Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
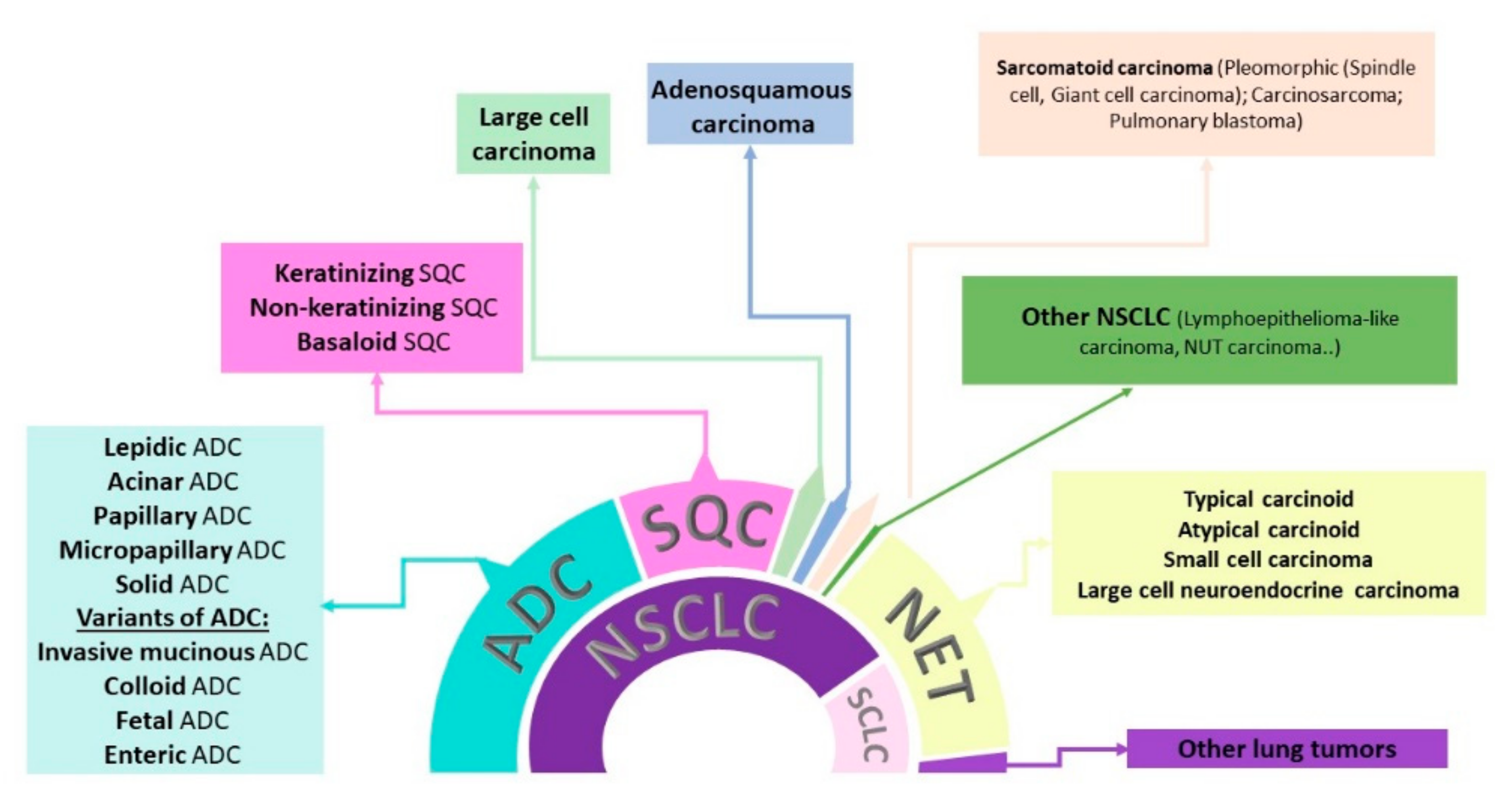
1.1. Lung Cancer Classification
1.2. Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
1.3. Treatment Options
2. Diagnostic Biomarkers Used in NSCLC Clinical Management
2.1. Immunohistochemical Biomarkers
2.2. Circulating Tumor Protein Biomarkers from the Blood and Serum
2.3. miRNAs—Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers
3. Predictive Biomarkers in NSCLC Management
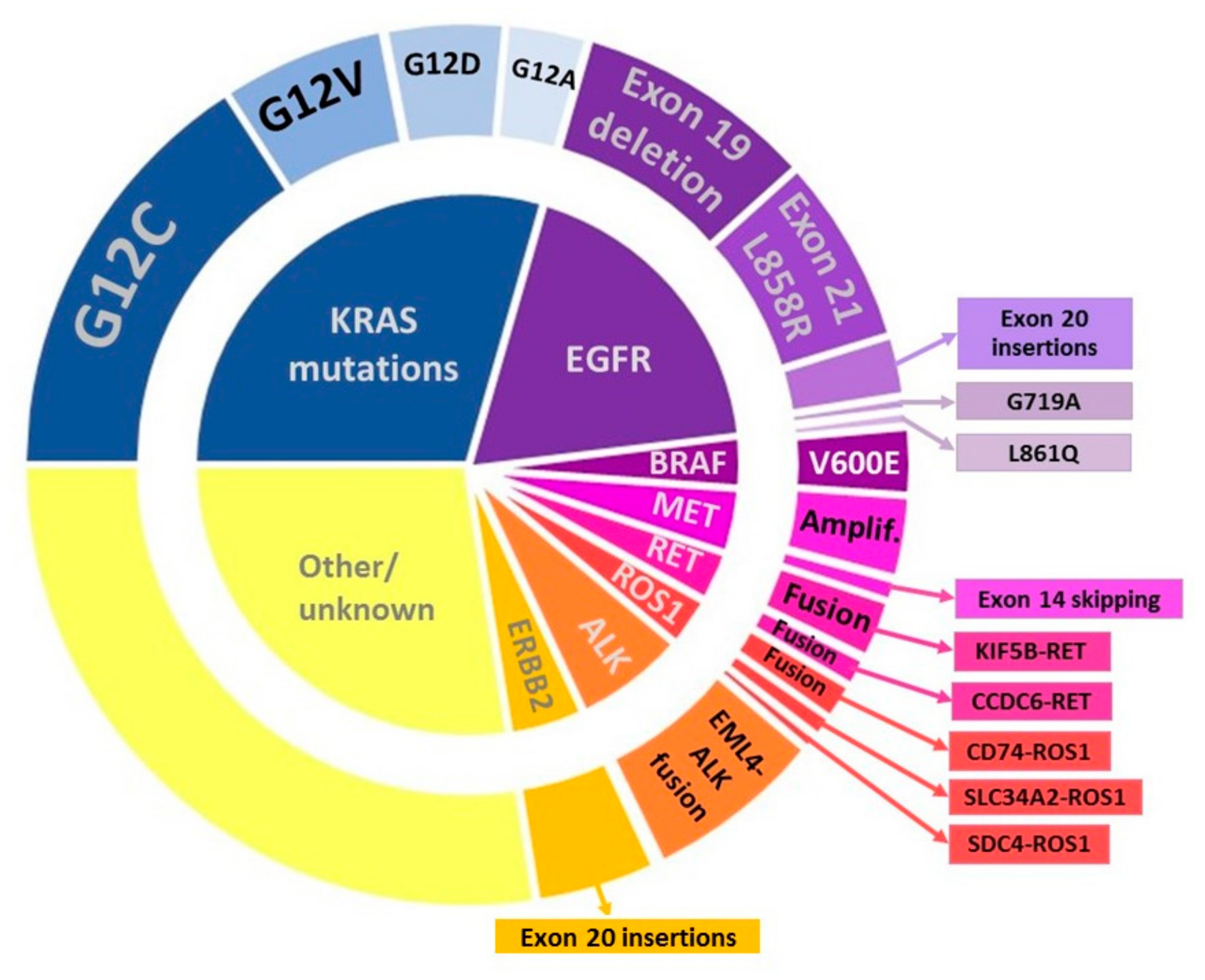
3.1. Predictive Biomarkers for Targeted Therapy in NSCLC Patients
3.2. Predictive Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in NSCLC Patients
3.3. Novel Predictive Biomarkers for Targeted Therapy
| Gene | Alteration | Drug | Eligible Patients | Trial Name | Treatment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KRAS | G12C | AMG 510 (Sotorasib) | Previously treated, locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic NSCLC | CodeBreak 200 NCT04303780 Phase 3 | AMG 510 vs. Docetaxel | [142] |
| MRTX849 (Adagrasib) | Previously treated for metastatic NSCLC | KRYSTAL-12 NCT04685135 Phase 3 | MRTX849 vs. Docetaxel | [143] | ||
| KRAS mutation in codons 12 or 13 | Selumetinib + Docetaxel | Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC | SELECT-1 NCT01933932 Phase 3 | Selumetinib + Docetaxel vs. Placebo + Docetaxel | [144] | |
| Abemaciclib (LY2835219) | Stage IV NSCLC patients who have progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy | JUNIPER NCT02152631 Phase 3 | Abemaciclib vs. Erlotinib | [145] | ||
| G12V, G12C | Carboplatin + paclitaxel + bevacizumab | IIIB or stage IV NSCLC patients eligible for platinum-based chemotherapy and are chemotherapy naïve | NCT02743923 Phase 3 | Carboplatin-paclitaxel-bevacizumab vs. Cisplatin-pemetrexed | [146] | |
| FGFR1 | FGFR1 amplification (>5 copies) | Dovitinib | Pretreated advanced SQC | NCT01861197 Phase 2 | Dovitinib | [121] |
| Aberrant signaling | E7080 + Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | NCT0083281 9Phase 1 | E7080 + Carboplatin+ Paclitaxel | [122] | |
| Pazopanib | Resectable stage I/II NSCLC | NCT0036767 9Phase 2 | Pazopanib | [123] | ||
| Nintedanib BIBF 1120 | Stage IIIB/IV or recurrent NSCLC after the failure of first-fine chemotherapy | LUME-Lung 1 NCT00805194 Phase 3 | Nintedanib + Docetaxel vs. Placebo + Docetaxel | [124] | ||
