Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Six Facets of Neuroticism in Korean Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Fecal Sample Collection and 16S rRNA Gene Compositional Analysis
2.3. Personality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Subjects
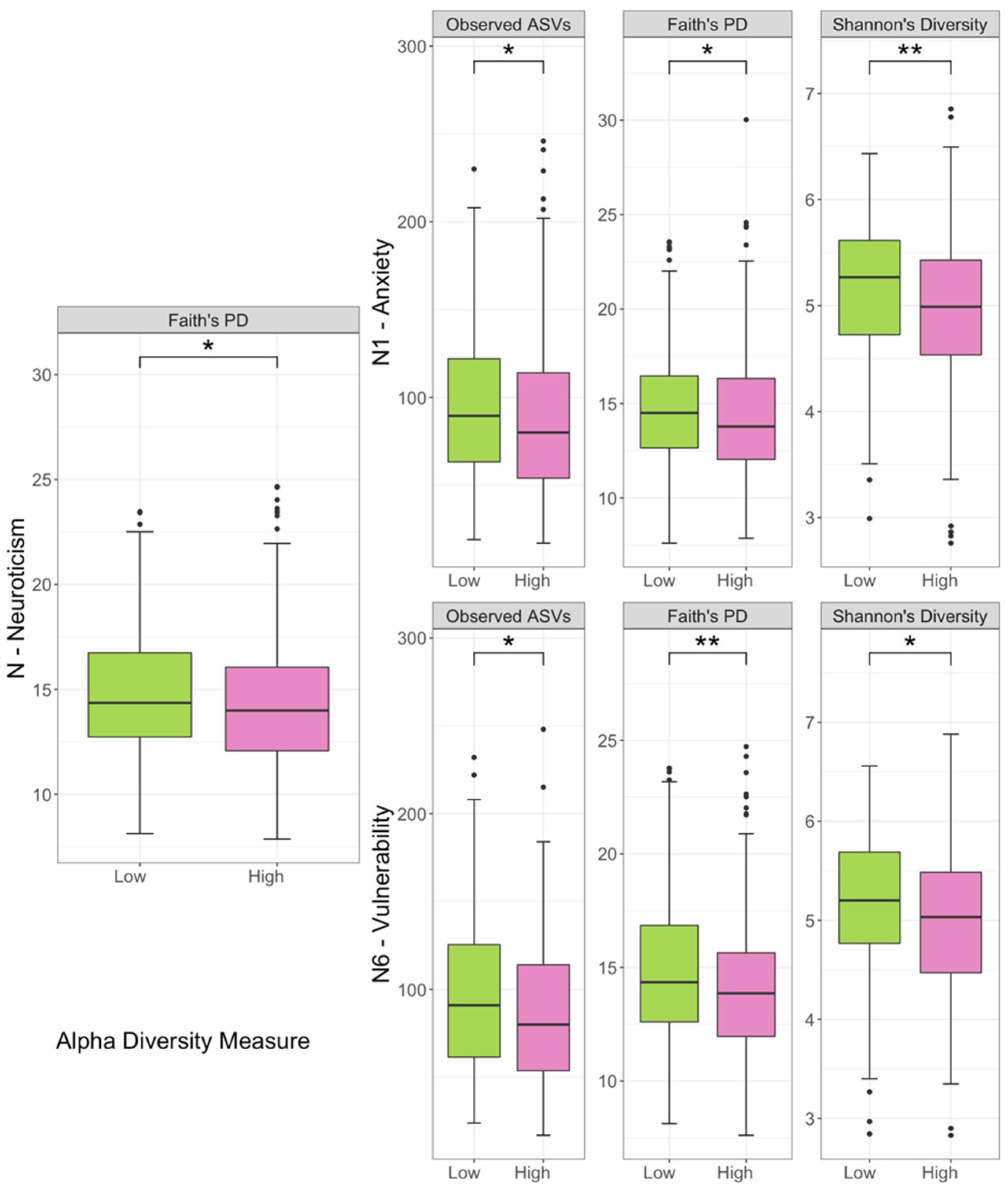
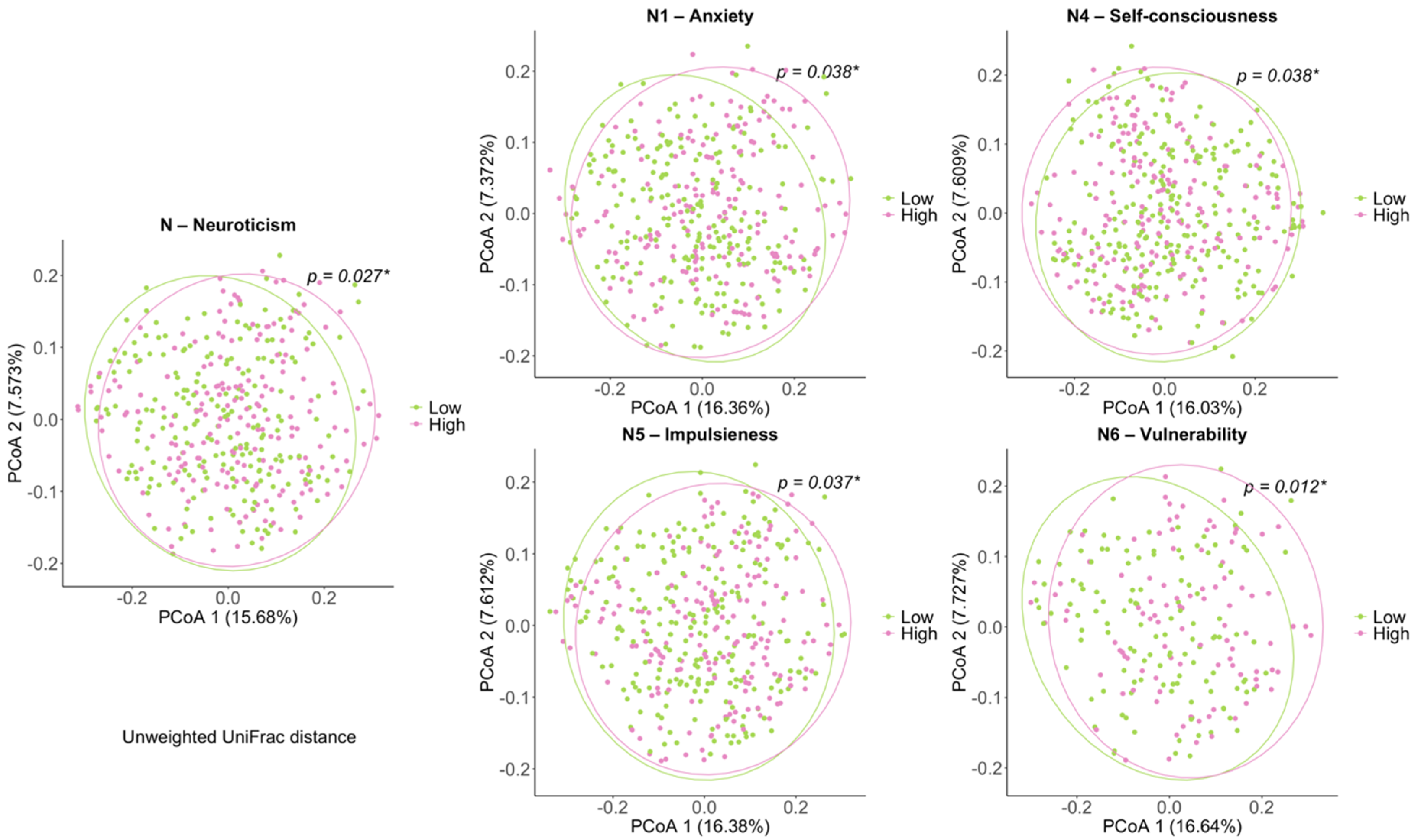
3.2. Comparison of Biodiversity between Low- and High-Scored Groups of Facets of Neuroticism Facets
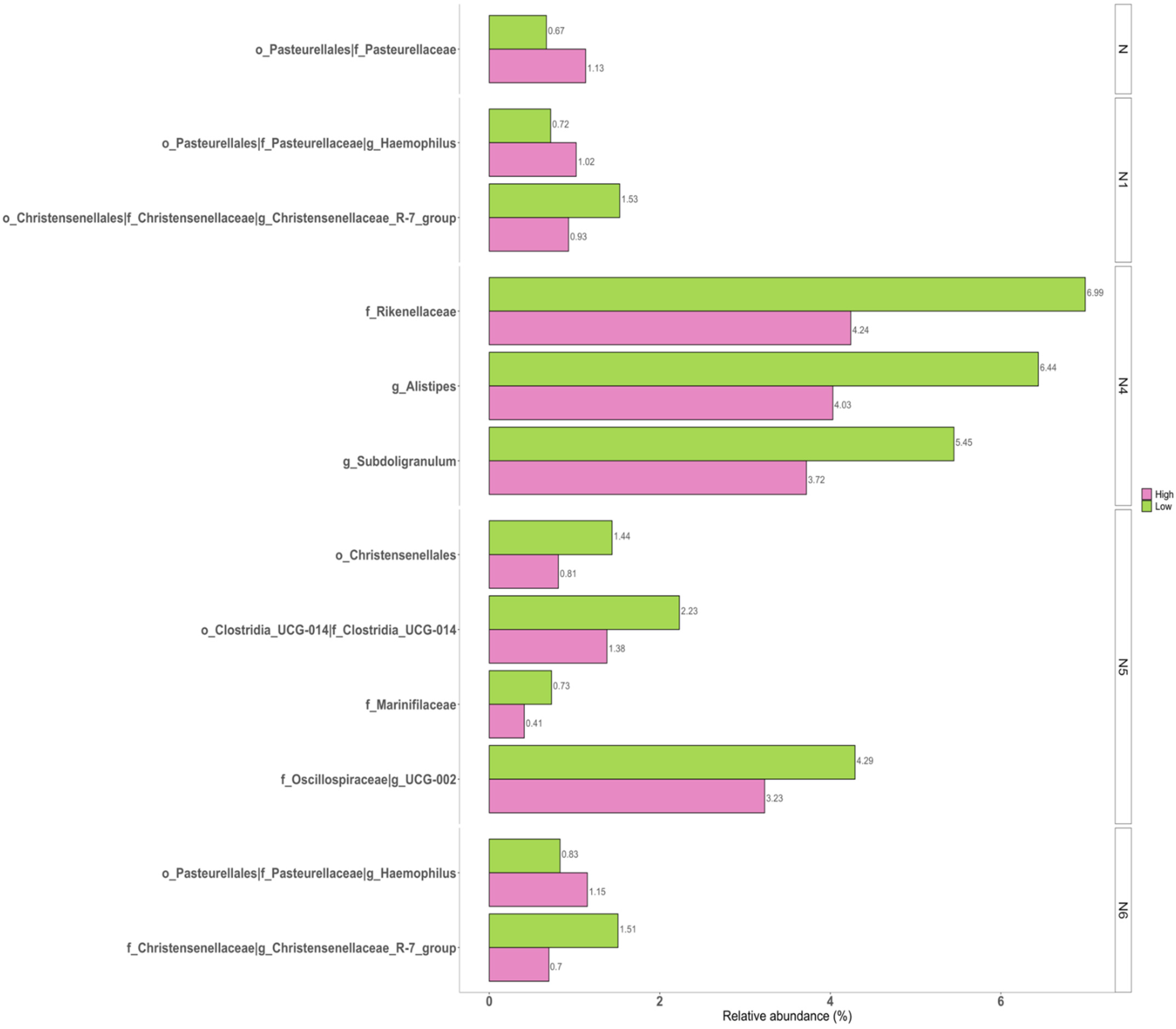
3.3. Correlations of Taxonomic Composition with Six Facets of Neuroticism
3.4. Predicted Functional Metagenome in Personality Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jokela, M.; Pulkki-Råback, L.; Elovainio, M.; Kivimäki, M. Personality traits as risk factors for stroke and coronary heart disease mortality: Pooled analysis of three cohort studies. J. Behav. Med. 2014, 37, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, I.J.; Weiss, A.; Batty, G.D. Intelligence and personality as predictors of illness and death: How researchers in differential psychology and chronic disease epidemiology are collaborating to understand and address health inequalities. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2010, 11, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, B.W.; DelVecchio, W.F. The rank-order consistency of personality traits from childhood to old age: A quantitative review of longitudinal studies. Psychol. Bull. 2000, 126, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gestel, S.; Van Broeckhoven, C. Genetics of personality: Are we making progress? Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.A.; Arnold, S.E.; Tang, Y.; Bennett, D.A. Chronic distress and incidence of mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2007, 68, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahey, B.B. Public health significance of neuroticism. Am. Psychol. 2009, 64, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.T., Jr.; McCrae, R.R. Four ways five factors are basic. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1992, 13, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Bates, T.C.; Luciano, M. Happiness is a personal(ity) thing: The genetics of personality and well-being in a representative sample. