Serum Interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Patients Could Differentiate between Severe and Non-Severe Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Protocol
2.2. Serum Cytokines Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. Standard Inflammatory Biomarker Levels in IBD Patients by Disease Severity vs. Healthy Participants
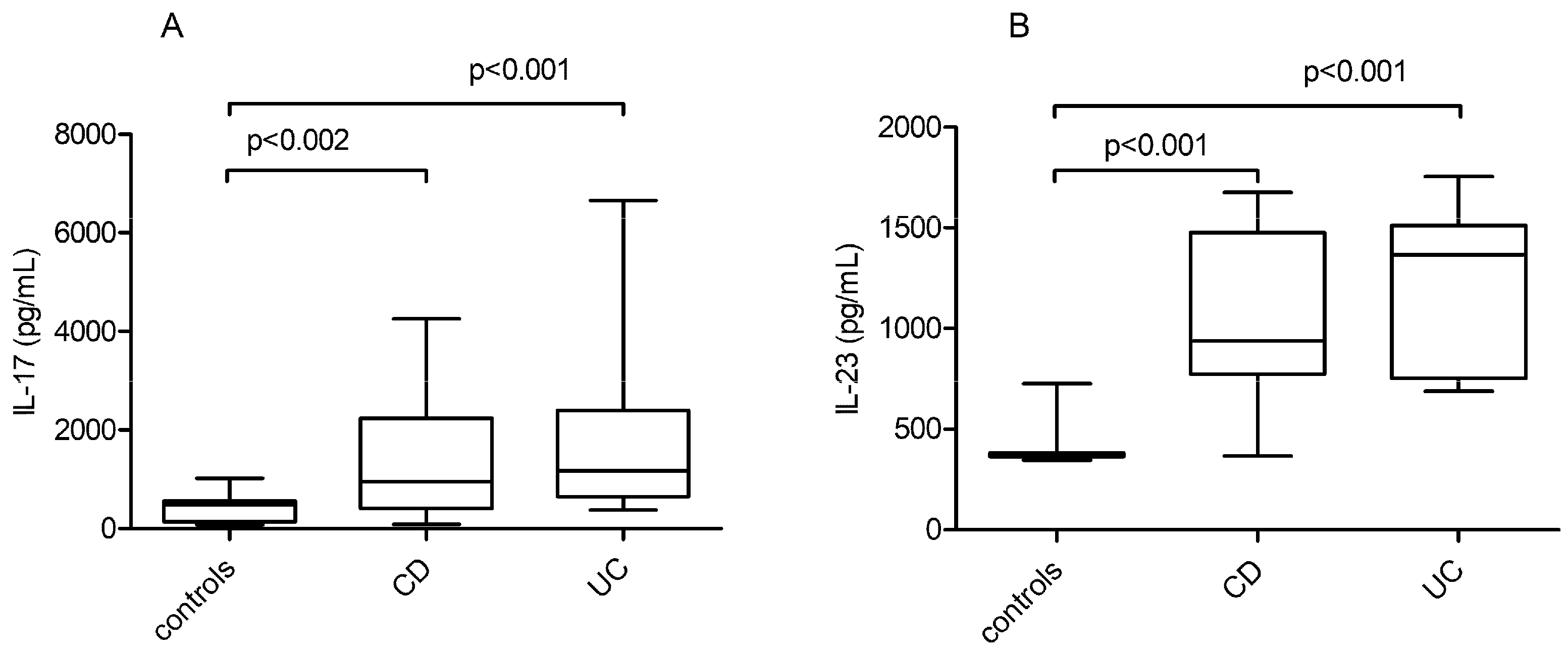
3.3. IL-17 and IL-23 Quantitative Serum Levels in IBD Patients vs. Healthy Controls
3.4. IL-17 and IL-23 Quantitative Serum Levels Associated with IBD Severity vs. Healthy Controls
3.5. Discriminating between Severe and Mild or Moderate IBD according to Biomarker Cut-Off Value
3.6. Assessment of CD Disease Complications according to Standard Inflammatory Biomarkers vs. IL-17 and IL-23 Serum Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marafini, I.; Sedda, S.; Dinallo, V.; Monteleone, G. Inflammatory cytokines: From discoveries to therapies in IBD. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. IL-23 in inflammatory bowel diseases and colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerr, R.H.; Taylor, K.D.; Brant, S.R.; Rioux, J.D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Daly, M.J.; Steinhart, A.H.; Abraham, C.; Regueiro, M.; Griffiths, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 2006, 314, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsheikh, M.M.; El-Shafey, A.M.; Gawish, H.H.; El-Desoky, E.T. Serum interleukin-23 level in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Relation to disease activity and severity. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.I.K.; Tye, G.J. Interleukin 23 and autoimmune diseases: Current and possible future therapies. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsattari, D.; Seyyedmajidi, M.; Zojaji, H.; Haghazali, M.; Orimi, P.G.; Shoushtarizadeh, T. The relation between the level of interleukin-23 with duration and severity of ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 5, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sabino, J.; Verstockt, B.; Vermeire, S.; Ferrante, M. New biologics and small molecules in inflammatory bowel disease: An update. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819853208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hueber, W.; Sands, B.E.; Lewitzky, S.; Vandemeulebroecke, M.; Reinisch, W.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Wehkamp, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Yao, M.D.; Karczewski, M.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: Unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 2012, 61, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyapati, R.K.; Kalla, R.; Satsangi, J.; Ho, G. Biomarkers in search of precision medicine in IBD. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarur, A.J.; Jain, A.; Quintero, M.A.; Czul, F.; Deshpande, A.R.; Kerman, D.H.; Abreu, M.T. Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Crohn’s Disease Nonresponders to Optimal Antitumor Necrosis Factor Therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E. Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 24, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, A.; Maaser, C.; Calabrese, E.; Annese, V.; Fiorino, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Vavricka, S.R.; Verstockt, B.; van Rheenen, P.; Tolan, D.