| DDR2 | DDR2 mutations | MGCD516 | Advanced solid tumor, including NSCLC | NCT02219711 Phase 1 | MGCD516 | |
| HER2 | exon 20 mutations | Afatinib | Pretreated patients with advanced NSCLC | NICHE NCT02369484 Phase 2 | Afatinib | [147] |
| Pyrotinib | Advanced non-squamous NSCLC patients who failed platinum-based chemotherapy | PYRAMID-1 NCT04447118 Phase 3 | Pyrotinib vs. Docetaxel | |||
| Pertuzumab+ Trastuzumab + Docetaxel | NSCLC patients harboring HER2 exon 20 mutation or insertion | NCT03845270 Phase 2 | Pertuzumab+ Trastuzumab + Docetaxel | |||
| HER2 mutations | Neratinib, temsirolimus | Advanced (stage IIIB) or metastatic (stage IV) NSCLC | NCT01827267 Phase 2 | Neratinib or Neratinib + Temsirolimus | [148] | |
| HER2 mutations or overexpression | Trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201a) | Unresectable and/or metastatic NSCLC | DESTINY-Lung01 NCT03505710 Phase 2 | Trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201a) | [149] |
3.4. Novel Predictive Biomarkers for Immunotherapy
4. Prognostic Biomarkers
4.1. Prognostic Biomarkers Used in NSCLC Clinical Management
4.2. Novel Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers
| Prognostic Biomarker | Alteration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| TP53 | p53 mutations | Poorer survival, increased resistance to therapy |
| VEGF | High expression | Poor prognosis, tumor recurrence, metastasis |
| TUBB3 | High expression | Poor prognosis |
| Ki-67 | High expression | Poor prognosis |
| ERCC1 | Low expression | Poor prognosis |
| TGF-β | High expression | Poor prognosis |
| LAG-3 | Low expression | Longer RFS and OS [203] |
| High expression | Better survival [204] | |
| KIAA1522 | High expression | Lower OS |
| High expression + platinum-based chemoterapy | Longer OS | |
| NLR & PLR | High NLR and PLR + Nivolumab | Worse OS, lower RR |
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, A.C. Cancer Facts & Figures 2020. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Osmani, L.; Askin, F.; Gabrielson, E.; Li, Q.K. Current WHO Guidelines and the Critical Role of Immunohistochemical Markers in the Subclassification of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC). Moving from Targeted Therapy to Immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Garshell, J.; Miller, D.; Altekruse, S.F.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019.