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paunonen, S.V.; Haddock, G.; Forsterling, F.; Keinonen, M. Broad versus narrow personality measures and the prediction of behaviour across cultures. Eur. J. Pers. 2003, 17, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracciano, A.; Löckenhoff, C.; Crum, R.M.; Bienvenu, J.; Costa, P.T., Jr. Five-Factor Model personality profiles of drug users. BMC Psychiatry 2008, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, S.H.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A. Principles and clinical implications of the brain–gut–enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Wu, X.; Jin, F. Gut-brain psychology: Rethinking psychology from the microbiota–gut–brain axis. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.N.; Yun, Y.; Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Kwon, M.J.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Kim, H.L. Correlation between gut microbiota and personality in adults: A cross-sectional study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K. Gut microbiome composition and diversity are related to human personality traits. Hum. Microbiome J. 2020, 15, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson-Leary, J.; Zhao, C.; Bittinger, K.; Eacret, D.; Luz, S.; Vigderman, A.S.; Dayanim, G.; Bhatnagar, S. The gut microbiome regulates the increases in depressive-type behaviors and in inflammatory processes in the ventral hippocampus of stress vulnerable rats. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Li, F. Association Between Gut Microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammen, C. Stress and depression. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, L.M.; Liberzon, I. The Neurocircuitry of Fear, Stress, and Anxiety Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 35, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C.; Lotrich, F.E. Inflammatory cytokines in depression: Neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience 2013, 246, 199–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raison, C.L.; Miller, A.H. Is Depression an Inflammatory Disorder? Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2011, 13, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson-Leary, J.; Eacret, D.; Chen, R.J.; Takano, H.; Nicholas, B.; Bhatnagar, S. Inflammation and vascular remodeling in the ventral hippocampus contributes to vulnerability to stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terracciano, A.; Tanaka, T.; Sutin, A.R.; Sanna, S.; Deiana, B.; Lai, S.; Uda, M.; Schlessinger, D.; Abecasis, G.