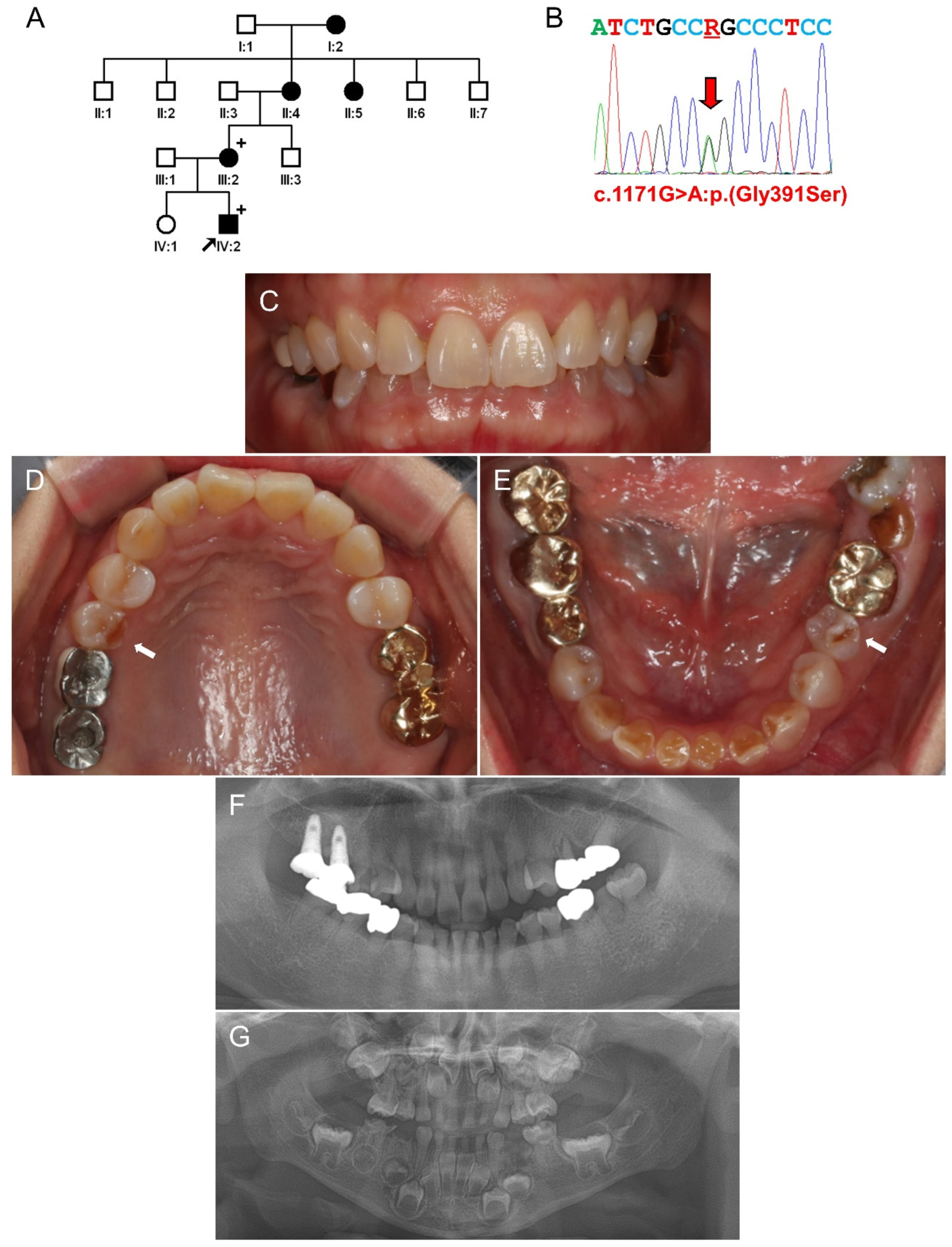
3.3. Family 3
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology, 8th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, M.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Young, M.; Boskey, A. Dentin structure composition and mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2011, E3, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Song, M.; Kim, E.; Shon, W.; Chugal, N.; Bogen, G.; Lin, L.; Kim, R.; Park, N.-H.; Kang, M. Pulp-dentin Regeneration: Current State and Future Prospects. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.D.; Bixler, D.; el-Kafrawy, A.M. A proposed classification for heritable human dentine defects with a description of a new entity. Arch. Oral Biol. 1973, 18, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.J.; McDonnell, S.T.; Mackie, I.; Dixon, M.J. Hereditary dentine disorders: Dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentine dysplasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Gao, S.; Qiu, C.; Liu, P.; Wu, G.; Qiang, B.; Lo, W.H.; Shen, Y. DSPP mutation in dentinogenesis imperfecta Shields type II. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yu, C.; Chou, X.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.; Bu, L.; Fu, G.; Qian, M.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; et al. Dentinogenesis imperfecta 1 with or without progressive hearing loss is associated with distinct mutations in DSPP. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Hu, J.C.-C.; Lee, J.-I.; Moon, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jang, K.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.-C.; Hahn, S.-H.; Simmer, J.P. Mutational hot spot in the DSPP gene causing dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 116, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, D.A.; Hart, P.S.; Hart, T.C.; Hartsfield, J.K.; Wilson, A.; Wright, J.T.; Fisher, L.W. A comprehensive analysis of normal variation and disease-causing mutations in the humanDSPPgene. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpar, M.H.; Koch, M.J.; Davies, R.M.; Mellody, K.T.; Kielty, C.M.; Dixon, M.J. Mutation of the signal peptide region of the bicistronic gene DSPP affects translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum and results in defective dentine biomineralization. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Simmer, J.P. Hereditary Dentin Defects. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Nam, S.-H.; Jang, K.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.-C.; Hahn, S.-H.; Hu, J.C.-C.; Simmer, J.P. A novel splice acceptor mutation in the DSPP gene causing dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 115, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, K.-E.; Kang, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, J.-C. Novel dentin phosphoprotein frameshift mutations in dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Clin. Genet. 2011, 79, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, J.; Seymen, F.; Koruyucu, M.; Zhang, H.; Kasimoglu, Y.; Bayram, M.; Tuna-Ince, E.; Bayrak, S.; Tuloglu, N.; et al. Alteration of Exon Definition Causes Amelogenesis Imperfecta. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ Data to High-Confidence Variant Calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit Best Practices Pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillence, D.O.; Senn, A.; Danks, D.M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Med. Genet. 1979, 16, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Bächinger, H.P.; Bishop, N.J.; Byers, P.H.; De Paepe, A.; Fassier, F.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Kozloff, K.M.; Krakow, D.; et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, F.; Lalic, L.; Roughley, P.; Glorieux, F.H. Genotype–phenotype correlations in nonlethal osteogenesis imperfecta caused by mutations in the helical domain of collagen type I. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Cabral, W.A.; Barnes, A.M.; Antonio, J.D.S.; Milgrom, S.; Hyland, J.C.; Körkkö, J.; Prockop, D.J.; De Paepe, A.; et al. Consortium for osteogenesis imperfecta mutations in the helical domain of type I collagen: Regions rich in lethal mutations align with collagen binding sites for integrins and proteoglycans. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, K.; Åström, E.; Rubin, C.-J.; Grigelioniene, G.; Malmgren, B.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Kindmark, A. Genetic epidemiology, prevalence, and genotype–phenotype correlations in the Swedish population with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-K.; Chan, H.-C.; Makovey, I.; Simmer, J.P.; Hu, J.C.-C. Novel PAX9 and COL1A2 Missense Mutations Causing Tooth Agenesis and OI/DGI without Skeletal Abnormalities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Chinadet, W.; Intachai, W.; Ngamphiw, C.; Cairns, J.R.K.; Tongsima, S. Isolated dentinogenesis imperfecta with glass-like enamel caused by COL1A2 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 2919–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Viswanathan, V.K. Osteogenesis Imperfecta. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2021; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, A.; Tournis, S.; Kämpe, A.; Ain, N.U.; Taylan, F.; Doulgeraki, A.; Mäkitie, O. Autosomal Recessive Osteogenesis Imperfecta Caused by a Novel Homozygous COL1A2 Mutation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 103, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomchaiprasertkul, W.; Kuptanon, C.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. A family with homozygous and heterozygous p.Gly337Ser mutations in COL1A2. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Hyun, H.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Lee, Z.H.; Kim, J.-W. Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
Lee Y, Kim YJ, Hyun H-K, Lee J-C, Lee ZH, Kim J-W. Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(6):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yejin, Youn Jung Kim, Hong-Keun Hyun, Jae-Cheoun Lee, Zang Hee Lee, and Jung-Wook Kim. 2021. "Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 6: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
APA StyleLee, Y., Kim, Y. J., Hyun, H.-K., Lee, J.-C., Lee, Z. H., & Kim, J.-W. (2021). Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(6), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526