- Ahmadzada, T.; Kao, S.; Reid, G.; Boyer, M.; Mahar, A.; Cooper, W. An Update on Predictive Biomarkers for Treatment Selection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Román, M.; Baraibar, I.; López, I.; Nadal, E.; Rolfo, C.; Vicent, S.; Gil-Bazo, I. KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.Y.D.; Cramb, S.M.; Baade, P.D.; Youlden, D.R.; Nwogu, C.; Reid, M.E. The international epidemiology of lung cancer: Latest trends, disparities, and tumor characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1653–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37,513,025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Novotny, W.F.; Herbst, R.S.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Jablons, D.M.; Langer, C.J.; DeVore, R.F.; Gaudreault, J.; Damico, L.A.; et al. Randomized phase II trial comparing bevacizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with carboplatin and paclitaxel alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh Mbbs, K.; Quinton, C.; Ellis, P.M. Medical Oncology Role of pemetrexed in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, with histology subgroup analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2012, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beth Beasley, M.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 world health organization classification of lung tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Noguchi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Geisinger, K.R.; Yatabe, Y.; Beer, D.G.; Powell, C.A.; Riely, G.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; et al. International association for the study of lung cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Thoracic Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Latimer, K.; Mott, T. Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Treatment Principles, and Screening. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D. ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 4), iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagle, P.T.; Allen, T.C.; Bernicker, E.H.; Ge, Y.; Haque, A.; Barrios, R. Impact of recent developments in lung cancer on the practice of pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, F.D.C.; Bernardi, M.D.C.; Takagaki, T.; Siqueira, S.A.C.; Dolhnikoff, M. Lung cancer biopsy: Can diagnosis be changed after immunohistochemistry when the H&E-Based morphology corresponds to a specific tumor subtype? Clinics 2018, 73, e361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Beasley, M.B.; Chitale, D.A.; Dacic, S.; Giaccone, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Saldivar, J.S.; Squire, J.; et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 823–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guibert, N.; Pradines, A.; Mazieres, J.; Favre, G. Current and future applications of liquid biopsy in nonsmall cell lung cancer from early to advanced stages. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 190052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro-Giner, F.; Gkountela, S.; Donato, C.; Alborelli, I.; Quagliata, L.; Ng, C.; Piscuoglio, S.; Aceto, N. Cancer Diagnosis Using a Liquid Biopsy: Challenges and Expectations. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Rodrigues Pereira, J.; Ciuleanu, T.; Tan, E.H.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Campos, D.; Maoleekoonpiroj, S.; Smylie, M.; Martins, R.; et al. Erlotinib in Previously Treated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thatcher, N.; Chang, A.; Parikh, P.; Pereira, J.R.; Ciuleanu, T.; Von Pawel, J.; Thongprasert, S.; Tan, E.H.; Pemberton, K.; Archer, V.; et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet 2005, 366, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crinó, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.; Gettinger, S.; Johnson, M.L.; Jänne, P.A.; Garassino, M.C.; Christoph, D.; Toh, C.K.; Rizvi, N.A.; Chaft, J.E.; Costa, E.C.; et al. Phase II trial of atezolizumab as first-line or subsequent therapy for patients with programmed death-ligand 1-selected advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (BIRCH). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csöszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohno, T.; Nakaoku, T.; Tsuta, K.; Tsuchihara, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K. Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other oncogene fusions in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Johnson, D.; Temin, S.; Baker, S.; Brahmer, J.; Ellis, P.M.; Giaccone, G.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jaiyesimi, I.; Leighl, N.B.; et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer: American Society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3484–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Luft, A.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Gümüş, M.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Çay Şenler, F.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy for Squamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 018-0360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, J.C.; Wainwright, C.E.; Canny, G.J.; Chilvers, M.A.; Howenstine, M.S.; Munck, A.; Mainz, J.G.; Rodriguez, S.; Li, H.; Yen, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ivacaftor in patients aged 6 to 11 years with cystic fibrosis with a G551D mutation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Califf, R.M. Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastel, D.; Ramaioli, A.; Cornillie, F.; Thirion, B. CYFRA 21-1, a sensitive and specific new tumour marker for squamous cell lung cancer. Report of the first European multicentre evaluation. Eur. J. Cancer 1994, 30, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Takayama, K.; Izumi, M.; Harada, T.; Furuyama, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Diagnostic value of CEA and CYFRA 21-1 tumor markers in primary lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wang, X.-Y.; Han, X.-H.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Diagnostic value of Cyfra21-1, SCC and CEA for differentiation of early-stage NSCLC from benign lung disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11295–11300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doseeva, V.; Colpitts, T.; Gao, G.; Woodcock, J.; Knezevic, V. Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Khadka, V.S.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, B.; Deng, Y. The Evaluation of Serum Biomarkers for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Diagnosis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, E.F.; Campa, M.J.; Gottlin, E.B.; Kusmartseva, I.; Guan, X.R.; Herndon, J.E. Panel of serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5578–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.F.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.L. Thymidine kinase 1 combined with CEA, CYFRA21-1 and NSE improved its diagnostic value for lung cancer. Life Sci. 2018, 194, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, R.; Li, Y.; Jin, R.; Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Che, Y.; Lu, Z.; Mao, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Enhancement of diagnostic performance in lung cancers by combining CEA and CA125 with autoantibodies detection. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1625689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, X.; Ren, T.; Yin, Y. Autoantibodies as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer: A systematic review. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, C.J.; Murray, A.; McElveen, J.E.; Sahin, U.; Luxemburger, U.; Türeci, Ö.; Wiewrodt, R.; Barnes, A.C.; Robertson, J.F. Autoantibodies in lung cancer: Possibilities for early detection and subsequent cure. Thorax 2008, 63, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Lien, C.T.; Kuo, P.L.; Hung, J.Y. The roles of microRNA in lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The MicroRNA Spectrum in 12 Body Fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; He, J.; Tian, H.; Shen, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; et al. A two-miRNA signature (miR-33a-5p and miR-128-3p) in whole blood as potential biomarker for early diagnosis of lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aharonov, R.; Lebanony, D.; Benjamin, H.; Gilad, S.; Ezagouri, M.; Dov, A.; Ashkenazi, K.; Gefen, N.; Izraeli, S.; Rechavi, G.; et al. Diagnostic assay based on hsa-miR-205 expression distinguishes squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.A.; Benjamin, H.; Cholakh, H.; Chajut, A.; Clark, D.P.; Westra, W.H. Accurate classification of non-small cell lung carcinoma using a novel microRNA-based approach. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, S.; Mallick, R.; Kannisto, E.; Sharma, R.; Bshara, W.; Yendamuri, S.; Dhillon, S.S. MIR-205 and MIR-375 MicroRNA assays to distinguish squamous cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma in lung cancer biopsies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhu, W.Y.; He, J.Y.; Chen, D.D.; Huang, Y.Y.; Le, H.B.; Liu, X.G. MiRNAs expression profiling to distinguish lung squamous-cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma subtypes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, S.; Lithwick-Yanai, G.; Barshack, I.; Benjamin, S.; Krivitsky, I.; Edmonston, T.B.; Bibbo, M.; Thurm, C.; Horowitz, L.; Huang, Y.; et al. Classification of the four main types of lung cancer using a microRNA-based diagnostic assay. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wei, F.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ren, X. Plasma miR-324-3p and miR-1285 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for early stage lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59664–59675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Ding, M.; Xia, M.; Chen, S.; Van Le, A.; Soto-Gil, R.; Shen, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Gu, W.; et al. A Five-miRNA Panel Identified from a Multicentric Case-control Study Serves as a Novel Diagnostic Tool for Ethnically Diverse Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Patients. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sozzi, G.; Boeri, M.; Rossi, M.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Bravi, F.; Roz, L.; Conte, D.; Grassi, M.; Sverzellati, N.; et al. Clinical Utility of a Plasma-Based miRNA Signature Classifier within Computed Tomography Lung Cancer Screening: A Correlative MILD Trial Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, F.; Jacopo Marzi, M.; Dezi, F.; Dama, E.; Mary Carletti, R.; Bonizzi, G.; Bertolotti, R.; Bellomi, M.; Rampinelli, C.; Maisonneuve, P.; et al. miR-Test: A Blood Test for Lung Cancer Early Detection. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Standfield, L.; Weston, A.R.; Barraclough, H.; Van Kooten, M.; Pavlakis, N. Histology as a treatment effect modifier in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review of the evidence. Respirology 2011, 16, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennell, N.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Gandara, D.R.; West, H. Biomarker Testing for Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Issues and Tough Choices. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, P.; Conde, E.; de Castro, J.; Gómez-Román, J.J.; Felip, E.; Pijuan, L.; Isla, D.; Sanz, J.; Paz-Ares, L.; López-Ríos, F. Updated guidelines for predictive biomarker testing in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A National Consensus of the Spanish Society of Pathology and the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors guideline from the college of American pathologists, the international association for the study of lung cancer, and the association for molecular pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.L.; Planchard, D.; Lu, S.; Sun, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kim, D.W.; Tan, D.S.W.; Yang, J.C.H.; Azrif, M.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Pan-asian adapted clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A csco-esmo initiative endorsed by jsmo, ksmo, mos, sso and tos. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popper, H.H.; Gruber-Mösenbacher, U.; Pall, G.; Müllauer, L.; Hochmair, M.; Krenbek, D.; Brcic, L.; Schmitz, K.; Lamprecht, B.; Eckmayr, J.; et al. The 2020 update of the recommendations of the Austrian working group on lung pathology and oncology for the diagnostic workup of non-small cell lung cancer with focus on predictive biomarkers. Memo Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2020, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leukam, M.J.; Villaflor, V.M. Advances in molecular and immunologic targeted therapies for squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Transl. Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.A.; O’toole, S.; Boyer, M.; Horvath, L.; Mahar, A. What’s new in non-small cell lung cancer forpathologists: The importance of accurate subtyping, EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements. Pathology 2011, 43, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S. Development of treatment options for Chinese patients with advanced squamous cell lung cancer: Focus on afatinib. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Hackshaw, A.; Feng, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, C.; Tang, J. Comparison of gefitinib, erlotinib and afatinib in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2805–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daaboul, N.; Nicholas, G.; Laurie, S.A. Algorithm for the treatment of advanced or metastatic squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: An evidence-based overview. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S77–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wecker, H.; Waller, C.F. Afatinib. In Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Hu, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ni, J.; et al. EGFR G796D mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49671–49679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Haderk, F.; Bivona, T.G. Non-canonical thinking for targeting ALK-fusion onco-proteins in lung cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadgeel, S. Approach to Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Gene Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). In Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: Approaches to Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.-F.; Tai, Y.-H.; Gao, H.-J. ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, S.I.; Gautschi, O. Crizotinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, P.M.; Rudin, C.M. Crizotinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2012, 13, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, T.A.; Khoo, C.; Solomon, B.J. Targeting ROS1 Rearrangements in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Crizotinib and Newer Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Drugs 2019, 79, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.I.; Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Massion, P.P.; Siwak-Tapp, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Fang, R.; et al. ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of lung cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Choi, Y.L.; Song, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, G.; Mao, M. ALK, ROS1 and RET rearrangements in lung squamous cell carcinoma are very rare. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, T.M.; Crinò, L.; Gridelli, C.; Kiura, K.; Liu, G.; Novello, S.; Bearz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mok, T.; et al. Ceritinib versus chemotherapy in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously given chemotherapy and crizotinib (ASCEND-5): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK -Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK -Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, F.; Ponce, S.; Patel, S.; Van Herpen, C.; Kurkjian, C.; Lou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ramsingh, G.; Pal, S.; Neal, J. P1.01-113 Phase 1b Trial of Cabozantinib or Cabozantinib Plus Atezolizumab in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S405–S406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Preeshagul, I.; Schoenfeld, A.; Mccarthy, C.; Makhnin, A.; Plodkowski, A.; Ginsberg, M.; Davare, M.; Delasos, L.; Somwar, R.; et al. P1.14-50 A Phase 2 Trial of Cabozantinib in ROS1-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S574–S575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Chiari, R.; Riely, G.J.; Besse, B.; Soo, R.A.; Kao, S.; Lin, C.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Clancy, J.S.; et al. Lorlatinib in advanced ROS1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ding, H.; Qian, J.; Lizaso, A.; Lin, J.; Han-Zhang, H.; Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H. The association between BRAF mutation class and clinical features in BRAF-mutant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brustugun, O.T.; Khattak, A.M.; Trømborg, A.K.; Beigi, M.; Beiske, K.; Lund-Iversen, M.; Helland, Å. BRAF-mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, C.; Couraud, S.; Tanguy, R.; Bringuier, P.P.; Girard, N.; Souquet, P.J. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with lung cancer harboring BRAF mutations. Lung Cancer 2016, 91, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante Alvarez, J.G.; Otterson, G.A. Agents to treat BRAF-mutant lung cancer. Drugs Context 2019, 8, 212566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, F.; Giovannetti, E.; Saso, L.; Firuzi, O. HGF/MET pathway aberrations as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in human cancers. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 56, 533–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paik, P.K.; Drilon, A.; Fan, P.D.; Yu, H.; Rekhtman, N.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Borsu, L.; Schultz, N.; Berger, M.F.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Response to MET inhibitors in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinomas harboring MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scagliotti, G.; Von Pawel, J.; Novello, S.; Ramlau, R.; Favaretto, A.; Barlesi, F.; Akerley, W.; Orlov, S.; Santoro, A.; Spigel, D.; et al. Phase III multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of tivantinib (ARQ 197) plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in previously treated patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Hirashima, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Okamoto, I.; Takahashi, T.; Nishio, M.; Hirata, T.; Kubota, K.; Kasahara, K.; Hida, T.; et al. Phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib (ARQ 197) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer just after progression on EGFR-TKI, gefitinib or erlotinib. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Hida, T.; De Jonge, M.J.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib (INC280) in METΔex14 -mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Efficacy data from the phase II GEOMETRY mono-1 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Su, C.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Zheng, L.; Fei, K.; Zhou, C. KIF5B-RET fusions in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2013, 119, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Guo, Y.; Shao, G.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Ma, K. RET fusion in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and response to cabozantinib: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Milia, J.; Filleron, T.; Wolf, J.; Carbone, D.P.; Owen, D.; Camidge, R.; Narayanan, V.; Doebele, R.C.; Besse, B.; et al. Targeting RET in patients with RET-rearranged lung cancers: Results from the global, multicenter RET registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, A.; Albano, M.; Van Voorthuysen, M.; Somwar, R.; Smith, R.S.; Montecalvo, J.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, single-centre, phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.K.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Sun, J.M.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Choi, Y.L.; et al. Vandetanib in pretreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer-harboring RET rearrangement: A phase II clinical trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawara, A. Trk receptor tyrosine kinases: A bridge between cancer and neural development. Cancer Lett. 2001, 169, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Capelletti, M.; Le, T.A.; Kako, S.; Butaney, M.; Ercan, D.; Mahale, S.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Pilling, A.B.; et al. Oncogenic and drug sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stransky, N.; Cerami, E.; Schalm, S.; Kim, J.L.; Lengauer, C. The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gullick, W.J. The epidermal growth factor system of ligands and receptors in cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willem, M. Proteolytic processing of Neuregulin-1. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 126, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonna, S.; Feldman, R.A.; Swensen, J.; Gatalica, Z.; Korn, W.M.; Borghaei, H.; Ma, P.C.; Nieva, J.J.; Spira, A.I.; Vanderwalde, A.M.; et al. Detection of NRG1 gene fusions in solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4966–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, N.D.; Wang, Y.; Beadling, C.; Warrick, A.; Neff, T.; Corless, C.L.; Tolba, K. Durable Response to Afatinib in Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring NRG1 Gene Fusions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e107–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, P.K.; Doherty, M.; Tsao, M.S. A Case of Invasive Mucinous Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with a CD74-NRG1 Fusion Protein Targeted with Afatinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e200–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.V.; Duruisseaux, M.; Tolba, K.; Branden, E.; Goto, Y.; Weinberg, B.A.; Renouf, D.J.; Doebele, R.C.; Heining, C.; Schlenk, R.F.; et al. Targeting NRG1-fusions in multiple tumour types: Afatinib as a novel potential treatment option. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v791–v792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.C.; Lim, K.-H.; Burkard, M.E.; Lin, J.J.; Chae, Y.K.; Socinski, M.A.; Khan, G.; Reckamp, K.L.; Leland, S.; Plessinger, D.; et al. Abstract PO-003: CRESTONE—Clinical study of response to seribantumab in tumors with neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Fusions—A phase 2 study of the anti-HER3 mAb for advanced or metastatic solid tumors (NCT04383210). In Proceedings of the AACR Virtual Special Conference on Pancreatic CancerCancer Research; American Association for Cancer Research (AACR): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; Volume 80, p. PO-003-PO-003. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grigg, C.; Rizvi, N.A. PD-L1 biomarker testing for non-small cell lung cancer: Truth or fiction? J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.M.G.; Dong, H. Functional expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (B7-H1) by immune cells and tumor cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelczyk, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Ciesielska, U.; Jablonska, K.; Gletzel-Plucinska, N.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P.; Nowinska, K. Role of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Prognostic Significance according to Clinicopathological Factors and Diagnostic Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.M.; George, D.J.; Lisi, S.; Salama, A.K.S. Immune Checkpoint Blockade: The New Frontier in Cancer Treatment. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoukalas, N.; Kiakou, M.; Tsapakidis, K.; Tolia, M.; Aravantinou-Fatorou, E.; Baxevanos, P.; Kyrgias, G.; Theocharis, S. PD-1 and PD-L1 as immunotherapy targets and biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. J. BUON 2019, 24, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liang, S.Q.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.W. New horizons in KRAS-mutant lung cancer: Dawn after darkness. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pao, W.; Wang, T.Y.; Riely, G.J.; Miller, V.A.; Pan, Q.; Ladanyi, M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Heelan, R.T.; Kris, M.G.; Varmus, H.E. KRAS Mutations and Primary Resistance of Lung Adenocarcinomas to Gefitinib or Erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells 2019, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chae, Y.K.; Ranganath, K.; Hammerman, P.S.; Vaklavas, C.; Mohindra, N.; Kalyan, A.; Matsangou, M.; Costa, R.; Carneiro, B.; Villaflor, V.M.; et al. Inhibition of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) pathway: The current landscape and barriers to clinical application. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16052–16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helsten, T.; Elkin, S.; Arthur, E.; Tomson, B.N.; Carter, J.; Kurzrock, R. The FGFR landscape in cancer: Analysis of 4853 tumors by next-generation sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.L.; Liu, R.J.; Zhou, J.H.; Meng, S.H. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 gene amplification in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, S.; Petti, F.; Sujka-Kwok, I.; Epstein, D.; Haley, J.D. Kinase switching in mesenchymal-like non-small cell lung cancer lines contributes to EGFR inhibitor resistance through pathway redundancy. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.H.; Sun, J.M.; Choi, Y.L.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dovitinib in pretreated patients with advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer with FGFR1 amplification: A single-arm, phase 2 study. Cancer 2016, 122, 3027–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishio, M.; Horai, T.; Horiike, A.