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan of Trait Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.; Highlander, S.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; A Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, M.; Beiko, R.G. 16S rRNA Gene Analysis with QIIME2. In Microbiome Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.-K.; Chae, J.-H. Standardization of the Korean version of the Revised NEO Personality Inventory. Korean J. Couns. Psychother. 1997, 9, 443–472. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, D.P.; Baker, A.M. Phylogenetic Diversity (PD) and Biodiversity Conservation: Some Bioinformatics Challenges. Evol. Bioinform. 2006, 2, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.L.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; LeLeiko, N.; Snapper, S.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G. PICRUSt2: An improved and customizable approach for metagenome inference. bioRxiv 2020, 672295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; Baines, J. Food matters: How the microbiome and gut–brain interaction might impact the development and course of anorexia nervosa. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Angelis, M.; Francavilla, R.; Piccolo, M.; De Giacomo, A.; Gobbetti, M. Autism spectrum disorders and intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audet, M.-C. Stress-induced disturbances along the gut microbiota-immune-brain axis and implications for mental health: Does sex matter? Front. Neuroendocr. 2019, 54, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodička, M.; Ergang, P.; Hrncir, T.; Mikulecká, A.; Kvapilová, P.; Vagnerova, K.; Šestáková, B.; Fajstová, A.; Hermanová, P.; Hudcovic, T.; et al. Microbiota affects the expression of genes involved in HPA axis regulation and local metabolism of glucocorticoids in chronic psychosocial stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.U.; Lumpkin, E.A. A gut feeling. Science 2018, 361, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, K.G.; Hsiao, E.Y. Linking the Gut Microbiota to a Brain Neurotransmitter. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, S.O.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, A.I.; Panagiotidou, S.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Stewart, J.M.; Conti, P.; Theoharides, T.C. Gut-Microbiota-Brain Axis and Its Effect on Neuropsychiatric Disorders with Suspected Immune Dysregulation. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espín, J.C. Gut Microbiota, Diet and Health. (We and our gut microbes). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1770015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, M.; Zhao, J.-H.; Ruan, B. Altered gut microbiota profile in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 104, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, Y.A.; Ba-M’Hamed, S.; Elhidar, N.; Nafis, A.; Soraa, N.; Bennis, M. Glyphosate based- herbicide exposure affects gut microbiota, anxiety and depression-like behaviors in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 67, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlett-Stevens, H.; Craske, M.G.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L.; Naliboff, B.D. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome among university students: The roles of worry, neuroticism, anxiety sensitivity and visceral anxiety. J. Psychosom. Res. 2003, 55, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.A.; Jones, M.P.; Talley, N.J.; Kjellström, L.; Nyhlin, H.; Andreasson, A.N.; Agréus, L. Abdominal pain is associated with anxiety and depression scores in a sample of the general adult population with no signs of organic gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 741-e576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, N.; Dinan, T.G.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota-gut-brain axis as a key regulator of neural function and the stress response: Implications for human and animal health. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 3225–3246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langgartner, D.; Peterlik, D.; Foertsch, S.; Füchsl, A.M.; Brokmann, P.; Flor, P.J.; Shen, Z.; Fox, J.G.; Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Lowry, C.; et al. Individual differences in stress vulnerability: The role of gut pathobionts in stress-induced colitis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyszkowicz, J.K.; Wong, A.; Anisman, H.; Merali, Z.; Audet, M.-C. Implications of the gut microbiota in vulnerability to the social avoidance effects of chronic social defeat in male mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetel, M.J.; De Vries, G.J.; Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.; O’Mahony, S.M. Steroids, stress and the gut microbiome-brain axis. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Hart, R.A.; Charlesworth, R.; Sharpley, C. Gut microbiome and depression: What we know and what we need to know. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Ahmari, N.; Schmidt, J.T.; Redler, T.; Arocha, R.; Pacholec, K.; Magee, K.L.; Malphurs, W.; Owen, J.L.; Krane, G.A.; et al. Shifts in the Gut Microbiota Composition Due to Depleted Bone Marrow Beta Adrenergic Signaling Are Associated with Suppressed Inflammatory Transcriptional Networks in the Mouse Colon. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, M.Y.; Inohara, N.; Nuñez, G. Mechanisms of inflammation-driven bacterial dysbiosis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galley, J.D.; Nelson, M.C.; Yu, Z.; Dowd, S.; Walter, J.; Kumar, P.S.; Lyte, M.; Bailey, M.T. Exposure to a social stressor disrupts the community structure of the colonic mucosa-associated microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Partrick, K.A.; Chassaing, B.; Beach, L.Q.; McCann, K.E.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Huhman, K.L. Acute and repeated exposure to social stress reduces gut microbiota diversity in Syrian hamsters. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 345, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konikoff, T.; Gophna, U. Oscillospira: A Central, Enigmatic Component of the Human Gut Microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Wouw, M.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: Modulator of host metabolism and appetite. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Carvalho, A.; Caso, J.; Sanz, Y.; Walder, K.; Maes, M. The Role of the Microbial Metabolites Including Tryptophan Catabolites and Short Chain Fatty Acids in the Pathophysiology of Immune-Inflammatory and Neuroimmune Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4432–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailey, M.T.; Dowd, S.E.; Galley, J.D.; Hufnagle, A.R.; Allen, R.G.; Lyte, M. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota: Implications for stress-or-induced immunomodulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Total | Low | High | p-Value 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroticism | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 398 | 205 | 193 | ||||
| Age | 43.4 | (8.2) | 44.2 | (7.9) | 42.6 | (8.5) | 0.050 |
| BMI | 23.8 | (3.3) | 23.6 | (3.3) | 24.0 | (3.4) | 0.314 |