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 2: IBD scores and general principles and technical aspects. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Eisenhut, M.; Shin, J.I. IBD immunopathogenesis: A comprehensive review of inflammatory molecules. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H.; Raine, T. IL-12, IL-23 and IL-17 in IBD: Immunobiology and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argollo, M.; Fiorino, G.; Hindryckx, P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Novel therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 85, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.; Dulai, P.S.; Vermeire, S.; Sandborn, W.J. Lessons Learned From Trials Targeting Cytokine Pathways in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omidian, Z.; Ahmed, R.; Giwa, A.; Donner, T.; Hamad, A.R.A. IL-17 and limits of success. Cell. Immunol. 2019, 339, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, S.; Andoh, A.; Bamba, S.; Ogawa, A.; Hata, K.; Araki, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fujiyama, Y. Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2003, 52, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, H. Elevated levels of Th17 cells and Th17-related cytokines are associated with disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, I.J.; Becker, C.; Yang, Z.; Groden, C.; Hornung, R.L.; Heller, F.; Neurath, M.F.; Strober, W.; Mannon, P.J. Both IL-12p70 and IL-23 are synthesized during active Crohn’s disease and are down-regulated by treatment with anti-IL-12 p40 monoclonal antibody. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheita, T.A.; El Gazzar, I.I.; El-Fishawy, H.S.; Aboul-Ezz, M.A.; Kenawy, S.A. Involvement of IL-23 in enteropathic arthritis patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Preliminary results. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstockt, B.; Noor, N.M.; Marigorta, U.M.; Pavlidis, P.; Deepak, P.; Ungaro, R.C. Results of the Seventh Scientific Workshop of ECCO: Precision medicine in IBD—Disease outcome and response to therapy. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 17, jjab050. [Google Scholar]
- Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease evaluation and treatment: Clinical decision tool. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Panés, L.; Sandborn, W.J.; Vermeire, S.; Danese, S.; Feagan, B.G.; Colombel, J.F.; Hanauer, S.B.; Rycroft, B. Defining Disease Severity in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Current and Future Directions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soubieres, A.A.; Poullis, A. Emerging Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Ishihara, S.; Yuki, T.; Fukuba, N.; Oshima, N.; Kazumori, H.; Sonoyama, H.; Yamashita, N.; Tada, Y.; Kusunoki, R.; et al. Fecal calprotectin level correlated with both endoscopic severity and disease extent in ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogler, G.; Biedermann, L. Clinical Utility of Biomarkers in IBD. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, G.R.; McGovern, D.P.B. Using Markers in IBD to Predict Disease and Treatment Outcomes: Rationale and a Review of Current Status. Am. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 2016, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.C.; Du, L.; Chong, R.Y.; Jackson, T.D. Hypoalbuminaemia and Postoperative Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The NSQIP Surgical Cohort. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Aggarwal, R.; Saraswat, V.A.; Choudhuri, G. Severe ulcerative colitis: Prospective study of parameters determining outcome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 19, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Bamba, S.; Takahashi, K.; Imaeda, H.; Nishida, A.; Inatomi, O.; Sasaki, M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Andoh, A. Prediction of clinical and endoscopic responses to anti-tumor necrosis factor-α antibodies in ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billiet, T.; Cleynen, I.; Ballet, V.; Claes, K.; Princen, F.; Singh, S.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Gils, A.; Vermeire, S. Evolution of cytokines and inflammatory biomarkers during infliximab induction therapy and the impact of inflammatory burden on primary response in patients with Crohn’s disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertani, L.; Baglietto, L.; Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Tapete, G.; Albano, E.; Ceccarelli, L.; Mumolo, M.G.; Pellegrini, C.; Lucenteforte, E.; et al. Assessment of serum cytokines predicts clinical and endoscopic outcomes to vedolizumab in ulcerative colitis patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, R.F.; Planell, N.; Kajekar, R.; Lozano, J.J.; Ordas, I.; Dotti, I.; Esteller, M.; Masamunt, M.C.; Parmar, H.; Ricart, E.; et al. Identification of inflammatory mediators in patients with Crohn’s disease unresponsive to anti-TNFα therapy. Gut 2015, 64, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.; Feagan, B.G.; Gasink, C.; Jacobstein, D.; Gao, L.-L.; Johanns, J.; Sands, B.E.; Hanauer, S.B.; Targan, S.; Ghosh, S.; et al. 768 A Phase 3 Randomized, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Ustekinumab Maintenance Therapy in Moderate—Severe Crohn’s Disease Patients: Results From IM-UNITI. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, S157–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mild or Moderate CD (n = 16) | Severe CD (n = 15) | p Value | Mild or Moderate UC (n = 14) | Severe UC (n = 17) | p Value | Controls (n = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years), Mean ± SD | 40.62 ± 10.54 | 31.8 ± 9.01 | 0.01 | 52.14 ± 18.79 | 37.47 ± 13.08 | 0.01 | 30.8 ± 6.12 | |
| Gender (F), n (%) | 11 (68.75) | 7 (46.67) | 0.3 | 3 (21.43) | 4 (23.53) | 1 | 6 (5.3) | |
| CDAI/Mayo Score, Median (IQR) | 105(80.5–147.75) | 368 (294–434) | <0.001 | 6 (2.25–7) | 10 (10–12) | <0.001 | ||
| Age at Diagnosis, n, % (Montreal Classification, CD) | ||||||||
| A1 (n, %): <16 | 0 (0) | 2 (13.33) | ||||||
| A2 (n, %): 17–40 | 13 (81.25) | 13 (86.67) | 1 | |||||
| A3 (n, %): >40 | 3 (18.75) | 0 (0) | ||||||
| Location, n, % (Montreal Classification, CD) | ||||||||
| L1: Ileum | 10 (62.5) | 5 (33.33) | ||||||
| L2: Colon | 2 (12.5) | 2 (13.33) | 0.2 | |||||
| L3: Ileocolonic | 4 (25) | 8 (53.33) | ||||||
| Location, n, % (Montreal Classification, UC) | ||||||||
| E1 (Distal Colitis) | - | - | 1 | 1 | ||||
| E2 (Left-Sided Colitis) | - | - | 10 | 13 | ||||
| E3 (Pancolitis) | - | - | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Behaviour, n, % (Montreal Classification, CD) | ||||||||
| B1: Non-Stricturing, Non-Penetrating | 11 (68.75) | 0 (0) | ||||||
| B2: Stricturing | 2 (12.5) | 6 (40) | <0.001 | |||||
| B3: Penetrating | 2 (12.5) | 7 (46.67) | ||||||
| Mayo Endoscopic Score, Median, (IQR) | 1 (0.5–1) | 3 (2–3) | ||||||