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, T.; Murakami, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Koizumi, F.; Nishio, K.; et al. Phase 1 study of lenvatinib combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altorki, N.; Lane, M.E.; Bauer, T.; Lee, P.C.; Guarino, M.J.; Pass, H.; Felip, E.; Peylan-Ramu, N.; Gurpide, A.; Grannis, F.W.; et al. Phase II proof-of-concept study of pazopanib monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with stage I/II resectable non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3131–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.L.; Ratain, M.J.; O’dwyer, P.J.; Siu, L.L.; Jassem, J.; Medioni, J.; Dejonge, M.; Rudin, C.; Sawyer, M.; Khayat, D.; et al. Phase II randomised discontinuation trial of brivanib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, T.L.; Yu, H.; Smith, D.; Boyle, T.A.; York, E.R.; Leedy, S.; Gao, D.; Heasley, L.; Hirsch, F.R.; Camidge, D.R. Preselection of lung cancer cases using FGFR1 mRNA and gene copy number for treatment with ponatinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Cereda, R.; Litten, J.B.; Allen, A.R.; Giaccone, G.; Socinski, M.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Besse, B. A single arm, open-label, phase II study to assess the efficacy of lucitanib in patients with FGFR1 -amplified squamous NSCLC (sqNSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, TPS8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wu, L.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, M.L.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, C. The anti-tumor effect of regorafenib in lung squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumarola, C.; Bozza, N.; Castelli, R.; Ferlenghi, F.; Marseglia, G.; Lodola, A.; Bonelli, M.; La Monica, S.; Cretella, D.; Alfieri, R.; et al. Expanding the Arsenal of FGFR Inhibitors: A Novel Chloroacetamide Derivative as a New Irreversible Agent with Anti-proliferative Activity Against FGFR1-Amplified Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carafoli, F.; Mayer, M.C.; Shiraishi, K.; Pecheva, M.A.; Chan, L.Y.; Nan, R.; Leitinger, B.; Hohenester, E. Structure of the discoidin domain receptor 1 extracellular region bound to an inhibitory Fab fragment reveals features important for signaling. Structure 2012, 20, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rammal, H.; Saby, C.; Magnien, K.; Van-Gulick, L.; Garnotel, R.; Buache, E.; El Btaouri, H.; Jeannesson, P.; Morjani, H. Discoidin domain receptors: Potential actors and targets in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, P.S.; Sos, M.L.; Ramos, A.H.; Xu, C.; Dutt, A.; Zhou, W.; Brace, L.E.; Woods, B.A.; Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fathi, Z.; Mousavi, S.A.J.; Roudi, R.; Ghazi, F. Distribution of KRAS, DDR2, and TP53 gene mutations in lung cancer: An analysis of Iranian patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi-Watanabe, N.; Sato, A.; Watanabe, T.; Abe, T.; Nakashima, C.; Sueoka, E.; Kimura, S.; Sueoka-Aragane, N. Functional analysis of Discoidin domain receptor 2 mutation and expression in squamous cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 110, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Zimmermann, S. Targeted therapy in NSCLC driven by HER2 insertions. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.C. The role of HER2, EGFR, and other receptor tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furrer, D.; Paquet, C.; Jacob, S.; Diorio, C. The Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker: Molecular Insights into HER2 Activation and Diagnostic Implications. In Cancer Prognosis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawasaki, N.; Taguchi, M.; Kabasawa, K. Association of HER-2 overexpression with prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: A metaanalysis. Cancer 2005, 103, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.A.; Veve, R.; Chen, L.; Helfrich, B.; Zeng, C.; Baron, A.; Bunn, P.A. Evaluation of HER-2/neu gene amplification and protein expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.K.; Kim, K.A.; Lee, C.Y.; Shim, H.S. The frequency and clinical impact of HER2 alterations in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazières, J.; Peters, S.; Lepage, B.; Cortot, A.B.; Barlesi, F.; Beau-Faller, M.; Besse, B.; Blons, H.; Mansuet-Lupo, A.; Urban, T.; et al. Lung cancer that harbors an HER2 Mutation: Epidemiologic characteristics and therapeutic perspectives. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reck, M.; Spira, A.; Besse, B.; Wolf, J.; Skoulidis, F.; Borghaei, H.; Goto, K.; Park, K.; Griesinger, F.; Font, E.F.; et al. MO01.32 CodeBreaK 200: A Phase 3 Multicenter Study of Sotorasib, a KRAS(G12C) Inhibitor, versus Docetaxel in Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring KRAS p.G12C Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Lawler, W.E.; Shum, M.K.; Dakhil, S.R.; Spira, A.I.; Barlesi, F.; Reck, M.; Garassino, M.C.; Spigel, D.R.; Alvarez, D.; et al. KRYSTAL-12: A randomized phase 3 study of adagrasib (MRTX849) versus docetaxel in patients (pts) with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with KRASG12C mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, TPS9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Van Den Heuvel, M.M.; Barlesi, F.; Cobo, M.; Mazieres, J.; Crinò, L.; Orlov, S.; Blackhall, F.; Wolf, J.; Garrido, P.; et al. Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared with Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The SELECT-1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 317, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, J.W.; Mazieres, J.; Barlesi, F.; Dragnev, K.H.; Koczywas, M.; Göskel, T.; Cortot, A.B.; Girard, N.; Wesseler, C.; Bischoff, H.; et al. A Randomized Phase III Study of Abemaciclib Versus Erlotinib in Patients with Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with a Detectable KRAS Mutation Who Failed Prior Platinum-Based Therapy: JUNIPER. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Smit, E.F.; De Langen, J.; van Tinteren, H. Chemotherapy in KRAS-mutated chemotherapy naive non-small cell lung cancer patients: A phase III comparing cisplatin-pemetrexed with carboplatin-paclitaxel-bevacizumab: NVALT 22 (NCT02743923). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, TPS9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.F.; Peters, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Dafni, U.; Wolf, J.; Wasąg, B.; Biernat, W.; Finn, S.; Kammler, R.; Tsourti, Z.; et al. A single-arm phase II trial of afatinib in pretreated patients with advanced NSCLC harboring a HER2 mutation: The ETOP NICHE trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Besse, B.; Mazieres, J.; Waqar, S.; Cortot, A.; Barlesi, F.; Quoix, E.; Otterson, G.; Ettinger, D.; Horn, L.; et al. MA04.02 Neratinib ± Temsirolimus in HER2-Mutant Lung Cancers: An International, Randomized Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S358–S359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q. Mismatch repair deficiency/microsatellite instability-high as a predictor for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy efficacy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyiadzis, M.M.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Marshall, J.L.; Pritchard, C.C.; Azad, N.S.; Gulley, J.L. Significance and implications of FDA approval of pembrolizumab for biomarker-defined disease. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marchi, P.; Berardinelli, G.N.; Cavagna, R.; De Paula, F.; Da Silva, E.A.; Miziara, J.; Leal, L.; Reis, R. EP1.04-11 Frequency of Microsatellite Instability (MSI) in Brazilian TKI Non-Treatable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamochi, K.; Takahashi, F.; Suehara, Y.; Sato, E.; Kohsaka, S.; Hayashi, T.; Kitano, S.; Uneno, T.; Kojima, S.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. DNA mismatch repair deficiency in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma: Microsatellite instability analysis using the Promega panel. Lung Cancer 2017, 110, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Galeas, J.; Cheng, H. Tumor mutation burden in lung cancer: A new predictive biomarker for immunotherapy or too soon to tell? J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S3994–S3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Pluzanski, A.; Lee, J.S.; Otterson, G.A.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Minenza, E.; Linardou, H.; Burgers, S.; Salman, P.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.H.; Maher, S.G.; Young, H.A. Clinical Use of Interferon-gamma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1182, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachaliou, N.; Gonzalez-Cao, M.; Crespo, G.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Aldeguer, E.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Teixido, C.