| N score | 126.9 | (28.0) | 102.2 | (11.2) | 153.1 | (12.1) | |
| Total energy intake | 1471.6 | (650.8) | 1401.0 | (608.9) | 1546.8 | (686.6) | 0.046 * |
| Carbohydrate | 244.6 | (112.3) | 234.1 | (105.3) | 255.9 | (118.7) | 0.084 |
| Protein | 50.8 | (25.5) | 48.8 | (24.3) | 52.9 | (26.6) | 0.151 |
| Fat | 30.7 | (19.8) | 28.5 | (17.8) | 33.1 | (21.5) | 0.041 * |
| Fiber | 3.8 | (2.2) | 3.7 | (2.1) | 4.0 | (2.4) | 0.354 |
| N1 Anxiety | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 407 | 218 | 189 | ||||
| Age | 43.5 | (8.2) | 44.7 | (8.3) | 42.2 | (8.0) | 0.002 ** |
| BMI | 23.6 | (3.2) | 23.7 | (3.2) | 23.5 | (3.2) | 0.422 |
| N score | 22.9 | (6.5) | 17.3 | (2.5) | 29.3 | (2.7) | |
| Total energy intake | 1483.3 | (625.1) | 1433.2 | (581.0) | 1537.2 | (667.0) | 0.134 |
| Carbohydrate | 249.3 | (108.5) | 242.0 | (103.3) | 257.3 | (113.6) | 0.204 |
| Protein | 50.3 | (23.8) | 49.0 | (21.8) | 51.7 | (25.7) | 0.292 |
| Fat | 30.1 | (19.0) | 28.5 | (16.5) | 31.7 | (21.3) | 0.125 |
| Fiber | 3.8 | (2.2) | 3.9 | (2.4) | 3.8 | (2.0) | 0.706 |
| N2 Hostility | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 382 | 220 | 162 | ||||
| Age | 43.8 | (8.1) | 43.9 | (8.1) | 43.6 | (8.2) | 0.755 |
| BMI | 23.7 | (3.3) | 23.5 | (3.1) | 23.9 | (3.5) | 0.331 |
| N score | 19.2 | (6.0) | 14.5 | (2.2) | 25.7 | (2.5) | |
| Total energy intake | 1452.2 | (617.8) | 1412.9 | (587.1) | 1509.6 | (658.2) | 0.186 |
| Carbohydrate | 245.0 | (109.1) | 239.4 | (102.3) | 253.2 | (118.3) | 0.291 |
| Protein | 49.7 | (24.0) | 48.4 | (23.3) | 51.6 | (24.9) | 0.260 |
| Fat | 28.8 | (17.8) | 27.4 | (17.2) | 30.8 | (18.6) | 0.106 |
| Fiber | 3.9 | (2.4) | 3.8 | (2.2) | 4.1 | (2.5) | 0.355 |
| N3 Depression | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 413 | 236 | 177 | ||||
| Age | 43.6 | (8.2) | 43.1 | (8.0) | 44.3 | (8.5) | 0.143 |
| BMI | 23.9 | (3.3) | 24.0 | (3.3) | 23.8 | (3.3) | 0.595 |
| N score | 19.2 | (6.5) | 14.1 | (2.2) | 26.0 | (3.2) | |
| Total energy intake | 1450.3 | (598.6) | 1440.0 | (549.8) | 1463.7 | (658.9) | 0.729 |
| Carbohydrate | 242.8 | (106.0) | 241.9 | (96.5) | 244.1 | (117.6) | 0.851 |
| Protein | 49.6 | (22.6) | 49.7 | (22.2) | 49.6 | (23.1) | 0.851 |
| Fat | 29.6 | (17.9) | 28.8 | (16.7) | 30.7 | (19.4) | 0.353 |
| Fiber | 3.8 | (2.0) | 3.7 | (2.0) | 3.8 | (2.1) | 0.667 |
| N4 Self-consciousness | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 446 | 252 | 194 | ||||