| SES-CD, Median (IQR) | 5 (4–7) | 13.5 (12–17.5) | ||||||
| Complications, n, %, CD and UC | ||||||||
| Intestinal Complications, n (%) | With | 6 (37.5) | 13 (86.67) | 0.01 | 0 (0) | 2 (11.76) | ||
| Without | 10 (62.5) | 2 (13.3) | 14 (100) | 15 (88.2) | ||||
| Fistula, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.88) | 0.08 | - | - | - | ||
| Stenosis, n (%) | 2 (12.5) | 7 (46.7) | 0.05 | - | 1 (5.9%) | 1 | ||
| Abscess, n (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (13.33) | 0.2 | - | - | - | ||
| Extraintestinal Complications, n (%) | 3 (18.75) | 2 (13.33) | 1 | - | 1 (5.9) | 1 | ||
| Anti-TNF Therapy, n (%) | 5 (31.25) | 4 (26.67) | 1 | 3 (21.43) | 4 (25) | 1 | ||
| Variable | AUC (CI 95%) | Cut-off | Sensitivity (CI 95%) | Specificity (CI 95%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | Albumin | 0.733 (0.545–0.875) | 3.7 g/dL | 93.75 (69.8–99.8) | 53.33 (26.6–78.7) | 0.010 |
| CRP | 0.781 (0.597–0.909) | 1.26 mg/L | 73.33 (44.9–92.2) | 87.50 (61.7–98.4) | 0.001 | |
| FCal | 0.877 (0.709–0.967) | 50 µg/g | 100 (78.2–100) | 62.5 (35.4–84.8) | <0.001 | |
| IL23 | 1 (0.888–1.000) | 937.4 pg/mL | 100 (78.2–100.0) | 100 (79.4–100.0) | <0.001 | |
| IL-17 | 0.667 (0.475–0.825) | >1536.15 pg/mL | 53.33 (26.6–78.7) | 87.50 (61.7–98.4) | 0.010 | |
| UC | Albumin | 0.773 (0.588–0.903) | 3.7 g/dL | 92.86 (66.1–99.8) | 47.06 (23.0–72.2) | <0.001 |
| FCal | 0.857 (0.685–0.956) | 400 µg/g | 94.12 (71.3–99.9) | 71.43 (41.9–91.6) | <0.001 | |
| IL-17 | 0.803 (0.621–0.923) | 1512.05 pg/mL | 64.71 (38.3–85.8) | 100 (76.8–100) | <0.001 | |
| IL-23 | 0.979 (0.851–1) | 946.11 pg/mL | 94.12 (71.3–99.9) | 100 (76.8–100) | <0.001 | |
| CRP | 0.645 (0.453–0.808) | >0.89 mg/L | 52.94 (27.8–77.0) | 85.71 (57.2–98.2) | 0.010 | |
| Biomarkers’ Serum Levels (Median, IQR) | Intestinal Complications | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 19) | No (n = 12) | ||
| CRP | 1.26 (0.36–3.80) | 0.44 (0.33–6.44) | 0.60 |
| Albumin | 4 (3.7; 4.2) | 3.9 (3.65; 4.37) | 0.90 |
| Calprotectin | 400 (150–850) | 135 (50–400) | 0.20 |
| ESR | 52 (21–82) | 27 (13–90) | 0.40 |
| IL-17 | 1449.05 (708.50–2531.60) | 638.77 (242.93–1322.96) | 0.05 |
| IL-23 | 1417.01 (799.22–1486.13) | 797.06 (744.14–912.63) | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucaciu, L.A.; Ilieș, M.; Vesa, Ș.C.; Seicean, R.; Din, S.; Iuga, C.A.; Seicean, A. Serum Interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Patients Could Differentiate between Severe and Non-Severe Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111130
Lucaciu LA, Ilieș M, Vesa ȘC, Seicean R, Din S, Iuga CA, Seicean A. Serum Interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Patients Could Differentiate between Severe and Non-Severe Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucaciu, Laura A., Maria Ilieș, Ștefan C. Vesa, Radu Seicean, Shahida Din, Cristina Adela Iuga, and Andrada Seicean. 2021. "Serum Interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Patients Could Differentiate between Severe and Non-Severe Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111130
APA StyleLucaciu, L. A., Ilieș, M., Vesa, Ș. C., Seicean, R., Din, S., Iuga, C. A., & Seicean, A. (2021). Serum Interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Patients Could Differentiate between Severe and Non-Severe Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111130