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Viteri, S.; Gil, M.D.L.L.; et al. Interferon gamma, an important marker of response to immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma patients. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Andreu, P.; Coussens, L.M. Interactions between lymphocytes and myeloid cells regulate pro-versus anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumet, J.D.; Richard, C.; Ledys, F.; Klopfenstein, Q.; Joubert, P.; Routy, B.; Truntzer, C.; Gagné, A.; Hamel, M.A.; Guimaraes, C.F.; et al. Prognostic and predictive role of CD8 and PD-L1 determination in lung tumor tissue of patients under anti-PD-1 therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uryvaev, A.; Passhak, M.; Hershkovits, D.; Sabo, E.; Bar-Sela, G. The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) as a predictive biomarker of response to anti-PD1 therapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer or metastatic melanoma. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM3 comes of age as an inhibitory receptor. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limagne, E.; Richard, C.; Thibaudin, M.; Fumet, J.D.; Truntzer, C.; Lagrange, A.; Favier, L.; Coudert, B.; Ghiringhelli, F. Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway and mMDSC control primary and secondary resistances to PD-1 blockade in lung cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1564505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Tsao, M.S. Prognostic markers in lung cancer: Is it ready for prime time? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paesmans, M. Prognostic and predictive factors for lung cancer. Breathe 2012, 9, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- A 25-Signal Proteomic Signature and Outcome for Patients with Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17551146/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Der, S.D.; Sykes, J.; Pintilie, M.; Zhu, C.Q.; Strumpf, D.; Liu, N.; Jurisica, I.; Shepherd, F.A.; Tsao, M.S. Validation of a histology-independent prognostic gene signature for early-stage, non-small-cell lung cancer including stage IA patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roepman, P.; Jassem, J.; Smit, E.F.; Muley, T.; Niklinski, J.; Van Develde, T.; Witteveen, A.T.; Rzyman, W.; Floore, A.; Burgers, S.; et al. An immune response enriched 72-gene prognostic profile for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shedden, K.; Taylor, J.M.G.; Enkemann, S.A.; Tsao, M.S.; Yeatman, T.J.; Gerald, W.L.; Eschrich, S.; Jurisica, I.; Giordano, T.J.; Misek, D.E.; et al. Gene expression-based survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma: A multi-site, blinded validation study. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvornikov, D.; Schneider, M.A.; Ohse, S.; Szczygieł, M.; Titkova, I.; Rosenblatt, M.; Muley, T.; Warth, A.; Herth, F.J.; Dienemann, H.; et al. Expression ratio of the TGFβ-inducible gene MYO10 is prognostic for overall survival of squamous cell lung cancer patients and predicts chemotherapy response. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methylation-Driven Genes PMPCAP1, SOWAHC and ZNF4 as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7002985/pdf/mmr-21-03-1285.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Gao, C.; Zhuang, J.; Zhou, C.; Ma, K.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Feng, F.; Sun, C. Prognostic value of aberrantly expressed methylation gene profiles in lung squamous cell carcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6519–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Gao, T.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, T.-H.; Wu, J. Prognostic Value of Survival of MicroRNAs Signatures in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5793–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Boffa, D.J.; Kim, A.W.; Tanoue, L.T. The Eighth Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification. Chest 2017, 151, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer on behalf of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee, Advisory Boards, and Participating Institutions. JTHO 2015, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malalasekera, A.; Tan, C.S.Y.; Phan, V.; Yip, P.Y.; Vardy, J.; Clarke, S.; Kao, S. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score: Agreement between non-small-cell lung cancer patients and their oncologists and clinical implications. Cancer Treat. Commun. 2016, 5, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. TP53 Mutations in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 583929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huszno, J.; Grzybowska, E. TP53 mutations and SNPs as prognostic and predictive factors in patients with breast cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Lin, H.; He, P.; He, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y. A TP53-associated gene signature for prediction of prognosis and therapeutic responses in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1731943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, K.; Hou, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of TP53 concurrent mutations for EGFR- TKIs and ALK-TKIs based targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Ou, W.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, B. TP53 mutation is associated with a poor clinical outcome for non-small cell lung cancer: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Le Teuff, G.; Lacas, B.; Tsao, M.S.; Graziano, S.; Pignon, J.P.; Douillard, J.Y.; Le Chevalier, T.; Seymour, L.; Filipits, M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive effect of TP53 mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer from adjuvant cisplatin-based therapy randomized trials: A LACE-bio pooled analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Silverman, J.F.; Santucci, T.S.; Macherey, R.S.; d’Amato, T.A.; Tung, M.Y.; Weyant, R.J.; Landreneau, R.J. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Correlates with Neoangiogenesis and a Poor Prognosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 8, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.J.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, L.X.; Lin, X.Q.; Yu, L.K.; Song, Y. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Guo, L.; Lin, G.; Chen, Z.; Chen, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, B.; Gu, X. Clinical and prognostic significance of OPN and VEGF expression in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, T.; Higashiyama, M.; Funai, H.; Imamura, F.; Uematsu, K.; Seki, N.; Eguchi, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Ichinose, Y. Prognostic value of expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its flt-1 and KDR receptors in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhilahti, E.M.; Peltonen, S.; Peltonen, J. Class III β-tubulin is a component of the mitotic spindle in multiple cell types. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sève, P.; Lai, R.; Ding, K.; Winton, T.; Butts, C.; Mackey, J.; Dumontet, C.; Dabbagh, L.; Aviel-Ronen, S.; Seymour, L.; et al. Class III β-tubulin expression and benefit from adjuvant cisplatin/vinorelbine chemotherapy in operable non-small cell lung cancer: Analysis of NCIC JBR.10. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Herman, M.M.; Mörk, S.J. Class III β-tubulin in human development and cancer. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2003, 55, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, T.; Lai, R.; Veillard, A.S.; Paris, E.; Soria, J.C.; Rosell, R.; Taron, M.; Graziano, S.; Kratzke, R.; Seymour, L.; et al. Cross-validation study of class III beta-tubulin as a predictive marker for benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in resected non-small-cell lung cancer: Analysis of four randomized trials. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2012, 23, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Scagliotti, G.; Danenberg, K.D.; Lord, R.V.N.; Bepler, G.; Novello, S.; Cooc, J.; Crinò, L.; Sánchez, J.J.; Taron, M.; et al. Transcripts in pretreatment biopsies from a three-arm randomized trial in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3548–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sève, P.; Mackey, J.; Isaac, S.; Trédan, O.; Souquet, P.J.; Pérol, M.; Lai, R.; Voloch, A.; Dumontet, C. Class III β-tubulin expression in tumor cells predicts response and outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving paclitaxel. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sève, P.; Isaac, S.; Trédan, O.; Souquet, P.J.; Pachéco, Y.; Pérol, M.; Lafanéchère, L.; Penet, A.; Peiller, E.L.; Dumontet, C. Expression of class III β-tubulin is predictive of patient outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving vinorelbine-based chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5481–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Endl, E.; Gerdes, J. Posttranslational Modifications of the KI-67 Protein Coincide with Two Major Checkpoints During Mitosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhou, W.; Li, C.M.; Hu, J.; Hu, X.M.; Chen, P.; Shao, G.L.; Guo, W.H. Ki-67 as a prognostic marker in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer in Asian patients: A meta-analysis of published studies involving 32 studies. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, B.; Paesmans, M.; Mascaux, C.; Berghmans, T.; Lothaire, P.; Meert, A.P.; Lafitte, J.J.; Sculier, J.P. Ki-67 expression and patients survival in lung cancer: Systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.M.; Chen, W.J.; Meng, R.M.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liao, D.Y.; Chen, G. Augmented expression of Ki-67 is correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis for lung cancer patients: An up-dated systematic review and meta-analysis with 108 studies and 14,732 patients. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.M.; Yang, S.C.; Jo, H.J.; Song, S.Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Jang, T.W.; Kim, D.J.; Jang, S.H.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, Y.D.; et al. Proteins involved in DNA damage response pathways and survival of stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, M.; Bordi, P.; Bortesi, B.; Boni, L.; Boni, C.; Baldini, E.; Grossi, F.; Recchia, F.; Zanelli, F.; Fontanini, G.; et al. ERCC1/BRCA1 expression and gene polymorphisms as prognostic and predictive factors in advanced NSCLC treated with or without cisplatin. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luwor, R.B.; Kaye, A.H.; Zhu, H.J. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and brain tumours. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.L.; Liu, S.G.; Qi, W.J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Li, Y.M.; Lei, B.; Sheng, W.J.; Shen, H. TGF-β1 protein expression in non-small cell lung cancers is correlated with prognosis. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8143–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Che, G. Prognostic value of TGF-β in lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, L.P.; Marciscano, A.E.; Drake, C.G.; Vignali, D.A.A. LAG3 (CD223) as a cancer immunotherapy target. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yu, H.; Rozeboom, L.; Rivard, C.J.; Ellison, K.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Suda, K.; Ren, S.; Wu, C.; Hou, L.; et al. LAG-3 Protein Expression in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hald, S.M.; Rakaee, M.; Martinez, I.; Richardsen, E.; Al-Saad, S.; Paulsen, E.E.; Blix, E.S.; Kilvaer, T.; Andersen, S.; Busund, L.T.; et al. LAG-3 in Non–Small-cell Lung Cancer: Expression in Primary Tumors and Metastatic Lymph Nodes Is Associated with Improved Survival. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 249–259.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Yang, H.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, M.R. KIAA1522 is a novel prognostic biomarker in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, G.J.K.; Charles, K.A.; Roxburgh, C.S.D.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in patients with cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, S.; Schmid, S.; Krapf, M.; Flatz, L.; Born, D.; Jochum, W.; Templeton, A.J.; Früh, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Alley, E.W.; Evans, T.L.; Kosteva, J.A.; Ciunci, C.A.; Gabriel, P.E.; Thompson, J.C.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | Alteration | Targeted Therapy | Year of FDA Approval | Year of EMA Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Exon 19 deletion | Erlotinib | 2013 | 2011 |
| Gefitinib | 2015 | 2009 | ||
| Afatinib | 2013 | 2013 | ||
| Exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutation | Osimertinib | 2018 | 2018 | |
| Dacomitinib | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| Erlotinib + Ramucirumab | 2020 | |||
| T790M | Osimertinib | 2015 | 2016 | |
| L861Q, G719X, S768I | Afatinib | 2018 | ||
| ALK | ALK rearrangement | Crizotinib | 2011 | 2012/2015 |
| Ceritinib | 2014/2017 | 2015/2017 | ||
| Alectinib | 2017 | 2017 | ||
| Brigatinib | 2017 | 2018/2020 | ||
| Lorlatinib | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| ROS1 | ROS1 rearrangement | Crizotinib | 2016 | |
| Entrectinib | 2019 | |||
| Ceritinib | 2019 | |||
| BRAF | V600E mutation | Dabrafenib + Trametinib | 2017 | |
| NTRK 1/2/3 | Gene fusion | Larotrectinib | 2018 | 2019 |
| Entrectinib | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| MET | Exon 14 skipping | Capmatinib | 2020 | |
| Tepotinib | 2021 | |||
| RET | RET rearrangement | Selpercatinib | 2020 | |
| Praseltinib | 2020 |
| Antibody | Target | Therapeutic Indication | Line of Therapy | Year of FDA Approval | Year of EMA Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Advanced/mNSCLC that express PD-L1 (TPS ≥ 1%) | Second-line | 2015 | 2016 |
| mNSCLC with high PD-L1 expression (TPS ≥ 50%) 1 | First-line | 2016 | 2017 | ||
| Metastatic non-squamous NSCLC, regardless of PD-L1 expression | First-line (+ Carboplatin & Pemetrexed) | 2017/2018 | 2018 | ||
| Metastatic SQC | First-line (+ Carboplatin and Paclitaxel or Nabpaclitaxel) | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| Stage III NSCLC with PD-L1 expression (TPS ≥ 1%) 2 | First-line | 2019 | |||
| Nivolumab | PD-1 | Advanced/mSQC | Second-line | 2015 | 2015 |
| Advanced/mNSCLC 3 | Second-line | 2015 | 2016 | ||
| Recurrent/mNSCLC 4 | First-line (+ Ipilimumab and 2 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy) | 2020 | |||
| mNSCLC with PD-L1 expression (≥ 1%) | First-line | 2020 | |||
| Atezolizumab | PD-L1 | mNSCLC 5 | Second-line | 2016 | 2017 |
| Metastatic non-SQC NSCLC 6 | First-line (+ Bevacizumab, Carboplatin, and Paclitaxel) | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| Metastatic non-SQC NSCLC (PD-L1 ≥ 5%) 7 | First-line (+ Nab-paclitaxel and Carboplatin) | 2019 | 2019 | ||
| mNSCLC with high PD-L1 expression (≥ 50%) 8 | First-line | 2020 | |||
| Durvalumab | PD-L1 | Stage III NSCLC 9 | Maintenance therapy | 2018 | 2018 |
| Gene | Drug | Eligible Patients | Trial Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| dMMR & MSI-H | SL-279252 (PD1-Fc-OX40L) | MSI high and mismatch repair deficient NSCLC patients, excluding subjects with known EGFR sensitizing (activating) mutation or an ALK fusion | NCT03894618 Phase 1 |
| L-NMMA + Pembrolizumab | MSI high and mismatch repair deficient NSCLC patients | NCT03236935 Phase 1 | |
| TMB | L-NMMA + Pembrolizumab | Unresectable or metastatic tumor, TMB ≥ 10 mut/Mb | NCT03236935 Phase 1 |
| Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab | Stage IIIB or IV non-squamous NSCLC with TMB ≥ 10 mut/Mb | NCT03836066 (TELMA) Phase 2 | |
| TIM-3 | TSR-022 | NSCLC patients that have received no more than 2 prior lines of therapy, which must include a platinum-based chemotherapy and an anti-PD-(L)1 antibody | NCT02817633 (AMBER) Phase 1 |
| TILs | LN-145 | NSCLC patients that have received a single line of systemic therapy that included checkpoint inhibitor and chemotherapy with documented radiographic disease progression on or following this single line of systemic therapy | NCT04614103 Phase 2 |
| LN-145 + Pembrolizumab | Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with ≤ 3 prior lines of systemic therapy, excluding checkpoint inhibitors or ≤ 4 prior lines if 2 or more of the lines are TKI therapy | NCT03645928 Phase 2 | |
| LN-145 | Stage III or Stage IV NSCLC, who have previously received 1–3 lines of prior systemic therapy | NCT03645928 Phase 2 | |
| LN-145 + Ipilimumab and Nivolumab | Stage III or Stage IV NSCLC who have previously received 1 line of approved checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy as the only prior line of systemic therapy | NCT03645928 Phase 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šutić, M.; Vukić, A.; Baranašić, J.; Försti, A.; Džubur, F.; Samaržija, M.; Jakopović, M.; Brčić, L.; Knežević, J. Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111102
Šutić M, Vukić A, Baranašić J, Försti A, Džubur F, Samaržija M, Jakopović M, Brčić L, Knežević J. Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111102
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠutić, Maja, Ana Vukić, Jurica Baranašić, Asta Försti, Feđa Džubur, Miroslav Samaržija, Marko Jakopović, Luka Brčić, and Jelena Knežević. 2021. "Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111102
APA StyleŠutić, M., Vukić, A., Baranašić, J., Försti, A., Džubur, F., Samaržija, M., Jakopović, M., Brčić, L., & Knežević, J. (2021). Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111102