| Age | 43.8 | (8.4) | 43.6 | (8.1) | 43.9 | (8.7) | 0.710 |
| BMI | 23.7 | (3.3) | 23.6 | (3.2) | 23.7 | (3.3) | 0.866 |
| N score | 23.5 | (5.3) | 19.3 | (2.3) | 29.0 | (1.9) | |
| Total energy intake | 1438.2 | (602.6) | 1396.9 | (584.4) | 1492.8 | (623.7) | 0.143 |
| Carbohydrate | 239.0 | (103.8) | 230.1 | (96.6) | 250.8 | (111.8) | 0.069 |
| Protein | 49.9 | (24.3) | 49.4 | (25.2) | 50.6 | (23.2) | 0.658 |
| Fat | 29.8 | (19.8) | 29.5 | (20.1) | 30.3 | (19.6) | 0.693 |
| Fiber | 3.7 | (2.1) | 3.6 | (2.0) | 3.8 | (2.3) | 0.369 |
| N5 Impulsiveness | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 407 | 228 | 179 | ||||
| Age | 44.0 | (8.2) | 45.5 | (7.5) | 42.1 | (8.7) | <0.001 ** |
| BMI | 23.6 | (3.1) | 22.9 | (2.9) | 24.4 | (3.3) | <0.001 ** |
| N score | 20.7 | (5.5) | 16.2 | (1.9) | 26.5 | (2.3) | |
| Total energy intake | 1516.4 | (652.1) | 1388.1 | (538.3) | 1689.3 | (747.5) | <0.001 ** |
| Carbohydrate | 254.6 | (112.2) | 240.3 | (97.2) | 274.0 | (127.5) | 0.009 ** |
| Protein | 51.6 | (25.2) | 45.9 | (19.6) | 59.2 | (29.6) | <0.001 ** |
| Fat | 30.7 | (20.6) | 25.4 | (14.6) | 37.9 | (25.1) | <0.001 ** |
| Fiber | 4.0 | (2.4) | 3.8 | (2.1) | 4.2 | (2.7) | 0.150 |
| N6 Vulnerability | |||||||
| No. of subjects | 407 | 235 | 172 | ||||
| Age | 44.0 | (8.0) | 44.8 | (7.5) | 43.0 | (8.5) | 0.025 * |
| BMI | 23.8 | (3.2) | 23.7 | (3.2) | 23.9 | (3.2) | 0.698 |
| N score | 19.5 | (5.4) | 15.4 | (2.2) | 25.1 | (2.8) | |
| Total energy intake | 1467.9 | (614.8) | 1400.4 | (569.1) | 1561.0 | (663.8) | 0.024 * |
| Carbohydrate | 245.2 | (107.7) | 237.0 | (101.3) | 256.6 | (115.4) | 0.115 |
| Protein | 50.4 | (23.1) | 48.2 | (21.9) | 53.5 | (24.5) | 0.049 * |
| Fat | 30.1 | (18.2) | 27.3 | (15.7) | 34.0 | (20.6) | 0.002 ** |
| Fiber | 3.9 | (2.3) | 3.8 | (2.2) | 3.9 | (2.3) | 0.755 |
| Taxa | W 1 (Coefficients 2) from the Pairwise Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 | N5 | N6 | ||
| family | p__Bacteroidota; c__Bacteroidia; o__Bacteroidales; f__Marinifilaceae | 76 (−0.905 4) | ||||||
| family | p__Bacteroidota; c__Bacteroidia; o__Bacteroidales; f__Rikenellaceae | 71 (−0.896 4) | ||||||
| genus | p__Bacteroidota; c__Bacteroidia; o__Bacteroidales; f__Rikenellaceae; g__Alistipes | 204 (−0.844 4) | ||||||
| order | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Christensenellales | 41 (−1.251 4) | 39 (−0.584) | |||||
| family | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Christensenellales; f__Christensenellaceae | 71 (−1.251 4) | 68 (−1.055 4) | |||||
| genus | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Christensenellales; f__Christensenellaceae; g__Christensenellaceae_R.7_group | 221 (−1.249 4) | 215 (−0.981 4) | |||||
| order | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Clostridia__UCG.014 | 44 (−0.803 3) | ||||||
| family | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Clostridia__UCG.014; f__Clostridia_UCG.014 | 73 (−0.803 3) | ||||||
| genus | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Oscillospirales; f__Oscillospiraceae; g__UCG.002 | 216 (−0.736 3) | ||||||
| genus | p__Firmicutes; c__Clostridia; o__Oscillospirales; f__Ruminococcaceae; g__Subdoligranulum | 215 (−0.766 4) | ||||||
| order | p__Proteobacteria; c__Gammaproteobacteria; o__Pasteurellales | 43 (1.411 4) | 43 (1.112 4) | 42 (1.062 4) | ||||
| family | p__Proteobacteria; c__Gammaproteobacteria; o__Pasteurellales; f__Pasteurellaceae | 79 (1.411 4) | 77 (1.111 4) | 77 (1.061 4) | ||||
| genus | p__Proteobacteria; c__Gammaproteobacteria; o__Pasteurellales; f__Pasteurellaceae; g__Haemophilus | 231 (1.113 4) | 218 (1.061 4) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, E.; Yun, K.E.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, J.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.-L.; Kim, H.-N.; Jung, S.-C. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Six Facets of Neuroticism in Korean Adults. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121246
Park E, Yun KE, Kim M-H, Kim J, Chang Y, Ryu S, Kim H-L, Kim H-N, Jung S-C. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Six Facets of Neuroticism in Korean Adults. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121246
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Eunkyo, Kyung Eun Yun, Mi-Hyun Kim, Jimin Kim, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Hyung-Lae Kim, Han-Na Kim, and Sung-Chul Jung. 2021. "Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Six Facets of Neuroticism in Korean Adults" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121246
APA StylePark, E., Yun, K. E., Kim, M.-H., Kim, J., Chang, Y., Ryu, S., Kim, H.-L., Kim, H.-N., & Jung, S.-C. (2021). Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Six Facets of Neuroticism in Korean Adults. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121246








